文章编号:1004-0609(2008)08-1426-06
AM50A镁合金激光表面熔凝层的强化效果与机理
陈菊芳1, 2,张永康2,李仁兴1,秦海永2
(1. 江苏技术师范学院 机械工程学院,常州 213001;
2. 江苏大学 机械工程学院,镇江 212013)
摘 要:采用 CO2 连续激光对 AM50A 镁合金表面进行熔凝处理,分析激光熔凝层的组织、性能和强化机理。结果表明:激光熔凝层晶粒得到高度细化,且随着扫描速度的增大,晶粒细化更为明显;熔凝层内合金元素 Al 的固溶度增加,β相(Mg17Al12) 的含量有所减少,但β相的分布更加均匀弥散;熔凝层的显微硬度(HV55~75)明显高于基体的显微硬度(约HV40)。磨损实验表明,激光熔凝试样的磨损体积是未处理试样的35%,耐磨性有了较大提高。熔凝层的强化机理主要是细晶强化,此外合金元素 Al 固溶度的增加及β相的弥散析出也有一定的强化效果。
关键词:AM50A镁合金;激光表面熔凝;细晶强化;固溶强化;弥散强化
中图分类号:TN 249; TG 156.99 文献标识码:A
Strengthening effect and mechanism of laser surface melted AM50A magnesium alloy
CHEN Ju-fang1, 2, ZHANG Yong-kang2, LI Ren-xing1, QIN Hai-yong2
(1. School of Mechanical Engineering, Jiangsu Teachers University of Technology, Changzhou 213001,China;
2. School of Mechanical Engineering, Jiangsu University, Zhenjiang 212013,China;)
Abstract: AM50A magnesium alloy was surface melted using a continuous wave CO2 laser, the microstructure properties and strengthening mechanism of the laser melted layer were analyzed. The results show that the grain of the laser surface melted layer is highly refined and the grain size decreases with increasing scanning speed. In the melted layer, the amount of element Al in solid solution increases, the amount of β-phase (Mg17Al12) decreases, and the distribution of β-phase becomes more uniform. The micro-hardness of the melted layer is improved to HV55?75 as compared to that of the substrate (about HV40). The wear volume of the laser surface melted sample is 35% of the untreated sample, the wear resistance of the laser surface melted layer is improved obviously. The main strengthening mechanism of the laser surface melted layer is grain refinement, the increase of element Al in solid solution and the dispersive precipitation of β-phase can also result in strengthening the melted layer.
