掺杂合金元素面向等离子体钨基材料的研究现状与发展趋势
来源期刊:中国有色金属学报2016年第9期
论文作者:罗来马 施静 昝祥 李萍 罗广南 陈俊凌 吴玉程
文章页码:1899 - 1912
关键词:面向等离子体材料;钨基材料;合金元素;作用机理;改善措施
Key words:plasma facing material; tungsten-based material; alloying element; action mechanism; improvement measure
摘 要:钨基复合材料因其优良的性能逐渐取代碳基材料和铍等,成为最有可能应用于国际热核聚变实验堆中面向等离子体材料,但其存在低温脆性、再结晶脆化、辐照脆化和燃料粒子滞留等问题。目前,主要是从合金化、第二相颗粒弥散强化以及制备超细晶(UFG)/纳米晶钨基材料等方面来改善钨及其复合材料的性能。合金化是最常用的改善合金性能的手段之一,合金元素或扩散溶解于钨基体中,或作用于缺陷和杂质,改变钨基材料的组织结构从而提高其性能。综述主要介绍合金元素在钨合金中性能提升和作用机理,同时也指出合金元素改善钨合金性能方面存在的问题、可能的改善措施以及未来的发展趋势。
Abstract: Tungsten matrix composites have gradually replaced the traditional carbon-based materials and beryllium, becoming the most promising candidates for plasma-facing materials for the international thermonuclear experimental reactor attributing to their superior properties. However, tungsten exhibits some problems as a plasma-facing material, including low temperature embrittlement, recrystallization embrittlement, radiation embrittlement and fuel particle retention. Hence, attempts for improving its mechanical behavior have been carried out via doping alloying elements or stable dispersed phases and fabricating UFG/nanocrystalline tungsten, etc. Alloying is one of the most common methods to improve the performance of tungsten-based materials. The doping elements can diffuse and dissolve into tungsten matrix or act on the defects and impurities to change the contexture and structure of tungsten, thus improving its properties. The change of properties and the correlative mechanism of alloyed tungsten-based materials were reviewed and some problems on it and the improvement measures and development trend in future were pointed out.
文章编号:1004-0609(2016)-09-1899-13
罗来马1, 3,施 静1,昝 祥1, 3,李 萍1, 3,罗广南2,陈俊凌2,吴玉程1, 3
(1. 合肥工业大学 材料科学与工程学院,合肥 230009;
2. 中科院 等离子体物理研究所,合肥 230031;
3. 安徽省有色金属材料与加工工程实验室,合肥 230009)
摘 要:钨基复合材料因其优良的性能逐渐取代碳基材料和铍等,成为最有可能应用于国际热核聚变实验堆中面向等离子体材料,但其存在低温脆性、再结晶脆化、辐照脆化和燃料粒子滞留等问题。目前,主要是从合金化、第二相颗粒弥散强化以及制备超细晶(UFG)/纳米晶钨基材料等方面来改善钨及其复合材料的性能。合金化是最常用的改善合金性能的手段之一,合金元素或扩散溶解于钨基体中,或作用于缺陷和杂质,改变钨基材料的组织结构从而提高其性能。综述主要介绍合金元素在钨合金中性能提升和作用机理,同时也指出合金元素改善钨合金性能方面存在的问题、可能的改善措施以及未来的发展趋势。
关键词:面向等离子体材料;钨基材料;合金元素;作用机理;改善措施
中图分类号:TG146.1 文献标志码:A
受控热核聚变能是最理想的清洁能源,几乎不会带来放射性污染等环境问题,其燃料氘和氚大量存在于海水之中,氘氚聚变反应释放出大量能量,其所需燃料在地球上预计约能使用3000万年以上,被认为是有效解决人类未来能源需求的主要途径[1]。经过国际间的不懈努力,产生聚变能的科学可行性已在磁约束聚变装置托卡马克(Tokamak)上得到了证实。20世纪80年代,国际上设立了国际热核试验堆计划(ITER),并在21世纪初确定了ITER的设计概要,这标志着热核聚变技术从基础研究阶段进入了工程可行性阶段[2-4]。
然而,这一目标的实现还有诸多技术难题需要解决,其关键问题之一就是面向等离子体材料(PFMs)的选择。PFMs是指在磁约束可控热核聚变反应装置中直接面对等离子体的第一壁(FW)和偏滤器、限制器的装甲材料,它可以有效地控制进入等离子体的杂质,传递辐射到材料表面的热量并保护非正常停堆时其它部件免受等离子体轰击而损坏。但目前尚无任何PFM可以同时满足与等离子体相容性好、耐高热负荷、耐高通量低能离子和中性粒子辐照、耐高通量高能中子辐照射等苛刻的要求[1, 5-6]。W因具有高熔点、高热导率、低蒸气压、低热膨胀率、低物理溅射系数和低的氢及其同位素滞留率等优异性能而被认为是最具前景的面向等离子体材料[7-8],尽管如此其应用仍受到韧脆转变温度(DBTT)高、再结晶温度(RCT)低、辐照硬化和燃料粒子滞留等缺点的限制。
未来聚变堆中PFMs将面临很大的准稳态热流负荷(>10 MW/m2)[9],局部表面需要承受的峰值热流密度高达20 MW/m2[10]。强热负荷在PFM表层产生陡峻的温度梯度场,导致严重的热应力使得PFM表层开裂。当受热作用温度低于DBTT时,开裂尤为严重,大大降低材料的使用寿命并给等离子体造成污染。当温度超过RCT时,W发生再结晶,晶粒长大导致其热力学性能降低,加重材料的脆性开裂。因此,改善W的热力学性能以及解决W脆性大等问题以满足聚变装置要求成为当前研究的热点[11]。目前可有效改善W性能的方法包括合金化增强、改善微观结构细化晶粒、第二相弥散增强和优化制造工艺等[12]。本文作者结合近年来的相关研究,详细综述了合金元素对钨材料的影响和作用机理,提出了一些存在的问题和改进的措施。
