快速凝固对Sn-8Zn-3Bi合金特性及高温时效钎料/铜焊点结构演变的影响
来源期刊:中国有色金属学报(英文版)2017年第1期
论文作者:赵国际 文光华 盛光敏
文章页码:234 - 240
关键词:快速凝固;Sn-8Zn-3Bi 钎料;熔化特性;时效;显微组织演变
Key words:rapid solidification; Sn-8Zn-3Bi solder; melting characteristic; aging; microstructural evolution
摘 要:研究了快速凝固工艺对Sn-8Zn-3Bi 合金显微组织和熔化特性的影响,分析了经150 °C 高温时效后钎料/铜焊点显微组织演变以评估连接的可靠性。结果表明:经快速凝固后,Sn-8Zn-3Bi 合金中的Bi完全固溶于Sn基体并形成枝晶结构;与常规熔铸态合金相比,Bi在Sn基体中的过饱和固溶导致快速凝固态钎料的熔点上升至接近Sn-Zn共晶合金熔点,但同时减小了由于Bi添加对Sn-Zn合金熔化行为产生的不利影响,钎料/铜焊点界面金属间化合物(IMC)层更为致密和均匀;使用快速凝固态钎料能够显著抑制高温时效过程中钎料/铜焊点界面IMC的形成与生长并改善其界面高温稳定性。
Abstract: The effects of rapid solidification on the microstructure and melting behavior of the Sn-8Zn-3Bi alloy were studied. The evolution of the microstructural characteristics of the solder/Cu joint after an isothermal aging at 150 °C was also analyzed to evaluate the interconnect reliability. Results showed that the Bi in Sn-8Zn-3Bi solder alloy completely dissolved in the Sn matrix with a dendritic structure after rapid solidification. Compared with as-solidified Sn-8Zn-3Bi solder alloy, the melting temperature of the rapid solidified alloy rose to close to that of the Sn-Zn eutectic alloy due to the extreme dissolution of Bi in Sn matrix. Meanwhile, the adverse effect on melting behavior due to Bi addition was decreased significantly. The interfacial intermetallic compound (IMC) layer of the solder/Cu joint was more compact and uniform. Rapid solidification process obviously depressed the formation and growth of the interfacial IMC during the high-temperature aging and improved the high-temperature stability of the Sn-8Zn-3Bi solder/Cu joint.
基金信息:国家自然科学基金资助项目
Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 27(2017) 234-240
Guo-ji ZHAO, Guang-hua WEN, Guang-min SHENG
College of Materials Science and Engineering, Chongqing University, Chongqing 400044, China
Received 2 November 2015; accepted 22 March 2016
Abstract: The effects of rapid solidification on the microstructure and melting behavior of the Sn-8Zn-3Bi alloy were studied. The evolution of the microstructural characteristics of the solder/Cu joint after an isothermal aging at 150 °C was also analyzed to evaluate the interconnect reliability. Results showed that the Bi in Sn-8Zn-3Bi solder alloy completely dissolved in the Sn matrix with a dendritic structure after rapid solidification. Compared with as-solidified Sn-8Zn-3Bi solder alloy, the melting temperature of the rapid solidified alloy rose to close to that of the Sn-Zn eutectic alloy due to the extreme dissolution of Bi in Sn matrix. Meanwhile, the adverse effect on melting behavior due to Bi addition was decreased significantly. The interfacial intermetallic compound (IMC) layer of the solder/Cu joint was more compact and uniform. Rapid solidification process obviously depressed the formation and growth of the interfacial IMC during the high-temperature aging and improved the high-temperature stability of the Sn-8Zn-3Bi solder/Cu joint.
Key words: rapid solidification; Sn-8Zn-3Bi solder; melting characteristic; aging; microstructural evolution
1 Introduction
The lead-containing alloys have been banned in many countries due to their toxicity in recent years. Sn-Zn alloys, which have some advantages, such as relatively low melting point, cost-saving and superior mechanical property, are considered as a kind of candidates that could replace Pb-containing solder in microelectronic packaging and interconnects [1,2]. However, the key problems of Sn-Zn alloys that retarded their application are their poor properties in wettability, spreading, and high temperature oxidation resistance due to the Zn content [2,3]. Alloying is a frequently used method to improve the properties of solder alloys. Many different kinds of alloying elements are selected by lots of researchers as alloys addition into Sn-Zn solders to further improve the properties of Sn-Zn alloys [4].
