Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 27(2017) 1180-1187
Recovery of valuable metals from zinc leaching residue by sulfate roasting and water leaching
Guo-min JIANG1,3, Bing PENG1,2, Yan-jie LIANG1,2, Li-yuan CHAI1,2, Qing-wei WANG1,2, Qing-zhu LI1,2, Ming HU3
1. School of Metallurgy and Environment, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China;
2. Chinese National Engineering Research Center for Control & Treatment of Heavy Metal Pollution, Changsha 410083, China;
3. Changsha Science Environmental Technology Co., Ltd., Changsha 410000, China
Received 30 June 2016; accepted 11 January 2017
Abstract: Zinc leaching residue (ZLR), produced from traditional zinc hydrometallurgy process, is not only a hazardous waste but also a potential valuable solid. The combination of sulfate roasting and water leaching was employed to recover the valuable metals from ZLR. The ZLR was initially roasted with ferric sulfate at 640 °C for 1 h with ferric sulfate/zinc ferrite mole ratio of 1.2. In this process, the valuable metals were efficiently transformed into water soluble sulfate, while iron remains as ferric oxide. Thereafter, water leaching was conducted to extract the valuable metals sulfate for recovery. The recovery rates of zinc, manganese, copper, cadmium and iron were 92.4%, 93.3%, 99.3%, 91.4% and 1.1%, respectively. A leaching toxicity test for ZLR was performed after water leaching. The results indicated that the final residue was effectively detoxified and all of the heavy metal leaching concentrations were under the allowable limit.
Key words: zinc leaching residue; sulfate roasting; water leaching; valuable metals recovery
1 Introduction
In China, a large amount of zinc leaching residue (ZLR) is produced from the traditional zinc hydrometallurgy process. The huge stockpiles of ZLR not only pose an environmental problem, but also result in a great loss of valuable metals, since ZRL contains a high content of heavy metal elements, such as zinc, lead, manganese, cadmium and arsenic [1]. It has been demonstrated that such toxic elements have the potential to be dissolved in rain water, resulting in a negative impact on the environment [2-7]. Therefore, it is urgent to develop a method for ZLR disposal, including the recycling of valuable metals to relieve environmental pollution [8,9]. Zinc and iron, presenting in the form of zinc ferrite, are the major elements in ZLR. Moreover, the cadmium can replace zinc in the crystal lattice of zinc ferrite and form cadmium-bearing zinc ferrite [10]. These compounds are very stable and difficult to dissolve through conventional leaching process. Generally, pyrometallurgical and hydrometallurgical processes are employed to treat such residues. Onsan refinery of Korea Zinc uses top submerged lancing (TSL) technology to recover the valuable metals in such residues. Approximately 82% of Zn, 92% of Pb, 86% of Ag and 61% of Cu in the residue can be recovered in this process [11]. In China, Waelz kilns have been adopted in some factories to fume metal elements by using coal as heat source. Approximately 75% of Zn, 68% of Pb and 80% of Ge in the residue can be recovered [12,13]. However, these processes have some shortcomings due to a high fixed investment and operating costs, as well as a serious air pollution during fuming.
Recently, a series of cleaner recovery technologies have been developed for ZRL recovery. It has been proved that high metal recovery rate can be achieved in these processes, such as high pressure acid leaching, two-staged acid leaching, microwave caustic leaching and highly concentrated alkaline leaching [8,14-22]. However, during these leaching processes, the iron component is easy to be extracted, and it requires a sophisticated process to remove the iron impurities. The traditional purification technologies, such as roasting with Na2CO3, reduction roasting magnetization technologies and sulfate roasting have been studied [23-27]. These pyrometallurgy methods can avoid highly sophisticated multi-stepped hydrometallurgical procedures, but these studies have not shown how to recover the cadmium, copper and manganese present in the waste.
This work aims to present a clean and effective approach to recover valuable metal components from ZLR, and avoid the potential risk in environmental pollution. The presented procedure comprises ferric sulfate roasting and water leaching. In the first stage, the valuable heavy metals can be efficiently converted into metal sulfates. Then the metal sulfates can be easily separated from the sludge with water leaching, leaving a detoxified residue. And the sulfate roasting and water leaching processes were optimized.
2 Experimental
2.1 Materials and analysis
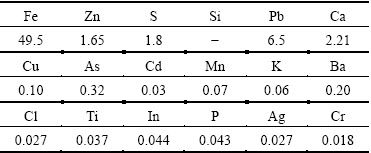
Zinc leaching residue used in this work was provided by a zinc hydrometallurgical plant in Hunan Province, China. The samples were dry ground and sieved to yield a particle size below 74 μm before using in the experiment. The chemical composition obtained by X-ray fluorescence spectrometer (XRF) is listed in Table 1. It indicates that Zn and Fe are the major components in the residue. Additionally, the toxic heavy metals such as Pb, As, Cd are also observed in the residue. Based on the XRD analysis (Fig. 1), it is suggested that Zn and Fe mainly exist in the form of ZnFe2O4. The characteristic peak corresponding to CaSO4 is also identified.
