文章编号:1004-0609(2016)02-0402-13
青海省果洛龙洼金矿多因复成成矿作用
赖健清1, 2,鞠培姣1, 2,周 凤1, 2
(1. 中南大学 有色金属成矿预测与地质环境监测教育部重点实验室,长沙 410083;
2. 中南大学 地球科学与信息物理学院,长沙 410083)
摘 要:果洛龙洼金矿位于东昆仑造山带东段,华力西-印支期是最重要的成矿期。矿体受近东西向断裂控制,地层为矿源层和隔挡层,对矿质进行圈闭,变质热液及岩浆提供热源和物质。成矿作用分为变质热液期和岩浆热液期,前者包括乳白色石英脉阶段(A)和含金石英黄铁矿阶段(B),为主成矿期,后者对应石英硫化物再富集阶段(C),起叠加改造作用。综合稳定同位素及包裹体的特征,从多因复成的角度探讨其成矿作用。稳定同位素反映成矿物质及流体为多来源。包裹体研究表明:B、C阶段发育3种包裹体:I型水溶液包裹体、II型水溶液-CO2包裹体、III型纯CO2包裹体。B阶段发育的3种包裹体温度集中于260~360℃,I型、II型包裹体盐度分别为10.70%~22.69%和3.52%~12.42%,流体可能来源于变质热液,属变质热液期。C阶段发育I型包裹体及少量II型包裹体,温度集中于160~320℃,I型、II型包裹体盐度分别为15.90%~23.32%和10.62%~13.57%,成矿热液可能主要来源于岩浆热液,为岩浆热液期。矿床在变质热液期成矿,后期受到岩浆热液叠加改造,矿质进行再富集。因此,矿床具多大地构造阶段、多控矿因素、多成矿物质来源、多成矿作用及多成因类型,属多因复成矿床。
关键词:成矿作用;多因复成;果洛龙洼金矿
中图分类号:P611.1 文献标志码:A
东昆仑造山带位于青藏高原东北缘,在构造上具有多岛洋、软碰撞和多旋回造山的特征[1],是我国著名的成矿带之一,素有“金腰带”之称。果洛龙洼金矿区位于东昆仑东段昆中隆起南缘沟里地区[2],有研究者对该矿床的地质-地球化学特征[3-4]、成矿物质来源[5-6]、矿床成因等进行较为详细的研究。流体包裹体及氢氧同位素研究表明成矿流体具有多来源性[7],东西向构造、晚古生代碳硅泥建造和华力西-印支期的岩浆活动均为重要的成矿因素[6]。在成矿物质来源及矿床成因方面存在着争议:一种观点认为其成矿物质来自于深部岩浆,为典型的造山型金矿,是与华力西-印支期中酸性岩浆活动有关的中温热液型金矿床[4,8],也有学者认为成矿物质来自于早期陆缘海相火山喷发形成的矿源层,后期受到韧性剪切活动及岩浆活动改造而成矿,属于构造-岩浆叠加改造成矿系统的剪切带型矿床[6],文雪峰等[5]则认为成矿物质来源于早期的热水沉积建造,后期受到挤压、变形变质作用而形成了韧性剪切带型金矿床。但前人均未对矿床成因提出十分可靠的地质依据,亦未对成矿流体特征作深入探讨。本文作者通过综合稳定同位素及流体包裹体特征,从多因复成的角度对果洛龙洼金矿床的成矿作用进行了研究。
1 大地构造演化
研究区位于青海省都兰县沟里地区,大地构造位置为柴达木地块的东南缘东昆仑造山带东段[9],按地洼学说理论,其构造分区属祁连-昆仑地洼区东南部(见图1)。东昆仑构造带呈近东西向延伸,经历了复杂的地质演化历史,受到加里东期、华力西期、印支期以及燕山期的叠加和改造,形成了规模宏大的花岗变质杂岩带[8],金属元素富集成矿作用也极为强烈。其中加里东期构造-岩浆活动剧烈,华力西期的海相火山活动发育,对区内矿床的形成起重要的作用。
新太古代-古元古代,研究区处于前地槽阶段[10]。
区域经历了热动力变质作用,并伴有强烈的混合岩化,古老的地块以及陆缘沉积物经历变质结晶后形成该区的变质结晶基底[11],构造层为一套深变质岩群,变质相为角闪岩相,甚至可达麻粒岩相,以古元古界金水口群为代表,岩性主要有片岩、片麻岩、大理岩等。
地槽阶段始于中元古代,区内中部出现昆仑中间隆起带-地背斜,南北两侧发生地槽坳陷[10]。自中元古代到泥盆纪,地壳的活动强度增大,地层为一套陆屑-火山岩建造,主要由中-新元古界万保沟群浅变质碎屑岩、火山岩和浅变质碳酸盐岩及下古生界纳赤台群的片岩、千枚岩、变质火山岩组成,变质程度较低,地槽特征明显。加里东期,东昆仑地区火山喷发频繁,岩浆侵入活动强烈,形成以花岗岩为主的岩浆建造。加里东运动以后,东昆仑地区形成南北三分(昆南带、昆中带、昆北带)的构造格局[11],昆中断裂以北率先进入褶皱带期,地槽南移至昆中断裂以南。石炭纪时,地槽继续发展,区内地层为一套由海相火山-沉积、碳酸盐岩建造,包括下石炭统哈拉郭勒组和上石炭统浩特洛洼组,哈拉郭勒组岩性为轻变质粉砂岩、粉砂质板岩、石英砂岩、大理岩、蚀变火山岩,浩特洛洼组岩性主要有千枚岩、大理岩、灰岩、碎屑岩等。至晚二叠世末,区域进入地槽余动期,构造层为下二叠统马尔争组和上二叠统格曲组,马尔争组为一套海陆交互相沉积[12],岩性为碳酸盐岩、变火山岩夹碎屑岩、硅质岩、灰岩,格曲组为一套河流相-浅海相碎屑岩及灰岩沉积[2],岩性为碎屑岩、变碎屑岩夹灰岩、板岩及火山岩。由上可知,石炭系-二叠系地层,海相、陆相均有分布,岩石可见浅变质,应属于褶皱带的山前坳陷。华力西晚期,岩浆活动强烈,构成昆中花岗质杂岩带的主体。在华力西-印支构造活动期间,区内的几条东西向巨型断裂发生左旋压扭性活动,并形成了大量的北西向线性构造[13]。晚华力西-印支期,断裂带发生继承性活动,并形成一系列NW-NWW向小型断裂裂隙。
二叠纪末,东昆仑地区全面地槽褶皱回返,形成一系列线状紧闭型褶皱[10]。地槽阶段形成的褶皱带型山脉由于受到剥蚀作用而不断被削低夷平,地貌的起伏反差越来越小,最终发展成为准平原地貌,标志着地台阶段的开始。
研究区只在早-中三叠世经历了相对平静而又短暂的地台阶段[14],该阶段地壳活动较弱,构造及岩浆活动不发育,大部分地区缺失地台构造层[10],区内地层为下-中三叠统洪水川组海-陆交互相碎屑岩。
