激光增材制造Ti64.51Fe26.40Zr5.86Sn2.93Y0.30生物医用合金的显微组织与性能
来源期刊:中国有色金属学报(英文版)2020年第12期
论文作者:韩立影 王存山
文章页码:3274 - 3286
关键词:激光增材制造;成分设计;生物医用钛合金;显微组织;性能
Key words:laser additive manufacturing; composition design; biomedical titanium alloy; microstructure; property
摘 要:从生物力学和成形技术的角度出发,利用“团簇+连接原子”结构模型设计Ti-Fe-Zr-Sn-Y共晶合金,并利用激光增材制造技术在纯钛板上制备该合金的成形体。利用显微硬度计、压缩试验机、纳米压痕仪分别测试合金的硬度、压缩性能及弹性模量。结果表明,合金的硬度、压缩强度和断裂应变分别高达HV (788±10)、2229 MPa和14%,弹性模量则低至87.5 GPa。合金还具有良好的摩擦磨损性能、耐蚀性、成形性及生物相容性。合金的综合性能优于Ti70.5Fe29.5共晶合金和商用Ti-6Al-4V合金。该合金的上述性能使其成为一种很有前途的激光增材制造生物材料。
Abstract: From the perspective of biomechanics and forming technology, Ti-Fe-Zr-Sn-Y eutectic alloy was designed using a “cluster-plus-glue-atom” model, and then the alloy was prepared by laser additive manufacturing (LAM) on pure titanium substrate. The mechanical properties of the alloy were evaluated using micro-hardness and compression tester, and the elastic modulus was measured by nanoindenter. The results show that the alloy exhibits a high hardness of HV (788±10), a high strength of 2229 MPa, a failure strain of 14%, and a low elastic modulus of 87.5 GPa. The alloy also has good tribological, chemical, forming, and biological properties. The comprehensive performances of the Ti64.51Fe26.40Zr5.86Sn2.93Y0.30 alloy are superior to those of the Ti70.5Fe29.5 eutectic alloy and commercial Ti-6Al-4V alloy. All the above-mentioned qualities make the alloy a promising candidate as LAM biomaterial.
Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 30(2020) 3274-3286
Li-ying HAN1,2, Cun-shan WANG2
1. School of Materials and Metallurgy, University of Science and Technology Liaoning, Anshan 114051, China;
2. Key Laboratory of Materials Modification by Laser, Ion and Electron Beams of Ministry of Education, Dalian University of Technology, Dalian 116024, China
Received 2 September 2019; accepted 18 October 2020
Abstract: From the perspective of biomechanics and forming technology, Ti-Fe-Zr-Sn-Y eutectic alloy was designed using a “cluster-plus-glue-atom” model, and then the alloy was prepared by laser additive manufacturing (LAM) on pure titanium substrate. The mechanical properties of the alloy were evaluated using micro-hardness and compression tester, and the elastic modulus was measured by nanoindenter. The results show that the alloy exhibits a high hardness of HV (788±10), a high strength of 2229 MPa, a failure strain of 14%, and a low elastic modulus of 87.5 GPa. The alloy also has good tribological, chemical, forming, and biological properties. The comprehensive performances of the Ti64.51Fe26.40Zr5.86Sn2.93Y0.30 alloy are superior to those of the Ti70.5Fe29.5 eutectic alloy and commercial Ti-6Al-4V alloy. All the above-mentioned qualities make the alloy a promising candidate as LAM biomaterial.
Key words: laser additive manufacturing; composition design; biomedical titanium alloy; microstructure; property
1 Introduction
Laser additive manufacturing (LAM) is a process of laser cladding to make a metal component directly from a 3-D CAD model. It can significantly reduce the “concept to product” time by eliminating several intermediate steps, and has distinct advantage in manufacturing complex shapes of customized medical implants [1-4].
Titanium alloys have been widely used in biomedical field due to high specific strength, superior biocompatibility, and excellent corrosion resistance in biological environment [5-7]. In particular, Ti-6Al-4V alloy has been used as a structural biomaterial for replacing failed hard tissues [8], and the LAM products of the alloy have been widely used in clinical practice abroad, which are still in the development stage in our country. However, the application of the alloy will be limited in the future, as it contains toxic vanadium and has a high elastic modulus [9]. The modulus mismatch between the alloy and natural bone can induce stress shielding effect, resulting in bone resorption over a long period of time. Thus, recent research of biomedical titanium alloys has been focused on the design of new β-type titanium alloys with low elastic modulus and excellent biocompatibility, such as Ti-Mo, Ti-Nb, Ti-Zr and Ti-Sn based alloys [10-13]. So far, the LAM β-type titanium alloy products have been widely used in clinical practice abroad. Unfortunately, the formability of β-type titanium alloys was poor and the microsegregation was easily caused, resulting from the wide temperature range of solidification. Moreover, the strength and the wear resistance were insufficient.
The LAM biomaterials should not only have high biological and mechanical properties, but also possess good formability. It would be worth to develop eutectic microstructure with high biological and mechanical properties, since such alloys have single melting temperature. With this respect, the binary Ti70.5Fe29.5 eutectic alloy having a novel combination of high mechanical properties and good formability is potential candidacy [14,15]. But, it still has limitations. One is that the alloy was easily oxidized forming harmful Ti4Fe2O phase, because residual oxygen in the original powder particles was involved in the LAM process. The other is that the elastic modulus of the alloy (149-154 GPa) was higher than that of natural bone [15]. To develop it into a LAM biomaterial, the most important thing is to improve oxygen removal ability and to decrease elastic modulus.
Previous research [7] has demonstrated that non-toxic yttrium had a good purification effect on the liquid composition of the Ti-Fe alloy, which could effectively suppress the formation of Ti4Fe2O phase, owing to higher chemical affinity between Y and O. Elastic modulus is an intrinsic feature of materials, which is determined by the inter-atomic bonding force [10,16]. To decrease the elastic modulus of the binary Ti-Fe alloy, it is of significance to choose proper alloying elements to adjust the combination of the components. Non-toxic Zr (68 GPa, 0.162 nm) or Sn (50 GPa, 0.172 nm) elements are both good candidates because they have lower modulus and large atomic radius compared with Ti (116 GPa, 0.145 nm) and Fe (211 GPa, 0.127 nm). When single element Zr or Sn dissolves in β-Ti solid solution, the lattice constant of the solid solution will be increased and the bonding force between components will be weakened, which will help to reduce the elastic modulus of the alloy. However, the results of preliminary experiments showed that the role of Zr or Sn in decreasing the elastic modulus of the alloy is at a comparable level, and there is a certain limitation in decreasing the modulus through single alloying element. Therefore, it is necessary to further decrease the elastic modulus through multi-alloying of Zr and Sn elements.
