文章编号:1004-0609(2009)05-0785-08
AZ31镁合金铸轧板材的热变形空洞演化行为
卢志文1, 2,彭伟平3,李培杰1,雷丽萍1
(1. 清华大学 机械工程系 先进成形制造教育部重点实验室,北京 100084;
2. 南阳师范学院 材料科学与工程系,南阳 473004;
3. 中铝郑州研究院 绿色冶金研究所,郑州 450001)
摘 要:通过疲劳试验机/扫描电镜的原位观察、以及扫描电镜/图像分析软件的定量分析,研究AZ31镁合金铸轧板材热变形过程中的空洞演化行为。结果表明:镁合金板材热变形过程中,空洞首先在晶界尤其是在三叉交界处形核,随后不断长大和聚合,导致材料断裂;空洞的长大具有方向选择性,与拉伸轴方向垂直的空洞容易长大。空洞长大机制的理论模型计算与试验结果对照表明:孔径小于2 μm小空洞的圆度系数接近1,其主要长大机制为晶界扩散;孔径大于2 μm大空洞的圆度系数和取向角均比较分散,其主要长大机制是塑性变形。关键词:AZ31镁合金;铸轧板材;空洞;扩散;塑性变形
中图分类号:TG 111.91 文献标识码:A
Cavity evolution behavior of twin-roll-cast AZ31 alloy sheet during
hot deformation
LU Zhi-wen1, 2, PENG Wei-ping3, LI Pei-jie1, LEI Li-ping1
(1. Key Laboratory for Advanced Manufacturing by Materials Processing Technology, Ministry of Education,
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Tsinghua University, Beijing 100084, China;
2. Department of Materials Science and Engineering, Nanyang Normal University, Nanyang 473006, China;
3. Green Metallurgy Research Department, Zhengzhou Research Institute, CHAICO, Zhengzhou 450001, China)
Abstract: The cavity evolution behavior of twin-roll-cast AZ31 magnesium alloy sheet during hot deformation was investigated by in-situ SEM observation on the fatigue testing machine, and the characteristics of cavity were quantitative measured using graphical analysis software. The results show that the cavity nucleates while the twin-roll-cast AZ31 alloy sheet deforms, and the cavity starts on the tri-grain boundary. The continuously growth and coalescence of the cavities induce the material fracture. The cavities grow directionally and prefer to grow along axis perpendicular to the loading axis. The comparison between the theory analysis and experimental results shows that the shape of the cavity with diameter less than 2 μm is nearly spherical, and the main cavity growth mechanisms is diffusion. In contrast, the cavities with diameter larger than 2 μm tend to be elongated with the long axis parallel to the loading axis, the main cavity growth mechanisms is plasticity deformation.
Key words: AZ31 magnesium alloy; twin-roll-cast sheets; cavity; diffusion; plasticity deformation
镁合金是HCP晶体结构,塑性变形能力较差,传统轧制板材工艺生产困难,成材率低,价格较高,制约其应用。连续铸轧工艺是将材料的连续铸造和轧制结合在一起,在短时间内完成熔体的凝固和热轧,具有简化生产工序、降低生产成本、节约能源、细化组织等优点,受到了国内外学者的广泛关注[1-3]。铸轧板材由液态直接成形,在板材中容易存在铸造缺陷,如疏松和夹渣等,这些缺陷经过短轧制工序难以完全去除,在板材的后续热变形中为空洞形核提供条件。通常,空洞随着塑性变形发生长大,继而聚合或连接,最终导致材料的断裂。
目前,有关铸轧镁合金板材热变形过程中空洞行为的研究较少,但在超塑性变形工艺中,对空洞的演化行为已经有了充分研究,包括空洞的形核[4-6]、长 大[5, 7-10]和聚合[11-15],而且给出了相关的数学模型。SOMEKAWA等[16]研究了点阵扩散机制和晶界扩散机制对AZ61板材超塑性变形中空洞长大行为的影响。LEE和HUANG[17]对AZ31低温超塑性和高温高速超塑性中空洞的行为进行了较为深入的研究,并给出不同长大机制对空洞长大贡献的定量分析。WANG等[18]对AZ31B超塑性变形过程中的空洞损伤演化行为也做了较深入的研究。
本文作者主要通过热拉伸试验,研究了AZ31镁合金铸轧板材热变形过程中的空洞演化行为,建立相关的空洞长大数学模型,定量分析不同热变形条件下扩散机制、塑性变形机制和超塑性扩散机制对空洞长大的影响,为优化镁合金板材成形工艺提供依据,并为进一步改善镁合金铸轧板材的成形性能奠定基础。
1 实验
试验材料为AZ31镁合金铸轧板材,其主要的化学成分为(质量分数,%):2.82 Al,0.854 Zn,0.355 Mn,余量为Mg。图1所示为AZ31镁合金铸轧板材的原 始组织。由图1可知,AZ31镁合金的原始组织主要为细小均匀的退火再结晶晶粒,平均晶粒尺寸约为16.7 μm。
热变形过程中空洞演化行为的原位观察采用带扫描电子显微镜(SEM)的疲劳试验机。该试验机具有在高温环境(室温至800 ℃)用SEM实时观测加载过程中孔洞萌生和长大的功能。原位观察试样平行于轧制方向切取,首先机械抛光,再用5 mL乙酸+5 g苦味酸+100 mL酒精溶液轻微腐蚀10 s,随后立即放入疲劳试验机真空加热室,轻微腐蚀的目的是为了显示空洞演化和原始微观组织间的联系。试验拉伸温度为200、250和300 ℃,应变速率为4×10-4 s-1。

