粘结剂对C-LiFePO4/石墨电池电化学性能的影响
刘云建,李新海,郭华军,王志兴,胡启阳,彭文杰,杨 勇,梁如福
(中南大学 冶金科学与工程学院,湖南 长沙,410083)
摘 要:采用商品化的LiFePO4作为原料,对比水系粘结剂和油性粘结剂(PVDF)对LiFePO4电池初始放电容量、循环性能,倍率性能和内阻的影响。利用XRD对循环后的电池正极进行分析。研究结果表明,油性粘结剂体系中LiFePO4的容量较高,首次放电容量达到124 mA?h/g,且循环性能较好,200次循环容量保持率为96.3%。发现水性粘结剂电池循环后LiFePO4结构变化较大。水性粘结剂的倍率性能良好,1C(C为充放电倍率)容量是0.1C的92.2%,而对于油性粘结剂,1C容量是0.1C的85.5%;水性体系中电极界面阻抗要小于油性体系中的界面阻抗,并且水性粘结剂电池的内阻要小于油性粘结剂的内阻。
关键词:LiFePO4;粘结剂;循环性能;倍率性能;交流阻抗
中图分类号:TM 912 文献标识码:A 文章编号:1672-7207(2009)01-0031-05
Influence of binder on performance of C-LiFePO4/graphite battery
LIU Yun-jian, LI Xin-hai, GUO Hua-jun, WANG Zhi-xing, HU Qi-yang,
PENG Wen-jie, YANG Yong, LIANG Ru-fu
(School of Metallurgical Science and Engineering, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China)
Abstract: The commercial LiFePO4 was used to produce full battery. The first discharge capacity, cycle performance, rate performance, and impedance of battery with water-binder battery and PVDF-binder battery were compared. The experiment indicates that the battery with PVDF-binder shows a higher capacity. The first discharge capacity is 124 mA?h/g. It also shows a good cycle performance, and the capacity retains 96.3% after 200 cycles. The battery with water-binder shows a good rate performance, and the ratio of 1C/0.1C is 92.2% compared with PVDF-binder battery’s 85.5%. Impedance spectra analyses indicate that the impedance of cathode interface with water-binder is lower than that of cathode interface with PVDF-binder. And the impedance of battery with water-binder battery is lower than that with PVDF-binder.
Key words: LiFePO4; binder; cycle performance; rate performance; AC impedance
橄榄石形结构的LiFePO4作为锂离子蓄电池新型正极材料,以其较高的理论比容量(170 mA?h/g)、适中的电压平台、良好的循环性能、安全性能以及原料广泛、对环境友好、价格便宜,而受到国内外研究者的广泛关注[1-3]。随着研究的深入,LiFePO4电池被认为是新一代EV和HEV动力电源的理想选择。
目前,随着LiFePO4正极材料的逐渐产业化,LiFePO4电池的制作也逐渐成为人们研究的热点[4-5]。由于LiFePO4的电导率比较低[6],锂离子扩散系数比较低,所以,一般在合成过程中,都把LiFePO4的颗粒控制在3~10 μm,以希望提高其电化学性能。由于LiFePO4的颗粒细小,所以,在涂布过程中,容易出现脱落的现象。可见,在LiFePO4电池的制作工艺中,粘结剂是一个非常关键的因素。关于LiFePO4电池的制作,国内正处在小批量的实验室制作阶段[4],并且未对LiFePO4电池的制作进行系统研究。为此,本文作者分别采用油性粘结剂PVDF和水性粘结剂LA133为正极粘结剂,制备LiFePO4全电池,研究粘结剂对LiFePO4电池容量、循环性能、倍率性能以及内阻的影响。
1 实 验
1.1 物相和形貌分析
