DOI: 10.11817/j.issn.1672-7207.2019.09.002
加热工艺对Nb-Ti微合金化高强钢的影响
梁文1, 2,吴润1,胡俊2,杜涛2,尹云洋2
(1. 武汉科技大学 材料与冶金学院,湖北 武汉,430081;
2. 宝钢中央研究院武汉分院,湖北 武汉,430080)
摘要:采用金相显微镜、透射电镜(TEM)以及电解分析等仪器和方法对不同加热工艺下,含Nb钢、含Ti钢以及Nb-Ti钢的奥氏体晶粒粒径长大规律和第二相固溶规律进行研究。研究结果表明:随着加热温度增加或保温时间延长,奥氏体晶粒粒径逐渐增大,钢中第二相析出物数量减少、粒径增大;在相同加热工艺下,Nb-Ti钢的奥氏体晶粒粒径比含Ti钢和含Nb钢的小;加热至1 200 ℃时含Nb钢中Nb基本全部固溶,而当加热温度升至1 300 ℃时,含Ti钢中仍有TiN无法固溶。Nb-Ti的复合添加使Nb元素的全固溶温度从1 200 ℃提高至1 250 ℃;当加热温度为1 150 ℃和1 200 ℃时,细小的第二相粒子TiC和NbC的固溶是造成该温度区间奥氏体晶粒粒径显著增加的主要原因。
关键词:Nb;Ti;奥氏体晶粒粒径;第二相析出;固溶量
中图分类号:TF777 文献标志码:A 文章编号:1672-7207(2019)09-2063-11
Effect of heating process on Nb-Ti microalloyed high strength steel
LIANG Wen1, 2, WU Run1, HU Jun2, DU Tao2, YIN Yunyang2
(1. College of Materials and Metallurgy, Wuhan University of Science and Technology, Wuhan 430081, China;
2. Wuhan Branch of Baosteel Central Research Institute, Wuhan 430080, China)
Abstract: The austenite grain size growth and the second phase solid solution of the Nb bearing steel, Ti bearing steel and Nb-Ti bearing steel with different heating process were studied by optical microscope(OM), transmission electron microscope(TEM) and electrolytic analysis. The results show that with the increase of the heating temperature or the holding time, the austenite grain size increases, while the number of the second phase precipitate decreases and the size increases. At the same heating process the austenite grain size of the Nb-Ti bearing steel is smaller than that of the Ti-bearing steel and the Nb-bearing steel. At 1 200 ℃, the Nb is almost completely solid solution for the Nb-bearing