文章编号:1004-0609(2016)-11-2433-07
氧化铝赤泥堆场盐分组成变化
黄 玲1, 2,李义伟1,薛生国1, 2,朱 锋1,吴 川1, 2,王琼丽1
(1. 中南大学 冶金与环境学院,长沙 410083;
2. 中南大学 国家重金属污染防治工程技术研究中心,长沙 410083)
摘 要:以典型赤泥堆场为研究对象,分析自然环境条件下赤泥堆场的盐分组成变化。结果表明:随着堆存年限的增加,赤泥中盐含量呈降低趋势;CO32-是赤泥中占主导地位的阴离子,约占阴离子组成比例的34.14%~73.26%;赤泥可交换态阳离子及水溶态阳离子以Na+为主,可交换态Na+占可交换态阳离子组成比例60.50%~83.94%,水溶态Na+占水溶态阳离子组成比例71.32%~91.16%;随着堆置年限的增加,赤泥中Ca2+、HCO3-含量升高,而Na+、SO42-、CO32-含量降低,K+、Mg2+含量变化趋势不明显;赤泥中盐含量和SO42-、CO32-、Na+含量呈正相关关系,而与HCO3-、Ca2+、Mg2+含量呈负相关关系。Na+含量和CO32-含量过高是赤泥高盐分含量的主要原因,这为赤泥堆场土壤化处置和植被重建过程中盐分调控提供科学依据。
关键词:赤泥;赤泥堆场;堆存年限;盐分组成;土壤化
中图分类号:X173;Q142 文献标志码:A
铝是国民经济发展和国防建设必不可少的战略金属材料,而氧化铝是生产铝的主要原材料。赤泥是氧化铝工业生产过程中产生的高碱性废弃物,盐分含量高,综合利用难度大。由于生产工艺和矿石品位的不同,每生产1 t氧化铝大约排放1.5~2.0 t赤泥。全球积存的待处理赤泥约3×1010 t,并以每年1.2×109 t的速度递增[1]。氧化铝工业过程的赤泥减排和规模化处置已成为世界性难题。为降低赤泥堆存量,科研人员对赤泥减排技术及其二次利用进行了大量研究,开发赤泥工业制品、回收其中有价金属、作为吸附剂应用于环境修复领域等[2-6]。赤泥二次利用受到工艺条件限制并且成本费用较高,综合利用难度大,因此堆存仍然是赤泥的主要处置方式。赤泥堆存不仅占用大量的土地,耗费大量的堆场建设和维护费用,而且污染物迁移风险大,易导致周边环境污染[7]。
赤泥堆场是氧化铝工业产生的强碱性固体废弃物堆存场所。由于赤泥碱性强、盐分含量高、自然风化慢、养分极度缺乏、一般植物难以生长、生态重建难度大,赤泥堆场环境安全问题正严重威胁氧化铝工业的可持续发展。赤泥土壤化是实现氧化铝工业外排赤泥规模化处置的一种可行方法[1],有助于实现赤泥堆场的生态重建、经济安全地消除赤泥堆场环境安全隐患。
基质改良是赤泥土壤化的基础,国外赤泥改良的研究主要围绕盐分控制、碱性调节、改良剂筛选等方面。施用石膏能明显降低赤泥的pH值,通过Ca2+置换可交换性Na+,Na+含量显著降低,为植物在堆场上正常生长提供条件[7];添加粗砂可以提高渗水率,有利于赤泥中的可交换性Na+随水排出,提高植物对赤泥中元素的吸收和生长[7];添加有机物质可以增加赤泥中营养元素生物活性[7];海水淋洗堆场,海水中富含大量Ca2+、Mg2+等,Ca2+、Mg2+可置换出赤泥中Na+,Na+随水渗出,降低赤泥中Na+含量,部分Ca2+、Mg2+和CO32-生成沉淀,降低pH[8]。西洋菜在未经改良的赤泥中表现的非常敏感[9],种子发芽率只有40%,而经添加堆肥改良后的赤泥种子发芽率达到90% [10-11]。尽管国内外学者在赤泥基质改良方面做了大量研究,但主要限于碱性调控和环境修复材料筛选[12]。
