液固分离和喷射沉积制备Al-45%Si合金的组织及性能
来源期刊:中国有色金属学报(英文版)2013年第4期
论文作者:李艳霞 刘俊友 王文韶 刘国权
文章页码:970 - 976
关键词:铝硅合金;Si 颗粒;液固分离;喷射沉积;热导率;热膨胀系数
Key words:aluminum-silicon alloy; Si particle; liquid-solid separation; spray deposition; thermal conductivity; thermal expansion coefficient
摘 要:对液固分离法(LSS)和喷射沉积法(SD)制备的Al-45%Si合金组织和性能进行研究。结果表明,两种方法制备的合金中初生Si相具有不同的尺寸、形态和分布,从而对合金性能产生不同的影响。采用喷射沉积法制备的合金中硅相形状不规则,尺寸细小并在空间连续分布。液固分离法制备的合金中硅相形态呈近球形,尺寸较大并被连续的铝基体包覆。与喷射沉积合金相比,液固分离制备合金具有更高的热导率和更低的低温热膨胀系数,但由于硅颗粒尺寸较大,力学性能低于喷射沉积合金。硅相的分布形式对热膨胀系数的增加速率影响显著,其中喷射沉积法制备的合金中硅相连续分布有利于获得低的增加速率。由于组织特征的不同,液固分离制备合金的热膨胀系数预测模型与喷射沉积制备的合金有区别。
Abstract: The microstructures and properties of Al-45%Si alloy prepared by liquid-solid separation (LSS) process and spray deposition (SD) were studied. The results show that the size, shape and distribution of the primary Si phase have different influence on the properties of alloys. Comparing with the Si particles with irregular shape, fine size and continuous distribution in SD alloy, the primary Si phase in LSS alloy is sphere-like, coarse and surrounded by the continuous Al matrix. The microstructure features of LSS alloy are beneficial to the higher thermal conductivity and lower thermal expansion coefficient at room temperature. The fine Si particle in SD alloy is advantageous to improving the mechanical properties. The increasing rates of thermal expansion coefficient with temperature are influenced by the distribution of the Si particles, where a lower rate is obtained in SD alloy with continuous Si particles. The agreement of thermal expansion coefficient with the model in LSS alloy differs from that in the SD alloy because of the different microstructure characteristics.
Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 23(2013) 970-976
Yan-xia LI1,2, Jun-you LIU1, Wen-shao WANG1, Guo-quan LIU1
1. School of Materials Science and Engineering, University of Science and Technology Beijing, Beijing 100083, China;
2. Department of Materials, North China Institute of Aerospace Engineering, Langfang 065000, China
Received 6 January 2012; accepted 15 May 2012
Abstract: The microstructures and properties of Al-45%Si alloy prepared by liquid-solid separation (LSS) process and spray deposition (SD) were studied. The results show that the size, shape and distribution of the primary Si phase have different influence on the properties of alloys. Comparing with the Si particles with irregular shape, fine size and continuous distribution in SD alloy, the primary Si phase in LSS alloy is sphere-like, coarse and surrounded by the continuous Al matrix. The microstructure features of LSS alloy are beneficial to the higher thermal conductivity and lower thermal expansion coefficient at room temperature. The fine Si particle in SD alloy is advantageous to improving the mechanical properties. The increasing rates of thermal expansion coefficient with temperature are influenced by the distribution of the Si particles, where a lower rate is obtained in SD alloy with continuous Si particles. The agreement of thermal expansion coefficient with the model in LSS alloy differs from that in the SD alloy because of the different microstructure characteristics.