1 合金元素对面向等离子体钨基材料性能的影响
W基材料中添加一定量的合金元素可以提高密度、强韧性和热稳定性并且改善其辐照性能等。目前常见的添加元素有Re、Ti、V、Zr、Nb以及稀土元素(Y)等,它们在W基材料的制备过程中对其性能的改善有着显著的作用,但也存在着一些问题和不足。下面分别介绍这些元素对W及其复合材料性能的影响。
1.1 Re元素
Re属于稀有元素,熔点高达3180 ℃,W中加入一定量的Re元素能够显著提高材料低温下的塑韧性和高温的抗蠕变性能[13],并改善材料的加工性能。W作为体心立方结构有3个滑移面,分别为{110}、{112}和{123},变形时在哪个面上优先滑移取决于许多因素,包括形变方式、应变速率、温度以及合金化的影响[14]。密度泛函理论(Density-functional theory,DFT)被用来解释合金元素Re对W的影响。通过计算机模拟,研究人员探讨了Re对W位错中心结构,佩尔斯力σP,和1/2<111>螺型位错滑移面的影响,结果发现Re的加入可以改变位错中心的对称性(如图1所示),降低位错滑移的阻力(佩尔斯应力 Peierls stress),增加滑移面的数目,有利于塑性变形的进行从而显著改善W的塑性和延展性[12, 14]。此外,Re可以降低W合金的DBTT同时提高其RCT[15-16],拓宽W作为面向等离子体材料在反应堆中的可运行温度范围,提高其安全性。
在辐照性能方面,TYBURSKA等[17]研究了不同温度下纯W和W-3%Re(质量分数,下同)合金的氘滞留性能,发现少量Re可以显著降低W中的氘滞留水平。即使是在3倍于纯W的注入通量下,W-3%Re合金中受损伤部位的氘滞留量也低于纯W的。空位扩散至晶界会发生湮灭而消失,W-3%Re合金中的高密度晶界使得材料中空位的湮灭几率大大增加,减少了氘原子在空位中的聚集,滞留量随之降低。然而,在反应堆的中子辐照下Re会与其他元素生成脆性相产生严重危害[18]。FUKUDA等[19]研究了W和W-Re合金在中子辐照下的结构和性能,发现两者均产生了含Re和Os元素的脆性析出相(部分Re和Os是纯钨在中子辐照下嬗变的产物),但相比于纯钨,W-Re合金中析出相的尺寸和密度较小,这是由于W-Re合金中辐照所致空位、位错等缺陷较少,降低了脆性相在缺陷处析出和聚集的程度,但这些小尺寸的脆性相仍会显著降低材料的性能。
Re的加入也显著影响W的热导率。FUJITSUKA等[20]研究了中子辐照前后以及不同温度下W-(0%,5%, 10%, 25%)Re合金热导率的变化情况。结果发现,辐照前后W的热导率均随Re含量的增加而降低,温度升高,W和W-10%Re合金的热导率降低,而W-10%Re和W-25%Re合金的热导率却略微上升,如图2和3所示。尽管Re加入量较大时,W的热导率有所增加,但仍远小于纯W的,所以Re对W的热导率是不利的。
因此,Re虽然可以改善W的塑韧性,减少W中的氘滞留量,但在聚变反应堆中子辐照下会产生脆性相并且导致材料热导率显著降低,再之成本高等原因,使得Re在聚变堆材料方面的应用受到限制。
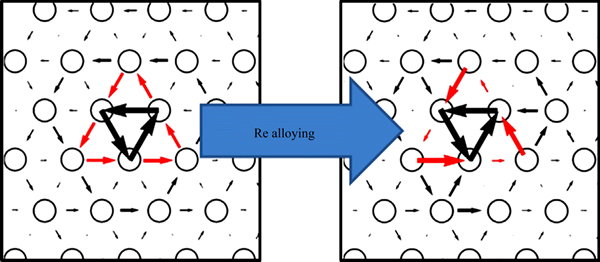
图1 Re掺杂引起的位错中心对称性的变化(空圆圈表示(111)面上的原子,连接相邻原子的箭头表示[111]方向的位移)
Fig. 1 Transition of dislocation-core symmetry introduced by Re alloying (Empty circles are atoms projected on (111) surface; displacements along [111] direction are represented by arrows connecting neighboring atoms)
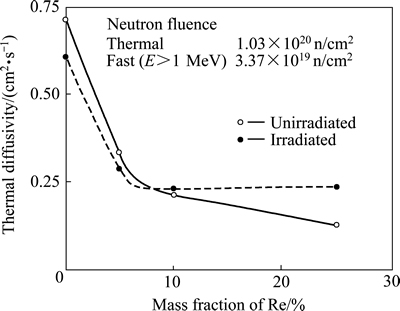
图2 室温下W-Re合金热导率随Re含量的变化情况
Fig. 2 Thermal diffusivity of W-Re alloys at room temperature as a function of Re content
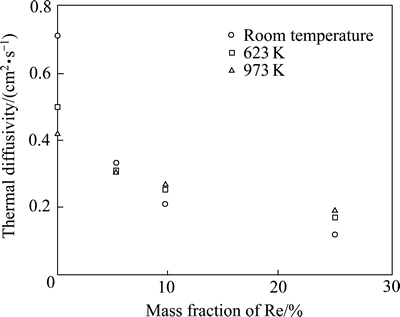
图3 未经辐照W-Re合金在室温、673 K和973 K温度下的热导率
Fig. 3 Thermal diffusivity of unirradiated W-Re alloys at room temperature, 673 and 973 K
1.2 Y元素
适量的稀土元素可以富集W中的杂质元素,改变杂质分布状态,净化晶界,减少气体的析出和空隙的产生从而提高材料密度[21]。钇作为稀土元素的一种,可以和氧形成的细小氧化物颗粒,弥散分布于晶界和晶内,阻碍位错和晶界的运动,细化晶粒,而直接加入Y2O3虽然强化效果显著,但并不能改变W中的杂质元素分布,对材料密度的提高作用较小,杂质含量较高时材料的脆性会显著增加。VELEVA等[22]采用传统粉末冶金方法制备了W-(0.3%~2%)Y2O3和W-(0.3%~2%)Y合金。图4所示为不同成分合金烧结体和烧结后材料的密度和显微硬度均随Y和Y2O3含量的增加而增加。其中,W-2%Y合金的密度最高,而W-2%Y2O3合金具有最高硬度1790HV0.2。这说明与Y2O3相比,Y对提高密度的贡献较大而对硬度的提高作用相对较小(最高硬度只有1435HV0.2)。
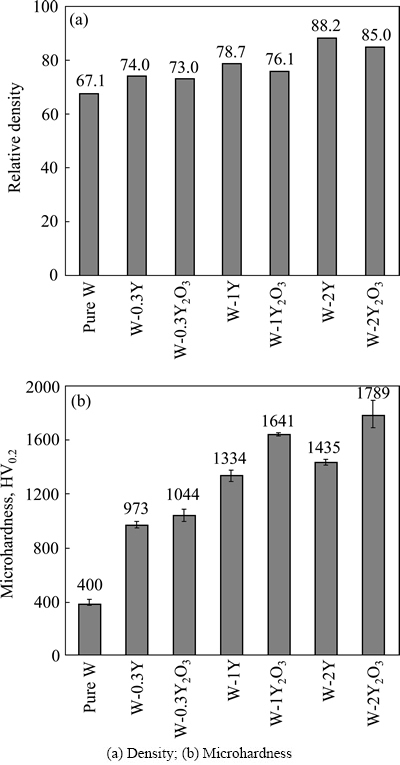
图4 不同成分合金烧结体的密度和显微硬度
Fig. 4 Density and microhardness of sintered ingots of various chemical compositions
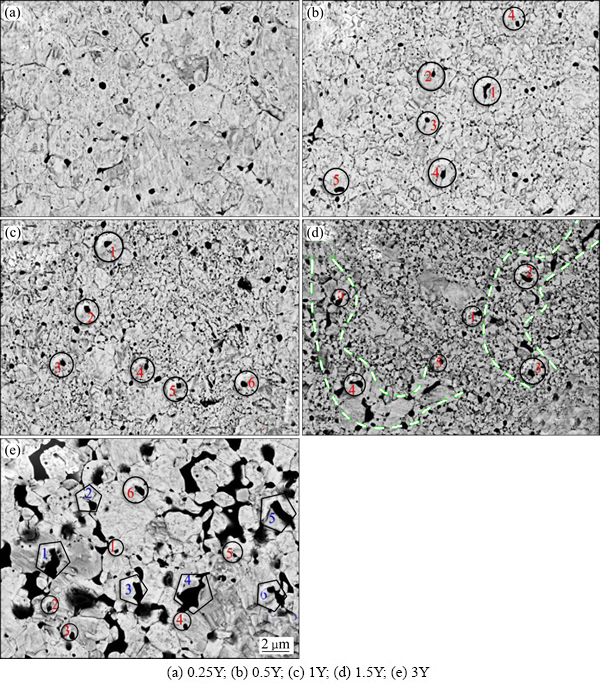
图5 W-(0.25%~3%)Y合金显微组织图像(暗色部分为富Y第二相(用数字标出),红色为亚微观尺度第二相,蓝色为微观尺度第二相)
Fig. 5 Microstructures of W-(0.25%-3%)Y alloys (Dark areas are Y rich phases (marked with numbers). Red numbers represent for sub-micro-scale second phase, blue numbers represent for micro-scale second phase)
