文章编号:1004-0609(2013)08-2098-06
断续时效对2519A铝合金组织和力学性能的影响
顾 刚1, 2,叶凌英1, 2,张新明1, 2,蒋海春1, 2,孙大翔1, 2,张 盼1, 2
(1. 中南大学 材料科学与工程学院,长沙 410083;
2. 中南大学 有色金属材料科学与工程教育部重点实验室,长沙 410083)
摘要:通过硬度试验、拉伸试验、扫描电镜以及透射电镜研究断续时效对2519A铝合金板材微观组织和力学性能的影响。研究表明:2519A铝合金经断续时效(T9I6)后,其屈服强度、抗拉强度和伸长率分别为501 MPa、540 MPa和14%,相比于2519A-T87状态铝合金的450 MPa、480 MPa和9%,分别提高了51 MPa、60 MPa和5%。在断续时效过程中,低温保温可以使基体内不断形成大量临界尺寸的密集、细小的GP区,而使时效相也趋于细小、密集,从而提高了合金的力学性能。
关键词:2519A铝合金;断续时效;组织;力学性能
中图分类号:TG146 文献标志码:A
Effects of interrupted ageing on microstructure and mechanical properties of 2519A aluminum alloy
GU Gang1, 2, YE Ling-ying1, 2, ZHANG Xin-ming1, 2, JIANG Hai-chun1, 2, SUN Da-xiang1, 2, ZHANG Pan1, 2
(1. School of Materials Science and Engineering, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China;
2. Key Laboratory of Nonferrous Metals Materials Science and Engineering, Ministry of Education, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China)
Abstract: The effect of interrupted ageing on the microstructure and mechanical properties of 2519A aluminum alloy was studied by means of hardness, tensile test, SEM and TEM. After the T9I6 heat treatment, the yield strength, tensile strength and elongation of 2519A aluminum alloy can reach 501 MPa, 540 MPa and 14%, respectively. Compared to T87 temper, which is 450 MPa, 480 MPa and 9%, respectively, the mechanical properties of 2519A-T9I6 increases by 51 MPa, 60 MPa and 5%, respectively. During the process of interrupted aging, keeping the alloy in a lower temperature contributes to forming the numerous, finer and denser GP zone with critical size. So, the following precipitated phase will also be finer and denser, which results in the increasing mechanical properties of 2519A aluminum alloy.
