基于BP人工神经网络的大气颗粒物PM10质量浓度预测
石灵芝,邓启红,路婵,刘蔚巍
(中南大学 能源科学与工程学院,湖南 长沙,410083)
摘要:根据2008年长沙市火车站监测点全年大气PM10及气象参数的小时平均数据,建立BP人工神经网络预测模型,预测PM10小时平均浓度。为证明人工神经网络模型用于预测PM10质量浓度的准确性,研究中考虑2种预测模型:多元线性回归模型与人工神经网络模型。研究结果表明:与传统的多元线性回归模型相比,人工神经网络模型能够捕捉污染物浓度与气象因素间的非线性影响规律,能更好地预测PM10质量浓度,拟合优度R2有较大提高;所选取气象参数及污染源强变量能较准确地描述大气PM10质量浓度的实时变化,用于PM10质量浓度的预测准确度较高,整体R2可达0.62;人工神经网络预测模型不仅适用于一般污染浓度情况,对于高污染时期PM10质量浓度的预测也较为准确。
关键词:BP人工神经网络;PM10;预测;多元线性回归;高污染
中图分类号:X831 文献标志码:A 文章编号:1672-7207(2012)05-1969-06
Prediction of PM10 mass concentrations based on BP artificial neural network
SHI Ling-zhi, DENG Qi-hong, LU Chan, LIU Wei-wei
(School of Energy Science and Engineering, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China)
Abstract: The back-propagation (BP) artificial neural network model for prediction of PM10 mass concentrations was developed using atmospheric PM10 mass concentration and meteorological data in 2008, which was monitored in Changsha railway-station. In order to show the accuracy of PM10 mass concentration prediction based on artificial neural network, two models were developed: multiple linear regression model and artificial neural network model. The results show that the BP artificial neural network model can be trained to model the highly non-linear relationships between PM10 mass concentration and meteorological parameters, and to provide better results than the traditional multiple linear regression models with much higher goodness of fit (R2). The meteorological parameters and emission source variation variables can accurately describe PM10 variation, and thus provide satisfactory prediction results, with R2 of 0.62. In addition, the developed BP artificial neural network model for prediction of PM10 mass concentrations also works well for PM10 modelling during episode.
Key words: BP artificial neural network; PM10; prediction; multiple linear regression; pollution episode
