文章编号:1004-0609(2011)03-0675-05
石灰和氢氧化钠对黄铁矿浮选抑制的电化学行为
张 英1, 覃武林2, 孙 伟1, 何国勇1
(1. 中南大学 资源加工与生物工程学院,长沙 410083;2. 湖南辰州矿业股份有限公司,怀化 419607)
摘 要:采用热力学计算及交流阻抗和循环伏安等电化学方法研究石灰和氢氧化钠对黄铁矿浮选抑制行为的影响。单矿物浮选试验结果表明:当pH值为7.0~11.5时,石灰对黄铁矿的抑制作用强于氢氧化钠;当pH>11.5时,石灰和氢氧化钠均对黄铁矿表现出强烈的抑制作用。热力学计算和电化学测试结果表明:黄铁矿表面法拉第反应电阻Rp随pH值的升高而减小,利于黄铁矿表面的电子传递,从而使得黄铁矿表面更易于氧化,导致Fe(OH)3和SO42-等亲水性物质的生成;在碱性条件下,黄铁矿表面电阻Rs增大,说明其表面覆盖不良导电物质;在石灰体系中,同时存在钙膜的影响,使得Rs增加的幅度比在氢氧化钠体系中的大,该结果与浮选试验结果一致。
关键词:黄铁矿;石灰;氢氧化钠;浮选;交流阻抗;循环伏安
中图分类号:TD913 文献标志码:A
Electrochemical behaviors of pyrite flotation using lime and sodium hydroxide as depressantors
ZHANG Ying1,QIN Wu-lin2,SUN Wei1,HE Guo-yong1
(1. School of Resources Processing and Bioengineering, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China;
2. Hunan Chenzhou Mining Co., Ltd., Huaihua 419607, China)
Abstract: Thermodynamic calculations, alternating current impedance and cyclic voltammetry were adopted to study the flotation behaviors of lime and sodium hydroxide on the pyrite. Single mineral flotation test results show that lime depresses pyrite more strongly than sodium hydroxide when pH is in the range of 7.0-11.5; at pH> 11.5, lime and sodium hydroxide depress pyrite intensely. By thermodynamic calculations and electrochemical tests, the Faraday resistance Rp of pyrite surface is declined by increasing pH, which is helpful for the electron transfer and oxidation on the surface of pyrite, resulting in producing hydrophilic substance, such as Fe(OH)3 and SO42-. Under alkaline conditions, the surface resistance Rs of pyrite increases, and unconductive material appears on its surface. The increment of Rs in lime system is larger than that in sodium hydroxide system for the adsorption of calcium membrane on the surface of pyrite, which is the reason why lime has stronger depression effect on the pyrite flotation than sodium hydroxide.