steel, and at 1 300 ℃, the TiN can not be solid solution for the Ti-bearing steel. For the Nb-Ti bearing steel, the total solid solution temperature of the Nb element increases from 1 200 ℃ to 1 250 ℃. At 1 150 ℃ and 1 200 ℃, the solid solution of fine second phase precipitate is the main reason for the significant increase of the austenite grain size during heating process.
Key words: Nb; Ti; austenite grain size; second phase precipitate; solid solution
在低合金钢中添加微合金化元素来改善钢铁材料的力学性能是目前高强钢普遍采用的技术手段。微合金元素在钢中主要以固溶物和第二相析出物(碳氮化物)形式存在,不同的存在形式具有不同的作用,且在不同温度下形成的碳氮化物的析出特点及其作用也不相同。微合金元素在钢中的主要作用为:在钢中形成高度弥散的碳氮化合物颗粒以有效固定奥氏体晶界,从而细化奥氏体晶粒和成品晶粒;微合金化元素原子的固溶阻塞、拖曳作用以及碳氮化物的动态析出可显著阻滞形变奥氏体的动态再结晶;在低温阶段通过析出强化等方式改善钢的力学性能[1-2]。学者们对微合金钢的强化机理进行了大量研究[3-7]。在实际的生产中,含Ti钢的力学性能波动比含Nb钢的大。如抗拉强度600 MPa级的含0.07%~0.12%Ti钢(质量分数)强度的波动范围为180 MPa,而同强度级别含0.04%~0.06%Nb钢(质量分数)强度的波动范围仅为120 MPa。但因Ti元素具有明显的成本优势,钢铁企业仍大量使用Ti来提高强度,同时也带来了性能波动等问题。影响微合金钢性能的热轧工艺主要包括加热温度、精轧温度、冷却速度以及卷取温度等。选择加热工艺时,一般考虑2个因素:较小的奥氏体晶粒粒径和较高的微合金元素固溶量[8]。特别是在钢铁材料的奥氏体化过程中,微合金碳氮化物的回溶行为将直接影响奥氏体晶粒粒径和均匀化程度以及轧制过程中奥氏体再结晶规律、轧制过程中和轧制后微合金元素的析出行为,进而显著影响钢材成品的综合力学性能[9-12]。因此,研究不同加热制度下,不同微合金元素种类和含量的高强钢所形成的碳氮化物分子式、固溶析出规律,对制定加热和轧制工艺,并了解析出物析出的动力学有非常重要的作用[13]。在此,本文作者研究加热工艺对含Nb钢、含Ti钢以及含Nb-Ti钢奥氏体晶粒的长大规律、第二相固溶规律的影响,以便为微合金化高强钢制定合理的加热工艺提供依据。
1 实验材料及方法
实验材料采用真空感应炉冶炼,浇铸成锭后,锻造成直径为15 mm的圆棒和长×宽×高为100 mm×25 mm×15 mm的条状试样,3种试样钢的化学成分如表1所示。在每种试样钢中选取一组试样在箱式加热炉内分别加热至1 150,1 200,1 250和1 300 ℃,保温20 min后出炉立即水淬;另一组试样加热至1 250 ℃和1 300 ℃分别保温10,15,20,25和30 min后出炉立即水淬。
表1 试验钢的化学成分(质量分数)
Table 1 Chemical composition of steel%
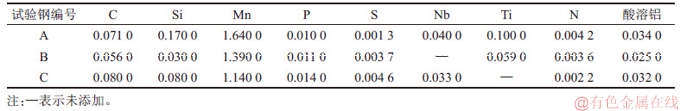