Key words: aluminum-silicon alloy; Si particle; liquid-solid separation; spray deposition; thermal conductivity; thermal expansion coefficient
1 Introduction
The Al-Si alloy is an ideal material for electronic packaging with high thermal conductivity (TC), low thermal expansion coefficient (CTE) and low density. Several methods were exploited to prepare Al-Si alloy [1-3]. The successful process included liquid infiltration (LIF) [2], spray deposition (SD) [3], and powder metallurgy (PM) [4]. The primary Si phase is the main constituent in the Al-Si alloy and its size, shape and distribution are determined by processes. In the microstructure of spray deposition prepared alloy, the Si phase was fine and interconnected each other [5]. The general microstructure features of the powder metallurgy alloy were the dispersive Si particles distributing in the continuous Al matrix [4]. As for in the liquid infiltration alloy, the Si particles and Al matrix formed an interpenetrating network [2]. It is necessary to clarify the dependence of the properties on the microstructures, including the size, shape and distribution of the primary Si phase in the different process.
For the metal-matrix composite with particle reinforcement, lots of researches about the influence of the particle size, shape and distribution on the TC and CTE had been done. CHIEN [6] and PARK et al [7] studied the effect of the particle size on the TC, and a same conclusion was drawn that the composite with fine particles often had a low conductivity because of much more interface area. Referring to the studies of YAN and GENG [8] and PARK et al [7] in SiC/Al composites, the CTE was proportional to the size of particles, while CHIEN et al [6] indicated that the composite with fine particles had a low CTE compared with the coarse particles. The regular particles often produced small interface area and had advantage of improving the TC, which was confirmed by ZHANG et al [9]. TAKEI and HATTA [10,11] studied the CTE of SiC/Al composite with different shapes and found that the composite of spherical particles had the lowest CTE, which agreed with the result of ZHANG et al [12]. SHEN and NEEDLEMAN [13,14] made series of theory calculations and experimental research about the CTE of composites with different phases. The results showed that there was a significant dependence of the overall CTE on the phase contiguity, i.e., on the continuity of the matrix or the reinforcement. About the continuity of the constituents in the composite, WANG et al [15] proposed that the favorable structure of the composite with high TC was that the particles interconnected and formed a continuous network. However, the continuous reinforcement produced the maximum interface area [16] and was disadvantageous to the TC.
In view of the size, shape and distribution of particles have a significant influence on the composite properties, the microstructures and properties of Al-Si alloy prepared by two processes were studied. The aim of this study is to reveal the effect of the size, shape and distribution of the primary Si phase on the strength, thermal conductivity and thermal expansion coefficient of Al-Si alloy. Two kinds of models were applied to calculating the CTE and compared with the measured values. The appropriate model was established based on the microstructure features in the different processes. A new method of liquid-solid separation was put forward and the microstructure characterization of Al-Si alloy fabricated by it was analyzed. The method will provide an alternative process to prepare the Al-Si alloy for the electronic packaging.
2 Experimental
Al-45%Si alloy samples were fabricated by liquid-solid separation (LSS) process and spray deposition (SD) [17], respectively. The main procedures in LSS were as flows: the cast Al-25%Si alloy was remelted at 600 °C into semi-solid; the liquid and solid semi-solid alloys were separated under the pressure; the quantitative liquid was discharged out of the alloy and the remanent alloy with 45% Si element was solidified; Al-45% Si alloy was annealed at 490 °C for 3 h.
The microstructure and fracture morphology were observed by a NEOPHOT2 optical microscope and LEO-1450 scanning electron microscope (SEM). The area distributions of elements were studied with a JEOL JXA-8230 electron probe X-ray microanalysis (EPMA). CTE tests were performed on a DIL 402 thermal dilatometer at a rate of 5 °C/min, the dimensions of specimen were d5 mm×25 mm. The densities of alloys were determined based on the Archimedes drainage method and compared with the theoretical density to obtain the relative density. TC was measured by the laser flash method with the LFA 427 instrument at 25 °C. The 3-point bending tests with 36 mm span were carried out at room temperature on a RGM-3010 electron universal testing machine. Brinell hardness measurements were performed on a XHB-3000 Brilled durometer.