In the present work, Ti-Fe-Zr-Sn-Y eutectic alloy was designed using a “cluster-plus-glue atom” model, and then was prepared by LAM on pure titanium substrate. The microstructure and the properties of the alloy were investigated and compared to those of Ti70.5Fe29.5 eutectic alloy and Ti-6Al-4V alloy.
2 Design of Ti-Fe-Zr-Sn-Y alloy
In terms of a recently proposed “cluster-plus- glue-atom” model, any structure can be dissociated into a cluster part and a glue atom part, so that the phase composition is always described by the cluster formula [cluster][glue atoms]x [17-19].
In the Ti-Fe binary alloy, for instance, there are two clusters near the binary Ti70.50Fe29.50 eutectic point, as shown in Fig. 1. One is a Fe-centered CN14 [Fe-Ti14] cluster derived from Fe-containing bcc β-Ti phase, and the other is a Ti-centered cluster CN14 [Ti-Fe8Ti6] derived from TiFe phase with CsCl structure. The eutectic Ti70.5Fe29.5, which corresponds to the most stable melt, can be formulated as being composed of two stable subunits [Fe-Ti14]Fe1+[Ti-Fe8Ti6]Ti3=Ti24Fe10= Ti70.6Fe29.4 (at.%), in accordance with the dual- cluster model for eutectic liquids [20]. When Zr, Sn and Y are added to the binary eutectic alloy, Zr and Sn will enter into the [Fe-Ti14]Fe1 cluster of β-Ti solid solution, as they do not form CsCl structure with Fe. Moreover, according to the cluster close- packing principle, the cluster is the nearest-shell polyhedron centered by any non-equivalent atomic site in the unit cell of the alloy, which generally consists of elements having strong negative mixing enthalpies, while glue atoms, located among the clusters, are composed of elements having weak mixing enthalpies. Because the mixing enthalpy between Sn and Ti is more negative than that between Fe and Ti, the only site for Sn to occupy is to replace Fe at the central site of the [Fe-Ti14]Fe1 cluster. The mixing enthalpy between Zr and Ti is weaker than that between Fe and Ti, so Zr will substitute the Ti atoms at the first shell of the [Fe-Ti14]Fe1 cluster. A new dual cluster formula for the quaternary eutectic melt should be [Sn-Ti12Zr2]Fe1+[Ti-Fe8Ti6]Ti3=Ti22Fe9Zr2Sn1= Ti64.71Fe26.47Zr5.88Sn2.94 (at.%). Y is not mutually soluble with Ti or Fe, and thus, it will not enter into any cluster formula. Its function lies in the purification of the melt against high-temperature oxidation. Here, it is needed to emphasize that the Y content should be strictly controlled, as too much Y content could cause the formation of some harmful phases. Based on the preliminary experiments, the added amount of Y in the alloy was determined to be 0.3 at.%. Thus, the final composition of the multi-component eutectic alloy is Ti64.51Fe26.40Zr5.86- Sn2.93Y0.30 (at.%).
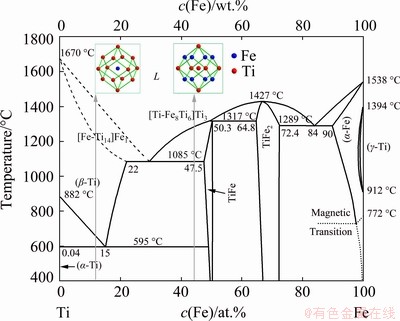
Fig. 1 Ti-Fe binary phase diagram and cluster structure
3 Experimental
The pure Ti plate with dimensions of 30 mm × 20 mm × 20 mm was chosen as substrate material. Master alloys with nominal composition of Ti70.5Fe29.5, Ti64.51Fe26.40Zr5.86Sn2.93Y0.30 and Ti- 6Al-4V were prepared by arc-melting in an argon atmosphere, and then were ground into powder with size of 30-100 mm by ball grinder, which were chosen as LAM materials. A 6 kW CO2 laser unit was used for producing deposited layers. The optimized laser processing parameters were adopted as follows: laser power 2.6 kW, laser beam diameter 6 mm, and scanning velocity 9 mm/s.
Phase identification of these LAM specimens was carried out using XRD-6000 X-ray diffracto- meter. The microstructural characteristics were analyzed using a Zeiss Supra 55 (VP) scanning electron microscope (SEM). Vickers hardness was measured with a DMH-2LS micro-hardness tester under a load of 0.981 N for a dwell time of 30 s. The compressive property was measured with an Instron-type testing machine at a strain rate of 0.1 mm/min. The specimens for compressive testing were 6 mm-long rectangle parallel-piped with 3 mm × 3 mm cross-section. Elastic modulus was measured using a nano Indenter XP with a Berkovich indenter at constant loading rate of 0.05 s-1 and maximum indentation depth of 1000 nm. To obtain reliable results, 30 indentation tests were performed for each specimen. To verify the reliability of the data, the elastic moduli of the binary Ti-Fe eutectic, Ti-6Al-4V, and Ti-Ta-Zr alloys were also measured using a nano indenter. The measured data were basically the same as those obtained with the conventional approach, indicating the method is feasible for measuring elastic modulus of bulky materials. Reciprocating friction- wear test was performed using a CETR UMT-2 testing machine. A Si3N4 ball with a diameter of 5.96 mm and a hardness of HV 1500 was selected as the wear couple. The corrosion behavior was evaluated using a M352 system composed of EG&G273 potentiostat connected to a computer. The corrosive medium was Hank’s simulated balanced salt solution (HBSS), whose temperature during the test was maintained at (37±1) °C. The surface roughness was tested using NV5000 surface profiler.
For evaluation of apatite growth on the surface of alloys, the specimens were soaked for 4 d, in 10 mL of a simulated body fluid (SBF) solution at 37 °C. Then, the specimens were rinsed with deionized water, and then dried at 40 °C. The cytotoxicity evaluation of the alloys was carried out according to GB/T 16886.5 standard. The samples were respectively placed in several petri dishes containing DMEM culture medium (hereafter referred to as serum-free medium, SFM) to extract samples for cytotoxicity testing. Then, the extracts were respectively diluted to 100%, 50%, 10% and 1%. The SFM medium was used as a negative control and the SFM medium with 0.64% phenol was used as a positive control. The morphology of cells was checked using an inverted microscope (DMI 1, Leica). The optical density (OD) was read spectrophotometrically at 490 nm with molecular devices (SpectraMax 190). The RGR was converted into 0-5 material toxicity levels. The level 0 and 1 reactions are non-toxic. Cell adhesion and proliferation tests were carried out according to the following steps. The cells contained in culture plates with samples were cultured at 37 °C in a humidified atmosphere with 5% CO2 for 30 min, 60 min, 120 min, 1 d, 4 d and 8 d, and a cell culture plate without sample was also included as a control. The wells were rinsed twice with PBS after the cell culture. Then, the MTT and DMEM were added into the wells and the cells were incubated at 37 °C for 4 h. After that, 1 mL DMSO was added to the wells and shaken for 10 min to dissolve the product. Finally, the OD of the solving liquid was read spectrophotometrically at 490 nm by molecular devices.
