DOI:10.11817/j.ysxb.1004.0609.2021-42010
湘南香花岭锡矿田碎屑岩中似层状锡多金属矿体铟富集特征及成因
郑 旭1,2, 刘建平1,2※, 陈卫康1,2, 邵拥军1,2, 田旭峰3, 文一卓3, 刘少青1,2, 丁 涛1,2
(1.有色金属成矿预测与地质环境监测教育部重点实验室(中南大学),湖南 长沙,410083;
2.中南大学地球科学与信息物理学院,湖南 长沙,410083;
3.湖南省湘南地质勘察院,湖南 郴州,423000)
摘 要:湘南香花岭矿田是华南地区典型的岩浆热液型铟富集成矿区,新勘探的似层状锡矿体是矿田内重要的锡矿化类型,也是南岭地区较为独特的锡矿化类型,对该类矿体中的铟的分布规律和富集机制缺乏系统研究。为揭示矿田内似层状锡多金属矿体中的铟富集特征及成因,在矿床野外地质调查及样品采集基础上,采用光学显微镜、等离子体光谱仪、电子探针等技术手段,开展了矿物组成显微鉴定、矿石化学成分分析、矿物微区成分分析等研究。研究显示碎屑岩发育两类似层状锡矿体:三合圩式以泥质碎屑岩为容岩的锡多金属矿体和泡金山式以石英砂岩为容岩的锡矿体。矿石化学分析显示三合圩式矿体In含量12.94 μg/g~70.80 μg/g,Zn含量0.61%~2.62%,Sn含量0.13%~0.86%,为富铟的锡多金属矿体;泡金山式矿体In含量为0.04 μg/g~1.06 μg/g,Sn含量为Sn含量为0.06 %~1.87 %,为贫铟的锡矿体。矿物研究显示载铟矿物有闪锌矿和黝锡矿,尤以闪锌矿最为重要。三合圩式矿体中的闪锌矿In含量最高0.15%,泡金山式矿体中为最高0.19%,闪锌矿中元素替代关系为:In2++Cd2+ 2Cu2+。黝锡矿在三合圩式矿体中含In 0.25%,而泡金山式低于检测限,黝锡矿中元素替代关系为:In2++Zn2+
2Cu2+。黝锡矿在三合圩式矿体中含In 0.25%,而泡金山式低于检测限,黝锡矿中元素替代关系为:In2++Zn2+ Cu2++Sn2+。综合矿床地质特征及铟富集研究,认为碎屑岩中似层状矿体成因与岩浆热液关系密切,两类矿体铟富集差异明显受成矿地质环境和成矿作用控制,在泥质砂岩中以交代为主的成矿作用形成了富铟的锡多金属矿体,而在石英砂岩中以充填为主的成矿作用则形成了贫铟的锡矿体。
Cu2++Sn2+。综合矿床地质特征及铟富集研究,认为碎屑岩中似层状矿体成因与岩浆热液关系密切,两类矿体铟富集差异明显受成矿地质环境和成矿作用控制,在泥质砂岩中以交代为主的成矿作用形成了富铟的锡多金属矿体,而在石英砂岩中以充填为主的成矿作用则形成了贫铟的锡矿体。
关键词:铟富集;矿物化学;成因;碎屑岩中似层状锡多金属矿体;香花岭;湘南
文章编号:1004-0609(2019)-11-2627-10 中图分类号:P618.82 文献标志码:A
铟在地壳中是一种低丰度的分散元素[1],独立矿物种类少且分布少,常以类质同象替代形式存在于闪锌矿、黝锡矿、黄铜矿等硫化物中[2]。铟矿产资源无独立矿床,常作为锡矿床、铅锌矿床和铜矿床的伴生组分在选冶过程中回收[3]。作为高科技领域如太阳能电池板和液晶显示器的关键性原料,其资源需求量逐渐强劲[4]。鉴于铟在未来科技领域的重要性和资源的稀缺性,已被多国政府和组织列为关键金属矿产[5]。铟资源的分布规律和形成机制已成为当前矿床学研究热点[6]。
华南地区是全球最大锡矿富集区,同时也是最大的铟富集区[7-8]。著名的广西大厂[9-10]、云南个旧[11]、都龙[12]、白牛厂[13]、湖南香花岭[14]和柿竹园[15]等大型-超大型锡矿床伴生大量的铟资源,尤其以广西大厂、云南都龙等矿床研究较为深入[13-14],而南岭中段湘南地区铟富集研究关注较少。湘南地区是典型的岩浆热液成矿区,其矿化类型多样,是解剖岩浆热液成矿过程铟富集作用的理想地区,笔者前期研究显示湘南地区的斑岩型、矽卡岩型和热液脉型锡多金属矿床均不同程度富集铟资源[14-15]。随着勘探的深入,一种新的锡矿化类型——碎屑岩中似层状锡矿在湘南地区被识别,这种类型在香花岭矿田和荷花坪矿田中广泛分布[16-17],成为近年区内锡储量增长最快的矿化类型。该类型锡矿化呈层状赋存于中泥盆统跳马涧组砂岩、泥岩中,与斑岩、矽卡岩和热液脉型锡矿化显著的差异是矿石中贫硫化物。在作者研究中发现该类型也富集一定程度的铟,成为区内新的富铟矿体。本文以香花岭矿田为例,基于碎屑岩中似层状锡矿体野外调查基础上,详细了开展矿相学、矿石化学及富铟矿物的电子探针研究,最后探讨了铟在该类矿体的富集规律和形成机制。
1 地质背景
1.1 湘南区域地质
湘南地区处于东西向南岭成矿带与北东向钦杭成矿带交汇部位,独特的大地构造环境使湘南成为华南地区著名的钨锡铅锌多金属矿集区[18]。区内出露最老地层为南华系-寒武系浅变质碎屑岩,不整合覆盖其上的为中泥盆统-下三叠统滨海相-浅海相碳酸盐岩和碎屑岩,之后为上三叠统至中侏罗统湖盆相碎屑岩及煤系地层,下白垩统-第四系陆相碎屑岩及沉积物[19]。区内构造以北东向郴州-临武深大断裂带为界,北西为桂阳-宁远坳陷区类侏罗山式褶皱带,南东为隆起区隔槽式褶皱带[20]。区内中酸性岩浆岩广泛发育,除少量晚三叠世花岗岩外,大量为中晚侏罗世花岗岩岩基、岩株及岩脉,代表性岩体有骑田岭、王仙岭、千里山、癞子岭等[21]。围绕中晚侏罗世花岗岩岩体及岩脉发育强烈的稀有金属、有色金属矿床,形成了著名的柿竹园、瑶岗仙、香花岭、新田岭、芙蓉、宝山-黄沙坪、白云仙等大型-超大型钨锡铅锌多金属矿田(床)[22]。
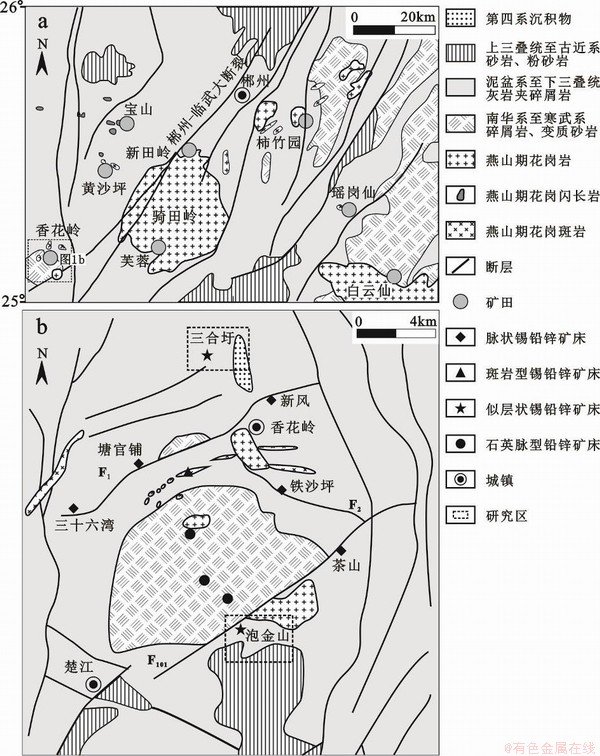
图1 (a)湘南区域地质矿产简图[22]和(b)香花岭矿田地质简图[23]
Fig. 1 (a) Simplified geological and mineral map of Southern Hunan[22] and (b) simplified geological map of the Xianghualing ore field[23]
1.2 香花岭矿田地质
香花岭矿田位于湘南矿集区的西南段(图1a),矿田内出露最老地层为寒武系,岩性为变质砂岩及板岩等浅变质岩,分布于香花岭背斜的核部(图1b)。不整合覆盖在寒武系之上的地层为泥盆系至三叠系,为滨海相-浅海相碎屑岩和碳酸盐岩。三叠纪之后沉积的下侏罗统的陆相碎屑岩及新生界沉积层[24]。构造上整体处于短轴背斜和北东南断裂控制,主要断裂为北东向F1和F101断层,以及北西向F2断层[25]。矿田内岩浆岩发育,地表出露了三个相对较大的花岗岩岩株,分别为北部的癞子岭岩体、通天庙岩体和南部的尖峰岭岩体,围绕这些岩体,发育众多的岩脉,尤其以癞子岭岩体周缘岩脉发育,如花岗斑岩、细晶岩脉。花岗岩岩石学及地球化学研究显示这些岩体为高分异花岗岩[26],其形成时代集中在165-150 Ma[27]。
围绕花岗岩岩株及岩脉,矿田内发育完善的岩浆热液成矿系统,根据矿体产状、元素组合及控制因素,可分为6类:①与花岗岩顶部和细晶岩脉内的Nb、Ta矿化;②花岗岩体与灰岩接触带的矽卡岩型W、Be矿化;③岩体周缘浅变质岩中的石英脉型W、Sn矿化;④岩体周缘断裂带的脉状Sn、Pb、Zn矿化;⑤花岗斑岩中Sn、Pb、Zn矿化;⑥产于碎屑岩中的似层状Sn矿化。其中后三者是区内主要的锡矿化类型,第6类即本文研究对象,是最近新发现的具有重要意义的锡矿体。前人对该区成矿年龄进行了测点,获得了主要年龄为160-150 Ma[28-29],与成岩时代一致,为南岭地区第二阶段成矿大爆发事件的产物[30]。
2 碎屑岩中似层状锡矿体特征
