DOI: 10.11817/j.issn.1672-7207.2015.07.006
7055铝合金板材搅拌摩擦焊接头的组织与力学性能
吴豫陇1, 2,郑英3,刘胜胆1, 2, 4,谈琦1, 2,张盼1, 2,张新明1, 2, 4
(1. 中南大学 材料科学与工程学院,湖南 长沙,410083;
2. 中南大学 有色金属材料科学与工程教育部重点实验室,湖南 长沙,410083;
3. 湖南交通职业技术学院 机电工程学院,湖南 长沙,410004;
4. 中南大学 有色金属先进结构材料与制造协同创新中心,湖南 长沙,410083)
摘要:利用光学显微镜、透射电子显微镜、室温拉伸和硬度测试等方法,研究1.8 mm厚7055铝合金板材搅拌摩擦焊接头的微观组织和力学性能。研究结果表明:焊接头的抗拉强度和伸长率分别约为母材的63%和32%;接头区硬度曲线呈W形,硬度最低值出现在前进侧热机影响区附近。焊核区和热机影响区都观察到细小等轴再结晶组织,晶内可观察到较粗大的η相;热影响区的晶粒组织与母材的类似,但晶内的η′沉淀强化相粗化。根据这些区域的微观组织特征揭示了焊接头硬度和拉伸强度的下降的原因。
关键词:搅拌摩擦焊接;7055铝合金;微观组织;力学性能
中图分类号:TG453 文献标志码:A 文章编号:1672-7207(2015)07-2426-06
Microstructure and mechanical properties of 7055 Al alloy sheet friction stir welded joint
WU Yulong1, 2, ZHENG Ying3, LIU Shengdan1, 2, 4, TAN Qi1, 2, ZHANG Pan1, 2, ZHANG Xinming1, 2, 4
(1. School of Materials Science and Engineering, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China;
2. Key Laboratory of Nonferrous Materials Science and Engineering, Ministry of Education,
Central South University, Changsha 410083, China;
3. Department of Mechanical & Electrical Engineering, Hunan Communication Polytechnic, Changsha 410004, China;
4. Nonferrous Metals Oriental Advanced Structural Materials and Manufacturing Cooperative Innovation Center,
Central South University, Changsha 410083, China)
Abstract: The microstructure and mechanical properties of a friction stir welded joint of 7055 aluminum sheet of 1.8 mm in thickness were investigated by optical microscope, transmission electron microscope, tensile test and hardness test. The results show that the tensile strength and elongation of the joint are about 63% and 32% of that of the base material, respectively. The hardness curve of the joint exhibits a W shape and the minimal hardness value is in the thermo-mechanically affected zone in the advancing side. In the nugget zone and the thermo-mechanically affected zone, fine and equiaxed recrystallized grains can be observed, and some coarse η phase particles can be observed in the matrix. In the heat affected zone, the grain structure is similar to that in the base material but η′ strengthening precipitates in the matrix are coarser. According to these microstructural characteristics, the reason for lower hardness and tensile strength is revealed.