4 Results and discussion
4.1 Microstructure
Figure 2 shows X-ray diffraction patterns of the alloys. The data reveal that Ti70.5Fe29.5 alloy consists of a disordered β-Ti solid solution, an ordered TiFe intermetallic compound, and a small fraction of Ti4Fe2O oxide. The Ti4Fe2O oxide is generally regarded as oxygen-stabilized Ti2Fe intermetallic phase, which causes the embrittlement of the alloy [21]. In the case of the Ti64.51Fe26.40- Zr5.86Sn2.93Y0.30 alloy, the Ti4Fe2O oxide disappears due to purifying effect of Y element. Meanwhile, an additional Zr2Fe intermetallic compound is clearly observed. The data also reveal that the lattice constants of β-Ti and TiFe phases in the Ti70.5Fe29.5 alloy are 0.319 and 0.305 nm, respectively; while those of these phases in the Ti64.51Fe26.40Zr5.86- Sn2.93Y0.30 alloy are 0.328 and 0.302 nm, respectively. This indicates that the additions of Zr and Sn enlarge the lattice constant of β-Ti, resulting from the dissolution of alloying elements in β-Ti. On the contrary, the lattice constant of the TiFe phase decreases due to the deviation from the stoichiometric composition of TiFe.
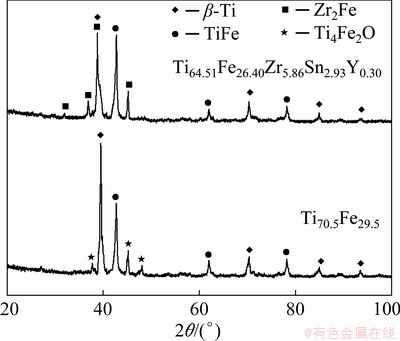
Fig. 2 X-ray diffraction patterns of Ti70.5Fe29.5 and Ti64.51Fe26.40Zr5.86Sn2.93Y0.30 alloys
Figure 3 shows the typical SEM micrographs of the alloys. As shown in Fig. 3(a), the Ti70.5Fe29.5 alloy has a cellular eutectic structure with interlamellar spacing of 1.27 mm. Since residual oxygen in the original powder particles is involved in the LAM processing, Ti4Fe2O oxides with an average size of 12 mm are also found at eutectic colony boundaries. The oxide is generally regarded as oxygen-stabilized Ti2Fe intermetallics, which results in undesirable brittleness.
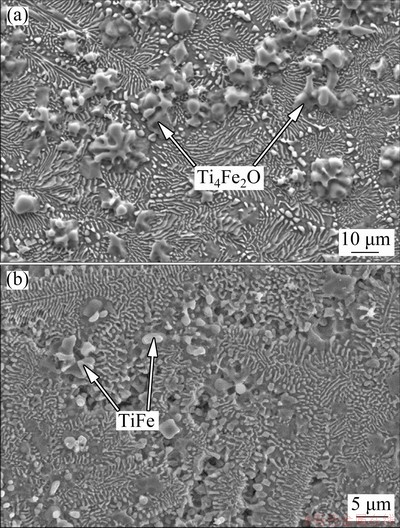
Fig. 3 SEM morphologies of Ti70.5Fe29.5 (a) and Ti64.51- Fe26.40Zr5.86Sn2.93Y0.30 (b) alloys
Likewise, the Ti64.51Fe26.40Zr5.86Sn2.93Y0.30 alloy also exhibits a cellular eutectic structure (Fig. 3(b)). But, there is a clear change in the constituent phases of eutectic, a multi-component eutectic consisting of β-Ti, TiFe, and Zr2Fe phases is formed instead of the binary eutectic as revealed by XRD, and the TiFe particles at the center of the eutectic colonies are clearly observed. Meanwhile, the purifying effect of Y not only restrains the formation of brittle Ti4Fe2O oxide, but also increases supercooling degree of the melt, leading to the grain refinement. The average interlamellar spacing of the eutectic is measured to be 0.45 mm, and is much smaller than that of Ti70.5Fe29.5 alloy. Here, it is worth mentioning that the observed structures of the alloys are in non-equilibrium state, because the β-Ti phase often undergoes a martensitic transformation upon rapid cooling. However, the martensitic transformation is suppressed due to β-stabilizing effect of Fe, resulting in the stabilization of high-temperature β-Ti phase.
4.2 Mechanical properties
Vickers hardness test shows that the hardness of Ti70.5Fe29.5 alloy is about HV (658±10), while that of Ti64.51Fe26.40Zr5.86Sn2.93Y0.30 alloy is HV (788±10). Such an improved hardness for the studied alloy can be attributed to the combination of grain refinement, enhancement effect of intermetallic compounds, and dissolution of alloying elements in β-Ti (solution hardening). As compared to the commercial Ti-6Al-4V alloy (HV 358), the hardness of the Ti64.51Fe26.40Zr5.86Sn2.93Y0.30 alloy is improved significantly.
The strain-stress curves of both alloys under compressive test are shown in Fig. 4. The data reveal that the Ti70.5Fe29.5 alloy fails just after yielding with a failure strain of 5.2% at a maximum stress of about 988 MPa. The fractographic observation displays that radial cracking occurs at the Ti4Fe2O oxide (Fig. 5(a)), which acts as stress-concentrating site. It is believed that the brittle oxides offer no resistance to crack growth. Once the crack is formed in the case of the crack-nucleation controlled fracture, it immediately propagates to cause the fracture of the alloy. The Ti64.51Fe26.40Zr5.86Sn2.93Y0.30 alloy exhibits improved mechanical properties (the maximum stress of 2230 MPa, strain to fracture of 14%) compared with the Ti70.5Fe29.5 alloy. The high strength exceeding 2.0 GPa is also superior to that of the conventional Ti-based alloys having α-Ti, β-Ti or (α+β)-Ti structure (typical values for the Ti-based alloys are 0.8-1.3 GPa) [22]. This fact may be related with the purifying effect of yttrium, which not only restrains the formation of brittle Ti4Fe2O oxide, but also increases supercooling degree of the melt, leading to the grain refinement. Moreover, the enhancement effect of intermetallic compounds and dissolutions of Sn and Zr in β-Ti also play important role in improving the strength of the alloy. The TiFe phase having rounded morphology is believed to be one of factors improving ductility of the alloy, which acts as efficient barriers for shear strain and cracks propagation [23-25]. It can be visualized from Fig. 5(b) that cracks are blocked at the TiFe boundaries (indicated by arrows).