Key words: pyrite; lime; sodium hydroxide; flotation; alternating current impedance; cyclic voltammetry
黄铁矿作为最普遍的金属硫化矿床,常与铅、锌和铜等金属共生。常规浮选一般是先抑制黄铁矿,回收有价主元素金属,再活化浮硫。高碱电位调控技 术[1-6]是分选多金属硫化矿的有效方法,该技术使用石灰作为黄铁矿的抑制剂,抑制后的黄铁矿浮游性差。国内外许多学者对黄铁矿的抑制和活化浮选进行了大量的研究[7],LI等[8]通过计算黄铁矿(100)面的电子结构和表面能级分布密度,得出在石灰体系中,黄铁矿表面易于吸附OH-和Ca(OH)+而使浮选行为恶化,降低其可浮性。WOODS[9]、 LI等[10]及BUSWELL等[11]基于硫化矿浮选抑制的电化学机理,研究了黄铁矿在高碱环境中由于表面氧化电位降低,促进表面氧化生成Fe(OH)3和SO42-等亲水性物质的机理。
陈建华等[12]采用硫化矿电化学调控能带模型得出高碱条件会改变弯曲黄铁矿的边缘能级,使之更易于氧化的结论。根据XPS能谱分析,在高碱高钙条件下,黄铁矿表面存在CaSO4、Ca(OH)2和Fe(OH)3 等亲水物质[3, 13]。本文作者通过单矿物浮选实验、热力学计算、交流阻抗及循环伏安曲线的测定,对石灰和氢氧化钠形成的高碱体系中黄铁矿的浮选行为和电化学机理进行研究,为应用高碱电位调控技术浮选黄铁矿提供技术基础。
1 实验
1.1 矿样和试剂
黄铁矿单矿物取自安徽铜陵冬瓜山铜矿,经手选除杂及瓷筒磨碎后,筛分选取0.040~0.074 mm粒级的矿样进行单矿物浮选,矿样纯度为95.43%。矿样的XRD谱如图1所示。

图1 矿样的XRD谱
Fig.1 XRD pattern of ore sample
实验用硫酸、石灰、氢氧化钠、丁基黄原酸钾及硝酸钾等均为分析纯。
1.2 单矿物浮选
单矿物浮选试验在有效容积为25 mL的挂槽式浮选机中进行。每次试验取单矿物2.1 g,加一次蒸馏水50 mL,置于超声波清洗器中清洗5 min,澄清,倒去上面悬浮液,然后进行浮选。浮选时捕收剂丁基黄原酸钾的浓度为1×10-4 mol/L,起泡剂用量为16 mg/L,刮泡前测量矿浆的pH值,浮选时间为3 min。
1.3 电化学测试
矿物电极:选取大块结晶良好的黄铁矿颗粒,切片,逐级打磨成直径为10 mm、厚度为3 mm的圆片,经丙酮除油后,用银粉导电胶与直径为1.5 mm的铜线连接,用树脂封装于管径为15 mm的塑料管中,铜线封装于玻璃管中,露出长度为20 mm的铜线以便接线,玻璃管两端灌以树脂以保密封。
电化学测试采用三电极系统,矿物电极为工作电极,铂电极为辅助电极,饱和甘汞电极作为参比电极。使用二次蒸馏水,以浓度为0.1 mol/L的硝酸钾为支持电解质。试验在如图2所示的电解槽中进行,电解槽为H型,槽容积为300 mL,阴极与阳极用多孔材料分隔,如图2所示。测量仪器为美国普林斯顿EG&G PARC公司生产的 Model 283电化学测量系统,交流阻抗测量软件为Powersuit电化学工作站中的PowerSine模块,在开路电位下进行,测试频率为0.01~100 Hz,正弦波振幅为5 mV。测量结果用交流阻抗分析软件Zview拟合分析。循环伏安扫描测试使用Powersuit电化学工作站中的PowerCV模块。

图2 三电极H型电解槽装置示意图
Fig.2 Schematic diagram of device of H-type three-electrode cell
2 结果及讨论
2.1 石灰和氢氧化钠对黄铁矿浮选性能的影响及热力学行为
在黄铁矿浮选中,一般采用硫酸和氢氧化钠作为调整剂,基于此,本文作者研究了石灰和氢氧化钠碱性pH调整剂对黄铁矿浮选性能的影响,结果如图3所示。
从图3可看出:黄铁矿在酸性和中性环境中均表现出良好的可浮性;当使用氢氧化钠作为调整剂且pH<11.5时,黄铁矿依然保持较好的可浮性,此后继续加大氢氧化钠的用量,提高矿浆的pH值,黄铁
