文章编号:1004-0609(2007)04-0547-07
熔体过热处理对Al-4.7%Cu合金定向凝固组织的影响
司乃潮,孙克庆,吴 强
(江苏大学 材料科学与工程学院,镇江 212013)
摘 要:分别在750、850、950和1 050 ℃下,研究熔体过热处理对Al-4.7%Cu(质量分数)合金定向凝固组织的影响,利用综合热分析仪测定Al-4.7%Cu合金熔体结构特征及变化过程。结果表明:经过950 ℃和1 050 ℃过热处理的一次枝晶间距比在750 ℃常规过热直接定向凝固的分别减小了31.2%和36.2%;随着熔体过热时间的延长,一次枝晶间距减小,组织越来越细密;但随着低温保持时间的延长,一次枝晶间距增大,组织越来越粗大,表明熔体高温处理对定向凝固组织形态的影响逐渐衰退;熔体过热处理对Al-4.7%Cu合金定向凝固组织有显著影响的原因在于熔体过热处理改变了熔体结构状态。
关键词:定向凝固;过热处理;一次枝晶间距;熔体结构;凝固组织
中图分类号:TG 132.3 文献标识码:A
Influence of melt superheat treatment on directional solidification microstructure of Al-4.7%Cu alloy
SI Nai-chao, SUN Ke-qing, WU Qiang
(School of Materials Science and Engineering, Jiangsu University, Zhenjiang 212013, China)
Abstract: The influence of melt superheat treatment on the directional solidification microstructure of Al-4.7%Cu(mass fraction) alloy was studied at 750, 850, 950 and 1 050 ℃, respectively. The characteristics of the melt were measured by integrated thermal gravimetric analyzer. The results show that the primary dendrite arm spacing of the superheated samples at 950 and 1 050 ℃ decreases 31.2% and 36.2%, respectively, compared with the sample treated at 750 ℃. Along with the increase of melt superheat time, the primary dendrite arm spacing decreases and the microstructure is refined. However, if the melt stays at low temperature for a long time, the primary dendrite arm spacing increases and the microstructure coarsens, which indicates that the effect of melt superheat treatment on the morphology of directional solidification microstructure declines. The radical reason is that the superheat treatment makes the alloy microstructure changed.
Key words: directional solidification; superheat treatment; primary dendrite arm spacing; melt structure; solidification microstructure
