文章编号:1004-0609(2010)10-1913-09
纵向磁场作用下DZ417G高温合金的枝晶生长行为
李 旭,任忠鸣,任维丽,李 喜,钟云波,邓 康,董建文,陈 超
(上海大学 材料科学与工程学院,上海 200072)
摘 要:研究纵向磁场对高温合金DZ417G定向凝固显微组织的影响。结果表明:在较低生长速率下,磁场能显著影响高温合金柱状枝晶的生长;低磁场(<0.1 T)能使枝晶生长规则化,生长方向逐渐统一并平行于磁场方向,一次枝晶臂间距减小;高磁场(>2 T)破坏枝晶生长,枝晶发生断裂,逐渐出现一些云状组织;随着生长速率的增大,磁场的影响逐渐减弱。并从磁场诱发热电磁对流和熔体流动影响枝晶生长的角度对实验结果进行分析。
关键词:Ni基高温合金;纵向磁场;定向凝固;枝晶生长行为
中图分类号:TG146 文献标志码:A
Dendrite growth behavior of DZ417G superalloy under longitudinal magnetic field
LI Xu, REN Zhong-ming, REN Wei-li, LI Xi, ZHONG Yun-bo, DENG Kang, DONG Jian-wen, CHEN Chao
(Department of Materials Science and Engineering, Shanghai University, Shanghai 200072, China)
Abstract: The influence of longitudinal magnetic field on the microstructures of DZ417G superalloy at different growing rates was investigated. The results show that the magnetic field (<0.1 T) can affect significantly the regular dendrite growth and primary dendrite arm spacing of DZ417G superalloy at low growing rate, and the growth direction is parallel to the direction of magnetic field. But the high magnetic field(>2 T)can disturb the regular morphology of dendrite growth. The dendrite morphologies are destroyed when the magnetic field is applied. The effect of magnetic field is weak when the growing rate increases. Based on the theory of the influence of magnetic field on fluid, the above phenomenon was analyzed.
Key words: Ni-based superalloy; longitudinal magnetic field; directional solidification; dendrite growth behavior