香花岭矿田内似层状矿体产于中泥盆统跳马涧组碎屑岩中,在矿田内分布广泛[31]。据前人资料和笔者的调查,该类矿体集中分布在北部癞子岭、三合圩隐伏岩体周围和南部尖峰岭岩体的周围,勘探工程已揭露的矿体主要分布于三合圩矿床[32-33]、长冲矿床[34-35]、塘官铺矿床、铁砂坪矿床[26,36]、泡金山矿床[16,37]。该类矿体包含两种矿化样式:①以泥质碎屑岩为容岩的层状矽卡岩型矿体,以三合圩矿床最为典型,称为三合圩式;②以石英砂岩为容岩的网脉型矿体,以泡金山矿床最为典型,称为泡金山式。下面分别以三合圩矿床和泡金山矿床为例简述似层状锡矿体的特征。
2.1 三合圩似层状锡矿体
位于香花岭北部的三合圩矿床为香花岭背斜的北倾伏端[32],出露地层为跳马涧组砂岩、棋梓桥组碳酸盐岩和第四系河流沉积物、残坡积物,其中跳马涧组是主要含锡矿层位,为跳马涧组中段,包含两个岩层:第一层为紫红色砂岩夹少量灰白色石英砂岩及含豆状赤铁矿砂岩,第二层为白色中厚-厚层状石英砂岩及杂色砂岩、页岩层[33]。含矿层主要赋存于第一层中。矿区断层构造发育,主要为北东向(图2a),地表未出露岩浆岩,钻探工程揭露地下400 m以下深部发育隐伏花岗岩体(图2b)。矿区地表发育铁帽,在跳马涧组中段第一层紫红色砂岩中发育锡多金属矿体。经勘查工程揭露矿化范围南北1 km和东西1 km,层位中断续矿化厚度超过200 m,目前圈出4层工业矿体,矿体产状与地层产状一致,倾向北东,倾角10° ~ 25°,矿石为斑杂状锡石闪锌矿矿石,Sn品位0.231%[38]。
2.2 泡金山似层状锡矿体
泡金山矿床位于尖峰岭花岗岩体西侧,出露地层为寒武系浅变质岩、中泥盆统跳马涧组碎屑岩、棋梓桥组碳酸盐岩及第四系。矿田尺度的北西走向F101断裂带通过矿区,F101及其三条次级断裂(F101-1、F101-2、F101-3)成为脉状矿体的容矿断裂[16]。新发现的似层状锡矿体整体处于F101-3断层上盘,赋存于跳马涧组石英砂岩及泥质砂岩中。该类矿体可以分为两种矿化:①发育在石英砂岩中裂隙的网脉状锡矿化;②泥质砂岩中矽卡岩型锡矿化。矿体产状与岩层一致,倾向南西,沿走向均长约200 m,目前控制两个矿体,充填型矿体规模较大,平均厚度2.73 m,矽卡岩型矿体较薄,平均厚度仅0.88 m,矿体以第一种矿化为主[16]。矿石类型根据矿化不同可以分为网脉状石英砂岩型锡矿石和矽卡岩型锡矿石,矿石平均Sn品位多在1.06%。
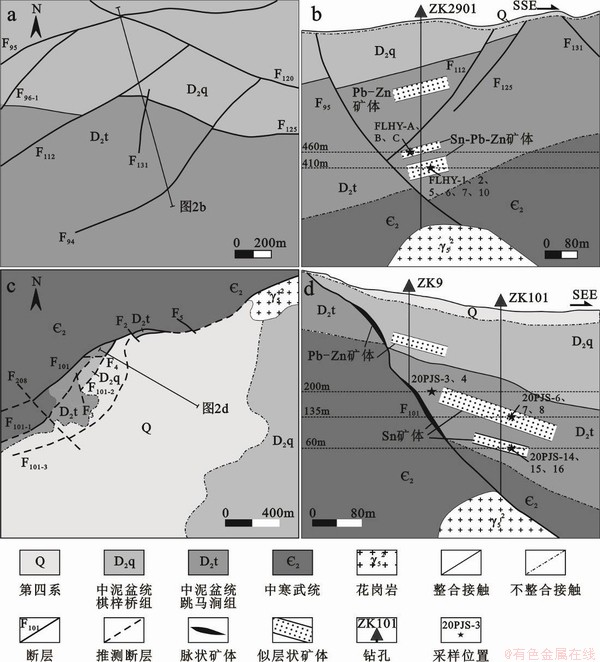
图2 (a) 三合圩矿床地质平面图[32]和(b) 29线剖面地质图[32]、(c) 泡金山矿床地质平面图[16]和(d) 1线剖面地质图[16]
Fig. 2 Geological map[32] (a) and cross section of line 29[32] (b) of the Sanhexu deposit; geological map[16] (c) and cross section of line 1[16] (d) of the Paojinshan deposit
3 采样及分析方法
3.1 采样位置
在香花岭矿田野外地质调查基础上,重点对三合圩似层状矿体和泡金山似层状矿体开展了探采工程野外调查和采样,共采集了总共17样矿石样品,进行了矿石化学分析,并对典型的矿石样品进行了光片和探针片制片,用于显微观察和电子探针分析。样品具体采样位置及矿石特征见表1和图2。
3.2 显微鉴定
对矿石样品典型位置进行岩石切片,磨制探针片。在光学显微镜下进行详细的矿相学观察,鉴定矿石的矿物组成,对矿石结构和构造进行观察,为厘定成矿期次提供详实的资料。矿石显微观察在在有色金属成矿预测与地质环境监测教育部重点实验室完成。
3.3 化学分析
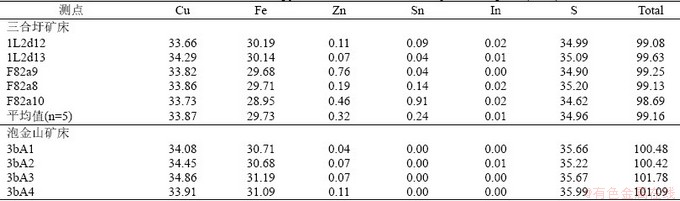
典型矿石成矿元素分析首先经过破碎、研磨等后获得<200目的粉末,对样品参考锡矿石、铜矿石、铅矿石和锌矿石化学分析方法等国家相关标准及要求在湖南省地质调查院测试中心完成,其检测限为Sn、As、WO3为0.05 wt%,Cu、Sb为0.03 wt%、Bi为0.02 wt%,Pb、Zn、Cd为0.01 wt%,In、Ga、Ag为10 μg/g。为统计及分析的方便在结果列出时统一了部分单位。
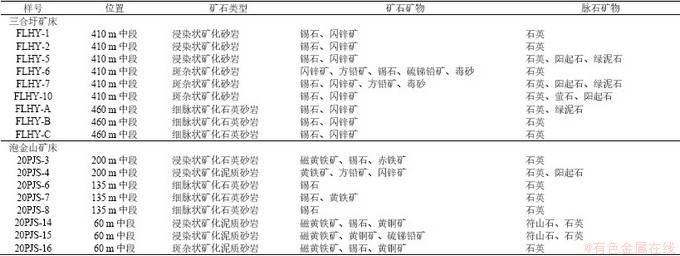
表1 三合圩和泡金山矿床似层状锡矿体样品采样位置及矿石特征
Table 1 Sampling location, ore characteristics of stratoid tin orebody in the Sanhexu and Paojinshan deposit.
3.4 电子探针分析
对典型显微视域中的矿物进行电子显微观察、能谱和波谱定性,对不同产状的可能的富铟硫化物(闪锌矿、黝锡矿、黄铜矿)进行了波谱的点定量分析和波谱的X射线面扫描。电子探针分析在有色金属成矿预测与地质环境监测教育部重点实验室完成。仪器型号为Shimadzu EPMA-1720H,点定量分析条件:加速电压15 KV,电流60 nA,束斑为1 μm。元素特征X射线选择:S(Kα)、Mn(Kα)、Fe(Kα)、Cu(Kα)、Zn(Kα)、Cd(Lα)、In(Lα)、Sn(Mα)、Pb(Mα);元素选用标样:黄铁矿(S、Fe)、金属锰(Mn)、黄铜矿(Cu)、闪锌矿(Zn)、硫化镉(Cd)、锑化铟(In)、硫化锡(Sn)、方铅矿(Pb),数据处理采用仪器自带数据处理软件,校正方法采用ZAF法。
4 结果
4.1 矿石矿物组成及成矿期次
4.1.1 三合圩锡矿体
(1) 矿石矿物组成
经过矿物显微观察及能谱鉴定,三合圩似层状锡矿体矿石含有的金属矿物包括磁铁矿、锡石、毒砂、磁黄铁矿、黄铁矿、白铁矿、闪锌矿、黄铜矿、黝锡矿、方铅矿、硫锑铅矿、赤铁矿等(图3和图4);非金属矿物包括阳起石、绿泥石、石英、萤石、菱铁矿等。其中锡石:呈细脉状充填在石英砂岩中(图3b),也可在矽卡岩化矿石中呈它形粒状充填在针柱状阳起石粒间(图4a),可被黝锡矿交代(3e),粒径几十微米至几百微米,大小不一,赋存在矽卡岩化砂岩和细脉状石英砂岩中。闪锌矿:多存在于矽卡岩化矿石中,与石英、萤石、黄铁矿、磁黄铁矿等共生,可分为两个世代:闪锌矿Ⅰ和闪锌矿Ⅱ。闪锌矿Ⅰ内部发育乳滴状黄铜矿,按结构可分为Ⅰa、Ⅰb、Ⅰc3个亚类,闪锌矿Ⅰa被叶片状磁黄铁矿交代(图3d),或呈它形充填在阳起石(图4a)、黄铁矿及白铁矿粒间(图4b)、与萤石共生(图4c);闪锌矿Ⅰb及闪锌矿Ⅰc可交代磁黄铁矿,局部呈它形充填在磁黄铁矿粒间,其中闪锌矿Ⅰc晚期受方铅矿交代形成残余结构(图4e)。闪锌矿Ⅱ局部出溶黄铜矿,并被黝锡矿所交代,按结构分为Ⅱa、Ⅱb。闪锌矿Ⅱa受黝锡矿沿解理交代、边部出溶蠕虫状黄铜矿,黝锡矿旁出溶定向叶片状黄铜矿(图4f);闪锌矿Ⅱb受黝锡矿交代形成残余结构(图4g)。黝锡矿:主要呈它形,粒径不等,有交代结构和充填结构。交代它形锡石呈镶边结构,或充填在毒砂闪锌矿粒间(图4g)。可将黝锡矿分成三种类型,Stn-a类为被黄铜矿交代的形成镶边结构的黝锡矿,如图4i所示;Stn-b类为充填闪锌矿粒间并初步交代闪锌矿的黝锡矿,如图4h所示;Stn-c类为充填在毒砂粒间并充分交代闪锌矿的黝锡矿,如图4g。黄铜矿:主要呈它形,闪锌矿 内的黄铜矿出溶体可呈乳滴状、蠕虫状、叶片状,其常交代磁黄铁矿、黝锡矿。

图3 三合圩典型矿石及矿物显微照片
Fig. 3 Photographs of typical ores and micrographs of minerals of the Sanhexu deposit.