盐分含量过高是限制植物生长的主要因素之一,对受赤泥污染的土壤进行植物发芽试验,结果表明受污染的土壤植物发芽率下降25%,影响植物发芽率的主要因素是钠盐含量过高[13]。盐分过高导致持水性差、pH过高,限制植物对营养元素的吸收,影响土壤颗粒大小、微生物的活性和有机物质的转化[14]。环境介质盐分状况直接影响植物生长,也是赤泥土壤化和堆场生态重建关注的重要因素。目前对于赤泥堆场盐分组成现状的研究未见报道,本文作者以华中地区某大型氧化铝企业赤泥堆场为研究对象,通过对自然堆存条件下的赤泥盐分组成状况调查,分析不同堆存年限赤泥含盐量、阴离子、可交换态阳离子以及水溶态阳离子组成的变化,探讨赤泥盐分含量过高的原因,为赤泥堆场植被重建过程中盐分调控提供科学依据。
1 实验
1.1 研究区概况
赤泥样品取自华中地区某大型氧化铝企业赤泥堆场。该区域属温带大陆性季风气候,四季分明,冬季寒冷少风雪,春季干燥多风沙,夏季暖热多降雨,秋季明朗。年均气温14.9 ℃,年均降水量603.5 cm,降雨量分布不均,主要集中在夏季,占全年降雨量的45%~60%。
1.2 样品采集

图1 赤泥堆场样点分布图
Fig. 1 Distribution of sampling point in bauxite residue disposal areas
2014年8~10月,选择已闭库的赤泥堆场为研究区域,赤泥均为拜耳法赤泥(用拜耳法生产工艺提炼铝土矿产生的赤泥)。根据堆置时间的不同选择了环境条件基本一致的6个堆层(见图1)。每个堆层设置3个采样点,每个点位采用梅花形采样并混合均匀,采用便携式采样土钻(荷兰Eijakamp),在每个样点按0~30 cm层、30~60 cm层、60~90 cm层取样,装入取样袋,并对表层(0~30 cm)进行环刀采样。将赤泥样品置于室内自然风干后,去除石砾及植物根系,过孔径2 mm尼龙筛,密封于有编号的聚乙烯样品袋中保存备用。6个堆层对应的赤泥排放年份见表1。
表1 赤泥堆场采样点堆存时间
Table 1 Discharge years of bauxite residue in BRDAs

1.3 样品分析
制备赤泥水比为1:5的浸出液,盐分含量用烘干残渣-质量法测定[15],pH用pH计(雷磁PHS-3C型)测定[15],EC值用电导率仪(雷磁DDS-307型)测定[15],双指示剂中和滴定法测定浸出液中的碳酸根离子和碳酸氢根离子[15],其他阴离子由离子色谱仪测定(861 IC双抑制型,瑞士万通公司生产),水溶态阳离子用ICP-AES(Optima 5300DV型电感耦合等离子体光谱仪,美国 Perkin Elmer公司生产)测定;制备赤泥醋酸铵比为1:5的浸出液,用ICP-AES(Optima 5300DV型电感耦合等离子体光谱仪,美国 Perkin Elmer公司生产)测定浸出液中的可交换性阳离子[16]。
1.4 数据处理
实验数据均采用Microsoft Office Excel 2007进行整理,通过SPSS Statistics 19对赤泥样品数据进行相关性分析,所有图表均采用Origin75绘制。
2 结果与讨论
2.1 不同堆存年限赤泥盐分含量变化
随着堆置年限的增加,赤泥堆场盐分含量呈下降趋势(见图2)。赤泥堆场表层0~30 cm盐含量随堆置年限的增加下降趋势明显(R2=0.9139),赤泥堆场30~60 cm层和60~90 cm层含盐量变化趋势较平缓(R2分别为0.3594和0.3916), 这可能是由于赤泥表层(0~30 cm)受自然风化影响,物理性质得到有效改善,影响盐分的分布。随着堆置年限增加,赤泥经自然风化作用出现土壤化现象,堆存20年的赤泥堆场上发现少量的植物生长,EC值从3.73 mS/cm(新鲜赤泥)降低至0.36 mS/cm [17],表明自然风化过程中盐分含量逐渐降低。盐分易随水迁移,而水分运动受质地影响,新鲜赤泥的物理性质接近于粉砂粘土类的物理性质,颗粒间孔隙度小,黏性强,水分不易渗透,盐分离子滞留在赤泥溶液中导致新鲜赤泥盐分含量较高。容重反应土壤通透性,影响土壤孔隙度及土壤通气透水性能,进而影响盐分离子随水的渗透能力,在自然堆存过程中,赤泥容重降低、孔隙度增加,赤泥透水透气性能增强,盐分随水流失,因此随堆存年限的增加,盐分含量逐渐降低。