Key words: friction stir welding; 7055 aluminum alloy; microstructure; mechanical properties
7000系铝合金具有强度高、密度低等特点,广泛用作航空领域的结构材料。采用熔焊方法对这些合金进行焊接时易产生热裂纹、气孔等缺陷,焊接头的力学性能很低。因此,这些合金通常被认为是不可焊的。搅拌摩擦焊(FSW) 是一种固相连接方法,避免了熔焊时易出现的系列缺陷,焊接头力学性能高,在实现7000系铝合金的高质量连接方面具有独特的优势[1],引起了人们广泛的关注。国内外学者对一些典型7000系铝合金搅拌摩擦焊接后的微观组织和性能等开展了大量研究工作,但是主要集中在7050和7075等铝合金[2-6]。在超高强7055铝合金方面,许俊华等[7-8]对喷射成形材料的搅拌摩擦焊接开展了一些工作,而铸锭冶金制备材料的搅拌摩擦焊接尚未见报道。7055铝合金在时效后具有超高强度,被用于制造大型飞机的机翼、龙骨梁、地板梁等[9]。由于合金化程度高,凝固时结晶范围宽,极易形成热裂纹,采用熔焊方法难以进行焊接。本文作者对铸锭冶金制备的7055铝合金进行搅拌摩擦焊接,研究焊接头的力学性能和微观组织,以便增加对超高强7000系铝合金搅拌摩擦焊接了解和认识。
1 实验材料与方法
实验材料采用1.8 mm厚的时效态7055铝合金板材,其力学性能如表1所示。搅拌摩擦焊接时采用圆柱形搅拌针,直径为2 mm,长度为1.7 mm,轴肩直径为8 mm。焊接过程中压下量约为0.1 mm,倾斜角为1.5°,旋转速度为1 500 r/min,焊接速度为80 mm/min。焊接方向垂直于板材的轧制方向,板材焊完后在空气中自然冷却,图1所示为工艺示意图。
在焊后的板材上切取试样测试焊接头的硬度及室温拉伸性能,并分析不同位置的微观组织。采用HV-10B型硬度计测定硬度,沿着垂直焊缝方向每隔0.5 mm测试1个点。根据GB/T 228—2002标准沿垂直于焊缝方向切取拉伸试样,并在MTS810电子拉伸机上测试室温拉伸性能。金相样品经粗磨、细磨和抛光后在Graff Sargent试剂(1 mL HF+16 mL HNO3+3gCRO3+83 mL H2O) 浸蚀,然后在MX3000光学显微镜上观察晶粒组织。另外,制备试样在Tecnai G2 20 型透射电镜(TEM)上观察焊缝不同区域的微观组织,加速电压为200 kV。电镜样品先预磨至约0.08 mm厚,冲成直径3 mm薄片,然后在80% CH3OH+20% HNO3 (体积分数)溶液中进行双喷减薄,采用液氮冷却,温度控制在-20 ℃以下。
表1 7055铝合金初始板材及焊接接头的力学性能
Table 1 Mechanical properties of 7055 aluminum alloy sheet
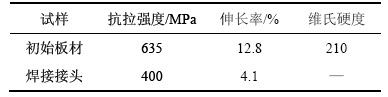
图1 搅拌摩擦焊接原理示意图
Fig. 1 Schematic diagram of FSW process
2 结果和分析
2.1 焊接头力学性能
图2所示为焊接头硬度分布情况,很明显硬度曲线呈W形,但左右不完全对称。母材区(BM)硬度最高,到热影响区(HAZ)和热机影响区(TMAZ)的硬度不断下降,在热机影响区附近出现最低值,到焊核区(NZ)硬度又升高。焊核区的维氏硬度分布比较均匀,在145 左右,约为母材的69%。前进侧(AS)的维氏硬度最低值约为112,为母材的52%;后退侧(RS)的维氏硬度最低值稍高,约为115,为母材的55%。
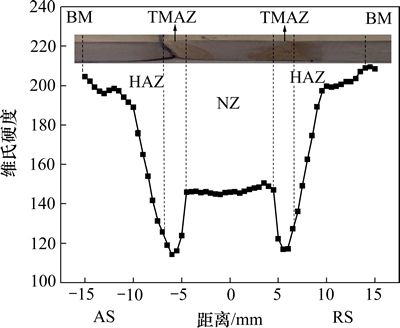
