DOI: 10.11817/j.ysxb.1004.0609.2020-35794
原地浸矿经验注液下离子型稀土浸出和氨氮残留规律
王观石2,谢芳芳1, 3, 4,罗嗣海2,彭陈亮2,秦 磊2,洪本根1,姚 康2
(1. 江西理工大学 资源与环境工程学院,赣州 341000;
2. 江西理工大学 建筑与测绘工程学院,赣州 341000;
3. 江西离子型稀土工程技术研究有限公司采矿研究室,赣州 341000;
4. 国家离子型稀土资源高效开发利用工程技术研究中心,赣州 341000)
摘 要:离子型稀土原地浸矿注液过程多凭经验决策,缺乏理论指导,导致稀土资源回收率低,氨氮污染严重。本文选取我国南方某生产中的离子型稀土矿山进行原地浸矿现场实验,测试浸矿前后山体不同位置(山顶、山腰和注液边界)稀土品位和尾矿氨氮残留量,揭示原地浸矿经验注液下离子型稀土浸出和氨氮残留规律。结果表明:1) 离子型稀土原地浸矿经验注液下,浸矿山体不同位置稀土浸出情况不同。从稀土浸出率在深度上的变化规律推断,浸出效果山顶优于山腰优于注液边界。2) 经验淋洗下,尾矿不同位置氨氮残留情况不同。从矿体内氨氮残留量最大值及其所在深度推断,淋洗程度注液边界较山腰充分,山腰较山顶充分。3) 受注液孔辐射程度不同、矿体渗透性空间变异性、杂质离子、注液量和淋洗量、注液时间和淋洗时间等影响,经验注液下稀土浸出与氨氮残留皆呈非均匀性。因此,根据浸矿影响因素建立区块化均衡注液模型,科学指导注液具有重要的现实意义。
关键词:原地浸矿;离子型稀土;氨氮;注液;淋洗
文章编号:1004-0609(2020)-06-1454-12 中图分类号:TD865 文献标志码:A
离子型稀土矿的开采从池浸到原地浸,均以巨大的环境代价换取资源。对我国南方离子型稀土矿区尾矿土体、河水、沉积物及农田土壤采样测试分析表明矿区周边稀土离子含量严重超标,环境污染严重[1]。过去这种掠夺式、粗放式开采导致多数离子型稀土矿山目前处于停休整顿状态。国内外众多专家学者从不同方面对离子型稀土矿的提取进行了深入研究,力图探索一套绿色、高效、安全的离子型稀土提取工艺。离子型稀土浸出机理随其成矿岩体风化程度和矿物成分不同而不同,肖燕飞等[2]分别研究了花岗岩风化壳淋积型稀土矿和火山风化壳淋积型稀土矿的浸出机理和动力学。ALSHAMERI等[3]对不同黏土矿物上稀土的吸附-解吸研究表明稀土的吸附-解吸主要受黏土矿物结构和表面性质影响。为解决离子型稀土矿浸出过程氨氮污染和钙、镁流失问题,肖燕飞等[4]分析了稀土和杂质浸出传质差异,创新性提出钙、镁盐复合浸出法。为解决母液沉淀过程氨氮污染问题,黄莉&等[5]探究了氧化镁沉淀剂的最佳沉淀条件及其效果。为提高离子型稀土浸出率,田君等[6]应用田菁胶作为助浸剂,并取得良好效果。为浸出稀土矿中的胶态相稀土,肖燕飞等[7]提出硫酸亚铁还原浸出法。以低品位离子型稀土矿为研究对象,邱廷省等[8]采用响应曲面法优化得到低品位稀土矿最佳浸取条件。根据离子型稀土矿中交换态铝主要赋存于腐殖层,稀土富集于风化层的特点,张臻悦等[9]提出“跨层”注液浸矿的方法。为了强化稀土浸出,降低母液杂质含量,何正艳等[10]提出NH4Cl和NH4NO3复合浸矿。杨丽芬等[11]提出先(NH4)2SO4后Al2(SO4)3浸矿,再清水淋洗、石灰中和的多级浸出工艺。铝是影响离子型稀土母液后处理的主要杂质,罗仙平等[12]提出用六亚甲基四胺调节pH值的去除方法。
离子型稀土原地浸矿工艺的优化,也主要围绕高效、环保和安全三方面。众多学者为此做了大量工作。高国华等[13]应用抗坏血酸强化稀土浸出,减少了氨氮污染,提高了稀土浸出率。尹升华等[14]基于Green- Ampt模型,通过柱浸模拟原地浸分析了浸矿液的合理入渗水头。冯秀娟等[15]对离子型稀土原地浸矿部分污染物扩散规律研究表明尾矿中污染物含量均随时间推移而下降,污染物在尾矿中的迁移速率较原矿高。谢芳芳等[16]探究了浸矿液对离子型稀土矿孔隙的影响机制。张臻悦等[17]分析了不同浸矿剂下黏土矿物溶胀程度。陈勋等[18]对浸矿作用下稀土矿力学弱化规律进行了研究。但上述研究均基于室内试验,缺乏现场实践。研究成果现场推广的可行性有待研究。目前,离子型稀土原地浸矿现场多凭经验决策,缺乏理论指导。例如注液步骤均按“先上后下”、“先浓后淡”、“先液后水”的“三先”原则进行。汤洵忠等[19]虽从有效减小稀土离子再吸附的角度探讨了该注液步骤的优点,但该步骤并未给出注液工程具体的设计依据、标准及参数,未能针对同矿山不同区块具体情况做科学调整,仍为经验的总结。按该步骤注液,依然会出现矿体内浸矿液分布不均、稀土离子再吸附[20]、稀土浸出率低[21]、氨氮残留量高[22]、诱发滑坡等地质灾害的情况[23-24]。本文拟选取一离子型稀土矿山进行现场试验,测试浸矿前后山体不同位置(山顶、山腰和注液边界)稀土品位和氨氮含量,揭示经验注液下稀土浸出和氨氮残留规律,为矿山区块化均衡注液提供背景依据和技术指导。
