网络首发时间: 2016-12-09 17:04
稀有金属 2017,41(06),709-713 DOI:10.13373/j.cnki.cjrm.xy16110011
稀土对镁合金微弧氧化层的作用综述
马跃宇 何德山 涂思京 车聪 李大全
北京有色金属研究总院科技信息研究所
北京有色金属研究总院国家复合中心工程中心
摘 要:
镁合金具有密度小、比强度高、可回收、优异的铸造性能和切削加工性能等特点, 在航空航天、交通工具、3C产品等领域具有十分广泛的应用前景。然而, 镁合金的耐蚀耐磨性能差, 限制了其更广泛应用。采用微弧氧化技术处理镁合金表面, 来提高镁合金的耐蚀耐磨性能是近几年新兴的表面技术。在微弧氧化过程中, 镁合金表面不断地陶瓷化, 最终获得与镁合金基体结合紧密的致密耐蚀耐磨陶瓷层。本文介绍了镁合金微弧氧化反应原理, 综述了稀土对镁合金微弧氧化层作用形式, 包括前处理、作为添加剂添加在电解液中以及稀土合金化方式。探讨了稀土对镁合金微弧氧化层的影响作用, 稀土通过影响微弧氧化过程、改变微弧氧化层的形貌和提高耐蚀相比例来改善微弧氧化层的耐磨耐蚀性能。指出今后可能的研究方向, 通过选择电导率合适、降低Mg O熔点和粘度的稀土盐添加剂, 从而提高微弧氧化膜层的致密性和耐蚀相比例, 有利于镁合金微弧氧化层性能的改善。
关键词:
稀土;镁合金;微弧氧化;耐腐蚀;
中图分类号: TG174.451
作者简介:马跃宇 (1970-) , 女, 辽宁人, 硕士, 教授级高级工程师, 研究方向:有色金属信息咨询;电话:010-82241918;E-mail:mayy2007@126.com;
收稿日期:2016-11-07
基金:国家科技部重点研发计划项目 (2016YFB0301001) 资助;
Effects of Rare Earths on Micro-Arc Oxidation of Magnesium Alloys: A Review
Ma Yueyu He Deshan Tu Sijing Che Cong Li Daquan
Division of Science and Technology Information, General Research Institute for Nonferrous Metals
National Engineering Technology Research Center for Nonferrous Metals Composites, General Research Institute for Nonferrous Metals
Abstract:
Due to low density, high strength-to-weight ratio, easy recycling, excellent casting and cutting properties, magnesium alloys have broad application prospects in traffic tools, aerospace, 3C products. However, poor corrosion resistances and wear resistances of magnesium alloys restrict wide applications. Micro-arc oxidation was a newly developed technique of dealing with magnesium alloys to improve the corrosion resistances and the wear resistances. During the micro-arc oxidation process, ceramic coatings which were compact and combined with magnesium alloys tightly grew constantly on the surface of magnesium alloys. In this paper, principles of micro-arc oxidation reactions were introduced. Functioning forms of rare earths, including pretreatment, additives in electrolyte and rare earths alloying were reviewed. Effects of rare earths including processing effects, improving morphology and changing phase ratios were discussed. Applying rare earths which had suitable conductivities and could decrease the melting point and the viscosity of Mg O might be the future research direction.