图2 焊接头硬度分布
Fig. 2 Hardness profiles of joint
表1所示为焊接头的拉伸性能。由表1可知:与初始板材相比,焊接头的拉伸性能明显下降,抗拉强度从635 MPa降至400 MPa,伸长率从12.8%降至4.1%。焊接头的抗拉强度约为母材的63%,伸长率约为32%。焊接头拉伸试样和母材拉伸试样的断裂面与拉伸方向都呈45°,可以观察到明显的颈缩现象。焊接试样拉伸时的断裂位置均出现在前进侧热机影响区,即大概对应于图2中硬度最低值的位置,说明该位置是焊接头最薄弱的地方。
2.2 焊接头组织分析
图3给出了焊接头的整体形貌。由图3可知:焊接头形状呈“V”形,可以大概辨认出焊核区,热机影响区和热影响区;焊核区中心有非对称的同心圆环,称为“洋葱环”[10],前进侧(AS)和后退侧(RS)的形貌有较大的差异,即热影响区和焊核区的分界线不同。在前进侧,这种分界线较明显,呈弧形,如图3所示,说明热机影响区的范围较大;但在后退侧2个区域的过渡很模糊。通常认为焊接时两侧材料的塑性流动状态不同导致了这种差异[1]。为了对焊接头组织有全面的了解,对不同区域进行了分析,结果如图4~7所示。
热影响区的组织在焊接过程中没有受到搅拌头的搅拌作用,不发生变形,只受到热循环作用,而且温度低于固溶温度。因此,该区域的组织在金相显微镜下观察时与母材的基本上没有差别,典型的照片如图4所示。图4中白色区域是再结晶晶粒,黑色(或深灰色)区域是未再结晶晶粒,包含大量的亚晶,这是含Zr7000系铝合金非常典型的固溶时效态组织[11]。由于添加了微量Zr,生成的Al3Zr弥散粒子可起到强烈地抑制再结晶和晶粒长大的作用[12],从而使热影响区的晶粒组织基本不发生变化。此外,还可观察到一些黑色的第二相粒子,大都分布在白色的再结晶晶粒之中,如图4中的箭头所示。以往的研究表明[13]:这是Al7Cu2Fe或残留的S(Al2CuMg)相,在固溶时起到粒子激发形核的作用,促使再结晶的发生。
热机影响区的组织在焊接时不仅受到机械搅拌作用,还受到热循环的作用。材料在搅拌针周围产生剪切和流动,晶粒发生扭曲并被破碎,可观察到呈弧形分布的细小等轴晶粒组织,如图5(a)所示,这在前进侧更为明显。在后退侧的热机影响区观察到的也是细小的等轴状晶粒组织,如图5(b)所示。前进侧热机影响区的晶粒平均粒径约为12 μm,后退侧的晶粒略小,约为10 μm。
焊核区的组织经受了搅拌头的强烈机械搅拌和高温热循环作用而发生了动态再结晶,形成细小的等轴晶粒,但不同位置的组织略有些差别,如图6所示。为了定量分析晶粒组织,每个区域对大概200个晶粒的尺寸进行了测试计算平均值。焊核区上部的晶粒比较均匀,平均粒径约为5 μm,如图6(a)所示。焊核区的左部晶粒不均匀,尺寸差别比较大,大的晶粒近10 μm,小的约2 μm,平均粒径约6 μm,如图6(b)所示。
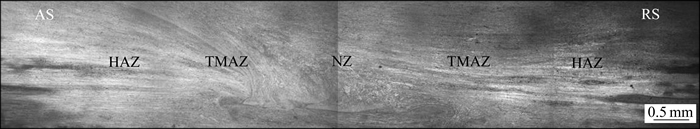
图3 焊接头的整体形貌
Fig. 3 Morphology of welded joint
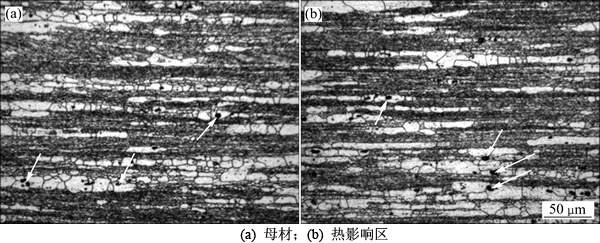
图4 母材与热影响区的金相照片
Fig. 4 Optical micrographs of base metal and heat affected zone
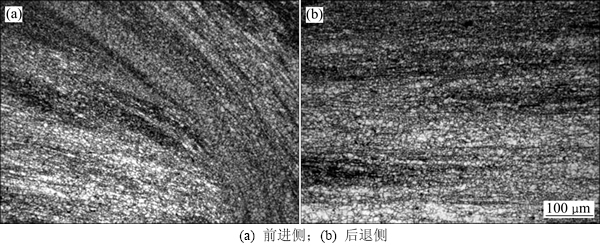
图5 热机影响区金相照片
Fig. 5 Optical micrographs of thermal-mechanical affected zone

图6 焊核区不同区域的金相照片