定向凝固技术是伴随着高温合金的发展而逐步发展起来的。该技术最初用来消除结晶过程中生成的横向晶界,从而提高材料的单向力学性能[1-2]。由于定向凝固技术能得到一些具有特殊组织取向和优异性能的材料,因而自它诞生以来得到了迅速发展[3-4]。近年来,随着定向凝固技术的发展,定向凝固的实验研究也不断深入[5-6]。
熔体结构的变化对合金的凝固过程、凝固组织和性能都有重要影响,改变熔体结构的重要措施之一是对合金熔体进行过热处理(BTOP)[7]。所谓 BTOP工艺,是将合金熔体加热到高于合金液相线200~400 ℃的临界温度下保温,然后冷却到合金浇注温度再进行凝固。临界温度取决于合金的化学成分与相成分,在临界温度附近合金熔体的性质会发生突变,从而影响合金的凝固组织和力学性能。国内外学者针对熔体过热处理问题展开了大量的工作,主要集中于Al-Si合金、Al-Cu合金、Cu-Zn-Al形状记忆合金及Ni基高温合金熔体过热处理与组织的关系[8-10],但是涉及到熔体过热处理影响定向凝固组织与性能的研究尚不多。同时BTOP工艺虽然表明了高温熔体处理对定向凝固高温合金组织、性能的影响和作用,但BTOP工艺没有排除温度梯度变化的影响。而且,液态合金结构、熔体过热对液态合金结构的影响以及液态合金结构与凝固组织之间联系还有待进一步研究[11-12]。
本文作者在温度梯度、抽拉速率一定的条件下,研究熔体过热温度对定向凝固组织的影响,探索熔体过热温度影响定向凝固组织的内在机制。
1 实验
实验前将纯度为99.99%的电解铝和99.999%的电解铜按要求的成分熔配并浇注成原始试棒,然后在快速凝固法定向凝固技术设计制造的定向凝固炉中制备定向凝固试样。为了在温度梯度、抽拉速率等工艺因素相同的条件下观察熔体过热温度θs对定向凝固组织影响,确定定向凝固温度θ0和抽拉速率v0,再选定熔体的过热温度θs,在每次实验过程中,均是将其加热至θs并保温ts后迅速冷却至θ0,在相同的抽拉速率v0下进行定向凝固,以保证液固界面前沿温度梯度、抽拉速率等工艺因素相同。本实验选定θ0=750 ℃,v0=90 μm/s,ts=60 min,θs分别为750、850、950和1 050 ℃。
将定向凝固试样在稳定生长50 mm的位置上截取长度约为20 mm的样品,制成沿横截面和纵截面的2块金相试样。采用V(HF)?V(HCl)?V(HNO3)=2?3?5的腐蚀液进行微观侵蚀,在NIKON 卧式光学显微镜上进行组织观察与照相,采用定量金相分析仪测定枝晶一次间距。利用STA449C综合热分析仪测定Al-4.7%Cu合金的反应阶段及相转变温度。
2 定向凝固工艺参数的确定
熔体合金在熔点以上不同的温度下,其内部结构会发生可逆的或不可逆的转变,从而影响到最终定向凝固组织,因此,为了确定单一的对应关系,选用了比较简单的方式来实现其过热处理过程,如图1所示。

图1 熔体过热处理工艺流程
Fig.1 Schematic diagram of melt superheat treatment
2.1 定向凝固温度的选定
熔体过热处理实验所要求的前期熔体热处理,需要尽可能宽的热处理温度范围。实验中的真空凝固可大大减小合金氧化,但当温度较高时,合金的高温、低气压环境也降低了液态合金组分的稳定性。特别是对低熔点合金系,就必须限制定向凝固温度θ0,防止液态合金的挥发。定向凝固中所使用的正温度梯度只有达到一定高度后,才能得到稳定、可靠的定向凝固质量,即在选定合金系与定向凝固设备后,定向凝固温度θ0不应低于稳定的定向凝固所要求的最小值。此外,还应考虑熔体过热处理对定向凝固组织性能的影响程度,因为过高的正温度梯度,有可能完全抑制了这种影响的表现。因此,在本实验条件下如何确定定向凝固温度θ0,使其能够综合满足上述条件,成为本实验的关键所在。根据图2可知,Al-4.7%Cu合金的液相线温度为648.0 ℃,合金在660~750 ℃范围内,差热曲线基本保持平直无变化,之后,合金熔体有大范围、较强烈的吸热出现,因此选定θ0为750 ℃。

图2 Al-4.7%Cu合金的热重-差热曲线
Fig.2 TG-DSC curves of Al-4.7%Cu alloy
2.2 定向凝固抽拉速率的选定
在定向凝固中,液固界面前沿的温度梯度和凝固速率是影响界面形态凝固组织及力学性能的2个主要参数。在温度梯度确定的情况下,凝固组织形态取决于定向凝固速率。蔡英文等[13]研究表明,在低速凝固状态下,定向凝固固液界面的推移速率与设备的机械抽拉速率可看作相等。随着速率的增大,界面形态由平向胞和枝转化。因此,如何选择v0也成为本实验能否成功的关键。