Studies indicate that an appropriate amount of Bi addition in Sn-Zn alloys can play a role in solution strengthening and improve the creep deformation resistance [5,6]. MAHMUDI et al [7] reported that the fast cooled process decreases the steady state creep rate of the Sn-8Zn-3Bi solder markedly. The addition of Bi in Sn-Zn alloys can also decrease the difference of linear expansion between solder and Cu substrate, reducing the tearing tendency in interface during soldering process. However, hardening and tendering occur due to the excessive addition of Bi in Sn-Zn alloy. On the other hand, with the Bi addition in Sn-Zn alloys, the decrease of melting point can increase the pasty range of the alloys and result in the grain coarsening and an excessive growth of the IMC layer at interface [4,6-9].
A rapidly solidified alloy usually has a good overall performance, therefore the rapid solidification process has been used to optimize the properties and performance of solder alloys in recent years [10,11]. GUSAKOVA and SHEPELEVICH [12] studied the effect of rapid solidification on the microstructure and microhardness of Sn-x%Zn-(11-x)% Bi (x=11, 9, 8, 5, 3) alloys, and the results indicated that the rapidly solidified Sn-Zn alloys had a fine microstructure and more uniform component distribution. JING et al [13,14] showed that the rapid solidification process could improve the corrosion resistance and soldering joint reliability of Sn-9Zn and Sn-9Zn-0.1Ni alloys. Previous studies also analyzed the better overall properties of a rapidly solidified Sn-9Zn-0.1Cr alloy [15,16].
Sn-8Zn-3Bi alloy has a relatively good wettability and joint reliability and has been used successfully in some microelectronic packaging fields. However, up to this date, the research on rapidly solidified Sn-8Zn-3Bi alloy is far from adequacy. The aim of this work is to study the effect of rapid solidification on the microstructure and thermodynamic behavior of the Sn-8Zn-3Bi alloy. Furthermore, the evolution of microstructural characteristics of solder/Cu after an isothermal aging at 150 °C was analyzed to evaluate the interconnect reliability. As-solidified Sn-8Zn-3Bi solder alloy was included for reference.
2 Experimental
The Sn-8Zn-3Bi alloy was melted by using pure Sn (99.99%), Zn (99.99%) and Bi (99.99%) according to mass percent. A ZG-001 vacuum induction melting furnace was used to smelt the alloys with the aerated argon protection after vacuum-pumping. The melting temperature was about 600 °C, and was held for 10 min, and then was molded by casting in a stainless-steel mold. To ensure the homogenization of the composition, the massive solder alloys were remolded 2 times. By using the massive Sn-8Zn-3Bi alloy, the rapidly solidified solder foils were obtained upon crystallization of the melt drop on the internal-polished surface of a copper cylinder with a diameter of 350 mm rotating at a frequency of 25 r/s, which provided a melt cooling rate on the order of 106 K/s [12,17]. The thickness of the foil is about 60 μm.
The differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) was used to analyze the melting characteristics of the solder alloys by a Mettler-Toledo TGA/DSC 1/1100 thermal analysis machine. The heating rate of the testing was 10 °C/min under the argon atmosphere from 30 °C to 250 °C. The specimens were about 20 mg cut from the ingots and the rapidly solidified foils.