Fig. 6 Optical micrographs of weld nugget zone
焊核区中部晶粒似乎更大一些,尺寸差别也较大,小的晶粒粒径为3 μm左右,大的晶粒粒径可达6~12 μm,平均粒径约为5 μm,如图6(c)所示。焊核区右部和底部的晶粒看起来更加均匀,平均粒径分别为5 μm和4 μm,尺寸差别不明显,如图6(d)和6(e)所示。
7055铝合金是时效强化合金,其硬度和强度主要决定于基体中的沉淀强化相状态。因此,采用TEM对焊接头不同区域组织进行了观察,典型的结果如图7所示。由图7(a)可知:母材基体中分布着高密度的细小沉淀强化相,其粒径为5 nm左右,对应的 选区衍射花样显示这些强化相主要是亚稳的η′相。这些细小的η′相可有效地阻碍位错的运动,强化基体,因此母材具有高的强度和硬度,如表1所示。另外,从图7还能观察到近球状的Al3Zr弥散粒子,粒径约为30 nm,可起到抑制再结晶的作用[12]。由图7(b)可知:与母材相比,热影响区中沉淀强化相发生了粗化,大部分粒径为15~25 nm。对应的
选区衍射花样显示这些强化相主要是亚稳的η′相。这些细小的η′相可有效地阻碍位错的运动,强化基体,因此母材具有高的强度和硬度,如表1所示。另外,从图7还能观察到近球状的Al3Zr弥散粒子,粒径约为30 nm,可起到抑制再结晶的作用[12]。由图7(b)可知:与母材相比,热影响区中沉淀强化相发生了粗化,大部分粒径为15~25 nm。对应的 选区衍射花样表明,这些沉淀强化相主要是η′相及少量的η相。显然这是由于焊接过程中的热循环作用引起了η′相长大,并有一些转变成η相。沉淀强化相的粗化必然降低强化效果,因此,热影响区的硬度必然低于母材,而且离焊核区越近的位置温度越高,η′相粗化越严重,硬度会不断地降低,这就形成了图1所示的硬度分布。图7(c)所示为热机影响区的TEM照片。与母材和热影响区明显不同的是,晶内观察到大量粗大的棒状η相粒子,大的粒子长度近200 nm。在7000系铝合金中,焊接时热机影响区的温度较高,导致大部分的沉淀强化相回溶[14]。7055铝合金淬火敏感性高,在焊后的空冷过程中极易析出粗大的η相。这些粒子尺寸太大,强化效果很弱,因此,该区域的硬度很低,如图1所示。图7(d)所示为焊核区的TEM照片。晶内能看到大量粒径较大的η相,粒径小的为20 nm左右,粒径大的可达100 nm,较热机影响区的η相明显更小。7000系铝合金焊核区在焊接时的温度可达到固溶温度[15],初始的η′沉淀强化相完全回溶至基体得到固溶体,在后续的冷却过程中固溶体发生分解,析出了许多η相。η相通常会在一些有利的位置,如弥散粒子处优先形成。图7(d)中黑色的Al3Zr弥散粒子和η相联系在一起证实了这一点。和热机影响区相比,焊核区的η相粒子更小,晶粒更细,因此硬度更高。
选区衍射花样表明,这些沉淀强化相主要是η′相及少量的η相。显然这是由于焊接过程中的热循环作用引起了η′相长大,并有一些转变成η相。沉淀强化相的粗化必然降低强化效果,因此,热影响区的硬度必然低于母材,而且离焊核区越近的位置温度越高,η′相粗化越严重,硬度会不断地降低,这就形成了图1所示的硬度分布。图7(c)所示为热机影响区的TEM照片。与母材和热影响区明显不同的是,晶内观察到大量粗大的棒状η相粒子,大的粒子长度近200 nm。在7000系铝合金中,焊接时热机影响区的温度较高,导致大部分的沉淀强化相回溶[14]。7055铝合金淬火敏感性高,在焊后的空冷过程中极易析出粗大的η相。这些粒子尺寸太大,强化效果很弱,因此,该区域的硬度很低,如图1所示。图7(d)所示为焊核区的TEM照片。晶内能看到大量粒径较大的η相,粒径小的为20 nm左右,粒径大的可达100 nm,较热机影响区的η相明显更小。7000系铝合金焊核区在焊接时的温度可达到固溶温度[15],初始的η′沉淀强化相完全回溶至基体得到固溶体,在后续的冷却过程中固溶体发生分解,析出了许多η相。η相通常会在一些有利的位置,如弥散粒子处优先形成。图7(d)中黑色的Al3Zr弥散粒子和η相联系在一起证实了这一点。和热机影响区相比,焊核区的η相粒子更小,晶粒更细,因此硬度更高。