此外,VELEVA等[23]采用热等静压烧结技术制备了W-2%Y合金并对其组织和性能进行了研究。发现在球磨过程中,Y由于活性较高,夺取了W中的O形成细小的Y2O3颗粒,细小弥散分布的第二相颗粒在拉伸过程中可有效积累位错,提高材料的加工硬化能力,起到细化晶粒和弥散强化效果。晶粒呈现出50 nm和150 nm两种尺寸,晶界和晶粒内部均观察到Y2O3存在。尽管材料的相对密度(97%)和硬度(1800HV0.2)较高且晶粒细小,但高温脆性较大,在1000 ℃仍表现为脆性断裂,1300 ℃时表现出塑性特征,这表明材料的DBTT提高至1100~1200 ℃。这是由于在2000 ℃以下时,W和Y的热膨胀系数相差较大(Y的是W的2倍),从而产生较大的内应力,使脆性增加。LEMAHIEU等[24]研究了W-(0.25%~1%)Y合金在瞬态热载荷下的结构和性能。结果发现,Y提高了W的抗热震性能,且随Y含量的增加,晶粒的平均尺寸减小,硬度及抗拉强度明显增加,但Y也提高了材料的DBTT,降低了韧性。ZHAO等[25]利用机械合金化和SPS烧结技术制备了W-(0.25%~3%)Y合金,发现Y显著提高了材料的相对密度(最高达99.95%),并在烧结过程中伴有W-Y-O氧化物形成。W的平均晶粒尺寸随Y含量的增加而减小,W-1.5%Y合金具有最细晶粒和最高硬度,当Y含量继续增加时晶粒反而粗化,硬度也显著降低。图5所示为W-(0.25%~3%)Y合金的显微组织图像,随着Y含量的增加,第二相(暗色部分)在晶界发生明显的团聚,造成应力集中,导致材料脆性增加。
可见,合金元素Y会与W中的O元素结合成为一定成分的氧化物,对W的性能产生影响,尽管能提高材料的密度、强度和硬度,但也提高了DBTT,使得脆性增加。
1.3 Ti元素
Ti具有比强度高、韧性好、高低温耐受性能好、在急冷急热条件下应力小等特点,被用来掺杂钨合金以改善性能。研究表明,Ti能够提高纳米W晶粒在高温下的稳定性,保持其纳米结构防止晶粒长大[26-27]。AGUIRRE等[28-30]采用粉末冶金的方法制备了少量Y2O3掺杂的W-Ti合金,并在25~1000 ℃下对材料的强度和韧性进行了测试和评估。结果发现,当温度小于600 ℃时,材料强度、硬度和韧性均随温度和Ti含量的增加而增加;温度大于600 ℃,材料的韧性显著降低,如图6所示。当温度小于600 ℃时,W-Ti合金的强度和韧性均优于W-Ti-Y2O3的;温度大于600 ℃时,氧化会使其性能显著降低。Ti和Y2O3共同存在时,材料内部孔隙较多,晶粒之间结合力减弱,造成韧性下降脆性增加,因此,W-Ti-Y2O3合金的强度和韧性较W-Ti合金的低。研究还发现,尽管Ti促进了W烧结时的致密化过程并形成了Ti-W固溶体,但提高了材料的DBTT,且Y2O3的存在削弱了Ti对致密化的促进作用。
SAVOINI等[31-32]采用机械合金化和热等静压技术分别制备了ODS增强(添加La2O3)的W-Ti、W-V合金并研究了其硬度随温度的变化情况。烧结后材料的相对密度随合金元素含量的增加而增加,最高可达98%和100%,说明Ti和V有助于烧结致密化。图7所示为各合金中元素的分布情况。其中,纳米La2O3颗粒均匀分布于基体中,起到弥散强化作用,Ti和V富集在W颗粒之间形成Ti池和V池,并具有马氏体特征。研究发现,两种成分合金的硬度均随着温度的上升而下降,当温度达473~773 K时,W-4V-1La2O3的硬度保持不变,而W-Ti-La2O3合金的硬度反常增加,如图8所示。Ti和V的热膨胀系数大约是W的2倍,随着温度的上升,在产生的内应力诱导下发生马氏体转变,材料的硬度随之提高。
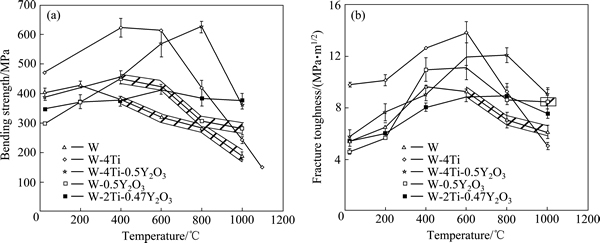
图6 材料弯曲强度和断裂韧性随温度的变化情况
Fig. 6 Evolution of bending strength(a) and fracture toughness(b) of samples with test temperature
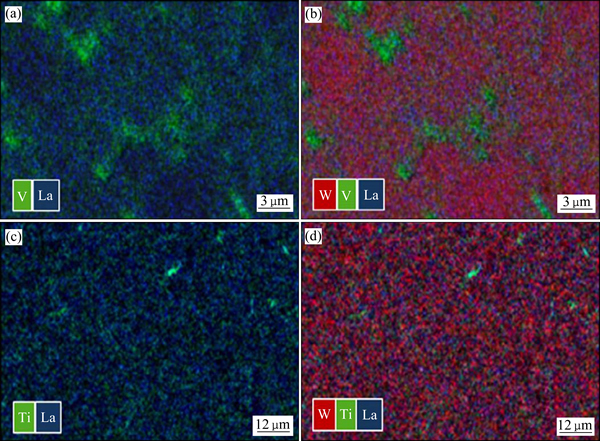
图7 W-4%V-1%La2O3和W-4%Ti-1%La2O3合金的元素分布
Fig. 7 Element map images showing distribution of alloying elements for W-4%V-1%La2O3((a), (b)) and W-4%Ti-1%La2O3((c), (d))
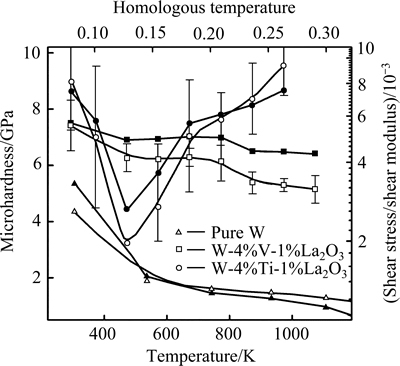
图8 纯W、W-4%V-1%La2O3和W-4%Ti-1%La2O3合金的硬度(空心)及剪切模量(实心)随温度的变化情况
Fig. 8 Evolution of microhardness values (open symbols) and shear modulus (solid symbols) with temperature for pure W, W-4%V-1%La2O3 and W-4%Ti- 1%La2O3
MUNOZ等[33]采用机械合金化和热等静压技术制备了W-2%Ti合金和W-1%TiC合金并比较了两者的性能。结果发现,W-2%Ti合金的相对密度高于W-1%TiC合金的,其显微硬度是后者的两倍。三点弯曲试验研究了两种材料的应力应变曲线随温度的变化情况,结果如图9所示。由图9可知,两种合金均在1000 ℃以上才表现出塑性,表明在加入Ti和TiC之后大大提高了W的韧脆转变温度(>1000 ℃),造成高温脆性。经过75 h球磨之后,部分Ti与W形成固溶体,热等静压烧结后W晶界处形成Ti池;在W-1%TiC合金中,TiC弥散分布于晶内和晶界。此外,球磨过程伴有O杂质的进入且含氧量随球磨时间的延长而增加,杂质元素偏聚于晶界形成复杂的氧化物,造成应力集中并降低晶界的结合力,大大增加W的脆性。
TAN等[3]研究了纯钨和超细晶W-1%Ti-0.5%Y2O3合金在强流脉冲离子束作用下的抗瞬态热负荷性能,发现在高热流密度的条件下,W-1%Ti-0.5%Y2O3合金表现出较差的抗热冲击性能。Ti和Y2O3的熔点相对较低,在强的热冲击作用下,使得W的表面发生熔融、起泡和开裂,可见Ti对W在强瞬态热负荷下的稳定性是不利的。
综上所述,Ti可以提高W基材料的密度和强度,但同样也会提高W的DBTT,高温下的脆性仍然很大,此外Ti也不利于W的抗热冲击性能。
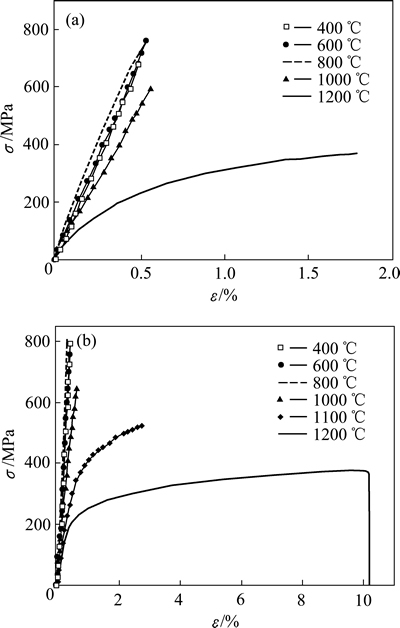
图9 不同温度下W-1%TiC合金和W-2%Ti合金三点弯曲应力-应变曲线
Fig. 9 Stress-strain curves of three point bending tests for W-1%TiC(a) and W-2%Ti(b) at different temperatures
1.4 V元素
V不仅具有高的熔点和良好的延展性,还与W有着很好的互溶性,能够显著改善W基材料的某些性能。PALACIOS等[34]采用高能球磨和热等静压技术制备了纯W、W-4%V、W-1%La2O3和W-4%V-1%La2O3合金来探究合金化及添加氧化物对W性能的影响。表1所列为材料的密度和硬度,由表1可知,加入V之后,W的相对密度和显微硬度均显著增加;而加入La2O3之后,密度和硬度反而降低,W-4%V-1%La2O3合金具有最高硬度。图10和11分别为三点弯曲试验测得的弹性模量、弯曲强度及断裂韧性。如图10所示,添加V之后,W的弹性模量显著增加。图11表明,材料的强韧性随着温度的升高先增加后降低,W-4%V和W-4%V-1%La2O3的强度和韧性始终高于纯W和W-1%La2O3的,当温度升至873 K时,W-4%V合金的强度达到最高850 MPa,约为纯W的3倍,而W-La2O3合金的强度和韧性与纯W相比大致相同并无明显提高。PALACIO等[35]的后续实验也进一步证明了V在提高W基材料密度、细化晶粒和改善强韧性方面的作用。