The tensile-shear test was used to evaluate the mechanical properties of joining. According to China’s National Standard GB 11363-2008 [18], the Cu-solder- Cu joints for the test were prepared with two pure copper (99.8%) plates, as shown in Fig. 1. Based on the pervious experimental work [15,16], two pure Cu specimens were soldered together with a solder sheet at 240 °C for different time with the aid of commercial RMA flux. The soldering and isothermal aging processes were carried out in a SX-12 box-type furnace with recirculating air. An ANS electronic universal testing machine was employed to carry out the tensile-shear tests with a strain rate of 0.5 mm/min at room temperature. Four joints were evaluated for each set of conditions. A VEGA3 TESCAN scanning electron microscope (SEM) was used to observe the interfacial microstructure of the joints. The element contents were analyzed by an OXFORD ISIS300 energy dispersion spectroscopy (EDS) system. The samples for microstructural observation were etched slightly by 3% HCl + 5% HNO3 + 92% CH3OH (volume fraction) solution after mechanical polishing. The computer aided design software was used to measure and calculate the interfacial reaction layer thickness of the soldering joints, as shown in Fig. 2. The location of datum line in Fig. 2 was determined by both the shape of interfacial reaction layer and the elements distribution at the interface by an energy spectrum analysis [19,20].
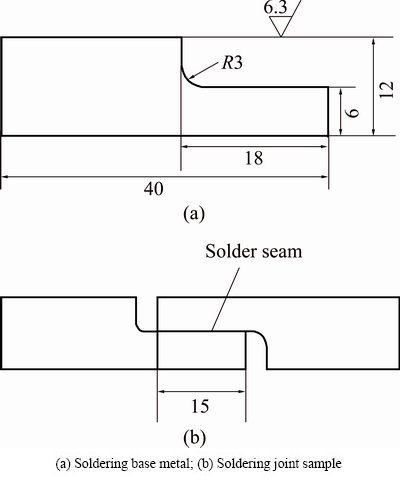
Fig. 1 Schematic diagram of test specimen for soldering joint (unit: mm)
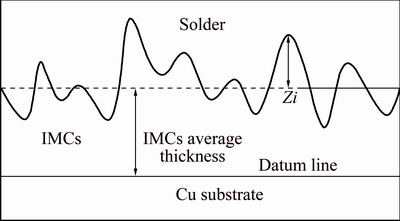
Fig. 2 Thickness measuring schematic diagram of solder/ substrate interface
3 Result and discussion
3.1 Microstructural observation
The Bi addition in Sn-Zn binary alloy can improve the wettability and decrease the melting point. However, the embrittlement tendency of the alloy increases due to the Bi addition. Studies show that the appropriate adding quantity of Bi in Sn-Zn alloys is not more than 6%. The pasty range and the precipitation of the primary Zn-rich phase and Bi-rich phase obviously increase with the Bi addition in higher level. Both the Zn-rich phase and Bi-rich phase are brittle, thus the mechanical properties will become poor due to the overmuch Bi addition in Sn-Zn alloy [21]. Figure 3(a) shows the microstructure of as-solidified Sn-8Zn-3Bi alloy. The EDS result of Bi-rich phase (point A in Fig. 3(a)) is shown in Fig. 3(b).
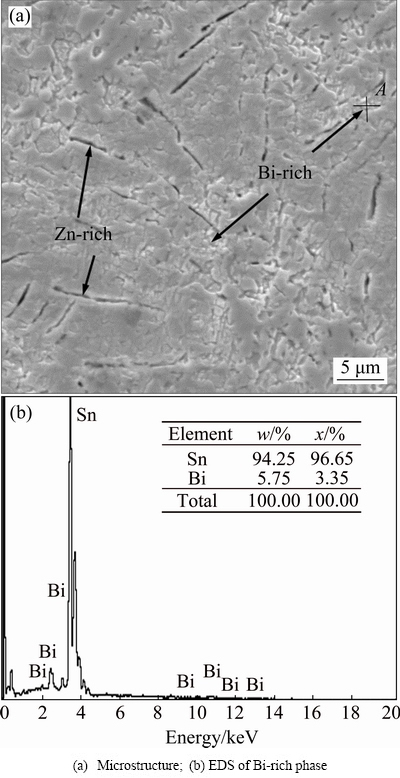
Fig. 3 Microstructure of as-solidified Sn-8Zn-3Bi alloy and EDS analysis result of Bi-rich phase
From Fig. 3, the rod-like Zn-rich phase formed in Sn-rich matrix and the Bi-rich phase precipitation in partial range occurred in as-solidified Sn-8Zn-3Bi alloy. After rapid solidification, the microstructure of alloys changed noticeably. Figure 4 shows the microstructures of the flat surface (Fig. 4(a)) and cross section (Fig. 4(b)) of the rapidly solidified alloy foils of Sn-8Zn-3Bi alloy.