Keyword:
rare earths; magnesium alloy; micro-arc oxidation; corrosion resistance;
Received: 2016-11-07
镁合金具有密度小、比强度高、可回收、优异的铸造性能和切削加工性能等特点, 在航空、航天、交通工具、3C产品、纺织和印刷行业等领域具有十分广泛的应用前景。然而, 镁合金的耐蚀性和耐磨性能差, 限制了其更广泛应用。因此, 提高耐腐蚀性和耐磨性, 是扩大镁合金应用的关键[1,2,3,4,5]。
在镁合金表面采用传统的化学氧化和阳极氧化的表面处理技术, 由于氧化膜较薄, 耐蚀性差及污染环境等问题, 而难以满足防腐和环保的要求。微弧氧化技术是一种新兴的金属表面处理技术[6,7,8,9,10,11,12], 金属表面在微弧氧化过程中不断地陶瓷化。采用微弧氧化技术处理镁合金, 可获得与镁合金基体结合紧密的耐蚀耐磨陶瓷层, 从而改善镁合金的表面性能, 因而, 近年来, 微弧氧化技术是科研人员的研究热点[13,14,15,16,17,18,19,20,21,22]。
稀土元素具有改善陶瓷的致密性、韧性和烧结性能的作用[23,24,25,26,27], 但是, 有关稀土对镁合金微弧氧化层影响的综述文章很少, 因此, 分析总结稀土在微弧氧化中的作用十分必要。本文介绍了镁合金微弧氧化反应原理, 综述了稀土对镁合金微弧氧化层作用形式, 探讨了稀土对镁合金微弧氧化层的影响作用, 指出添加稀土元素提高微弧氧化层性能的研究方向。
1 镁合金微弧氧化反应原理
当在电解液中的镁合金通电后, 镁合金表面立即生成很薄的绝缘膜。当镁合金表面形成完整的绝缘膜, 施加的电压超过某一临界值时, 绝缘膜上阻值低的位置被击穿, 发生微弧放电现象, 膜层随之生长增厚。等离子体放电区瞬间温度很高, 镁合金表面的反应物经高温烧结成为陶瓷体, 与镁基体紧密结合。随着微弧氧化的继续, 膜层增厚, 击穿电压逐渐增高, 火花也由小变大。微弧氧化膜层表面有许多微孔, 但不是贯穿的, 所以能阻挡环境中的腐蚀物质进入膜层。微孔既是放电通道, 又是电解液中的氧或氢氧根离子生成氧气的气体通道。
以在硅酸钠电解液中进行反应为例, 镁合金微弧氧化过程主要有以下几种反应发生:
阴极反应:2H++2e→H2↑ (1)
阳极反应:4OH--4e→2H2O+O2↑ (2)
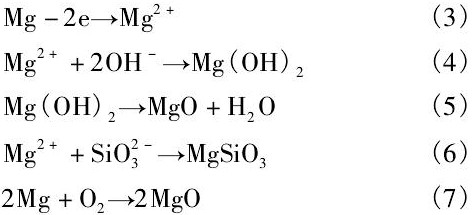
2 稀土对微弧氧化层的影响方式
稀土可以作为合金元素加入镁合金中, 也可以作为添加剂添加到电解液中使用, 还可以采用稀土溶液浸泡镁合金进行表面预处理, 由此可见, 稀土元素可以参与到微弧氧化的各个阶段、各种反应材料中对镁合金微弧氧化膜层的性能施加影响。
2.1 预处理方式
李建中等[28,29]研究了将镁合金浸泡在添加了硝酸铈、硝酸镧稀土添加剂的硅酸钠碱溶液中, 镁合金微弧氧化层的变化。实验结果表明经过稀土盐的预处理, 镁合金在微弧氧化过程中, 起弧电压下降, 镁合金微弧氧化膜层表观均匀致密, 厚度均匀, 耐蚀性提高, 膜层的成分没有改变。史敬伟等[30]也获得了类似结果。表1所示未经稀土和不同稀土前处理微弧氧化层比较[30]。
2.2 稀土添加到电解液中
徐涛涛和赵世明[31]研究了在硅酸钠溶液中分别添加硝酸镧、硝酸铈、氧化镧及硫酸铈稀土添加剂对镁合金微弧氧化层的影响, 研究表明在电解液中添加硝酸镧或硝酸铈, 可降低起弧电压, 膜层增厚, 孔洞与内膜层不连通, 稀土元素也提高了微弧氧化膜层的腐蚀电位, 降低了腐蚀电流。Shen等[32]也有类似的研究成果。
表1 未经稀土和不同稀土前处理的微弧氧化层比较Table 1Comparison of micro-arc oxidation coatings un-treated or treated by different rare earths 下载原图
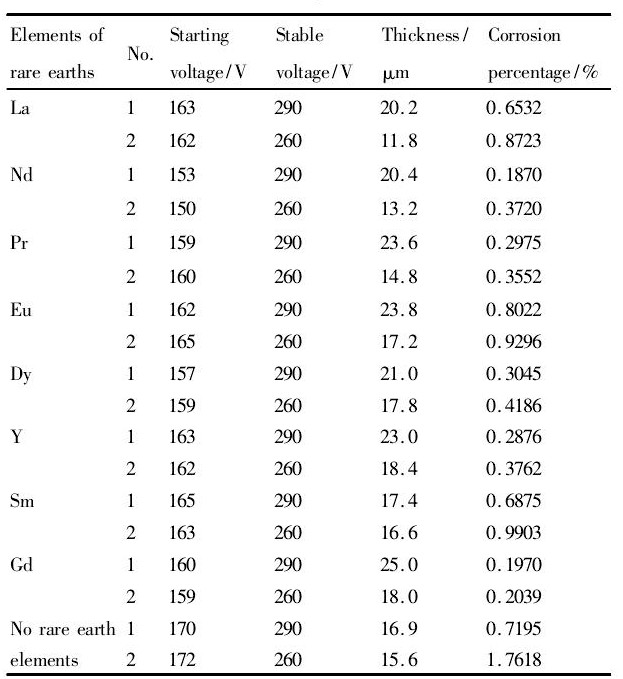
表1 未经稀土和不同稀土前处理的微弧氧化层比较Table 1Comparison of micro-arc oxidation coatings un-treated or treated by different rare earths