Key words: AM50A magnesium alloy; laser surface melting; fine grain strengthening; solid solution strengthening; dispersion strengthening
镁合金具有密度小,比强度、比刚度高,电磁屏蔽性、减震性好以及优良的切削加工等性能,在航空、汽车和 3C 产品中具有很大的应用潜力[1?3]。但镁合金的耐蚀、耐磨性能较差,严重制约了其在应用中发挥优势[4?5]。由于腐蚀与磨损是材料的表面行为,因此,采用适当的表面改性技术改善镁合金的表面性能具有重要的现实意义。目前,镁合金所采用的表面改性措施主要有化学转化处理、阳极氧化处理、微弧氧化、激光表面处理、化学镀及电镀等[6?7]。激光表面处理一直受到人们的重视,具有非接触加工、能源清洁、便于精确定位和自动控制等优点[8?10]。激光表面熔凝,是用高能激光束辐照金属表面,使一定厚度的表层材料瞬间熔化,之后依靠处于低温的基体,将熔池急冷从而使材料表层组织发生较大变化,包括晶粒细化、提高合金元素的固溶度等,这些因素可使材料的耐蚀、耐磨等性能得到改善[8?9]。高亚丽等[9]在真空条件下对AZ91HP 镁合金进行了激光熔凝处理,使熔凝层的晶粒得到显著细化,硬度、耐磨、耐蚀性能得到显著提高;ABBAS等[10]对AZ31和AZ61镁合金进行了激光熔凝处理,使熔凝层组织得到高度细化,硬度、耐磨性能得到显著提高。目前,国内外对激光熔凝镁合金的研究虽有一些报道,但对工程中广泛使用的AM系列镁合金的研究未见报道,且对激光熔凝层的强化机理缺乏深入的研究。本文作者采用轴快流CO2连续激光,对 AM50A 镁合金表面进行了熔凝处理,系统研究了激光熔凝层的组织、物相、硬度和耐磨性能,并对其强化机理进行分析探讨。
1 实验
实验用材料为 AM50A 镁合金,其化学成分为(质量分数):4.83%Al,0.32%Mn,0.001%Cu,0.001%Fe,0.003%Si,余量为 Mg。试样采用线切割法加工成 25 mm×20 mm×5 mm 的试块,将试样表面依次采用 100~1000# SiC 砂纸打磨,乙醇清洗,吹干。由于镁合金表面对波长为 10.6 μm 的 CO2 激光强烈反射,为了提高试样表面对激光能量的吸收,在试样表面喷涂一层碳黑涂料。为减少熔凝过程中镁的蒸发与氧化,采用氩气对激光熔池进行保护,气流量为 5 L/min。实验采用 2 kW RS2000SM 轴快流 CO2 激光器对试样表面进行熔凝处理,激光能量连续,波长 10.6 μm,激光光束为准高斯 TEM10 模式,光束内激光能量分布比较均匀。激光熔凝工艺参数为:激光功率 1 000 W,光斑直径 3 mm,扫描道间的搭接量为 50%,扫描速度分别采用 300、500和800 mm/min,相应的激光熔凝后的试样编号为样品1、样品2和样品3。
激光熔凝处理后,采用XRD?6000型X射线衍射仪对试样表面进行物相分析;用体积分数为5%的冰乙酸蒸馏水溶液浸蚀后,采用XJL?02金相显微镜观察、拍摄试样表面及横截面的金相组织,并采用SISC IAS V8.0金相图像分析软件对晶粒尺寸进行分析计算;采用HV?1000型显微硬度计测试激光熔凝层表面及横截面由表及里的显微硬度,每隔30 μm测试3次,取其算术平均值,加载1 N,保荷时间10 s。磨损实验在 UMT?2微摩擦磨损实验机上进行,采用球-平面往复干摩擦方式,实验在大气和室温环境下进行,室温18 ℃,相对湿度 65%。对磨偶件采用直径为4 mm,硬度为HRC 62的440-C不锈钢球,加载0.1 N,行程5 mm,往复频率1 Hz,时间20 min。磨损实验后,采用JSM ?6480型扫描电镜对磨痕表面进行观察与分析,采用 VEECO NT1100光学轮廓仪测试磨痕的横截面轮廓。
2 结果与分析
2.1 组织形貌
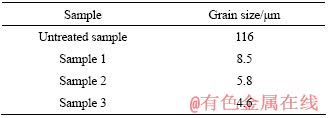
图1所示为激光熔凝区横截面典型的组织形貌,在激光表面熔凝过程中,激光对材料的作用时间很短,材料的熔化与凝固都在极短时间内完成,可以只影响表层材料的性能,底层材料充当了无限大的热扩散体,由于激光能量高度集中,激光熔池内的温度梯度很高,可高达106 K/m,凝固速率达每秒数米,促使组织定向生长[11]。由图可见,熔凝层组织主要为柱状枝晶,由于熔池中温度梯度的方向主要是向上的,因此,枝晶向上的生长占了主导地位,熔池顶部由于受合金熔体流动的干扰,使得组织的生长失去明显的方向性。激光熔池表层的冷却速度最快,晶粒的生长速度最快,晶粒最为细密,随着到表面距离的增加,冷却速度逐渐降低,枝晶间距随之增大。图2所示为未处理试样及激光熔凝试样表面的组织形貌。未处理试样的晶粒尺寸粗大,而激光熔凝层的晶粒细密,采用 SISC IAS V8.0 金相图像分析软件对晶粒尺寸进行分析计算,平均晶粒尺寸见表1。可见,激光熔凝使晶粒得到高度细化,且随着扫描速度的提高,激光熔凝过程中的冷却速度加快,晶粒细化更为明显。