将热处理后的圆棒试样沿轴线方向切开,取一半试样进行研磨、抛光成金相试样,用过饱和苦味酸水溶液加少量缓蚀剂(海鸥牌洗头膏1~2 g)在80~85 ℃水浴中进行加热侵蚀,以显示原始奥氏体晶界,并在Olympus GX71光学显微镜下观察;按照GB/T 6394—2002的要求,通过Siscias8 图像分析软件用截点法测定不同加热温度和保温时间下的奥氏体晶粒粒径。取另一半试样加工成金相试样后,在4%(体积分数)的硝酸酒精溶液中侵蚀,用喷涂仪在其表面沉积一层碳膜,将碳膜划分为长×宽3 mm×3 mm的小格,然后将其放入盛有10%(体积分数)硝酸酒精溶液中,待碳膜与试样分离后,将碳膜放入去离子水中展开,用铜网捞起干燥,用带有能谱(EDS)的JEM-2100F型透射电镜(TEM)对析出物进行形貌观察和成分分析。
将长条试样去除表面氧化层,加工成长×宽×高为90 mm×20 mm×10 mm的试样,在1%(质量分数)柠檬酸+7.5%(质量分数)氯化钾溶液中进行电解,电流密度为20 mA/cm2,电解8 h后将过滤后的残渣变成溶液。在ICP Spectro Blue下测量溶液中Ti和Nb的浓度,计算试样中未固溶的Nb和Ti质量分数。
2 实验结果
2.1 加热工艺对奥氏体晶粒度的影响
试验钢在1 150,1 200,1 250和1 300 ℃下保温20 min和1 250 ℃下保温10,15,20,25和30 min的平均晶粒粒径分别如图1和图2所示。
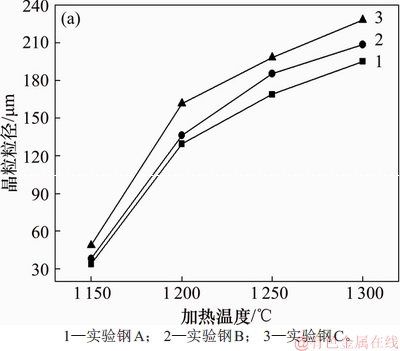
图1 奥氏体粒径随温度的变化规律
Fig. 1 Variation of austenite grain size with temperature
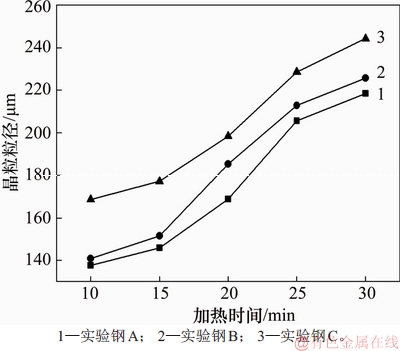
图2 奥氏体粒径随时间的变化规律
Fig. 2 Variation of austenite grain size with time
由图1可知:随着加热温度升高,3种试验钢的奥氏体晶粒粒径均增大,但增大的幅度不同;在1 150 ℃加热时,3种试验钢的粒径区别不大,试验钢C的奥氏体晶粒粒径略大,约为48 μm;当温度升至1 200 ℃时,3种试验钢的晶粒粒径发生了明显变化,其中试验钢C的晶粒粒径增加最多,达162 μm;试验钢B次之,试验钢A最小;当温度增至1 250 ℃时,3种试验钢奥氏体晶粒增大的趋势相同,但它们的增长速率均放缓;当温度增至1 300 ℃时,3种试验钢的增速与1 250 ℃时的基本相同。
由图2可知:保温时间对试验钢奥氏体晶粒粒径的影响规律与加热温度的相同,即随着保温时间延长,奥氏体晶粒粒径长大,且均有快速长大区间,如当加热温度为1 150~1 200 ℃和保温时间为15~25 min时。可见:试验钢在1 250 ℃下保温,在前15 min内,奥氏体晶粒粒径缓慢增长;保温15~25 min时,长大速率显著增加,即保温时间大于25 min时,长大速率又有所放缓。
试验钢A在不同加热温度下保温20 min的奥氏体晶粒照片如图3所示。
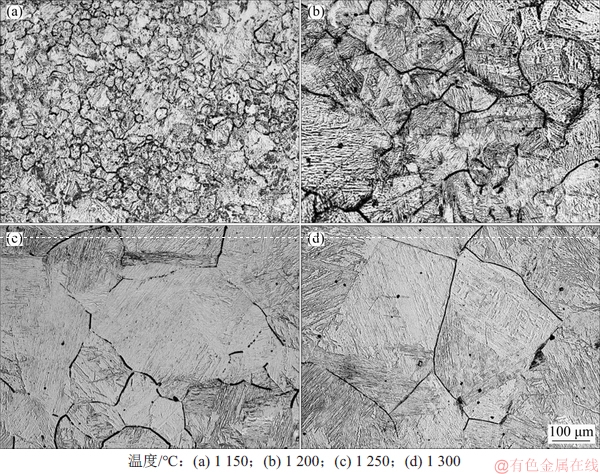
图3 试验钢A在不同温度下保温20 min的奥氏体晶粒照片
Fig. 3 SEM images of austenite for steel A holding at different temperatures for 20 min
由图3可知:当加热温度为1 150 ℃时,奥氏体晶粒细小均匀(图3(a));当温度升至1 200 ℃时,奥氏体晶粒发生了不同程度的长大,奥氏体的大晶粒吞噬周围的小晶粒,呈现出粒度不均的现象(图3(b));当加热温度为1 250 ℃时,奥氏体的不均匀程度进一步加剧(图3(c));而到1 300 ℃时,晶粒的均匀度提高,小晶粒全部被吞噬(图3(d))。