利用X射线衍射仪(Rigaku公司,日本)对LiFePO4样品粉末进行物相分析,以Cu Kα靶作为辐射源,电压为40 kV,电流为50 mA,步宽为0.02?,扫描速度为2 (?)/min,扫描范围(2θ)为10?~90?。
用JSM-5600型扫描电子显微镜对LiFePO4的表面形貌进行表征。
1.2 电池制作
采用国内某公司的生产的LiFePO4为正极,上海杉杉科技有限公司生产的改性石墨为负极,正极粘结剂分别采用上海三爱富的PVDF和成都茵地乐生产的LA133,其质量分数分别为4%和7%。正极材料的各组分通过搅拌,涂布在正极集流体铝箔上,经过120 ℃真空脱气烘干压膜,然后制成小片。通过卷绕,装入钢壳,脉冲脱气48 h,注液(1 mol/L LiPF6+ (EC+DMC+EMC),其中EC,DMC和EMC之体积比为1?1?1)。搁置后预充、化成。
1.3 电池性能测试
将化成后的动力型锂离子电池在BK-7064测试柜上进行循环和倍率测试,充放电电压为2.2~3.8 V,充放电电流分别为0.1C,1/3C和1C(C为充放电倍率)。
利用BK-300内阻测试仪测试电池内阻。
2 结果与讨论
2.1 物相和形貌分析
图1所示为正极材料LiFePO4的XRD图谱。从图1可以看出,样品的X射线衍射图谱与LiFePO4标准谱图(PDFNo.40 1499)吻合,无任何杂质峰。且各条衍射峰尖锐,基线平整,这说明原料LiFePO4的结构发育较为完整。
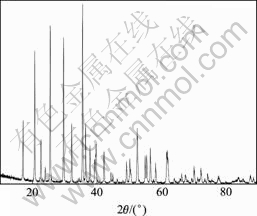
图1 LiFePO4的XRD图谱
Fig.1 XRD pattern of LiFePO4
图2所示为原料LiFePO4的SEM像。可以看出,原料LiFePO4的形貌呈块状,颗粒粒径一般在10 μm左右,且表面较粗糙。但是,通过进一步观察发现,LiFePO4大颗粒是由粒径为1 μm左右的小颗粒团聚而成,团聚后的颗粒较大,便于涂布。并且表面有包覆的碳。因为LiFePO4的电导率较低,故通常在制备过程中,包覆一定量的碳[7]。

图2 LiFePO4的SEM像
Fig.2 SEM images of LiFePO4
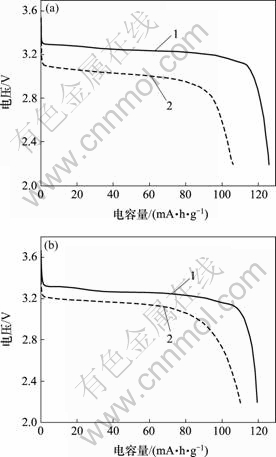
2.2 粘结剂对放电容量的影响
图3所示为不同粘结剂电池的放电曲线。放电电流为0.1C,充放电电压为2.2~3.8 V。2条放电曲线的放电平台基本一致,放电平台为3.2 V,水性和油性粘结剂体系的中LiFePO4的比容量分别为120和124 mA?h/g。水性体系中LiFePO4的克容量要略低于油性体系中LiFePO4的比容量。这可能是LiFePO4的表面较粗糙,并且在水性体系中LiFePO4颗粒表面吸附的水分较难除,残留的部分水分和电解液发生反应,生成HF。当Li+脱出时,活性Li+与HF发生反应,生成LiF沉淀,损失了一部分活性锂,进而导致比容量降低。具体反应如下[8]:
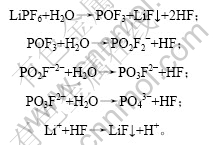
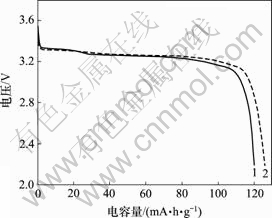
1—水性粘结剂;2—油性粘结剂
图3 不同粘结剂电池的放电曲线
Fig.3 Discharge curves of batteries with different binders
2.3 粘结剂对循环性能的影响
LiFePO4优异的循环性能一直是其受到人们青睐的主要原因之一,其循环寿命一般可以达到1 000次以上。图4所示为不同粘结剂体系LiFePO4电池的循环性能曲线,充放电电流为1/3C。循环200次以后,水系和油系粘结剂电池的容量保持率分别为93.2%和96.3%。由此可见,水性粘结剂体系中LiFePO4的循环性较差。因为在水性体系中,LiFePO4颗粒比较细小,且表面形貌不规则,易于吸附水分,不利于正极材料中水分的脱除,而目前用的锂离子电池电解液是非水系的,水分会促使电解质分解,具体反应如下:
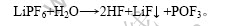
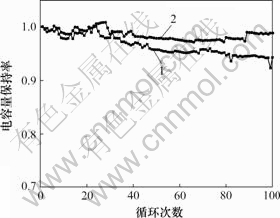
1—水性粘结剂;2—油性粘结剂
图4 不同粘结剂电池的循环性能
Fig.4 Cycle performances of batteries with different binders
从而严重影响电解液的电导率。并且因为存在水分,在充放电过程中,电压比较高(3.2 V),而水的分解电压只有2 V左右,所以,水分被分解,产生气体,而不能排出,造成电池鼓胀现象,从而影响正极材料的循环性能以及安全性能。此外,在循环过程中,电解液和水分不断反应,生成的HF不断地和Li+反应生成LiF,从而影响了放电容量。由此可见,在LiFePO4制作过程中水分的控制是非常重要的。
为了进一步研究不同粘结剂影响LiFePO4循环性能的原因,将循环后的电池放电至2.2 V,然后在手套箱中拆开,刮取正极料,进行XRD分析。