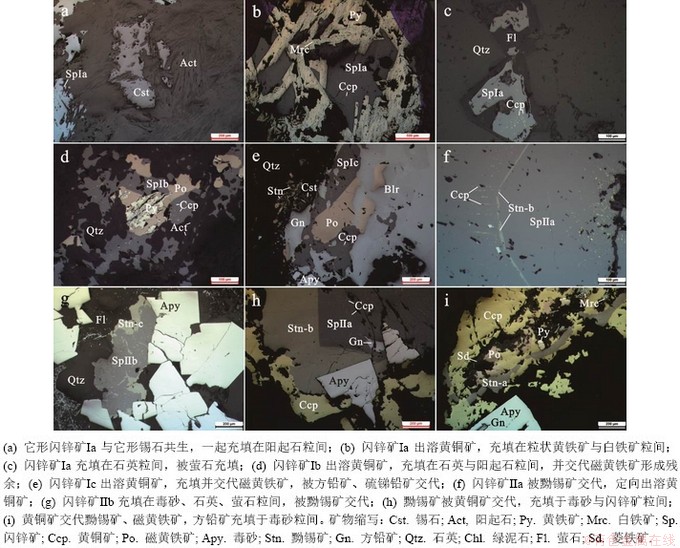
图4 三合圩富铟矿物显微照片
Fig. 4 Micrographs of indium-rich minerals of the Sanhexu deposit.
(2) 成矿期次
结合前人研究成果、矿石结构构造和矿物共生组合,认为三合圩矿床似层状矿体为热液成矿作用的产物,经历了两期五阶段成矿过程:矽卡岩期包含①湿矽卡岩阶段,主要形成阳起石等;②氧化物阶段,主要形成锡石、石英、萤石等;热液期包含③锡石硫化物阶段,形成锡石、毒砂、黄铁矿;④铜铅锌硫化物阶段,形成磁黄铁矿、黄铜矿、第一世代闪锌矿、黝锡矿、方铅矿;⑤碳酸盐-铅锌硫化物阶段,形成第二世代闪锌矿、硫锑铅矿、菱铁矿、方解石和铁白云石等碳酸盐矿物。
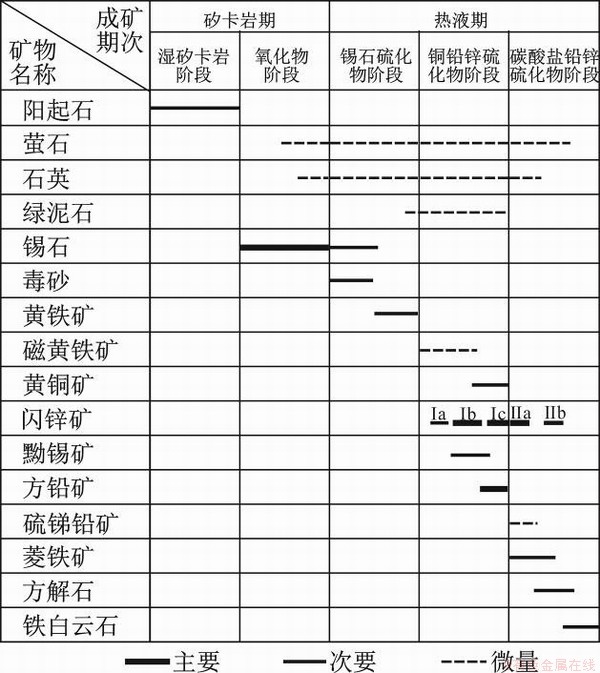
图5 三合圩矿床矿物生成顺序表
Fig. 5 Paragenetic sequences of minerals of the Sanhexu deposit
4.1.2 泡金山锡矿体
(1) 矿石矿物组成
泡金山矿床金属矿物包含锡石、毒砂、磁黄铁矿、黄铁矿、白铁矿、闪锌矿、黄铜矿、黝锡矿、方铅矿、赤铁矿等;非金属矿物有符山石、阳起石、绿泥石、石英、萤石等。其中锡石主要分布在细脉状充填矿石(图6b),矿物形态主要呈它形粒状,粒径几十微米至数百微米,可见包含细粒黄铁矿(图6d),被黝锡矿交代形成残余结构(图6e)。闪锌矿:主要集中在浸染状矽卡岩化矿石中,充填在粗粒黄铁矿粒间,与方铅矿共生(图6i)。黝锡矿:主要集中在矽卡岩化矿石中,主要呈它形,部分可呈半自形(图6e),粒径差异大,主要为交代结构。可交代锡石(图6e),被磁黄铁矿(图6f)、黄铜矿交代(图6g)形成残余结构。黄铜矿:主要集中在矽卡岩化矿石中,形态呈它形,交代黝锡矿、磁黄铁矿构成镶边结构或残余结构(图6e、图6g、图6h)。
(2) 成矿期次
结合前人研究成果、矿石结构构造和矿物共生组合,认为泡金山锡多金属矿床中似层状矿体同三合圩锡多金属矿床类似,也为热液成因,将其成矿期次划分为两期与六阶段。分别为:矽卡岩成矿期包含①干矽卡岩阶段,主要形成符山石;②湿矽卡岩阶段,主要形成阳起石等;③氧化物阶段,主要形成磁铁矿、锡石、石英、萤石等;热液成矿期包含④锡石硫化物阶段,形成锡石、毒砂、黄铁矿;⑤铜铅锌铟硫化物阶段,形成绿泥石、闪锌矿、黝锡矿、磁黄铁矿、方铅矿;⑥碳酸盐铅锌硫化物阶段,形成菱铁矿、方解石和铁白云石等碳酸盐矿物。

图6 泡金山典型矿石及矿物显微照片
Fig. 6 Photographs of typical ores and micrographs of minerals of the Sanhexu deposit.
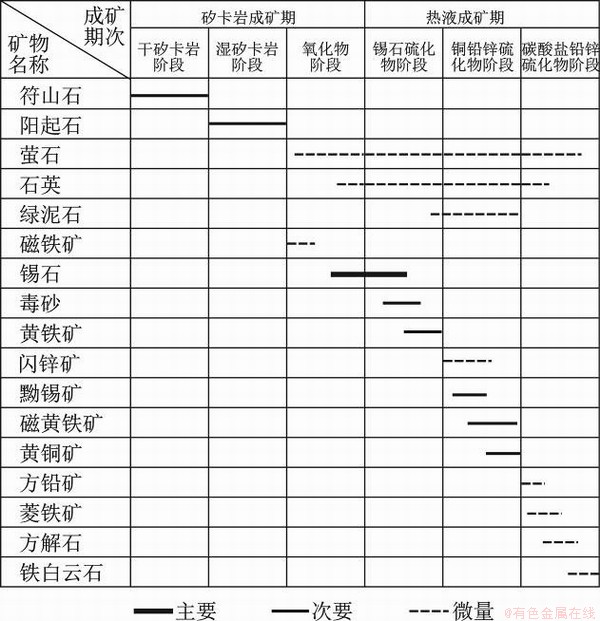
图7 泡金山矿床矿物生成顺序表
Fig. 7 Paragenetic sequences of minerals of the Sanhexu deposit
4.2 矿石化学
三合圩矿床9件和泡金山矿床6件矿石样品化学元素分析结果见表2。结果显示三合圩矿床矽卡岩化锡铅锌矿石含Sn 0.13%~0.86%,In 12.94 μg/g~70.80 μg/g,Pb 124.17 μg/g~4122.95 μg/g,Zn 0.61%~2.62%,Sn、Zn、Pb不均匀分布,伴生Sb、In、Cd,为锡铅锌矿体;细脉状矿化石英砂岩近少数伴生锌矿化,铟、锡含量很低;泡金山矿床细脉状矿化石英砂岩中的为Sn含量为0.06%~1.87%,Cu、Pb、Zn含量很低,In含量非常低0.04 μg/g ~1.06 μg/g,为单一的锡矿体;矽卡岩化矿石中Sn含量为16 μg/g~15490 μg/g,Cu含量0.02%~0.22%,Pb、Zn含量均很低,为锡铜矿体。
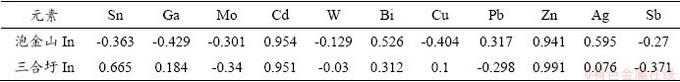
对两矿床成矿元素进行In元素的相关性分析,结果见表3。结果显示泡金山矿床中In与Zn、Cd呈强的正相关关系,相关系数可达0.9以上,In与Ag呈正相关关系,与Sn、Ga、Mo、Cu呈弱的负相关关系。三合圩矿床矿石中In与Zn、Cd同样呈强相关关系,可达0.95以上,In与Sn、Bi呈弱的正相关关系。
表2 三合圩和泡金山矿床矿石元素分析结果(μg/g)
Table 2 Bulk chemical composition of ores from the Sanhexu and Paojinshan deposit(μg/g)
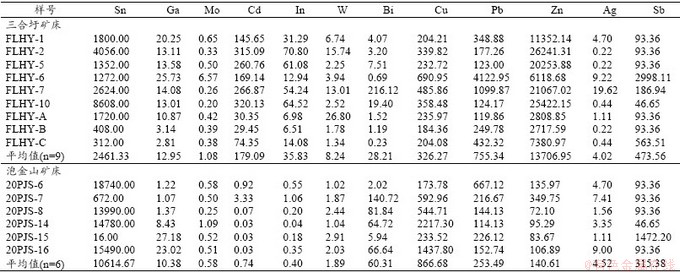
表3 泡金山及三合圩矿床In与其他元素相关系数表
Table 3 Correlation coefficient between indium with other elements of the Sanhexu and Paojinshan deposit.