2.3 稀土合金化
贾方舟等[33]在硅酸钠碱溶液中研究了稀土镁合金的微弧氧化膜, 结果表明, 镁合金中的稀土元素有利于提高基体中Mg2+在微弧氧化过程中向膜层表面迁移的速度。
刘瑞霞等[34]在硅酸盐体系中研究了在镁合金中添加稀土元素钇和铈对微弧氧化层的影响。结果表明, 稀土元素使微弧氧化层表面更加光滑致密, Mg O和Mg2Si O4相增多, 微弧氧化层的耐磨、耐蚀性能提高。
3 稀土对镁合金微弧氧化层的作用
稀土元素对镁合金微弧氧化层的影响作用, 大致可分为3个方面:一是对微弧氧化过程的影响[28,29], 二是增加了微弧氧化层的厚度和改变了氧化层的形貌[31,33,34,35], 三是提高了耐腐蚀相的比例[34,35]。
3.1 稀土对微弧氧化过程的影响
由于稀土氧化物可促使金属阳极钝化, 从而降低了起弧电压和电流密度等参数。经稀土处理的电解液或镁合金, 在微弧氧化过程中, 镁合金微弧氧化的起弧时间、起弧电压和电流密度均有明显的降低。起弧电压可降低10~50 V, 未采用稀土元素处理前起弧电压越高, 经稀土元素处理后电压下降的幅度越大, 使氧化过程易于控制, 改善了微合金微弧氧化的成膜性能, 减少了电能能耗[28,29]。
3.2 稀土对氧化层厚度和微弧氧化层形貌的影响
微弧氧化过程中, 稀土元素有利于提高镁合金中的Mg2+向膜层表面迁移的速度, 镁元素在微弧氧化层的含量从内层到外层逐渐增加[33], 这可促进微弧氧化膜层上的反应发生, 有利于膜层的增长, 从而提高了镁合金微弧氧化膜层的生长速率, 相同的处理条件下膜层厚度有大幅增长, 而且氧化层厚度均匀, 与基体金属结合紧密[31], 这都有利于膜层的耐腐蚀、耐磨性能提高。
由于稀土离子的电价高、极化力强, 稀土盐的添加改变了电解液的电导率, 微弧氧化过程中, 等离子电弧相对平稳, 降低了微弧氧化烧结过程中金属氧化物的烧结温度, 从而氧化膜层的微观形貌发生了很大变化。经稀土元素处理的镁合金微弧氧化层表面光滑, 致密, 裂纹及孔洞数量减小, 孔径细小, 孔洞未与内膜层相连通。在微弧氧化前期, 陶瓷层主要为镁合金基体所形成的Mg O。Mg O的熔点比较高, 粘度比较大, 稀土氧化物的掺入能够降低其熔点, 减小粘度, 从而利于电弧通道的封闭和熔体中气体的逸出[35], 因而表面的孔洞与内膜层并不连通, 表面上只有较浅的火山口形貌。
3.3 稀土对耐蚀相比例的影响
经稀土处理的镁合金微弧氧化层耐蚀性明显提高, 稀土元素处理后的镁合金微弧氧化层主要包括Mg O和Mg Si O3相, 而未有稀土相, 与未经稀土处理的镁合金微弧氧化层的相组成相同。在微弧氧化前期, 陶瓷层主要为镁合金基体所形成的Mg O。Mg O的熔点比较高, 粘度比较大, 稀土氧化物的掺入能够降低其熔点, 减小粘度, 从而利于电弧通道的封闭和熔体中气体的逸出;同时, 稀土可阻止陶瓷晶粒的长大, 从而细化陶瓷组织。Mg2Si O4是在微弧氧化的后期, 由电解液中的硅酸根离子和已形成的Mg O在高温下合成的, 集中在陶瓷层的表层, 即疏松层中。由于稀土提高了Mg O的致密度, 陶瓷层的绝缘性能提高, 微弧氧化过程相对平稳, 电位对膜层的击穿能力降低, 使疏松层的厚度减小, 硅酸镁的数量也相对减少。因此, 加入稀土会起到降低陶瓷层孔隙率、提高致密度和提高陶瓷层中Mg O的作用, 也会使陶瓷层表面更加平整光滑, 这些作用有利于改善镁合金微弧氧化层的耐磨耐蚀等性能[35]。
由此可以看出, 在今后的研究中, 可选择电导率合适、降低Mg O熔点和粘度的稀土盐添加剂, 从而提高微弧氧化膜层的致密性和耐蚀相比例, 有利于镁合金微弧氧化层性能的改善。
4 结语
耐腐蚀磨损性能差是制约镁合金广泛应用的主要原因之一, 采用微弧氧化技术处理镁合金表面生成的陶瓷层可有效地提高镁合金的耐蚀耐磨性, 而稀土具有改善陶瓷的致密性和烧结性能的作用。稀土可以通过前处理、作为添加剂添加在电解液中以及稀土合金化方式对微弧氧化膜层施加影响。稀土通过影响微弧氧化过程、改变微弧氧化层的形貌和提高耐蚀相比例来改善微弧氧化层的性能。通过选择电导率合适、降低Mg O熔点和粘度的稀土盐添加剂, 可对微弧氧化膜层的封孔起到较大的作用, 从而提高微弧氧化膜层的致密性和耐蚀相比例, 有利于镁合金微弧氧化层性能的提高。