表1 不同成分样品的密度(理论密度、实验密度、相对密度)和显微硬度值(载荷为0.98N和9.8N)
Table 1 Densities (theoretical (ρth), experimental (ρexp) and relative (ρr) density) and microhardness of samples with different composition (load of 0.98 N and 9.8 N)
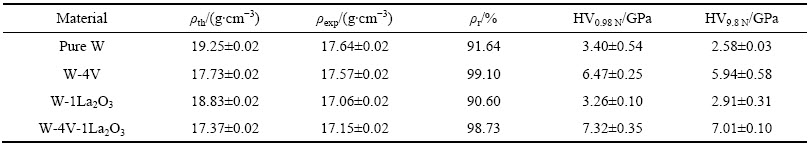
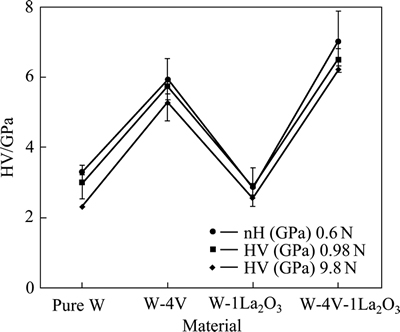
图10 不同成分材料的弹性模量
Fig. 10 Average elastic modulus of each materials
研究还发现,V在W合金中形成了W-V固溶体,这些固溶体紧紧围绕在W晶粒之间,减少了空隙,使密度增加,同时提高了晶界结合力,起到了强化效果;而W-1%La2O3合金相对密度低(仅90.60%),晶粒间的孔隙大大削弱了晶界的结合力,使得性能降低。温度超过673 K时,由于氧化作用材料的性能逐渐下降。反应堆在运行的过程中可能发生真空度下降的现象,无论是水蒸气还是空气在高温下,均会使材料氧化,生成易挥发的氧化物使材料的性能急剧降低[36]。因此,对于面向等离子体材料来说,其高温下抗氧化的性能也十分重要。研究还发现,V可以延缓氧化的开始,可一旦发生氧化其程度反而增加。
ARSHAD等[37]采用球磨和SPS烧结的方法制备了W-(1%, 5%, 7%, 10%)V合金,研究了V掺杂W对其性能的影响。发现材料的相对密度、显微硬度和弯曲强度均随着V含量的增加而增加,晶粒尺寸则逐渐减小,但W-10%V合金的晶粒出现异常长大,可能是由于V的加入使得所需烧结温度降低,1600 ℃下晶粒发生了粗化。研究还发现,材料的硬度主要是受V含量的影响,而强度的提高同时与密度和V含量的增加有关。XRD、EDS和SEM表明,球磨后,大部分V溶解于W,烧结后未溶解的V均匀分布于基体中,阻碍了W晶粒的长大,填充了空位有利于提高密度,如图12所示。相比于其他位置,V颗粒周围的W晶粒更细,这是W晶粒长大受阻碍所致。
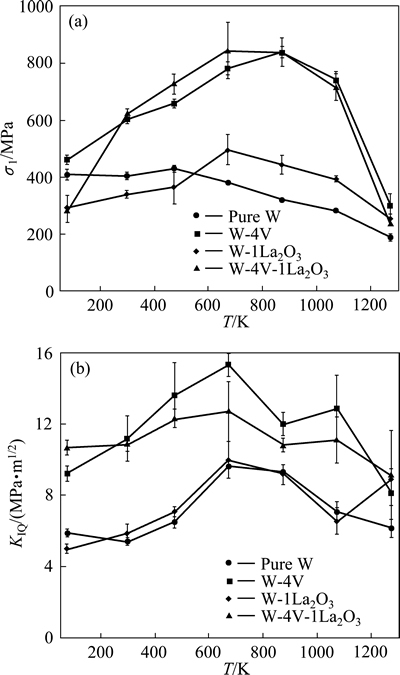
图11 不同成分材料弯曲强度和断裂韧性随温度的变化
Fig. 11 Change of average flexure strength(a) and fracture toughness(b) with test temperature for each material
ARSHAD等[38]还进一步研究了W-(1%, 5%, 10%)V合金在高热流密度(340~675 MW/m2)的瞬时热载荷条件下的抗热负荷性能。研究表明,相对于W-1%V合金,W-5%V和W-10%V合金在高热流密度载荷下的表面损伤程度显著降低,裂纹产生和扩展的临界值较高,说明V能够有效改善W的抗热负荷性能。其中W-5%V合金的裂纹密度最低,表现优于W-10%V合金的。V的热导率小于W的,会降低W的热导率,因此,W-10%V合金热导率最低,其表面的温度最高,导致其表面损伤反而多于W-5%V合金。
综上所述可知,V可以提高W的密度和强韧性,细化晶粒,也有利于W的抗热负荷性能,可以用来作为钨基材料的合金化元素。
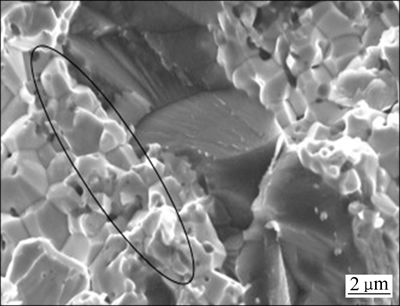
图12 W-1%V合金的SEM断口形貌(W细晶位于V颗粒周围,圆圈中为W细晶粒)
Fig. 12 SEM image of fracture surface of W-1%V alloy (Small tungsten grains are in surrounding of vanadium particle, circle represents small tungsten grains)
1.5 Zr元素
纯W的韧脆转变温度较高,添加强化相之后,DBTT还会进一步提高。造成其低韧性的主要原因之一是W中含有的杂质元素(如O,N,P等)在W晶界发生偏聚,降低晶界的结合力,所以改变杂质元素在W中的分布、强化晶界是提高W强度和韧性的有效手段之一[39]。除细化晶粒之外,添加少量的活性元素亦可起到改善晶界强度的作用。和稀土元素(如La、Y)一样,Zr、Hf等与C、N、O均有较强的亲和力,在高温下能吸收C、N、O元素,形成高熔点化合物,有效减少杂质原子在晶界的偏聚,净化晶界,提高材料强度。XIE等[40]制备了W-(0.1%,0.2%,0.5%,1.0%)Zr合金并对其性能进行了研究,结果发现,虽然Zr的添加使得材料的密度有所下降,但提高了材料的强度和硬度,晶粒尺寸则变化不大。在烧结的过程中,Zr捕获了W中残留的杂质O元素形成纳米ZrO2颗粒,均匀分布于晶界和晶内,阻碍位错的运动,强化了基体,其颗粒尺寸随含Zr量的增加而增加,有少量的Zr与W形成Zr-W固溶体和ZrW2相。相比于纯钨的沿晶断裂,W-Zr合金表现出一些穿晶断裂的特征,表明W的韧性有所改善。W-0.2%Zr合金具有最佳强度和韧性。随Zr含量的增加,合金的强度和韧性逐渐下降,这可能是氧化物颗粒的尺寸增加所致,过大的第二相颗粒会造成应力集中,容易萌生裂纹并快速扩展以释放应力,从而增加材料的脆性。此外,XIE等[41]还制备了W-1%Zr-1%ZrC合金,并与纯W、W-1%Zr、W-1%ZrC合金进行了对比。图13所示为不同成分合金在400~700 ℃的应力-应变曲线。由图13可以看到,纯W的强度最低,塑性最差,在600 ℃时,仍表现为脆性断裂,断裂强度只有309 MPa;W-1%Zr合金在400 ℃时就存在塑性特征,即其DBTT小于400 ℃。在各个温度下,W-1%Zr合金的伸长率都高于其他合金的,表明Zr有效地改善了W的塑性。研究发现,Zr同样是以纳米ZrO2和W-Zr-O颗粒的形式存在于晶内和晶界,改善合金的性能。W-1%Zr-1%ZrC合金的强度最高,但塑性低于W-1%Zr合金,DBTT在400~500 ℃之间,这是由于材料内部的第二相颗粒数量过多,引起的应力集中大,使得塑性有所下降。在提高材料强度方面,直接添加ZrC的效果更加显著。总的来说,添加Zr元素有利于改善W的强度和塑性,但加入量过高时性能反而下降。
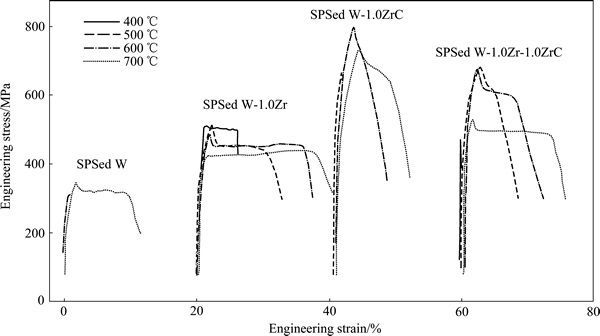
图13 纯钨、W-1%Zr、W-1%Zr和W-1%Zr-1%ZrC合金在400~700 ℃的拉伸行为
Fig. 13 Tensile behaviors of pure W、W-1%Zr、W-1%Zr and W-1%Zr-1%ZrC alloys at temperatures between 400 and 700 ℃
1.6 Nb元素