From Fig. 4, the Bi-rich phase disappeared due to the marked increasing of the solubility of Bi in Sn after rapid solidification. These Zn particles have the size of 1-3 μm and distribute in the solder matrix uniformly. This means that the conglomeration of small Zn phases is difficult during the rapid solidification process and the large rod-like Zn phases cannot be formed in the alloy foils. Meanwhile, the Sn-rich phase formed with a dendritic crystal structure and the Bi dissolved in it, forming supersaturated solid solution.
3.2 Melting properties
The melting temperature is a critical solder characteristic. Figure 5 shows the DSC heating curves of the as-solidified Sn-8Zn-3Bi alloy and the rapidly solidified Sn-8Zn-3Bi alloy foils.
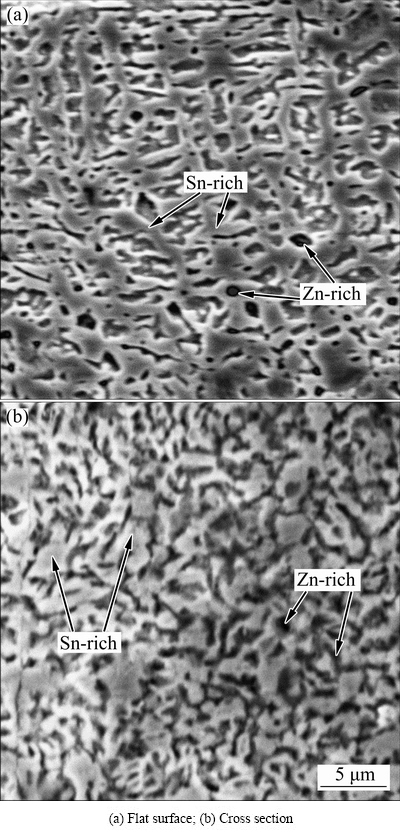
Fig. 4 SEM images of Sn-8Zn-3Bi alloy foils prepared by rapid solidification
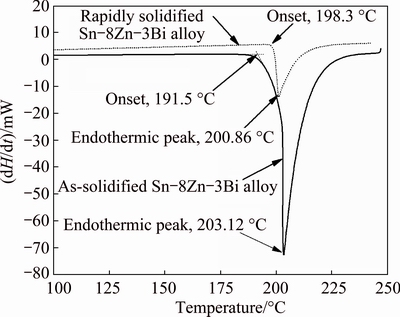
Fig. 5 DSC analysis results of as-solidified and rapidly solidified Sn-8Zn-3Bi solders
From Fig. 5, the melting temperature of as-solidified Sn-8Zn-3Bi solder alloy was 191.5 °C, which is lower than that of the Sn-Zn eutectic alloy (Sn-8.8%Zn, melting point 198.5 °C) obviously. Figure 5 also showed that the pasty range of as-solidified Sn-8Zn-3Bi solder alloy was 11.6 °C, significantly larger than that of the as-solidified Sn-9Zn solder alloy (about 7.2 °C [16]).
After rapid solidification, the melting temperature of Sn-8Zn-3Bi solder alloy rose to about 198.3 °C and closed to that of the Sn-Zn eutectic alloy. The added Bi element in Sn-Zn alloy was dissolved completely in Sn matrix and formed the supersaturated solid solution during the rapid solidification process, as shown in Fig. 4. Thus, the alloying role of Bi addition was not evident and the melting temperature of rapidly solidified Sn-8Zn-3Bi solder alloy increased. Besides, DSC testing results indicated that the pasty range of the rapidly solidified Sn-8Zn-3Bi solder alloy was about 2.5 °C, which was smaller than that of the as-solidified Sn-8Zn-3Bi solder alloy (Fig. 4). It was also slightly smaller than that of the rapidly solidified Sn-9Zn solder alloy (about 3.5 °C [13]).