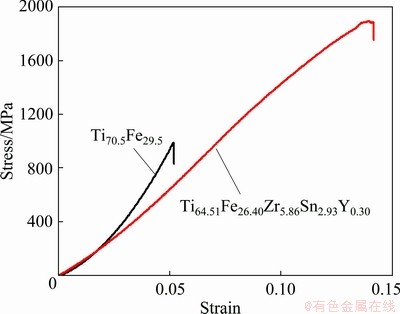
Fig. 4 Strain-stress curves of Ti70.5Fe29.5 and Ti64.51- Fe26.40Zr5.86Sn2.93Y0.30 alloys in compressive test
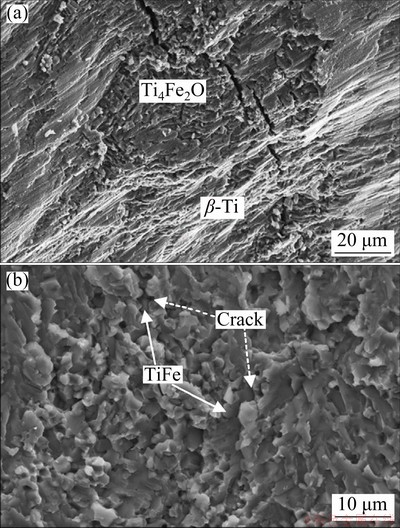

Fig. 5 Compression fracture micrographs of Ti70.5Fe29.5 (a) and Ti64.51Fe26.40Zr5.86Sn2.93Y0.30 (b) alloys
Previous analysis shows that the elastic modulus of the Ti70.5Fe29.5 alloy obtained from its strain-stress curve is only more than 10 GPa and has a large deviation from the data reported in Ref. [22]. To correct the data, a nanoindentation method was adopted. The results show that elastic modulus of the Ti70.5Fe29.5 alloy is 147 GPa and very close to the reported value, indicating that the method is reliable. A significant decrease in elastic modulus (87.5 GPa) is obtained for the Ti64.51- Fe26.40Zr5.86Sn2.93Y0.30 alloy, because the additions of Zr and Sn reduce the bonding force of the lattice of β-Ti and TiFe phases by expanding unit-cell volume and they have low modulus. Moreover, grain refinement also plays a positive role in decreasing the modulus of the alloy.
4.3 Tribological properties
Under dry sliding condition, the friction coefficient and the worn volume of the Ti70.5Fe29.5 alloy are measured to be 0.881 and 0.0782 mm3, respectively, while those of the Ti64.51Fe26.40Zr5.86- Sn2.93Y0.30 alloy are 0.620 and 0.0232 mm3, respectively. This indicates that the studied alloy has significantly better tribological properties than the Ti70.5Fe29.5 alloy. Moreover, the studied alloy exhibits enhanced tribological properties compared with the commercial Ti-6Al-4V alloy (its friction coefficient and the worn volume are measured to be 0.665 and 0.0757 mm3, respectively).
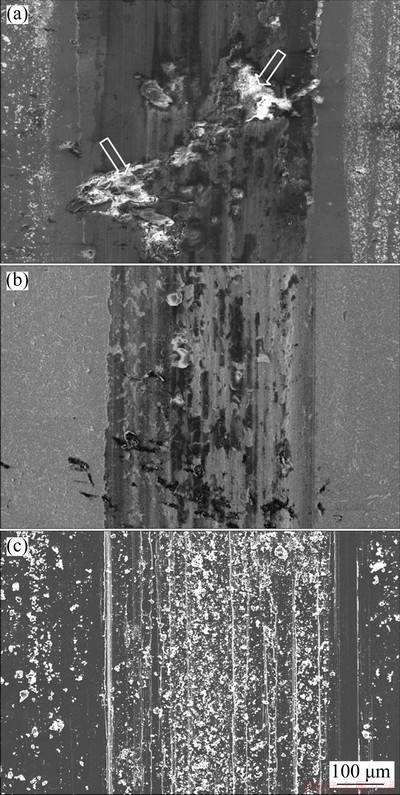
Fig. 6 Worn surface morphologies of Ti70.5Fe29.5 (a), Ti64.51Fe26.40Zr5.86Sn2.93Y0.30 (b) and Ti-6Al-4V (c) alloys
In order to investigate the wear mechanism, the worn surface morphologies of alloys are observed by SEM. As shown in Fig. 6(a), besides the desquamating pits induced by adhesive wear and the furrow characterizing abrasive wear, a large crack is formed on the worn surface of the Ti70.5Fe29.5 alloy and has an angle of about 45° to the sliding direction. The formation of the crack is attributed to the existence of the Ti4Fe2O oxide at eutectic colony boundaries, which acts as stress-concentrating site, leading to the initiation and propagation of crack, even oxide shedding as indicated by arrows. However, only adhesive and abrasive wears take place on the worn surface of the Ti64.51Fe26.40Zr5.86Sn2.93Y0.30 alloy (Fig. 6(b)). Compared with the Ti70.5Fe29.5 alloy, the desquamating pits decrease in number and size, and the furrows become narrower in width and shallower in depth, owing to decreased adhesive tendency between the alloy and wear couple, as well as high hardness [26-29]. As for the commercial Ti-6Al-4V alloy, there are a lot of wide and deep plowing grooves and debris on the worn surface induced by severe abrasive wear (Fig. 6(c)). This makes the tribological properties of commercial Ti-6Al-4V alloy lower than those of the studied alloy.
4.4 Corrosion resistance
Figure 7 displays potentiodynamic polarization curves of the alloys in Hank’s solution. It can be seen that the current density of the Ti64.51Fe26.40- Zr5.86Sn2.93Y0.30 alloy increases first with increasing potential from null-current to 0.3213 V (vs SCE), and then remains a slow rise up to 0.4055 V, which is characteristic of passive behavior. The corrosion current density of this alloy obtained from Tafel plots using both cathodic and anodic branches of the polarization curves is 6.660×10-7 A/cm2, and the corrosion potential is -0.0297 V (vs SCE). The similar curve is also found in the Ti70.5Fe29.5 alloy. But the difference is that the corrosion current density (8.286×10-5 A/cm2) significantly increases, and the corrosion potential (-0.5156 V (vs SCE)) becomes more negative. This indicates that the studied alloy has better corrosion resistance in Hank’s solution. Furthermore, the corrosion resistance of the studied alloy is superior to that of the commercial Ti-6Al-4V alloy (its corrosion current density and corrosion potential are respectively measured to be 5.469×10-6 A/cm2 and -0.2030 V (vs SCE)).