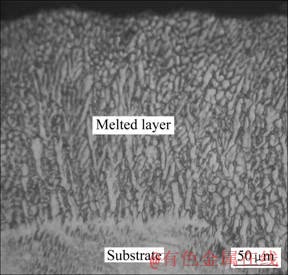
图1 样品3激光熔凝区横截面的显微组织
Fig.1 Microstructure of cross-section of laser melted zone in sample 3
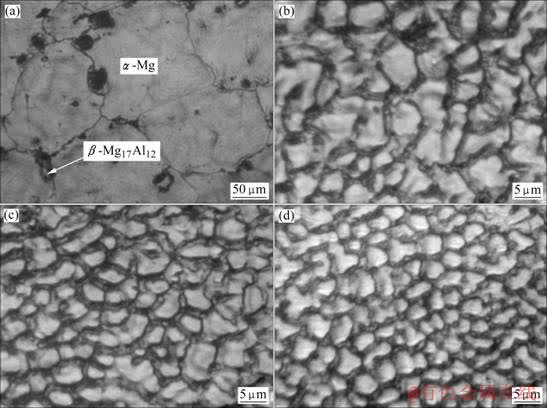
图2 试样表面的显微组织
Fig.2 Microstructures of sample top surface: (a) Untreated sample; (b) Sample 1; (c) Sample 2; (d) Sample 3
表1 试样表面的平均晶粒尺寸
Table 1 Average grain size of sample top surface
2.2 物相分析
图3所示为未处理试样及激光熔凝试样表面的 XRD谱。由图可见,激光熔凝并没有生成新的物质,基体和激光熔凝层都是由α-Mg相和少量的β(Mg17- Al12)相构成。但进一步分析表明,激光熔凝层中β相的含量较未处理试样中β相的含量都有不同程度的减少,且随着扫描速度的提高,β相的减少量更为明显。由于激光熔凝层的晶粒得到高度细化,沿晶界析出的β相的分布也变得更加均匀弥散。文献[8]的研究结果表明,激光熔凝过程中的快速凝固,抑制了合金成分的偏析,促使基相α-Mg固溶体中合金元素 Al 的固溶度增加,β相的析出量减少。合金元素Al的固溶度的增加可对材料起到固溶强化作用。
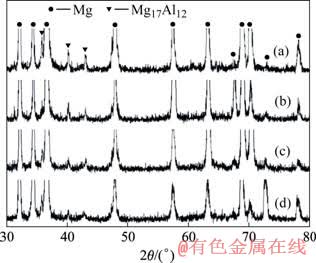
图3 试样表面的 XRD谱
Fig.3 XRD patterns of sample top surface: (a) Untreated sample; (b) Sample 1; (c) Sample 2; (d) Sample 3
2.3 显微硬度
激光熔凝层沿横截面由表及里的显微硬度分布见图4。可见,激光熔凝层的显微硬度(HV55~75)明显高于基体的显微硬度(约HV40),随着扫描速度的提高,熔凝过程中冷却速度加快,晶粒更为细密,显微硬度增加,但同时由于激光与材料的作用时间减少,使熔凝层的深度减小。由于激光熔池表层冷却速度最快,晶粒最为细密,表层的显微硬度最高,随着到表面距离的增加,晶粒变粗,显微硬度逐渐降低。
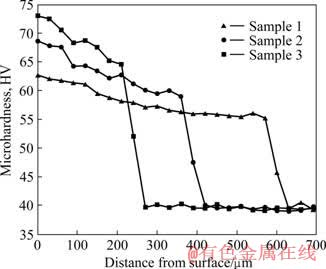
图4 激光熔凝层沿深度方向显微硬度的分布
Fig.4 Micro-hardness profiles as function of depth from surface on cross sectional plane of laser melted layers
2.4 磨损实验
为检测激光熔凝层的耐磨性能,将未处理试样与硬度最高的激光熔凝试样(样品3)进行磨损对比实验,每个试样表面重复磨损实验5次。图5所示为磨痕表面的典型形貌。可见,在未处理试样和激光熔凝试样表面均出现了平行于磨削方向的犁沟,说明磨损的主要机制为磨料磨损,但未处理试样磨痕表面的犁沟更深。磨痕的横截面轮廓见图6,将磨痕的截面积乘以磨痕长度可得磨损体积。计算可得,激光熔凝试样的平均磨损体积(2.9×10?3 mm3)是未处理试样磨损体积(8.2×10?3 mm3)的35%,耐磨性有了较大提高。文献[12]指出,金属材料对磨料磨损的抗力与材料的硬度成正比,材料硬度越高,其抗磨料磨损的能力也越强。由于熔凝层硬度较未处理试样显著增加,所以熔凝层的耐磨性能也相应提高。
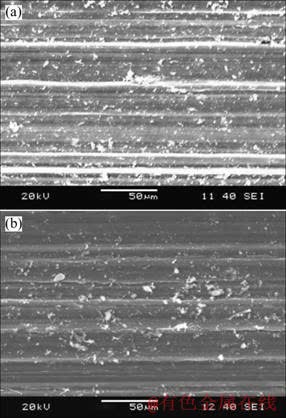
图5 磨损表面形貌的SEM像
Fig.5 SEM images of worn surface: (a) Untreated sample; (b) Laser melted sample (Sample 3)