The rapidly solidified Sn-Zn alloys were in a metastable state of thermodynamics. The releasing of crystal latent heat in the heating process could promote the fusion of the solder alloys markedly. This suggested that the rapid solidification process could obviously improve the melting property of the Sn-8Zn-3Bi alloy and decreased the adverse effect of Bi content in Sn-Zn solder alloy. This implies that the use of rapidly solidified Sn-8Zn-3Bi is a significant attempt to shorten the soldering time and decrease the thermal shock for components and parts.
3.3 Interfacial characteristics and evolution
Rapidly solidified solder alloys usually have a good wettibility and soldering processing properties [10,11]. Figure 6 shows the SEM images of the two types of Sn-8Zn-3Bi solder/Cu joints after soldering at 240 °C for 3 min.
Formation and growth of the interfacial IMC layer during the soldering process are the essential prerequisite to form a reliable connection. From Fig. 6, the interfacial reactions between the two types of Sn-8Zn-3Bi solder alloys and Cu substrate were sufficient and the IMC layer formed at the interface. Compared with the as-solidified Sn-8Zn-3Bi solder/Cu joints, the uniformity of interfacial reaction layer of solder/Cu joint using the rapidly solidified alloy was improved obviously. It could be considered to be the result of the more homogeneous composition distribution and the metastable microstructure of the rapidly solidified solder alloy.
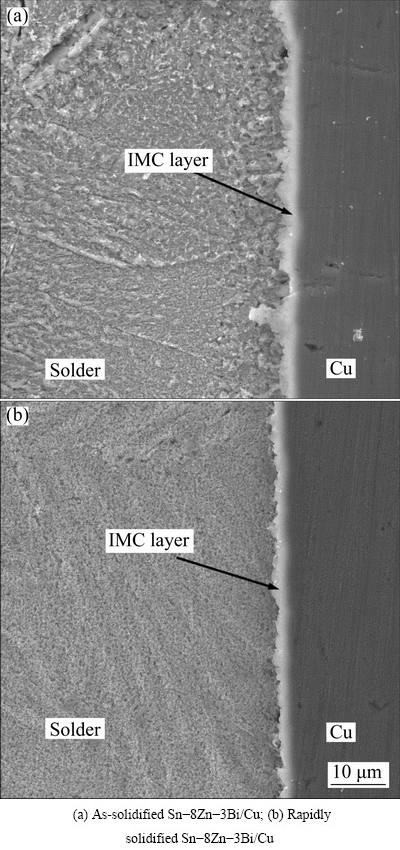

Fig. 6 Microstructures of cross section of solder/Cu joints (240 °C, 3 min)
The evolution of interfacial microstructure of solder/Cu joints after an isothermal aging at 150 °C for different time was analyzed to evaluate the interconnect reliability. The typical interfacial microstructures using the as-solidified and rapidly solidified Sn-8Zn-3Bi solder alloys are shown in Fig. 7. The thickness of interfacial IMC layers after different aging time is shown in Fig. 8.
The IMCs layer at the interface of the soldering joints for Sn-Zn solder/Cu is composed of a γ-Cu5Zn8 layer and a thin CuZn layer. Besides, the granular Cu5Zn8 can be formed in the region nearby the reaction layer due to the diffusion of Cu atoms from substrate to solder during soldering process [2-4]. The high temperature stability of interfacial IMC layer for Sn-Zn solder/Cu is poor. Under a condition of high-temperature isothermal aging, the IMC in large masses formed and the continuity of the interfacial layer was destroyed due to the decomposition of IMC at the interface [22].