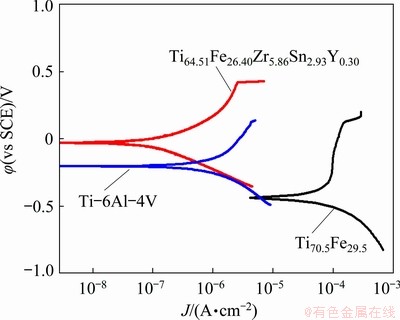
Fig. 7 Potentiodynamic polarization curves of Ti70.5Fe29.5, Ti64.51Fe26.40Zr5.86Sn2.93Y0.30 and Ti-6Al-4V alloys in Hank’s solution
The corroded surface observation displays that the passive film on the Ti64.51Fe26.40Zr5.86Sn2.93Y0.30 alloy is very homogeneous (Fig. 8(a)), which results from the “enveloping effect” of finer eutectic structure, giving rise to a protective barrier against corrosion [30-32]. However, large eroding pits, caused by the dissolution of the Ti4Fe2O oxide, are observed on the Ti70.5Fe29.5 alloy, which leads to the continuity of the passive film decreased (Fig. 8(b)). Compared with the studied alloy, commercial Ti-6Al-4V alloy has suffered slight corrosion and the eroded structures are clearly visible (Fig. 8(c)).
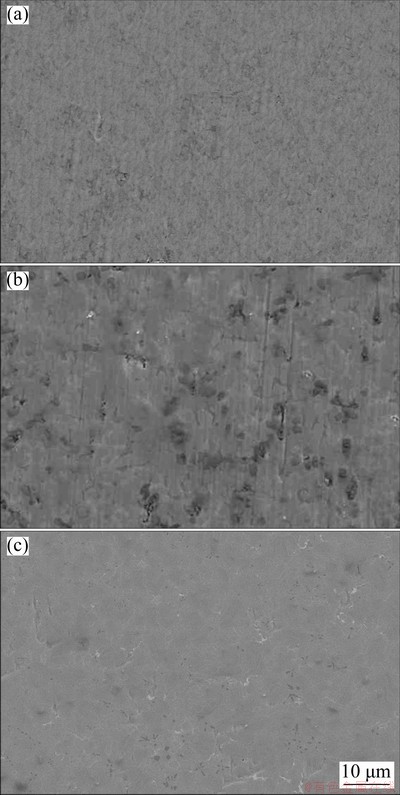
Fig. 8 Corroded surface morphologies of Ti64.51Fe26.40- Zr5.86Sn2.93Y0.30 (a), Ti70.5Fe29.5 (b) and Ti-6Al-4V (c) alloys
4.5 Surface roughness
In checking the surface roughness, the top surface and the side wall were tested from the alloys. From a few initial measurements, it was found that the roughness on top surface was approximately 4% greater than that on side wall. Since the largest roughness on each alloy was of primary interest, measurements were only taken on the top surface. Figure 9 shows the typical 3D profiles taken from the top surfaces of Ti70.5Fe29.5, Ti64.51Fe26.40Zr5.86Sn2.93Y0.30 and Ti-6Al-4V alloys. The data reveal that the surface roughness of the Ti70.5Fe29.5 alloy is 4.721 mm, while that of the Ti64.51Fe26.40Zr5.86Sn2.93Y0.30 alloy is 4.685 mm, indicating that the studied alloy has better formability. The reason is that the purifying effect of Y restrains the formation of Ti4Fe2O oxide, leading to decreased viscosity of the melt [33,34], despite the fact that the studied alloy undergoes wider solidification temperature range than the binary eutectic alloy. In addition, the formability of the studied alloy is better than that of Ti-6Al-4V alloy prepared by LAM using commercial Ti-6Al-4V alloy powder, for the surface roughness of the studied alloy is smaller than that of the Ti-6Al-4V alloy (7.013 mm).
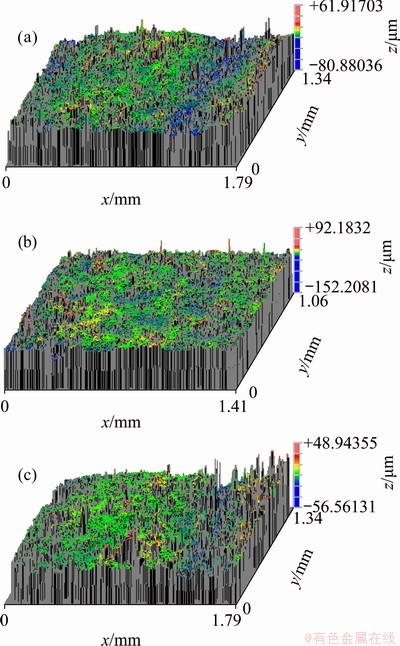
Fig. 9 Typical 3D profiles taken from top surfaces of Ti70.5Fe29.5 (a), Ti64.51Fe26.40Zr5.86Sn2.93Y0.30 (b) and Ti- 6Al-4V (c) alloys
4.6 SBF bioactivity
Figure 10 shows the surface morphologies of the alloys after immersion in SBF solution for 4 d. As shown in Fig. 10(a), the surface of the Ti64.51Fe26.40Zr5.86Sn2.93Y0.30 alloy is almost fully covered by the sediment layer. EPMA analysis reveals that the sediments mostly contain Ca, P, C, O, Ti and Fe, among which the molar ratio of Ca to Ti is 0.548:1, giving the evidence that the sediments may be composed of apatite containing carbonate ions [35-37]. As for the Ti70.5Fe29.5 alloy, the sediment layer is not continuous and becomes thin, on which some flocculent sediment is clearly observed (Fig. 10(b)). As a result, the molar ratio of Ca to Ti decreases to 0.032:1, and is much lower than that of the Ti64.51Fe26.40Zr5.86Sn2.93Y0.30 alloy. With regard to the Ti-6Al-4V alloy, some fine sediment, growing in the form of partition aggregates, occurs on the local surface (Fig. 10(c)). In a consequence, the molar ratio of Ca to Ti decreases to 0.039:1, much lower than that of the Ti64.51Fe26.40Zr5.86Sn2.93Y0.30 alloy.