1 试验场地及方法
试验场地位于我国南方某离子型稀土矿山。选取该矿4号未开采矿块,在其所处区域钻取5个勘探孔(d 10 cm),分别编号H1、H2、H3、H4、H5。其中H1位于山顶,H2位于山腰,H3、H4、H5位于注液边界内侧附近。因注液边界区域广,地质条件较复杂,为尽量减小试验结果的偶然性,故设置3个勘探孔。各勘探孔均钻至无法钻取为止。勘探过程,每米取1试样,试样均用保鲜袋封装送入实验室。试样放入温度设置105℃、型号DHG-9070A的鼓风干燥箱内12 h后待测。采取杯浸方式,利用质量分数2%的硫酸铵作浸矿剂,固液质量比1:5,置于恒温振荡器(温度25 ℃、振荡频率180 r/min)中浸矿2 h。浸矿结束后,分离上清液,采用EDTA滴定法测试上清液稀土浓度,计算试样离子型稀土品位。分别测试各勘探孔不同深度离子型稀土品位。试验现场和5个勘探孔在矿块所处山头等高地形图上的分布如图1所示。
勘探工作结束后,开始注液。勘探孔H1附近布置6个注液孔,H2、H3、H4经扩孔、回填后分别作为注液孔,并另在附近布置5个注液孔。注液孔d=18 cm,孔深均超矿层约1 m。采用硫酸铵溶液浸矿,浸矿液浓度1%~2.5%(质量分数),按照“先浓后淡”的原则进行注液,即注液初期浸矿液浓度为2.5%。其中勘探孔H1附近的注液孔从第1 d开始注液,H2和H4分别从第8 d和第14 d开始,H3和H5从第13 d开始。注液52 d后,停止注液,改注pH=5的清水对浸出山体进行淋洗,淋洗时间90 d。注液浓度与注液量随时间的变化如图2,淋洗量随时间的变化见图3。

图1 试验现场及勘探孔布置
Fig. 1 Test site and exploration hole layout

图2 注液浓度与注液量随时间的变化
Fig. 2 Injection concentration and volume vary with time

图3 淋洗量随时间的变化
Fig. 3 Elution volume vary with time
取样化验淋洗结束2个月后的尾矿离子型稀土品位和氨氮含量。在各勘探孔附近分别钻取6个取样孔(d 10 cm),各取样孔钻至无法钻取为止。取样孔内每米取一试样,试样用保鲜袋封装好送入实验室。为减少氨氮挥发,试样放置温度设置40 ℃、型号DHG- 9070A的鼓风干燥箱内12 h后待测。尾矿稀土品位的测试与勘探孔稀土品位测试方法相同(取2%的硫酸铵浸矿后的上清液用EDTA滴定)。 含量的测试:2%(质量分数)氯化钾溶液,固液质量比1:5,恒温振荡下杯浸2 h,取上清液以ICP-MS法测试。勘探孔H1、H2、H3、H4、H5附近注液孔、取样孔的布置如图4所示。
含量的测试:2%(质量分数)氯化钾溶液,固液质量比1:5,恒温振荡下杯浸2 h,取上清液以ICP-MS法测试。勘探孔H1、H2、H3、H4、H5附近注液孔、取样孔的布置如图4所示。
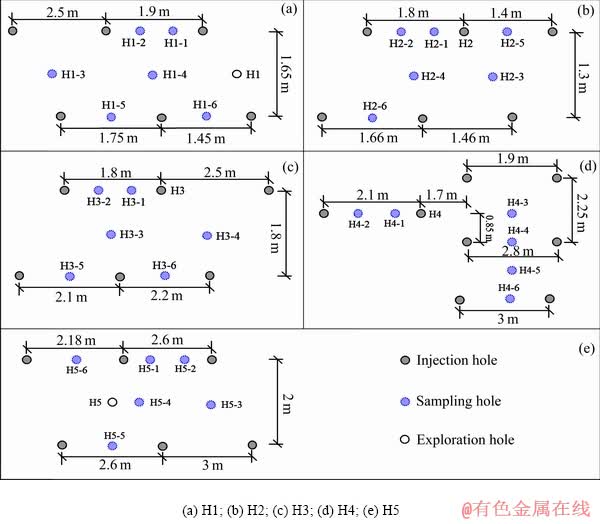
图4 勘探孔附近注液孔和取样孔布置
Fig. 4 Layout of injecting and sampling holes near exploration holes
2 结果与讨论
2.1 山体不同位置原矿品位
原矿离子型稀土品位测试结果如图5所示。勘探孔H1钻至深9 m处钻取不动,而H2钻至深20 m。此处排除勘探孔钻取过程遇石,因后期在勘探孔H1附近钻取样孔时,最大钻取深度也均为9 m。5个勘探孔内离子型稀土品位的分布情况不同:勘探孔H1内,稀土品位几乎随深度的增加而增大;H2内稀土品位随深度的增加先增后减,在深度6 m处达到最大值;H3内稀土品位随深度的增加而减小;H4、H5内稀土品位随深度的变化无明显规律,整体分布较为均匀。以该矿稀土边界品位0.035%对各勘探孔深度方向稀土品位进行划分,大于边界品位的区域,H1、H2、H3分别在3~9 m、3~8 m和3~6 m,H4在2~9 m和11 m、14 m处,H5只在15 m处。由此可知该稀土矿体边界品位以上的矿块主要位于地下2~9 m。根据文献[25]对离子型稀土矿品位随深度变化形式的分类,该矿属于浅伏式分布,即稀土主要富集于2 m以下的全风化层中。
2.2 山体不同位置稀土浸取和氨氮残留情况
山顶勘探孔H1附近尾矿化验结果如图6所示,图6(a)、(b)分别给出了尾矿稀土品位和氨氮含量随深度的变化规律。以同深度各取样点稀土浸取率、氨氮含量平均值随深度的变化作为山顶尾矿垂向稀土浸取率和氨氮含量的整体分布规律。深度1~4 m范围内,稀土浸取率随深度的增加而增大;深度>4 m后,浸取率趋稳趋同,在95%的附近小幅波动。深度1~3 m范围内,尾矿氨氮含量随深度的增加而增大,在深度3 m处达到最大值(1.38 mg·g-1);深度>3 m后,氨氮含量逐渐减小。