图1 AZ31镁合金铸轧板材的原始组织
Fig.1 Initial microstructure of twin-roll-cast AZ31 alloy sheet
高温拉伸试验在Gleeble-1500D热-力学模拟试验机上进行。拉伸试样沿着轧制方向切取,其标距为27 mm×10 mm×0.8 mm。试验温度分别为200、250、300、350和400 ℃,应变速率均为4×10-4 s-1。试样采用电阻加热至设定温度,控温精度为±1 ℃。每个温度都拉伸至应变为0.2、0.4和0.6以及断裂,拉伸后的试样首先机械研磨,再用0.05 μm的Al2O3抛光,然后在丙酮中超声清洗,使得材料中的空洞完全显现出来。采用FEI Quanta 200 FEG 环境电子扫描显微镜对空洞进行观察、采集图像,每种状态采集30张图片,用Image-Pro Plus图象处理软件对空洞特征进行分析,测定空洞的体积分数、等效直径、圆度系数以及空洞长轴与拉伸轴的夹角ψ(下文简称夹角ψ)。空洞的体积分数与空洞的面积分数是等值的,故只需测定空洞的面积分数即可。
2 实验结果
2.1 空洞演化的原位观察
图2所示为变形温度250 ℃、应变速率4×10-4 s-1条件下材料拉伸至断裂(ε=0.57)过程的空洞演化原位观察。空洞的形核难以直接观察到,因为空洞形核的临界直径大约在0.2 μm左右[19],但对细小空洞的观察可以推测热变形中空洞形核的位置。从图2(a)可以看出,在应变为0.2时,已经可以看到一些细小的空洞出现(白色箭头所指),且主要分布在晶界处,尤其是三叉交界处,这说明空洞的形核主要发生在晶界和三叉交界处。随着变形程度的增加,一方面细小的空洞继续增多(图2(b)中白色箭头所指),另一方面垂直于拉伸方向的空洞出现明显长大,空洞沿拉伸轴方向被拉长。图2(b)中所示A和B处说明空洞的长大具有选择性,与拉伸轴方向垂直的空洞容易长大。当应变增大到0.4时,一些空洞开始聚合,并出现连接现象,如图2(c)中C和D处所示。拉伸至材料快要断裂时(ε=0.55),长大的空洞之间相互连接,并平行拉伸轴方向,如图2(d)中所示E和F处,随后拉伸至ε=0.57即发生断裂,说明空洞的聚合和连接是导致材料断裂的重要原因之一。