Key words: 2519A aluminum alloy; interrupted ageing; microstructure; mechanical properties
2519A铝合金是在美国2519铝合金基础上发展而来的铝合金。作为一种装甲材料,2519A需要不断提高抗弹性能,关键需要提高合金的强度。2519A-T87状态合金的抗拉强度可达475 MPa,伸长率为9.9%[1],但随着预变形量的提高,2519A铝合金的强度也随之提高[2-3],然而塑性明显降低,例如80%冷变形后峰时效强度可达551 MPa,且伸长率仅为4%。强变形工艺通过加工硬化提高了材料的强度,但却损失了材料的塑性和韧性。LI等[4]研究了Y对2519A铝合金力学性能的影响,发现添加0.1%Y的2519A-T87铝合金屈服强度、抗拉强度、伸长率分别为445 MPa、485 MPa和9%。WANG等[5]也发现,添加0.21%Ce的2519A-T87铝合金的屈服强度、抗拉强度、伸长率可分别提高至 436 MPa、493 MPa、10.7%。微合金化处理在保持良好塑性、韧性和腐蚀性能[6]的情况下,提高2519A铝合金的力学性能。本研究探求一种新的热处理技术,以期2519A铝合金在获得良好强度的同时不损失塑性和韧性。
多级时效制度在Al-Zn-Mg-Cu[7-8]和Al-Li[9]铝合金上得到了广泛的应用,对于提高材料的服役性能,多级时效效果较为明显。断续时效是多级时效制度的一种,相比于传统的单级热处理工艺,其能使材料得到更理想的服役性能[10-12]。而T9I6则是断续时效工艺中研究得相对较少的制度,国内外都鲜有报道。T9I6热处理制度就是打断传统的T8热处理制度,先进行预时效,随后进行一定量的冷变形,冷变形后则是低温长时保温,长时保温结束以后再回到T8热处理达到峰时效状态。而T9I6中间的低温长时保温就是所说的“断续”。本文作者探索适用于2519A铝合金的断续时效制度(即T9I6制度)在时效过程中的作用机理,以提高2519A铝合金的性能为目的,并对2519A-T87和2519A-T9I6进行比较。
1 实验
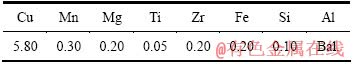
实验的原材料为在西南铝生产的2519A板材,其名义成分如表1所列。T87热处理制度为:固溶+冷轧+峰值时效。T9I6的工艺冷变形量选取与T87一致的7%,时效温度参照T87的时效制度制定,基本工艺为固溶+预时效+冷轧+断续时效+再时效,T9I6的工艺路线如图1所示。
表1 2519A铝合金的化学成分
Table 1 Chemical compositions of 2519A (mass fraction, %)
对获得的板材进行室温力学性能测试,在SEM上观察断口形貌,并通过TEM对不同状态样品进行分析。TEM试样采用双喷减薄制备,电解液为20%HNO3+80%CH3OH(体积分数),采用液氮冷却,温度控制在-20 ℃以下。实验中的主要检测设备如下:HV-10B硬度仪,MTS Landmark电液伺服试验系统,FEI Sirion200型扫描电镜及TecnaiG220透射电镜。
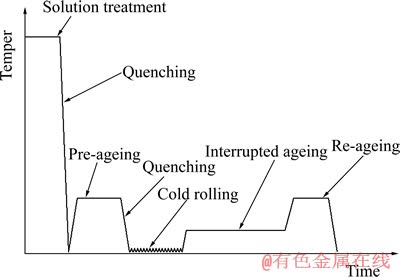
图1 T9I6工艺路线图
Fig. 1 Process route of T9I6
2 结果与分析
2.1 T9I6时效硬化曲线
按图1所示工艺,对2519A铝合金板材进行人工时效,得到2519A-T87和2519A-T9I6两种不同的状态铝合金。固溶态的2519A铝合金硬度为85.0 HV,预时效阶段,硬度值有一个“阶跃”式的提高,这主要是因为时效析出强化。预时效后,硬度达到122.9 HV。冷轧后,硬度提高到了143.2 HV,这主要是由加工硬化所致,另外,冷轧增加晶体的位错和空位密度,促使GP区和第二相的析出。在断续时效阶段,硬度缓慢地上升,整个阶段硬度提高不明显。随后,将合金随炉加热再时效,峰时效硬度值为167.2 HV。再时效过程的后期阶段,时效硬化曲线的上升趋于平缓,说明合金的时效强化潜力在不断地减少。相比于2519A-T87在的峰时效硬度值(144.6 HV),提高了约22.5 HV,效果比较明显。