图 5 原矿稀土品位分布
5 原矿稀土品位分布
Fig. 5 Rare earth grade distribution of raw ore
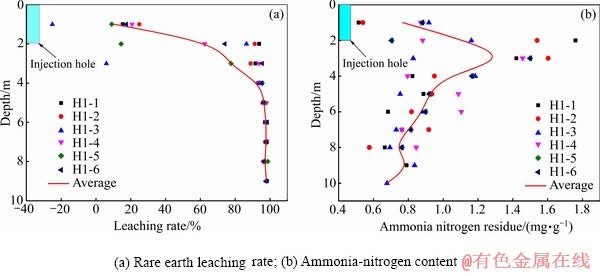
图6 山顶(H1)稀土浸取率和氨氮含量分布
Fig. 6 Distribution of rare earth leaching rate and ammonia-nitrogen content at hilltop (H1)
山腰勘探孔H2,其邻近区域垂向稀土浸取率和尾矿氨氮含量分布分别见图7(a)、(b)。由图中同深度各取样点稀土浸取率和氨氮含量平均值随深度的变化曲线可知,深度<4 m时,稀土浸取率随深度的增加不断增大;深度4~8 m时,稀土浸取率稳定在95%左右;深度>8 m后,稀土浸取率略有减小后稳定于92%左右。深度<4 m时,氨氮含量亦随深度增加而增大,在深度4 m处达到最大值(1.10 mg·g-1);此后随深度的增加氨氮含量有所下降,最后亦趋于稳定。
注液边界勘探孔H3周边稀土浸取率和尾矿氨氮含量如图8(a)、(b)所示,深度≤6 m,稀土浸取率波动很大,约35%的取样点处浸取率为负值(发生了稀土再吸附);深度>6 m后,稀土浸取率不断升高,未见负值;由同深度各取样点稀土浸取率平均值随深度呈先增后减的趋势,整体偏小,在深度7 m处达到最大值(91.20%)。同深度各取样点氨氮含量平均值随深度整体呈增长的趋势,在深度9 m 处达到最大值(0.77 mg·g-1)。
注液边界勘探孔H4附近稀土浸取率和尾矿氨氮含量见图9(a)、(b)。深度2~6 m内,同深度各取样点稀土浸取率平均值随深度的增加而增大,17%的取样点处稀土浸取率为负值(发生了稀土再吸附);深度>6 m后,各取样点稀土浸取率平均值增幅放缓,在80%~95%的区间小幅波动。同深度各取样点氨氮含量平均值随深度呈“波浪状”变化,在深度6 m处出现最大波峰,峰值约0.94 mg·g-1。
如图10(a)、(b)注液边界勘探孔H5附近稀土浸取率和氨氮含量分布,由同水平各取样点稀土浸取率平均值随深度的变化规律可知,稀土浸取率随深度整体呈先增后减的趋势,深度8~15 m范围内,浸取率保持在75%~90%的相对稳定区间。同深度各取样点氨氮含量平均值随深度呈先增后减、再增再减的波浪式起伏,最大值(0.91 mg·g-1)出现在深度16 m处。勘探孔H5附近氨氮含量随深度变化与稀土浸取率随深度变化规律相似。

图7 山腰(H2)稀土浸取率和氨氮含量分布
Fig. 7 Distribution of rare earth leaching rate and ammonia-nitrogen content at hillside (H2)
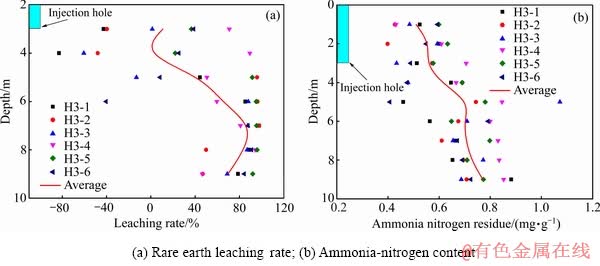
图8 注液边界(H3)稀土浸取率和氨氮含量分布
Fig. 8 Distribution of rare earth leaching rate and ammonia-nitrogen content near injection boundary (H3)

图9 注液边界(H4)稀土浸取率和氨氮含量分布
Fig. 9 Distribution of rare earth leaching rate and ammonia-nitrogen content near the injection boundary (H4)

图10 注液边界(H5)稀土浸取率和氨氮含量分布
Fig. 10 Distribution of rare earth leaching rate and ammonia-nitrogen content near injection boundary (H5)
忽略原矿本体氨氮的影响,尾矿化验出的氨氮含量即看作浸矿过程氨氮残留量;均以同深度各取样点稀土浸取率和氨氮残留量平均值随深度的变化曲线进行分析。由此可得,在该实验矿山工况下,山顶、山腰和注液边界的稀土浸取和氨氮残留呈非均匀性分布。山顶稀土浸取率最高(深度>4 m,稀土平均浸取率约为97%),各取样点浸取率波动性最小;氨氮残留量最大值靠近地表(深度3 m),此后随深度增加而减小。山腰稀土浸取率较高(深度>4 m,稀土平均浸取率约为93%),各取样点浸取率波动性较大;氨氮残留量最大值亦靠近地表(深度4 m),后随深度增加而减小并逐渐趋稳。注液边界稀土浸取率整体偏小(3个勘探孔附近稀土浸取率趋稳时均<86%),各取样点浸取率波动明显;氨氮残留量最大值所处位置(深度≥9 m)较山顶和山腰深,且最大值比山顶和山腰的最大值小。
2.3 山体不同位置稀土浸取和氨氮残留非均匀性分析

图11 单孔注液及勘探孔H1附近群孔注液影响范围