Z1、Z2、Z3 3个堆积年限的赤泥盐分主要聚集在赤泥堆场0~30 cm层,而Z4、Z5、Z6 3个堆积年限的赤泥盐分主要聚集在30~60 cm层和60~90 cm层,Z4盐分含量分布由大到小的区域为30~60 cm层、60~90 cm层、0~30 cm层,Z5盐分含量在30~60 cm层和60~90 cm层相近,Z6盐分含量由大到小的区域为60~90 cm层、30~60 cm层、0~30 cm层(见图2),Z4、Z5、Z6表现出盐分逐渐向下渗透的现象。查询当地气象局资料显示,八月份降雨量达到120 mm,对赤泥盐分起淋溶脱盐的作用,表层(0~30 cm)含盐量随水向下渗透,降雨量也是影响盐分分布的主要因素。Z1、Z2、Z3盐分含量分布由大到小的区域为:0~30 cm层、60~90 cm层、30~60 cm的层,可能是由于容重和孔隙度虽然随着堆置年限的增加有所改善,但仍然限制表层含盐量向下渗透。因此,降雨量和孔隙度都是影响赤泥盐分分布的重要因素。

图2 赤泥堆场不同堆积年限的赤泥盐含量
Fig. 2 Salt content of bauxite residue in different stacking ages
2.2 不同堆存年限赤泥阴离子组成变化
采用离子色谱分析赤泥浸提液阴离子成分(CO32-、HCO3-采用双指示剂中和滴定法测定),检测到的阴离子有F-、SO42-等。不同堆存年限赤泥各阴离子含量如表2所列,赤泥中阴离子主要有CO32-、SO42-、HCO3-。经过不同堆存年限,阴离子组成发生变化。CO32-在Z1中占阴离子总量的73.26%,随着堆存年限的增加,CO32-占阴离子总量的比例逐渐降低,Z6 CO32-占阴离子总量的53.66%;SO42-占阴离子总量的比例也是随着堆置年限的增加而下降(从Z1的28.10%降低至Z6的6.10%);HCO3-变化趋势与CO32-正好相反,其占阴离子总量的比例从3.49%增加到34.15%;赤泥中F-、Cl-含量较低,F-变化不明显,Cl-在Z3、Z4、Z5和Z6中都未检测到。
CO32-、HCO3-和SO42-主要来源于赤泥中各矿物的溶解。赤泥物相复杂,主要矿物有赤铁矿、针铁矿、方钠石、水化石榴石、石灰石、伊利石和方解石等[18-19]。CO32-主要是方解石(CaCO3)、菱镁矿(MgCO3)、白云石(CaMg(CO3)2)、碳钠铝石(NaAlCO3(OH)2)等溶解析出,SO42-主要是天青石(SiSO4)、磷钙铝石(CaAl3(PO4)(SO4)(OH)6)溶解析出[20]。由于这些矿物的大量存在,赤泥中CO32-和SO42-含量比例较高。CO32-与HCO3-存在水解平衡,如式(1)所列:
CO32-+H2O HCO3-+OH- (1)
HCO3-+OH- (1)
由于赤泥pH值过高,CO32-水解平衡向着产生CO32-的方向进行,HCO3-的浓度较低。自然风化过程中赤泥pH值降低,堆存20年的赤泥pH值从新鲜赤泥的10.98降低至9.45[17]。赤泥堆存过程中由于降雨淋溶、植物枯枝落叶、禽类粪便等的作用,增加赤泥营养成分,易产生有机酸等酸性物质,使pH值降低,CO32-水解平衡向着HCO3-的方向进行,因此CO32-含量降低,HCO3-含量增加。
对盐分含量与主要阴离子进行相关性分析,盐分含量与CO32-、SO42-在0.01水平呈显著正相关(相关性系数分别为0.990、0.969),与HCO3-在0.05水平呈著负相关(相关性系数为-0.850)。CO32-是盐分阴离子的主要成分(见表2),且与盐含量呈显著正相关,降低赤泥中CO32-含量是调控盐分含量的有效措施。伊元荣等[21]利用CO2对赤泥进行改良,CO2属于弱酸物质,在溶液中发生的主要反应:CO2与水溶液反应生成H2CO3;CO2与OH-反应生成HCO3-;HCO3-水解生成CO32-;HCO3-是与OH-反应生成CO32-,赤泥属于强碱性物质,CO2与OH-反应生成HCO3-的速度大于HCO3-反应生成CO32-的速度,使得赤泥pH下降,进一步增加HCO3-的浓度。另外,海水中和赤泥、盐卤降碱和石膏改良赤泥其中一个主要原理是海水、盐卤和石膏中富含Ca2+、Mg2+等离子与赤泥CO32-反应生成沉淀物,降低盐分离子含量。