参考文献
[1] Gray J E, Luan B.Protective coatings on magnesium and its alloys—a critical review[J].Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2002, 336:88.
[2] Zhou W Q, Shan D Y, Han E H.Structure and formation mechanism of phosphate conversion coating on diecast AZ91D magnesium alloy[J].Corrosion Science, 2008, 50 (2) :329.
[3] Senf J, Broszeit E.Wear and corrosion protection of aluminum and magnesium alloys using chromium and chromium nitride PVD coatings[J].Advanced Engineering Materials, 1999, 1 (2) :133.
[4] Jiang Y F, Zhou H T, Zeng S M.Microstructure and properties of oxalate conversion coating on AZ91D magnesium alloy[J].Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2009, 19 (6) :1416.
[5] Zhu L Q, Liu H C.The effect of sol ingredient to anodic oxidation film on magnesium alloys[J].Journal of Functional Materials, 2005, 36 (6) :923.
[6] Jiang B L, Zhang X F, Zhu J.Study situation and industrial prospect on micro-arc oxidation of aluminum and magnesium alloys[J].Heat Treatment of Metals, 2004, 29 (1) :22. (蒋百玲, 张先锋, 朱静.铝、镁合金微弧氧化技术研究现状和产业化前景[J].金属热处理, 2004, 29 (1) :22.)
[7] Ma Y, Nie X, Northwood D O, Hu H.Systematic study of the electrolytic plasma oxidation process on a Mg alloy for corrosion protection[J].Thin Solid Films, 2006, 494 (1-2, 3) :296.
[8] Ma Y, Nie X, Northwood D O, Hu H.Corrosion and erosion properties of silicate and phosphate coatings on magnesium[J].Coatings and Thin Films, 2004, 469-470:472.
[9] Ma Y Y, Hu H, Northwood D O, Nie X Y.Optimization of the electrolytic plasma oxidation processes for corrosion protection of magnesium alloy AM50 using the Taguchi method[J].Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 2007, 182 (1-3) :58.