Fig. 11 Influencing range of single hole injection and group hole injection near exploration hole H1
勘探孔附近同深度各取样点稀土浸取率和氨氮残留量波动较大,分析其原因可能是注液和淋洗过程同深度溶液分布不均。桂勇等[26]假设注液孔底以上孔周湿润部分为椭球状,孔周溶液入渗与孔底溶液下渗强度相等,基于现场单孔注液亮蓝示踪试验,建立了稳渗状态原地浸矿单孔注液影响半径计算模型。利用该模型分析论文研究试验矿块渗透性及注液强度下单孔注液影响半径,其值小于1.2 m。以勘探孔H1附近的注液孔为研究对象,假设各注液孔径向矿体渗透性均一,以1.2 m为半径划出各注液孔影响范围,见图11。各取样孔所处位置受注液孔的辐射程度不同。例如取样孔H1-3只受注液孔⑥的影响,而取样孔H1-5同处于注液孔⑤、⑥辐射范围,取样孔H1-4更是受注液孔①、②、⑤的共同影响。此外,单孔注液影响范围内,不同点位含水率也可能不同。王观石等[27]以实测饱和导水率等效成一维入渗饱和导水率,基于入渗湿润锋簇上含水率增量相等的假设,建立了原地浸矿注液孔周含水率分布模型,计算显示入渗过程孔底垂向附近将出现一近饱和高含水率区,远离孔底处含水率随深度增加而减小至初始值。
高度变异性和各向异性是土壤的基本特性[29]。因此,类土体性质的离子型稀土矿体孔隙结构的空间变异性决定了其渗透系数的非均匀性,导致注液和淋洗过程溶液分布的不均。罗嗣海等[30]通过亮蓝、硫酸铵混合溶液浸矿试验(亮蓝用于示踪,硫酸铵浸矿),分析了浸矿液非均匀渗透对离子型稀土浸取的影响,结果表明随着矿体内优先流面积占比的增加稀土浸取率降低。

图12 勘探孔附近离子型稀土浸出量与氨氮残留量随深度的变化
Fig. 12 Variations of ionic rare earth leaching and ammonia- nitrogen residue with depth near exploration holes
根据各勘探孔某深度稀土浸出率平均值计算各深度处稀土浸出量,并与氨氮残留量作对比(见图12)。由硫酸铵与离子型稀土的可逆反应方程式(见式(1))可知,3 mol( )交换1 mol(RE3+),交换反应后吸附在固相上的氨氮被称为离子交换态,弱酸性清水淋洗条件下该部分氨氮淋出量很少[31],此时氨氮交换量可认为等于残留量。因此,稀土浸出量应与交换反应后固相上氨氮的吸附量存在对应比例关系,稀土浸出量随深度变化曲线应与氨氮残留量随深度变化曲线相似。而图10显示氨氮残留量随深度变化与稀土浸出量随深度变化曲线相似度不高。由表1可知,稀土浸出量和氨氮残留量最大值所处位置不同,氨氮残留量与稀土浸出量不存在明显的比例关系。5个勘探孔附近稀土浸出量最大值对应深度处氨氮残留量均>0.700 mg·g-1(平均值为0.827 mg·g-1),且均小于各勘探孔附近对应的氨氮残留量最大值;各勘探孔附近氨氮残留量最大值对应深度处稀土浸出率均大于69%,其中H2附近稀土浸出率最大,达94.358%。
)交换1 mol(RE3+),交换反应后吸附在固相上的氨氮被称为离子交换态,弱酸性清水淋洗条件下该部分氨氮淋出量很少[31],此时氨氮交换量可认为等于残留量。因此,稀土浸出量应与交换反应后固相上氨氮的吸附量存在对应比例关系,稀土浸出量随深度变化曲线应与氨氮残留量随深度变化曲线相似。而图10显示氨氮残留量随深度变化与稀土浸出量随深度变化曲线相似度不高。由表1可知,稀土浸出量和氨氮残留量最大值所处位置不同,氨氮残留量与稀土浸出量不存在明显的比例关系。5个勘探孔附近稀土浸出量最大值对应深度处氨氮残留量均>0.700 mg·g-1(平均值为0.827 mg·g-1),且均小于各勘探孔附近对应的氨氮残留量最大值;各勘探孔附近氨氮残留量最大值对应深度处稀土浸出率均大于69%,其中H2附近稀土浸出率最大,达94.358%。


 (1)
(1)


 (2)
(2)


 (3)
(3)
式中:[X]表示黏土矿物。
分析认为,浸矿过程 除与RE3+发生反应外,如式(2)所示,还会与主要杂质Al3+发生反应[10]。被交换下来的Al3+在随溶液下渗过程亦能与RE3+发生反应,见式(3)。在浸矿剂充分、不含杂质离子的理想条件下,矿体内硫酸铵浸矿过程如图13(a)所示,
除与RE3+发生反应外,如式(2)所示,还会与主要杂质Al3+发生反应[10]。被交换下来的Al3+在随溶液下渗过程亦能与RE3+发生反应,见式(3)。在浸矿剂充分、不含杂质离子的理想条件下,矿体内硫酸铵浸矿过程如图13(a)所示, 与RE3+发生交换,RE3+从黏土矿物上解吸,
与RE3+发生交换,RE3+从黏土矿物上解吸, 被黏土矿物吸附;当考虑杂质离子(Al3+)和浸矿剂不充分的情况,溶液在矿体内的浸矿过程较为复杂,存在Al3+和RE3+与