大气颗粒物浓度的准确预测是人们提前做好防备工作并予以控制的基础,是保护人们健康甚至生命的重要手段,因此准确预测大气颗粒物浓度具有非常重要的意义。由于1 d之中PM10质量浓度的变化很大,有时很剧烈,小时平均峰值浓度甚至可达到天平均浓度的几倍[1],人体短时间暴露在超高浓度的大气污染中的健康危害可能要比长时间暴露在平均浓度污染中的危害更大[2],所以进行PM10小时平均浓度的准确预测显得更为重要。大气颗粒物浓度的时空变化受污染散发源强与气象条件等多种因素的共同影响[3-5]。研究表明颗粒物浓度的变化与气象条件之间呈现很强的非线性关系,因此应用传统的多元线性回归模型预测PM10质量浓度存在很大局限性,不能捕捉到PM10质量浓度与气象参数之间的关系及影响规律,导致预测结果不准确[1, 6-7]。人工神经网络可以克服这一局限性,它能够建立非常复杂的非线性模型,很好地反映PM10质量浓度与气象参数之间的非线性关系[8-9]。人工神经网络已经成功地用于多种污染物的预测研 究[10-12]。现有相关研究主要针对颗粒物天平均浓度进行预测,由于PM10小时质量浓度变化太大,要进行准确预测更加困难,有关颗粒物小时平均质量浓度预测的研究也更少。McKendry[8]利用人工神经网络模型预测1 d中最大PM10和PM2.5小时平均质量浓度;Kukkonen等[13]运用多种人工神经网络模型预测芬兰首都赫尔辛基市区PM10小时平均质量浓度。本文作者以长沙市火车站监测点PM10为研究对象,应用BP人工神经网络模型预测PM10小时平均质量浓度,并与传统的多元线性回归预测结果作比较,说明人工神经网络模型进行PM10小时平均质量浓度预测的准确性。
1 BP人工神经网络模型
神经网络系统通过“学习”所研究的输入输出数据对得到一个描述输入变量与输出变量间关系的非线性映射。神经网络的类型很多,其中BP (Back- propagation)神经网络是一种利用误差反向传播算法的人工神经网络,是人工神经网络模型中使用最广泛的1种。神经网络由1个输入层、1个或多个隐藏层和1个输出层构成。研究表明:1个有足够神经元的单隐藏层的神经网络,通过选择合适的连接权值和传递函数,可以逼近任意1个输入和输出间的光滑的、可测量的函数[14]。因此,本文考虑简单的单隐藏层BP人工神经网络。
单隐藏层BP人工神经网络结构如图1所示,输入层、隐藏层和输出层各层均由大量简单互不相连的神经元组成,而不同层之间通过权值连接。输入神经元将收到的输入数据传输到隐藏层神经元,而隐藏层和输出层神经元将它们各自的输入通过一个非线性传递函数计算后输出。BP神经网络为多层前馈网络,数据信息单方向地从输入层传输到隐藏层再传输到输出层,而前层神经元的输出不能反馈到更前层。
BP人工神经网络的基本原理是:给定网络1个输入,它由输入层单元传递到隐藏层单元,经隐藏层单元处理后再传递到输出层单元,由输出层单元处理后产生1个输出,这是1个前向传播过程;计算实际输出与期望输出之间的误差,将误差值沿网络反向传播并修正连接权值,此为误差反向传播过程;给定另一个输入,重复上述过程,直到全局误差达到满意为止,学习结束。
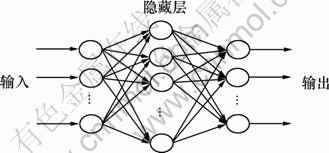
图1 单隐藏层BP人工神经网络结构示意图
Fig.1 BP artificial neural network with one hidden layer
2 PM10质量浓度预测模型建立
2.1 数据处理
本研究主要基于2008年长沙市火车站监测点全年大气PM10小时平均质量浓度数据进行展开,PM10质量浓度采用大气颗粒物监测仪TEOM1400a (Rupprecht & Patashnick, Co., USA)实时监测得到。由于气象条件直接影响大气污染物浓度的变化,因此,要对大气PM10质量浓度进行预测,必须同时考虑PM10基值及气象条件导致的PM10质量浓度变化。
基值浓度:对于PM10基值浓度,本文采取在预测PM10浓度参数中加入每日零点时刻的PM10质量浓度作为初始参考值,即基值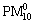 。
。
气象参数:气象参数包括混合层高度(hM)、风速(vW)、太阳辐射强度(ISR)、温度(T)、压力(p)、相对湿度(H)数据直接进入分析。风向(θ)经正弦、余弦转换成2个变量sin θ和cos θ [13],即将风向分别转换为东西方向与南向方向2个变量。降雨量(RF)作为双变量使用:令RF=0代表无降雨,RF=1代表有降雨[1]。
其他变量:污染散发源强等会对PM10质量浓度变化产生很大影响,但是源强数据很难获得且源强变化的不确定性很大,本文考虑到源强的时间变化特性引进以下几个变量:
(1) 考虑1 d中不同时刻污染散发源强的瞬时差异,引进时刻变量sin(2πh/24)和cos(2πh/24)[6],这是由于源强在1 d中是连续变化的,有高峰也有低谷,因此使用时刻的正弦余弦曲线综合表示1 d中源强的变化趋势。
(2) 考虑1周中星期几污染散发源强的短期变化,引进周变量Aweek,其取值参照文献[3],这主要是根据一周中对应每一天的交通量与一周平均交通量之比 得到。
(3) 考虑1 a中不同季节污染散发源强的长期变化,引进季节变量Aseason,根据常见气候特征分别定义为冷季与暖季:1~3月与10~12月为冷期,Aseason=0;4~9月为暖期,Aseason=1。
本文建立模型所用的全部输入变量如表1所示。
表1 预测模型全部输入变量