[10] Xue W B, Deng Z W, Lai Y C, Chen R Y, Zhang T H.Review of micro oxidation technique on surface of nonferrous metals[J].Heat Treatment of Metals, 2000, (1) :1. (薛文斌, 邓志威, 来永春, 陈如意, 张通和.有色金属表面微弧氧化技术评述[J].金属热处理, 2000, (1) :1.)
[11] Tang W X, Yan J K, Ni E X, Duan Z C, Wu Y F, Yang G.Mechanism and development trend of microarc oxidation[J].Hot Working Technology, 2016, 45 (14) :6. (唐婉霞, 严继康, 倪尔鑫, 段志操, 吴云峰, 杨钢.微弧氧化的机理及其发展趋势[J].热加工工艺, 2016, 45 (14) :6.)
[12] Duan G W, Gao X J, Man H, Zhang W, Jiang G H, Li J F.Research process in micro-arc oxidation[J].Ordnance Material Science and Engineering, 2010, 33 (5) :102. (段关文, 高晓菊, 满红, 张武, 姜光华, 李金富.微弧氧化研究进展[J].兵器材料科学与工程, 2010, 33 (5) :102.)
[13] Yerokhin A L, Nie X, Leyland A, Matthew A, Dowey S J.Plasma electrolysis for surface engineering[J].Surface and Coating Technology, 1999, 122 (2) :73.
[14] Liu Y H, Li S, Pang L.Micro-arc oxidation of AZ91D die cast magnesium alloys in phosphate electrolyte[J].Foundry, 2006, 55 (11) :1123.
[15] Bai A, Chen Z J.Effect of electrolyte additives on anticorrosion ability of micro-arc oxide coatings formed on magnesium alloy AZ91D[J].Surface and Coatings Technology, 2009, 203 (1) :1956.
[16] Liang J, Guo B G, Tian J, Liu H W, Xu T.Influence of process parameters on micro-arc oxidation coatings on AZ91C magnesium alloys[J].Journal of Materials Science and Engineering, 2005, 23 (2) :262.
[17] Mordike B L, Ebert T.Magnesium properties-applications-potential[J].Materials Science and Engineering A, 2001, 302 (1) :37.
[18] Xue W B, Wang C, Tian H.Corrosion behaviors and galvanic studies of microarc oxidation films on Al-Zn-MgCu alloy[J].Surface and Coatings Technology, 2007, 201:8695.
[19] Guo H F, An M Z.Growth of ceramic coatings on AZ91D magnesium alloys by micro-arc oxidation in aluminate-fluoride solutions and evaluation of corrosion resistance[J].Applied Surface Science, 2005, 246 (1-3) :229.
[20] Rama K L, Poshal G.Influence of electrolyte chemistry on morphology and corrosion resistance of micro-arc oxidation coatings deposited on magnesium[J].Metallurgical and Materials Transactions, 2010, A9:1.
[21] Gu Y H, Cai X J, Ning C Y, Xiong W M, Yue W, Hao B H.Effect of voltage on the microstructure and corrosion performance of microarc oxidation coated AZ31 magnesium alloys[J].China Surface Engineering, 2012, 25 (6) :21. (顾艳红, 蔡晓君, 宁成云, 熊文名, 岳文, 郝保红.电压对AZ31镁合金微弧氧化涂层微观结构及腐蚀性能的影响[J].中国表面工程, 2012, 25 (6) :21.)
[22] Lv W L, Ma Y, Chen T J, Xu W J, Yang J, Hao Y.Effects of oxidation time on microstructures and properties of micro-arc oxidation coatings of AZ91D magnesium alloy[J].The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2009, 19 (8) :1385. (吕维玲, 马颖, 陈体军, 徐卫军, 杨建, 郝远.氧化时间对AZ91D镁合金微弧氧化膜微观组织和性能的影响[J].中国有色金属学报, 2009, 19 (8) :1385.
[23] He K S, Cheng X Y, Li Z H.Surface modification on cermet coating microstructure by rare earths and its application development[J].Lubrication Engineering, 2009, 34 (3) :100. (何科杉, 程西云, 李志华.稀土对金属陶瓷涂层微观组织改性作用研究现状和应用进展[J].润滑与密封, 2009, 34 (3) :100.)