根据相关性分析结果,对矿石中In元素进行相关元素图解,结果显示三合圩矿床的矿石中,In与Cd成矿呈显著正相关,Cd/In比值介于1~10之间,而泡金山矿床的矿石中In、Cd线性相关性弱于三合圩矿床的矿石,In/Cd比值集中于0.1~10(图8a);两矿床中In、Zn呈显著的线性相关,Zn/In比值介于102~103之间,表明在似层状矿体中In是伴生Zn成矿的(图8b);三合圩矿床Bi/In比值主要集中在10-2~1之间,In、Bi呈显著正相关,泡金山矿床Bi/In比值集中在102~103,In、Bi相关性不明显(图8c);三合圩矿床中Sn/In比值集中于10~102之间,具有显著的正相关性,但弱于In、Zn之间的相关性,而泡金山矿床中Sn/In比值集中于103~105,相关性不明显(图8d);三合圩矿床中Cu/In比值集中于1~102之间,具有弱相关性,而泡金山矿床中Cu/In比值集中于102~104,相关性不明显(图8e);三合圩矿床Ag/In比值介于10-2~1之间,相关性不明显,泡金山矿床Ag/In比值介于1~10之间,In与Ag呈现正相关(图8f)。
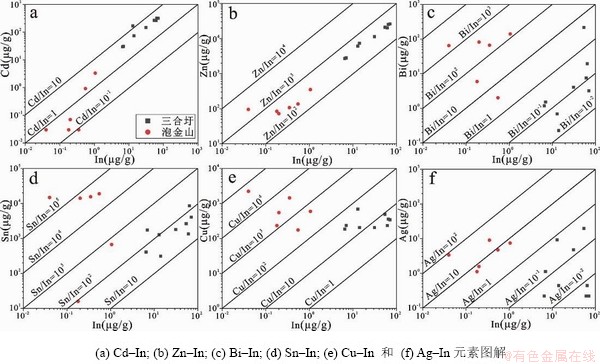
图8 三合圩和泡金山矿床矿石元素二元图解
Fig. 8 Binary plots of elements of ores from the Sanhexu and Paojinshan deposit.
4.3 矿物化学
4.3.1 闪锌矿
两矿床闪锌矿电子探针分析共获得45组数据,其结果见表4。三合圩矿床矿体中的闪锌矿除含Zn、S外还有杂质元素Sn、Mn、Fe、In、Cd、Cu。
闪锌矿Ⅰa中Fe、In、Mn、Zn变化大,Fe 8.26%~12.57%,平均值为10.69%,In 0.06%~0.13%,平均值为0.11%,Mn 0.06%~0.29%,平均值为0.16%,Zn 51.37%~55.49%,平均值为53.45%。闪锌矿Ⅰb中Zn变化比较大,Zn 52.83%~55.86%,平均值为53.59%,Fe、Mn含量较其他闪锌矿最高,分别为11.19%和0.26%,In 0.08~0.15%,平均值为0.11%。闪锌矿Ⅰc中Zn含量较其他闪锌矿是最低的,平均值为52.68%,而Cd含量是闪锌矿中最高的,平均值达1.98%,In 0.05~0.13%,平均值为0.09%。闪锌矿Ⅰ形成时In、Fe含量逐渐降低,Zn含量逐渐增高。
闪锌矿Ⅱa中In的含量变化较大(图9),低于检测限至0.13%,平均值0.05%,显著小于闪锌矿Ⅰ中In含量,同时Cd的含量进一步降低,平均值为0.44%,而Sn含量平均值0.11%,Cu含量平均值0.18%,均显著高于闪锌矿Ⅰ。同时Cd、Zn元素的分布较为均匀,In、Cu、Fe元素分布不均匀,Cu含量高的部分,In含量相对偏低,Cu元素集中在边缘部分,而In元素主要集中在闪锌矿Ⅱa内部,在闪锌矿Ⅱa与黝锡矿接触的边缘部分,In含量明显低于黝锡矿(图10e)。闪锌矿Ⅱb中In含量基本低于检测限,Cd含量进一步降低,平均值仅为0.26%,同时Cu、Sn含量进一步升高,Cu含量平均值为0.69%,Sn含量为0.45%。
泡金山矿床闪锌矿分析测点共13个,闪锌矿除Zn、S以外,还含Fe、Cu、In、Cd、Mn、Pb等杂质元素,其中Zn 55.29%~58.89%,平均值55.76%,Fe 5.18%~9.57%,平均值为6.73%,Cu 0.08%~0.15%,平均值为0.12%,In 0.13%~0.19%,平均值0.15%,Cd 0.13%~0.19%,平均值0.15%,较三合圩矿床闪锌矿In、Zn的含量更高,Fe、Mn的含量更低(图9)。各元素含量变化不大,在闪锌矿中分布较均匀(图10)。
表4 三合圩和泡金山矿床闪锌矿电子探针结果(wt %)
Table 4 EPMA data of sphalerite of the Sanhexu and Paojinshan deposit (wt %).
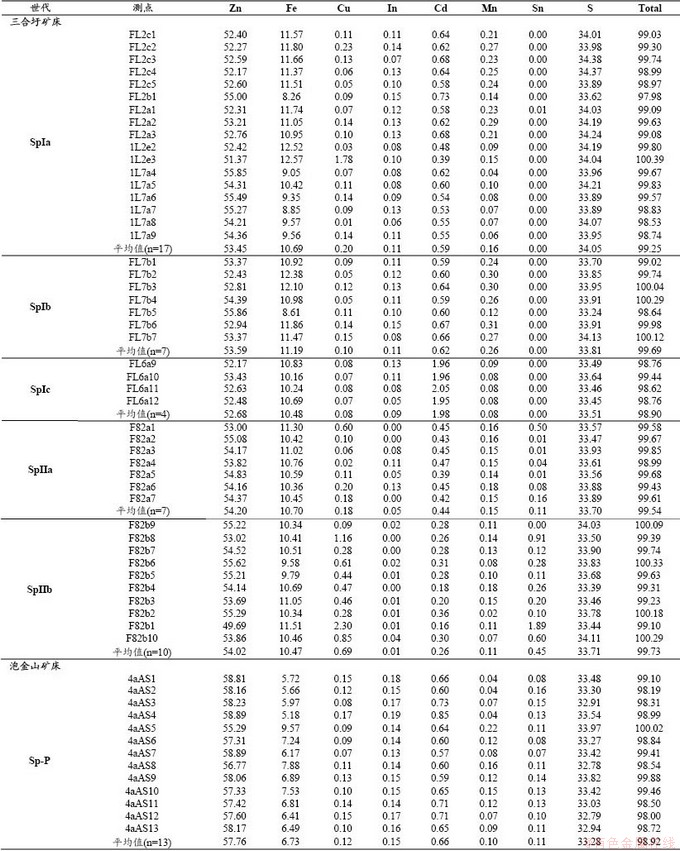
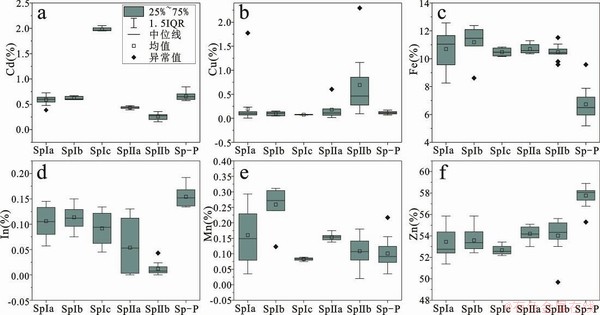
图9 三合圩和泡金山矿床各类闪锌矿Cd(a)、Cu(b)、Fe(c)、In(d)、Mn(e)和Zn(f)元素箱型图(wt %)
Fig. 9 Element Cd(a), Cu(b), Fe(c), In(d), Mn(e) and Zn(f) box plots of all types of sphalerite from the Sanhexu and Paojinshan deposit(wt %)
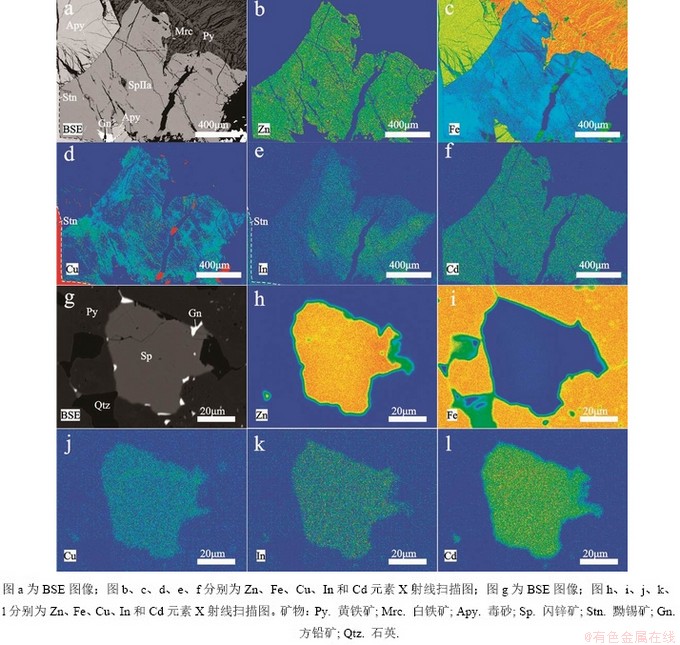
图10 三合圩(a-f)和泡金山(g-l)矿床闪锌矿X射线扫描图
Fig. 10 X-ray mappings of sphalerite of the Sanhexu(a-f) and Paojinshan(g-l) deposit.