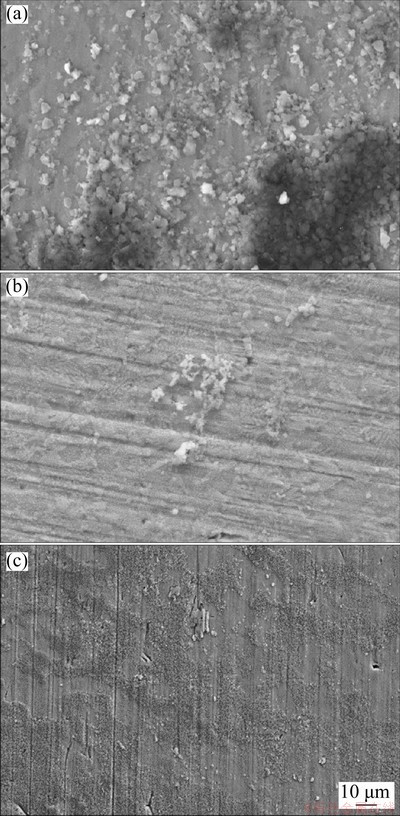

Fig. 10 Surface morphologies of Ti64.51Fe26.40Zr5.86- Sn2.93Y0.30 (a), Ti70.5Fe29.5 (b) and Ti-6Al-4V (c) alloys after immersion in SBF solution for 4 d
In the SBF test, hydroxyl groups (OH-) are adsorbed from SBF to form Ti—OH groups. When the pH is approximately 7.4, the Ti—OH groups are negatively charged, due to the presence of deprotonated acidic hydroxides. Calcium ions (Ca2+) are then adsorbed on the surface of the alloys. As a result, on the negatively charged surface, HOPO42- or H2PO4- can easily react with the as-adsorbed Ca2+ to finally produce calcium phosphate [35,38]. Therefore, the formation of Ti—OH groups on Ti alloy is crucial for apatite deposition. In current practice, two major phases of β-Ti and TiFe can generate galvanic microcells in SBF, of which β-Ti with the high reactivity is acted as the anode with respect to TiFe with the low reactivity. The corrosion attack initiates from the β-Ti phase, leading to the dissolution of the β-Ti phase and formation of Ti—OH groups. The finer the grain is, the larger the anode to cathode area ratio is, and the more the Ti—OH groups will be formed. This can be used to explain why the studied alloy has better apatite deposition ability than Ti70.5Fe29.5 alloy. In addition, the existence of Ti4Fe2O oxide in Ti70.5Fe29.5 alloy also plays a negative role in apatite deposition.
4.7 Cytotoxicity
Observation of cell morphology shows that L-929 fibroblasts in the extract of the Ti64.51Fe26.40- Zr5.86Sn2.93Y0.30 alloy adhere to the wall and display the morphological characteristics of spindle and polyon, as shown in Fig. 11(a), which is very similar to that in the SFM negative control (Fig. 11(b)). This indicates that the cells grow well and have active secretion and metabolish function. Unlike the studied alloy, most of cells in positive control group are small and round with karyopyknosis, being a poisoning morphology (Fig. 11(c)).
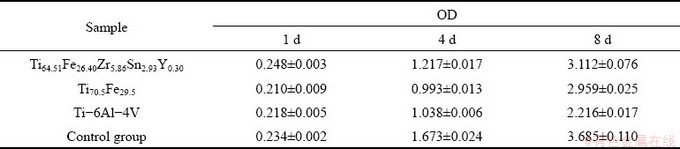
In the further MTT assay, needle-like crystals are observed in different concentrations of extracts of the Ti64.51Fe26.40Zr5.86Sn2.93Y0.30 alloy, and exhibit an obvious increase in amount with dilution of concentration (Figs. 12(a-d)). Similar crystals are also found in the negative control (Fig. 12(e)). In contrast, no crystals are observed in positive control (Fig. 12(f)), since the cytotoxicity of phenol leads to cell death. Table 1 lists optical density (OD) value, relative growth rate, and toxicity level of the Ti64.51Fe26.40Zr5.86Sn2.93Y0.30, Ti70.5Fe29.5 and Ti-6Al- 4V alloys. Statistical results display that OD value and relative growth rate of the Ti64.51Fe26.40Zr5.86- Sn2.93Y0.30, Ti70.5Fe29.5 and Ti-6Al-4V alloys have no obvious difference from that of the negative control. The toxicity level of the Ti64.51Fe26.40Zr5.86- Sn2.93Y0.30, Ti70.5Fe29.5 and Ti-6Al-4V alloys in different concentrations of extracts is 1. Thus, one can draw the conclusion that the above alloys have no cytotoxicity.
4.8 Cell adhesion and proliferation
Cell adhesion assay shows that round cells begin to adhere to the surface of the Ti64.51Fe26.40- Zr5.86Sn2.93Y0.30 alloy after being incubated for 30 min, and present rapid increase in amount with extension of incubation time, as shown in Fig. 13. Further statistic analysis reveals that the OD values of the cells adhered to the studied alloy have no significant difference from those of Ti70.5Fe29.5 alloy, Ti-6Al-4V alloy and control group (Table 2). This result suggests that the studied alloy can promote the early adhesion of cells, being beneficial to growth of the fibroblast cells.
In the further cell proliferation assay, L-929 fibroblast cells are clearly observed on the studied alloy after being incubated for one day (Fig. 14(a)). With the extension of incubation time, the cells exhibit significant increase in number, and almost fully cover the whole surface of the alloy after eight days (Figs. 14(b, c)). As shown in Table 3, the OD values of the cells proliferated on the studied alloy are higher than those of Ti70.5Fe29.5 alloy and Ti-6Al-4V alloy, indicating that proliferation ability of L-929 fibroblast cells on the studied alloy is superior to that on the Ti70.5Fe29.5 alloy and Ti-6Al-4V alloy.
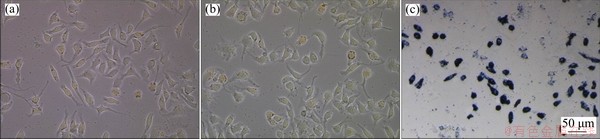
Fig. 11 Representative morphologies of L-929 fibroblast cell in Ti64.51Fe26.40Zr5.86Sn2.93Y0.30 alloy at strongest extract dilution of 100% (a), SFM negative control (b) and positive control (c)
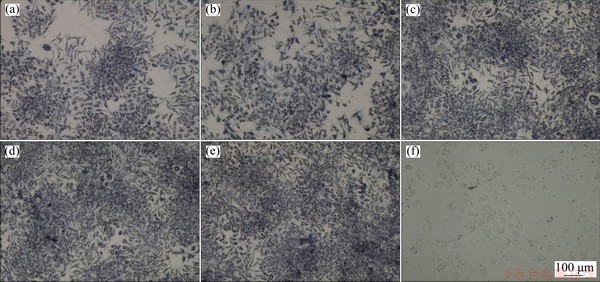
Fig. 12 Crystallographic morphologies of L-929 fibroblast cell in different concentration extracts from Ti64.51Fe26.40- Zr5.86Sn2.93Y0.30 alloy ((a) 100%, (b) 50%, (c) 10% and (d) 1%), negative control (e) and positive control (f)
Table 1 Optical density (OD), cell relative growth rate (RGR) and material toxicity level of L-929 cells cytotoxicity test of Ti64.51Fe26.40Zr5.86Sn2.93Y0.30, Ti70.5Fe29.5 and Ti-6Al-4V alloys