Nb是一种具有高熔点、不易氧化、延展性良好的活性元素,晶胞为体心立方结构,与W有良好的互溶性,在高温下形成Nb(W)固溶体。研究表明,当Nb含量较低时有利于获得细小均匀分布的Nb(W)固溶体,分布于晶界,阻碍晶粒粗化,且随Nb含量的增加,材料的强度、硬度及韧性均显著增加,晶粒尺寸逐渐减小[42]。另外,与Zr、Hf相似,Nb作为活性元素可以与C、N、O等杂质元素结合生成高熔点化合物,减少杂质在晶界的偏聚,强化晶界。LUO等[43]向W-TiC复合材料中添加了少量Nb元素,研究了Nb对W-TiC合金微观结构和性能的影响。结果发现,与W-1%TiC相比,W-1%Nb-1%TiC的密度增加,说明Nb促进了烧结中的致密化过程;材料的抗拉强度显著上升,前后分别为126 MPa和245 MPa, Nb与少量的C元素在高温下生成具有高熔点和高硬度的NbC,和TiC一起钉扎在晶界处阻碍位错运动,晶内弥散分布有Nb(W)固溶体,这些都使得材料强度提高。此外,Nb还使得W-TiC合金的热导率显著增加。图14所示为W-1%Nb-1%TiC合金在不同倍数下的表面微观结构图。
2 合金化钨基材料性能的改善措施
尽管合金化对钨基材料的密度、强度和硬度等性能有所改善,但依然存在不足,比如塑韧性降低,脆性增加,或热导率、抗热冲击性能下降等。合金元素的加入量也受到限制,过多反而使得材料性能显著降低。因此单靠添加成分(合金元素或第二相)来强化性能效果有限,还应改善制备过程和加工方式以进一步提高材料的性能。本文作者结合近年来的相关研究提出了一些可行的改进措施。
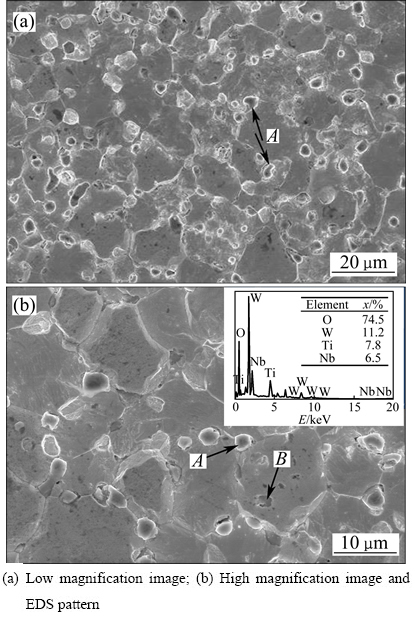
图14 W-1%Nb-1%TiC合金的表面微观结构
Fig. 14 Magnification images of W-1%TiC-1%Nb surface
2.1 减少杂质
在材料制备过程中,尤其是制粉阶段,会不可避免地混入杂质,如C、N、O、H以及粗大的杂质相等。杂质元素偏聚于晶界会削弱晶界的强度,造成晶间脆性[44]。因此,在制备过程中尽可能减少杂质的混入是改善材料韧性的有效手段之一。机械合金化可有效细化粉末颗粒,但因磨球和球磨罐的磨损容易引入大量杂质,且粉末易于成团成块,粘壁现象严重。相比于球磨法,溶胶-凝胶法、湿化学法和共沉淀法不但能制得更纯净的合金粉末还有着各自的优点。LIU等[45-46]通过溶胶-凝胶和微波烧结的方法制备了纳米W-1%La2O3和W-1%Y2O3复合材料,发现与球磨法相比,材料中氧化物颗粒的分布更加均匀。丁孝禹等[47]采用湿化学法和SPS烧结技术制备了超细晶W-TiC复合材料,实验对原始TiC粉进行了活化预处理,使TiC粉表面获得均匀分布的缺陷,提高了TiC粉表面的亲水性,通过化学还原使得TiC颗粒均匀弥散分布于W基体晶界和晶粒内,再结合SPS低温快速烧结有效地防止了W晶粒的长大,获得高密度超细晶W-TiC复合材料,显著提高了材料的性能。XIA等[48]通过共沉淀法制备出高纯度W-La2O3合金。实验所制备的纳米La2O3颗粒均匀存在于细晶W的晶界内和晶界处。所制备的试样具有更高和更稳定的显微硬度,实验结果也证实了共沉淀法是一种制备沉淀掺杂氧化物/W纳米颗粒的有效方法,并且在制备结构均匀的块体W基复合材料方面有很大优势。
单一地添加合金元素对材料性能的改善作用有限且存在不足,未来的钨基材料可能是同时加入多元增强相的复合材料,这就要求在制粉的过程中做到成分均匀且可控,而后3种方法在实现粉末成分精确可控、纯度高且均匀性良好等方面具有各自的优势。
2.2 制备超细晶/纳米晶钨基材料
钨基材料脆性大的问题是未来面向等离子体材料研究所需面对的难题之一,利用恰当的加工方式制备出超细晶/纳米晶钨基材料是改善W强韧性的有效手段。由Hall-Petch关系可知,晶粒尺寸越小,强度越高。此外,细晶的变形较均匀,每个晶粒中塞积的位错少,应力集中引起开裂的机会较少,裂纹不易萌生和扩展,表现出好的塑韧性。
常用的制备超细晶/纳米晶钨的方法分为深度塑性变形法(SPD)和粉末冶金法(PM)两种。深度塑性变形法又分为等通道角挤压(ECAP)和高压扭转(HPT)这两种工艺[49]。实验表明[50-52],经过SPD处理不仅可以获得高强度的超细晶W,还可显著改善W的低温脆性,兼具良好的强韧性。经SPD处理后,材料内部产生的非平衡的大角度晶界可能是导致其同时具有高强度和高韧性的原因。具有大角度晶界的超细等轴晶阻碍了位错运动从而提高材料的强度;同时,通过SPD获得的晶界常处于非平衡状态,晶界及其附近具有大量位错,这将有助于晶界滑动和晶粒转动这些变形机制的发生,且变形分散均匀,应力集中小,从而提高材料的韧性[53]。此外,杂质通过扩散沿这些晶界重新分布,降低了杂质原子在晶界处的平均浓度,也一定程度地改善了材料的塑韧性。采用SPD法还有着高密度和无杂质污染的工艺优势。
放电等离子体烧结(SPS)是粉末冶金烧结方法的一种,具有升温速度快、烧结时间短、晶粒均匀、组织结构可控等特点,被用来制备高密度的细晶复合材料,使材料具有良好的力学性能[25, 37, 43],但亦容易混入杂质。此外,热等静压烧结(HIP)[33-34]和超高压通电烧结(RSUHP)[54]等也是制备细晶钨基材料的有效手段。相比之下,传统高温烧结的烧结温度高,时间长,会使钨晶粒严重长大且很难获得较高的密度,不利于获得具有优异性能的细晶钨。因此,添加多元强化相以及优化制造工艺是改善未来面向等离子体钨基复合材料的性能的可靠途径。
3 结论
1) W基材料因其高熔点、低溅射、不与H反应、低的氚滞留等优点被看作未来托卡马克中最可能全面使用的面向等离子体材料。但要实现将来的工程化应用,必须解决W所面临的难加工、韧脆转变温度高、再结晶温度低以及辐照脆化等难题。
2) W的强化机制主要有固溶强化、细晶强化及第二相弥散强化等,可采用合金化、加入第二相颗粒(氧化物和碳化物)和制备超细晶/纳米晶钨基材料来改善其性能。合金化是最常用的改善材料性能的方式之一,对于材料性能的影响也最为复杂。
3) 在Re、Ti、V、Zr、Y、Nb等这些合金元素之中,大多都能显著提高W基材料的密度、强度和硬度,V还可改善W的抗热负荷性能。从改善W塑韧性的角度看,只有Re、Zr、V起到了不同程度的效果,而其他合金元素对材料塑韧性的改善少有贡献,有的甚至增加了W的脆性。但Re会降低W的热导率,且存在辐照致脆效应。此外,Ti不利于钨基材料的抗热冲击性能。因此,合金元素对W性能的影响有利有弊,应最大化发挥其性能优势,尽量减小合金化对W性能的危害作用。
4) 面向等离子体钨基材料不仅需要足够的强度,也要保证一定程度的韧性、良好的热学性能以及辐照性能,才能满足聚变反应堆的严苛要求。因此单靠合金化是不够的,仍需通过优化制备工艺,获得高纯度和高密度的超细晶/纳米晶钨基材料来改善性能,如深度塑性变形法和特种烧结方法等等,在合金化和多元复合强化方面的研究也需进一步开展。
REFERENCES
[1] 葛昌纯. 面向等离子体材料与可控核聚变[J]. 中国科技财富, 2009(17): 28-31.
GE Chang-chun. Plasma facing materials and controlled nuclear fusion[J]. Fortune World, 2009(17): 28-31.