表2 不同堆存年限赤泥阴离子组成
Table 2 Anion composition of bauxite residue in different stacking ages

2.3 赤泥堆场交换态阳离子组成变化
Na+是赤泥交换态阳离子组成主要成分,其次是Ca2+(见表3)。阳离子组成随堆置年限的增加发生变化,Ca2+含量随堆存年限增加呈升高趋势,从4.60×10-2 mol/kg(Z1)增加到8.58×10-2 mol/kg(Z6),而Na+含量变化趋势与Ca2+相反,从27.61×10-2 mol/kg(Z1)下降到14.84×10-2 mol/kg(Z6),Mg2+和K+变化较为平缓(见表3)。此现象与河南某氧化铝企业赤泥堆场研究结果一致[22]。
表3 不同堆存年限堆场赤泥可交换阳离子含量
Table 3 Exchangeable cation of bauxite residue in different stacking ages
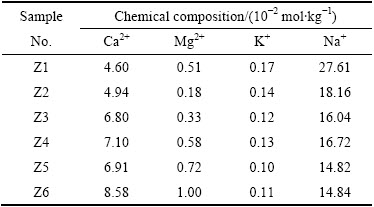
随着堆置年限的增加,赤泥物理性质改善,赤泥pH值降低,促使赤泥中矿物如方解石、白云石等的溶解,使赤泥中Ca2+含量增加,Ca2+通过与胶体上吸附的Na+交换,降低可交换Na+含量。
对盐分含量与各交换态阳离子进行相关性分析,盐分含量与Ca2+、Mg2+含量呈负相关关系,与Ca2+含量负相关关系显著(相关性系数为-0.924);含盐量与Na+含量呈显著正相关关系(相关性系数为0.924);含盐量与K+含量的相关性较弱(相关性系数为-0.347);Ca2+含量和Na+含量呈负相关关系(相关系数为-0.771),表明适当增加Ca2+含量可以降低Na+含量,降低盐分含量。Ca2+可以促使有机成分和带负电的粘土颗粒胶结,增加土壤结构中的有机物质,降低有机物质的分解,有利于土壤胶体团聚。Na+过高不利于土壤胶体团聚,影响植物的发芽率,且Na+浓度过高时会降低土壤中Ca2+离子浓度,影响植物对Ca2+的吸收。当Na+浓度超过0.2%~0.32%时对红苜蓿的生长具有抑制作用[23]。适当增加 Ca2+含量,降低Na+含量,有利于赤泥堆场盐分调控,实现堆场植被重建。
2.4 不同堆存年限赤泥水溶态阳离子组成变化
不同堆存年限赤泥水溶态离子含量: >
> >
>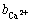 (见表4),Na+是赤泥中主要的水溶态阳离子,占水溶态阳离子的71.34%~91.25%,并且随着堆存年限的增加呈下降趋势(从20.62×10-2 mol/kg降低到1.94×10-2 mol/kg);水溶态Mg2+并未检测到;K+的变化趋势和Na+一致,随着堆存年限的增加而降低,降低幅度达到71.86%;Ca2+的变化趋势与Na+、K+相反,随着堆存年限的增加含量升高,从0.04×10-2 mol/kg增加到0.22×10-2 mol/kg(见表4)。这与LIU等[22]对郑州不同年代的赤泥研究结果一致。
(见表4),Na+是赤泥中主要的水溶态阳离子,占水溶态阳离子的71.34%~91.25%,并且随着堆存年限的增加呈下降趋势(从20.62×10-2 mol/kg降低到1.94×10-2 mol/kg);水溶态Mg2+并未检测到;K+的变化趋势和Na+一致,随着堆存年限的增加而降低,降低幅度达到71.86%;Ca2+的变化趋势与Na+、K+相反,随着堆存年限的增加含量升高,从0.04×10-2 mol/kg增加到0.22×10-2 mol/kg(见表4)。这与LIU等[22]对郑州不同年代的赤泥研究结果一致。