据以上的结果认为:焊接头中基体沉淀强化相的粗化及溶解,及焊后冷却时粗大η相的析出,导致热影响区、热机影响区和焊核区特别是热机影响区的硬度大大低于母材的硬度,拉伸强度下降。但是,通过微观组织的有效地调控来改善7055铝合金焊接头的力学性能是完全可能的,比如焊后快速冷却抑制η相析出,选择合理的焊接工艺参数减少η′相粗化以及通过焊后的热处理重新析出GP区或η′相[14],有待于开展进一步研究。
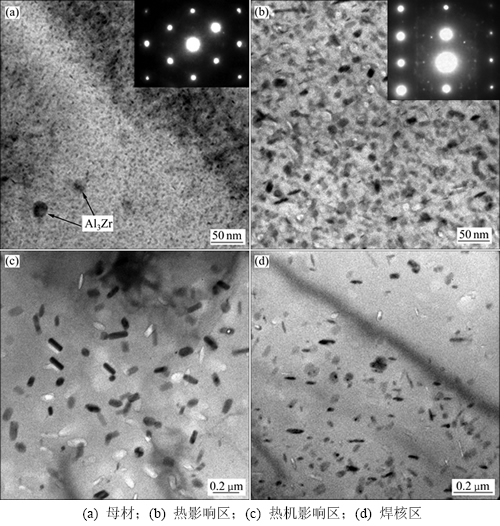
图7 焊接头不同区域的透射电镜照片
Fig. 7 TEM micrographs of different zones in joint
3 结论
1) 在转速为1 500 r/min、焊速为80 mm/min条件下,7055铝合金板材焊接头的抗拉强度为400 MPa,为母材的63%,伸长率为4.1%,为母材的32%。焊接头区域硬度曲线呈W形,硬度最低值出现在前进侧热机影响区,拉伸试样的断裂位置也在该区域。
2) 焊核区和热机影响区都观察到细小等轴再结晶组织,晶内可观察到较粗大的η相。焊核区晶粒的平均粒径在5 μm左右,热机影响区的晶粒为10~12 μm;焊核区晶内η相更细小。因此,焊核区的硬度高于热机影响区的硬度。热影响区的晶粒组织与母材的类似,但晶内的η′沉淀强化相粗化,因此硬度低于母材。
3) 焊接时,接头区域的η′沉淀强化相的粗化及回溶,后续冷却时析出了粗大的η相,是焊接头硬度和拉伸强度下降的主要原因。
参考文献:
[1] 王国庆, 赵衍华. 铝合金的搅拌摩擦焊接[M]. 北京: 中国宇航出版社, 2010: 121, 241.
WANG Guoqing, ZHAO Yanhua. Friction stir welding of aluminum alloy[M]. Beijing: China Astronautic Publishing House, 2010: 121, 241.
[2] Fuller C B, Mahoneya M W, Calabresea M, et al. Evolution of microstructure and mechanical properties in naturally aged 7050 and 7075 Al friction stir welds[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2010, 527(9): 2233-2240.
[3] Canaday C T, Moore M A, Tang W, et al. Through thickness property variations in a thick plate AA7050 friction stir welded joint[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2013, 559: 678-682.
[4] 何建军, 李玉斌, 李盛和, 等. 焊接速度对7075铝合金搅拌摩擦焊接头强度和微观组织的影响[J]. 热加工工艺, 2011, 40(21): 114-116.