4.3.2 黝锡矿
两矿床的黝锡矿电子探针分析结果见表5,两矿床典型黝锡矿颗粒X射线面扫描结果见图11。三合圩三类黝锡矿(Stn-a、Stn-b、Stn-c)显示黝锡矿中的元素分布并不均匀,其中Zn含量平均值依次为2.67%、2.31%、2.09%,In含量平均值依次为0.19%、0.10%、0.05%,Fe含量平均值依次为12.6%、12.48%、12.33%,Zn、In、Fe含量逐渐降低;而Cu含量平均值依次为28.84%、29.10%、29.25%,Sn含量平均值依次为25.22%、26.03%、26.30%,Cu、Sn含量在增高。
面扫描结果显示,Stn-a颗粒中,Zn元素富集在边部,呈乳滴状、浑圆状,在旁侧的黄铜矿颗粒内也有Zn元素呈点状富集;Fe元素在颗粒内部呈不均匀分布;In元素在颗粒内部同Zn元素类似,呈边缘分布;而Sn元素主要呈中心富集,并且Sn含量高的区域In、Zn元素含量较低(图11)。
泡金山矿床的黝锡矿Zn含量平均值0.94%,Fe含量为13.28%,Cu含量平均值为28.99%,In含量低于检测限,较之三合圩矿床黝锡矿颗粒,Zn、In含量最低,而Fe含量最高。泡金山黝锡矿面扫描结果显示,在黝锡矿颗粒内部,元素分布均匀,而在边部环带中,可见Fe、Sn的乳滴状富集。
表5 三合圩和泡金山矿床黝锡矿电子探针分析结果(wt %)
Table 5 EPMA data of stannite of the Sanhexu and Paojinshan deposit (wt %)
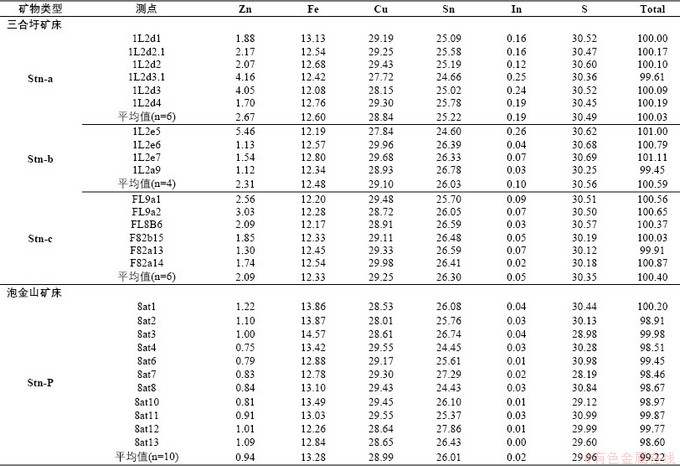
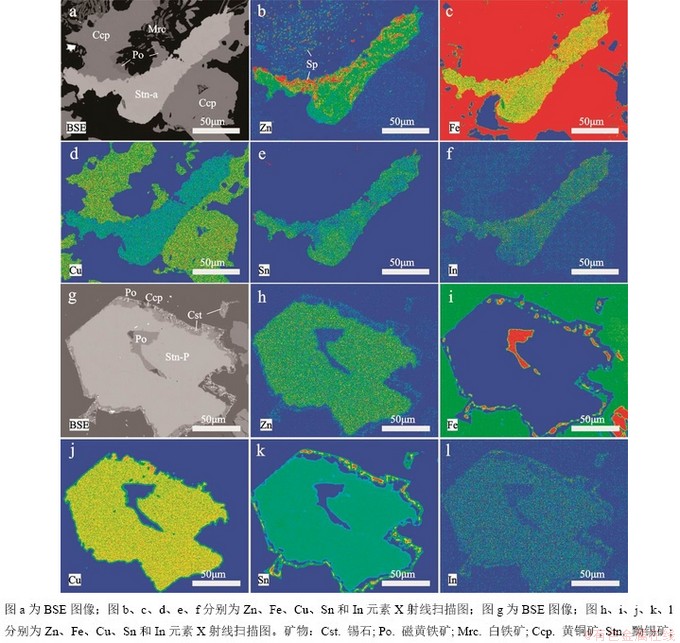
图11 三合圩(a-f)和泡金山(g-l)矿床黝锡矿X射线扫描图
Fig. 11 X-ray mappings of stannite of the Sanhexu(a-f) and Paojinshan(g-l) deposit.
4.3.3 黄铜矿
两矿床黄铜矿电子探针分析结果见表6。三合圩矿床黄铜矿除Cu、Fe、S以外,还含有杂质元素Zn、Sn、In,并且Cu、Fe含量较泡金山矿床黄铜矿更低,Sn、Zn含量更高,而In含量均低于检测限。
表6 三合圩和泡金山矿床黄铜矿电子探针分析结果(wt %)
Table 6 EPMA data of chalcopyrite of the Sanhexu and Paojinshan deposit (wt %).
5 讨论
5.1 铟在矿物中的类质同象替代关系
矿床中独立铟矿物分布极少,对大量富铟矿床研究显示载铟矿物主要为闪锌矿、黝锡矿和黄铜矿等[39]。湘南香花岭矿田三合圩和泡金山矿床碎屑岩中似层状锡矿体的矿物电子探针分析显示不同矿物In含量差异明显,其中闪锌矿In含量最高为0.18%,黝锡矿In含量最高为0.25%,而黄铜矿中In含量均低于检测限,因此闪锌矿和黝锡矿是该类矿体的主要载铟矿物,这与矿田内热液脉型、斑岩型锡多金属矿体载铟矿物具有一致的特点[14-15],由于黝锡矿在矿床中为少量或微量矿物,从工业利用角度主要载铟矿物为闪锌矿。
矿物电子探针点分析显示闪锌矿和黝锡矿中除主要元素外,其他杂质组分含量较高,如闪锌矿中除Zn、S外普遍含有较高的Fe、Cu、In、Cd、Mn,黝锡矿除Sn、Fe、Cu、S外,含有一定量的Zn和In。闪锌矿和黝锡矿颗粒X射线扫面(图10和11)显示尽管In在矿物分布不均匀,但可以明显排除以细小包体形式存在。闪锌矿和黝锡矿电子探针数据主成分分析结果见图12,闪锌矿的元素可分为两组主因子,其中PC1占49.9%,PC2占32.9%(图12a),总贡献率达到82.8%,降维是可信的。从元素向量分布来看In、Cd向量夹角极小,呈显著正相关;Fe、Mn向量呈正相关;而In、Cd向量同Cu向量方向相反呈负相关,与Fe、Mn、Zn向量夹角几乎垂直,相关关系不明显;Zn与Fe、Mn向量方向相反呈负相关。黝锡矿的元素可分为两组主因子,PC1占58.7%,PC2占18.5%(图12b),总贡献率达到77.2%,降维是可信的。从元素向量图可以看出In、Zn向量夹角较小,呈正相关,Cu、Sn向量方向夹角相近,呈正相关,In、Zn与Cu、Sn呈负相关关系。
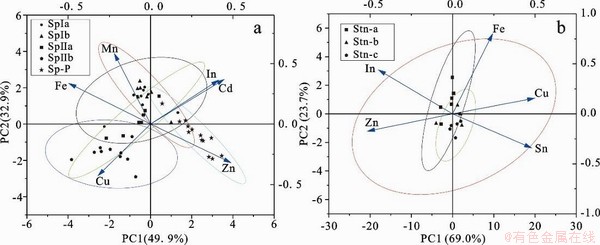
图12 闪锌矿(a)和黝锡矿(b)主成分分析得分及载荷图
Fig. 12 Score graph and loading graph of principal component analysis of sphalerite(a) and stannite(b).