图3所示为不同抽拉速率下Al-4.7%Cu合金的定向凝固组织。由图3可见,在θ0=750 ℃、θs=850 ℃、ts=60 min、th=60 min条件下,随着抽拉速率的增大,组织形态由柱状晶胞向枝晶组织转变。当v=90 μm/s时,凝固组织呈稳定的、有序的树枝晶。由于本实验研究熔体过热处理对定向凝固组织,即一次枝晶间距的影响,因此选择定向凝固抽拉速率v0为90 μm/s。

图3 不同抽拉速率下Al-4.7%Cu合金的定向凝固组织
Fig.3 Directional solidification microstructures of Al-4.7%Cu at different withdrawal rates: (a) 3.0 μm/s; (b) 45.0 μm/s; (c) 90.0 μm/s
3 熔体过热处理对定向凝固组织的影响
3.1 熔体过热温度对定向凝固组织的影响
图4所示为在θ0=750 ℃、v0=90 μm/s、ts=60 min、th=60 min条件下,熔体过热温度对Al-4.7%Cu合金定向凝固组织的影响。由图4可知,随着熔体过热温度θs的提高,Al-4.7%Cu合金的凝固组织从粗枝晶向细枝晶转变,合金一次枝晶间距λ1减小,即组织越来越细密。在过热处理的Al-Cu合金熔体中,由于熔体过热,导致不可逆类固型原子团簇熔化和原子集团平均尺度的变小,熔体结构发生变化,从而引起非均匀形核中心数量减少和形核过冷度增大,使均匀形核生长过程逐步占优[14]。图2所示的DSC曲线在780 ~900 ℃附近出现较明显的吸热反应,显示熔体结构发生变化。因此熔体加热到850 ℃和950 ℃时,熔体结构会发生变化,使形核过冷度增大。形核过冷度越大,形核率则越大[15],组织则越细密,从而使一次枝晶间距在850 ℃和950 ℃时明显减小。而且随着熔体过热温度θs的提高,一次枝晶生长方向由偏转逐渐变直。经过950 ℃和1 050 ℃过热处理的λ1比在750 ℃常规过热直接定向凝固的λ1分别减小了31.2%和36.2%。
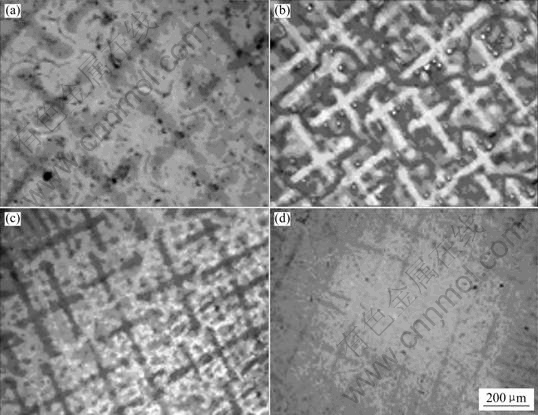
图4 熔体过热温度对Al-4.7%Cu合金定向凝固组织的影响
Fig.4 Influence of melt superheat temperature on directional solidification microstructures of Al-4.7%Cu alloy: (a) θs=750 ℃, λ1=230.9 μm; (b) θs=850 ℃,λ1=185.2 μm; (c) θs=950 ℃, λ1=158.9 μm; (d) θs=1 050 ℃, λ1=147.4 μm
由于熔体过热,导致不可逆类固型原子团簇熔化和原子集团平均尺度的变小,从而引起非均匀形核中心数量减少和形核过冷度Δθ增大。经小过热度处理的合金熔体仍可在相对较小的形核过冷度Δθ下形核生长,而经较大过热度处理的合金熔体则需要在大的形核过冷度Δθ下形核生长。
综上所述,熔体过热温度对定向凝固组织有显著影响,是因为随着熔体过热温度θs的提高,熔体的形核过冷度Δθ增加,使形核率增大及临界晶核半径变小,结果使组织细化,一次枝晶间距减小。
3.2 熔体过热时间对定向凝固组织的影响
在非平衡体系中,一切定态变量都是时间t和空间位置r的函数[16]。体系从一个定态到达另一个定态需要一定的弛豫时间t′。因此,当熔体由低温被加热到过热温度θs时,熔体的结构状态将随着时间的延长而不断趋向于过热温度θs时的平衡态。当ts达到或超过所需的弛豫时间t′时,熔体结构即达到过热温度θs时的平衡态。但当tss对定向凝固组织形态的影响。
图5所示为在θ0=750 ℃、v0=90 μm/s、ts=850 ℃、th=60 min条件下,熔体过热时间对Al-4.7%Cu合金定向凝固组织的影响。由图5可知,随着熔体过热时间ts的延长,Al-4.7%Cu合金定向凝固组织由粗枝晶向细枝晶转变,一次枝晶间距λ1减小,即组织越来越细密,这与过热温度θs对定向凝固组织的影响一致。但是,即使过热时间ts到了120 min,一次枝晶间距减小的幅度还比较大,说明熔体结构仍处于不平衡状态。在ts=60 min、θs=950 ℃时的组织形态及一次枝晶间距(图4(c))与在ts=120 min、θs=850 ℃时的组织形态及一次枝晶间距(图5(d))相当。总之,熔体过热时间对定向凝固一次枝晶间距有显著影响,可以细化定向凝固 组织。