利用磁场使材料在凝固过程中产生定向排列的规则组织,一直是人们感兴趣的研究课题。在1966年,UTECH和FLEMINGS[1]发现利用磁场能够抑制热对流从而消除半导体单晶生长中的溶质带。此后,在多个半导体熔体拉单晶过程中施加0.1~0.5 T磁场,都能有效地抑制熔体中的热对流和温度波动,并显著消除由此引起的生长条纹和溶质带等宏观偏析现象[2-4]。OREPER等[5]指出,磁场可以抑制流体中的自然对流,抑制程度与外磁场强度、体系几何形状及大小有关,但他们提出完全抑制自然对流非常困难。1994年,KANG等[6]提出,微弱的对流在磁场中产生的Lorentz力也很小,强磁场压制对流的作用有一定的限度,并提出应该用低对流模型[7]描述强磁场中熔体的对流状况。BOETTINGER等[8]和TEWARI等[9]分别对Pb-Sn合金进行研究,前者在定向凝固过程中分别施加0.1T的轴向和径向的磁场,发现磁场对组织形貌和宏观偏析并没有影响;后者在定向凝固的过程中施加0.45T的径向的磁场,发现胞晶列发生严重扭曲,而对枝晶列没有影响。本文作者所在课题组对强静磁场对典型凝固组织影响的研究表明[10-12],强静磁场能够影响枝晶的生长方向、改变胞晶到枝晶转变的临界凝固速率、规范枝晶生长、促进分枝,这意味着可以用磁场控制定向凝固树枝晶生长方向和枝晶形态,进而改善合金性能。
DZ417G定向凝固高温合金不含有稀缺昂贵金属元素W、Nb、Ta、Hf等元素,具有密度小、成本低的特点,用作先进航空发动机低压涡轮叶片等零 件[13]。目前,研究者已对DZ417G定向凝固高温合金的各项性能做出一定研究[14]。REN等[15]探索纵向磁场对DZ417G定向凝固显微组织的影响,发现纵向磁场能够影响枝晶的生长,导致一次枝晶臂间距减小。但是研究趋于高生长速率。低生长速率下,磁场对Ni基高温合金定向凝固的影响并无报道。所以进一步深入研究低生长速率下磁场对Ni基高温合金定向凝固的影响具有重要意义。
本文作者主要研究低生长速率下纵向磁场对DZ417G定向凝固显微组织的影响。从磁场诱发热电磁对流和熔体流动影响枝晶生长的角度对实验结果进行分析。
1 实验
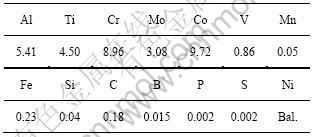
实验所采用的材料为DZ417G高温合金,该合金的成分如表1所列。
表1 DZ417G合金成分
Table 1 Composition of DZ417G (mass fraction, %)
在真空感应熔炼炉中熔炼成直径为100mm、长为400 mm的铸锭,然后用线切割机切出直径为4.0 mm、长度为180 mm的合金棒封装在内径为4.2 mm、长为200 mm的刚玉管中备用。
实验装置如图1所示,主要由超导磁体、水冷套、Bridgman定向凝固装置(加热炉、LMC冷却池及伺服抽拉系统)所组成。所用超导强磁体可以产生纵向静磁场,磁感应强度在0~14T连续可调。定向凝固装置为典型的Bridgman方法,冷却介质为液态Ga-In-Sn合金和循环水,抽拉速率在0.5~104 μm/s间连续可调。加热体为石墨电阻,用PID温控仪和双铂铑热电偶控制温度,精度为±1 ℃温度梯度的测量采用测量固-液界面前沿温度曲线的方法,然后根据公式G=ΔT/ΔS (其中,G为温度梯度;ΔT为温度变化;ΔS为距离的变化)算出温度梯度,本实验所测的温度梯度约为G=150 K/cm。
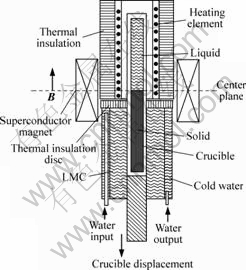
图1 纵向磁场下定向凝固装置示意图
Fig.1 Schematic diagram of bridgman solidification apparatus in superconducting magnet
实验时,先将装有试样的刚玉管与拉杆固定,然后调整加热炉位置使得试样的固液界面处于温恒磁场区域,充入Ar,加热到1 565 ℃后保温30 min,启动抽拉系统。当试样定向凝固生长达6 cm时,迅速拉入冷却介质进行淬火,以便观察固液界面生长形态。
将定向凝固试样沿纵截面、横截面切开,得到纵截面和横截面,经镶嵌、研磨、抛光、腐蚀,腐蚀剂为CuSO4(4 g),HCl(20 mL),H2SO4 (12 mL),H2O(25 mL),用Leica 光学金相显微镜观察枝晶组织。