[2] 邱励俭. 核聚变研究50年[J]. 核科学与工程, 2001, 21(1): 29-38.
QIU Li-jian. Fusion research in the world[J]. Chinese Journal of Nuclear Science and Engineering, 2001, 21(1): 29-38.
[3] TAN J, ZHOU Z, ZHU X, GUO S, QU D, LEI M, GE C. Evaluation of ultra-fine grained tungsten under transient high heat flux by high-intensity pulsed ion beam[J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2012, 22(5): 1081-1085.
[4] 刘丹华, 谌继明, 吴继红, 闫得胜. 国际热核实验堆第一壁材料CuCrZr合金及其与不锈钢焊接接头的力学性能[J]. 机械工程材料, 2009, 33(3): 46-49.
LIU Dan-hua, CHEN Ji-ming, WU Ji-hong, YAN De-sheng. Mechanical properties of the CuCrZr alloy and CuCrZr/SS joints for ITER first wall[J]. Materials for Mechanical Engineering, 2009, 33(3): 46-49.
[5] SHIMADA M, COSTLEY A E, FEDERICI G, IOKI K, KUKUSHKIN A S, MUKHOVATOV V, POLEVOI A, SUGIHARA M. Overview of goals and performance of ITER and strategy for plasma-wall interaction investigation[J]. Journal of Nuclear Materials, 2005, 337/339: 808-815.
[6] BOLT H, BARABASH V, KRAUSS W, LINKE J, NEU R, SUZUKI S, YOSHIDA N, ASDEX U T. Materials for Plasma- facing components of fusion reactors[J]. Journal of Nuclear Materials, 2004, 329/333: 66-73.
[7] ROEDIG M, KUEHNLEIN W, LINKE J, MEROLA M, RIGAL E, SCHEDLER B, VISCA E. Investigation of tungsten alloys as plasma facing materials for the ITER divertor[J]. Fusion Engineering and Design, 2002, 61/62: 135-140.
[8] PHILIPPS V. Tungsten as material for plasma-facing components in fusion devices[J]. Journal of Nuclear Materials, 2011, 415(1): S2-S9.
[9] BOLT H, BARABASH V, FEDERICI G, LINKE J, LOARTE A, ROTH J, SATO K. Plasma facing and high heat flux materials-needs for ITER and beyond [J]. Journal of Nuclear Materials, 2002, 307/311: 43-52.
[10] 丁文艺, 何海燕, 潘必才. 磁约束可控热核聚变堆中的第一壁材料钨的研究状况和面临的若干问题[J].安徽师范大学学报(自然科学版), 2014, 37(4): 314-319.
DING Wen-yi, HE Hai-yan, PAN Bi-cai. The review and some problems about the first wall materials tungsten in magnetic confinement fusion reactor[J]. Journal of Anhui Normal University (Natural Science), 2014, 37(4): 314-319.
[11] 朱玲旭, 燕青芝, 郎少庭, 徐 磊, 葛昌纯. 钨基面向等离子体材料的研究进展[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2012, 22(12): 3522-3528.
ZHU Ling-xu, YAN Qing-zhi, LANG Shao-ting, XU Lei, GE Chang-chun. Research progress of tungsten-base materials as plasma facing materials[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2012, 22(12): 3522-3528.
[12] WURSTER S, BALUC N, BATTABYAL M, CROSBY T, DU J, GARC A-ROSALES C, HASEGAWA A, HOFFMANN A, KIMURA A, KURISHITA H, KURTZ R J, LI H, NOH S, REISER J, RIESCH J, RIETH M, SETYAWAN W, WALTER M, YOU J H, PIPPAN R. Recent progress in R&D on tungsten alloys for divertor structural and plasma facing materials[J]. Journal of Nuclear Materials, 2013, 442: S181-S189.
A-ROSALES C, HASEGAWA A, HOFFMANN A, KIMURA A, KURISHITA H, KURTZ R J, LI H, NOH S, REISER J, RIESCH J, RIETH M, SETYAWAN W, WALTER M, YOU J H, PIPPAN R. Recent progress in R&D on tungsten alloys for divertor structural and plasma facing materials[J]. Journal of Nuclear Materials, 2013, 442: S181-S189.