Table 1 Chemical composition of zinc leaching residue by XRF (mass fraction, %)
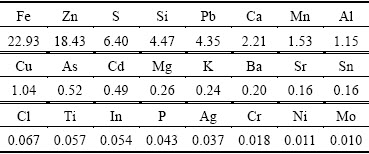
The chemical composition of the samples was characterized by XRF (Rigaku, ZSX-Ⅱ). The phases of initial and roasted zinc leaching residue were detected by XRD (Rigaku, TTR-Ⅲ). A TG differential scanning calorimetry investigation was carried out using a thermal analyzer (STA449F3A-0488M). The morphological changes during the roasting process were detected by SEM (JEOL Ltd., JSM-6360V). The heavy metal concentrations in the leachate were analyzed with inductively coupled plasma (ICP-OES (Opima 5300DV type).
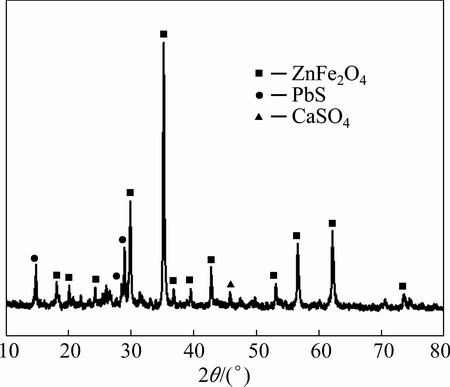
Fig. 1 XRD pattern of zinc leaching residue
2.2 Sulfate roasting
An appropriate amount of ferric sulfate was mixed with 10 g of ZLR ground by mortar and pestle. Then, the mixture was put into a corundum crucible with a cover and roasted in a muffle furnace at a setting temperature. The roasted products were subsequently weighed, ground and analyzed. Zinc ferrite is the major component in the residue, and it is hard to decompose sulfate. Therefore, two parameters, including decomposition rate of zinc ferrite and the proportion of zinc sulfate (ZnSO4/ZnT), were employed to evaluate the sulfate roasting effects. These parameters were calculated through the following equations:
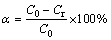 (1)
(1)
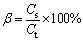 (2)
(2)
where α is the decomposition rate of zinc ferrite, and C0 and Cr represent the zinc ferrite contents in the initial and roasted residues, respectively. β is the proportion of zinc sulfate, Cs represents the zinc sulfate content in the roasted residue, and Ct is the total zinc content in the roasted residue.
2.3 Water leaching
Water leaching was conducted after sulfate roasting in order to dissolve the formed metals sulfate and detoxify the residue. After water leaching at a controlled temperature, the residue was separated from the liquid phase by filtration and the leachate was analyzed by ICP. The leaching rate of metals was used to evaluate the water leaching effects, determined as follows:
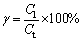 (3)
(3)
where γ is the recovery rate of valuable metals or iron, Cl is the zinc or iron content in the leaching liquid, and Ct is the total zinc or iron content in the roasted residue.
2.4 Leaching toxicity
The treated residues were dried at 80 °C for 12 h and finally used to evaluate leaching toxicity. The leaching toxicity test of the residue was performed according to USEPA Method 1311 [28].
3 Results and discussion
3.1 Sulfate roasting of ZLR
3.1.1 Optimization of sulfate roasting
During the sulfate roasting process, a series of possible sulfate reactions occurred as follows, where Me stands for metal, such as Cu, Mn, or Zn.