2 实验结果
2.1 弱磁场对DZ417G定向凝固枝晶生长的影响
本文作者研究低生长速率条件下低磁场对DZ417G定向凝固枝晶生长的影响。图2和3所示分别为温度梯度G=150 k/cm、生长速率为10 μm/s时无磁场和施加磁场条件下纵截面组织和横截面组织。从图2中可以看出,无磁场时,一次枝晶沿两个生长方向生长,且这两个生长方向之间存在较大的偏差角度(见图2(a));随着施加的磁场强度的增加,一次枝晶生长趋于规则(见图2(d));当磁场达到10 mT时,一次枝晶均沿同一方向生长,但生长方向与磁场方向偏斜;随着磁场进一步增加,一次枝晶不仅沿同一方向生长,而且生长方向也趋于磁场方向。由图3可以进一步观察到上述现象,且同时发现,随着磁场的施加与增大,一次枝晶间距逐渐减小(见图4)。
2.2 强磁场对DZ417G定向凝固枝晶生长的影响
图5所示为不同生长速率时不同磁场下定向凝固组织的纵截面组织照片。从图5中可观察到,在未施加磁场时,形成了标准的树枝状枝晶组织;但随着磁场强度的施加与增大,固液界面变得不平整,定向凝固枝晶组织受到破坏,出现断裂、破碎的现象,几乎无法看到枝晶组织存在。其中图5(a)、(b)、(c)所示分别为生长速率为5 μm/s,施加磁场为0T、2T、4T时的定向凝固纵截面组织。比较可知,在施加2T磁场后,糊状区一次枝晶完全塌陷,已经找不到规则的枝
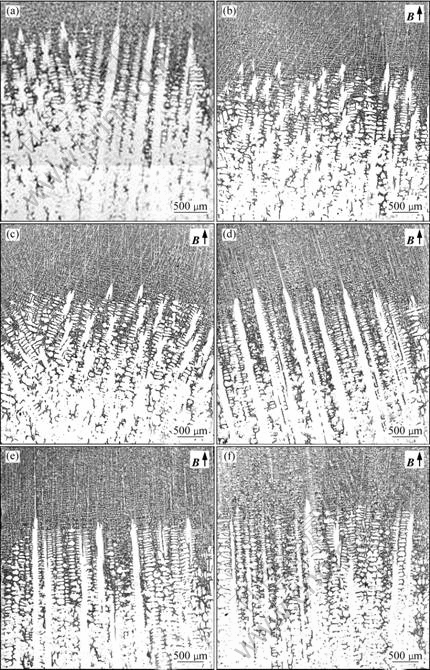
图2 生长速率为10 μm/s(G=150 K/cm)时不同磁场条件下定向凝固DZ417G纵截面组织
Fig.2 Longitudinal microstructures of directionally solidified DZ417G superalloy at growing rate of 10 μm/s and different magnetic field intensities (G=150 K/cm): (a) 0 T; (b) 1 mT; (c) 5 mT; (d) 10 mT; (e) 50 mT; (f) 100 mT
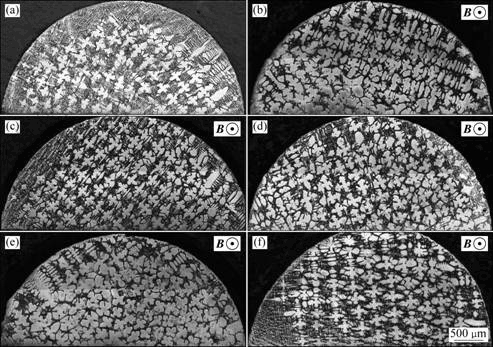
图3 生长速率为10 μm/s(G=150 K/cm)时不同磁场条件下定向凝固DZ417G的横截面组织
Fig.3 Transverse microstructures of directionally solidified DZ417G superalloy at growing rate of 10 μm/s and different magnetic field intensities (G=150 K/cm): (a) 0 T; (b) 1 mT; (c) 5 mT; (d) 10 mT; (e) 50 mT; (f) 100 mT
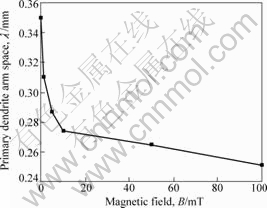
图4 磁场B对一次枝晶间距λ的影响(G=150 K/cm)
Fig.4 Effect of magnetic field on primary dendrite arm space (G=150 K/cm)
晶组织,而由一些海藻状的组织所替代,并且出现明显“斑状”组织;当磁场增加到4T时,组织进一步塌陷,液固界面右半侧塌陷尤为严重。图5(d)、(e)、(f)所示分别为生长速率为10 μm/s,施加磁场为0T、2T、4T时的定向凝固纵截面组织。从图5中可以发现,由于生长速率的增大,磁场作用减弱,当施加2T磁场时,糊状区分为两个区域:一个是中心区域,仍是枝晶组织;一个是两边区域,为海藻状组织,且存在大量“斑状”组织。随着磁场增大到4T时,枝晶组织继续退化,变为柱状枝晶,海藻状组织逐渐增多,但“斑状”组织减少。当生长速率继续增大到20 μm/s时,施加磁场为0T、2T、4T(见图5(g)、(h)、(i))时,磁场作用继续减弱,2T时,仍是枝晶组织;4T时,中心区域被破坏,出现海藻状组织,“斑状”组织基本消失。