赤泥中主要的矿物组分在碱性条件下不溶于水或微溶于水,而赤泥中矿物组分大部分是含钙矿物。随着堆存年限的延长,有机物质的腐殖化增加了赤泥中有机酸等物质,降低了赤泥pH值,促进矿物的水溶性,进而增加Ca2+含量;赤泥在自然风化过程中,理化性质得到有效改善,其渗透性增强,离子随水迁移的能力加强,离子的迁移能力受电荷和离子半径等的影响,在土壤中Ca2+、Na+、K+的迁移能力顺序:K+>Na+>Ca2+,在赤泥中Ca2+、Na+、K+的迁移能力可能和土壤中Ca2+、Na+、K+的迁移能力一致。赤泥渗透性增加,Na+、K+随水流失的速率大于其溶解的速率,因此Na+、K+随堆存年限的增加而降低,而Ca2+溶出的速率大于其流失的速率,Ca2+随堆存年限的增加而升高。
水溶态和交换态离子的变化趋势基本一致(见表3和4)。交换态Na+含量从Z1到Z6降低46.25%,水溶态Na+含量降低90.59%,交换态K+含量降低35.29%,水溶态K+含量降低71.13%;相比于交换态离子,水溶态离子降低幅度更大。Na+含量高是赤泥盐分过高的主要原因,赤泥盐分调控可通过降低赤泥Na+含量实现。Na+在赤泥中主要以交换态形式存在,且交换态Na+不易于随水排出,因此在进行赤泥盐分调控过程中,使交换态Na+向水溶态Na+转变,并增大赤泥渗透性使水溶态Na+更易于随水排出,有助于赤泥堆场盐分调控。
表4 不同堆存年限堆场赤泥可水溶态阳离子的含量
Table 4 Water-extractabe cations of bauxite residue in different stacking ages

3 结论
1) 随着堆存年限的增加,赤泥盐分含量降低,受赤泥堆场环境条件的影响,0~30 cm层盐含量呈明显降低趋势,而30~60 cm层、60~90 cm层赤泥含盐量变化平缓。
2) 赤泥中主要的阴离子成分是CO32-,Na+是主要的交换态阳离子及水溶态阳离子;含盐量和SO42-、CO32-、Na+呈正相关关系,和HCO3-、Ca2+、Mg2+呈负相关关系。
3) 赤泥盐分组成随着堆存年限的增加发生变化,赤泥CO32-、SO42-、Na+、K+含量呈下降趋势,HCO3-、Ca2+含量则呈上升态势;水溶态离子变化大于交换态离子。
4) 赤泥堆场盐分组成主要的阴阳离子是CO32-和Na+,Na+和CO32-含量高是赤泥盐分含量过高的主要原因,是赤泥堆场盐分调控和土壤化处置的关键环节。
致谢
感谢英国哈珀亚当斯大学的William Hartley博士对英文摘要进行润色修改!
REFERENCES
[1] 薛生国, 吴雪娥, 黄 玲, 黄 楠. 赤泥土壤化处置技术研究进展[C]//第十七届中国科协年会: 广州. 2015: 1-5.
XUE Sheng-guo, WU Xue-e, HUANG Ling, HUANG Nan. Research advances on soil formation of bauxite residues[C]//17th Annual Meeting of China Association for Science and Technology: Guangzhou, 2015: 1-5.
[2] JU S H, LU S D, PENG J H, ZHANG L B, SRINIVASAKANNAN C, GUO S H, LI W. Removal of cadmium from aqueous solutions using red mud granulated with cement[J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2012, 22(12): 3140-3146.