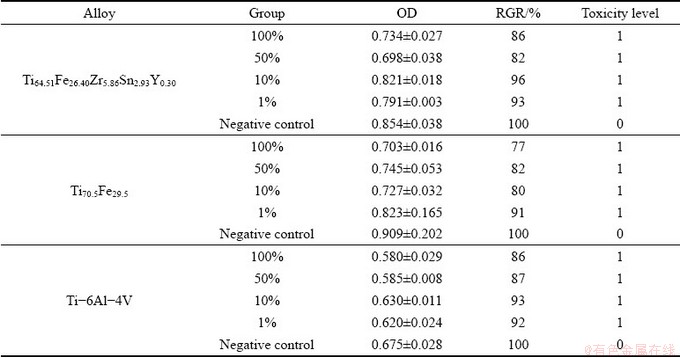
Table 2 OD values of L-929 cells adhered to surfaces of Ti64.51Fe26.40Zr5.86Sn2.93Y0.30, Ti70.5Fe29.5, Ti-6Al-4V alloys and control group
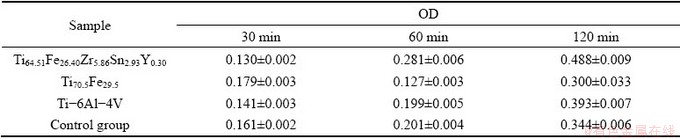
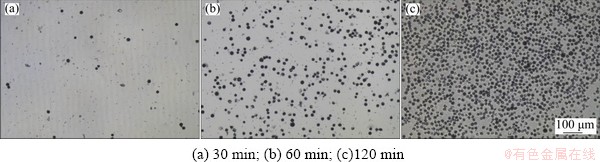
Fig. 13 Crystallographic morphologies of L-929 cells adhered to Ti64.51Fe26.40Zr5.86Sn2.93Y0.30 alloy at different incubation time

Fig. 14 Crystallographic morphologies of L-929 cells proliferated on surface of Ti64.51Fe26.40Zr5.86Sn2.93Y0.30 alloy at different incubation time
Table 3 OD values of L-929 cells proliferated on surfaces of Ti64.51Fe26.40Zr5.86Sn2.93Y0.30, Ti70.5Fe29.5, Ti-6Al-4V alloys and control group
5 Conclusions
(1) The Ti64.51Fe26.40Zr5.86Sn2.93Y0.30 alloy has a non-equilibrium eutectic structure consisting of disordered β-Ti solid solution, ordered TiFe intermetallic compound, and a small fraction of Zr2Fe intermetallic compound. The addition of yttrium not only restrains the formation of brittle Ti4Fe2O oxide, but also increases supercooling degree of the melt, leading to the grain refinement.
(2) The Ti64.51Fe26.40Zr5.86Sn2.93Y0.30 alloy not only exhibits a high hardness of HV (788±10), a strength of 2229 MPa, a large ductility of 14%, a low elastic modulus of 87.5 GPa, but also has good tribological properties, corrosion resistance in Hank’s solution, and formability.
(3) The Ti64.51Fe26.40Zr5.86Sn2.93Y0.30 alloy has no cytotoxicity and can promote the early adhesion of cells and growth of the fibroblast cells.
References
[1] YAN J J, ZHENG D L, LI H X, JIA X, SUN J F, LI Y L, QIAN M, YAN M. Selective laser melting of H13: Microstructure and residual stress [J]. Journal of Materials Science, 2017, 52: 12476-12485.
[2] ZHANG Qi, LIANG Zheng-long, CAO Miao, LIU Zi-fan, ZHANG An-feng, LU Bing-heng. Microstructure and mechanical properties of Ti6Al4V alloy prepared byselective laser meltingcombined with precision forging [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2017, 27: 1036-1042.
[3] MANTRI S A, ALAM T, CHOUDHURI D, YANNETTA C J, MIKLER C V, COLLINS P C, BANERJEE R. The effect of boron on the grain size and texture in additively manufactured β-Ti alloys [J]. Journal of Materials Science, 2017, 52: 12455-12466.
[4] ZHANG Qiang, CHEN Jing, TAN Hua, LIN Xin, HUANG Wei-dong. Microstructure evolution and mechanical properties oflaseradditivemanufactured Ti-5Al-2Sn-2Zr- 4Mo-4Cr [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2016, 26: 2058-2066.
[5] WU Chuan, ZHAN Mei. Effect of solution plus aging heat treatment on microstructural evolution and mechanical properties of near-beta titanium alloy [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2019, 29: 997-1006.
[6] CUI Wen-fang, NIU Feng-juan, TAN Yun-ling, QIN Gao-wu. Microstructure and tribocorrosion performance of nanocrystalline TiN graded coating on biomedical titanium alloy [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2019, 29: 1026-1035.
[7] WANG Cun-shan, HAN Li-ying. Microstructure and properties of Ti-Fe-Y alloy fabricated by laser-aided direct metal deposition [J]. Optical Engineering, 2018, 57: 041410-1-041410-8.
[8] ISMAEEL A, WANG C S. Effect of Nb additions on microstructure and properties of γ-TiAl based alloys fabricated by selective laser melting [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2019, 29: 1007-1016.
[9] SARAO T P S, SINGH H, SINGH H. Enhancing biocompatibility and corrosion resistance of Ti-6Al-4V alloy by surface modification route [J]. Journal of Thermal Spray Technology, 2018, 27: 1388-1400.
[10] LI Qiang, MA Guang-hao, LI Jun-jie, NIINOMI M, NAKAI M, KOIZUMI Y, WEI Dai-xiu, KAKESHITA T, NAKANO T, CHIBA A, LIU Xu-yan, ZHOU Kai, PAN Deng. Development of low-Young’s modulus Ti-Nb-based alloys with Cr addition [J]. Journal of Materials Science, 2019, 54: 8675-8683.
[11] LIU Y J, LI X P, ZHANG L C, SERCOMBE T B. Processing and properties of topologically optimised biomedical Ti-24Nb-4Zr-8Sn scaffolds manufactured by selective laser melting [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2015, 642: 268-278.
[12] KURODA P A B, BUZALAF M A R, GRANDINI C R. Effect of molybdenum on structure, microstructure and mechanical properties of biomedical Ti-20Zr-Mo alloys [J]. Materials Science and Engineering C, 2016, 67: 511-515.
[13] SANTOS P F, NIINOMI M, CHO K. Microstructures, mechanical properties and cytotoxicity of low cost beta Ti-Mn alloys for biomedical applications [J]. Acta Biomaterialia, 2015, 26: 366-376.
[14] PANDELAERS L, BLANPAIN B, WOLLANTS P. An optimized diffusion database for the disordered and ordered bcc phases in the binary Fe-Ti system [J]. Calphad, 2011, 35: 518-522.
[15] ZHU L F, FRIAK M, DICK A, GRABOWSKI B, HICKEL T, LIOT F, HOLEC D, SCHLIETER A, KUHN U, ECKERT J, EBRAHIMI Z, EMMERICH H, NEUGEBAUER J. First-principles study of the thermodynamic and elastic properties of eutectic Fe-Ti alloys [J]. Acta Materialia, 2012, 60: 1594-1602.