Fe2(SO4)3→Fe2O3+3SO3(g) (4)
ZnFe2O4+SO3(g)→ZnSO4+Fe2O3 (5)
CdxZn1-xFe2O4+SO3→(1-x)ZnSO4+xCdSO4+Fe2O3 (6)
MeO+SO3→MeSO4 (7)
The effects of ferric sulfate dosage, roasting temperature and reaction time on decomposition rate of zinc ferrite (α) and the proportion of ZnSO4/ZnT (β) are represented in Fig. 2. The effect of ferric sulfate dosage was investigated at 640 °C for 2 h. As shown in Fig. 2(a), with the increasing of ferric sulfate/zinc ferrite mole ratio to 1.2, the α and β rose to 86.5% and 91.7%, respectively. The increased proportion of zinc sulfate results from sulfate decomposition of zinc ferrite, and it is evident that sulfate roasting effect has a positive correlation with ferric sulfate concentration, because more ferric sulfate results in more sulfur trioxide, which can react with zinc ferrite, cadmium-bearing zinc ferrite and metallic oxide at 640 °C, as shown in Eqs. (5)-(7). However, the decomposition rates remain nearly constant when the mole ratio exceeds 1.2. Thus, it can be concluded that the mole ratio of ferric sulfate/zinc ferrite of 1.2 is sufficient for a complete sulfate reaction. Roasting temperature and time play important roles in the sulfate roasting of ZLR. Figure 2(b) shows the influences of temperature on sulfate roasting when the mole ratio of ferric sulfate/zinc ferrite is 1.2. As shown in Fig. 2(b), the decomposition rate of zinc ferrite and the proportion of zinc sulfate increase with temperature increasing up to 640 °C. The decomposition rate reaches its maximum (85.9%) when the temperature was 640 °C and then it falls slightly to 82.3% as the temperature continues to increase. It may be attributed to the fact that the ferric sulfate is more easily to transform into sulfur trioxide at higher temperatures, moreover, the sulfate reactions can be improved under such high-temperature. However, sulfur trioxide also easily lost at higher temperatures and reduced the degree of sulfating. Thus, the decomposition rate of zinc ferrite and the proportion of zinc sulfate decrease when the temperature exceeds 640 °C. The roasting duration also significantly influences the sulfate roasting effects. Figure 2(c) indicates that the decomposition rate of zinc ferrite and the proportion of zinc sulfate have a positive correlation with roasting time in the first 1 h. After that, the rates remain at a stable level. In conclusion, the optimum sulfate roasting operations should be performed at 640 °C for 1 h with ferric sulfate/zinc ferrite mole ratio of 1.2.
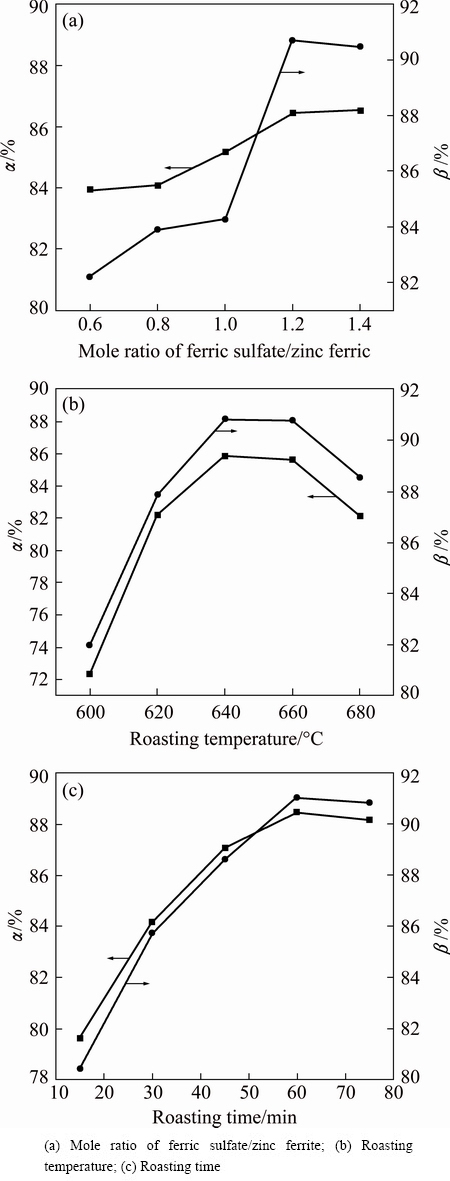
Fig. 2 Effects of roasting parameters on sulfate roasting
3.1.2 Sulfate roasting behavior and phase transition
The TG and DTG curves of the ZLR mixed with different contents of ferric sulfate are shown in Fig. 3. It shows that the mass fraction of the mixtures decreases gradually with the extension of time (Fig. 3(a)). Moreover, the mass loss is faster for the mixture with more ferric sulfate. The results indicate that ferric sulfate dosage causes a positive effect on the sulfate roasting of ZLR. After roasting with different ferric sulfate contents at 640 °C for 1 h, the mass loss is 16.0%, 22.3%, 25.7% and 29.4% with ferric sulfate/zinc ferrite mole ratio of 0.8, 1.0, 1.2, 1.4, respectively. In addition, Fig. 3(a) shows that the mass loss mainly occurs within the first 30 min, thereafter, the mass loss is almost constant. Simultaneously, Fig. 3(b) shows that the rate of mass loss is always less than zero in the first 30 min and it increases to zero then remains unchanged with the extension of time. These results indicate that the sulfate reactions are effectively completed in the first 30 min. In addition, Fig. 3(b) shows that the mass loss rate of the mixtures gradually increases with the mole ratio of ferric sulfate/zinc ferrite increasing up to 1.2, and the rate remains nearly unchanged when it exceeds 1.2. However, the rate of mass loss is determined by the rate of ferric sulfate decomposition (Eq. (4)) and the sulfate reactions (Eqs. (5)-(7)). Thus, this result reveals that the sulfate decomposition reaction and sulfation reactions reach dynamic balance when the mole ratio of ferric sulfate/zinc ferrite reaches 1.2. This conclusion is completely verified by our experimental results, which reveals that the decomposition rate of zinc ferrite and the proportion of zinc sulfate remain at a stable level when the mole ratio of ferric sulfate/zinc ferrite reaches 1.2.