Table 1 Input variables for prediction models

2.2 BP人工神经网络模型
本研究采用Matlab7.6中人工神经网络应用模块建立BP人工神经网络模型,神经网络模型中隐藏层的非线性传递函数选用简单而广泛使用的S形曲线传递函数,输出层中采用线性传递函数。建立模型首先读入输入变量(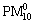 质量浓度及其他参数数据等)与输出变量(PM10质量浓度)。2008年全年样本数据被随机分成3组:
质量浓度及其他参数数据等)与输出变量(PM10质量浓度)。2008年全年样本数据被随机分成3组:
(1) 训练组70%样本,用于训练网络,并根据其误差调试网络,其中训练法则采用Levenberg- Marquardt运算法则;
(2) 验证组15%样本,用于检测网络的泛化能力,当泛化能力不再提高时终止网络训练;
(3) 测试组15%样本,用于独立测试所训练网络的性能,对训练过程无影响。
其次,预设隐藏层神经元个数,开始训练网络。结果误差如果较大,再次训练网络,或调整隐藏层神经元个数,反复训练网络,直到获得最佳结果为止,保存并输出。
2.3 多元线性回归模型
本文采用SPSS16.0建立多元线性回归(Multiple linear regression, MLR)模型,与人工神经网络模型进行比较。多元线性回归模型形式如下:
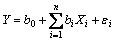 (1)
(1)
其中:Xi为输入变量i的值;Y为实测PM10质量浓度;常数项b0和回归系数bi通过最小二乘法计算求得;εi为回归误差,回归求解的过程即是使平均误差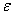 最小的过程。
最小的过程。
3 结果分析
3.1 与多元线性回归结果比较
全部输入变量经逐步(stepwise)回归法得到PM10质量浓度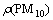 多元线性回归预测模型如下:
多元线性回归预测模型如下:
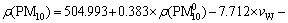
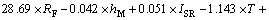
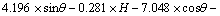
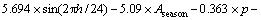

由预测模型可以看出:PM10预测时基值浓度的影响非常重要,其次是风速、降雨量、混合层高度等。有研究表明,气象参数中混合层高度和风速是衡量大气通风扩散能力的关键参数,对污染物浓度起着重要影响[15-16]。降雨对大气颗粒物的冲刷和清除作用也非常重要。本预测模型经逐步回归法保留了13个输入变量,唯独周变量Aweek没有进入回归,可能由于周变量对PM10质量浓度影响很小,因此可以忽略不计。
图2所示为人工神经网络模型与多元线性回归模型的拟合优度。由图2可以看出:人工神经网络模型拟合程度比多元线性回归模型有很大提高。多元线性回归模型预测PM10质量浓度拟合直线明显偏离期望值1:1直线,预测较差。人工神经网络模型预测PM10质量浓度拟合直线与期望值1:1直线较接近,预测结果相对多元线性回归模型有很大提高。
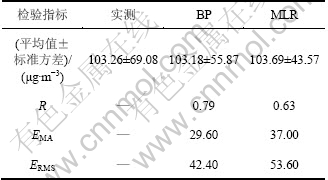
表2所示为人工神经网络模型(BP)与多元线性回归模型(MLR)的预测效果。全年实测PM10平均质量浓度为(103.26±69.08) μg/m3,对比表2中2种模型平均值结果可知:2种预测模型均能很好地预测PM10质量浓度的整体平均值。然而从预测结果的标准偏差值可以看出:2种预测模型都不能完全捕捉PM10质量浓度的变化信息。相对而言,人工神经网络模型预测结果中PM10质量浓度变化较多元线性回归模型结果更能接近实测值的变化,预测更准确,此结果与图2所示结果相一致。为了更好地描述预测模型的预测能力,表2中列出相应的几个常用的检验指标[7, 17-18]:R为相关系数,R越接近于1,表示相关性越高,预测值越接近于实测值;EMA为平均绝对误差,EMA越小预测结果越准确;ERMS为均方根误差,同样ERMS越小越好。由上述3个指标均可判断,人工神经网络模型预测结果更好。BP人工神经网络模型的拟合优度R2为0.62(图2(a)),与Grivas等[1]和Kukkonen等[13]得到的0.60和0.42相比,本文结果较为理想。本文预测PM10质量浓度时使用的气象参数包含了混合层高度,而混合层高度对提高PM10质量浓度预测准确度非常重要[19]。
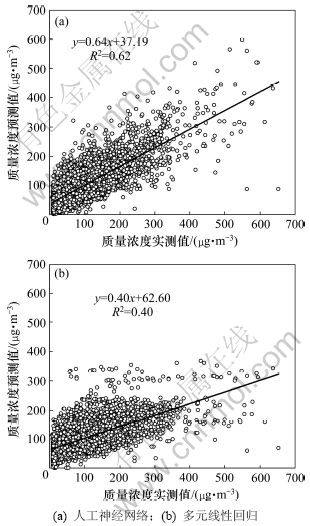
图2 PM10质量浓度预测值与实测值相关性
Fig.2 Scatter plots of predicted versus observed PM10 concentrations
表2 不同预测模型的预测效果