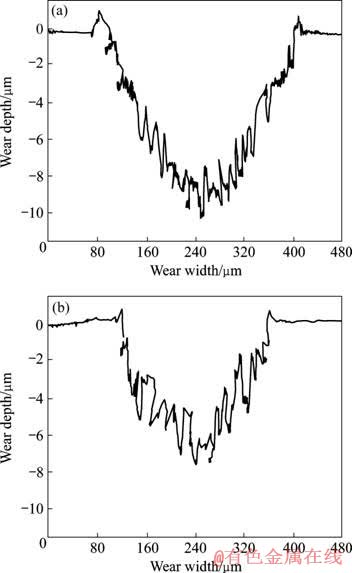
图6 磨痕横截面轮廓
Fig.6 Wear track profiles: (a) Untreated sample; (b) Laser melted sample (Sample 3)
3 强化机理分析
激光熔凝可导致熔凝层产生细晶强化,根据 Hall-Petch 公式[13]:

纯镁及常规镁合金的Hall-Petch常数K为280 MPa?μm1/2[14]。另外材料的屈服强度和显微硬度值HV存在如下近似关系[15]:

将所得实验数据代入式(1)和(2)进行验证,首先将不同的激光熔凝试样进行对比。以样品1和样品2为例,将样品表面的平均晶粒尺寸(见表1)代入式(1),得
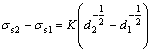 = 20.2 MPa
= 20.2 MPa
再计算由于显微硬度变化导致的材料屈服强度的变化,将样品1和样品2表面的显微硬度值HV62.7和HV68.6(见图4)代入式(2),得
 =19.7 MPa≈20.2 MPa
=19.7 MPa≈20.2 MPa
由以上计算可知,由于晶粒细化程度不同导致的屈服强度的变化和由于显微硬度变化导致的屈服强度的变化基本一致,由此可见,晶粒细化是提高材料强度与显微硬度的重要因素。将其余实验数据代入式(1)和(2)进行比较,也得到了相似的结论。
再将激光熔凝试样与未处理试样进行对比。以样品1为例,先将两者的晶粒尺寸(见表1)代入式(1)得
 = 70.0 MPa
= 70.0 MPa 
再将样品1表面的显微硬度值HV62.7和基体的显微硬度值HV39.5(见图4)代入式(2)得
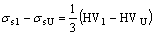 = 77.3 MPa>70.0 MPa
= 77.3 MPa>70.0 MPa
式中 下标 U 表示未处理试样,将其余实验数据代入式(1)和(2)进行比较也能得到相似的结论。由计算结果可知,晶粒细化是熔凝层显微硬度提高的主要因素,但就晶粒细化一种因素不足以使显微硬度有这么大的提高,合金元素 Al 固溶度的增加及β相的弥散析出也起着强化作用。
4 结论
1) 采用 CO2 连续激光对 AM50A 镁合金表面进行熔凝处理,熔凝层的晶粒得到高度细化,且随着扫描速度的增加,晶粒细化更为明显。
2) 熔凝层由α-Mg 相和少量的β相(Mg17Al12)构成,因激光熔凝过程中加热与冷却速度很高,促使合金元素 Al 的固溶度增加,β相的析出量有所减少,由于晶粒的高度细化,沿晶界析出的β相的分布也更加均匀弥散。
3) 熔凝层的显微硬度(HV55~75) 明显高于基体的显微硬度(约HV40),磨损实验表明,激光熔凝试样的磨损体积是未处理试样的35%,耐磨性有了较大幅度的提高。
4) 根据熔凝层表面的晶粒尺寸和显微硬度计算得到,熔凝层的强化机制主要是细晶强化,合金元素Al固溶度的增加及β相的弥散析出也起着强化作用。
REFERENCES
[1] MORDIKE B L, EBERT T. Magnesium properties–applications– potential[J]. Mater Sci Eng A, 2001, 302(1): 37?45.
[2] 全亚杰, 陈振华, 黎 梅, 俞照辉, 龚晓叁. AM60 变形镁合金薄板激光焊接接头的组织与性能[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2007, 17(4): 525?529.
QUAN Ya-jie, CHEN Zhen-hua, LI Mei, YU Zhao-hui, GONG Xiao-san. Microstructure and properties of joints of wrought magnesium alloy AM60 plates welded by laser beam welding[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2007, 17(4): 525?529.
[3] 徐锦锋, 翟秋亚, 袁 森. AZ91D镁合金的快速凝固特征[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2004, 14(6): 939?944.