XRD analyses were performed to identify the phase transformation that occurs during sulfate roasting, as shown in Fig. 4. It indicates that the main phase in the residue is zinc ferrite. When the residue is roasted under appropriate conditions (1.2 mole ratio, 640 °C, 1 h), the characteristic peaks of zinc ferrite completely disappear. Simultaneously, a new characteristic peak of ferric oxide and zinc sulfate appear. This result indicates that the zinc ferrite is transformed into zinc sulfate. Besides, the transformation of lead sulfide in the ZLR into lead sulfate in the roasted residue can be also observed in Fig. 4. These findings prove that the sulfate reactions happen in the process of roasting.
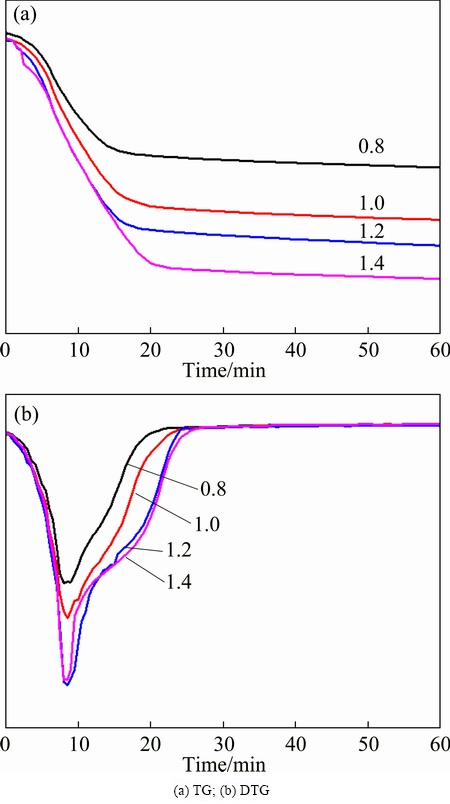
Fig. 3 TG-DTG curves for sulfate roasting with various ferric sulfate/zinc ferrite mole ratio
Fig. 4 XRD patterns of residue
The morphological changes of the ZLR after the sulfate roasting were examined by SEM, and the results are given in Fig. 5. It shows that the particles size of the raw material and the roasted ZLR (under the optimum conditions) is smaller than 5 μm. This result can be verified by the particle size distributions analyzed by LPSA. The result presented in Fig. 6 indicates that the d90 values of the raw sample and roasted ZLR are 7.50 μm and 7.87 μm, respectively, and their d50 values are 1.71 μm and 2.05 μm, respectively. Obviously, the particle size slightly increases after the sulfate roasting, however, the roasted ZLR particle size is still very small, which is favorable for the subsequent water leaching process.
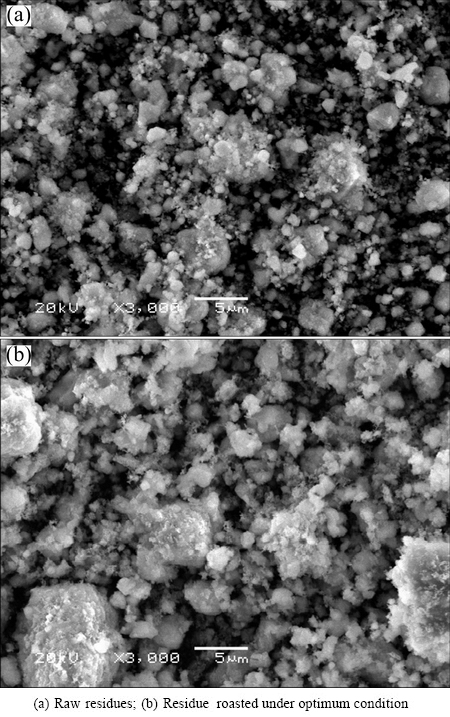
Fig. 5 SEM images of residues
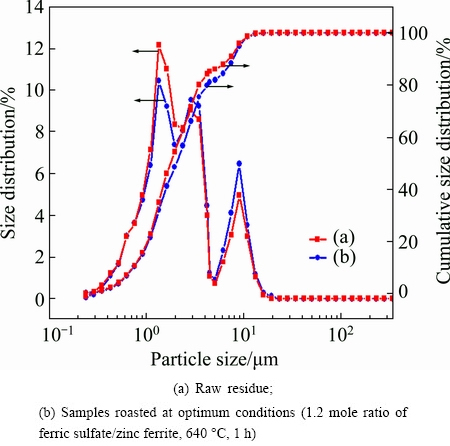
Fig. 6 Particle size distribution of residues
3.1.3 Molecular bonding structure variation
Figure 7 shows the FTIR spectra of raw residue and roasted sample in the frequency region between 400 and 1100 cm-1. For the spectrum of raw residue, the bands around 680 cm-1 and 1050 cm-1 are due to  bending mode, which can be attributed to the existence of CaSO4 according to XRD pattern in Fig. 1. The bands at ~430 cm-1 and 520 cm-1 have been assigned to the bending vibration of Zn—O, and the band located at 450 cm-1 is related to vibration of Fe—O [29], which demonstrates the presence of ZnFe2O4. Moreover, the strong and broad band at 870 cm-1 is related to the vibration mode of Si—O, caused by the zinc silicate containing in the raw residue. Structure changes in the residue are reflected especially in the disappearance of peaks at ~430, 520, 450 and 870 cm-1 as well as the appearance of new peak at 700 cm-1 which corresponds to vibration of