Table 2 Performance indicators for developed predictive models
3.2 预测结果时间序列分析
为了更好地描述人工神经网络模型与多元线性回归模型的预测情况,本文根据预测的PM10小时平均质量浓度数据分别分析经统计的全年24 h变化、日均值时间序列变化及具体高污染时期PM10小时平均质量浓度时间序列变化。
全年整体预测值与实测值的24 h变化如图3所示。从图3中可以非常明显地看出BP人工神经网络和MLR多元线性回归模型预测结果间的巨大差异。BP人工神经网络模型非常好地预测了PM10质量浓度 24 h变化,尽管傍晚时段预测结果稍差些,整体预测效果还是非常理想的。MLR多元线性回归模型预测效果较BP人工神经网络模型差很多,多元线性回归模型仅仅能预测PM10质量浓度的平均变化趋势,根本无法预测到较准确的PM10高/低质量浓度值。图3所示结果充分体现了BP人工神经网络模型相对传统多元线性回归模型的优势。另外,BP人工神经网络模型在傍晚时段拟合稍差的情况很可能由于下班高峰期源强影响很大,利用气象因素影响预测的PM10质量浓度变化跟不上实际值变化的速度与幅度。
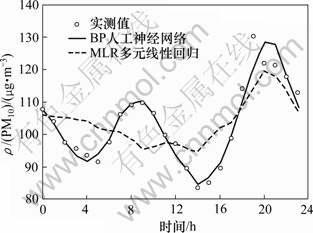
图3 预测值与实测值全年24 h变化
Fig.3 Comparison between predicted and observed PM10 concentration for 24 h variation
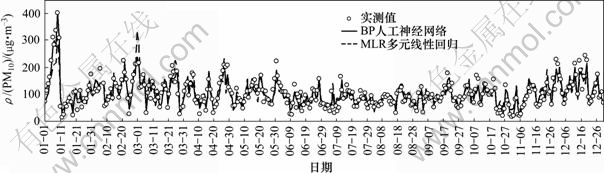
图4 预测与实测日均值比较
Fig.4 Comparison between predicted and observed PM10 concentration for daily variation
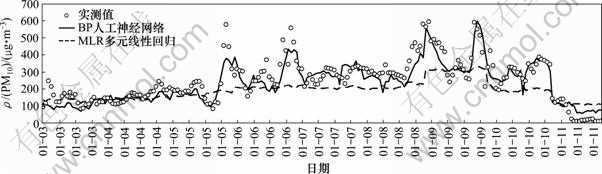
图5 高污染时期预测与实测PM10小时平均质量浓度时间序列比较
Fig.5 Comparison between predicted and observed PM10 hourly concentration time series during PM10 episodes.
图4所示为2种模型2008年预测与实测PM10质量浓度日均值时间序列变化的比较。由图4可以看出:对于统计天平均值,多元线性回归模型和人工神经网络模型预测PM10质量浓度结果都很理想,而人工神经网络模型预测结果相对更好。
为了更清楚具体地看到PM10小时平均质量浓度预测的准确情况,以及判断本文所建立预测模型用于预测高污染浓度时PM10小时平均质量浓度的准确性,本文选取2008年冬季高污染时期2008-01-05至2008-01-09前后共9 d进行具体分析。所选取高污染时段预测情况如图5所示。从图5可见:对于BP人工神经网络模型,与前面统计平均结果相比,预测高污染时段实时PM10小时平均质量浓度效果稍差,但是,整个高污染时期PM10小时平均质量浓度预测结果与已有文献结果对比较理想[1]。预测结果中有些时刻点尤其是浓度变化较剧烈的时段,预测值难以跟上实际值的变化,预测不准,但绝大多数时刻点预测结果还是准确的。对于MLR多元线性回归模型,预测效果与图3结果类似,其仅能预测PM10质量浓度的平均变化趋势,预测值无法跟上实际PM10质量浓度变化的幅度。总体而言,传统的多元线性回归模型不能预测大气PM10小时平均质量浓度,预测效果很差,而运用人工神经网络预测PM10小时平均质量浓度结果较 准确。
4 结论
(1) 人工神经网络模型可以很好地预测大气PM10质量浓度,其预测结果较传统多元线性回归模型能更好地捕捉污染物浓度与气象因素间的非线性影响规律,预测更准确。人工神经网络可以作为预测PM10质量浓度的首选方法。
(2) 本文选取的气象参数及污染源强变量能较准确地描述大气PM10质量浓度的变化,用于PM10质量浓度的预测准确度较高。
(3) 对于PM10统计天平均浓度,多元线性回归模型和人工神经网络模型预测结果都很理想。对于PM10小时平均质量浓度,多元线性回归模型仅仅能预测PM10质量浓度的平均变化趋势,无法准确预测较高或较低的PM10质量浓度,而BP人工神经网络模型能较准确地预测PM10小时平均质量浓度的变化。
(4) 运用人工神经网络方法建立的PM10质量浓度预测模型不仅适用于一般污染浓度情况,对于高污染时期PM10质量浓度的预测也较为准确,适用性广。
参考文献:
[1] Grivas G, Chaloulakou A. Artificial neural network models for prediction of PM10 hourly concentrations, in the Greater Area of Athens, Greece[J]. Atmospheric Environment, 2006, 40(7): 1216-1229.