图2 250 ℃和4×10-4 s-1变形条件下空洞的原位观察(垂直拉伸)
Fig.2 In-situ SEM observation of cavity deformed at 250 ℃ and 4×10-4 s-1 (vertical stretching): (a) ε=0.2; (b) ε=0.3; (c) ε=0.4; (d) ε=0.55
2.2 空洞尺寸和形态的测定
图3所示为试样拉伸后断口附近轧制平面的SEM像。从图3(a)中可以看出,在200 ℃时(ε=0.42),空洞体积分数较小,且主要为细小空洞,尺寸在2 μm以下。在400 ℃时(ε=0.78),空洞的体积分数和等效直径均明显增大,空洞沿拉伸轴方向被拉长,并相互聚合和连接,如图3(b)中B所示。
空洞面积和空洞直径测量结果如图4所示。在本试验的所有条件下,80%以上的空洞直径小于2 μm,说明空洞的形核数量较多,空洞密度较大,但只有部分空洞能够在随后的变形过程中长大。为了方便分析,定义空洞直径小于2 μm的为小空洞,大于2 μm的为大空洞。根据大小空洞的不同,分别测量空洞的圆度系数以及空洞长轴与拉伸轴的夹角ψ,结果如图5和6所示。从图5可以看出,小空洞大部分的圆度系数值在0.9~1.0之间,这表明空洞的形状接近圆形,对于不同的温度和应变,圆度系数没有明显的差别。从能量的角度看,圆形表面积小,能量最低,有利于小空洞保持稳定存在。大的空洞圆度系数比较分散,且随着温度和应变量的增高,圆度系数较小的空洞数量增多,这说明变形程度越大,大空洞被拉长的现象越明显。

图3 不同热变形条件下断口附近轧制面的SEM形貌(垂直拉伸)
Fig.3 SEM micrographs showing rolling plane of specimen deformed at various conditions (vertical stretching): (a) 200 ℃, ε=0.42; (b) 400 ℃, ε=0.78
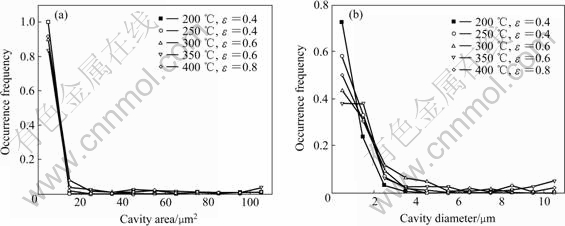
图4 不同变形状态下空洞尺寸的分布状况
Fig.4 Size distribution of cavity under various deformation conditions: (a) Distribution of area; (b) Distribution of nominal diameter

图5 不同变形状态下空洞圆度系数的分布状况
Fig.5 Roundness coefficient distribution of cavity under various deformation conditions: (a) Small cavities with diameter less than 2 μm; (b) Large cavities with diameter larger than 2 μm

图6 不同变形状态下空洞长轴与拉伸轴夹角(ψ)的分布状况
Fig.6 Distribution of angle (ψ) between cavity long axis and loading direction under various deformation conditions: (a) Small cavities with diameter less than 2 μm; (b) Large cavities with diameter larger than 2 μm
从图6可以看出,小空洞在0?~10?分布较高,达到0.20~0.35,其它角度比较均匀,说明部分小空洞沿拉伸方向被拉长,如图3(a)所示的A位置空洞。对于大空洞而言,夹角ψ在各个角度均匀分布,这是因为大空洞夹角ψ的变化主要受空洞长大机制的影响。
3 分析与讨论
3.1 空洞的长大机制
空洞的演化行为主要包括空洞的形核、长大和聚合。在这3个阶段中,长大阶段是最重要的,因为大多材料的变形和使用都在这个阶段。根据超塑性研究给出的理论,塑性变形中空洞的长大存在如下3种主要机制:1) 扩散机制(Diffusion,DIF)[5, 8-9];2) 塑性变形机制(Plasticity,PLA)[10];3) 超塑性扩散机制(Superplasticity diffusion,SPD)[11]。本文作者将采用这3种机制来解释AZ31镁合金铸轧板材中的空洞长大现象。
对于扩散机制控制的空洞长大,空洞半径增长速率和空洞体积增长速率分别为[5, 8]