[3] 黄 凯, 李一飞, 焦树强, 朱鸿民. 柠檬酸活化赤泥对亚甲基蓝染料废水的吸附净化作用[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2011, 21(12): 3182-3188.
HUANG Kai, LI Yi-Fei, JIAO Shu-Qiang, ZHU Hong-Min. Adsorptive removal of methylene blue dye wastewater from aqueous solution using citric acid activated red mud[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2011, 21(12): 3182-3188.
[4] 郭曦尧, 马淑花, 吕松青, 郑诗礼, 邹 兴. 以脱铝赤泥-脱铝粉煤灰为原料制备硬硅钙石[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2015, 25(2): 534-544.
GUO Xi-yao, MA Shu-hua,  Song-qing, ZHENG Shi-li, ZOU Xing. Preparation of xonotlite using red mud and fly ash after removal alumina as raw materials[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2015, 25(2): 534-544.
Song-qing, ZHENG Shi-li, ZOU Xing. Preparation of xonotlite using red mud and fly ash after removal alumina as raw materials[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2015, 25(2): 534-544.
[5] 周秋生, 范旷生, 李小斌, 彭志宏, 刘桂华. 采用烧结法处理高铁赤泥回收氧化铝[J]. 中南大学学报(自然科学版), 2008, 39(1): 92-97.
ZHOU Qiu-sheng, FAN Kuang-sheng, LI Xiao-bin, PENG Zhi-hong, LIU Gui-hua. Alumina recovery from red mud with high iron by sintering process[J]. Journal of Central South University (Science and Technology), 2008, 39(1): 92-97.
[6] 南相莉, 张廷安, 刘 燕, 豆志河. 我国赤泥综合利用分析[J]. 过程工程学报, 2010, 10(S1): 264-270.
NAN Xiang-li, ZHANG Ting-an, LIU Yan, DOU Zhi-He. Analysis of red mud comprehensive utilization in China[J]. The Chinese Journal of Process Engineering, 2010, 10(S1): 264-270.
[7] XUE S G, ZHU F, KONG X F, WU C, HUANG L, HUANG N, WILLIAM H. A review of the characterization and revegetation of bauxite residues (Red mud)[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2016, 23(2): 1120-1132.
[8] JOHNSTON M, CLARK M W, MCMAHON P, WARD N. Alkalinity conversion of bauxite refinery residues by neutralization[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2010, 182(1/3): 710-715.
[9] COURTNEY R, MULLEN G. Use of germination and seedling performance bioassays for assessing revegetation strategies on bauxite residue[J]. Water Air and Soil Pollution, 2008, 197(1/4): 15-22.
[10] JONES B E H, HAYNES R J, PHILLIPS I R. Addition of an organic amendment and/or residue mud to bauxite residue sand in order to improve its properties as a growth medium[J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 2012, 95(1): 29-38.
[11] JONES B E H, HAYNES R J, PHILLIPS I R. Influence of organic waste and residue mud additions on chemical, physical and microbial properties of bauxite residue sand[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2011, 18(2): 199-211.
[12] 彭光菊, 张健伟, 张 磊, 饶玉学. 赤泥耕土制备技术[J]. 金属矿山, 2011(8): 159-161.
PENG Guang-ju, ZHANG Jian-wei, ZHANG Lei, RAO Yu-xue. Preparation process of cultivated soil rehabilitated from red mud[J]. Metal Mine, 2011(8): 159-161.
[13] RUYTERS S, MERTENS J, VASSILIEVA E, DEHANDSCHUTTER B, POFFIJIN A, SMOLDERS E. The red mud accident in Ajka (Hungary): Plant toxicity and trace metal bioavailability in red mud contaminated soil[J]. Environmental Science and Technology, 2011, 45(4): 1616-1622.
[14] 崔立强, 严金龙, 丁 成, 陈天明, 陈 伟. 土壤盐分对酶活性和镉形态的影响[J]. 中国农学通报, 2016, 32(5): 83-89.
CUI Li-qiang, YAN Jin-long, DING Cheng, CHEN Tian-ming, CHEN Wei. Effect of soil salt on enzyme activities and Cd forms[J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2016, 32(5): 83-89.
[15] 鲍士旦. 土壤农化分析[M]. 北京: 中国农业出版社, 2005: 178-200.
BAO Shi-dan. Soil agro-chemistrical analysis[M]. Beijing: China Agriculture Press, 2005: 178-200.