[2] Gold D R, Litonjua A, Schwartz J, et al. Ambient pollution and heart rate variability[J]. Circulation, 2000, 101(11): 1267-1273.
[3] Ziomas I C, Melas D, Zerefos C S, et al. Forecasting peak pollutant levels from meteorological variables[J]. Atmospheric Environment, 1995, 29(24): 3703-3711
[4] Chaloulakou A, Kassomenos P, Spyrellis N, et al. Measurements of PM10 and PM2.5 particle concentrations in Athens, Greece[J]. Atmospheric Environment, 2003, 37(5): 649-660.
[5] Hussein T, Karppinen A, Kukkonen J, et al. Meteorological dependence of size-fractionated number concentrations of urban aerosol particles[J]. Atmospheric Environment, 2006, 40(8): 1427-1440.
[6] Gardner M W, Dorling S R. Statistical surface ozone models: An improved methodology to account for non-linear behaviour[J]. Atmospheric Environment, 2000, 34(1): 21-34.
[7] Chaloulakou A, Saisana M, Spyrellis N. Comparative assessment of neural networks and regression models for forecasting summertime ozone in Athens[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2003, 313(1/2/3): 1-13.
[8] McKendry I. Evaluation of artificial neural networks for fine particulate pollution (PM10 and PM2.5) forecasting[J]. Journal of the Air & Waste Management Association, 2002, 52(9): 1096-1101.
[9] Perez P, Reyes J. Prediction of maximum of 24-h average of PM10 concentrations 30h in advance in Santiago, Chile[J]. Atmospheric Environment, 2002, 36(28): 4555-4561.
[10] Kolehmainen M, Martikainen H, Ruuskanen J. Neural networks and periodic components used in air quality forecasting[J]. Atmospheric Environment, 2001, 35(5): 815-825.
[11] Papanastasiou D K, Melas D, Kioutsioukis I. Development and assessment of application of neural network and multiple regression models in order to predict PM10 levels in a medium-sized Mediterranean city[J]. Water, Air & Soil Pollution, 2007, 182(1/2/3/4): 325-334.
[12] Cai M, Yin Y, Xie M. Prediction of hourly air pollutant concentrations near urban arterials using artificial neural network approach[J]. Transportation Research Part D, 2009, 14(1): 32-41.
[13] Kukkonen J, Partanen L, Karppinen A, et al. Extensive evaluation of neural network models for the prediction of NO2 and PM10 concentrations, compared with a deterministic modelling system and measurement in central Helsinki[J]. Atmospheric Environment, 2003, 37(32): 4539-4550.
[14] Hornik K, Stinchcombe M, White H. Multilayer feedforward networks are universal approximators[J]. Neural Networks, 1989, 2(5): 359-366.
[15] Chou C C K, Lee C T, Chen W N, et al. Lidar observations of the diurnal variations in the depth of urban mixing layer: A case study on the air quality deterioration in Taipei, Taiwan[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2007, 374(1): 156-166
[16] Wise E K, Comrie A C. Meteorologically adjusted urban air quality trends in the Southwestern United States[J]. Atmospheric Environment, 2005, 39(16): 2969-2980.
[17] Chaloulakou A, Grivas G, Spyrellis N. Neural network and multiple regression models for PM10 prediction in Athens: Acomparative assessment[J]. Journal of the Air & Waste Management Association, 2003, 53(10): 1183-1190.
[18] Liu W Z, Wang W J, Wang X K, et al. Potential assessment of a neural network model with PCA/RBF approach for forecasting pollutant trends in Mong Kok urban air, Hong Kong[J]. Environment Research, 2004, 96(1): 79-87.
[19] Hooyberghs J, Mensink C, Dumont G, et al. A neural network forecast for daily average PM10 concentrations in Belgium[J]. Atmospheric Environment, 2005, 39(18): 3279-3289.
(编辑 杨幼平)
收稿日期:2011-05-23;修回日期:2011-07-18
基金项目:高等学校全国优秀博士学位论文作者专项资金资助项目(200545);国家自然科学基金资助项目(51178466);国家“十一五”科技支撑计划项目(2008BAJ12B03)
通信作者:邓启红(1973-),男,河南潢川人,博士,教授,从事室内空气质量研究;电话:0731-88877175;E-mail: qhdeng@csu.edu.cn