图5 熔体过热时间对Al-4.7%Cu合金定向凝固组织的影响
Fig.5 Influence of melt superheat time on directional solidification microstructures of Al-4.7%Cu alloy: (a) ts=30 min, λ1=244.9 μm; (b) ts=60 min, λ1=185.2 μm; (c) ts=90 min, λ1=168.0 μm; (d) ts=120 min, λ1=154.9 μm
综上所述,Al-4.7%Cu合金熔体结构达到其平衡态需要相当长的时间,在90 min内不能达到850 ℃的平衡态;在950 ℃过热60 min的组织形态及一次枝晶间距与850 ℃过热120 min的组织形态及一次枝晶间距相当。
3.3 熔体低温保温时间对定向凝固组织的影响
弛豫过渡过程的存在是非平衡体系的重要标 志[8]。当高温熔体快速冷却到低温时,由于合金体系的热扩散系数与溶质扩散系数的数值不同,使得合金熔体在冷却过程中,体系的宏、微观状态不能同步地发生变化。通常情况下,由于合金体系热扩散系数比溶质扩散系数大几个数量级,导致热量传输进行的速率也快几个数量级,即体系达到热平衡所需的弛豫时间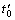 远远小于达到结构平衡所需的弛豫时间t′。因此,当高温熔体以相同的速率快速冷却到低温时,熔体结构并不能同步地达到低温时相应地平衡状态,而是需要更多的时间才能达到。而且冷却速率越快,时间相差的也越长。也就是说,当高温熔体快速冷却到低温时,在经过足够长的低温静置时间th达到低温时相应的平衡状态以前,合金的熔体结构状态是th的函数。因此,考察熔体th对定向凝固组织形态的影响规律对于认识熔体结构状态变化的非平衡属性以及指导熔体热处理工艺规程都具有现实意义。
远远小于达到结构平衡所需的弛豫时间t′。因此,当高温熔体以相同的速率快速冷却到低温时,熔体结构并不能同步地达到低温时相应地平衡状态,而是需要更多的时间才能达到。而且冷却速率越快,时间相差的也越长。也就是说,当高温熔体快速冷却到低温时,在经过足够长的低温静置时间th达到低温时相应的平衡状态以前,合金的熔体结构状态是th的函数。因此,考察熔体th对定向凝固组织形态的影响规律对于认识熔体结构状态变化的非平衡属性以及指导熔体热处理工艺规程都具有现实意义。
图6所示为在θ0=750 ℃、v0=90 μm/s、θs=850 ℃、ts=60 min条件下,熔体低温保持时间对Al-4.7%Cu合金定向凝固组织的影响。由图6可见,随着低温保持时间th的延长,Al-4.7%Cu合金凝固组织由细枝晶向粗枝晶转变,一次枝晶间距λ1增加,即组织越来越粗大。当低温保持时间大于60 min时,定向凝固组织开始排列不整齐,二次枝晶越来越发达。

图6 熔体低温保持时间对Al-4.7%Cu合金定向凝固组织的影响
Fig.6 Influence of holding time of melt under low temperature on directional solidification microstructures of Al-4.7%Cu alloy: (a) th=30 min, λ1=175.0 μm; (b) th=60 min, λ1=185.2 μm; (c) th=90 min, λ1=194.1 μm; (d) th=120 min, λ1=233.3 μm
对比图4和图6可以发现,经850 ℃、60 min高温熔体过热处理再迅速冷却到750 ℃低温静置120 min以后,Al-4.7%Cu合金的组织形态及一次枝晶间距与不经过过热处理在相同条件下于700 ℃直接定向凝固的组织形态及一次枝晶间距相当(图4(a)和图6(d))。在其他条件完全相同时,熔体过热处理对定向凝固组织形态的影响在于熔体过热处理改变了熔体的结构状态。由此可以推断,经850 ℃、60 min高温熔体过热处理再迅速冷却到750 ℃静置120 min时,其熔体结构状态与750 ℃常规过热处理的熔体结构状态相似。经850 ℃、60 min高温熔体过热处理再迅速冷却到750 ℃时达到对应的熔体结构状态所需的弛豫时间t′为60~120 min。这表明随着低温保持时间th的延长,熔体高温处理对定向凝固组织形态的影响逐渐 衰退。