3 Results and discussion
3.1 Microstructure
Figure 1 shows the optical micrographs of Al-45%Si alloy samples prepared by the LSS and SD processes. The gray particle is primary Si phase and the white matrix is rich in Al-phase. In LSS alloy, the primary Si phase is regular with dull angular, and the mean diameter is 40-50 μm. The short stick-like eutectic Si phase distributes in the Al matrix in Fig. 1(a). Some black dots in Fig. 1(a) were analyzed with X-ray energy spectrum, and the results show that it consists of Al, P and O elements (see Fig. 2) which were formed during Al-25%Si casting process [18]. In SD alloy, the Si particles are irregular with sharp angles, the size distribution is non-uniform and the mean diameter is 20-30 μm.

Fig. 1 Optical micrographs of Al-45%Si alloys prepared by different processes
Figure 3 shows the SEM images of alloys after being deep-leached. The surface of primary Si in LSS alloy is smooth, the stick or flake-like eutectic Si exists on its surface. The Al matrix which was leached off fills the continuous channels of primary Si particles. By contrast, the surface of primary Si in SD alloy is rough and the Si particles are interconnected into a skeleton.
Figures 4 and 5 show the secondary electron image and area distribution maps of Al and Si elements in LSS and SD alloys. The brightness level reflects the content of the element. It can be seen from Fig. 4 that the matrix of Al-rich phase is continuous to form a network in LSS alloy, and the sphere-like Si particles with distinct interface are surrounded by the network. In Fig. 5, the Al matrix is dissevered into island by the connected Si particles, and the interface of Si particle is fuzzy.
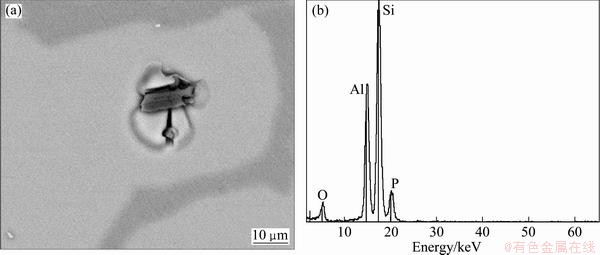
Fig. 2 SEM image (a) and EDS pattern (b) of black dots in Fig. 1(a)
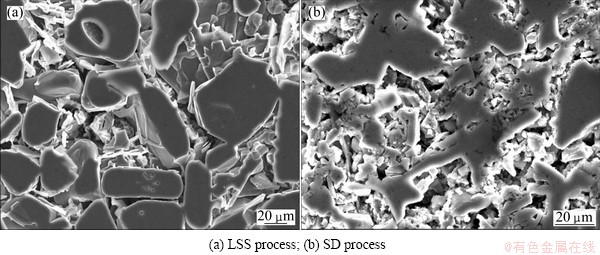
Fig. 3 SEM images of Al-45%Si alloy after being deep-leached
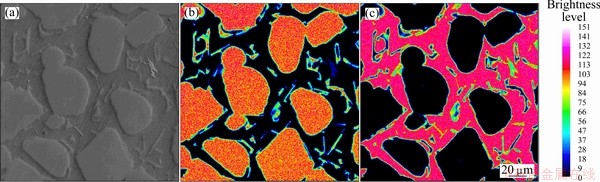
Fig. 4 Secondary electron image (a) and element area distribution of Si (b) and Al (c) in LSS alloy
According to the feature of LSS process, when Al-25%Si alloy is heated to semi-solid temperature, the eutectic phase will melt into the liquid and the primary Si phase is wrapped by the liquid. In order to reduce the interface energy, the edge of the primary Si with a larger curvature radius, which is unstable in thermodynamics, will dissolve. The dull angular of primary Si phase in Al-45%Si alloy is the result of dissolution. As the separating flowing occurs between the liquid and primary Si under the pressure, the fraction of primary Si increases with the liquid discharged-out. The remanent liquid phase in the semi-solid alloy solidifies in the narrow channel among the primary Si particles. On the basis of the inhomogeneous solidification theory of the liquid-metals, the primary Si particles supplied favorable energy and geometry conditions for the nucleation of the eutectic Si phase in the liquid. With the same crystal structure and without lattice mismatch, the eutectic Si phase would preferentially nucleate on the surface of primary Si phase with a low interface energy. Furthermore, the surface of primary Si supplied nature edge for the nucleation which promoted the epitaxial growth of the eutectic Si on the primary Si phase and suppressed the couple growth of eutectic Si and α(Al) phase. The α(Al) phase was divorced by eutectic Si and solidified among the gaps of primary Si.