被黏土矿物吸附;当考虑杂质离子(Al3+)和浸矿剂不充分的情况,溶液在矿体内的浸矿过程较为复杂,存在Al3+和RE3+与 的竞争交换、溶液下渗过程Al3+和
的竞争交换、溶液下渗过程Al3+和 与RE3+的竞争交换以及因溶液中RE3+浓度过大、
与RE3+的竞争交换以及因溶液中RE3+浓度过大、 不足产生的RE3+再吸附现象(见图13(b))。矿体内这种多离子竞争交换与稀土离子的再吸附导致稀土浸出量与氨氮残留量的非成比例的同步变化。
不足产生的RE3+再吸附现象(见图13(b))。矿体内这种多离子竞争交换与稀土离子的再吸附导致稀土浸出量与氨氮残留量的非成比例的同步变化。
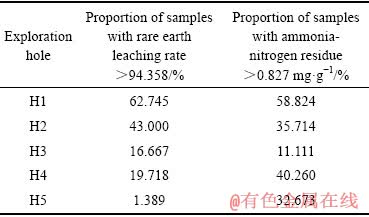
受上述因素及清水淋洗过程影响,稀土浸出量最大值与氨氮残留量最大值所处位置并不对应。各勘探孔附近稀土浸出量最大值处对应氨氮残留量均小于各勘探孔附近氨氮最大残留量。而同样淋洗量和淋洗时间条件下,理论氨氮含量最大处(即稀土浸出量最大处),氨氮淋洗越困难,越不充分。因此,将各勘探孔附近稀土最大浸出量处对应的氨氮残留量平均值(0.827 mg·g-1)作为反映清水淋洗充分程度的标准。氨氮最大残留量处,可认为NH4+与矿体内可与其发生交换的阳离子反应最充分,因而可以氨氮最大残留量处对应稀土浸出率中的最大值(94.358%)作为评判浸矿充分程度的标准。分别以94.358%和0.827 mg·g-1对各勘探孔附近取样点稀土浸出率和氨氮残留量进行比较分析,结果见表2所列。
由表2可知,稀土浸出率>94.358%的取样点占比,H1>H2>H4>H3>H5,即浸矿效果:山顶优于山腰优于注液边界;氨氮残留量>0.827 mg·g-1的取样点占比,H1>H4>H2>H5>H3,即淋洗效果:山顶差于注液边界H4差于山腰差于注液边界H5、H3;整体表现为山顶差于山腰差于注液边界。
表1 勘探孔附近稀土浸出量与氨氮残留量的最大值和平均值
Table 1 Maximum and average values of rare earth leaching and ammonia-nitrogen residue near exploration holes

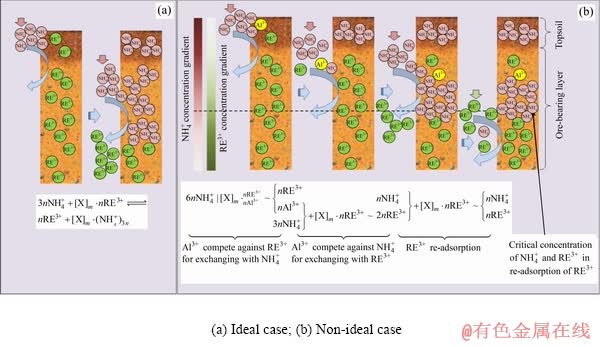
图13 理想和非理想情况下矿体内的浸矿过程
Fig. 13 Leaching process in ore-body under ideal and non-ideal conditions
表2 勘探孔附近稀土浸出率和氨氮残留量分析
Table 2 Analysis of rare earth leaching rate and ammonia-nitrogen residue near exploration holes
上述分析得到山顶和山腰氨氮最大残留量所处位置更靠近地表,而注液边界氨氮最大残留量处埋藏更深。淋洗过程,偏酸性的清水能将尾矿部分水溶态和少量离子态的铵淋洗出来。将矿柱分成N段等长的不连续矿块,从上到下依次编号1, 2, 3, …, r。假设铵均匀分布在矿柱上,各矿块含量均为1;淋洗液脉动式注入,每次注入1个矿块淋洗体积,忽略溶液纵向扩散;铵在固、液两相中的分配瞬间平衡,分配于液相的质量分数为p(0<p<1),则淋洗n个矿块淋洗体积后,矿柱中铵的分布见表3。
表3中假设p=0.5代入计算可知,注入单位淋洗体积后所能影响的最末矿块上铵含量最大,其表达式:
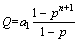 (4)
(4)
因
 (5)
(5)
故式(4)可转化为
 (6)
(6)
式中:Q表示铵含量;a1表示淋洗前单位矿块上铵含量,此处a1=1;r表示注入单位淋洗体积后所能影响的最末矿块号。
由式(4)、(5)可得,当淋洗体积n越大,Q越大,r也越大。即随着淋洗体积的增加,铵含量最大值越靠近矿柱底部。忽略稀土浸出量对氨氮最大残留量所在位置的影响(前述分析已表明二者对应性不强),认为氨氮最大残留量所在位置主要受淋洗影响,因而由山顶、山腰和注液边界氨氮最大残留量所在位置推断:注液边界较山腰淋洗充分,山腰较山顶淋洗充分。
3 结论
1) 离子型稀土原地浸矿经验注液下,浸矿山体不同位置(山顶、山腰和注液边界)稀土浸出情况不同。稀土浸出率波动:山顶<山腰<注液边界;趋稳时的稀土浸出率:山顶(95%)>山腰(92%)>注液边界(<90%)。浸出效果:山顶优于山腰优于注液边界,稀土再吸附主要发生在注液边界。
2) 经验注液下,浸矿山体不同位置(山顶、山腰和注液边界)氨氮残留情况不同。矿体深度上氨氮残留量最大值:山顶(1.38 mg·g-1)>山腰(1.10 mg·g-1)>注液边界(<1 mg·g-1),所在深度:山顶(3 m)<山腰(4 m)<注液边界(≥9 m)。淋洗效果:注液边界较山腰充分,山腰较山顶充分。