[16] JONES B E H, HAYNES R J, PHILLIPS I R. Addition of an organic amendment and/or residue mud to bauxite residue sand in order to improve its properties as a growth medium[J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 2012, 95(1): 29-38.
[17] ZHU F, XUE S G, HARTLEY W, HUANG L, WU C, LI X F. Novel predictors of soil genesis following natural weathering processes of bauxite residues[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2016, 23(3): 2856-2863.
[18] 李小斌, 赵东峰, 章 宣, 刘桂华, 彭志宏, 周秋生. 赤泥主要物相的表面性质对其沉降性能的影响[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2012, 22(1): 281-286.
LI Xiao-bin, ZHAO Dong-feng, ZHANG Xuan, LIU Gui-hua, PENG Zhi-hong, ZHOU Qiu-sheng. Effect of surface property of main minerals in red mud on their sedimentation ability[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2012, 22(1): 281-286.
[19] 刘万超, 杨家宽, 肖 波. 拜耳法赤泥中铁的提取及残渣制备建材[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2008, 18(1): 187-192.
LIU Wan-chao, YANG Jia-kuan, XIAO Bo. Recovering iron and preparing building materrial with residues from Bayer red mud[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2008, 18(1): 187-192.
[20] AUTHIER-MARTIN M, FORTE G, OSTAP S. SEE J. The mineralogy of bauxite for producing smelter-grade alumina[J]. The Journal of Minerals Metals and Materials Society, 2001, 53(12): 36-40.
[21] 伊元荣, 韩敏芳. 废气和废渣协同作用脱钠反应特性及机制研究[J]. 环境科学, 2012, 33(7): 2522-2527.
YI Yuan-rong, HAN Min-fang. Characteristics and mechanism of sodium removal by the synergistic action of flue gas and waste solid[J]. Environmental Science, 2012, 33(7): 2522-2527.
[22] LIU Y, LIN C X, WU Y G. Characterization of red mud derived from a combined Bayer process and bauxite calcination method[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2007, 146(1/2): 255-261.
[23] COURTNEY R G, TIMPSON J P. Reclamation of fine fraction bauxite processing residue (red mud) amended with coarse fraction residue and gypsum[J]. Water Air and Soil Pollution, 2005, 164(1/4): 91-102.
Salt composition changes in different stacking ages of bauxite residue
HUANG Ling1, 2 , LI Yi-wei1, XUE Sheng-guo1, 2, ZHU Feng1, WU Chuan1, 2, WANG Qiong-li1
(1. School of Metallurgy and Environment, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China;
2. Chinese National Engineering Research Center for Control and Treatment of Heavy Metal Pollution,
Central South University, Changsha 410083, China)
Abstract: Residue samples from different stacking times were collected to investigate the salt composition change with the increasing stacking time in bauxite residue disposal areas (BRDAs). The results show that the salt contents in BRDAs decrease with the increasing stacking time. The dominant anion is CO32-, which accounted for 34.14%-73.26% whilst water- and ammonium acetate-extractable Na+ accounted for 60.50%-83.94% and 71.32%-91.16%. Sodium, CO32- and SO42- concentrations decrease, while HCO3- and Ca2+ concentrations increase, but K+ and Mg2+ concentrations have no obvious changes. The correlations between salt contents and CO32-, SO42-, Na+ concentrations are positive. The relatively high concentrations of Na+ and CO32- contribute to the high salinity in bauxite residue disposal areas, and prevent the potential for the revegetation of bauxite residue.
Key words: bauxite residue; bauxite residue disposal area; stacking age; salt component; soil formation
Foundation item: Project(41371475) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China; Project (201509048) supported by the Enviromental Protection’s Special Scientific Research for Chinese Public Welfare Industry
Received date: 2015-04-02; Accepted date: 2015-12-04
Corresponding author: XUE Sheng-guo; Tel: +86-13787148441; E-mail: sgxue@csu.edu.cn
(编辑 王 超)
基金项目:国家自然科学基金资助项目(41371475);国家环保公益性行业科研专项(201509048)
收稿日期:2015-04-02;修订日期:2015-12-04
通信作者:薛生国,教授,博士;电话:13787148441;E-mail:sgxue@csu.edu.cn