4 结论
1) 熔体处理温度θs对定向凝固一次枝晶间距λ1有显著影响,可以细化定向凝固组织,经过950 ℃和1 050 ℃过热处理的λ1比在750 ℃常规过热直接定向凝固的分别减小了31.2%和36.2%。
2) 随着熔体过热时间ts的延长,Al-4.7%Cu合金定向凝固组织由粗枝晶向细枝晶转变,一次枝晶间距λ1降低,组织越来越细密。
3) 随着低温保持时间th的延长,Al-4.7%Cu合金凝固组织由细枝晶向粗枝晶转变,一次枝晶间距λ1增加,组织越来越粗大,表明熔体高温处理对定向凝固组织形态的影响逐渐衰退。
4) 熔体过热处理对Al-4.7%Cu合金定向凝固组织有显著影响的根本原因在于熔体过热处理改变了熔体结构状态。
REFERENCES
[1] 傅恒志. 铸钢和铸造高温合金及其熔炼[M]. 西安: 西北工业大学出版社, 1985.
FU Heng-zhi. Melting of Cast Steel and Cast Superalloy[M]. Xi’an: Northwestern Polytechnical University Press, 1985.
[2] 郭建亭, 张光业, 杜兴蒿. 定向凝固NiAl合金的超塑性行为[J]. 中国有色金属学报,2004, 14(4): 521-527.
GUO Jian-ting, ZHANG Guang-ye, DU Xing-hao. Investigation of superplasticity in directionally solidified NiAl alloys[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2004, 14(4): 521-527.
[3] 杨 森, 黄卫东, 林 鑫, 周尧和. 定向凝固技术的研究进展[J]. 兵器材料科学与工程, 2000, 23(2): 44-50.
YANG Sen, HUANG Wei-dong, LIN Xin, ZHOU Yao-he. Recent development of directional solidification technology[J]. Ordnance Material Science and Engineering, 2000, 23(2): 44-50.
[4] 朱耀产, 杨根仓, 王锦程, 赵达文, 樊建锋. 二元共晶定向凝固的多相场法数值模拟[J]. 中国有色金属学报,2005, 15(7): 1026-1032.
ZHU Yao-chan, YANG Gen-cang, WANG Jin-cheng, ZHAO Da-wen, FAN Jian-feng. Multi-phase field simulation of unidirectional solidification for binary eutectic alloys[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2005, 15(7): 1026-1032.
[5] 周振平, 李荣德. 定向凝固试验研究现状[J]. 特种铸造及有色合金, 2003(2): 35-38.
ZHOU Zhen-ping, LI Rong-de. Research status of unidirectional solidification development[J]. Special Casting & Nonferrous Alloys, 2003(2): 35-38.
[6] 傅恒志, 李新中, 刘 畅, 苏彦庆, 李双明, 郭景杰. Ti-Al包晶合金定向凝固及组织选择[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2005, 15(4): 495-505.