3.2 Properties
The properties of Al-45%Si alloy are listed in Table 1. Comparing with the SD alloy, the hardness and strength of LSS alloy are lower. The high strength and hardness of SD alloy are attributed to the refined size of primary Si phase referring to the Hall-Petch formula [19] which described an inverse relation of the materials strength and the particles size. Figure 6 shows the fracture morphologies of the alloys. The fracture surface of Si particle in LSS alloy is smooth and some microcracks appear on it. Whereas, the fracture surface of Si particles in SD alloy are uneven and there exist some dimples in the Al matrix. The in-situ synthesized primary Si particles during the LSS and SD processes have high bond strength with the matrix, so the crack at the interface is not observed in both alloys. The source of crack was generated from the brittle fracture of primary Si particles.

Fig. 5 Secondary electron image (a) and element area distribution of Si (b) and Al (c) of SD alloy
Table 1 Properties of Al-45%Si alloy
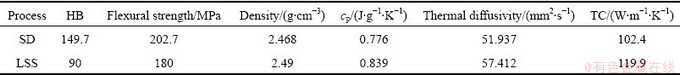
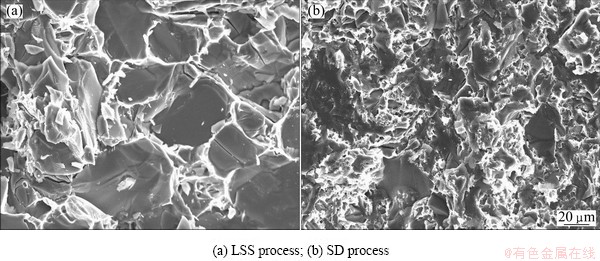
Fig. 6 Fracture morphologies of Al-45%Si alloy by different processes
Although the LSS alloy with coarse size is unbeneficial to its strength, the sphere-like primary Si particles and the continuous Al matrix would be helpful to the strength. The sphere-like particles with dull angular particles could reduce the stress concentration at the interface [20,21] and favor to alleviate the initiation and growth rates of crack induced by the stress. The results show that the probability of the low stress brittle fracture of Al-Si alloy would reduce and the fracture toughness would improve. The continuous Al matrix will enhance the successfully plastic flow in the deforming alloy, which could increase the load carrying capacity and improve the strength of the alloy [22]. However, as the effect of coarse size on the low strength was more prominent, the advantageous effects above were not reflected in this study. Some future works need to do in the LSS process to improve the strength of Al-Si alloy, including the refinement of the primary Si phase in initial Al-25%Si alloy and controlling its size without coarsening at the semi-solid temperature.