bending mode, which can be attributed to the existence of CaSO4 according to XRD pattern in Fig. 1. The bands at ~430 cm-1 and 520 cm-1 have been assigned to the bending vibration of Zn—O, and the band located at 450 cm-1 is related to vibration of Fe—O [29], which demonstrates the presence of ZnFe2O4. Moreover, the strong and broad band at 870 cm-1 is related to the vibration mode of Si—O, caused by the zinc silicate containing in the raw residue. Structure changes in the residue are reflected especially in the disappearance of peaks at ~430, 520, 450 and 870 cm-1 as well as the appearance of new peak at 700 cm-1 which corresponds to vibration of  . Besides, roasting of ZLR resulting in an increased intensity of the 1050 cm-1 indicates the increase of
. Besides, roasting of ZLR resulting in an increased intensity of the 1050 cm-1 indicates the increase of  . It means that zinc ferrite and zinc silicate in the raw residue are effectively converted into zinc sulfate by sulfate roasting.
. It means that zinc ferrite and zinc silicate in the raw residue are effectively converted into zinc sulfate by sulfate roasting.
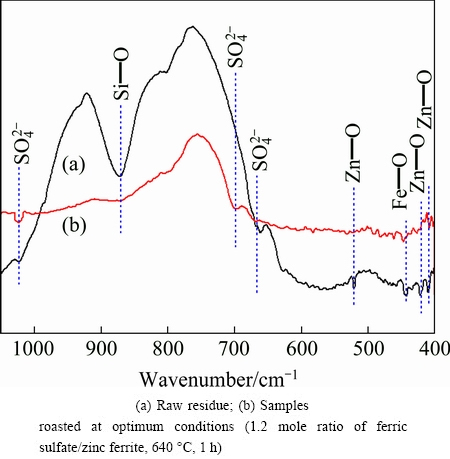
Fig. 7 FTIR spectra of residues
3.2 Water leaching of sulfate-roasted ZLR
3.2.1 Effect of leaching conditions on recovery of valuable metals
To obtain a high recovery rate of valuable metals, the sulfate roasted residues were subjected to leaching with water. The effects of leaching temperature, leaching time and liquid/solid ratio on the recovery of valuable metals were investigated, and the results are shown in Fig. 8. It shows that, under room temperature (25 °C), zinc, manganese, copper, cadmium and iron recovery rates are 92.4%, 93.3%, 99.3%, 91.4% and 1.1%, respectively. However, there is no significant change in recovery rate with the increase of temperature. Therefore, the optimum temperature is determined to be 25 °C. The effects of leaching time and liquid/solid ratio on the recovery rates of valuable metals were also studied. As shown in Figs. 8(b) and (c), the recovery rates of valuable metals increase, but the iron concentration remains in a low level and does not change with the change of leaching time or liquid/solid ratio. It is attributed to the high water solubility of the sulfate and the insolubility of the ferric oxide. A short leaching periods and small liquid/solid ratios are more beneficial in practical application. Therefore, the optimum leaching parameters are temperature of 25 °C, leaching for 10 min with a liquid/solid ratio of 10.