自晚三叠世开始,研究区的构造演化进入地洼发展阶段,代表构造层为上三叠统鄂拉山组及以后的地层,鄂拉山组为一套陆相火山碎屑岩及不稳定沉积碎屑岩的地层,侏罗系至白垩系及以后的地层为陆相河湖沉积,没有区域变质,岩性主要为长石石英砂岩、岩屑砂岩[12],是一套地洼沉积。东昆仑地区在地洼阶段广泛发育褶皱、剪切带、断裂等多种构造类型,造山作用使区内的构造地貌反差强烈,形成高山、深谷等地貌相间。白垩纪时,地洼发展到中期(激烈期),地貌发生大幅度的隆起,岩浆活动及变质作用也增强。区内岩浆活动特别强烈,形成以花岗岩为主的燕山期岩浆建造。至地洼阶段发展的余动期(新生代),大地热流的降低导致壳体发生收缩,块断构造运动活跃,形成张性构造,包括张性断裂及张性盆地等[10]。
因此,东昆仑地区以加里东期造山作用为其主造山期,后期又叠加有华力西晚期-印支期俯冲-碰撞造山作用与燕山中晚期陆内造山作用,具多期多阶段、多类型造山作用复合叠加的特点。
2 矿床地质特征
区内地层主要有古元古界金水口群白沙河组、奥陶-志留系纳赤台群、下石炭统哈拉郭勒组以及第四系的残坡积(见图1)[15-16]。矿区含矿地层奥陶-志留系纳赤台群是一套中低级变质岩系,属大陆裂解形成的小洋盆或裂陷槽环境的产物,岩性主要为绿泥石石英千枚岩、绢云母石英千枚岩、千糜岩、硅质板岩等[7]。前人曾先后定为中-新元古界的万保沟群[17-18]、下石炭统的哈拉郭勒组[6,19],但近年来的研究表明应归属纳赤台群[4,20]。
区内断裂构造发育,按其展布方向可分为3组:北西西-近东西向、北西向和北东向(见图2),具有多期活动的特点。其中近东西向断裂为主要的控矿断裂,规模大,延伸远,矿体受其控制或产于其中[9]。北西向和北东向断裂为成矿期后断裂,一般规模不大,分布在近东西向主断裂两侧,对矿体、矿化带具有破坏作用[20]。
区内岩浆活动剧烈,侵入岩有前加里东期、加里东期、印支-燕山期超基性-基性、中-酸性岩浆岩,部分地区发育有岩脉[21]。岩性主要为斜辉橄榄岩、闪长岩、花岗闪长岩、斜长花岗岩以及花岗岩等。该区的岩浆活动在华力西期和印支期达到高潮[5]。
果洛龙洼原生金矿化主要有石英脉型和蚀变岩型,硫化物为金的重要载体矿物,按照金属硫化物的产出特征,矿区金矿化类型又可分为脉状矿化和细脉浸染状(或稠密浸染状)矿化[3]。目前已发现的矿体均产于厚大石英脉和构造破碎带中的破碎蚀变岩中,形态简单,多呈脉状、透镜状、囊状、不规则状,在走向及倾向上具有分枝复合、尖灭再现和膨大收缩的现 象[22]。在区内由南向北、自东向西划分出AuI、AuII、AuIII、AuIV、AuV、AuVI、AuVII等7条成矿带(见图2),均产于纳赤台群。金矿带走向近东西,倾向南,倾角陡、缓变化大,一般在45°~75°之间,产状与区域地层一致。

图1 果洛龙洼金矿床区域地质略图(据文献[15]修改,大地构造图据文献[16]修改)
Fig.1 Sketch geological map of Guoluolongwa gold ore field (Modified from Ref. [15]; tectonic map according to Ref. [16] ): 1—Quaternary; 2—Lower Permian; 3—Lower Carboniferous Halaguole group; 4—Nachitai group; 5—Paleoproterozoic Jinshuikou group; 6—Indosinian granite; 7—Variscan granodiorite; 8—Variscan granite; 9—Clinopyroxene peridotite; 10—Normal fault; 11—Reverse fault; 12—Unknown fault; 13—Gold deposit(occurrence)
矿石中主要金属矿物有黄铁矿、黄铜矿、磁黄铁矿、方铅矿、闪锌矿等,微量的自然金和银金矿,脉石矿物主要为石英,绢云母、方解石[4,7],矿石结构以半自形-他形粒状、填隙、反应边及隐晶状为主,构造为裂隙浸染状、块状、网脉状及蜂窝状构造[8]。区内围岩蚀变类型多样,与矿化关系最为密切的是黄铁绢英岩化。
根据野外矿脉穿插关系、矿物组合及矿石组构特征,果洛龙洼金矿床的形成经历了多期多阶段,其中热液成矿作用主要包括变质热液期和岩浆热液期,变质热液期为金的主成矿期,又可划分为乳白色石英脉阶段(A)、含金石英黄铁矿阶段(B);后期有岩浆热液期的叠加,对应石英硫化物阶段(C),对金矿起着叠加改造再富集的作用。
乳白色石英脉阶段(A):以发育乳白色石英脉为特征,脉中金属硫化物少见。该阶段石英脉基本上不含金,黄铁矿颗粒较粗,呈立方体自形晶(见图3(a))。
含金石英黄铁矿阶段(B):该阶段以细粒黄铁矿细脉、石英细脉发育为特征。石英脉体较小,充填和交代早阶段的石英脉,石英的透明度优于前者的(见图3(b))。
石英硫化物再富集阶段(C):在含金石英脉中穿插不规则状石英硫化物细脉(见图3(c)),硫化物主要包括黄铁矿、方铅矿、闪锌矿等(见图3(d))。金的品位升高,有进一步富集作用[15]。
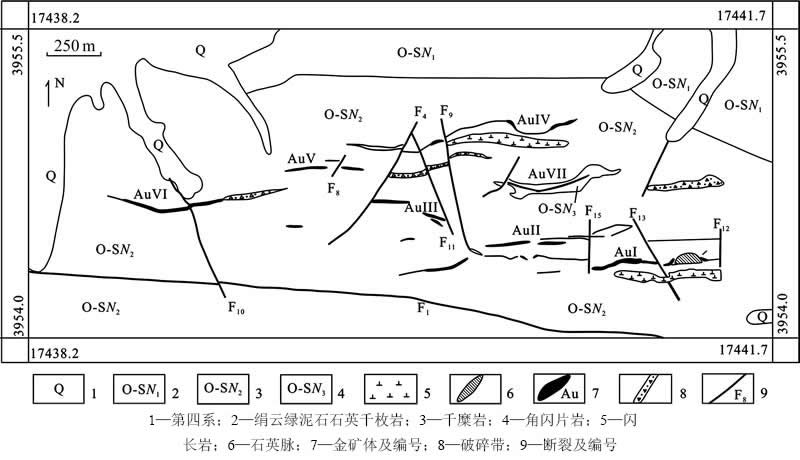
图2 果洛龙洼金矿区地质图(据文献[7]修改)
Fig. 2 Geological map of Guoluolongwa gold deposit (Modified from Ref.[7]): 1—Quaternary; 2—Chlorite quartz sericite phyllite; 3—Phyllonite; 4—Hornblende schist; 5—Diorite; 6—Quartz vein; 7—Orebody and its number; 8—Fracture zone; 9—Fault and its number

图3 不同成矿阶段特征(Qtz—石英;Py—黄铁矿)
Fig. 3 Characteristics of different mineralization stages in Guoluolongwa gold deposit (Qtz—Quartz; Py—Pyrite): (a) Euhedral coarse-grained pyrite of stage A; (b)Smoky quartz of stage B; (c) Quartz veins of different stages interspersed with each other; (d)Auriferous quartz vein of stage C