From Table 1, it can be seen that the TC of LSS alloy is higher than that of SD alloy, and two reasons were involved. One was the lower interface area in LSS alloy. The interface is often considered as the barrier of the heat transfer and would reduce the TC owing to the heat flow scattering. At the same volume fraction, the primary Si of coarse size and sphere-like shape in LSS alloy produced a lower interface area [10] than the fine and irregular Si particle in SD alloy. In addition, the continuous distribution of Al matrix also helped to reduce the interface area. Figure 7 shows the ideal structure of Si-Al composite [23], where the dispersive Si particles are surrounded by the continuous Al matrix. It was confirmed that the interface area in the structure of Fig. 7 was lower than the interface area in the structure of discontinuous Al phase by LIN et al [16]. In brief, the microstructure of coarse, sphere-like primary Si particles and continuous matrix produced a lower interface in LSS alloy which reduced the heat scattering probability and helped to get a higher thermal conductivity. The advantage of the continuous Al matrix phase to the heat flowing was another reason for the high TC in LSS alloy. In Al-Si alloy, the Al phase has high TC and takes more function to transfer the heat. When the Al phase makes up a continuous network shown in Fig. 4(c), the heat fluently flows through the network with little scattering, which increased the heat transformation efficiency and improved the thermal conductivity. The advantage of the continuous Al matrix for the high TC was contra to result of WANG et al [15] who proposed that the advantageous structure for the high TC in Si/Al composite was the continuous Si particles. More detail researches about the dependence of the continuity of constituents in Al-Si alloy on the TC need to carry out in the future work.
Figure 8 shows the measured CTE curves of Al-45%Si alloys and the CTEs at 50 °C and 100 °C calculated by the Kerner model and Turnal model [24]. The CTE of LSS alloy is lower than that of SD alloy at 60 °C, and with the temperature rising above 60 °C, it increases and is higher than that of SD alloy.
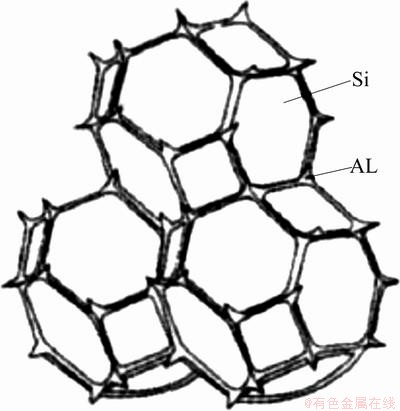
Fig. 7 Ideal structure of Si-Al composite [23]
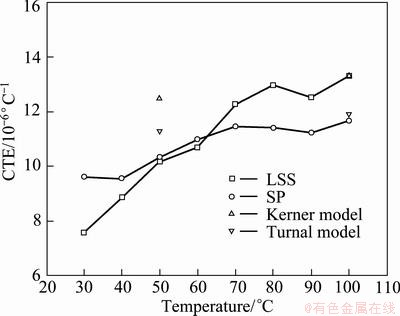
Fig. 8 CTE curve of Al-45%Si alloy
Due to the mismatch of CTE between Si phase and Al phase, the residual stress would generate in the Al-Si alloy during preparation process. The particles with dull angular in LSS alloy would induce lower stress at the interface than the irregular particle in SD alloy. The stress in the composite playing the role of adding the plastic strain of the matrix and promoting the thermal expansion had been verified [13,24]. The slight stress level in the LSS alloy resulted on the low CTE at the original temperature. With the temperature increasing, the stress relived gradually in both alloys, meanwhile the Si phase with a low CTE of 4.1×10-6 °C-1 would restrict the expansion deformation of Al phase which has a high CTE of 23.2×10-6 °C-1. As the Al phase was surrounded by the connected Si phase, the restriction effect could enhance, leading to a less CTE in SD alloy. While in the LSS alloy, the restrict effect could be weakened by the dispersive Si phase, the restriction was little or did fats())LEMAN y demonstrated in not occur even [13,14] as the Al phase composed the continuous matrix. As a result, the CTE of LSS alloy increased with a greater rate and was higher than that of SD alloy over 60 °C.
In Fig. 8, the CTEs of both alloys at 50 °C are near to Turner’s model, while at 100 °C, the CTE of LSS alloy is agreed with the Kerner’s model. In the Kerner’s model, it is assumed that the reinforcement is spherical and wetted by a uniform layer of matrix; thus the CTE of the composite is identical to that of a volume element composed of a spherical reinforcement particles surrounded by a shell of matrix. The structure of LSS alloy is consistent with Kerner’s assumption, so it is feasible to predict the CTE of LSS alloy with Kerner model at 100 °C, here the stress relived completely. The Turner model considered that the internal stress system in a mixture is not sufficient to disrupt the composite, and the sum of internal forces will be equal to zero. Moreover, the dimension of the components is constrained by each other and changes with the same rate. Without the effect of residual stress, the CTE of composite with continuous reinforcement has good agreement with Turner model by ELOMARI [24] and NAM [25], here the CTE of SD alloy is also concordant with the Turner model.