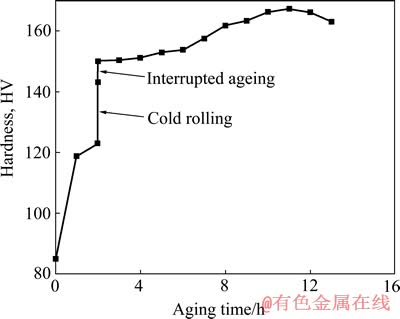
图2 T9I6工艺的时效硬化曲线
Fig. 2 Relationship between hardness and aging time on T9I6 process
2.3 拉伸性能测试
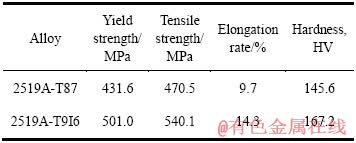
2519A-T87和2519A-T9I6的室温力学性能如表2所列。2519A-T9I6的力学性能有显著提高,抗拉强度高达540.1 MPa,相比于2519A-T87提高了近70 MPa,伸长率也有着显著的提高,达到14.33%。
对拉伸后的样品在SEM上观察断口形貌。两者的断口形貌如图3所示,两种状态下,2519A板材均是韧性断裂,都有着沿晶、穿晶韧窝,是一种典型的混合断裂的形式。其中图3(a)和(b)为2519A-T87的断口形貌。由图3(a)可以看出,T87态的断口韧窝深浅、大小不一,没有明显的分布规律,但局部有尺寸非常大的韧窝,这种形式的断裂很可能是由粗大第二相引起的;在局部放大图3(b)中可以观察到,韧窝的尺寸约在几个μm到几十个μm之间,韧窝内可以明显看到一些较大的粒子,EDS分析(结果如图4所示)后发现,其Al、Cu摩尔比约为2:1,推断其应该是一些较为粗大的Al2Cu相。图3(c)和(d)所示为2519A-T9I6的断口形貌,其中一部分区域韧窝的分布更为细小、弥散。在对韧窝分布均匀的区域进行局部放大后得到如图3(d)所示的微观组织,可以发现T9I6状态下,部分区域韧窝相对于T87状态下的更深。根据LUMLEY等[10-11]对二次时效现象的研究,2519A铝合金在T9I6工艺过程中的低温保温阶段,只有少量的Cu原子向晶界、亚晶界扩散,因此晶界、亚晶界上的析出相较少,合金在变形时不易在晶界、亚晶界处形成微裂纹,因而,T9I6状态下的合金相比于T87状态的合金,其塑性及断裂韧性有了较为明显的提高。
表2 2519A-T87和2519A-T9I6的室温力学性能
Table 2 Mechanical properties of 2519A-T87 and 2519A- T9I6 at room temperature
2.4 显微组织分析
在TecnaiG220透射电镜下分别对2519A经T87和T9I6峰时效后进行观察,其TEM像如图5所示。

图3 2519A-T87和2519A-T9I6拉伸断口的SEM像
Fig. 3 SEM images of fracture surfaces of 2519A-T87 ((a), (b)) and 2519A-T9I6 ((c), (d))
相比图5(a)所示的T87状态,可以明显观察到T9I6工艺下θ′相的尺寸明显小于T87状态的,且在图中所示的视场下,T9I6处理后的θ′相分布更为密集。可见断续时效工艺对2519A铝合金中θ′相的析出起到了促进作用,且析出相的分布更为均匀。
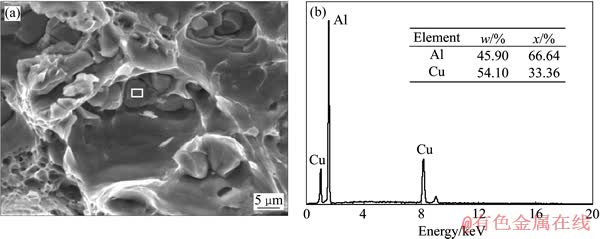
图4 断口形貌及其第二相能谱分析
Fig.4 Morphology of fracture surfaces(a) and energy spectrum of second phase(b)
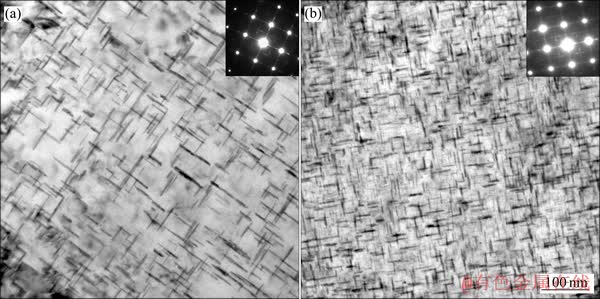
图5 2519A铝合金经T87和T9I6工艺峰时效状态的TEM像
Fig. 5 TEM images of 2519A aluminum alloy in T87(a) and T9I6(b) temper
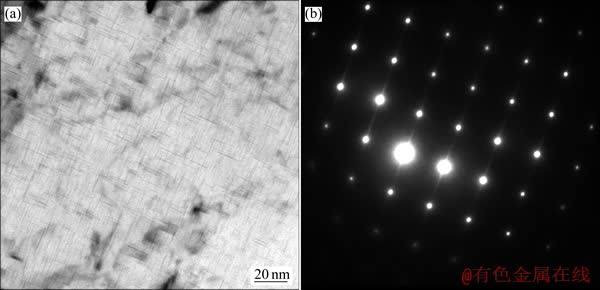
图6 2519A铝合金在T9I6工艺中经断续时效后的TEM像及其衍射斑
Fig. 6 TEM image of 2519A aluminum alloy obtained after interrupted ageing in T9I6 temper(a) and its selected electron diffraction pattern(b)