为揭示元素之间的替代关系,基于矿物元素主成分分析结果对闪锌矿和黝锡矿的元素进行相关性分析,结果见图13。两矿床中闪锌矿的元素替代关系基本类似,Fe和Mn元素正相关(图13a),Fe+Mn与Zn负相关(图13b),结合闪锌矿元素主成分分析图解(图12a),其可能替代关系为Fe2++Mn2+ 2Zn2+。In和Cd元素的正相关(图13c),In+Cd与Cu元素负相关(图13d),其可能替代关系为In2++Cd2+
2Zn2+。In和Cd元素的正相关(图13c),In+Cd与Cu元素负相关(图13d),其可能替代关系为In2++Cd2+ 2Cu2+,表明与前人[7]提出的Cu++In3+
2Cu2+,表明与前人[7]提出的Cu++In3+ 2Zn2+是有所不同(图13e)。泡金山黝锡矿电子探针分析显示In元素大多低于检测限,现将三合圩黝锡矿元素相关性及替代关系进行分析,In与Cu元素负相关(图13f)、In与Sn元素负相关(图13g),而In与Zn元素正相关(图13h),Cu+Sn与In+Zn负相关(图13i),其元素的可能替代关系为In2++Zn2+
2Zn2+是有所不同(图13e)。泡金山黝锡矿电子探针分析显示In元素大多低于检测限,现将三合圩黝锡矿元素相关性及替代关系进行分析,In与Cu元素负相关(图13f)、In与Sn元素负相关(图13g),而In与Zn元素正相关(图13h),Cu+Sn与In+Zn负相关(图13i),其元素的可能替代关系为In2++Zn2+ Cu2++Sn2+。
Cu2++Sn2+。
5.2 碎屑岩中锡多金属矿体铟的富集机制
高分异花岗岩是稀有金属成矿的重要条件,其具有一定的大地构造背景、明显的岩相分带以及独特的地球化学特征[40]。香花岭矿田的锡多金属成矿与高分异花岗岩关系密切,矿田内主要锡多金属矿床如F1断裂带新风、塘官铺、三十六湾矿床[26,41],F2断裂带中铁砂坪矿床[42],F101断裂带中泡金山和茶山矿床[43-44]均围绕岩体周围的断裂产出。新发现的碎屑岩中似层状矿体产出位置与花岗岩关系密切,三合圩似层状矿体产于隐伏岩体的顶部,泡金山碎屑岩中似层状矿体产在尖峰岭岩体的南西侧。对这些花岗岩地球化学研究显示来源于壳源重熔系列花岗岩,具有富挥发分、铝过饱和、富含锂矿物、稀土元素强烈的负Eu异常、锆石高Zr/Hf比值等特征,演化过程中发生熔体与流体交代作用,有利于岩浆充分演化和含矿岩浆热液的形成,为锡铅锌矿的成矿提供前提[45-46]。大量的研究显示铟成矿与高分异花岗岩有关,如英国西南部富铟矿集区[47],德国东南部Erzgebirge地区[48],加拿大东部的Mount Pleasant矿区[49],华南的都龙、个旧等均显示与高分异花岗岩有关[50]。因此,高分异花岗岩岩浆是铟成矿的重要条件。
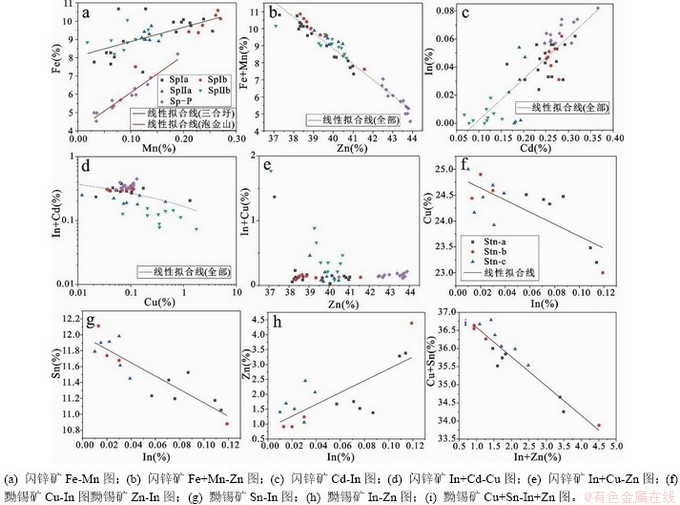
图13 闪锌矿(a-e)及黝锡矿(f-i)元素二元图解(at %)
Fig. 13 Binary plots of elements of sphalerite(a-e) and stannite(f-i) (at %)
矿石化学分析显示香花岭碎屑岩中似层状锡矿体具有明显的In富集,In平均含量相比矿田内其他类型的矿体,如断裂控矿为主的脉状矿体(In平均含量216.72 μg/g)、多因素联合控矿的接触交代型矿体(In平均含量114 μg/g)较低,而比侵入岩岩体控矿为主的斑岩型矿体(In平均含量17 μg/g)高[14-15],其中尤以三合圩矿床似层状矿体中的In具有一定的工业价值。碎屑岩中两类似层状矿体In富集差异明显,其原因可能是地层岩性差异引起的。三合圩矿床的浸染状-斑杂状矿石产于含钙质较高的泥质砂岩中,矿化类型为含铟的锡多金属矿化,矿石交代构造、矿物交代结构发育,重要的铟矿物闪锌矿发育且In平均含量最高为0.11%,而泡金山矿床的细脉-网脉状矿石产于较纯的石英砂岩中,矿化类型为贫铟的单锡矿化,矿石脉状-网脉状构造、矿物充填结构发育,尽管闪锌矿In平均含量为0.15%,但闪锌矿含量少导致矿体铟含量低。因此,不同地质环境中的似层状矿体In富集差异明显。
似层状矿体矿石化学分析显示In与Cd、Zn高度正相关,相关系数可达0.9以上,表明In与Cd、Zn具有相似的地球化学行为。矿物化学分析显示闪锌矿中的In与其他元素替代关系为In2++Cd2+ 2Cu2+,黝锡矿中In与其他元素替代关系为Cu2++Sn2+
2Cu2+,黝锡矿中In与其他元素替代关系为Cu2++Sn2+ In2++Zn2+。从元素相关性看,Cd主要赋存在闪锌矿中[51],前述元素替代关系显示闪锌矿中In和Cd替代Cu,黝锡矿中In和Zn替代Cu、Sn,因此,成矿过程中载铟矿物中In的含量受Zn沉淀量的限制,这可能是矿石化学中In、Cd、Zn高度正相关的原因。此外,三合圩矿床不同类型富铟矿物元素分布不均,矿物内部元素分布也不均,其中不同世代富铟闪锌矿沉淀时物理化学条件差异导致Fe、Cu、Sn、In含量分布不均,而矿物共生关系显示黝锡矿元素差异是与其交代的闪锌矿有关,交代富In闪锌矿导致In含量较高,甚至高于被交代的闪锌矿,例如三合圩矿床的黝锡矿a交代闪锌矿Ⅱa的X射线扫面(图10e)显示晚期黝锡矿In含量显著高于早期的闪锌矿Ⅱa,交代富In闪锌矿的黝锡矿(图11b)In富集现象明显(图11f),而不与富In闪锌矿共生的黝锡矿通常In含量很低(图11l),这些矿物学信息暗示了In可以通过交代作用在晚期矿物中进一步富集。
In2++Zn2+。从元素相关性看,Cd主要赋存在闪锌矿中[51],前述元素替代关系显示闪锌矿中In和Cd替代Cu,黝锡矿中In和Zn替代Cu、Sn,因此,成矿过程中载铟矿物中In的含量受Zn沉淀量的限制,这可能是矿石化学中In、Cd、Zn高度正相关的原因。此外,三合圩矿床不同类型富铟矿物元素分布不均,矿物内部元素分布也不均,其中不同世代富铟闪锌矿沉淀时物理化学条件差异导致Fe、Cu、Sn、In含量分布不均,而矿物共生关系显示黝锡矿元素差异是与其交代的闪锌矿有关,交代富In闪锌矿导致In含量较高,甚至高于被交代的闪锌矿,例如三合圩矿床的黝锡矿a交代闪锌矿Ⅱa的X射线扫面(图10e)显示晚期黝锡矿In含量显著高于早期的闪锌矿Ⅱa,交代富In闪锌矿的黝锡矿(图11b)In富集现象明显(图11f),而不与富In闪锌矿共生的黝锡矿通常In含量很低(图11l),这些矿物学信息暗示了In可以通过交代作用在晚期矿物中进一步富集。
矿床地质显示三合圩和泡金山矿床似层状矿体的形成与花岗岩关系密切,但因围岩岩性与构造不同导致形成了两种样式的似层状锡矿体,分别称为三合圩式和泡金山式。三合圩式矿体(图14a)的形成可能是岩浆热液沿着弱活动的断层进入泥质砂岩层面,成矿流体与含钙质较高的泥质砂岩发生强烈的水岩反应形成矽卡岩化,导致成矿流体性质和物理化学条件改变从而使得Sn、Pb、Zn等成矿元素沉淀,最终形成了富铟的锡铅锌多金属矿体;泡金山式矿体(图14b)的形成可能是岩浆热液沿着开放的断裂运移,进入断裂产状变化及裂隙发育的石英砂岩等开放容矿构造中导致成矿流体物理化学条件改变,最终以充填作用为成矿方式导致大量Sn沉淀,但伴随的Zn、In微量的沉淀,形成了在石英砂岩贫铟的锡矿体。综合对比上述两矿床发育特点及成矿过程分析,认为交代作用为重要的铟成矿作用方式,最后建立了两种样式的In成矿模式(图14)。
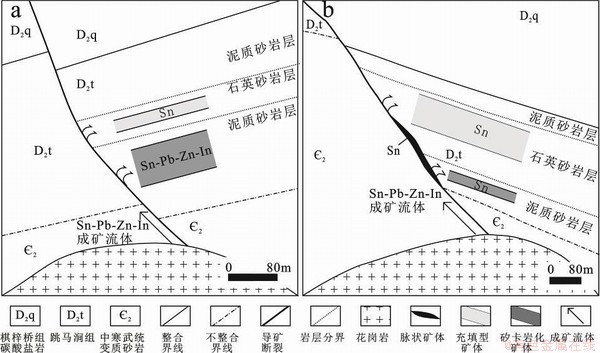
图14 三合圩矿床(a)和泡金山矿床(b)碎屑岩中似层状锡矿体铟富集成矿模式
Fig. 14 Indium mineralation model of stratoid tin orebodies hosted by clastic rocks of the Sanhexu and Paojinshan deposit.
6 结论
1) 香花岭矿田泥盆系碎屑岩中发育两类似层状锡矿体:三合圩式以泥质砂岩为容岩的矽卡岩型富铟的锡铅锌矿体和泡金山式以石英砂岩为容岩的脉状-网脉状贫铟的锡矿体,不同地质环境中的似层状矿体In富集差异明显。
2) 矿石矿物学研究显示载铟矿物有闪锌矿和黝锡矿,其中以闪锌矿最为重要。三合圩式矿体中的闪锌矿In含量最高0.15%,泡金山式矿体中为最高0.19%,闪锌矿中元素替代关系为:In2++Cd2+ 2Cu2+。黝锡矿仅在三合圩式矿体中含In含量0.25%,而泡金山式低于检测限,黝锡矿中元素替代关系为:In2++Zn2+
2Cu2+。黝锡矿仅在三合圩式矿体中含In含量0.25%,而泡金山式低于检测限,黝锡矿中元素替代关系为:In2++Zn2+ Cu2++Sn2+。
Cu2++Sn2+。
3) 碎屑岩中似层状锡多金属矿体受高分异花岗岩、断裂构造和围岩岩性综合控制,当岩浆热液沿着沿着断裂向上运移,在断裂活动弱而围岩性质活泼的含钙泥质砂岩中以交代成矿作用为主形成富铟的矽卡岩型锡铅锌矿体,而在容矿构造较为开放的石英砂岩中以充填成矿作用为主形成贫铟的锡矿体。
REFERENCES
[1] TAYLOR S.R. MCLENNANS.M. The continental crust: its composition and evolution[M]. London: Blackwell Scientific Publication, 1985, 1-312.
[2] BRISKEY J.A. Indium in zinc-lead and other mineral deposits: a reconnaissance survey of 1118 indium analyses published before 1985[R]. U. S. Geological Survey, Open-File Report, 2005, 1209.
[3] SCHWARZ-SCHAMPERA, U., HERZIG, P.M. Indium: geology, mineralogy and economics[M]. Heidelberg: Springer-Verlag, 2002: 1–257.
[4] U.S. DOE. Critical materials strategy[R]. U.S. Department of Energy, 2011: 1-189.
[5] CHAKHMOURADIAN, A.R., SMITH, M.P., KYNICKY, J. From “strategic” tungsten to “green” neodymium: a century of critical metals at a glance[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2015, 64, 455–458.
[6] 侯增谦, 陈骏, 翟明国. 战略性关键矿产研究现状与科学前沿[J]. 科学通报, 2020, 65(33): 7-8.