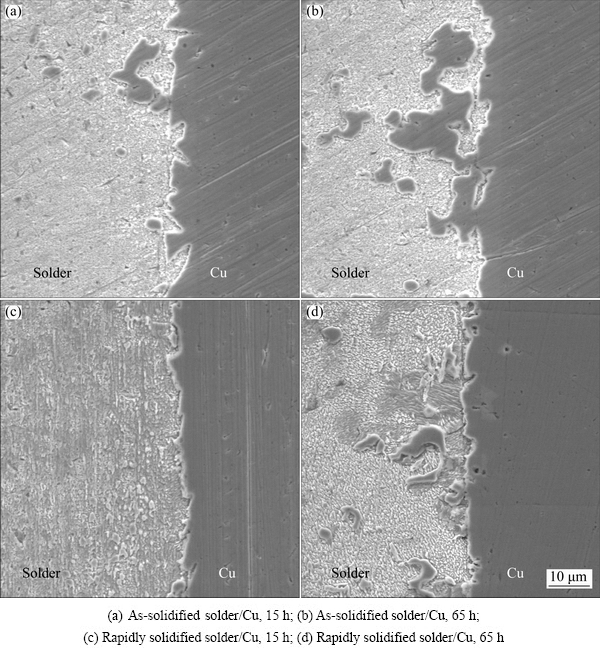
Fig. 7 Interfacial microstructure of two types of Sn-8Zn-3Bi/Cu joints after aging at 150 °C for different time
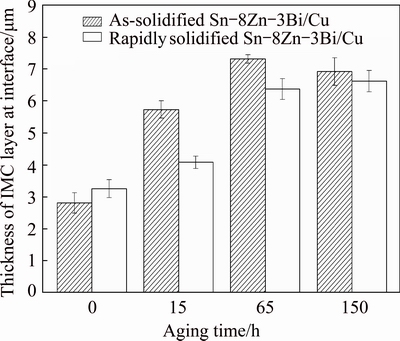
Fig. 8 Thickness of Sn-8Zn-3Bi/Cu joints (T=240 °C, t=3 min) after aging at 150 °C for various time
From Fig. 7, under a condition of same isothermal aging time at 150 °C, the relatively slight microstructural changes of solder/Cu joints were observed using the rapidly solidified Sn-8Zn-3Bi solder alloy (Figs. 7(c) and (d)). The interfacial reaction and IMC distribution at the interface were also held relatively uniform. By increasing the aging time, a number of protrusions into the solder were found and the boundary layer fractured locally. The IMC layer at the interface became irregular and a decomposed region appeared. A large amount of the Cu-Zn IMC phases could form in the solder matrix due to the outward diffusion of Cu. By using the rapidly solidified solder, the dendritic crystal structure of the solder evolved to be a lamellar-type structure in a uniform type. Besides, as the aging time increased, the lamellar-type structure of the solder became more uniform, but more coarse. These changes could result from the severe interfacial reaction occurred at the interface, as shown in Figs. 7(c) and (d). By comparison with interfacial characteristics of Sn-Zn/Cu [22], the high temperature stability of interfacial IMC layer was obviously improved with the Bi addition. It was more significant using the rapidly solidified Sn-8Zn-3Bi solder alloy.
The component and microstructure of as-solidified Sn-8Zn-3Bi solder alloy was markedly uneven (Fig. 3). The composition segregation at the interface resulted in the fact that the interfacial reaction was not uniform. Rapidly solidified Sn-8Zn-3Bi solder alloy had a finer microstructure (Fig. 4) and a faster melting process (Fig. 5), which improved the uniformity of interfacial reaction and promoted the compactness of IMC layer. The compact and uniform IMC layer depressed the diffusion of Cu atoms and decreased the epitaxial growth tendency of the interfacial IMC. Therefore, the high-temperature stability of interfacial IMC layer was improved.
On the other hand, compared with Sn-Zn solder/Cu joints [22], the decomposition of interfacial IMC layer of Sn-8Zn-3Bi solder/Cu joint was obviously slighter (Fig. 7). The thickness increasing of interfacial layer using rapidly solidified alloy was relatively slow and uniform during the aging process (Fig. 8). The results showed that the Bi addition in Sn-Zn alloy can depress the formation and growth of the interfacial IMC during the high- temperature aging obviously.