图6所示为T9I6工艺中经第二级长时低温保温(即所谓的“断续”)后的TEM像。由图6可以看出,合金内部主要是一些尺寸相当小的析出相,对于该相的尺寸统计如图7所示。在图6(b)所示的衍射斑点上,还未见有明显的θ′相衍射斑,对于铝基体斑点周围出现的“芒线”,推测其为图6(a)中所示的细小相的影响。
对于2519A铝合金的析出序列,一般是[13]:过饱和固溶体→GP区→θ′′→θ′ →θ。其中GP区和θ′′相与A1基体共格、θ′相半共格、θ相不共格。θ′相为主要的强化相,获得均匀、细小、密集的θ′相是2519A合金获得优良力学性能的主要途径。

图7 图中所示6个区域中相的平均直径与厚度
Fig. 7 Mean diameter and thickness of six areas shown in figure
经T9I6工艺处理以后的2519A铝合金相比于原有的T87工艺,合金力学性能显著提高。2519A铝合金经535℃固溶后淬火,固溶体中的Cu原子未能立即析出,形成过饱和固溶体。淬火不仅获得过饱和固溶体,还使空位被“冻结”在晶格内。过饱和空位为时效过程中GP区形成提供条件。在预时效阶段,与传统的T6人工时效处理相当,为过饱和固溶体分解提供动力。在图2所示的合金的时效硬化曲线上,合金在预时效过程中,硬度呈“阶跃”式上升,这主要是因为在时效前,未引入冷变形,时效初期,GP区的硬化作用明显,引入冷变形会抑制与基体共格的GP区的析出[2]。
随即进行的冷轧变形一方面引入了加工硬化,使得后续的时效强化在更高的起点开始;另一方面,预变形可以增加基体的位错密度,大大减小晶格畸变能,为后续与Al基体半共格的θ′相形核提供有利的条件。尽管进行了冷变形,但预变形量不大,不易产生可动性较强的位错,即位错分布弥散,难以产生交滑移、攀移[1]。
合金再回到低温保温阶段时,基体的过饱和度增加,GP区的相变自由能也增大。在此阶段中,Cu原子继续缓慢地在{100}面上偏聚,与预时效阶段的变化类似,形成Cu原子富集的GP区[14-15],但考虑冷轧预变形后空位数量的减少,该过程相比于预时效阶段更为缓慢。同时,较低的温度下,溶质原子的扩散速率也比较慢,GP区的形核也比预时效阶段下更加均匀,这些GP区达到一定尺寸后就成为后续时效析出相的核心。根据图6观察到的结果,由其衍射斑点可以发现,仅在铝基体衍射斑的周围形成了“芒线”的结构,而未见“十字花”形[16]的典型θ′相斑点,可见在该阶段只形成了少量的θ′相。而根据图6(a)所示的第二相形貌,可以推测其仍是一种盘片状的相,与θ′相形态类似,并且该相的尺寸较小。对图7所示的结果,不同区域内,该相的直径在7~10 nm、厚度在0.35~0.47 nm之间。而Al-Cu合金中GP区为厚0.3~0.6 nm、直径约8 nm的盘片状结构[17]。因而,推测图6(a)所示的细小相可能为GP区。
在时效的第三阶段,合金进行再时效,GP区→θ′′相→θ′相的转变逐渐完成。图5(b)所示为T9I6峰时效状态的TEM像,图中主要为互成90°分布的θ′相,在衍射斑点上,Al基体斑点四周出现了明显的“十字花”结构,为典型的θ′相衍射斑。对图5、图6所示的析出相的面积进行统计可得,T9I6状态下析出相面积约为32.9%,T87状态下的约为23.3%。另外,从相的尺寸上来说,T87状态的相尺寸大约在50 nm,而T9I6的则大约在30 nm。相比与图5(a)所示的T87状态,T9I6状态下,θ′相分布明显更为细小、弥散,而这种明显的差异也表明2519A-T9I6的力学性能明显优于2519A-T87的。
3 结论
1) 2519A经固溶+预时效+轧制+断续时效+再时效的T9I6工艺处理后,强度明显上升。其中,最优工艺下,屈服强度为501.0 MPa,抗拉强度540.1 MPa,伸长率为14.3%。相比于2519A-T87的431.6 MPa、470.5 MPa、9.7%分别提高了69.4 MPa、69.6 MPa、4.6%。这是时效强化与加工硬化共同作用的结果。