图6所示不同生长速率不同磁场下定向凝固组织的横截面组织。从图6(a)和(b)中可以清楚地看出,当生长速率为5 μm/s时,未施加磁场时横截面组织为标准十字枝晶组织;而在施加4T磁场时,枝晶组织被破坏,已无法观察到枝晶组织,取而代之的是大量的云状组织。图6(d)所示为生长速率为10 μm/s、4T磁场作用下的组织照片。由图6(d)可以看到,试样中心区域仍有少量枝晶组织存在,取而代之的是大量的云状组织。由图6(f)可看出,当磁场为4T,生长速率为20 μm/s时,截面四周出现部分云状组织。
3 分析与讨论
3.1 材料磁晶各向异性对定向凝固枝晶生长的影响
材料的磁晶各向异性一直受到研究人员的关注。在最近的研究中,LI等[16]通过对Al-12%Ni合金的研
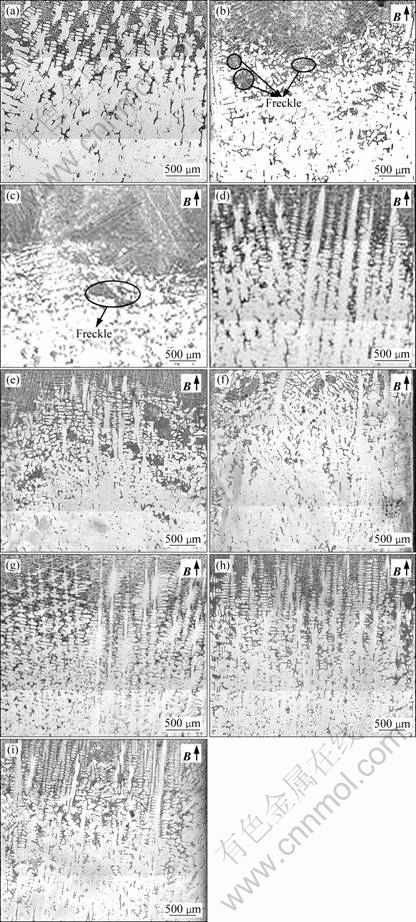
图5 不同生长速率条件下(G=150 K/cm)时不同磁场强度时定向凝固DZ417G的纵截面组织
Fig.5 Longitudinal microstructure of directionally solidified DZ417G superalloy at different growing rates and magnetic field intensities (G=150 K/cm): (a) 0 T, 5 μm/s; (b) 2 T, 5μm/s; (c) 4 T, 5 μm/s; (d) 0 T, 10 μm/s; (e) 2 T, 10 μm/s; (f) 4 T, 10 μm/s; (g) 0 T, 20 μm/s; (h) 2 T, 20 μm/s; (i) 4 T, 20 μm/s
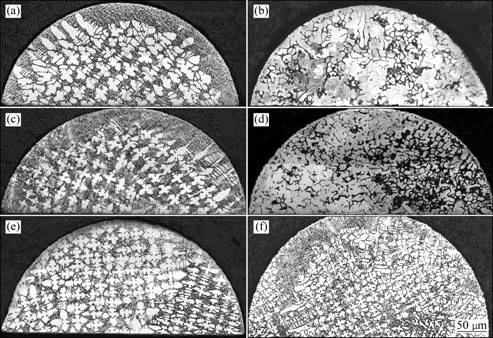
图6 不同生长速率条件下(G=150 K/cm)时不同磁场强度时DZ417G定向凝固横截面组织
Fig.6 Transverse microstructures of directionally solidified DZ417G superalloy at different growing rates and different magnetic field intensities: (a) 0T, 5 μm/s; (b) 4T, 5 μm/s; (c) 0T, 10 μm/s; (d) 4T, 10 μm/s; (e) 0T, 20 μm/s; (f) 4T, 20 μm/s
究,发现施加磁场后,组织的生长方向发生偏转。
因为晶体具有磁晶各向异性,在磁场中会发生取向。如图7所示,假如一个磁各向异性的晶体处于磁场中,单位体积的磁矩(Ms)可以表示为
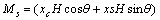 (1)
(1)
Mc 和Mab 分别为沿c轴和ab轴方向的单位体积磁矩,可以表示为
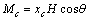 (2)
(2)
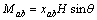 (3)
(3)
式中:x为物质的磁化系数;H为磁场强度;θ为c轴与磁场方向的夹角。当磁场发生变化时,放在其中的磁各向异性晶体的磁化能改变为
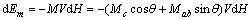 (4)
(4)
将式(2)和式(3)代入式(4)得
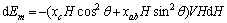 (5)
(5)
积分得
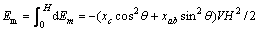 (6)
(6)
将 代入式(6)得:
代入式(6)得:
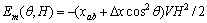 (7)
(7)
这里 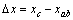 是c轴和ab轴方向的磁化率差。当
是c轴和ab轴方向的磁化率差。当 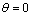 ,得
,得
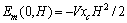 (8)
(8)
当 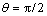 ,得
,得
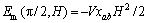 (9)
(9)
当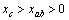 , 得
, 得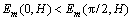 ,这意味c轴方向转向磁场;相反,当
,这意味c轴方向转向磁场;相反,当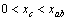 ,得
,得 ,ab轴方向转向磁场。以上可以看出,当一个顺磁性的各向异性的颗粒放入磁场中,其易磁化轴转向磁场方向,而抗磁性的各向异性的颗粒放入磁场中其易磁化轴转向垂直于磁场方向的平面上。
,ab轴方向转向磁场。以上可以看出,当一个顺磁性的各向异性的颗粒放入磁场中,其易磁化轴转向磁场方向,而抗磁性的各向异性的颗粒放入磁场中其易磁化轴转向垂直于磁场方向的平面上。
本研究中DZ417G高温合金为顺磁性材料,由实验所定,晶粒生长方向为á001?,但晶粒的易磁化方向为á111?,与生长方向成一定角度。从实验结果中并未发现枝晶的明显偏转,可能由于磁场强度较低,不足以产生足够的磁化能用于偏转晶粒,而当磁场增大到2T和4T时,生长方向与易磁化方向发生强烈竞争,由于晶粒自身的形核能足够大,以至于磁化能仍然无法偏转晶粒,两应力互相作用,最终导致枝晶断裂(见图8)。
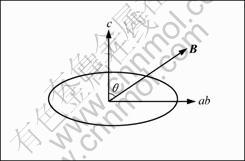
图7 颗粒的磁各向异性
Fig.7 Anisotropic grain in magnetic field (B is magnetic field direction; c and ab are crystallographic axes, respectively)
3.2 磁场对定向凝固枝晶组织的影响
目前,普遍认同的强静磁场对金属合金定向凝固过程的影响机理主要集中在两个方面:一是磁阻尼 (Magnetic damping)效应;二是热电流引起的热电磁对流(Thermoelectromagnetic convection,TEMC)效应。
磁阻尼效应是指静磁场对熔体内部流动的抑制作用,在凝固过程中,金属熔体的流动(如自然对流)受到磁场作用而产生感应电流,从而产生洛仑兹力,如图9(a)
所示,在处于x方向的直流磁束Bx作用下,若有z方向的流速为Vz的金属液流,则在y方向上产生感应电流Jy,根据左手定则,该金属流体中的体积力为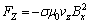 (10)
(10)
式中:σ为金属熔体电导率; μ0为熔体磁导率; vz为熔体运动速度; Bx为磁场强度。体积力Fz方向与流速反向,大小与流速成正比。
已有研究表明[10],磁阻尼效应在定向凝固过程中可减少界面处的扰动,有利于柱状晶的生长,抑制等轴晶的生成。
热电磁对流是由于熔体和晶体的热电因子不同,且二者间存在温度梯度,从而产生热电流,热电流与磁场相互作用产生一个洛仑兹力JTE×B,这个力将驱动凝固界面附近的熔体在一定区域内流动,从而产生了热电磁对流,如图9(b)所示。它能够使界面处的流动加剧,促进溶质的传输。热电电流和磁场作用,产生热电磁洛仑兹力,其大小表示为