HE Jianjun, LI Yubin, LI Shenghe, et al. Effect of welding speed on microstructure and mechanical properties of welded joint of high-strength aluminum alloy by friction stir welding[J]. Hot Working Technology, 2011, 40(21): 114-116.
[5] 王希靖, 孙桂苹. 7075铝合金搅拌摩擦焊接头组织及性能[J]. 宇航材料工艺, 2008, 38(6) : 77-80.
WANG Xijin, SUN Guiping. Microstructure and properties of friction stir welding joints for 7075 aluminum alloy[J]. Aerospace Materials &Technology, 2008, 38(6): 77-80.
[6] 张成聪, 常保华, 陶军, 等. 7050 铝合金搅拌摩擦焊动态再结晶组织影响因素[J]. 焊接学报, 2012, 33(8): 89-92.
ZHANG Chengcong, CHANG Baohua, TAO Jun, et al. Influence factors of dynamic recrystallization of 7050 aluminium alloy friction stir weld[J]. Transactions of the China Welding Institution, 2012, 33(8): 89-92.
[7] 许俊华, 赵立军, 施林波, 等. 喷射成形7055铝合金搅拌摩擦焊的焊缝组织与力学性能[J]. 粉末冶金材料科学与工程, 2011, 16(4): 547-552.
XU Junhua, ZHAO Lijun, SHI Linbo, et al. Microstructure and mechanical properties of joints of friction stir welding 7055 Al alloys by spray formation[J]. Materials Science and Engineering of Powder Metallurgy, 2011, 16(4): 547-552.
[8] 严铿, 刘俊, 史超. 喷射成型7055铝合金FSW焊工艺与性能[J]. 焊接学报, 2012, 33(6): 51-54.
YAN Keng, LIU Jun, SHI Chao. Study on process and property of FSW of spray formed 7055 aluminum alloy[J]. Transactions of the China Welding Institution, 2012, 33(6): 51-54.
[9] Williams J C, Starke E A Jr. Progress in structural materials for aerospace systems[J]. Acta Materialia, 2003, 51(19): 5775-5779.
[10] 王希靖, 达朝炳, 李晶, 等. 搅拌摩擦焊缝中的洋葱环形成分析[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2006, 16(10): 1672-1677.
WANG Xijing, DA Chaobing, LI Jing, et al. Analysis of formation of onion rings in friction stir welding[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2006, 16(10): 1672-1677.
[11] 张新明, 刘胜胆, 刘瑛, 等. 淬火速率和锆含量对7055型铝合金晶间腐蚀的影响[J]. 中南大学学报(自然科学版), 2007, 38(2): 181-185.
ZHANG Xinming, LIU Shengdan, LIU Ying, et al. Influence of quench rate and zirconium content on intergranular corrosion of 7055 type aluminum alloy[J]. Journal of Central South University (Science of Technology), 2007, 38(2): 181-185.
[12] LIU Shengdan, ZHANG Xinming, CHEN Mingan. Effect of zirconium content on quench sensitivity of AlZnMgCu alloys[J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2007, 17(4): 787-792.
[13] Liu S D, Yuan Y B, Li C B, et al. Influence of cooling rate after homogenization on microstructure and mechanical properties of aluminum alloy 7050[J]. Metals and Materials International, 2012, 18(4): 679-683.
[14] Sullivan A, Robson J D. Microstructural properties of friction stir welded and post-weld heat-treated 7449 aluminium alloy thick plate[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2008, 478(1/2): 351-360.
[15] Jata K V, Sankaran K K, Ruschau J J. Friction-stir welding effects on microstructure and fatigue of aluminum alloy 7050-T7451[J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A: Physical Metallurgy and Materials Science, 2000, 31(9): 2181-2192.
(编辑 杨幼平)
收稿日期:2014-07-02;修回日期:2014-10-09
基金项目(Foundation item):国家国际科技合作专项(2013DFG51890);中南大学“升华育英计划”项目(2012年) (Project(2013DFG51890) supported by the Ministry of Science and Technology of China; Project(2012) supported by Shenghua Yu Ying Project in Central South University)
通信作者:刘胜胆,博士,副教授,从事高强铝合金制备、组织与性能研究;E-mail: lsd_csu@csu.edu.cn