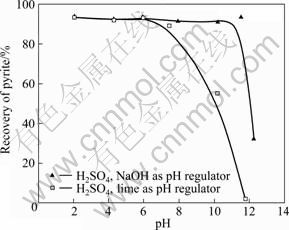
图3 丁基黄原酸钾(KBX)浓度为1×10-4 mol/L 时pH调整剂对黄铁矿浮选的影响
Fig.3 Influence of various pH regulators on pyrite flotation at KBX concentration of 1×10-4 mol/L
矿的可浮性急剧下降;当使用石灰作为碱性调整剂时,在弱碱性条件下,黄铁矿的可浮性开始出现下降,并随着石灰用量的增加急剧降低,当pH=11.73时黄铁矿完全被抑制。
在碱性条件下,黄铁矿的氧化反应如下:
FeS2+11H2O=Fe(OH)3+2SO42-+19H++15e (1)
φ0=0.402 V (2)
令c(SO42-)=1×10-6 mol/L,由于形成SO42-存在300 kJ/mol的势垒,将这一能量转换成电位,其值约为3.114 nV,则有
φ′h=0.768 1 – 0.074 73pH (3)
由式(3)可知,随着pH值的提高,φ′h越低,越有利于黄铁矿的氧化。
从图3可以看出,在强碱条件下黄铁矿的可浮性变差。这是由于在高碱体系中黄铁矿表面发生如式(1)所示的反应,生成亲水性的Fe(OH)3和SO42-,降低了黄铁矿的可浮性。当有游离氧化钙存在时,黄铁矿表面吸附CaSO4和Ca(OH)2等亲水性物质,进一步抑制了黄铁矿的浮选。
2.2 石灰和氢氧化钠对黄铁矿表面电化学行为的影响
图4所示为黄铁矿在不同环境下的交流阻抗谱。其中空白溶液表示只添加支持电解质硝酸钾的溶液体系,石灰体系的浓度为400 mg/L(7.13×10-3 mol/L),pH=12.13,调节氢氧化钠体系的pH值,使之与石灰体系的相同。图4显示黄铁矿在不同环境中表现出单一的容抗弧,在石灰体系和氢氧化钠体系中,黄铁矿的容抗弧明显比其在空白溶液体系中的小,说明黄铁矿在高碱环境中更易于被氧化。这个结论与式(1)一致。

图4 黄铁矿在不同溶液体系中的Nyquist谱
Fig.4 Nyquist plots of pyrite at open-circuit potential in different solution systems
为了考察石灰与氢氧化钠对黄铁矿浮选作用机理的差异,根据图4的试验结果,设计了如图5所示的模拟电路[14-15]。图5中Ro为仅有支持电解质体系时工作电极与辅助电极之间的电阻。影响Ro的因素包括电极材料、表面粗糙度、支持电解质的浓度、温度以及分隔两电极的多孔材料的性质等,这些因素基本保持不变,在高频1 kHz时Ro为58.7 Ω/cm2,模拟时固定Ro的值。Rs表征表面吸附膜的形成对电极表面的影响,影响Rs的因素包括吸附膜的导电性能、厚度及致密度等;Rp为法拉第反应电阻,表征表面氧化还原反应的难易程度,影响Rp的因素包括反应类型、电极表面过电位、实际表面积及吸附膜的性质等;Cs为双电层电容,RW代表平面电极由半无限扩散引起的抗阻,可以用一个恒相角元件模拟,相角固定为45°。模拟结果见表1。
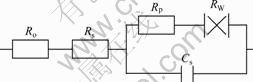
图5 黄铁矿/溶液表面电极反应模拟等效电路图
Fig.5 Simulated equivalent circuit of electrolytic reaction of pyrite/solution surface
表1 不同体系对黄铁矿/溶液界面模拟电路参数的影响
Table 1 Effects of different solution systems on parameters of simulated equivalent circuit for pyrite/solution interface
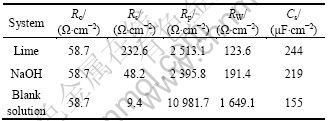