4 Conclusions
1) The primary Si phase in LSS alloy is sphere-like with size of 40-50 μm and well distributes in the continuous Al matrix. The eutectic Si phase grows on the surface of the primary Si phase because of the epitaxial growth. In SD alloy, the Si particles are irregular with size of 20-30 μm and interconnect to a continuous skeleton which isolates the Al matrix phase.
2) The SD alloy with fine Si particles has higher hardness and strength than LSS alloy, but its TC is lower and CTE at room temperature is higher than those of LSS alloy. The high TC in LSS alloy is related to microstructure features of the Si particle with sphere- like shape, coarse size and the continuous Al matrix. In additional, the sphere-like Si phase is favorable to the low CTE.
3) The increasing rate of CTE in the SD alloy with temperature is lower than that in the LSS alloy. The reason of lower rate is that continuous Si particles in SD alloy will impose much more restriction effect on the Al matrix and help to reduce the CTE.
4) The CTEs of the alloys have different agreement with the Kerner’s model and Turnal’s model according to the different microstructure characteristics. At the temperature of 50 °C, the CTEs of both alloys are near to Turnal’s model, but at 100 °C, the CTE of LSS alloy agrees with the Kerner’s model without the effect of the stress.
References
[1] ZWEBEN C. Advances in composites materials for thermal management in electronic packaging [J]. JOM, 1998, 50(6): 47-51.
[2] CHEN Y Y, CHUNG D D L. Silicon-aluminum network composites fabrication by liquid metal infiltration [J]. Journal of Materials Science, 1994, 29(3): 6069-6075.
[3] JACOBSON D M. Spray-formed silicon-aluminum [J]. Advanced Materials Process, 2006, 157(3): 36-39.
[4] YANG Pei-yong, ZHENG Zi-qiao, CAI Yang, LI Shi-chen, FENG Xi. PM process of Si-Al electronic packaging materials [J]. Chinese Journal of Rare Metals, 2004, 28(1): 160-165.
[5] HOGG S C, LAMBOURNE A, OGILVY A. Microstructural characterization of spray formed Si-30Al for thermal management applications [J]. Scripta Materialia, 2006, 55(1): 111-114.
[6] CHIEN C W, LEE S L, LIN J C. Effects of SiP size and volume fraction on properties of Al/Sip composites [J]. Materials Letters, 2002, 52(4-5): 334-341.
[7] PARK C S, KIM C H, KIM M H. The effects of particle size and volume fraction of the reinforced phases on the linear thermal expansion in the Al-Si-SiCp system [J]. Materials Chemistry and Physics, 2004, 88(1): 46-52.
[8] YAN Yi-wu, GENG Lin. Effects of particle size on the thermal expansion behavior of SiCp/Al composites [J]. Journal of Material Science, 2007, 42(15): 6433-6438.
[9] ZHANG Jian-yun, WANG Yin, CUI Xia, ZHOU Xian-liang. Numerical simulation of thermal conductivity of SiCp/Al composites [J]. Transactions of Materials and Heat Treatment, 2010, 31(8): 146-150. (in Chinese)
[10] TAKEI T, HATTA H. Thermal expansion behavior of particulate-filled composites I: Single reinforced phase [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 1991, 131(1): 133-143.
[11] TAKEI T, HATTA H. Thermal expansion behavior of particulate-filled composites II: Multi-reinforcing phase (hybrid composites) [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 1991, 131(1): 145-152.
[12] ZHANG Wei, YANG Fu-liang, GAN Wei-ping. Study on thermal expansion property of high-silicon aluminum alloy for electronic packaging [J]. Materials Review, 2006, 20(6): 348-350.