试验钢A在1 250 ℃保温不同时间的奥氏体晶粒照片如图4所示。
由图4可知:随着保温时间的延长,奥氏体晶粒粒径增大;保温20 min时,奥氏体晶粒粒径增长最大(图4(b));保温10 min时,奥氏体晶粒已发生了不同程度的长大,这种趋势随着保温时间的延长而有所缓和。
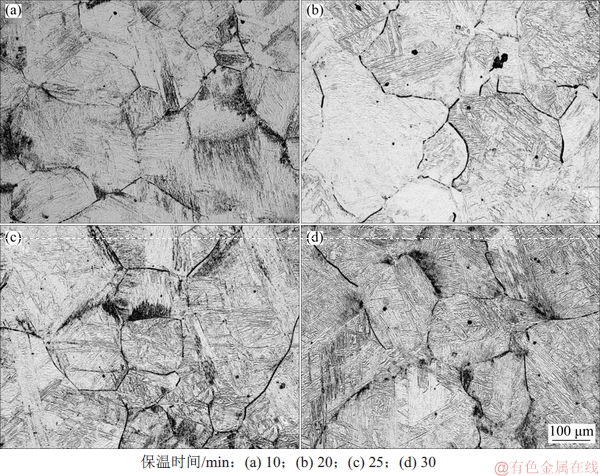
图4 试验钢A在1 250 ℃下保温不同时间的奥氏体晶粒照片
Fig. 4 SEM images of austenite for steel A holding at 1 250 ℃ for different time
2.2 加热工艺对第二相析出物的影响
试验钢A原始态以及在1 150,1 200,1 250和1 300 ℃下保温20 min时,钢中第二相析出物的照片及成分如图5所示。
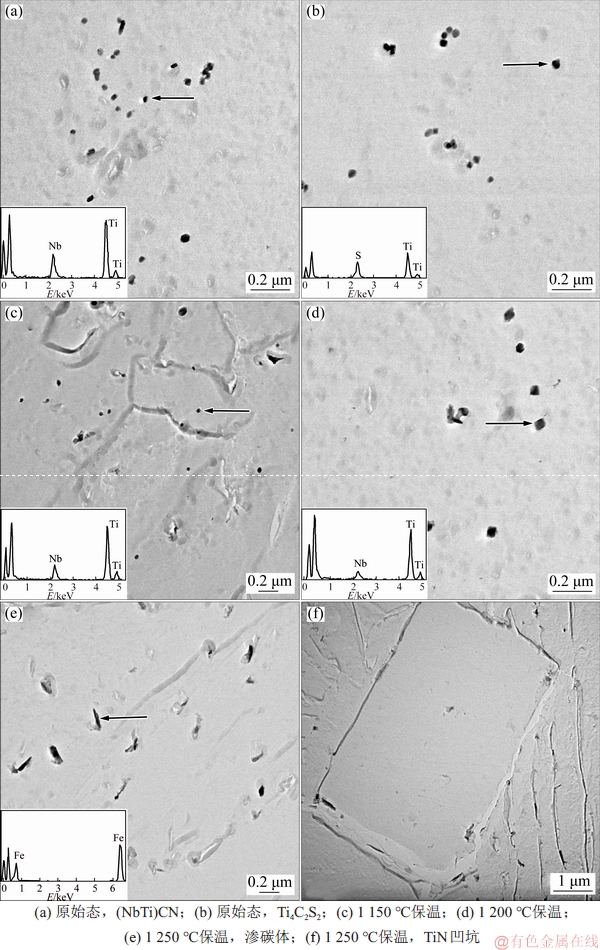
图5 试验钢A在不同温度下第二相的TEM照片及能谱图
Fig. 5 TEM image and energy spectrum of the second phase for steel A at different temperatures
试验钢A的原始态试样中第二相析出物数量较多,形态主要为矩形或不规则形,粒径主要为20~60 nm,少量为60~200 nm,成分主要为Ti+Nb(图5(a)),还存在极少量成分为Ti+S的析出物,为Ti4C2S2[14](图5(b))。在1 150 ℃保温的固溶试样中的析出物数量比原始试样的略少,形态不变,粒径略有增大,主要为40~80 nm,少量为100~180 nm,成分主要为Ti+Nb(图5(c))。而1 200 ℃保温的试样中的析出物数量更少,形态主要为矩形,粒径进一步增大,主要为60~200 nm,成分主要为Ti+Nb(图5(d))。而在1 250 ℃下保温的试样中,除渗碳体(图5(e))以及微米级的TiN形成的矩形凹坑(图5(f))外,未见其他类型析出物。随着加热温度升高,第二相粒子除了数量下降,粒径增加外,Nb元素和Ti元素的质量比改变。从EDS能谱可知:随着加热温度升高,Nb元素质量分数下降,而Ti元素质量分数增加。惠亚军等[15]研究也表明,随着加热温度的升高,Ti与Nb质量比从77:23增至82:18,再增至98:2。
在1 250 ℃下保温不同时间,第二相析出物存在同样的规律。且保温15 min后,第二相析出物数量开始减少,粒径逐渐增加,形状由方形+不规则形状为主转变为以方形为主,Ti与Nb质量比逐渐增大。
2.3 加热工艺对Nb和Ti固溶量的影响
3种试验钢在1 150,1 200,1 250和1 300 ℃保温20 min,第二相未固溶量(质量分数,下同)如图6所示。从图6可见:对于试验钢C,于1 150 ℃保温时,Nb元素固溶量为0.023%,在1 200 ℃保温时已基本固溶(图6(c));对于试验钢B,1 250 ℃时Ti元素仅固溶0.036%,即使加热温度增至1 300 ℃,仍有0.021%的Ti未固溶(图6(b))。而对于试验钢A,随着加热温度升高,微合金元素固溶速率更慢。当温度升至1 250 ℃,Nb元素才完全固溶,即Nb-Ti的复合添加使Nb元素第二相析出物的热稳定性提高了约50 ℃,这与齐亮等[13]的研究结果一致,Ti元素提高了含Nb钢中(TiNb)(CN)的热稳定性。而温度增至1 300 ℃时,试验钢A中仍有0.028%的Ti未固溶。

图6 加热温度与微合金元素未固溶量的关系