2) 断续时效为θ′的析出提供了有利条件,在断续时效过程中,由于温度较低,时效过程缓慢且稳定,基体内不断形成密集、细小的GP区,这使得后续θ′相的形成也趋于细小、密集。最终,2519A-T9I6的θ′相体积分数大于T87态的,同时,2519A-T9I6的θ′相尺寸及小于T87态的,且第二相强化效果显著。
REFERENCES
[1] 张新明, 贾寓真, 刘 玲, 叶凌英, 陈明安, 高志国, 王文韬, 匡小月. 冷轧预变形对2519A铝合金时效析出的影响[J]. 中南大学学报: 自然科学版, 2011, 42(1): 46-49.
ZHANG Xin-ming, JIA Yu-zhen, LIU Ling, YE Ling-ying, CHEN Ming-an, GAO Zhi-guo, WANG Wen-tao, KUANG Xiao-yue. Effects of cold-pre-rolling reduction on precipitation of 2519A aluminum alloy plate[J]. Journal of Central South University: Science and Technology, 2011, 42(1): 46-49.
[2] 张新明, 刘 玲, 贾寓真. 拉伸与冷轧预变形对2519A铝合金组织和力学性能的影响[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2010, 20(6): 1088-1094.
ZHANG Xin-ming, LIU Ling, JIA Yu-zhen. Effects of stretching and rolling pre-deformation on microstructures and mechanical properties of 2519A aluminum alloy[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2010, 20(6): 1088-1094.
[3] 李慧中, 梁霄鹏, 陈明安, 张新明. 冷轧变形量对2519铝合金组织和力学性能的影响[J]. 材料热处理学报, 2008, 9(2): 86-89.
LI Hui-zhong, LIANG Xiao-peng, CHEN Ming-an, ZHANG Xin-ming. Effect of cold rolling reduction on microstructure and mechanical property of 2519 aluminum alloy[J]. Transactions of Material and Heat Treatment, 2008, 9(2): 86-89.
[4] LI Hui-zhong, LIANG Xiao-peng, LI Fang-fang, GUO Fei-fei, LI Zhou, ZHANG Xin-ming. Effect of Y content on microstructure and mechanical properties of 2519 aluminum alloy[J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2007, 17(6): 1194-1198.
[5] WANG Wen-tao, ZHANG Xin-ming, GAO Zhi-guo, JIA Yu-zhen, YE Ling-ying, ZHENG Da-wei, LIU Ling. Influences of Ce addition on the microstructures and mechanical properties of 2519A aluminum alloy plate[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2010, 419(1/2): 366-371.
[6] 陈志国, 杨文玲, 王诗勇, 舒 军. 微合金化铝合金的研究进展[J]. 稀有金属材料与工程, 2010, 39(8): 1499-1530.