[13] SHEN Y L, NEEDLEMAN A. Thermal expansion of metal-ceramic composites: A three-dimensional analysis [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 1998, 252(2): 269-275.
[14] SHEN Y L, NEEDLEMAN A. Coefficient of thermal expansion of metal-matrix composites for electronic packaging [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 1994, 25(4): 839-850.
[15] WANG Xiao-feng, WU Gao-hui, WANG Ri-chu. Fabrication and properties of Al-Si interpenetration phase composites for electronic packaging [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2007, 17(s1): s1039-s1042.
[16] LIN Jun-pin, ZHANG Yong, CHEN Guo-liang. Microstructure and properties of Skeleton reinforced composite [J]. Journal of Materials Engineering, 2000, 6: 20-21. (in Chinese)
[17] GRANT P S. Spray forming [J]. Progress in Materials Science, 1995, 39(4-5): 497-545.
[18] ZHANG Qian, LIU Xiang-fa, DAI Hong-shang. Re-formation of AlP compound in Al-Si melt [J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2009, 480(2): 376-381.
[19] CLYNE T W,WITHERS P J. A introduction to metal matrix composites [M]. YU Yong-ning, FANG Zhi-gang, trans. Beijing: Metallurgical Industry Press, 1996: 11.
[20] QIN Shu-yi, ZHANG Guo-ding. Method and mechanisms to improved ductility and toughness of particle reinforced metal matrix composites [J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2000, 10(5): 621-629. (in Chinese)
[21] XU Fei, LI Yu-long, GUO Wei-guo. Influences of particle shape, volume fraction and matrix materials on the compressive behavior of MMCs [J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica, 2003, 20(6): 36-41. (in Chinese)
[22] JIA Cheng-chang, GUO Hong. Composites course [M]. Beijing: Higher Education Press, 2010: 11. (in Chinese)
[23] LIN Feng, FENG Xi, LI Shi-chen. Research on high performance novel electronic packaging materials of silicon-based aluminum [J]. Materials Review, 2006, 20(3): 107-111. (in Chinese)
[24] ELOMARI S. Thermal expansion behavior of particulate metal-matrix composites [J]. Composites Science and Technology, 1998, 58(3): 369-376.
[25] NAM T H, REQUENA G, DEGISCHER P. Thermal expansion behavior of aluminum matrix composites with densely packed SiC particles [J]. Composites: Part A, 2008, 39(5): 856-865.
李艳霞 1,2,刘俊友1,王文韶1,刘国权1
1. 北京科技大学 材料科学与工程学院,北京 100083;
2. 北华航天工业学院 材料系,廊坊 065000
摘 要:对液固分离法(LSS)和喷射沉积法(SD)制备的Al-45%Si合金组织和性能进行研究。结果表明,两种方法制备的合金中初生Si相具有不同的尺寸、形态和分布,从而对合金性能产生不同的影响。采用喷射沉积法制备的合金中硅相形状不规则,尺寸细小并在空间连续分布。液固分离法制备的合金中硅相形态呈近球形,尺寸较大并被连续的铝基体包覆。与喷射沉积合金相比,液固分离制备合金具有更高的热导率和更低的低温热膨胀系数,但由于硅颗粒尺寸较大,力学性能低于喷射沉积合金。硅相的分布形式对热膨胀系数的增加速率影响显著,其中喷射沉积法制备的合金中硅相连续分布有利于获得低的增加速率。由于组织特征的不同,液固分离制备合金的热膨胀系数预测模型与喷射沉积制备的合金有区别。
关键词:铝硅合金;Si 颗粒;液固分离;喷射沉积;热导率;热膨胀系数
(Edited by Xiang-qun LI)
Corresponding author: Jun-you LIU; Tel: +86-10-62334314; E-mail: ljy158@163.com
DOI: 10.1016/S1003-6326(13)62554-6