3 稳定同位素特征
3.1 铅同位素特征
果洛龙洼含金石英脉矿石中的黄铁矿和方铅矿的206Pb/204Pb、207Pb/204Pb、208Pb/204Pb摩尔比值表明其具有典型放射成因铅的特征。东昆仑造山带造山过程中发生的多次构造热事件,导致果洛龙洼金矿区放射成因铅含量的增加[8]。
根据单阶段铅演化模式,计算得出铅同位素各特征参数(见表1),测试单位为国土资源部中南矿产资源监督检测中心,数据来源于文献[4]。Th/U摩尔比值介于3.66~3.73之间,变化范围很小,表现出稳定铅同位素的特征,均值为3.68,位于中国大陆上地壳平均值3.47和全球上地壳平均值3.88之间[23-24],表明矿质来源于上地壳。一般来说,μ值(238U/204Pb)可用来判断铅的来源,μ>9.58的铅为高放射性壳源铅,μ<9.58的铅为低放射性深源铅[25]。本矿床矿石μ值介于9.35~9.47,变化范围很窄,具有深源铅的特征。
利用朱炳泉等[26]的公式计算出地幔铅所占比例如式(1)所示:
μ=μC(1-X)+μ0X (1)
式中:μ为238U/204Pb值;μC为地壳中238U/204Pb值,取μC=9.81;μ0为原始地幔中238U/204Pb值,取μ0=7.80;X为地幔铅所占比例,(1-X)为地壳铅所占比例。计算结果见表中地幔组分和地壳组分,地幔组分为0.17~0.23,地壳组分为0.77~0.83,显示了铅的壳幔混合来源特征。
利用路远发[27]的Geokit软件计算出矿区每个样品的△β和△γ,并将其投到△β-△γ图解中(图4)。矿区所有样品均限制于俯冲作用下上地壳与地幔混合岩浆作用范围内。说明矿区成矿物质主要来源于俯冲作用时上地壳与地幔混合的岩浆岩。
3.2 流体包裹体特征
用于研究的样品主要取自果洛龙洼矿区的坑道和钻孔内,选取3个不同成矿阶段的样品进行观测。对各阶段的石英中的流体包裹体进行岩相学研究,A阶段乳白色石英脉中未见包裹体发育,B阶段和C阶段的石英中发育大量流体包裹体。最终挑选5件包裹体较发育、类型具有代表性的样品进行显微测温,涵盖2个成矿阶段(B阶段和C阶段),样品特征见表2。
流体包裹体的显微测温工作在中南大学地球科学与信息物理学院流体包裹体实验室完成,测试所用仪器为Linkam THMS-600型冷热台,测温范围在-120~600 ℃之间。其中在10~600 ℃之间精度为±1 ℃;在-120~10 ℃之间,精度为±0.1 ℃。测试前用人工合成包体(国际标样)对仪器进行了校正。测定了包裹体的完全冷冻温度tf、完全均一温度th、固态CO2的熔化温度tm(CO2)、CO2相部分均一温度th(CO2)、笼合物的最终熔化温度tm(cla)以及冰的最终熔化温度tm(ice)。利用冰的最终熔化温度tm(ice)(水溶液包裹体)或笼合物的最终熔化温度tm(cla)(水溶液-CO2包裹体),利用Flincor程序[28]采用BROWN等[29]方程计算流体包裹体的盐度。
表1 果洛龙洼金矿铅同位素组成分析结果
Table 1 Analytical results of lead isotope compositions of Guoluolongwa gold deposit

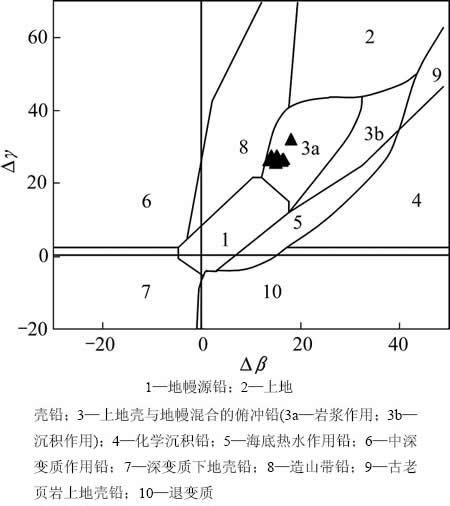
图4 果洛龙洼矿床△β-△γ图解[26]
Fig. 4 △β-△γ diagram of genetic classification of ores from Guoluolongwa gold deposit[26]: 1—Mantle lead; 2—Upper crust lead; 3—Mixed upper crust and mantle lead (3a—Magmatism; 3b—Sedimentation); 4—Chemical deposit lead; 5—Submarine hydrothermal lead; 6—Intermediate metamorphic lead; 7—High level metamorphic lead; 8—Orogenic belt lead; 9—Upper crust lead of ancient shale; 10—Retrograde metamorphic lead
1) 包裹体岩相学特征
根据在室温下的相态特征,矿区流体包裹体可分为3种类型(见表3):Ⅰ型水溶液包裹体,Ⅱ型水溶液-CO2包裹体,III型纯CO2包裹体。
Ⅰ型包裹体:室温下呈两相产出,由盐水溶液及气泡组成,气相占包裹体总体的比例(V/T)为10%~38%,最终完全均一为液相。该类包裹体直径约4~8 μm,多呈椭圆、长条及不规则状(见图5(a)),随机孤立分布在石英中。
Ⅱ型包裹体:室温下由水溶液相、气相CO2及液相CO2三相组成,CO2相占包裹体总体积的比例(C/T)为8%~50%,最终完全均一为水溶液相。该类包裹体的形态以椭圆、长条及不规则状为主,直径约为4~12 μm(见图5(b)和(c))。在同一石英颗粒中,可见II型包裹体与I型包裹体共生,表明推其捕获时间可能相近。
Ⅲ型包裹体:在室温下呈液相CO2、气相CO2两相产出(图5(d))。包裹体大小为4~6 μm,气相占包裹体总体积的比例为10%~40%,以椭圆形为主,最终完全均一为液相。
包裹体岩相学特征表明,多数产于B阶段含金石英脉中的Ⅰ型、II型包裹体及产于C阶段石英硫化物细脉中的Ⅰ型包裹体常成群出现,少量呈孤立状产出,为原生成因。另外,在C阶段铅锌硫化物细脉旁侧的B阶段石英中还可见许多I型包裹体或II型包裹体沿裂隙排列成行,具次生包裹体的特征。这些包裹体可能与C阶段石英硫化物脉中的原生包裹体为同时形成。可见,包裹体可能有两个主要形成阶段,分别与B阶段和C阶段有关,前者包括水溶液包裹体(Ⅰ型)、水溶液-CO2包裹体(II型)和纯CO2包裹体(III型),后者以水溶液包裹体(I型)为主,还发育少量水溶液-CO2包裹体(II型)。