表3 矿柱中铵的分布
Table 3 Distribution of ammonium in ore pillar

3) 受注液孔辐射程度不同、矿体渗透性空间变异性、杂质离子、注液量和淋洗量、注液时间和淋洗时间等影响,经验注液下稀土浸出与氨氮残留皆呈非均匀性,二者对应的反应摩尔比例关系不强。因此,根据注液影响因素建立区块化均衡注液模型,科学指导注液具有重要的现实意义。
REFERENCES
[1] LIU W S, GUO M N, LIU C, YUAN M, CHEN X T, HUOT H, ZHAO C M, TANG Y T, MOREL J L, QIU R L. Water, sediment and agricultural soil contamination from an ion-adsorption rare earth mining area[J]. Chemosphere, 2019, 216: 75-83.
[2] XIAO Y F, LIU X S, FENG Z Y, HAUNG X W, HUANG L, CHEN Y Y, WU W Y. Role of minerals properties on leaching process of weathered crust elution-deposited rare earth ore[J]. Journal of Rare Earths, 2015, 33(5): 545-552.
[3] ALSHAMERI A, HE H P, XIN C, ZHU J X, HU W X, ZHU R L, WANG H L. Understanding the role of natural clay minerals as effective adsorbents and alternative source of rare earth elements: Adsorption operative parameters[J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2019, 185: 149-161.
[4] XIAO Y F, FENG Z Y, HU G H, HUANG L, CHEN Y Y, LI M L. Leaching and mass transfer characteristics of elements from ion-adsorption type rare earth ore[J]. Rare Metals, 2015, 34(5): 357-365.
[5] HUANG L, GAO G H, WU R, ZHANG Q, LAI F G, XIAO Y F. Non-ammonia enrichment of rare earth by magnesium oxide from rare earth leaching liquor in magnesium salt system[J]. Journal of Rare Earths, 2019, 37(8): 886-894.
[6] TIAN J, TANG X K, YIN J Q, CHEN J, LUO X P, RAO G H. Enhanced leach ability of a lean weathered crust elution-deposited rare-earth ore: Effects of sesbania gum filter-aid reagent[J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions B, 2013, 44: 1070-1077.
[7] XIAO Y F, FENG Z Y, HU G H, HUANG L, HUANG X W, CHEN Y Y, LONG Z Q. Reduction leaching of rare earth from ion-adsorption type rare earths ore with ferrous sulfate[J]. Journal of Rare Earths, 2016, 34(9): 917-923.
[8] QIU T S, YAN H S, LI J F, LIU Q S, AI G H. Response surface method for optimization of leaching of a low-grade ionic rare earth ore[J]. Powder Technology, 2018, 330: 330-338.