[13] GAO H P, ZEE R H. Effects of rhenium on creep resistance in tungsten alloys[J]. Journal of Materials Science Letters, 2001, 20: 885-887.
[14] LI H, WURSTER S, MOTZ C, ROMANER L, AMBROSCH-DRAXL C, PIPPAN R. Dislocation-core symmetry and slip planes in tungsten alloys: Ab initio calculations and microcantilever bending experiments[J]. Acta Materialia, 2012, 60(2): 748-758.
[15] NORAJITRA P, BOCCACCINI L V, DIEGELE E, FILATOV V, GERVASH A, GINIYATULIN R, GORDEEV S, HEINZEL V,JANESCHITZ G, KONYS J, KRAUSS W, KRUESSMANN R, MALANG S, MAZUL I, MOESLANG A, PETERSEN C, REIMANN G, RIETH M, RIZZI G, RUMYANTSEV M, RUPRECHT R, SLOBODTCHOUK V. Development of a helium-cooled divertor concept: Design-related requirements on materials and fabrication technology[J]. Journal of Nuclear Materials, 2004, 329/333: 1594-1598.
[16] SETYAWAN W, KURTZ R J. Effects of transition metals on the grain boundary cohesion in tungsten[J]. Scripta Materialia, 2012, 66(8): 558-561.
[17] TYBURSKA P B, ALIMOV V K. On the reduction of deuterium retention in damaged Re-doped W[J]. Nuclear Fusion, 2013, 53: 123021.
[18] NEMOTO Y, HASEGAWA A, SATOU M, ABE K. Microstructural development of neutron irradiated W-Re alloys[J]. Journal of Nuclear Materials, 2000, 283/287: 1144-1147.
[19] FUKUDA M, YABUUCHI K, NOGAMI S, HASEGAWA A, TANAKA T. Microstructural development of tungsten and tungsten-rhenium alloys due to neutron irradiation in HFIR[J]. Journal of Nuclear Materials, 2014, 455(1/3): 460-463.
[20] FUJITSUKA M, TSUCHIYA B, MUTOH I, TANABE T, SHIKAMA T. Effect of neutron irradiation on thermal diffusivity of tungsten-rhenium alloys[J]. Journal of Nuclear Materials, 2000, 283/287: 1148-1151.
[21] 谭敦强, 李亚蕾, 杨 欣, 陆 磊, 陆德平. 杂质元素对钨产品结构及性能的影响[J]. 材料导报, 2013, 27(9): 98-100.
TAN Dun-qiang, LI Ya-lei, YANG Xin, LU Lei, LU De-ping. The influence of impurity elements on structure and performance of tungsten products[J]. Materials Review, 2013, 27(9): 98-100.
[22] VELEVA L, OKSIUTA Z, VOGT U, BALUC N. Sintering and characterization of W-Y and W-Y2O3 materials[J]. Fusion Engineering and Design, 2009, 84: 1920-1924.
[23] VELEVA L, SCH UBLIN R, PLOCINSKI T, WALTER M, BALUC N. Processing and characterization of a W-2Y material for fusion power reactors[J]. Fusion Engineering and Design, 2011, 86: 2450-2453.
UBLIN R, PLOCINSKI T, WALTER M, BALUC N. Processing and characterization of a W-2Y material for fusion power reactors[J]. Fusion Engineering and Design, 2011, 86: 2450-2453.
[24] LEMAHIEU N, LINKE J, PINTSUK G, OOST G V, WIRTZ M, ZHOU Z. Performance of yttrium doped tungsten under ‘edge localized mode’-like loading conditions[J]. Physica Scripta, 2014, T159: 014035.
[25] ZHAO M Y, ZHOU Z J, DING Q M, ZHONG M, TAN J. The investigation of Y doping content effect on the microstructure and microhardness of tungsten materials[J]. Materials Science & Engineering A, 2014, 618: 572-577.
[26] CHOOKAJORN T, MURDOCH H A, SCHUH C A. Design of Stable Nanocrystalline Alloys[J]. Science, 2012, 24: 951-954.
[27] CHOOKAJORN T, SCHUH C A. Nanoscale segregation behavior and high-temperature stability of nanocrystalline W-20at.% Ti[J]. Acta Materialia, 2014, 73: 128-138.
[28] MONGE M A, AUGER M A, LEGUEY T, ORTEGA Y, BOLZONI L, GORDO E, PAREJA R. Characterization of novel W alloys produced by HIP[J]. Journal of Nuclear Materials, 2009, 386/388: 613-617.
[29] AGUIRRE M V, MART N A, PASTOR J Y, LLORCA J, MONGE M A, PAREJA R. Mechanical properties of Y2O3-doped W-Ti alloys[J]. Journal of Nuclear Materials, 2010, 404: 203-209.
N A, PASTOR J Y, LLORCA J, MONGE M A, PAREJA R. Mechanical properties of Y2O3-doped W-Ti alloys[J]. Journal of Nuclear Materials, 2010, 404: 203-209.
[30] AGUIRRE M V, MART N A, PASTOR J Y, LLORCA J, MONGE M A, PAREJA R. Mechanical properties of tungsten alloys with Y2O3 and titanium additions[J]. Journal of Nuclear Materials, 2011, 417: 516-519.
N A, PASTOR J Y, LLORCA J, MONGE M A, PAREJA R. Mechanical properties of tungsten alloys with Y2O3 and titanium additions[J]. Journal of Nuclear Materials, 2011, 417: 516-519.
[31] MART NEZ J, SAVOINI B, MONGE M A, MUNOZ A, PAREJA R. Development of oxide dispersion strengthened W alloys produced by hot isostatic pressing[J]. Fusion Engineering and Design, 2011, 86: 2534-2537.
NEZ J, SAVOINI B, MONGE M A, MUNOZ A, PAREJA R. Development of oxide dispersion strengthened W alloys produced by hot isostatic pressing[J]. Fusion Engineering and Design, 2011, 86: 2534-2537.
[32] SAVOINI B, MART NEZ J, MU
NEZ J, MU OZ A, MONGE M A, PAREJA R. Microstructure and temperature dependence of the microhardness of W-4V-1La2O3 and W-4Ti-1La2O3[J]. Journal of Nuclear Materials, 2013, 442: S229-S232.
OZ A, MONGE M A, PAREJA R. Microstructure and temperature dependence of the microhardness of W-4V-1La2O3 and W-4Ti-1La2O3[J]. Journal of Nuclear Materials, 2013, 442: S229-S232.
[33] MU OZ A, SAVOINI B, TEJADO E, MONGE M A, PASTOR J Y, PAREJA R. Microstructural and mechanical characteristics of W-2Ti and W-1TiC processed by hot isostatic pressing[J]. Journal of Nuclear Materials, 2014, 455: 306-310.
OZ A, SAVOINI B, TEJADO E, MONGE M A, PASTOR J Y, PAREJA R. Microstructural and mechanical characteristics of W-2Ti and W-1TiC processed by hot isostatic pressing[J]. Journal of Nuclear Materials, 2014, 455: 306-310.
[34] PALACIOS T, PASTOR J Y, AGUIRRE M V, MART N A, MONGE M A, MU
N A, MONGE M A, MU
 Z A, PAREJA R. Mechanical behavior of tungsten-vanadium-lanthana alloys as function of temperature[J]. Journal of Nuclear Materials, 2013, 442: S277-S281.
Z A, PAREJA R. Mechanical behavior of tungsten-vanadium-lanthana alloys as function of temperature[J]. Journal of Nuclear Materials, 2013, 442: S277-S281.
[35] PALACIO T, MONGE M A, PASTOR J Y. Tungsten-vanadium-yttria alloys for fusion power reactors (Ⅰ): Microstructural characterization[J]. International Journal of Refractory Metals and Hard Materials, 2016, 54: 433-438.
[36] DRUYTS F, FAYS J, WU C H. Interaction of plasma-facing materials with air and steam[J]. Fusion Engineering and Design, 2002, 63/64: 319-325.