2) 包裹体显微测温结果
本文作者共测得65个包裹体,其测温结果见表3。表3中主矿物均为石英。φv为20 ℃时包裹体气相占包裹体总体积的分数。tm(CO2)为CO2熔化温度;tm(ice)为冰点温度;tm(cla)为CO2笼合物熔化温度;th(CO2)为CO2部分均一温度。不同阶段流体包裹体的均一温度和盐度均有不同特征(见图6)。
A阶段包裹体显微测温特征:果洛龙洼矿区的金矿化作用主要是叠加在乳白色石英脉上的后期含金石英黄铁矿细脉和石英硫化物细脉,先期的乳白色石英(A阶段)在岩相学研究中未见包裹体发育。
表2 果洛龙洼矿区流体包裹体测温样品特征
Table 2 Characteristics of microthermometric samples in Guoluolongwa gold deposit


图5 果洛龙洼金矿流体包裹体镜下显微特征(Aq—水溶液相;V—气相;Cl—CO2液相;Cv—CO2气相)
Fig. 5 Microphotographs of fluid inclusions in Guoluolongwa deposit (Aq—Aqueous solution; V—Vapor; Cl—CO2 liquid; Cv—CO2 vapor): (a) Type I inclusion; (b) Type II inclusion; (c) Type II inclusion; (d) Type III inclusion
B阶段包裹体显微测温特征:该阶段石英脉中发育的包裹体比较复杂,共测得32个,3种类型包裹体均可见,以Ⅰ型和Ⅱ型包裹体最为发育,Ⅰ型占包裹体总数的28%,Ⅱ型占包裹体总数的56%。
Ⅰ型包裹体:该类型包裹体冰的最终融化温度范围为-7.2~-18.3 ℃,对应盐度为10.70%~22.69%(质量分数,下同)(见图6(b)),均一温度变化较大,范围为142~280℃(见图6(a)),最终完全均一为液相,计算得到包裹体密度为0.88~1.05g/cm3。
Ⅱ型包裹体:固态CO2熔化温度为-55.0~-58.9 ℃,笼合物的最终熔化温度为2.6~7.9 ℃,相应盐度为3.52%~12.42%(见图6(b)),CO2相部分均一温度为24.8~27.5 ℃,最终均一温度为280~350 ℃(见图6(a)),完全均一为水溶液相,包裹体密度为0.67~0.78 g/cm3。
III型包裹体:固态CO2熔化温度为-57.3~-58.9 ℃,CO2相均一温度为9.6~25.0 ℃,最终均一为液相,包裹体密度为0.71~0.87 g/cm3。
C阶段包裹体显微测温特征:该成矿阶段发育原生Ⅰ型水溶液包裹体及少量Ⅱ型水溶液-CO2包裹体,共测得33个包裹体,其中Ⅰ型的24个,Ⅱ型的9个。
Ⅰ型包裹体:该类型包裹体冰的最终融化温度范围为-12.0~-19.5 ℃,对应盐度为15.90%~23.32%(见图6(d)),均一温度变化较大,范围为159~383 ℃(见图6(c)),最终均一为液相,计算所得包裹体密度为0.80~1.04 g/cm3。
Ⅱ型包裹体:笼合物的最终熔化温度为1.7~3.9 ℃,相应盐度为10.62%~13.57%(见图6(d)),最终均一温度为180~224 ℃(见图6(c)),完全均一为水溶液相,包裹体密度为0.72~0.82 g/cm3。
由上述显微测温结果可见,B阶段发育的包裹体为原生包裹体群,水溶液包裹体与含碳质包裹体共存,代表H2O和CO2分离阶段[30-31],中高温温度范围较窄,集中于260~360 ℃,Ⅰ型包裹体盐度较高,集中于18%~24%,Ⅱ型包裹体为低盐度,约4%~14%(见图7),可能是由于气泡比较大,内部有气态H2O及其他气体,导致了盐度的降低。该阶段包裹体的特征反映流体可能来源于变质热液[32],为金的主成矿期-变质热液期。C阶段Ⅰ型水溶液包裹体的盐度较高,比较均一,集中于18%~24%,Ⅱ型包裹体的盐度为10%~14%,成矿热液可能主要来源于岩浆热液,为岩浆热液期。成矿温度范围广,为159~383 ℃,可能代表较长的成矿阶段,温度从中高温向低温转变,成金作用可能发生于低温时期,随着温度的降低,流体的盐度没有明显变化(图7),说明是一种自然降温的过程。此外,在靠近C阶段硫化物细脉的B阶段石英中亦见有次生的包裹体发育,可能与C阶段原生包裹体同时形成,推断是由于C阶段的岩浆热液叠加改造B阶段的变质热液而形成。

图6 不同成矿阶段流体包裹体均一温度和盐度直方图
Fig. 6 Histograms of homogenization temperature and salinities of fluid inclusions in different stages: (a) B stage homogenization temperatures; (b) C stage homogenization temperatures; (c) B stage salinities; (d) C stage salinities
表3 果洛龙洼金矿流体包裹体特征
Table 3 Characteristics of fluid inclusions in Guoluolongwa gold deposit

综上所述,果洛龙洼金矿的形成经历了多期多阶段,主要包括变质热液期和岩浆热液期,其中变质热液期为金的主成矿期,又可划分为乳白色石英脉阶段(A)、含金石英黄铁矿阶段(B);后期有岩浆热液期的叠加,对应石英硫化物阶段(C),对金矿起着叠加改造再富集的作用。
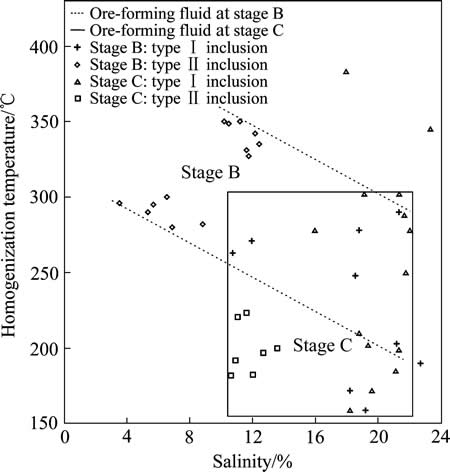
图7 不同成矿阶段流体包裹体温度-盐度散点图
Fig. 7 Diagrams of homogenization temperatures versus salinities of fluid inclusions in different stages
4 多因复成成矿作用