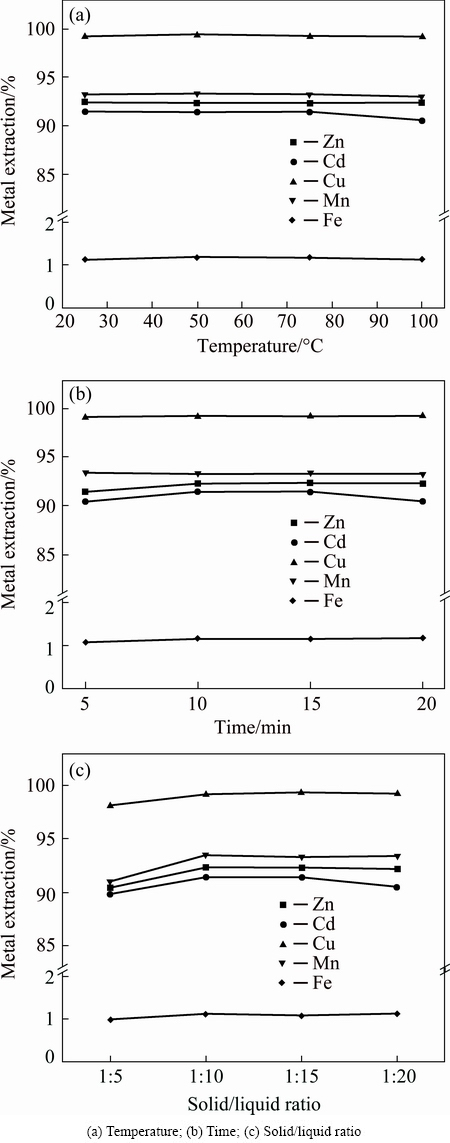
Fig. 8 Effects of leaching parameters on valuable metals recovery
3.2.2 Chemical composition and phase transformation of water-leached residue
The chemical composition of the sample after leaching under the optimum conditions is shown in Table 2. Compared to the raw residue, the contents of Zn, as well as other toxic heavy metals such as As and Cd, are decreased, while Fe and Pb are enriched, whose contents account for 49.5% and 6.5% respectively.
Table 2 Chemical composition of water-leached residue by XRF (mass fraction, %)
XRD pattern of the water-leached residue is shown in Fig. 9. The characteristic peaks of zinc sulfate disappear while ferric oxide and lead sulfate become the main phases of water-leached residue. This result indicates that the zinc sulfate is completely dissolved in water, leaving the ferric oxide and lead sulfate in the residue.
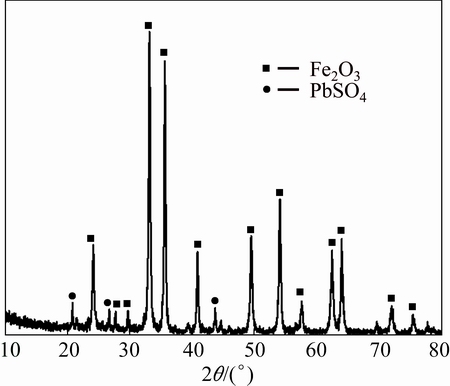
Fig. 9 XRD pattern of water leaching residue
3.3 Leaching toxicity
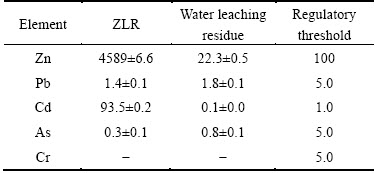
The water-leached residue was finally used to evaluate leaching toxicity and the results are shown in Table 3. It shows that Zn and Cd leaching concentrations for raw sludge are 4589 mg/L and 93.5 mg/L, respectively, far exceeding the regulatory thresholds, indicating that the ZLR exhibits high environment toxicity and serious potential ecological risk. However, the zinc and cadmium concentrations decrease sharply to 22.3 mg/L and 0.1 mg/L respectively after sulfate roasting and water leaching, which are far below the thresholds. It is attributed to extraction of zinc and cadmium with sulfate roasting and water leaching. Moreover, the concentrations of other toxic elements such as lead and arsenic are already lower than the thresholds. Therefore, the final water-leached residue is harmless to the environment and safe to be stockpiled for future treatment or recycle.
Table 3 TCLP test results of ZLR and water leaching residue (mg/L)
4 Conclusions
A combination process of sulfate roasting and water leaching was developed for recovery and detoxification of ZLR. The optimum process parameters of sulfate roasting were determined to be reaction time of 1 h, temperature of 640 °C and ferric sulfate/zinc ferrite mole ratio of 1.2. Employing these experimental conditions resulted in a zinc ferrite decomposition rate of 85% and ZnSO4/ZnT of 91.7%. After sulfate roasting, the water leaching rates of zinc, manganese, copper and cadmium in ZLR are 92.4%, 93.3%, 99.3%, and 91.4%, respectively, while the iron remains in the water-leached residue. Moreover, the heavy metal leaching concentrations were significantly decreased after the treatments, so it will be beneficial to the ultimate disposal of the leaching residue.
References
[1] MIN Xiao-bo, XIE Xian-de, CHAI Li-yuan, LIANG Yan-jie, LI Mi, KE Yong. Environmental availability and ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in zinc leaching residue [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2013, 23: 208-218.