[9] ZHANG Z Y, HE Z Y, YU J X, XU Z G, CHI R A. Novel solution injection technology for in-situ leaching of weathered crust elution-deposited rare earth ores[J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2016, 164: 248-256.
[10] HE Z Y, ZHANG Z Y, YU J X, XU Z G, CHI R A. Process optimization of rare earth and aluminum leaching from weathered crust elution-deposited rare earth ore with compound ammonium salts[J]. Journal of Rare Earths, 2016, 34(4): 413-419.
[11] YANG L F, LI C C, WANG D S, LI F Y, LIU Y Z, ZHOU X Z, LIU M B, WANG X F, LI Y X. Leaching ion adsorption rare earth by aluminum sulfate for increasing efficiency and lowering the environmental impact[J]. Journal of Rare Earths, 2019, 37: 429-436.
[12] LUO X P, ZOU L P, MA P L, LUO C G, XU J, TANG X K. Removing aluminum from a low-concentration lixivium of weathered crust elution-deposited rare earth ore with neutralizing hydrolysis[J]. Rare Metals, 2017, 36(8): 685-690.
[13] 高国华, 颜 鋆, 赖安邦, 吴 冉, 肖燕飞. 离子吸附型稀土矿抗坏血酸强化-还原浸取过程[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2019, 29(6): 1289-1297.
GAO Guo-hua, YAN Yun, LAI Aa-bang, WU Ran, XIAO Yan-fei. Intensification-reduction leaching process of ion-adsorption type rare earths ore with ascorbic acid[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2019, 29(6): 1289-1297.
[14] 尹升华, 谢芳芳. 基于Green-Ampt模型离子型稀土柱浸试验入渗水头的确定[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2016, 26(12): 2668-2675.
YIN Sheng-hua, XIE Fang-fang. Infiltration head of ion-absorbed rare earth with column leaching experiment determined based on Green-Ampt model[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2016, 26(12): 2668-2675.
[15] FENG X J, TAO T, ZHUY C. Transport kinetics of pollutants in in-situ leaching of ionic type rare-earth ore[J]. Procedia Environmental Sciences, 2012, 12: 917-925.
[16] 谢芳芳, 尹升华, 袁长林, 齐 炎, 梁 健, 朱志成, 李 刚. 浸矿液对离子型稀土矿孔隙影响机制研究[J]. 稀土, 2018, 39(6): 48-56.
XIE Fang-fang, YIN Sheng-hua, YUAN Chang-lin, QI Yan, LIANG Jian, ZHU Zhi-cheng, LI Gang. Study on the influence mechanism of leaching solution on pore of ionic rare earth ore[J]. Chinese Rare Earths, 2018, 39(6): 48-56.
[17] ZHANG Z Y, HE Z Y, ZHOU F, ZHONG C B, SUN N J, CHI R A. Swelling of clay minerals in ammonium leaching of weathered crust elution-deposited rare earth ores[J]. Rare Metals, 2018, 37(1):72-78.
[18] 陈 勋, 齐 炎, 尹升华, 李希雯, 谢芳芳, 刘伽伟, 陈 威, 严荣富. 溶浸作用下稀土矿力学弱化规律研究[J]. 中南大学学报(自然科学版), 2019, 50(4): 939-945.
CHEN Xun, QI Yan, YIN Sheng-hua, LI Xi-wen, XIE Fang-fang, LIU Jia-wei, CHEN Wei, YAN Rong-fu. Law of weakening mechanical properties of rare earth ore with leaching[J]. Journal of Central South University(Science and Technology), 2019, 50(4): 939-945.
[19] 汤洵忠, 李茂楠, 杨 殿. 离子型稀土原地浸析采矿的再吸附问题及对策[J]. 中南工业大学学报, 1998, 29(6): 13-16.
TANG Xun-zhong, LI Mao-lan, YANG Dian. The problem of reabsorption of ion-absorbed rare earth mineral in situ leaching mining and the measure to overcome it[J]. Journal of Central South University of Technology, 1998, 29 (6): 13-16.
[20] WANG L, WANG C, LI L, YANG Y M. Readsorption of rare earth elements during leaching process of ion-adsorption-type rare earth ore[J]. Rare Metals, 2018. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12598-018-1162-3.
[21] 李 春, 邵亿生. 离子型稀土矿原地浸矿中反吸附问题的探讨[J]. 江西有色金属, 2001(4): 5-8.
LI Chun, SHAO Yi-sheng. The study of anti-adsorption in the in-situ leaching of ionic RE mine[J]. Jiangxi Nonferrous Metals, 2001(4): 5-8.
[22] 王炯辉, 张 喜, 陈道贵, 马 翀. 南方离子型稀土矿开采对地下水的影响及其监控[J]. 科技导报, 2015, 33(18): 23-27.
WANG Jiong-hui, ZHANG Xi, CHEN Dao-gui, MA Chong. Influence of during south ion-absorbed-type rare earth deposit mining on groundwater and it’s monitoring[J]. Science and Technology Review, 2015, 33(18): 23-27.
[23] 饶 睿, 李明才, 张树标, 饶运章, 钟健民. 离子型稀土原地浸矿采场滑坡特征及防控试验研究[J]. 稀土, 2016, 37(6): 26-31.