果洛龙洼金矿位于东昆仑造山带东侧、昆中断裂的南侧。晚古生代末,陆缘活动型沉积盆地闭合、造山,经历华力西-印支等多期造山活动叠加,与此同时还形成大规模的断层、剪切带及与之配套的低级构造体系,这些构造为流体的运移和成矿物质的沉淀成矿提供了路径和场所。
1) 成矿物质来源:果洛龙洼金矿区黄铁矿单矿物的δ34SCDT为0.02%~0.388%,方铅矿单矿物的δ34SCDT为-0.203%~-0.595%[4]。地幔来源的34S值约为0.1%~ 0.2%,大多数花岗岩的34S值约为-0.4%~0.9%,将果洛龙洼矿区的硫同位素组成与之对比发现,该区金矿的硫质主要是地幔来源,并且有地层硫的混入[33]。将该矿床的硫同位素与区域上的五龙沟金矿(0.398%)和开荒北金矿(0.44%)进行对比,认为该矿床硫为深源地幔硫和沉积地层硫混合来源[19]。铅同位素特征表明该区金矿的铅具壳幔混合来源特征。丁清峰等[7]、丰成友等[34]对不同成矿阶段的石英进行氢氧同位素测试发现成矿流体以原生岩浆水/变质水为主,混合了少量的大气降水,证明成矿流体的多来源性。由此可见,无论是成矿物质还是成矿流体均具有多来源的特点,以深部来源为主。
2) 控矿因素:区内赋矿地层纳赤台群为一套中低级变质岩系,化学性质不甚活泼,作为围岩可形成隔挡层,圈闭成矿物质。果洛龙洼地区的矿床分布于昆中大断裂附近,受到北西向和近东西向构造的控制。东西向断裂和北西向断裂可能是昆中大断裂的次级断裂,在本区起到重要的控岩、控矿作用,是区域性的导矿构造[2]。在果洛龙洼金矿区,矿体的分布明显受到北西西-近东西向断裂的控制,该断裂形成较早、规模较大、发育程度较高,是区内主要的控矿断裂[23],断裂带内发育强的硅化、绢云母化、绿泥石化、黄铁矿化等,地表矿化带则出现褐铁矿化、高岭石化。后期形成的北北西和近南北向的断裂多期活动性较为明显,对区内的成矿起着一定的破坏作用。此外,果洛龙洼矿区发育的侵入体主要为华力西期花岗岩、花岗闪长岩和印支期花岗岩[35],金矿脉中含绢云母的样品测年结果表明成岩年代及金矿形成时代为201.8~ 229.3 Ma[18]。附近的阿斯哈金矿的容矿围岩即为印支期花岗斑岩、花岗闪长岩和石英闪长岩[36-37],测得其年龄值分别为(228.5±2.9) Ma、(232.6±1.4) Ma[38]和(238.4±1.6) Ma,该期岩体对阿斯哈金矿的形成具有重要作用[37]。张德全等[39-40]认为东昆仑地区金矿的成矿年龄有一组为晚华力西-印支期(284~218 Ma)。由上可知,区域矿化在时间、空间和成因上与华力西-印支期岩浆活动有关。
3) 矿床成因:上述研究表明,本矿床的成矿物质具有多来源性,成矿流体主要来源于岩浆水和变质水。矿相研究及流体包裹体分析结果说明果洛龙洼金矿的形成经历了多期多阶段,主成矿期-变质热液期进行成矿,在后期受到岩浆热液的叠加改造,对矿质起到再富集的作用。因此,矿床是在变质热液成矿作用的基础上,叠加了岩浆热液成矿作用。成矿作用经历了大地构造演化的不同时期,成矿物质来源于沉积地层和岩浆热液,具备复杂的控矿因素组合及成矿作用过程,属于多因复成矿床的范畴。
4) 成矿作用过程分析:新太古代-古元古代,东昆仑地区处于前地槽阶段,区域发生强烈的热动力变质作用及混合岩化,形成古老的变质结晶基底,构造层为金水口群地层。对东昆仑东段金水口群变质岩进行Au、Ag等微量元素分析,金水口群金含量低于地壳克拉克值,个别高值是由于矿化影响所致[41-42],不能为成矿提供物质[12]。中元古代开始进入地槽阶段,前期沉积了巨厚的沉积物,形成大量微细粒黄铁矿、胶黄铁矿,并沉积了Au、Sb等成矿元素[43],区内地层主要为中-新元古界万保沟群至早下古生界的纳赤台群,岩性以碎屑及中基性火山沉积为主,前人认为果洛龙洼金矿容矿围岩纳赤台群为金的初始矿源层,提供了部分成矿物质[12,15,44]。到晚古生代,东昆仑地区全面进入褶皱带期,区内地层强烈挤压揉皱并发生区域变质作用。变质作用使深部基底地层发生脱水、脱挥发分,形成变质流体,并在地热增温的驱动下向上迁移,不断与围岩发生反应,导致成矿物质进入流体中,逐步形成温度较高的含矿流体。昆中断裂带北侧发育的大量NW向次级断裂,深断裂及大型剪切带则为流体的运移提供通道。区域地壳不断隆升,富含成矿物质的超临界H2O-CO2流体在上升过程中,由于温度和压力的降低,发生液相不混溶分离作用,直接导致热液中金等成矿元素的沉淀,形成成矿物质的初步富集[34]。随着地槽褶皱的加强,断裂带深抵地壳深部,诱发中酸性岩浆侵入活动,一方面从深部带来丰富的成矿物质,另一方面又从途经的围岩中萃取活化更多的成矿物质,形成含矿岩浆热液。这些富含成矿物质的流体进入到浅部断裂裂隙系统中并沿其向上运移,对原有的变质热液型金矿进行叠加和改造,使金矿得以进一步富集。
5 结论
1) 果洛龙洼金矿位于东昆仑造山带东段,区内断裂构造发育,矿体明显受到近东西向断裂构造的控制,原生金矿化主要为石英脉型和蚀变岩型。矿区经历多个构造发展演化阶段,其中与成矿关系最为密切的为加里东期与华力西-印支期。
2) 硫铅及氢氧同位素特征表明该区的成矿物质与成矿流体具有多来源性。流体包裹体显微测温研究表明该矿床主要的成矿作用有变质热液期及岩浆热液期。变质热液期为金矿的主成矿期,可以划分为乳白色石英脉阶段(A)和含金石英黄铁矿阶段(B),岩浆热液期对应石英硫化物再富集阶段(C),矿床是在变质热液成矿作用的基础上,叠加了岩浆热液成矿作用。
3) 果洛龙洼金矿在新太古代-古元古代形成古老的变质结晶基底,深部基底地层的变质作用产生变质流体,并与围岩反应萃取成矿物质,形成含矿流体,在上升过程中发生不混溶作用,导致热液中金等成矿元素的初步富集;晚华力西-印支期中酸性岩浆的侵入带来丰富的成矿物质,形成含矿岩浆热液,并萃取围岩中的矿质,含矿流体沿断裂裂隙系统向上运移,对原有的变质热液型金矿进行叠加和改造,使金矿得以进一步富集。因此,果洛龙洼金矿具备多大地构造阶段、多成矿物质来源、多控矿因素、多成矿作用以及多种成因类型,具多因复成特点。
REFERENCES
[1] 殷鸿福, 张克信. 中央造山带的演化及其特点[J]. 地球科学, 1998, 23(5): 438-442.