Fig. 6 Relationship between heating temperature and unsolidified precipitate of microalloy elements
试验钢在1 300 ℃下分别保温10,20和30 min,微合金元素未固溶量如图7所示。从图7可见:当保温10 min时,Nb元素已基本全固溶,Ti元素的固溶量也基本稳定,继续延长保温时间,两者的未固溶量均保持不变。
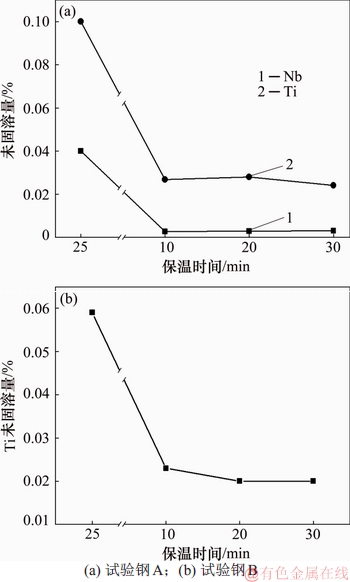
图7 保温时间与微合金元素未固溶量的关系
Fig. 7 Relationship between holding time and unsolidified precipitate of microalloy elements
3 分析讨论
3.1 第二相粒子的溶解行为
微合金元素形成的第二相在高温下会重新固溶形成固溶体,当温度高于全固溶温度并达到平衡时,第二相完全固溶,第二相形成元素只会以固溶元素的形式发挥相应的作用,因此,高温下未溶的第二相具有钉扎奥氏体晶界从而阻止其长大的作用,但固溶原子未发挥作用。二元第二相MX的固溶度公式[16]如下:
lg(w(M)·w(X))=A-B/TAS (1)
式中:w(M)和w(X)分别为第二相元素M和X在钢中的质量分数,%;TAS为元素固溶温度,K;A和B为固溶度积中的常数,常用数值如表2所示。
将3种试验钢的成分代入式(1)可得到第二相微合金全固溶温度,如表3所示。
由表3可知,对于单纯的二元第二相,除了TiN的全固溶温度很高外,其他第二相的全固溶温度差别不大。第二相全固溶温度与其原始质量分数密切相关,如TiC在试验钢A中的全固溶温度较试验钢B的高60 ℃。对于试验钢A,第二相全固溶温度由低到高的顺序为TiC,NbC,NbN,TiN。
钢中碳化物或氮化物的晶体结构均为“NaCl”型fcc点阵,且点阵常数相近(TiN,TiC,NbN和NbC的点阵常数a分别为0.423 0,0.432 0,0.438 8,0.445 8),可以相互溶解,形成MCxN1-x的三元第二相[14],其固溶量与第二相析出物之间的关系为:
 (2)
(2)
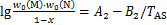 (3)
(3)
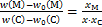 (4)
(4)
 (5)
(5)
式中:A1和B1分别为MC二元相固溶度积常数,A2和B2分别为MN二元相的固溶度积常数(见表2);w0(M), w0(C),w0(N)分别为M,C和N元素的平衡固溶量;w(N)和w(C)分别为元素N和C的质量分数,%;xM,xC和xN分别为M,C和N元素的相对原子质量。
对于试验钢A,含有Nb和Ti元素,生成的四元第二相NbyTi1-yCxN1-x计算过于复杂,且准确率低,故对其进行简化。当加热温度为1 300 ℃,Ti与N元素在奥氏体中的固溶度积为
w0(Ti)·w0(N)=100.32-8000/1573 (6)
 (7)
(7)
由式(6)和式(7)计算得到氮元素的固溶量为1.98×10-6,约占N元素原始质量分数的4.3%。由此可见,当加热温度升至1 300 ℃时,固溶于奥氏体中的氮元素仍非常少,即TiN几乎未固溶。因此,计算微合金元素Nb与Ti的析出量时,可以忽略N元素和TiN的影响,即NbyTi1-yCxN1-x可简化为NbyTi1-yC,按三元第二相进行计算。
由式(2)~(5)可得试验钢中在温度TAS时M,C和N元素在基体中的平衡固溶量以及平衡存在的MCxN1-x或NbyTi1-yC相化学式中的x或y这4个未知数。结果如图8所示。