从表1的模拟结果可以看出,结合在两种体系环境中黄铁矿表面电阻Rs的差异分析,在添加石灰的溶液中,黄铁矿表面电阻Rs增加到232.6 Ω/cm2,在添加氢氧化钠的溶液中,Rs增加到48.2 Ω/cm2,说明黄铁矿在添加石灰的溶液中,表面氧化生成或吸附形成更厚的非导电膜,两者的主要差异在于石灰体系中黄铁矿表面可能生成亲水钙膜,钙膜也是不良导电体,从而导致其Rs升高,同时也使电极的反应面积减小、Rp增大。将高碱体系与空白溶液体系相比,碱性环境能降低黄铁矿表面电子跃迁的势垒,表现为Rp的降低,而在碱性环境中黄铁矿表面生成的亲水膜为不良导电体,将减少其表面参加反应的面积,导致Rp的增大。综合这两方面因素,前者占主导地位,总的表现为Rp的降低。
在添加石灰和氢氧化钠的溶液中,黄铁矿表面反应电阻Rp均由中性环境中的10 987.1 Ω/cm2降至2 500 Ω/cm2附近。结合黄铁矿表面电极过程热力学分析,在两种体系环境中,黄铁矿表面自身氧化电位均降低,使其表面电子更易于传递,表现为法拉第电阻Rp的降低。添加氢氧化钠的体系的Rp的值较添加石灰的小。
添加石灰和氢氧化钠后,黄铁矿表面反应电阻Rp和表面电阻Rs均发生了变化,且添加氢氧化钠后,体系的Rp和Rs较添加石灰的小,由此可以说明,石灰比氢氧化钠对黄铁矿抑制能力强是由于Rp和Rs的变化。
图6所示为黄铁矿在不同溶液体系中的循环伏安曲线。由图6可知,黄铁矿在空白溶液体系中,当电位范围较大时(φh<0.68V),极化电流保持较低,说明黄铁矿表面性质在该体系中比较稳定,而在石灰和NaOH体系中,黄铁矿在较低的电位下(φh=0.1 V),极化电流就开始上升,并随着电位的增加极化电流急剧增大,说明其表面发生了剧烈的阳极氧化。当φh<0.65 V时,黄铁矿在石灰体系的氧化反应弱于在NaOH体系中的(极化电流小),与交流阻抗测试结果相符(石灰体系中的Rp较NaOH体系中的大);当φh≥0.65 V时,电极过程转为浓差扩散控制阶段,在石灰体系中,黄铁矿表面氧化生成的SO42-与体系中Ca2+结合生成CaSO4沉淀,有利于SO42-的扩散,削弱浓差扩散控制,使得在黄铁矿在石灰体系中的极化电流反而小于在NaOH体系中的。这个现象与前述浮选结果和交流阻抗测试结果一致,表明添加石灰后形成的表面膜能更好地抑制黄铁矿表面电化学反应的发生。

图6 黄铁矿在不同溶液体系中的循环伏安曲线
Fig.6 CV curves of pyrite in different solution systems
3 结论
1) 石灰能强烈抑制黄铁矿的浮选,低用量的氢氧化钠(pH<11.5)不能有效地抑制黄铁矿的浮选。
2) 高碱体系降低了黄铁矿表面的氧化电位,使得矿石颗粒表面更易于被氧化,生成Fe(OH)3和SO42-等亲水性物质,降低矿物可浮性。在石灰存在的条件下,矿物表面同时吸附形成Ca(OH)2和CaSO4等亲水钙膜,使得浮选行为进一步恶化。
3) 电化学测试结果表明:黄铁矿表面的法拉第反应电阻Rp随pH值的升高而减小,极化电流随pH值的升高而增高,说明黄铁矿表面电子传递易于进行,表面氧化趋向容易,导致Fe(OH)3和SO42-等亲水性物质的生成。在碱性条件下黄铁矿的表面电阻Rs增大,也说明其表面有不良导电物质覆盖;在石灰体系中,还存在钙膜的影响,使得表面电阻Rs增加的幅度比在氢氧化钠体系中的大,在浮选实验中表现为石灰的抑制能力强于氢氧化钠的。
REFERENCES
[1] 胡岳华, 孙 伟, 覃文庆. 方铅矿浮选的机械电化学行为[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2002, 12(5): 1061-1064.
HU Yue-hua, SUN Wei, QIN Wen-qing. Mechanics- electrochemistry action in PbS flotation[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2002, 12(5): 1061-1064.
[2] GU Guo-hua, HU Yue-hua, QIU Guan-zhou, WANG Hui, WANG Dian-zuo. Potential control flotation of galena in strong alkaline media [J]. Journal of Central South University of Technology, 2002, 9(1): 16-20.