YIN Hong-fu, ZHANG Ke-xin. Evolution and characteristics of the central orogenic belt[J]. Earth Science-Journal of China University of Geosciences, 1998, 23(5): 438-442.
[2] 岳维好, 高建国, 周家喜. 青海果洛龙洼金矿基性岩脉锆石U-Pb年龄及岩石地球化学特征[J]. 矿物岩石, 2013, 33(3): 93-102.
YUE Wei-hao, GAO Jian-guo, ZHOU Jia-xi. LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Pb ages and lithogeochemistry of basic dykes in the Guoluolongwa Au ore field, Qinghai Province, China[J]. Journal of Mineralogy and Petrology, 2013, 33(3): 93-102.
[3] 马忠贤, 杨宝荣, 贾吉还. 青海果洛龙洼金矿地质特征及找矿潜力分析[J]. 黄金科学技术, 2012, 20(2): 32-36.
MA Zhong-xian, YANG Bao-rong, JIA Ji-huan. Analysis on the geological characteristics and potential of ore prospecting of the Guoluolongwa gold deposit in Qinghai Province[J]. Gold Science and Technology, 2012, 20(2): 32-36.
[4] 胡荣国, 赖健清, 张绍宁, 窦洪伟, 施根红, 杨宝荣. 青海省都兰县果洛龙洼金矿床地质地球化学特征[J]. 地质与勘探, 2010, 46(5): 0931-0941.
HU Rong-guo, LAI Jian-qing, ZHANG Shao-ning, DOU Hong-wei, SHI Gen-hong, YANG Bao-rong. Geological and geochemical characteristics of the Guoluolongwa gold deposit, Dulan County, Qingha Province[J]. Geology and Exploration, 2010, 46(5): 0931-0941.
[5] 文雪峰, 王怀超. 青海省都兰县果洛龙洼金矿床地质特征及成因探讨[J]. 黄金科学技术, 2006, 14(5): 27-29.
WEN Xue-feng, WANG Huai-chao. Geological characteristics and genesis of Guoluolongwa gold deposit in Qinghai Province[J]. Gold Science and Technology, 2006, 14(5): 27-29.
[6] 杨宝荣, 杨小斌. 青海都兰果洛龙洼金矿床地质特征及控矿因素浅析[J]. 黄金科学技术, 2007, 15(1): 26-30.
YANG Bao-rong, YANG Xiao-bin. Geological characteristics and ore-controlling factors of the Guoluolongwa gold deposit, Dulan County, Qinghai Province[J]. Gold Science and Technology, 2007, 15(1): 26-30.
[7] 丁清峰, 金圣凯, 王 冠, 张本龙. 青海省都兰县果洛龙洼金矿成矿流体[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 2013, 43(2): 415-426.
DING Qing-feng, JIN Sheng-kai, WANG Guan, ZHANG Ben-long. Ore-forming fluid of the Guoluolongwa gold deposit in Dulan County, Qinghai Province[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition), 2013, 43(2): 415-426.
[8] 邹定喜, 杨小斌, 芦文泉. 青海果洛龙洼金矿床同位素特征及成因[J]. 黄金科学技术, 2011, 19(2): 26-30.
ZOU Ding-xi, YANG Xiao-bin, LU Wen-quan. Isotope characteristic and ore genesis of Guoluolongwa gold deposit in Qinghai Province[J]. Gold Science and Technology, 2011, 19(2): 26-30.
[9] 贾福聚, 高建国, 周家喜, 岳维好, 刘心开. 青海果洛龙洼金矿床地球化学垂向分带研究[J]. 地质与勘探, 2013, 49(5): 907-913.
JIA Fu-ju, GAO Jian-guo, ZHOU Jia-xi, YUE Wei-hao, LIU Xin-kai. Geochemical vertical zonation in the Guoluolongwa gold deposit, Qinghai Province[J]. Geology and Explotarion, 2013, 49(5): 907-913.
[10] 陈国达. 地洼学说-活化构造及成矿理论体系概论[M]. 长沙: 中南工业大学出版社, 1996: 1-455.
CHEN Guo-da. Diwa theory-Introduction to tectonic activation and metallogenic theory system[M]. Changsha: Central South University Press, 1996: 1-455.
[11] 范丽琨, 蔡岩萍, 梁海川, 李宏录. 东昆仑地质构造及地球动力学演化特征[J]. 地质调查与研究, 2009, 33(3): 181-186.
FAN Li-kun, CAI Yan-ping, LIANG Hai-chuan, LI Hong-lu. Characters and evolution of the geodynamics in the eastern Kunlun[J]. Geological Survey and Research, 2009, 33(3): 181-186.
[12] 陈广俊. 青海东昆仑沟里地区及外围金矿成矿作用研究[D]. 长春: 吉林大学, 2014: 1-165.
CHEN Guang-jun. Metallogenesis of gold deposits in Gouli regional and peripheral area of East Kunlun, Qinghai province[D]. Changchun: Jilin University, 2014: 1-165.
[13] 许志琴, 李海兵, 杨经绥, 陈 文. 东昆仑山南缘大型转换挤压构造带和斜向俯冲作用[J]. 地质学报, 2001, 75(2): 156-164.
XU Zhi-qin, LI Hai-bing,YANG Jing-sui, CHEN Wen. A large transpression zone at the south margin of the east Kunlun mountains and oblique subduction[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2001, 75(2): 156-164.
[14] 陈国达, 黄瑞华, 王伏泉. 地洼构造与金成矿[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 1997: 1-223.
CHEN Guo-da, HUANG Rui-hua, WANG Fu-quan. Diwa structure and gold mineralization[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 1997: 1-223.
[15] 杨小斌, 刘洪川. 东昆仑造山带都兰县沟里地区金矿成矿特征及找矿潜力分析[J]. 青海国土经略, 2005(4): 32-35.
YANG Xiao-bin, LIU Hong-chuan. Gold mineralization characteristics and prospecting potential of the east Kunlun orogenic belt in Gouli district, Dulan County[J]. Management & Strategy of Qinghai Land & Resources, 2005(4): 32-35.
[16] 焦淑沛. 青藏高原大地构造性质归属地洼区的论证和分析[J]. 中国地质科学院院报, 1993, 26: 15-27.
JIAO Shu-pei. A diwa attribution of the Qinghai-Xizang (Tibet) plateau: evidende and analysis[J]. Bulletin of the Chinese Academy of Geological Sciences, 1993, 26: 15-27.
[17] 胡荣国. 青海省果洛龙洼金矿地质地球化学特征及矿床成因研究[D]. 长沙: 中南大学, 2008: 1-99.