HOU Zeng-qian, CHEN Jun, ZHAI Ming-guo. Research status and scientific frontiers of strategic key minerals[J]. Chinese science bulletin, 2020, 65(33):7-8.
[7] 李晓峰, 朱艺婷, 徐净. 关键矿产资源铟研究进展[J]. 科学通报, 2020, 65(33): 3678-3687.
LI Xiao-feng, ZHU Yi-ting, XU Jing. Research progress of key mineral resource: indium[J]. Chinese science bulletin, 2020, 65(33): 3678-3687.
[8] ISHIHARA SHUNSO, MURAKAMI HIROYASU, LI Xiao-feng. Indium concentration in zinc ores in plutonic and volcanic environments: examples at the Dulong and Dachang mines, South China[J]. Bulletin of the geological survey of Japan, 2011, 62(7-8): 259-272.
[9] 李晓峰, 杨锋, 陈振宇, 等. 广西大厂锡矿铟的地球化学特征及成因机制初探[J]. 矿床地质, 2010, 29(5): 903–914.
LI Xiao-feng, YANG Feng, CHEN Zhen-yu, et al. A tentative discussion on geochemistry and genesis of indium in Dachang tin ore district, Guangxi[J]. Mineral Deposits, 2010, 29(5): 903–914.
[10] 戴塔根, 杜高峰, 张德贤, 等. 广西大厂锡多金属矿床中铟的富集规律[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2012, 22(3): 703-714.
DA Ta-gen, DU Gao-feng, ZHANG De-xian, et al. Indium distribution in Dachang tin-polymetallic deposit of Guangxi Province[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2012, 22(3): 703-714.
[11] LI Yu-bang, TAO Yan, ZHU Fei-lin, et al. Distribution and existing state of indium in the Gejiu tin polymetallic deposit, Yunnan Province, SW China[J]. Chinese Journal of Geochemistry, 2015, 34(4): 469-483.
[12] XU Jing, Cook N.J., Ciobanu, C.L., et al. Indium distribution in sphalerite from sulfide–oxide–silicate skarn assemblages: a case study of the Dulong Zn-Sn-In deposit, Southwest China[J]. 2021, Mineralium Deposita. 56, 307-324.
[13] 刘建平, 郑旭, 陈卫康, 等. 滇东南白牛厂银多金属矿床铟分布规律及富集机制[J]. 中南大学学报(自然科学版), 2021, 出版中.
LIU Jian-ping, ZHENG Xu, CHEN Wei-kang, et al. Indium distribution and enrichment mechanism of the Bainiuchang silver polymetallic deposit in Southeastern Yunnan[J]. Journal of Central South University (Science and Technology), 2021, Publishing.
[14] LIU Jian-ping, RONG, Ya-nan, ZHANG Shu-gen, et al. Indium Mineralization in the Xianghualing Sn–Polymetallic orefield in Southern Hunan, Southern China[J]. Minerals, 2017, 7(9): 173.
[15] LIU Jian-ping, RONG Ya-nan, GU Xiang-ping, et al. Indium mineralization in the Yejiwei Sn–polymetallic deposit of the Shizhuyuan orefield, Southern Hunan, China[J]. Resource Geology, 2018, 68(1): 22-36.
[16] 毕艳玲,吴南川,宾文梁, 等. 湖南泡金山锡矿床地质特征及控矿因素分析[J]. 国土资源导刊, 2016, 13(4): 14-19.
Bi Yan-ling, Wu Nan-chuan, Bin Wen-liang, et al. Analysis of geological features and control factors of Paojinshan tin deposit in Hunan [J]. Land & Resources Herald, 2016, 13(4): 14-19.
[17] 吴寿宁. 湖南郴州荷花坪锡多金属矿床地质特征[J]. 矿产与地质, 2006, 20(1): 43-46.
WU Shou-ning. Geological characteristics of the Hehuaping tin polymetallic deposit in Chenzhou, Hunan Province[J]. Mineral Resources and Geology, 2006, 20(1): 43-46.
[18] 毛景文, 陈懋弘, 袁顺达, 等. 华南地区钦杭成矿带地质特征和矿床时空分布规律[J]. 地质学报, 2011, 85(5):636-658.
MAO Jing-wen, CHEN Mao-hong, YUAN Shun-da, et al. Geological characteristics of the Qinhang (or Shihang) metallogenic belt in South China and spatial-temporal distribution regularity of mineral deposits[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2011, 85(5):636-658.
[19] 柏道远, 贾宝华, 马铁球, 等. 1:25万郴州幅区域地质调查主要进展及成果[J]. 中国地质调查, 2016, 3(2): 24-33.
BAI Dao-yuan, JIA Bao-hua, MA Tie-qiu, et al. Major progress and achievements in regional geological survey of 1:250000 Chenzhou sheet[J]. Geological Survey of China, 2016, 3(2): 24-33.
[20] 柏道远, 王先辉, 马铁球, 等. 湘东南印支期褶皱特征及形成机制[J]. 华南地质与矿产, 2006, (4): 50-57.
BAI Dao-yuan, WANG Xian-hui, MA Tie-qiu, et al. Characteristics and forming mechanism of indosinian folds in the Southeast Hunan[J]. Geology and Mineral Resources of South China, 2006, 2(4): 50-57.
[21] 车勤建, 李金冬, 魏绍六, 等. 湖南千里山—骑田岭矿集区形成的构造背景初探[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 2005, 29(2): 204-214.
Chen Qin-Jian, Li Jin-Dong, Wei Shao-liu, et al. Elementary discussion on the tectonic background of deposit-concentrated Qianlishan-Qitianling area in Hunan[J]. Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 2005, 29(2): 204-214.
[22] 黄革非, 龚述清, 蒋希伟, 等. 湘南骑田岭锡矿成矿规律探讨[J]. 地质通报, 2003, 22(6): 445-451.
Huang Ge-fei, Gong Shu-qing, Jiang Xi-wei, et al. Exploration on the ore-forming regularities of tin deposits in Qitianling area, Southern Hunan[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2003, 22(6): 445-451.
[23] 钟江临. 湖南香花岭地区有色、稀有多金属矿床主要类型及找矿方向[J]. 华南地质与矿产, 2014, 30(2): 99-108.
ZHONG Jiang-lin. Major types and prospecting direction of nonferrous and rare polymetallic ore deposit in Xianghualing area, South China[J]. Geology and Mineral Resources of South China, 2014, 30(2): 99-108.
[24] 钟江临, 李楚平. 湖南香花岭矽卡岩型锡矿床地质特征及控矿因素分析[J]. 矿产与地质, 2006, 20(2): 147-151.
ZHONG Jiang-lin, LI Chu-ping. Geological characteristics and genesis of Xianghualing skarn type tin deposit[J]. Mineral Resources and Geology, 2006, 20(2): 147-151.
[25] 蔡宏渊. 香花岭锡多金属矿田成矿地质条件及矿床成因探讨[J]. 矿产与地质, 1991, 5(4): 272-283.
CAI Hong-yuan. The metallogenic geological setting and approach on ore genesis of Xianghualing tin-polymetallic ore field[J]. Mineral Resources and Geology, 1991, 5(4): 272-283.
[26] 来守华. 湖南香花岭锡多金属矿床成矿作用研究[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2014.
LAI Shou-hua. Research on mineralization of the Xianghualing tin polymetallic deposit, Hunan Province, China[D]. China University of Geosciences, Beijing, 2014.
[27] 彭建堂, 胡瑞忠, 袁顺达, 等. 湘南中生代花岗质岩石成岩成矿的时限[J]. 地质论评, 2008, 54(5): 617-625.
PENG Jian-tang, HU Rui-zhong, YUAN Shun-da, et al. The time ranges of granitoid emplacement and related nonferrousmetallic mineralization in Southern Hunan[J]. Geological Review, 2008, 54(5): 617-625.
[28] YUAN Shun-da, PENG Jian-tang, HU Rui-zhong, et al. A precise U–Pb age on cassiterite from the Xianghualing tin-polymetallic deposit (Hunan, South China)[J]. Mineralium Deposita. 2008, 43(4): 375-382.
[29] LI Huan, WU Jing-Hua, NOREEN J, et al. Zircon geochronology and geochemistry of the Xianghualing A-type granitic rocks: Insights into multi-stage Sn-polymetallic mineralization in South China[J]. Lithos, 2018, 43(4): 312-313.
[30] 毛景文, 谢桂青, 郭春丽, 等. 南岭地区大规模钨锡多金属成矿作用:成矿时限及地球动力学背景[J]. 岩石学报, 2007, 23(10): 2329-2338.
MAO Jing-wen, XIE Gui-qing, GUO Chun-li, et al. Large-scale tungsten–tin mineralization in the Nanling region, South China: metallogenic ages and correspondine geodvnamic processes [J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2007, 23(10): 2329-2338.
[31] 蒋喜桥. 香花岭底砾岩型锡矿床地质特征及控矿规律研究[J]. 南方国土资源, 2013, (11): 26-28.
JIANG Xi-qiao. Research on geological characteristics and ore controlling factors of the conglomerate tin deposit in Xianghualing[J]. Land and Resources of Southern China, 2013, (11): 26-28.
[32] 王庆, 孔华, 邹建林. 湘南三合圩锡多金属矿成矿规律及找矿方向[J]. 矿产与地质, 2020, 34(6): 1044-1050.
WANG Qing, KONG Hua, ZOU Jian-lin. Metallogenic regularity and prospecting direction of Sanhexu tin polymetallic deposit in South Hunan [J]. Mineral Resources and Geology. 2020, 34(6): 1044-1050.
[33] 姚伟, 王庆, 屈利军, 等. 湖南省香花岭三合圩锡多金属矿区地质特征及找矿预测[J]. 地质找矿论丛, 2020, 35(3): 287-292.
YAO Wei, WANG Qing, QU Li-jun, et al. Geological characteristics and ore prediction of Sanhexu tin polymetallic mining district in Xianghualing, Hunan Province[J]. Contributions to Geology and Mineral Resources Research, 2020, 35(3): 287-292.
[34] 何永帅. 湖南省临武县长冲矿区底砾岩型锡矿床地质特征及控矿因素浅析[J]. 世界有色金属, 2018, 4(8): 192-193.
HE Yong-shuai. Geological characteristics and ore controlling factors of the conglomerate tin deposit in the Changchong mining area, Linwu County, Hunan[J]. World Nonferrous Metals, 2018, 4(8): 192-193.