CHEN Zhi-guo, YANG Weng-ling, WANG Shi-yong, SHU Jun. Research progress of microalloyed aluminum alloy[J]. Rare Metal Materials and Engineering, 2010, 39(8): 366-371.
[7] 韩念梅, 张新明, 刘胜胆, 宋丰轩, 辛 星. 双级时效对7050铝合金厚板断裂韧性的影响[J]. 中南大学学报: 自然科学版, 2011, 42(3): 623-628.
HAN Nian-mei, ZHANG Xin-ming, LIU Sheng-dan, SONG Feng-xuan, XIN Xing. Influence of two-step aging on fracture toughness of 7050 aluminum alloy plate[J]. Journal of Central South University: Science and Technology, 2011, 42(3): 623-628.
[8] 张新明, 宋丰轩, 刘胜胆, 韩念梅. 双级时效对7050铝合金板材剥蚀性能的影响[J]. 中南大学学报: 自然科学版, 2011, 42(8): 2252-2258.
ZHANG Xin-ming, SONG Feng-xuan, LIU Sheng-dan, HAN Nian-mei. Influence of two-step aging on exfoliation corrosion properties of 7050 aluminum alloy plate[J]. Journal of Central South University: Science and Technology, 2011, 42(8): 2252-2258.
[9] 张新明, 罗智辉, 杜予晅, 叶凌英. 双级时效对1420 铝锂合金超塑性的影响[J]. 材料热处理学报, 2007, 28(4): 55-58.
ZHANG Xin-ming, LUO Zhi-hui, DU Yu-xuan, YE Ling-ying. Effect of two-stage ageing on super plasticity of 1420 Al-Li alloy[J]. Transactions of Materials and Heat Treatment, 2007, 28(4): 55-58.
[10] LUMLEY R N, POLMEAR I J, MPRTON A J. Temper Developments Using Secondary Ageing[C]// NIE J F, MORTON A J, MUDDLE B C. Proceedings of the 9th International Conference on Aluminum Alloys. Brisbane, Australia: Institute of Materials Engineering Australasia Ltd, 2004: 85-95.
[11] LUMLEY R N, POLMEAR I J, MPRTON A J. Interrupted aging and secondary precipitation in aluminum alloys[J]. Materials Science and Technology, 2003, 19(11): 1483-1490.
[12] LUMLEY R N, POLMEAR I J, MPRTON A J. Development of mechanical properties during secondary aging in aluminum alloys[J]. Materials Science and Technology, 2005, 21(9): 1025-1032.
[13] MASSALSKI T B. The Al-Cu (aluminum-copper) system[J]. Journal of Phase Equilibria, 1980, 1(1): 27-33.
[14] KARLIK M, JOUFFRY B. High resolution electron microscopy of Guinier-Preston(G.P.I) zones in an Al-Cu based alloys[J]. Acta Materialia, 1997, 45(8): 3251-3263.
[15] TAKEDAl M, MAEDAl Y, YOSHIDAl A, YABUTA K, KONUMA S, ENDOL T. Discontinuity of G.P.(I) zone and θ′ phase in all AI-Cu alloy[J]. Scripta Materialia, 1999, 41(6): 643-649.
[16] FONDA R W, BINGERT J F. Microstructural evolution in the heat-affected zone of a friction stir weld[J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A, 2004, 35(5): 1487-1499.
[17] 李松瑞, 周善初. 金属热处理[M]. 长沙: 中南大学出版社, 2005: 198-202.
LI Song-rui, ZHOU Shan-chu. Heat treatment of metals[M]. Changsha: Central South University Press, 2005: 198-202.
(编辑 李艳红)
基金项目:国家重点基础研究发展计划资助项目(2012CB619501)
收稿日期:2012-12-12;修订日期:2013-03-14
通信作者:叶凌英,讲师,博士;电话:13607435545;E-mail: 30575421@qq.com