[37] ARSHAD K, ZHAO M Y, YUAN Y, ZHANG Y, ZHAO Z H, WANG B, ZHOU Z J, LU G H. Effects of vanadium concentration on the densification, microstructures and mechanical properties of tungsten vanadium alloys[J]. Journal of Nuclear Materials, 2014, 455: 96-100.
[38] ARSHAD K, DING D, WANG J, YUAN Y, WANG Z, ZHANG Y, ZHOU Z J, LIU X, LU G H. Surface cracking of tungsten-vanadium alloys under transient heat loads[J]. Nuclear Materials and Energy, 2015, 3/4: 32-36.
[39] LIU R, XIE Z M, HAO T, ZHOU Y, WANG X P, FANG Q F, LIU C S. Fabricating high performance tungsten alloys through zirconium micro-alloying and nano-sized yttria dispersion strengthening[J]. Journal of Nuclear Materials, 2014, 451: 35-39.
[40] XIE Z M, LIU R, FANG Q F, ZHOU Y, WANG X P, LIU C S. Spark plasma sintering and mechanical properties of zirconium micro-alloyed tungsten[J]. Journal of Nuclear Materials, 2014, 444: 175-180.
[41] XIE Z M, ZHANG T, LIU R, FANG Q F, MIAO S, WANG X P, LIU C S. Grain growth behavior and mechanical properties of zirconium micro-alloyed and nano-size zirconium carbide dispersion strengthened tungsten alloys[J]. International Journal of Refractory Metals and Hard Materials, 2015, 51: 180-187.
[42] SHA J J, HAO X N, LI J, DAI J X, YANG X L, YOON H K. Mechanical properties and fracture characteristics of CNTs-doped W-Nb alloys[J]. Journal of Nuclear Materials, 2014, 445: 573-577.
[43] LUO L M, CHEN J B, CHEN H Y, LUO G N, ZHU X Y, CHENG J G, ZAN X, WU Y C. Effect of doped niobium on the microstructure and properties of W-Nb/TiC composites prepared by spark plasma sintering[J]. Fusion Engineering and Design, 2015, 90: 62-66.
[44] KOBYLANSKI A, 张廷杰. 杂质对钨晶界脆性的影响[J]. 稀有金属材料与工程, 1986, 1(1): 41-45.
KOBYLANSKI A, ZHANG Ting-jie. Effects of impurities on tungsten grain boundary brittleness[J]. Rare Metal Materials and Engineering, 1986, 1(1): 41-45.
[45] LIU R, WANG X P, HAO T, LIU C S, FANG Q F. Characterization of ODS-tungsten microwave-sintered from sol-gel prepared nano-powders[J]. Journal of Nuclear Materials, 2014, 450(1/3): 69-74.
[46] LIU R, ZHOU Y, HAO T, ZHANG T, WANG X P, LIU C S, FANG Q F. Microwave synthesis and properties of fine-grained oxides dispersion strengthened tungsten[J]. Journal of Nuclear Materials, 2012, 424(1/3): 171-175.
[47] 丁孝禹, 罗来马, 黄丽枚, 罗广南, 李 萍, 朱晓勇, 吴玉程. 湿化学法制备 W-TiC 复合粉体及其 SPS 烧结行为[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2014, 24(10): 2594-2600.
DING Xiao-yu, LUO Lai-ma, HUANG Li-mei, LUO Guang-nan, LI Ping, ZHU Xiao-yong, WU Yu-cheng. Synthesis of W-TiC composite powders by wet-chemical process and its sintering behavior by SPS[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2014, 24(10): 2594-2600.
[48] XIA M, YAN Q Z, XU L, GUO H Y, ZHU L X, GE C C. Bulk tungsten with uniformly dispersed La2O3 nanoparticles sintered from co-precipitated La2O3/W nanoparticles[J]. Journal of Nuclear Materials, 2013, 434(1/3): 85-89.
[49] 刘 凤, 李 强, 王万景, 罗广南, 刘 伟. 超细晶/纳米晶 钨-未来聚变堆面向等离子体材料[J]. 材料导报, 2011, 25(10): 43-48.
LIU Feng, LI Qiang, LUO Guang-nan, LIU Wei. Ultra-fine grained/nano-crystalline tungsten-plasma facing material for future fusion reactors[J]. Materials Review, 2011, 25(10): 43-48.
[50] WEI Q, JIAO T, RAMESH K T, MA E, KECSKES L J, MAGNESS L, DOWDING R, KAZYKHANOV V U, VALIEV R Z. Mechanical behavior and dynamic failure of high-strength ultrafine grained tungsten under uniaxial compression[J]. Acta Materialia, 2006, 54(1): 77-87.
[51] WEI Q, ZHANG H T, SCHUSTER B E, RAMESH K T, VALIEV R Z, KECSKES L J, DOWDING R J, MAGNESS L, CHO K. Microstructure and mechanical properties of super-strong nanocrystalline tungsten processed by high-pressure torsion[J]. Acta Materialia, 2006, 54(15): 4079-4089.
[52] FALESCHINI M, KREUZER H, KIENER D, PIPPAN R. Fracture toughness investigations of tungsten alloys and SPD tungsten alloys[J]. Journal of Nuclear Materials, 2007, 367/370: 800-805.
[53] VALIEV R Z, ALEXANDROV I V, ZHU Y T. Paradox of strength and ductility in metals processed by severe plastic deformation[J]. Journal of Materials Research, 2002, 17(1): 5-8.
[54] ZHOU Z J, PINTSUK G, LINKE J, HIRAI T, R DIG M, MA Y, GE C C. Transient high heat load tests on pure ultra-fine grained tungsten fabricated by resistance sintering under ultra-high pressure[J]. Fusion Engineering and Design, 2010, 85(1): 115-121.
DIG M, MA Y, GE C C. Transient high heat load tests on pure ultra-fine grained tungsten fabricated by resistance sintering under ultra-high pressure[J]. Fusion Engineering and Design, 2010, 85(1): 115-121.
LUO Lai-ma1, 3, SHI Jing1, ZAN Xiang1, 3, LI Ping1, 3, LUO Guang-nan2, CHEN Jun-ling2, WU Yu-cheng1, 3
(1. College of Material Science and Engineering, Hefei University of Technology, Hefei 230009, China;
2. Institute of Plasma Physics, Chinese Academic Sciences, Hefei 230031, China;
3. Laboratory of Nonferrous Metal Material and Processing Engineering of Anhui Province, Hefei 230009, China)
Abstract: Tungsten matrix composites have gradually replaced the traditional carbon-based materials and beryllium, becoming the most promising candidates for plasma-facing materials for the international thermonuclear experimental reactor attributing to their superior properties. However, tungsten exhibits some problems as a plasma-facing material, including low temperature embrittlement, recrystallization embrittlement, radiation embrittlement and fuel particle retention. Hence, attempts for improving its mechanical behavior have been carried out via doping alloying elements or stable dispersed phases and fabricating UFG/nanocrystalline tungsten, etc. Alloying is one of the most common methods to improve the performance of tungsten-based materials. The doping elements can diffuse and dissolve into tungsten matrix or act on the defects and impurities to change the contexture and structure of tungsten, thus improving its properties. The change of properties and the correlative mechanism of alloyed tungsten-based materials were reviewed and some problems on it and the improvement measures and development trend in future were pointed out.
Key words: plasma facing material; tungsten-based material; alloying element; action mechanism; improvement measure
Foundation item: Project(2014GB121001) supported by National Magnetic Confinement Fusion Program; Projects (51474083, 51574101) supported by the National Science Foundation of China
Received date: 2015-03-26; Accepted date: 2015-12-26
Corresponding author: WU Yu-cheng; Tel: +86-551-62901012; E-mail: ycwu@hfut.edu.cn
(编辑 王 超)
基金项目:国际热核聚变实验堆(ITER)计划专项(2014GB121001);国家自然基金面上项目(51474083,51574101)
收稿日期:2015-03-26;修订日期:2015-12-26
通信作者:吴玉程,教授,博士;电话:0551-62901012;E-mail: ycwu@hfut.edu.cn