FU Heng-zhi, LI Xin-zhong, LIU Chan, SU Yan-qing, LI Shuang-ming, GUO Jing-jie. Directional solidification and microstructure selection for Ti-Al peritectic alloy [J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2004, 15(4): 495-505.
[7] 桂忠楼. 镍基高温合金BTOP工艺的发展[J]. 航空制造工程, 1995(4): 12-14.
GUI Zhong-lou. Development of nickel-based superalloys technique BTOP[J]. Aviation Engineering & Maintenance, 1995(4): 12-14.
[8] 关绍康, 沈宁福, 石广新. 熔体预处理对过共晶Al-Si合金组织及性能的影响[J]. 郑州工业大学学报, 1999, 20(2): 5-7.
GUAN Shao-kang, SHEN Ning-fu, SHI Guang-xin. Effect of melt pretreatment on the microstructures and their properties in hypereutectic Al-Si alloy[J]. Journal of Zhengzhou University of Technology, 1999, 20(2): 5-7.
[9] 坚增运. 净化和熔体温度处理对铝合金凝固过程、组织和性能的影响[D]. 西安: 西北工业大学, 1995.
JIAN Zeng-yun. Effect of Purification and Melt Temperature Treatment on Solidification Process, Microstructure and Property of Al Alloy[D]. Xi’an: Northwestern Polytechnical University, 1995.
[10] 魏朋义. 合金凝固新技术及理论的研究——熔体处理组织改性及高梯度单晶制备[R]. 西安: 西北工业大学, 1995.
WEI Peng-yi. New Technology and Theory During Alloy Solidification-Microstructure Modification by Melt Treatments and Preparation of High-Gradient Single Crystal[R]. Xi’an: Northwestern Polytechnical University, 1995.
[11] 周振平, 李荣德.合金熔体过热处理研究的国内发展状况[J]. 铸造, 2003, 52(2): 79-83.
ZHOU Zhen-ping, LI Rong-de. Development status of study on molten melt superheat treatment[J]. Foundry, 2003, 52(2): 79-83.
[12] 司乃潮,孙克庆,刘海霞. 熔体过热处理对定向凝固界面形态及稳定性的影响[J]. 铸造, 2005, 54(5): 429-432.
SI Nai-chao, SUN Ke-qing, LIU Hai-xia. Study on influence of melt superheat treatment on morphology or stability of unidirectional solidified solid/liquid interface[J]. Foundry, 2005, 54(5): 429-432.
[13] 蔡英文, 俞 露, 许振明, 李建国, 傅恒志. 定向凝固界面速率对机械牵引速率的响应[J]. 人工晶体学报, 1998, 27(2): 141-145.
CAI Ying-wen, YU Lu, XU Zhen-ming, LI Jian-guo, FU Heng-zhi. Response of interface velocity to the traction rate during directional solidification[J]. Journal of Synthetic Crystals, 1998, 27(2): 141-145.
[14] 耿兴国, 陈 光, 傅恒志. 过热合金熔体的几种物性滞后效应[J]. 材料科学与工程, 2002, 20(4): 549-551.
GENG Xing-guo, CHEN Guang, FU Heng-zhi. Hysteresis effect on some physical properties of melt superheat[J]. Materials Science and Engineering, 2002, 20(4): 549-551.
[15] 陈 光, 颜银标, 崔 鹏. 熔体过热对Sb-Bi合金凝固组织的影响[J]. 材料科学与工艺, 2001, 9(2): 113-116.
CHEN Guang, YAN Yin-biao, CUI Peng. Effect of melt superheating on solidified structure of a Sb-Bi alloy[J]. Materials Science and Technology, 2001, 9(2): 113-116.
[16] 李如生. 非平衡态热力学和耗散结构[M]. 北京:清华大学出版社, 1986: 55.
LI Ru-sheng. Non-equilibrium Thermodynamics and Dissipative Structure[M]. Beijing: Tsinghua University Press, 1986: 55.
收稿日期:2006-10-28;修订日期:2007-01-17
通讯作者:司乃潮,教授;电话:0511-8780194;E-mail:snc@ujs.edu.cn
(编辑 杨幼平)