From Fig. 8, the total IMC thickness increased with the increasing of aging time at the early stage of the isothermal aging process. The diffusion of Zn and Cu atoms plays a dominant role and the Cu-Zn IMC grows up [23]. With a further increasing in the aging time, the interface became rough and the markedly epitaxial growth of Cu-Zn IMC from the interface to solder occurred (Figs. 7(a) and (c)). After a long temperature aging at 150 °C, the process of thermodynamic equilibrium results in the damage of the IMC layer at the interface (Figs. 7(b) and (d)). The adverse evolution can be obviously depressed using rapidly solidified Sn-8Zn-3Bi solder alloy. With the formation of the compact and uniform IMC layer using rapidly solidified Sn-8Zn-3Bi solder alloy (Fig. 7), the change of interfacial IMC layer thickness was relatively slight during the long elevated temperature aging at 150 °C (Figs. 7(b) and (d)). This indicated that the adverse evolution can be obviously depressed using rapidly solidified Sn-8Zn-3Bi solder alloy.
4 Conclusions
1) After rapid solidification, the Bi in Sn-8Zn-3Bi solder alloy completely dissolved in the Sn matrix with a dendritic structure. The Zn phases presented granular appearance in size of 1-3 μm and distributed in the solder matrix uniformly.
2) The rapid solidification process could obviously improve the melting property of the Sn-8Zn-3Bi alloy and decreased the adverse effect of Bi content in Sn-Zn solder alloy, while its melting temperature rose to close to that of the Sn-Zn eutectic alloy due to the extreme dissolution of Bi in Sn matrix.
3) Compared with as-solidified Sn-8Zn-3Bi, the interfacial IMC layer of solder/Cu joint using rapidly solidified alloy was more compact and uniform, which depressed the formation and growth of the interfacial IMC during the high-temperature aging and improved the high-temperature stability of solder/Cu joint.
References
[1] ABTEW M, SELVADURAY G. Lead-free solders in microelectronics [J]. Materials Science and Engineering R: Reports, 2000, 27: 95-141.
[2] SUGANUMA K, KIM K S. Sn-Zn low temperature solder [J]. Journal of Materials Science: Materials in Electronics, 2007, 18: 121-127.
[3] GARCIA L R, OSORIO W R, PEIXOTO L C, GARCIA A. Mechanical properties of Sn-Zn lead-free solder alloys based on the microstructure array [J]. Materials Characterization, 2010, 61: 212-220.
[4] LIU S, XUE S B, XUE P, LUO D X. Present status of Sn-Zn lead-free solders bearing alloying elements [J]. Journal of Materials Science: Materials in Electronics, 2015, 26: 4389-4411.
[5] MAHMUDI R, GERANMAYEH A R, NOORI H, KHANBAREH H, JAHANGIRI N. A comparison of impression, indentation and impression-relaxation creep of lead-free Sn-9Zn and Sn-8Zn-3Bi solders at room temperature [J]. Journal of Materials Science: Materials in Electronics, 2009, 20: 312-318.
[6] MAHMUDI R, GERANMAYEH A R, KHANBAREH H, JAHANGIRI N. Indentation creep of lead-free Sn-9Zn and Sn-8Zn-3Bi solder alloys [J]. Materials & Design, 2009, 30: 574-580.
[7] MAHMUDI R, GERANMAYEH A R, NOORI H, JAHANGIRI N, KHANBAREH H. Effect of cooling rate on the room-temperature impression: Creep of lead-free Sn-9Zn and Sn-8Zn-3Bi solders [J]. Materials Science & Engineering A, 2008, 487: 20-25.
[8] MAYAPPAN R, ISMAIL A B, AHMAD A Z, ARIGA T, HUSSAIN L B. The effect of crosshead speed on the joint strength between Sn-Zn-Bi lead-free solders and Cu substrate [J]. Journal of Alloys & Compounds, 2007,436: 112-117.
[9] ZHOU J, SUN Y S, XUE F. Properties of low melting point Sn-Zn-Bi solders [J]. Journal of Alloys & Compounds, 2005, 397: 260-264.
[10] JONES H. A perspective on the development of rapid solidification and nonequilibrium processing and its future[J]. Materials Science & Engineering A, 2001, 304-306: 11-19.
[11] LAVERNIA E J, SRIVATSAN T S. The rapid solidification processing of materials: Science, principles, technology, advances, and applications [J]. Journal of Materials Science, 2010, 45: 287-325.