图5所示为不同粘结剂电池循环200次以后的正极材料的X射线衍射图谱。从衍射图谱可以看出,经过200次循环以后,正极材料中除了LiFePO4的特征衍射峰以外,还出现了一定的杂质,这些杂质可能是导电碳黑以及锂盐等。水性和油性不同的是,水性粘结剂电池经过200次循环以后,LiFePO4的各条主要衍射峰都向右漂移,并且主要衍射峰的相对强度也发生了一定的变化。这都证明,在水性粘结剂体系中,经过200次循环,LiFePO4的结构发生了较大的变化,进而导致循环性能下降。而油性粘结剂电池经过200次循环,除出现一些杂相外,其各主要衍射峰的衍射角度及相对强度都未发生明显变化。这表明,经过200次循环以后,其橄榄石结构保持得较为完好,宏观表现为循环性能良好。
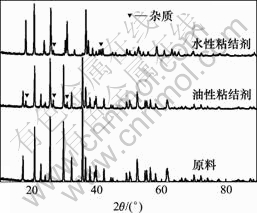
图5 LiFePO4 循环前后的XRD图谱
Fig.5 XRD patterns of LiFePO4 after cycling
LiFePO4作为动力电源的备选,其倍率性能一直是人们关注的焦点[9-10],LiFePO4电池的倍率性能受到多种因素的影响,除了受正极材料本身导电性的影响以外,还受到导电剂、粘结剂和电解液等因素的影响。本文研究了不同粘结剂对LiFePO4电池倍率性能的影响,图6所示为不同粘结剂电池的倍率性能比较结果。油性体系和水系LiFePO4电池1C的比容量分别为 106和110.5 mA?h/g,分别是0.1C比容量的85.5%和92.2%。由此可见,水性体系的倍率性能要优于油性体系的倍率性能。
(a) 油性;(b) 水性
1—0.1C;2—1C
图6 不同粘结剂电池的倍率性能
Fig.6 Rate performances of batteries with different binders
图7所示为不同粘结剂体系的充电态交流阻抗图谱。图中高频区的半圆代表电解液/电极表面钝化膜和双电层中的电荷转移反应,低频区的直线则代表锂离子在固相活性物质中的扩散。从图7可以清晰地看出,油性体系中电解液/电极表面钝化膜和双电层的阻抗要远远大于水性体系的阻抗。由于电极表面阻抗大,在大电流条件下,锂离子在界面的钝化膜和双电层中扩散受到影响,进而影响整个锂离子在电极中的脱/嵌过程,从而影响了电极的倍率性能。这可能是因为在油性体系中,粘结剂PVDF的含量要大于水性体系中LA133的含量,而LiFePO4活性物质量要少于水性体系的活性物质量,并且PVDF属大分子量聚合物,具有良好的绝缘性,因此,增大了油性体系中LiFePO4颗粒与电解液以及颗粒与颗粒之间的接触电阻,进而导致整个体系的电导率偏低,影响倍率性能。而LA133是聚丙烯酸,属Louis酸,具有一定电导率,因此,表现出较低的接触电阻。
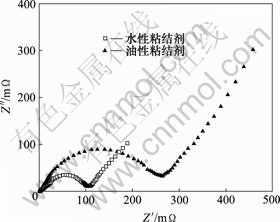
图7 不同粘结剂LiFePO4电池的阻抗曲线
Fig.7 AC impedance curves of LiFePO4 with different binders
2.4 粘结剂对电池内阻的影响
内阻是电池性能的一个很重要的参数,电池内阻直接影响到电池的端电压和输出功率以及使用效果。电池内阻一般由正负极电极的阻抗、电解液阻抗、电极和电解液界面阻抗以及电池极耳焊接阻抗等组成。本研究分别挑选不同粘结剂体系的电池8只,采用BK-300测试内阻,结果如图8所示。从图8可以看出,水性粘结剂体系电池的内阻只有6 mΩ左右,而油性体系电池的内阻则高达10 mΩ左右。在负极、电解液以及极耳焊接等因素相同的条件下,油性体系中,粘结剂PVDF的含量较高,电极的电导率降低,增大了LiFePO4颗粒与电解液以及颗粒与颗粒之间的阻抗,如图7所示,进而增大了整个电池的内阻。该结果与刘伯文等[11]报道的结果有些差别。因为刘伯文等采用的正极是LiCoO2,而LiCoO2的导电性要远远大于LiFePO4的导电性,所以,粘结剂对电池内阻的影响不是很大。LiFePO4的电导率不高,所以,粘结剂对电池内阻的影响容易得到体现。
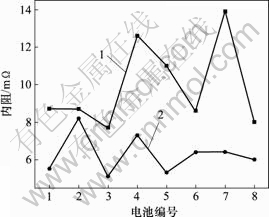
1—水性粘结剂;2—油性粘结剂
图8 不同粘结剂电池的内阻
Fig.8 Impedance curves of battery of different binders
3 结 论
a. 油性体系中LiFePO4的初始放电比容量达到124 mA?h/g,大于水性体系中的120 mA?h/g。油性粘结剂电池的循环性能优异,经200次循环,容量保持率96.3%,而水性粘结剂的只有93.2%。
b. 在水性体系中,LiFePO4经循环后,其橄榄石结构发生了较大的变化,这可能是导致其循环性能较差的原因。
c. 水性粘结剂电池的倍率性能良好,1C容量是0.1C容量的92.2%,而对于油性粘结剂,1C容量只是0.1C容量的85.5%。水性体系中电极界面阻抗小于油性体系中的界面阻抗,并且水性粘结剂电池的内阻小于油性粘结剂的内阻。
参考文献:
[1] Daiwon C, Prashant N K. Surfactant based sol-gel approach to nanostructured LiFePO4 for high rate Li-ion batteries[J]. J Power Sources, 2007, 163(2): 1064-1069.
[2] XIA Y G, Masaki Y, Hideyuki N. Improved electrochemical performance of LiFePO4 by increasing its specific surface area[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2006, 52(1): 240-245.
[3] Jae-Kwang K, Gouri C, Jae-Won C, et al. Effect of mechanical activation process parameters on the properties of LiFePO4 cathode material[J]. J Power Sources, 2007, 166(1): 211-218.
[4] GU Y J, ZENG C S, WU H K, et al. Enhanced cycling performance and high energy density of LiFePO4 based lithium ion batteries[J]. Material Letters, 2007, 61(25): 4700-4702.
[5] Guerfi A, Kaneko M, Petitclerc M, et al. LiFePO4 water-soluble binder electrode for Li-ion batteries[J]. J Power Sources, 2007,163(2): 1047-1052.
[6] Indrajeet V T, Vipul M, John N H, et al. Performance of carbon-fiber-containing LiFePO4 cathodes for high-power applications[J]. J Power Sources, 2006, 162(2): 673-678.
[7] Song M S, Kang Y M, Kim J H, et al. Simple and fast synthesis of LiFePO4-C composite for lithium rechargeable batteries by ball-milling and microwave heating[J]. J Power Sources, 2007, 166(1): 260-265.
[8] 吕东生, 李伟善, 刘 煦, 等. LiMn2O4的容量衰减机理和结构稳定方法[J]. 电池工业, 2004, 9(5): 244-246.
LU Dong-sheng, LI Wei-shan, LIU Xu, et al. Mechanisms of capacity fading and methods to stabilize structure of spinel LiMn2O4[J]. Chinese Battery Industry, 2004, 9(5): 244-246.
[9] WANG Y Q, WANG J L, YANG J, et al. High-rate LiFePO4 electrode material synthesized by a novel route from FePO4?4H2O[J]. Advanced Functional Material, 2006, 16(3): 2135-2140.
[10] WANG D Y, LI H, SHI S Q, et al. Improving the rate performance of LiFePO4 by Fe-site doping[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2005, 50(14): 2955-2958.
[11] 刘伯文, 耿海龙, 王新东, 等. 粘结剂对锂离子蓄电池性能的影响[J]. 电源技术, 2005, 29(5): 297-300.
LIU Bo-wen, GENG Hai-long, WANG Xin-dong, et al. Influence of binder on performance of Li-ion battery[J]. Chinese Journal of Power Sources, 2005, 29(5): 297-300.
收稿日期:2007-12-26;修回日期:2008-03-26
基金项目:国家重点基础研究资助项目(2007CB613607)
通信作者:李新海(1962-),男,湖南邵阳人,教授,从事能源材料及电化学研究;电话:0731-8836633;E-mail: lyjian122331@yahoo.com.cn