[35] 黄小波, 宾文梁, 曹能文, 等. 湖南临武长冲矿区层控型铅锌矿床成因分析及找矿前景[J]. 国土资源导刊, 2020, 17(1): 9-14.
HUANG Xiao-bo, BIN Wen-liang, CAO Neng-wen, et al. Genesis analysis and prospecting foreground of stratabound lead-zinc deposit in Changchong mine area, Linwu, Hunan Province[J]. Land & Resources Herald, 2020, 17(1): 9-14.
[36] 黎原, 黎传标, 陈长江, 等. 湖南临武县铁砂坪矿区锡多金属矿矿床地质特征及找矿前景浅析[J]. 资源环境与工程, 2017, 31(2): 142-148.
LI Yuan, LI Chuan-biao, CHEN Chang-jiang, et al. Geological characteristics and prospecting prospect of tin polymetallic deposit in Tieshaping mining area at Linwu county, Hunan[J]. Resources Environment & Engineering, 2017, 31(2): 142-148.
[37] 杨文翔. 湖南临武县泡金山锡铅锌矿地质特征及成因机理[J]. 世界有色金属, 2017, (21): 174-176.
YANG Wen-xiang. Geological characteristics and metallogenic mechanism of the Paojinshan Sn-Pb-Zn deposit in Linwu, Hunan[J]. World Nonferrous Metals, 2017, (21): 174-176.
[38] 屈利军, 王庆, 李波, 等. 综合物探方法在湖南香花岭矿田三合圩矿区深部成矿规律研究中的应用[J]. 物探与化探, 2020, 44(6): 1313-1321.
QU Li-jun, WANG Qing, LI Bo, et al. The application of multiple geophysical methods to the study of deep metallogenic regularity in the Sanhexu mining area, the Xianghualing orefield, Hunan Province[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2020, 44(6): 1313-1321.
[39] COOK N J, SUNDBLAD K, VALKAMA M, et al. Indium mineralization in A-type granites in southeastern Finland: insights into mineralogy and partitioning between coexisting minerals[J]. Chemical Geology, 2011, 284: 62-73.
[40] 吴福元, 刘小驰, 纪伟强, 等. 高分异花岗岩的识别与研究[J]. 中国科学:地球科学, 2017, 47(7): 745-765.
WU Fu-Yuan, LIU Xiao-chi, JI Wei-qiang, et al. Highly fractionated granites: Recognition and research[J]. Science China: Earth Sciences, 2017, 47(7): 745-765.
[41] 李勋贵. 湖南香花岭塘官铺蚀变花岗斑岩岩石学研究及蚀变矿化机理初探[D]. 长沙: 中南大学, 1989.
LI Xun-gui. Research on petrology of altered granite porphyry and its alteration mineralization in Tangguanpu, Xianghualing, Hunan Province[D]. Changsha: Central South University, 1989.
[42] 郭爱民, 廖兴钰. 临武铁砂坪锡石硫化物矿床地质特征及找矿意义[J]. 湖南地质, 2002, 21(4): 271-274.
GUO Ai-min, LIAO Xing-yu. Geological traits of cassiterite–sulfide deposit of Tieshanping at Linwu and its significance on exploring deposits[J]. Hunan Geology, 2002, 21(4): 271-274.
[43] 文国璋, 吴强. 湖南临武泡金山铅锌矿床的控矿因素及成因[J]. 桂林冶金地质学院学报, 1990, 10(4): 356-363.
WEN Guo-zhang, WU Qiang. The ore-controlling factors and genesis of Paojnshan Pb-Zn deposit, Linwu, Hunan[J]. Journal of Guilin Institute of Metallurgical Geology, 1990, 10(4): 356-363.
[44] 文国璋, 李和平, 李石波. 临武县茶山铅锌矿床成因[J]. 湖南地质, 1988, 7(1): 40-47.
WEN Guo-zhang, LI He-ping, LI Shi-bo. The genesis of Changshan Pb-Zn deposit of Linwu county[J]. Hunan Geology, 1988, 7(1): 40-47.
[45] 庄锦良. 湘南地区几个隐伏花岗岩体地质特征及产出的构造环境[J]. 湖南地质, 1988, 7(4): 40-48.
ZHUANG Jin-liang. Geologic features and tectonic setting of some covered granitic bodies in Southern Hunan[J]. Hunan Geology, 1988, 7(4): 40-48.
[46] 文春华, 邵拥军, 黄革非, 等. 湖南尖峰岭稀有金属花岗岩地球化学特征及成矿作用[J]. 矿床地质, 2017, 36(4): 879-892.
WEN Chun-hua, SHAO Yong-jun, HUANG Ge-fei, et al. Geochemical features and mineralization of Jianfengling rare metal granite in Hunan Province[J]. Mineral Deposits, 2017, 36(4): 879-892.
[47] ANDERSEN J.C., STICKLAND R.J., ROLLINSON G.K., et al. Indium mineralization in SW English: host parageneses and mineralogical relations [J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2016, 78, 213-238.
[48] BAUER M E, SEIFERT T, BURISCH M, et al, Indium-bearing sulfides from the Hammerlein skarn deposit, Erzgebirge, Germany: evidence for late-stage diffusion of indium into sphalerite [J]. Mineralium Deposita, 2017, 54, 175-192.
[49] SINCLAIR W D, KOOIMAN G J A, MARTIN D A, et al. Geology, geochemistry and mineralogy of indium resources at Mount Pleasant, New Brunswick, Canada[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2006, 28, 123-145.
[50] 王大鹏,张乾,武丽艳, 等. 花岗岩中铟与锡铜铅锌的关系及其富集成矿意义[J]. 岩石学报, 2019, 35(11): 3317-3332.
WANG Da-peng, ZHANG Qian, WU Li-yan, et al. The relationship between indium and tin, copper, lead and zinc in granite and its significance to indium mineralization[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 35(11): 3317-3332.
[51] WEN Han-jie, ZHU Chuan-wei, ZHANG Yu-xu, et al. Zn/Cd ratios and cadmium isotope evidence for the classification of lead-zinc deposits[J]. Scientific Reports, 2016, 6(1): 593-625.
Characteristics and genesis of In mineralization of stratoid Sn polymetallic orebodies hosted by clastic rock in Xianghualing orefield, Southern Hunan
ZHENG Xu1,2, LIU Jian-ping1,2*, CHEN Wei-kang1,2, SHAO Yong-jun1,2, TIAN Xu-feng3, WEN Yi-zhuo3, LIU Shao-qing1,2, DING Tao1,2
(1. Key Laboratory of Metallogenic Prediction of Nonferrous Metals and Geological Environment Monitoring, Central South University, Ministry of Education, Changsha 410083, China;
2. School of Geosciences and Info-Physics Engineering, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China;
3.Southern Hunan Institute of Geology Survey, Chengzhou 423000, China)
Abstract: The Xianghualing orefield in southern Hunan, Nanling area is a typical magmatic-hydrothermal type In mineralization area in South China. The newly explored stratoid Sn orebodies, an important Sn mineralization type in the orefield, are relatively unique type in the Nanling area. However, indium distribution and enrichment mechanism of these orebodies have not yet done enough research. In order to reveal characteristics and genesis of In enrichment of the stratoid Sn polymetallic orebodies, ore mineral microscopic observation and identification, ore chemical composition analysis, and mineral microanalysis were carried out using optical microscope, plasma spectrometer, and electron probe based on geological surveys and sample collection of the orebodies. There are two types of stratoid Sn orebodies hosted by clastic rock: one is Sanhexu type, Sn polymetallic mineralition hosted by argillaceous clastic rock; the other is Paojinshan type, Sn mineralization hosted by quartz sandstone. Chemical analysis of the ores show that the Sanhexu orebodies are In-rich Sn polymetallic orebodies with 12.94 μg/g ~ 70.80 μg/g In, 0.61% ~ 2.62% Zn, and 0.13% ~ 0.86% Sn; while the Paojinshan orebodies are In-poor Sn orebodies with 0.04 μg/g ~ 1.06 μg/g In, 0.06% ~ 1.87% Sn. Indium-bearing minerals include sphalerite and stannite, especially sphalerite. Sphalerite contains In up to 0.15% in the Sanhexu, and in the Sanhexu up to 0.19%. Element substitution mechanisms of sphalerite is In2++Cd2+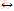 2Cu2+. Stannite contains 0.25% In in the Sanhexu orebodies, but below detection limit in the Paojinshan. Element substitution mechanisms of stannite is In2++Zn2+
2Cu2+. Stannite contains 0.25% In in the Sanhexu orebodies, but below detection limit in the Paojinshan. Element substitution mechanisms of stannite is In2++Zn2+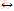 Cu2++Sn2+. Based on geological characteristics of the deposit and In enrichment, it was proposed that stratoid orebodies hosted by clastic rocks are related to magmatic-hydrothermal; different In enrichment of two orebody types is controlled by geological environment and mineralization style; metasomatic mineralization style in argillaceous sandstones forms In-rich tin polymetallic orebodies, while filling mineralization style in quartz sandstones forms In-poor Sn orebodies.
Cu2++Sn2+. Based on geological characteristics of the deposit and In enrichment, it was proposed that stratoid orebodies hosted by clastic rocks are related to magmatic-hydrothermal; different In enrichment of two orebody types is controlled by geological environment and mineralization style; metasomatic mineralization style in argillaceous sandstones forms In-rich tin polymetallic orebodies, while filling mineralization style in quartz sandstones forms In-poor Sn orebodies.
Key words: indium enrichment; mineral chemistry; genesis; stratoid tin polymetallic orebodies hosted by clastic rock; Xianghualing; Southern Hunan
Foundation item: Project (2018YFC0603901) supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China; Project (41872091) supported by the National Science Foundation of China.
Received date: 2021-07-07; Accepted date: 2021-08-03
Corresponding author: LIU Jian-ping; Tel: +86-18773149891; Email: liujianping303@163.com
(编辑 某某某)
基金项目:国家重点研发计划项目(2018YFC0603901)和国家自然科学基金资助项目(41872091)
收稿日期:2021-07-07;修回日期:2021-08-03
通信作者:刘建平, 副教授, 博士;电话:18773149891;Email:liujianping303@163.com