HU Rong-guo. Research on geological-geochemical characteristics and genesis of the Guoluolongwa gold deposit in Qinghai Province[D]. Changsha: Central South University, 2008: 1-99.
[18] 周 凤. 青海省果洛龙洼金矿区流体包裹体研究[D]. 长沙: 中南大学, 2010: 1-64.
ZHOU Feng. Research on fluid inclusions of Guoluolongwa gold area in Qinghai Province[D]. Changsha: Central South University, 2010: 1-64.
[19] 赵万顺, 李彦林, 高钢锁. 青海省都兰县果洛龙洼金矿的成因及找矿标志[J]. 陕西地质, 2009, 27(2): 34-40.
ZHAO Wan-shun, LI Yan-lin, GAO Gang-suo. The prospecting indicators and the genesis of Guoluolongwa gold deposit in Dulan County of Qinghai Province[J]. Geology of Shanxi, 2009, 27(2): 34-40.
[20] 肖 晔, 丰成友, 李大新, 刘建楠. 青海省果洛龙洼金矿区年代学研究与流体包裹体特征[J]. 地质学报, 2014, 88(5): 895-902.
XIAO Ye, FENG Cheng-you, LI Da-xin, LIU Jian-nan. Chronology and fluid inclusions of the Guoluolongwa gold deposit in Qinghai Province[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2014, 88(5): 895-902.
[21] 刘心开, 高建国, 周家喜. 青海东昆仑果洛龙洼金矿床东区I矿体群稀土元素地球化学[J]. 地球化学, 2013, 42(2): 131-142.
LIU Xin-kai, GAO Jian-guo, ZHOU Jia-xi. REE geochemistry of No.1 ore body group of Guoluolongwa Au deposit, east Kunlun orogenic belt, Qinghai Province, China[J]. Geochinima, 2013, 42(2): 131-142.
[22] 王凤林, 肖小强, 陈世顺. 青海沟里地区金矿地质特征及找矿前景[J]. 黄金科学技术, 2011, 19(4): 45-48.
WANG Feng-lin, XIAO Xiao-qiang, CHEN Shi-shun. Geological characteristics and prospecting of Gouli area gold mine, Qinghai Province[J]. Gold Science and Technology, 2011, 19(4): 45-48.
[23] 李 龙, 郑永飞, 周建波. 中国大陆地壳铅同位素演化的动力学模型[J]. 岩石学报, 2001, 17(1): 61-68.
LI Long, ZHENG Yong-fei, ZHOU Jian-bo. Dynamic model for Pb isotope evolution in the continental crust of China[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2001, 17(1): 61-68.
[24] ZARTMAN R E, DOE B R. Plumbo tectonics-the model[J]. Tectonophysics, 1981, 75: 135-162.
[25] 沈能平, 彭建堂, 袁顺达, 张东亮, 胡瑞忠. 湖北徐家山锑矿床铅同位素组成与成矿物质来源探讨[J]. 矿物学报, 2008, 28(2): 169-176.
SHEN Neng-ping, PENG Jian-tang, YUAN Shun-da, ZHANG Dong-liang, HU Rui-zhong. Lead isotope compositions and its significance for ore-forming material of the Xujiashan antimony deposit, Hubei Province[J]. Acta Mineralogica Sinica, 2008, 28(2): 169-176.
[26] 朱炳泉, 李献华, 戴橦谟. 地质科学中同位素体系理论与应用-兼论中国大陆壳幔演化[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1998: 1-226.
ZHU Bing-quan, LI Xian-hua, DAI Tong-mo. Isotopic system theory and application in geological sciences-On continental crust-mantle evolution of China[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 1998: 1-226.
[27] 路远发. GeoKit: 一个用VBA构建的地球化学工具软件包[J]. 地球化学, 2004, 33(5): 459-464.
LU Yuan-fa. Geokit-A geochemical toolkit for Microsoft Excel[J]. Geochimica, 2004, 33(5): 459-464.
[28] BROWN P E. FLINCOR: A microcomputer program for the reduction and investigation of fluid inclusion data[J]. American Mineralogist, 1989, 74: 1390-1393.
[29] BROWN P E, LAMB W M. P-V-T properties of fluids in the system CO2-H2O-NaCl: New graphical presentations and implication for fluid inclusions studies[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1989, 53: 1209-1221.
[30] MERNAGH T P, BASTRAKOV E N, ZAW K, WYGRALAK A S, WYBORN L A I. Comparison of fluid inclusion data and mineralization processes for Australian orogenic gold and intrusion-related gold systems[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2007, 23(1): 21-32.
[31] WILKINSON J J. Fluid inclusions in hydrothermal ore deposits[J]. Lithos, 2011, 55: 229-272.
[32] 陈衍景, 倪 培, 范宏瑞, PIRAJNO F, 赖 勇, 苏文超, 张 辉. 不同类型热液金矿系统的流体包裹体特征[J]. 岩石学报, 2007, 23(9): 2085-2108.
CHEN Yan-jing, NI Pei, FAN Hong-rui, PIRAJNO F, LAI Yong, SU Wen-zhao, ZHANG Hui. Diagnostic fluid inclusions of different types hydrothermal gold deposits[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2007, 23(9): 2085-2108.
[33] 王 冠. 青海果洛龙洼金矿床地质特征及成因探讨[D]. 长春: 吉林大学, 2012: 1-86.
WANG Guan. Study on geological characteristics and genesis of Guoluolongwa gold deposit in Qinghai Province[D]. Changchun: Jilin University, 2012: 1-86.
[34] 丰成友, 张德全, 王富春, 李大新, 佘宏全. 青海东昆仑造山型金(锑)矿床成矿流体地球化学研究[J]. 岩石学报, 2004, 20(4): 949-960.
FENG Cheng-you, ZHANG De-quan, WANG Fu-chun, LI Da-xin, SHE Hong-quan. Geochemical characteristics of ore-forming fluids from the orogenic Au (and Sb) deposits in the eastern Kunlun area, Qinghai Province[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2001, 20(4): 949-960.
[35] 薛培林, 肖 静, 薛福林, 董 琳. 青海祁漫塔格-都兰成矿带铜矿找矿前景初探[J]. 矿产与地质, 2006, 20(3): 247-250.
XUE Pei-lin, XIAO Jing, XUE Fu-lin, DONG Lin. Outlook on copper deposit exploration in Qimantage-Dulan ore belt[J]. Mineral Resources and Geology, 2006, 20(3): 247-250.
[36] 李碧乐, 沈 鑫, 陈广俊, 杨延乾, 李永胜. 青海东昆仑阿斯哈金矿I号脉成矿流体地球化学特征和矿床成因[J].吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 2012, 42(6): 1676-1687.
LI Bi-le, SHEN Xin, CHEN Guang-jun, YANG Yan-qian, LI Yong-sheng. Geochemical features of ore-forming fluids and metallogenesis of vein I in Asiha gold ore deposit, eastern Kunlun, Qinghai Province[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition), 2012, 42(6): 1676-1687.