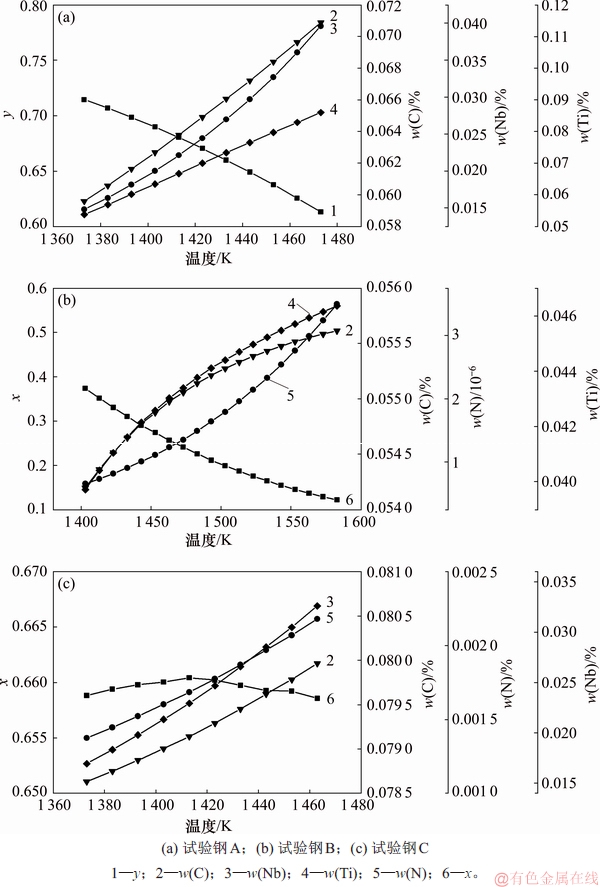
图8 钢中第二相固溶量及第二相组成系数与温度的关系
Fig. 8 Relationship between solid solution amount and composition coefficient of second phase in steel and temperature
表2 奥氏体中二元化合物的固溶度积中系数[16]
Table 2 Coefficients of solid solubility product for binary compounds in austenite

由图8(a)可知:当加热温度为1 373~1 473 K时,NbyTi1-yC的固溶量随着温度的增加而增大,Nb的固溶量从0.014 8%增加至0.039 6%,Ti的固溶量从0.053 8%增加至0.086 0%,而在该温度区间,y由0.71降至0.61。这说明随着温度升高,第二相析出物NbyTi1-yC中Ti的比例逐渐增加,而Nb逐渐降低,这与试验钢A中的Ti,Nb质量分数随着温度升高而增大的现象相同。当加热温度大于等于1 200 ℃时,试验钢A中的NbyTi1-yC全部固溶,基体中只剩下TiN第二相。
表3 试验钢中第二相固溶温度
Table 3 Solid solution temperature of the second phase in test steel K
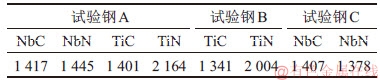
对于试验钢B(图8(b)),当加热温度为1 403~1 573 K时,Ti的固溶量从0.039 7%增至0.046 4%,C的固溶量稳定在0.054 2%~0.055 6%,N的固溶量由6.5×10-7增至32×10-7,x由0.37降至0.13。即在1 300 ℃下,试验钢C中仍有0.012 6%Ti未固溶,它主要以TiN的形式存在。
由图8(c)可知:当加热温度为1 373~1 463 K时,Nb的固溶量从0.016 9%增加至0.032 6%,即在1 190 ℃下,试验钢C中的NbCxN1-x全部固溶,且在该温度区间,x约为0.66,即该温度下形成的第二相析出物为NbC0.66N0.34。
由图8(a)和8(b)可知:即使加热温度高达1 300 ℃,仍有部分TiN未固溶,这与图6中观察到部分Ti未固溶的现象相同。但理论计算结果与电解试验的检测结果区别较大,这应该与连铸过程中生成的大颗粒NbyTi1-yCxN1-x有关[17]。即使在高温下保温,这些粗大的第二相也很难固溶,它们称之为无效的Nb和Ti含量。它们不但增加合金成本,对细化奥氏体晶粒和卷取后的沉淀析出无任何作用,而且方形的TiN大颗粒会严重影响微合金钢的力学性能[18-20]。
由三元第二相的固溶度公式可知,若MCxN1-x全固溶,则其全固溶公式可表示为[16]
 (8)
(8)
由于固溶度积公式中的常数总为正值,即式(8)中左边任一项均大于0小于1,因此,在化学成分确定的钢中,其三元第二相MCxN1-x的全固溶温度必高于二元相MC和MN的全固溶温度,即二元第二相互溶形成的三元第二相后将使第二相的全固溶温度升高。这就是试验钢A中Nb的全固溶温度比试验钢C的升高了约50 ℃的原因。
3.2 第二相粒子对奥氏体晶粒长大的影响
均热时,钢中第二相质点通过钉扎晶界机制而阻止奥氏体晶粒的粗化,第二相质点对均热时奥氏体晶界的阻碍作用可表示为:
 (9)
(9)
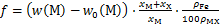 (10)
(10)