[16] OKAZAKI Y, ITO Y. New Ti alloy without Al and V for medical implants [J]. Advanced Engineering Materials, 2000, 2: 278-281.
[17] DONG Dan-dan, DONG Chuang. Composition interpretation procedures of bulk metallic glasses via example of Cu64Zr36 [J]. Journal of Non-Crystalline Solids, 2017, 460: 125-129.
[18] DONG Dan-dan, ZHANG Shuang, WANG Zi-jian, DONG Chuang, HAUSSLER P. Composition interpretation of binary bulk metallic glasses via principal cluster definition [J]. Materials & Design, 2016, 96: 115-121.
[19] GENG Yao-xiang, WANG Ying-min, QIANG Jian-bing, ZHANG Gui-feng, DONG Chuang, HAUSSLER P. Composition formulas of Fe-B binary amorphous alloys [J]. Journal of Non-Crystalline Solids, 2016, 432: 453-458.
[20] MA Y P, DONG D D, DONG C, LUO L J, WANG Q, QIANG J B, WANG Y M. Composition formulas of binary eutectics [J]. Scientific Reports, 2015, 5: 1-16.
[21] CONTIERI R J, LOPES E S N, M. TAQUIRE D L C, COSTA A M, AFONSO C R M, CARAM R. Microstructure of directionally solidified Ti-Fe eutectic alloy with low interstitial and high mechanical strength [J]. Journal of Crystal Growth, 2011, 333: 40-47.
[22] LOUZGUINE D V, KATO H, INOUE A. High strength and ductile binary Ti-Fe composite alloy [J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2004, 384: L1-L3.
[23] DAS J, KIM K B, XU W, LOSER W, ECKERT J. Formation of ductile ultrafine eutectic structure in Ti-Fe-Sn alloy [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2007, 449-451: 737-740.
[24] LOUZGUINE D V, LOUZGUINA L V, INOUE A. Deformation behavior of high strength metastable hypereutectic Ti-Fe-Co alloys [J]. Intermetallics, 2007, 15: 181-186.
[25] LOUZGUINE D V, KATO H, LOUZGUINA L V, INOUE A. High-strength binary Ti-Fe bulk alloys with enhanced ductility [J]. Journal of Materials Research, 2004, 19: 3600-3606.
[26] OZYUREK D, YAVUZER B, TUNCAY T. The effects of Cu and Al on dry sliding wear properties of eutectic Sn-9Zn lead-free solder alloy [J]. Journal of Adhesion Science Technology, 2016, 30: 1662-1670.
[27] WANG Zhuo, LI Yang-bo, BAI Feng, WANG Cheng-wei, ZHAO Quan-zhong. Angle-dependent lubricated tribological properties of stainless steel by femtosecond laser surface texturing [J]. Optics and Laser Technology, 2016, 81: 60-66.
[28] KOSITSKI R, MORDEHAI D. Role of dislocation pile-ups in nucleation-controlled size-dependent strength of Fe nanowires [J]. Acta Materialia, 2017, 136: 190-201.
[29] AZADI M, ROUHAGHDAM A S, AHANGARANI S. Mechanical behavior of TiN/TiC-n multilayer coatings and Ti(C,N) multicomponent coatings produced by PACVD [J]. Strength of Materials, 2016, 48: 279-289.
[30] SUEPTITZ R, DAS J, BAUNACK S, GEBERT A, SCHULTZ L, ECKERT J. Corrosion and pitting behaviour of ultrafine eutectic Ti-Fe-Sn alloys [J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2010, 503: 19-24.
[31] TSAO L C. Effect of Sn addition on the corrosion behavior of Ti-7Cu-Sn cast alloys for biomedical applications [J]. Materials Science and Engineering C, 2015, 46: 246-252.
[32] VASILESCU C, DROB S I, OSICEANU P, CALDERON J M, DROB P, VASILESCU E. Characterisation of passive film and corrosion behaviour of a new Ti-Ta-Zr alloy in artificial oral media: In time influence of pH and fluoride ion content [J]. Materials Corrosion, 2015, 66: 971-981.
[33] LIU Hui-xia, SUN Xian-qing, SHEN Zhong-bao, LI Cong, SHA Chao-fei, LI Li-yin, GAO Shuai, MA You-juan, WANG Xiao. The size effect on deformation behavior in microscale laser shock flexible drawing [J]. Optics and Laser Technology, 2016, 86: 93-102.
[34] BIROL Y. Effect of solute Mg on grain size of aluminium alloys [J]. Materials Science and Technology, 2012, 28: 924-927.
[35] AWAD N K, EDWARDS S L, MORSI Y S. A review of TiO2 NTs on Ti metal: Electrochemical synthesis, functionalization and potential use as bone implants [J]. Materials Science and Engineering C, 2017, 76: 1401-1412.
[36] CENGIZ S, AZAKLI Y, TARAKCI M, STANCIU L, GENCER Y. Microarc oxidation discharge types and bio properties of the coating synthesized on zirconium [J]. Materials Science and Engineering C, 2017, 77: 374-383.
[37] LI Hong-wei, FU Tao, LI Wen, ALAJMI Z, SUN Jia-mao. Hydrothermal growth of TiO2-CaP nano-films on a Ti-Nb based alloy in concentrated calcium phosphate solutions [J]. Journal of Nanoparticle Research, 2016, 18: 4.
[38] FENG Bo, CHU Xue-ji, CHEN Jian-min, WANG Jian-xin, LU Xiong, WENG Jie. Hydroxyapatite coating on titanium surface with titania nanotube layer and its bond strength to substrate [J]. Journal of Porous Materials, 2010, 17: 453-458.
韩立影1,2,王存山2
1. 辽宁科技大学 材料与冶金学院,鞍山 114051;
2. 大连理工大学 三束材料改性教育部重点实验室,大连 116024
摘 要:从生物力学和成形技术的角度出发,利用“团簇+连接原子”结构模型设计Ti-Fe-Zr-Sn-Y共晶合金,并利用激光增材制造技术在纯钛板上制备该合金的成形体。利用显微硬度计、压缩试验机、纳米压痕仪分别测试合金的硬度、压缩性能及弹性模量。结果表明,合金的硬度、压缩强度和断裂应变分别高达HV (788±10)、2229 MPa和14%,弹性模量则低至87.5 GPa。合金还具有良好的摩擦磨损性能、耐蚀性、成形性及生物相容性。合金的综合性能优于Ti70.5Fe29.5共晶合金和商用Ti-6Al-4V合金。该合金的上述性能使其成为一种很有前途的激光增材制造生物材料。
关键词:激光增材制造;成分设计;生物医用钛合金;显微组织;性能
(Edited by Bing YANG)
Foundation item: Project (51371041) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China
Corresponding author: Cun-shan WANG; Tel:+86-411-84707930; E-mail: laser@dlut.edu.cn
DOI: 10.1016/S1003-6326(20)65460-7