[3] 覃文庆. 硫化矿物颗粒的电化学行为和电位调控浮选技术[D]. 长沙: 中南工业大学矿物工程系, 1998: 98-109.
QIN Wen-qing. Electrochemistry mechanics of sulfide particle and potential-control technique[D]. Changsha: Department of Minerals Engineering, Central South University of Technology, 1998: 98-109.
[4] QIN Wen-qin, HE Ming-fei, CHEN Yu-ping. Improvement of flotation behavior of Mengzi lead-silver-zinc ore by pulp potential control flotation[J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2008, 18(4): 949-954.
[5] CHANDRA A P, GERSON A R. A review of the fundamental studies of the copper activation mechanisms for selective ?otation of the sul?de minerals, sphalerite and pyrite[J]. Advances in Colloid and Interface Science, 2009, 145(1/2): 97-110.
[6] 赵春艳, 余克峰. 多金属硫化矿的选硫技术改进[J]. 有色矿冶, 2008, 24(1): 17-19.
ZHAO Chun-yan, YU Ke-feng . The technical improvement of recovering sulphur from polymetallic sulphide ores[J]. Non-ferrous Mining and Metallurgy, 2008, 24(1): 17-19.
[7] WANG Dian-zuo, QIN Wen-qing, GU Guo-hua. Electrochemistry of flotation: Potential control flotation technology of sulfide minerals [C]//CIM 23rd International Mineral Processing Congress. Istanbul: Istanbul Technical University, 2006: 665-674.
[8] LI Quan, QIN Wen-qing, SUN Wei, QIU Guan-zhou. Calculation of electron structure by density function theory and electrochemical process of surface (100) of FeS2[J]. Journal of Central South University of Technology, 2007, 14(5): 618-622.
[9] WOODS R. Electrochemical potential controlling flotation[J]. International Journal of Mineral Processing, 2003, 72(1/4): 151-162.
[10] LI Wei-zhong, QIN Wen-qing, SUN Wei, QIU Guan-zhou. Electrodeposition of dixanthogen (TETD) on pyrite surface[J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2007, 17(1): 154-158.
[11] BUSWELL A M, BRADSHAW D J, HARRIS P J, EKMEKCI Z. The use of electrochemical measurements in the flotation of a platinum group minerals(PGM) bearing ore[J]. Minerals Engineering, 2002, 15(6): 395-404.
[12] 陈建华, 冯其明, 卢毅屏. 电化学调控浮选能带模型及应用(Ⅰ)—半导体能带理论及模型[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2000, 10(2): 240-244.
CHEN Jian-hua, FENG Qi-ming, LU Yi-ping. Energy band model of electrochemical flotation and its application(Ⅰ)—Theory and model of energy band of semiconductor-solution interface[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2000, 10(2): 240-244.
[13] MURPHY R, STRONGIN D R. Surface reactivity of pyrite and related sulfides[J]. Surface Science Reports, 2009, 64(1): 1-45.
[14] 王少芬, 方 正. 硫化矿阳极氧化的交流阻抗[J]. 中南大学学报: 自然科学版, 2006, 37(2): 274-279.
WANG Shao-fen, FANG Zheng. Anodic oxidation of sulfide minerals by alternating current impedance technique[J]. Journal of Central South University: Science and Technology, 2006, 37(2): 274-279.
[15] 孙 伟. 高碱石灰介质中电位调控浮选技术原理与应用[D]. 长沙: 中南大学矿物工程系, 2001: 70-75.
SUN Wei. Mechanism and applications of potential-controlled flotation in lime adjust high alkali pulp[D]. Changsha: Department of Minerals Engineering, Central South University, 2001: 70-75.
(编辑 陈卫萍)
基金项目:国家“十一五”科技支撑计划资助项目(2006BA02A06)
收稿日期:2010-03-09;修订日期:2010-06-21
通信作者:孙 伟,教授,博士;电话:0731-88830623;E-mail:sunmenghu@mail.csu.edu.cn