式中  为原子体积;δgb为晶界宽度;r为空洞半径;
为原子体积;δgb为晶界宽度;r为空洞半径; 为空洞表面能;ε为真应变;σ为流动应力;T为热力学温度;
为空洞表面能;ε为真应变;σ为流动应力;T为热力学温度; 为应变速率;k为Boltzmann常数;Dgb为晶界扩散系数;p为空洞内部压力;2l是两个空洞之间的距离。
为应变速率;k为Boltzmann常数;Dgb为晶界扩散系数;p为空洞内部压力;2l是两个空洞之间的距离。
假设空洞呈球形,对式(2)进行积分,可得
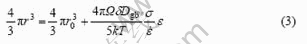
式中 r0是应变ε = 0时的空洞半径。假设空洞密度为常数,空洞密度N,空洞体积分数φV和应变ε的关系可以表示为

式中 φ0是应变ε = 0时的空洞体积分数,通常假设为0.4%[18]。
对于塑性变形控制的空洞长大,在单向应力状态下,空洞半径增长速率和空洞体积增长速率分别为[9]

对式(6)积分后得到
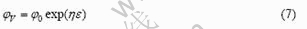
式中 η为与合金类型、晶粒尺寸、温度和应变速率有关的变值。
COCKS和ASHBY[20]基于对空洞长大的理论分析,给出了η的关系式如下

式中 m为应变速率敏感系数。
假设空洞呈球形,且空洞密度为常数,由式(7)可以得到空洞长大直径和应变量的关系

对于超塑性扩散控制的空洞长大,CHOKSHI和LANGDON[10]在充分研究了空洞在超塑性变形过程中的作用和影响以后,鉴于超塑变形时材料晶粒一般很细,提出一个当空洞尺寸大于晶粒尺寸时的空洞超塑性扩散长大模型。根据前面的测量结果可知,AZ31镁合金铸轧板材的晶粒尺寸约为16.7 μm,而空洞的尺寸基本都在10 μm以下,远小于晶粒尺寸,所以本文作者不考虑超塑性扩散机制的影响,只讨论扩散机制和塑性变形机制对空洞长大的影响。空洞的直径和体积分数对于扩散机制可以用式(3)和(4)表示,对于塑性变形机制可以用式(9)和(7)表示。
运用上述两种空洞长大机制,分别对200和 400 ℃两种状态进行分析。相关的参数分别为:原子体积 =2.33×10-28 m3,柏氏矢量b=3.21×10-10 m,波尔兹曼常数k=1.381×10-23 J/K,扩散系数为(200 ℃时,Dgb=5.33×10-13;400 ℃时,Dgb=5.59×10-10[21]),N = (1 000~2 000)×106 m-2 [18]。根据这两种机制控制的空洞长大模型,由式(4)和(7)分别计算得到的空洞体积分数与试验测得数据如图7所示。由式(3)和(9)分别计算得到的空洞等效直径与试验测得数据如图8所示。结果表明:随着温度的升高和应变量的增大,小空洞的体积分数和等效直径基本不变,而大空洞的体积分数和等效直径都有明显的增加。从图7可以看出,在200 ℃时,扩散是主要的空洞长大机制,空洞长大速度较慢;在400 ℃时,塑性变形是主要的空洞长大机制,空洞长大速度较快。从图8可以看出,在不同温度和变形量条件下,对于小空洞而言,其主要的长大机制是扩散;对于大空洞而言,其主要的长大机制是塑性变形。两种机制对于不同变形条件下空洞的影响可以半定量用图9表示。
=2.33×10-28 m3,柏氏矢量b=3.21×10-10 m,波尔兹曼常数k=1.381×10-23 J/K,扩散系数为(200 ℃时,Dgb=5.33×10-13;400 ℃时,Dgb=5.59×10-10[21]),N = (1 000~2 000)×106 m-2 [18]。根据这两种机制控制的空洞长大模型,由式(4)和(7)分别计算得到的空洞体积分数与试验测得数据如图7所示。由式(3)和(9)分别计算得到的空洞等效直径与试验测得数据如图8所示。结果表明:随着温度的升高和应变量的增大,小空洞的体积分数和等效直径基本不变,而大空洞的体积分数和等效直径都有明显的增加。从图7可以看出,在200 ℃时,扩散是主要的空洞长大机制,空洞长大速度较慢;在400 ℃时,塑性变形是主要的空洞长大机制,空洞长大速度较快。从图8可以看出,在不同温度和变形量条件下,对于小空洞而言,其主要的长大机制是扩散;对于大空洞而言,其主要的长大机制是塑性变形。两种机制对于不同变形条件下空洞的影响可以半定量用图9表示。