式中:Dc为阻止晶粒粗化所需的临界或最大的质点粒径;d为第二相质点的粒径;f为质点的体积分数[16];Z为质点不均匀因子;ρFe和ρMX分别为Fe和二元第二相MX的密度; 为MX中X的相对原子质量。
为MX中X的相对原子质量。
当第二质点的体积分数和粒径固定时,可计算出奥氏体晶粒粒径阈值Dc。当初始的奥氏体晶粒粒径D>Dc时,该类晶粒基本上不会长大,即第二相颗粒能够钉扎晶界。由式(9)可知,晶粒粒径阈值Dc正比于第二相质点粒径d而反比于第二相质点体积分数f。在加热过程中,随温度的升高和时间的延长,由于第二相的溶解,第二相质点的体积分数f减小;同时,由于第二相质点的Ostwald熟化(聚集长大),质点粒径d随温度升高和时间延长而增大,这二者的变化都将导致晶粒粒径阈值增大。因此,本实验中随着加热温度升高和保温时间延长,试验钢中奥氏体晶粒平均粒径都将增大[21]。
微合金钢中析出物颗粒的存在显著地改变了基体晶粒的粗化特征,这主要是晶界与质点间的相互作用所致。当晶界与析出物颗粒相交时,晶界面积减少,局部能量降低;而当晶界离开析出物颗粒进行迁移时,将使局部能量升高,导致析出物颗粒对晶界的“钉扎”效应,从而阻碍奥氏体晶粒的长大[15]。由图1、图3和图5可知:当加热温度为1 150~1 200 ℃时,钢中第二相TiC和NbC未固溶,这些第二相细小弥散,对奥氏体晶粒长大的阻碍作用最大;当加热温度大于1 200 ℃,TiC和NbC发生固溶,剩下的第二相主要是TiN和NbN,其粒径大、数量少,对奥氏体晶粒长大的阻碍作用降低,晶粒逐渐长大。
保温时间对奥氏体晶粒粒径的影响规律与加热温度的影响规律相同,即随着保温温度的延长,细小的第二相粒子逐渐溶解,未固溶的第二相粒径较大,对奥氏体晶粒长大的阻碍作用降低。奥氏体晶粒的长大速率v为[22]
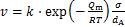 (11)
(11)
式中:k和R为常数;Qm为晶界移动的激活能;T为加热温度;dA为奥氏体晶粒的平均粒径;σ为晶界的界面能。由式(11)可知:晶粒的长大速率与温度成指数关系,随着温度的升高,晶界的迁移率变大,此时,晶粒长大,但随着平均晶粒粒径的增加,晶粒的长大速率又会逐渐趋于稳定。而且微合金元素的加入,使Qm增大,从而降低奥氏体的增长速率。
对于含Nb钢,当加热温度≥1 200 ℃时,Nb元素已基本全固溶,其对奥氏体晶粒长大无阻碍作用,奥氏体晶粒将粗化,但轧钢过程会细化奥氏体晶粒,消除了因奥氏体晶粒粗化带来的不良影响,因此,加热温度对含Nb钢的影响较小。但对含Ti钢,当加热温度为1 200~1 300 ℃时,随着加热温度的升高,Ti元素的固溶量逐渐增大,而奥氏体晶粒粒径变化要小。因此,在更高温度下加热,轧制后产生的析出强化效果更强,可见加热温度对含Ti钢的影响明显,这也是含Ti钢强度波动较大的原因之一。
4 结论
1) 当加热温度从1 150 ℃升至1 200 ℃时,细小的第二相粒子TiC和NbC逐渐固溶,对奥氏体晶界的钉扎作用下降,使得试验钢的奥氏体晶粒粒径显著增加;当加热温度从1 200 ℃升至1 300 ℃时,由于晶粒粒径已经长大,晶粒的长大速率逐渐趋于稳定,因而,实验钢的奥氏体晶粒粒径增大速率有所减缓。
2) 根据固溶曲线,含Nb钢、含Ti钢和含Nb-Ti钢中第二相粒子分别在1 200,1 250和1 300 ℃基本固溶。因此,为了提升微合金钢中第二相的析出钢化效果,含Nb,Ti和Nb-Ti试验钢的加热温度分别设定为1 200,1 250和1 300 ℃。
参考文献:
[1] 惠亚军, 潘辉, 刘锟, 等. 600 MPa级Nb-Ti微合金化高成形性元宝梁用钢的强化机制[J]. 金属学报, 2017, 53(8): 937-946.