RAO Rui, LI Ming-cai, ZHANG Shu-biao, RAO Yun-zhang, ZHONG Jian-min. Experimental study on landslide features and countermeasures of in-situ leaching stope of ion-type rare earth mines[J]. Chinese Rare Earths, 2016, 37(6): 26-31.
[24] 洪本根, 罗嗣海, 胡世丽, 王观石. 全覆式离子型稀土矿山临界注液范围的计算[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2019, 29(7): 1509-1518.
HONG Ben-gen, LUO Si-hai, HU Shi-li, WANG Guan-shi. Calculation of critical liquid injection range in full clad ion-absorbed rare earth mine[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2019, 29(7): 1509-1518.
[25] CHI R A, TIAN J. Weathered crust elution-deposited rare earth ores[M]. New York: Nova Science Publishers, 2008.
[26] 桂 勇, 王观石, 赖远明, 洪本根, 胡世丽, 龙 平. 原地浸矿单孔注液影响半径的计算模型[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2018, 28(5): 1050-1058.
GUI Yong, WANG Guan-shi, LAI Yuan-ming, HONG Ben-gen, HU Shi-li, LONG Ping. A calculation model of influence radius of single-hole injection in in-situ leaching[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2018, 28(5): 1050-1058.
[27] 王观石, 赖远明, 龙 平, 胡世丽, 洪本根, 桂 勇. 离子型稀土原地浸矿注液孔周含水率分布的计算模型[J]. 岩土工程学报, 2018, 40(5): 910-917.
WANG Guan-shi, LAI Yuan-ming, LONG Ping, HU Shi-li, HONG Ben-gen, GUI Yong. Calculation moisture content distribution around injection hole during in-situ leaching process of ion-adsorption rare earth mines[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2018, 40(5): 910-917.
[28] 桂 勇. 离子型稀土原地浸矿注液入渗与溶质运移规律及其应用[D]. 赣州: 江西理工大学, 2018.
GUI Yong. The law and applications of infiltration and solute transport in situ leaching of ionic rare earth deposits[D]. Ganzhou: Jiangxi University of Science and Technology, 2018.
[29] 朱 磊, 周 清, 王 康, 杨金忠. 基于多重分形理论的土壤水非均匀流动分析[J]. 水科学进展, 2009, 20(3): 392-397.
ZHU Lei, ZHOU Qing, WANG Kang, YANG Jin-zhong. Analysis of the heterogeneous soil water flow based on the multifractal theory[J]. Advances in Water Science, 2009, 20(3): 392-397.
[30] 罗嗣海, 罗 涛, 王观石, 刘 剑, 胡世丽, 朱冬梅. 离子型稀土矿体中溶液非均匀性渗透对浸取率的影响[J]. 土壤, 2018, 50(2): 421-427.
LUO Si-hai, LUO Tao, WANG Guan-shi, LIU Jian, HU Shi-li, ZHU Dong-mei. Effect of heterogeneity of leaching solution on leaching rate in ionic rare earth ore body[J]. Soils, 2018, 50(2): 421-427.
[31] 杨 帅. 离子型稀土矿开采过程中氨氮吸附解吸行为研究[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2015.
YANG S. Study on the adsorption and desorption behavior of ammonium in the mining process of ion-absorbed rare-earth mineral[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences (Beijing), 2015.
Law of ionic rare earth leaching and ammonia-nitrogen residue under in-situ leaching empirical injection
WANG Guan-shi2, XIE Fang-fang1, 3, 4, LUO Si-hai2, PENG Chen-liang2, QIN Lei2, HONG Ben-gen1, YAO Kang2
(1. School of Resources and Environment Engineering, Jiangxi University of Science and Technology, Ganzhou 341000, China;
2. School of Architectural and Surveying& Mapping Engineering, Jiangxi University of Science and Technology, Ganzhou 341000, China;
3. Mining Research Laboratory, Jiangxi Ionic Rare Earth Engineering Research Co., Ltd., Ganzhou 341000, China;
4. National Engineering Research Center for Ionic Rare Earth, Ganzhou 341000, China)
Abstract: In-situ leaching process of ion-rare earth is mostly based on experience and lack of theory guide, which leads to low resources recovery rate and heavy ammonia-nitrogen residue. An in-situ leaching injection experiment was conducted to unravel the law of ion-rare earth leaching and ammonia-nitrogen residue under empirical injection. The results show that: 1) Judging from the fluctuation rate of leaching rate and variation of leaching rate with depth, the leaching effect on the hilltop is better than hillside than injection boundary. 2) Based on the maximum residual ammonia-nitrogen amount and the depth it occurs, elution degree in injection boundary is higher than the hillside than hilltop. 3) Under the influence of different radiation degrees from injection hole, ore-body permeability spatial variation, et al, leaching rate and residual ammonia-nitrogen amount in empirical injection process present unevenly. Thus, sectional equilibrium injection model was established based on leaching influential factor to instruct scientific injection is of importance.
Key words: in-situ leaching; ionic rare earth; ammonia-nitrogen; injection; elution
Foundation item: Projects(51874147, 51664015) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China
Received date: 2019-04-25; Accepted date: 2019-10-23
Corresponding author: XIE Fang-fang; Tel: +86-797-8168913; E-mail: 593721604@qq.com
(编辑 王 超)
基金项目:国家自然科学基金资助项目(51874147,51664015)
收稿日期:2019-04-25;修订日期:2019-10-23
通信作者:谢芳芳, 博士;电话:0797-8168913;E-mail:593721604@qq.com