图7 200 ℃和400 ℃的空洞体积分数试验结果和采用两种长大模型计算结果的比较
Fig.7 Comparisons of volume fraction experimentally measured of cavity with theoretical prediction results based on diffusion model (DIF) and plasticity model (PLA) at 200 ℃(a) and 400 ℃(b)

图8 200 ℃和400 ℃大小空洞等效直径试验结果和采用两种长大模型计算结果的比较
Fig.8 Comparisons of experimentally measured average cavity diameter with theoretical prediction based on diffusion model (DIF) and plasticity model (PLA) at 200 ℃(a) and 400 ℃(b)
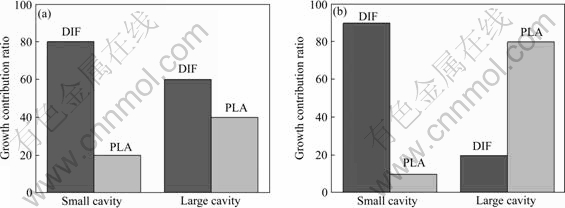
图9 扩散机制和塑性变形机制对大小空洞在200 ℃和400 ℃的长大贡献比例
Fig.9 Estimated growth contribution ratio by two cavity growth mechanisms for small (d<2 μm) and large (d>2 μm) cavities at 200 ℃(a) and 400 ℃(b)
3.2 空洞长大模型
对空洞夹角ψ的统计结果发现,小空洞在0~10?所占的比例为20%~35%,其它角度平均分散。根据前面的长大机制分析,对于小空洞而言,其主要的长大机制是扩散作用,而塑性变形的影响较小。扩散作用的结果就是夹角ψ在所有角度均匀分散,但是塑性变形还是会对一些小空洞产生影响,这样使得一些小空洞有沿拉伸方向拉长的趋势,结果如图10所示。对于大空洞而言,其主要的长大机制是塑性变形,从图2空洞演化的原位观察和图3空洞形貌的SEM观察都可以看出,空洞的长大具有一定的选择性,垂直于拉伸轴的空洞容易长大,这是因为此时的空洞主要是受拉应力作用。可以认为,大空洞都是由夹角ψ接近90?的小空洞长大形成的,在长大的过程中,受塑性变形机制的影响,空洞沿拉伸轴方向被拉长,这使得夹角ψ越来越接近0?,由于空洞开始长大的时间和长大速度的差别,断裂前不同长大阶段的空洞都有,使得夹角ψ成分散状态。可以推断,如果应变继续增加,进入超塑性状态,越来越多的大空洞夹角ψ会接近于0?,这与文献[18]的结果是一致的。