[24] Wang K L, Zhang Q G, Wei X G.Rare earth La2O3modification of laser clad coating[J].Journal of Materials Science, 1998, 33:3573.
[25] Cheng X Y, Shi L.Surface modification on ceramic coating by rare earths and its development trend[J].Lubrication Engineering, 2006, (1) :154. (程西云, 石磊.稀土对陶瓷层的改性作用研究现状及发展趋势[J].润滑与密封, 2006, (1) :154.)
[26] Fu P, Xu Z J, Chu R Q, Li W, Xie Q.Application study actuality and development foreground of rare earth oxides in ceramics materials[J].Ceramics, 2008, (12) :7. (付鹏, 徐志军, 初瑞清, 李伟, 谢倩.稀土氧化物在陶瓷材料中应用的研究现状及发展前景[J].陶瓷, 2008, (12) :7.)
[27] Tang Z Y.Application of rare earth elements in ceramics[J].Ceramics, 2008, (4) :37. (唐志阳.稀土元素在陶瓷中的应用[J].陶瓷, 2008, (4) :37.)
[28] Li J Z, Tian Y W, Cui Z X, Huang Z Q.Effects of rare earths on the microarc oxidation of a magnesium alloy[J].Rare Metals, 2008, 27 (1) :50.
[29] Li J Z, Tian Y W, Shao Z C.Effects of rare earths in the micro-arc oxidation process[J].Journal of the Chinese Rare Earth Society, 2006, 24 (S) :472. (李建中, 田彦文, 邵忠财.稀土在镁合金微弧氧化中的作用[J].中国稀土学报, 2006, 24 (S) :272.)
[30] Shi J W, Shao Z C, Tian Y W, Luan Y F, Sun Q.Effects of rare earths on micro-arc oxidation of a Mg alloy[J].Materials Protection, 2007, 40 (5) :7. (史敬伟, 邵忠财, 田彦文, 栾一凡, 孙全.稀土元素对镁合金微弧氧化的影响[J].材料保护, 2007, 40 (5) :7.)
[31] Xu T T, Zhao S M.Studies on the application of rare earth salt additive in micro-arc oxidation of magnesium alloys[J].Plating and Finishing, 2014, 36 (2) :5. (徐涛涛, 赵世明.稀土盐添加剂在镁合金微弧氧化中的应用研究[J].电镀与精饰, 2014, 36 (2) :5.)
[32] Shen D J, Ma H J, Guo C H, Cai J R.Effect of cerium and lanthanum additives on plasma electrolytic oxidation of AZ31 magnesium alloy[J].Journal of Rare Earths, 2013, 31 (12) :1208.
[33] Jia F Z, Tong W, Zhang L Y, Li J D, Liu B J, Yu J.Comparative study of micro-arc oxidation coatings on AZ31 and rare earth Mg alloy[J].Materials Review B, 2015, 29 (2) :46. (贾方舟, 佟玮, 张联英, 李吉丹, 刘宝军, 余剑.AZ31和稀土镁合金微弧氧化膜的对比研究[J].材料导报B, 2015, 29 (2) :46.)
[34] Liu R X, Guo F, Li P F, Liu L, Wang S, Zhao R R, Zhang Y L.Effect of RE elements in magnesium alloy on surface morphology and structure of ceramic coating by micro-arc oxidation[J].Heat Treatment of Metals, 2008, 33 (11) :70. (刘瑞霞, 郭峰, 李鹏飞, 刘亮, 王双, 赵瑞瑞, 张艳丽.稀土元素对镁合金微弧氧化陶瓷层表面形貌和结构的影响[J].金属热处理, 2008, 33 (11) :70.)
[35] Guo F, Liu R X, Li P F, Liu L.Effect of rare earth elements in electrolyte on ceramic coating prepared by micro-arc oxidation on AZ91D magnesium alloy[J].Transactions of Materials and Heat Treatment, 2011, 32 (2) :134. (郭峰, 刘瑞霞, 李鹏飞, 刘亮.电解液中的稀土对AZ91D镁合金微弧氧化陶瓷层的影响[J].材料热处理学报, 2011, 32 (2) :134.)