[2] ZENG Fan-fu, WEI Wei, LI Man-sha, HUANG Rui-xue, YANG Fei, DUAN Yan-ying. Heavy metal contamination in rice-producing soils of Hunan province, China and potential health risks [J]. International Journal of Environmental Research & Public Health, 2015, 12(12): 15584-15593.
[3] LI Yuan-cheng, Min Xiao-bo, CHAI Li-yuan, SHI Mei-qing, TANG Chong-Jian, WANG Qing-wei, LIANG Yan-jie, LEI Jie, LIYANG Wen-jun. Co-treatment of gypsum sludge and Pb/Zn smelting slag for the solidification of sludge containing arsenic and heavy metals [J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 2016, 181: 756-761.
[4] XIE Xian-de, MIN Xiao-bo, CHAI Li-yuan, TANG Chong-jian, LIANG Yan-jie, LI Mi, KE Yong, CHEN Jie, WANG Yan. Quantitative evaluation of environmental risks of flotation tailings from hydrothermal sulfidation–flotation process [J]. Environmental Science & Pollution Research, 2013, 20(9): 6050-6058.
[5] LI Chang-xin, ZHONG Hong, WANG Shuai, XUE Jian-rong. Leaching behavior and risk assessment of heavy metals in a landfill of electrolytic manganese residue in western Hunan, China [J]. Human & Ecological Risk Assessment, 2014, 20(5): 1249-1263.
[6] LIANG Yan-jie, MIN Xiao-bo, CHAI Li-yuan, WANG Mi, LIYANG Wen-jun, PAN Qing-lin, OKIDO Masazumi. Stabilization of arsenic sludge with mechanochemically modified zero valent iron [J]. Chemosphere, 2017, 168: 1142-1151.
[7] WANG Zhen-xing, CHAI Li-yuan, YANG Zhi-hui, WANG Yun-yan, WANG Hai-ying. Identifying sources and assessing potential risk of heavy metals in soils from direct exposure to children in a mine-impacted city, Changsha, China [J]. Journal of Environmental Quality, 2010, 39:1616-1623.
[8] ERDEM M,  A. Environmental risk assessment and stabilization/solidification of zinc extraction residue: II. Stabilization/ solidification [J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2011, 105(3): 270-276.
A. Environmental risk assessment and stabilization/solidification of zinc extraction residue: II. Stabilization/ solidification [J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2011, 105(3): 270-276.
[9]  A, ERDEM M. Environmental risk assessment and stabilization/solidification of zinc extraction residue: I. Environmental risk assessment [J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2010, 100: 103-109.
A, ERDEM M. Environmental risk assessment and stabilization/solidification of zinc extraction residue: I. Environmental risk assessment [J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2010, 100: 103-109.
[10] GRAYDON J, KIRK D. A microscopic study of the transformation of sphalerite particles during the roasting of zinc concentrate [J]. Metallurgical Transactions B, 1988, 19: 141-146.
[11] HOANG J, REUTER M A, MATUSEWICZ R, HUGHES S, PIRET N. Top submerged lance direct zinc smelting [J]. Minerals Engineering, 2009, 22: 742-751.
[12] HAY S M, RANKIN W J. Recovery of iron and zinc from blast furnace and basic oxygen furnace dusts: A thermodynamic evaluation [J]. Minerals Engineering, 1994, 7(8): 985-1001.
[13] JU Shao-hua, ZHANG Yi-fei, ZHANG Yi, XUE Pei-yi, WANG Yi-hui. Clean hydrometallurgical route to recover zinc, silver, lead, copper, cadmium and iron from hazardous jarosite residues produced during zinc hydrometallurgy [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2011, 192: 554-558.
[14] JHA M K, KUMAR V, SINGH R J. Review of hydrometallurgical recovery of zinc from industrial wastes [J]. Resources, Conservation and Recycling, 2001, 33: 1-22.
[15]  MATYSEK D. Selective leaching of zinc from zinc ferrite with hydrochloric acid [J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2009, 95: 179-182.
MATYSEK D. Selective leaching of zinc from zinc ferrite with hydrochloric acid [J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2009, 95: 179-182.
[16] LECLERC N, MEUX E, LECUIRE J M. Hydrometallurgical recovery of zinc and lead from electric arc furnace dust using mononitrilotriacetate anion and hexahydrated ferric chloride [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2002, 91: 257-270.
[17] LECLERC N, MEUX E, LECUIRE J M. Hydrometallurgical extraction of zinc from zinc ferrites [J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2003, 70: 175-183.