[37] 李金超, 贾群子, 杜 玮, 栗亚芝, 孔会磊, NAMKHA N, 杨宝荣. 东昆仑东段阿斯哈矿床石英闪长岩LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb定年及岩石地球化学特征[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 2014, 44(4): 1188-1199.
LI Jin-chao, JIA Qun-zi, DU Wei, LI Ya-zhi, KONG Hui-lei, NAMKHA N, YANG Bao-rong. LA-ICP-MS zircon dating and geochemical characteristics of quartz diorite in Asiha gold deposit in east segment of the eastern Kunlun[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition), 2014, 44(4): 1188-1199.
[38] 张激悟. 青海东昆仑沟里地区阿斯哈金矿床元素地球化学特征与成矿分析[D]. 昆明: 昆明理工大学, 2013: 1-97.
ZHANG Ji-wu. Element geochemistry and mineralization analysis of Asiha gold deposit in Gouli area, Qinghai[D]. Kunming: Kunming University of Science and Technology, 2013: 1-97.
[39] 张德全, 张 慧, 丰成友, 佘宏全, 李进文, 李大新. 柴北缘-东昆仑地区造山型金矿床的流体包裹体研究[J]. 中国地质, 2000, 37(5): 843-850.
ZHANG De-quan, ZHANG Hui, FENG Cheng-you, SHE Hong-quan, LI Jin-wen, LI Da-xin. Fluid inclusions in orogenic gold deposits in the northern Qaidam margin-east Kunlun region[J]. Geology in China, 2000, 37(5): 843-850.
[40] 张德全, 党兴彦, 佘宏全, 李大新, 丰成友, 李进文. 柴北缘-东昆仑地区造山型金矿床的Ar-Ar测年及其地质意义[J]. 矿床地质, 2005, 27(4): 87-98.
ZHANG De-quan, DANG Xing-yan, SHE Hong-quan, LI Da-xin, FENG Cheng-you, LI Jin-wen. Ar-Ar dating of orogenic gold deposits in northern margin of Qaidam and east Kunlun mountains and its geological significance[J]. Mineral Deposits, 2005, 27(4): 87-98.
[41] 吴庭祥, 张绍宁, 安汝龙, 施根红, 窦宏伟. 青海东昆仑东段金矿区地层含矿性分析[J]. 矿产与地质, 2009, 23(5): 431-441.
WU Ting-xiang, ZHANG Shao-ning, AN Ru-long, SHI Gen-hong, DOU Hong-wei. Analysis of ore-bearing stratum at the gold mine within the east segment of the East Kunlun in Qinghai province[J]. Mineral Resources and Geology, 2009, 23(5): 431-441.
[42] 祁月清, 何俊江. 青海省都兰县沟里金矿地球化学特征[J]. 西部探矿工程, 2012(7): 142-145, 147.
QI Yue-qing, HE Jun-jiang. Geochemical characteristics of the gold deposits in Gouli area, Dulan County, Qinghai Province[J]. West China Exploration Engineering, 2012(7): 142-145, 147.
[43] 赵俊伟. 青海东昆仑造山带造山型金矿床成矿系列研究[D]. 长春: 吉林大学, 2008: 1-189.
ZHAO Jun-wei. Study on orogenic gold metallogenic series in eastern Kunlun orogenic belt, Qinghai Province[D]. Changchun: Jilin University, 2008: 1-189.
[44] 郭跃进. 青海东昆仑东段果洛龙洼金矿床地球化学特征与成矿模式[D]. 昆明: 昆明理工大学, 2011: 1-125.
GUO Yue-jin. Geochemical characteristics and metallogenic model of Guoluolongwa gold deposit in East Kunlun, Qinghai Province[D]. Kunming: Kunming University of Science and Technology, 2011: 1-125.
Polygenetic compound mineralization of Guoluolongwa gold deposit in Qinghai Province, China
LAI Jian-qing1, 2, JU Pei-jiao1, 2, ZHOU Feng1, 2
(1. Key Laboratory of Metallogenic Prediction of Nonferrous Metals and Geological Environment Monitoring,
Ministry of Education, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China;
2. School of Geosciences and Info-Physics, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China)
Abstract: The Guoluolongwa gold deposit is located at the eastern part of east Kunlun orogenic belt. The Variscan- Indosinian period is the most important mineralization period in this region. EW trending faults take a significant control of the ore bodies, the formation is the ore source, and acts as a barrier to trap the ore-forming minerals, besides, metamorphic hydrothermal and magmatic activity play a role in providing materials and heat for mineralization. Mineralization can be classified into metamorphic hydrothermal episode and magmatic hydrothermal episode. The former is the main mineralization episode, which consists of milky quartz vein stage (A) and gold-bearing quartz pyrite stage (B), and the latter corresponds to quartz sulfide enrichment stage (C). Polygenesis of the deposit was discussed according to study of S—Pb isotope, fluid inclusion microthermometry and H—O isotope. S—Pb isotope and H—O isotope analysis show multiple origins of ore-forming materials and fluids. Based on fluid inclusion petrography, three types of fluid inclusions are identified in B and C stages: aqueous inclusion (type I), CO2-aqueous inclusion (type II) and pure CO2 inclusion (type III). All three types of inclusions are present in stage B, having homogenization temperatures at 260- 360 ℃, and salinities ranging from 10.70% to 22.69% for type I and 3.52%-12.42% for type II, showing that ore-forming fluid maybe derived from metamorphic fluids and this stage belongs to metamorphic hydrothermal episode. Type I and a small amount of type II inclusions are developed in stage C, with homogenization temperatures concentrating from 160 ℃ to 320 ℃, and salinities ranging from 15.90%-23.32% for type I and 10.62%-13.57% for type II, indicating that mineralization fluid maybe magmatic hydrothermal and this stage belongs to magmatic hydrothermal episode. Gold mineralization mainly occurs in metamorphic hydrothermal episode, and superposition of magmatic hydrothermal in the late leads to re-enrichment of ore-forming minerals. To sum up, the deposit has a long evolution history, sources for ore-forming materials and fluids are multiple, and there exists a variety of ore-controlling factors, as well as various genetic types, illustrating that the deposit belongs to polygenetic compound deposit.
Key words: metallogenesis; polygenetic compound; Guoluolongwa gold deposit
Foundation item: Project(2015CX008) supported by Innovation-driven Plan in Central South University, China; Project(2006BAA01B06) supported by the National 11th Five-year Plan of Science and Technology Support Program, China
Received date: 2015-05-06; Accepted date: 2015-12-01
Corresponding author: LAI Jian-qing; Tel: +86-13875983805; E-mail: ljq@csu.edu.cn
(编辑 王 超)
基金项目:中南大学“创新驱动项目”(2015CX008);国家“十一五”科技支撑计划(2006BAA01B06)
收稿日期:2015-05-06;修订日期:2015-12-01
通信作者:赖健清,教授,博士;电话:13875983805;E-mail: ljq@csu.edu.cn