XU Jin-feng, ZHAI Qiu-ya, YUAN Sen. Rapid solidification characteristics of melt-spun AZ91D magnesium alloy[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2004, 14(6): 939?944.
[4] YAMAUCHI N, DEMIZU K, UEDA N, CUONG N K, SONE T, HIROSE Y. Friction and wear of DLC films on magnesium alloy[J]. Surface & Coatings Technology, 2005, 193(1): 277?282.
[5] ZHANG T, LI Y, WANG F H. Roles of β phase in the corrosion process of AZ91D magnesium alloy[J]. Corrosion Science, 2006, 48(5): 1249?1264.
[6] SHI Z M, SONG G L, ATRENS A. The corrosion performance of anodised magnesium alloys[J]. Corrosion Science, 2006, 48(11): 3531?3546.
[7] 金华兰, 杨湘杰, 危仁杰, 陈 祥. 化学转化膜对镁合金抗腐蚀性的影响[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2007, 17(6): 963?967.
JIN Hua-lan, YANG Xiang-jie, WEI Ren-jie, CHEN Xiang. Effect of chemical conversion film on corrosion resistance of magnesium alloy[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2007, 17(6): 963?967.
[8] LIU S Y, HU J D, YANG Y, GUO Z X, WANG H Y. Microstructure analysis of magnesium alloy melted by laser irradiation[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2005, 252(5): 1723?1731.
[9] 高亚丽, 王存山, 刘红宾, 姚 曼. 高功率激光熔凝AZ91HP镁合金组织和性能[J]. 中国激光, 2007, 34(7): 1019?1024.
GAO Ya-li, WANG Cun-shan, LIU Hong-bin, YAO Man. Microstructure and properties of AZ91HP magnesium alloy treated by high power laser melting[J]. Chinese Journal of Lasers, 2007, 34(7): 1019?1024.
[10] ABBAS G , LI L, GHAZANFAR U, LIU Z. Effect of high power diode laser surface melting on wear resistance of magnesium alloys[J]. Wear, 2006, 260(1/2): 175?180.
[11] 杨 森, 黄卫东, 刘文今, 苏云鹏, 周尧和. 激光超高温度梯度快速定向凝固研究[J]. 中国激光, 2002, 29(5): 475?479.
YANG Sen, HUANG Wei-dong, LIU Wen-jin, SU Yun-peng, ZHOU Yao-he. Research on laser rapid directional solidification with ultra-high temperature gradient[J]. Chinese Journal of Lasers, 2002, 29(5): 475?479.
[12] 高彩桥, 雷廷权. 金属的摩擦磨损与热处理[M]. 北京: 机械工业出版社, 1988, 12: 6?46.
GAO Cai-qiao, LEI Ting-quan. Friction, wear and heat-treatment of metal[M]. Beijing: China Machine Press, 1988: 6?46.
[13] 王 强, 张治民, 张宝红, 张 星. 镁合金变形强韧化研究进展[J]. 材料导报, 2006, 20(6): 431?433.
WANG Qiang, ZHANG Zhi-min, ZHANG Bao-hong, ZHANG Xing. Development in strengthening and toughening magnesium alloys by deformation[J]. Materials Review, 2006, 20(6): 431?433.
[14] 张新明, 肖 阳, 陈健美, 蒋 浩. 挤压温度对 Mg-9Gd- 4Y-0.6Zr 合金组织与力学性能的影响[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2006, 16(3): 518?523.
ZHANG Xin-ming, XIAO Yang, CHEN Jian-mei, JIANG Hao. Influence of extrusion temperature on microstructures and mechanical properties of Mg-9Gd-4Y-0.6Zr alloy[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2006, 16(3): 518?523.
[15] 李鸿琦, 邢冬梅, 佟景伟, 王世斌, 岳 澄. 纳米固体材料的屈服应力与微观结构的关系[J]. 天津大学学报, 2000, 33(5): 671?675.
LI Hong-qi, XING Dong-mei, TONG Jing-wei, WANG Shi-bin, YUE Cheng. Relationship between yield stress and microcosmic structure of nanostructure material[J]. Journal of Tianjin University, 2000, 33(5): 671?675.
基金项目:国家自然科学基金资助项目(50735001, 50675089);江苏技术师范学院基础基金资助项目(KYY06105)
收稿日期:2007-11-12;修订日期:2008-03-05
通讯作者:陈菊芳,副教授;电话:0511-88797898;E-mail: jfchen1031@sina.com
(编辑 陈爱华)