 (11)
(11)
式中:JT为热电流;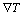 为温度差;αs为固体的热电
为温度差;αs为固体的热电
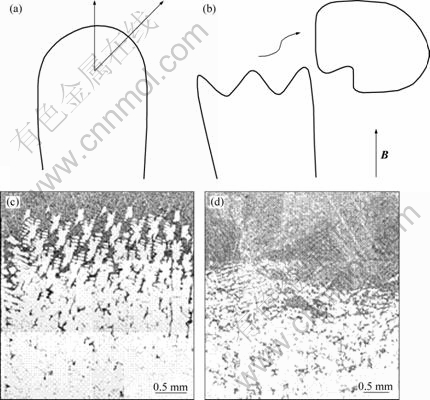
图8 枝晶生长方向和易磁化方向竞争示意图
Fig.8 Schematic diagrams of competition of easy magnetization axis and growth direction: (a) Easy axis different from dendrite growth direction; (b) Dendrite crash under magnetic force; (c) Dendrite growth, 0T; (b) Dendrite growth, 4 T
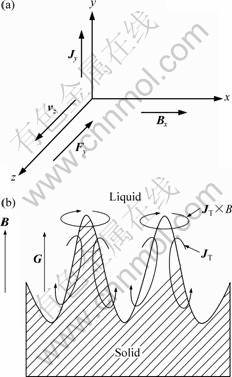
图9 电磁制动效应与热电磁对流效应的示意图
Fig.9 Schematic diagrams of EMB under magnetic field (a) and thermoelectromagnetic convection (b)
因子;αl为液体的热电子因子。
由上述可知,热电磁力(FT)与B成正比,电磁制动力Fz与B2成正比,因此,热电磁力和磁阻尼力表现出竞争作用关系。
当施加的磁场强度较低时(<0.1T),热电磁效应占到了主导地位,而磁阻尼效应几乎无法显现。这时,枝晶前沿只受到热电磁力的作用。热电磁力增强了凝固界面前沿液体的扰动,改变了固液界面和枝晶间的流动结构,从而改变固液界面前沿溶质的分布及局部的成分过冷度。枝晶两侧溶质浓度高于枝晶尖端前侧的溶质浓度,抑制了枝晶的粗化,约束了枝晶的生长方向。所以在低磁场作用下,枝晶生长规则,枝晶大小细化。
当施加的磁场强度较低时(>2T),虽然磁阻尼效应占据主导地位,但是根据前文所述,磁阻尼效应在定向凝固过程中主要起到可减少界面处的扰动,有利于柱状晶的生长,抑制等轴晶的生成的作用,这无法解释枝晶破坏的现象。不过随着施加的磁场强度增大,枝晶内部受到的热电磁力也在增大(见图10),由于热电磁环流的存在,枝晶顶端和枝晶底部同时受到方向相反的两个力的作用,顶部受一逆时针方向力的作用,而底部受到顺时针方向里的作用,当两个力足够大时,会将枝晶扭断,破坏枝晶的生长。这正好和本实验的结果吻合。所以枝晶的破坏可能是由磁各向异性和热电磁对流的综合影响而产生的。
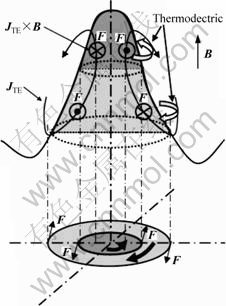
图10 磁场作用下晶体结构示意图[11]
Fig.10 Schematic diagram of thermoelectric moment applied on dendrite under magnetic field[11]
4 结论
1) 弱磁场(<0.1T)可以使枝晶生长规则化,枝晶细化,枝晶个数增多,且磁场越大,枝晶个数越多。
2) 强磁场(>2T)会破坏枝晶的规则生长,使界面坍塌。无磁场时,枝晶生长规则有序;施加磁场后,枝晶逐渐受到破坏,向海藻状组织转变。枝晶的破坏与磁场和生长速率有关,磁场越强,枝晶破坏越严重,随着生长速率的增加,枝晶破坏程度减小。
3) 在定向凝固过程中,施加磁场诱发热电磁对流(TEMC),可能是枝晶数目增加和枝晶被破坏的主要原因,同时磁各向异性也可能是破坏枝晶的原因。
REFERENCES
[1] UTECH H P, FLEMINGS M C. Elimination of solute banding in indium antimonide crystals by growth in a magnetic field[J]. J Appl Phys, 1966, 37(5): 2021-2024.