图10 空洞长大机制和选择长大模型
Fig.10 Cavity growth mechanism and preferred direction growth model
4 结论
1) 小空洞圆度系数主要分布在0.9~1.0,即大部分小空洞为圆形或接近圆形,说明其长大主要是由扩散机制引起的。由于受拉应力的影响,部分小空洞的夹角ψ趋向于0?。
2) 大空洞是由夹角ψ接近90?的小空洞长大而来,并沿着拉伸轴被拉长,在长大的过程中夹角ψ趋向于0?,使得大空洞的夹角ψ总体为均匀分布状态,圆度系数随应变增大而减小,说明大空洞的长大主要是由塑性变形机制引起的。
3) 空洞首先在晶界,特别是三叉交界处形核,随着变形的增加,夹角ψ接近90?的小空洞优先长大,长大的空洞相互聚合和连接,导致材料断裂。
REFERENCES
[1] LIANG D, COWLEY C B. The twin-roll strip casting of magnesium[J]. JOM, 2004, 55/56: 26-28.
[2] MINOA T, ASAKAWA M, LEE. Twin-roll strip casting of AZ61 magnesium alloy and improvement of formability by structure-control rolling[J]. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 2006, 177: 534-538.
[3] SONG S X, HORTON J A, KIM N J, NIEH T G. Deformation behavior of a twin-roll-cast Mg-6Zn-0.5Mn-0.3Cu-0.02Zr alloy at intermediate temperatures[J]. Scripta Materialia, 2007, 56: 393-385.
[4] YOO M H, TRINKAUS T. Crack and cavity nucleation at interfaces during creep[J]. Metall Trans A, 1983, 14(4): 547-561.
[5] RAJ R, ASHBY M F. Intergranular fracture at elevated temperature[J]. Acta Metallurgica, 1975, 23: 653-666.
[6] PILLING J, RIDLEY N. Superplasticity in aerospace[M]. Pennsylvania, PA: Metallurgical Society, 1988: 183.
[7] BEERE D, SPEIGHT M V. Creep cavitations by vacancy diffusion in plastically deforming solid[J]. Metal Science, 1978, 12: 172-176.
[8] MCCLINTOCK F A. A criterion for ductile fracture by the growth of holes[J]. J Appl Mech, 1968, 35(6): 363-371.
[9] HANCOCK J W. Creep cavitation without a vacancy flux[J]. Metal Science, 1976, 10: 319-325.
[10] CHOKSHI A H, LANGDON T G. A model for diffusional cavity growth in superplasticity[J]. Acta Metallurgica, 1987, 35: 1089-1101.
[11] STOWELL M J, LIVESEY D W, RIDLEY N. Cavity coalescence in superplastic deformation[J]. Acta Metallurgica, 1984, 32: 35-42.
[12] PILLING J, RIDLEY N. Effect of hydrostatic pressure on cavitation in superplastic aluminium alloys[J]. Acta Metallurgica, 1986, 34(6): 669-679.
[13] NICOLAOU P D, SEMIATIN S L. Deformation by a kink mechanism in high temperature materials[J]. Acta Materialia, 1999, 47: 3679-3694.
[14] NICOLAOU P D, SEMIATIN S L. An analysis of the effect of continuous nucleation and coalescence on cavitation during hot tension testing[J]. Acta Materialia, 2000, 48: 3441-3450.
[15] TAPLIN D M R, SMITH R F. Fracture during superplastic flow of industry Al-Mg alloy[M]. New York: Pergamon Press, 1977: 541
[16] SOMEKAWA H, MUKAI T. Effect of dominant diffusion process on cavitation behavior in superplastic Mg-Al-Zn alloy[J]. Scripta Materialia, 2007, 57: 1008-1011.
[17] LEE C J, HUANG J C. Cavitation characteristic in AZ31 Mg alloys during LTSP or HSRSP[J]. Acta Materialia, 2004, 52: 3111-3122.
[18] WANG Ling-yun, SONG Mei-juan, LIU Rao-chuan. Superplasticity and superplastic instability of AZ31B magnesium alloy sheet[J]. Trans Nonferrous Met Soc China, 2006, 16(2): 327-332.
[19] 张少明, 杨必成, 樊中云, 徐 骏, 石力开, 陈国良. 镁合金AZ61的流变挤压工艺和组织特征[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2007, 17(9): 1423-1428.
ZHANG Shao-ming, YANG Bi-cheng, FAN Zhong-yun, XU Jun, SHI Li-kai, CHEN Guo-liang. Rheo-extrusion of AZ61 Mg alloy and its microstructure[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2007, 17(9): 1423-1428.
[20] COCKS A C F, ASHBY M F. Creep fracture by coupled power-law creep and diffusion under multiaxial stress[J]. Metal Science, 1882, 16(10): 465-474.
[21] 刘俊伟, 陈振华, 陈 鼎. 镁合金轧制板材低温变形行为与微观机制[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2008, 18(9): 1577-1583.
LIU Jun-wei, CHEN Zhen-hua, CHEN Ding. Microstructure evolution and deformation behavior of hot-rolled Mg alloy at low temperatures[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2008, 18(9): 1577-1583.
基金项目:国家自然科学基金资助项目(50675115);河南省科技攻关基金资助项目(072102340010)
收稿日期:2008-03-17;修订日期:2009-02-09
通讯作者:彭伟平,博士;电话:0371-68918672;E-mail: david.wppeng@gmail.com
(编辑 龙怀中)