[12] GUSAKOVA O V, SHEPELEVICH V G. Structure and properties of rapidly solidified foils of alloys of Sn-Zn-Bi system [J]. Inorganic Materials: Applied Research, 2010, 1(4): 344-349.
[13] JING Y X, SHENG G M, ZHAO G J. Influence of rapid solidification on microstructure, thermodynamic characteristic and the mechanical properties of solder/Cu joints of Sn-9Zn alloy [J]. Materials & Design, 2013, 52: 92-97.
[14] JING Y X, SHENG G, HUANG Z, ZHAO G. Effects of 0.1 wt% Ni addition and rapid solidification process on Sn-9Zn solder [J]. Journal of Materials Science: Materials in Electronics, 2013, 24: 4868-4872.
[15] ZHAO G J, SHENG G M, LUO J, YUAN X J. Solder characteristics of a rapidly solidified Sn-9Zn-0.1Cr alloy and mechanical properties of Cu/Solder/Cu joints [J]. Journal of Electronic Materials, 2012, 41: 2100-2106.
[16] ZHAO G J, SHENG G M, XUE H F, YUAN X J. Improved mechanical property of a Cu/Sn-9Zn-0.1Cr/Cu joint using a rapidly solidified solder [J]. Materials Letters, 2012, 68: 129-132.
[17] SHEPELEVICH V G, GUSAKOVA O V. Structure and properties of rapidly solidified Sn-Zn foils [J]. Inorganic Materials, 2008, 44: 485-489.
[18] GB 11363-2008. Test method of the strength for brazed and soldered joint (National standard of the People Republic of China) [S]. Beijing: China Standards Press, 2008. (in Chinese)
[19] ZURUZI A S, CHIU C H, LAHIRI S K, TU K N. Roughness evolution of Cu6Sn5 intermetallic during soldering [J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 1999, 86: 4916-4921.
[20] YU D X, WANG L. The growth and roughness evolution of intermetallic compounds of Sn-Ag-Cu/Cu interface during soldering reaction [J]. Journal of Alloys & Compounds, 2008, 458: 542-547.
[21] ZHANG L, XUE S B, GAO L L, SHENG Z, YE H, XIAO Z X, ZENG G, CHEN Y, YU S L. Development of Sn-Zn lead-free solders bearing alloying elements [J]. Journal of Materials Science: Materials in Electronics, 2010, 21: 1-15.
[22] ZHAO G J, SHENG G M, WU L L, YUAN X J. Interfacial characteristics and microstructural evolution of Sn-6.5Zn solder/Cu substrate joints during aging [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2012, 22: 1954-1960.
[23] DUAN L L, YU D Q, HAN S Q, MA H T, WANG L. Microstructural evolution of Sn-9Zn-3Bi solder/Cu joint during long-term aging at 170°C [J]. Journal of Alloys & Compounds, 2004, 381: 202-207.
赵国际,文光华,盛光敏
重庆大学 材料科学与工程学院,重庆400044
摘 要:研究了快速凝固工艺对Sn-8Zn-3Bi 合金显微组织和熔化特性的影响,分析了经150 °C 高温时效后钎料/铜焊点显微组织演变以评估连接的可靠性。结果表明:经快速凝固后,Sn-8Zn-3Bi 合金中的Bi完全固溶于Sn基体并形成枝晶结构;与常规熔铸态合金相比,Bi在Sn基体中的过饱和固溶导致快速凝固态钎料的熔点上升至接近Sn-Zn共晶合金熔点,但同时减小了由于Bi添加对Sn-Zn合金熔化行为产生的不利影响,钎料/铜焊点界面金属间化合物(IMC)层更为致密和均匀;使用快速凝固态钎料能够显著抑制高温时效过程中钎料/铜焊点界面IMC的形成与生长并改善其界面高温稳定性。
关键词:快速凝固;Sn-8Zn-3Bi 钎料;熔化特性;时效;显微组织演变
(Edited by Xiang-qun LI)
Foundation item: Project (50675234) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China
Corresponding author: Guo-ji ZHAO; Tel: +86-23-61879020; E-mail: zhaoguoji2006@sina.com
DOI: 10.1016/S1003-6326(17)60027-X