[18] LI Cun-xiong, WEI Chang, FAN Gang, YANG Xiu-li, XU Hong-sheng, DENG Zhi-gan, LI Min-ting, LI Xing-bin. Pressure acid leaching high silicone zinc oxide ore [J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2009, 19(9): 1678-1683. (in Chinese)
[19] LIU Qing, ZHAO You-cai, ZHAO Guo-dong. Production of zinc and lead concentrates from lean oxidized zinc ores by alkaline leaching followed by two-step precipitation using sulfides [J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2011, 110: 79-84.
[20] MOGHADDAM J, SARRAF-MAMOORY R, ABDOLLAHY M, YAMINI Y. Purification of zinc ammoniacal leaching solution by cementation: Determination of optimum process conditions with experimental design by Taguchi's method [J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2006, 51: 157-164.
[21] RUSEN A, SUNKA A S, TOPKAYA Y A. Zinc and lead extraction from  leach residues by using hydrometallurgical method [J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2008. 93: 45-50.
leach residues by using hydrometallurgical method [J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2008. 93: 45-50.
[22] XU Hong-sheng, WEI Chang, LI Cun-xiong, FAN Gang, DENG Zhi-gan, LI Min-ting, LI Xing-bin. Sulfuric acid leaching of zinc silicate ore under pressure [J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2010, 105: 186-190.
[23] LI Mi, PENG Bing, CHAI Li-yuan, PENG Ning, YAN Huan, HOU Dong-ke. Recovery of iron from zinc leaching residue by selective reduction roasting with carbon [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2012, 237-238: 323-330.
[24] PENG Ning, PENG Bing, CHAI Li-yuan, LI Mi, WANG Ji-ming, YAN Huan, YUAN Yuan. Recovery of iron from zinc calcines by reduction roasting and magnetic separation [J]. Minerals Engineering, 2012, 35: 57-60.
[25] YAN Huan, CHAI Li-yuan, PENG Bing, LI Mi, PENG Ning, HOU Dong-ke. A novel method to recover zinc and iron from zinc leaching residue [J]. Minerals Engineering, 2014, 55: 103-110.
[26] YU Gang, PENG Ning, ZHOU Lan, LIANG Yan-jie, ZHOU Xiao-yuan, PENG Bing, CHAI Li-yuan, YANG Zhi-hui. Selective reduction process of zinc ferrite and its application in treatment of zinc leaching residues [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2015, 25: 2744-2752.
[27] ZHAI Xiu-jing, LI Nai-jun, ZHANG Xu, FU Yan, JIANG Lan. Recovery of cobalt from converter slag of Chambishi Copper Smelter using reduction smelting process [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2011, 21: 2117-2121.
[28] US-EPA. Test method for the evaluation of solid waste, physical/chemical methods, Method 1311: Toxicity characteristic leaching procedure [S]. Washington, DC: U. S. Environmental Protection Agency, 1992.
[29] LI Mi, PENG Bing, CHAI Li-yuan,PENG Ning, XIE Xian-de, YAN Huan. Technological mineralogy and environmental activity of zinc leaching residue from zinc hydrometallurgical process [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2013, 23(5): 1480-1488.
硫酸盐化焙烧-水浸回收锌浸渣中有价金属
蒋国民1,3,彭 兵1,2,梁彦杰1,2,柴立元1,2,王庆伟1,2,李青竹2,胡 明1,2
1. 中南大学 冶金与环境学院,长沙 410083;
2. 中南大学 国家重金属污染防治工程技术研究中心,长沙 410083;
3. 长沙赛恩斯环保科技有限公司,长沙 410000
摘 要:锌浸渣产生于传统湿法炼锌过程,它是一种危险废物同时也是一种潜在的有价固体废物。用硫酸盐化焙烧-水浸的组合工艺对锌浸渣中有价金属进行回收。首先,锌浸渣在640 °C下与硫酸铁进行混合焙烧,硫酸铁/铁酸锌摩尔比为1.2,硫酸盐化焙烧时间为1 h。在此过程中,废渣中的有价金属转化为可溶的硫酸盐,而铁以氧化铁形式存在。随后,采用水浸法提取有价金属硫酸盐,渣中锌、锰、铜、镉、铁的回收率分别为 92.4%、93.3%、99.3%,91.4%,1.1%。对水浸处理后的废渣进行浸出毒性检测。结果表明,上述工艺可以有效地实现锌浸渣的无害化处理,处理后各重金属浸出毒性均低于限值。
关键词:锌浸渣;硫酸盐化焙烧;水浸;有价金属回收
(Edited by Sai-qian YUAN)
Foundation item: Project (2014FJ1011) supported by Key Project of Science and Technology of Hunan Province, China; Project (201509050) supported by Program for Special Scientific Research Projects of National Public Welfare Industry
Corresponding author: Yan-jie LIANG; Tel: +86-731-88830511; Fax: +86-731-88710171; E-mail: liangyanjie2015@csu.edu.cn
DOI: 10.1016/S1003-6326(17)60138-9