[2] CHEDZEY H A, HURLE D T J. Avoidance of growth-striae in semiconductor and metal crystals grown by zone-melting techniques[J]. Nature, 1966, 210: 933-934.
[3] WITT A F, HERMAN C J, GATOS H C. Czochralski-type crystal growth in transverse magnetic fields[J]. J Mater Sci, 1970, 5: 822-824.
[4] SEN S, LEFEVER R A, WILCOX W R. Influence of magnetic field on vertical Bridgman-Stockbarger growth of InxGa1-xSb[J]. J Cryst Growth, 1978, 43: 526-530.
[5] OREPER G M, SZEKELY J. The effect of an externally imposed magnetic field on buoyancy driven flow in a rectangular cavity[J]. J Cryst Growth, 1983, 64: 505-515.
[6] KANG J Y, OKANO Y, HOSHIKAWA K. Influence of a high vertical magnetic field on Te dopant segregation in InSb grown by the vertical gradient freeze method[J]. J Cryst Growth, 1994, 140: 435-438.
[7] OSTROGORSKY A G. Model of the effective segregation coefficient applied to low-convection solidification in microgravity[J]. J Cryst Growth, 1993, 128: 207-212.
[8] BOETTINGER W J, BIANCANIELLO F, CORIELL S. Solutal convection induced macrosegregation and the dendrite to composite transition in off-eutectic alloys[J]. Met Trans A, 1981, 12(2): 321-327
[9] TEWARI S N, SHAH R, SONG H. Effect of magnetic field on the microstructure and macrosegregation in directionally solidified Pb-Sn alloys[J]. Met Mater Trans A, 1994, 25(7): 1535-1542.
[10] LI X, REN Z M, FAUTRELLE Y. Effect of a vertical magnetic field on the dendrite morphology during Bridgman crystal growth of Al-4.5wt%Cu[J]. Journal of Crystal Growth, 2006, 290: 571-575.
[11] LI X, REN Z M , FAUTRELLE Y. Influence of thermoelectric effects on the solid-liquid interface shape and cellular morphology in the mushy zone during the directional solidification of Al-Cu alloys under a magnetic field[J]. Acta Materialia, 2007, 55: 3803-3813.
[12] LI X, REN Z M, FAUTRELLEY. Influence of an axial high magnetic field on the liquid-solid transformation in Al-Cu hypoeutectic alloys and on the microstructure of the solid[J]. Acta Materialia, 2007, 55: 1377-1386.
[13] 郭建亭.一种性能优异的低成本定向凝固镍基高温合金DZ417G[J]. 金属学报, 2002, 38(11): 1163-1174.
GUO Jian-ting. A directionally solidified nickel-base superralloy DZ417G with excellent properties and low cost[J]. Acta Metallurgica Sinica, 2002, 38(11): 1163-1174.
[14] 肖 璇, 郭建亭, 于海朋. 固溶处理冷却速度对合金组织性能的影响[J]. 材料研究学报, 2006, 20(5): 533-537.
XIAO Xuan, GUO Jian-ting, YU Hai-peng. Effect of cooling rate from solution heat treatment on the microstructure and mechanical Properties of superalloy DZ417G[J]. Chinese Journal of Materials Research, 2006, 20(5): 533-537.
[15] REN W L, ZHANG T, REN Z M, ZHAO A K, ZHONG Y B, GUO J T. A dramatic increase in dendrite number for directionally solidified superalloy DZ417G with a strong static magnetic field[J]. Materials Letters, 2009, 63: 382-385.
[16] LI X, REN Z M, FAUTRELLEY. Effect of a high magnetic field on the microstructure in directionally solidified Al-12 wt%Ni alloy[J]. Journal of Crystal Growth, 2007, 306: 187-194.
(编辑 李艳红)
基金项目:国家基础研究发展计划资助项目(2007CB616904);上海市科委资助项目(071005103,08dj1400404,08DZ1130100);教委项目和长江学者和创新团队发展计划资助(IRT0739);国家自然科学基金资助项目(50701031)
收稿日期:2009-10-13;修订日期:2010-04-16
通信作者:任忠鸣,教授,博士;电话:021-56331102;E-mail:zmren@shu.edu.cn