HUI Yajun, PAN Hui, LIU Kun, et al. Strengthening mechanism of 600 MPa grade Nb-Ti microalloyed high formability crossbeam steel[J]. Acta Metallurgica Sinica, 2017, 53(8): 937-946.
[2] 王凤琴, 解家英, 胡本芙. X70管线钢中含Nb相的析出行为[J]. 北京科技大学学报, 2011, 33(11): 1354-1359.
WANG Fengqin, XIE Jiaying, HU Benfu. Precipitation behaviour of Nb in X70 pipeline steel[J]. Journal of University of Science and Technology Beijing, 2011, 33(11): 1354-1359.
[3] 张正延, 孙新军, 雍岐龙, 等. Nb-Mo微合金高强钢强化机理及其纳米级碳化物析出行为[J]. 金属学报, 2016, 52(4): 410-418.
ZHANG Zhengyan, SUN Xinjun, YONG Qilong, et al. Precipitation behavior of nanometer-sized carbides in Nb-Mo microalloyed high strengh steel and its strengthening mechanism[J]. Acta Metallurgica Sinica, 2016, 52(4): 410-418.
[4] HONG S G, KANG K B, PARK C G. Strain-induced precipitation of NbC in Nb and Nb-Ti microalloyed HSLA steels[J]. Scripta Materialia, 2002, 46(2): 163-168.
[5] 徐洋, 孙明雪, 周砚磊, 等. (Nb, Ti)C在轧后卷取中的析出及对铁素体相微观力学特征的影响[J].金属学报, 2015, 51(1): 31-39.
XU Yang, SUN Mingxue, ZHOU Yanlei, et al. Precipitation behavior of (Nb, Ti)C in coiling process and its effect on micro-mechanical characteristics of ferrite[J]. Acta Metallurgica Sinica, 2015, 51(1): 31-39.
[6] YEN H W, CHEN P Y, HUANG C Y, et al. Interphase precipitation of nanometer-sized carbides in a titanium-molybdenum-bearing low-carbon steel[J]. Acta Materialia, 2011, 59(16): 6264-6274.
[7] 石骁, 吴建中, 郭汉杰, 等. DH36高强度船板钢中碳化物及碳氮化物析出行为[J]. 中南大学学报(自然科学版), 2018, 49(3): 518-528.
SHI Xiao, WU Jianzhong, GUO Hanjie, et al. Precipitation behaviors of carbides and carbonitrides in DH36 high-strength ship plate steel[J]. Journal of Central South University(Science and Technology), 2018, 49(3): 518-528.
[8] 闻玉辉, 朱国明, 郝亮, 等. Nb-Ti微合金化热冲压成形用钢的微观组织与力学性能[J]. 工程科学学报, 2017, 39(6): 859-866.
WEN Yuhui, ZHU Guoming, HAO Liang, et al. Microstructure and mechanical properties of Nb-Ti micro-alloy hot stamping steels[J]. Chinese Journal of Engineering, 2017, 39(6): 859-866.
[9] 张鹏程, 武会宾, 唐荻, 等. Nb-V-Ti和V-Ti微合金钢中碳氮化物的回溶行为[J]. 金属学报, 2007, 43(7): 753-758.
ZHANG Pengcheng, WU Huibin, TANG Di, et al. Dissolving behaviors of carbonitrides in Nb-V-Ti and V-Ti microalloying steels[J]. Acta Metallurgica Sinica, 2007, 43(7): 753-758.
[10] 李永亮, 王福明, 李长荣, 等. Ti对700 MPa级汽车大梁钢奥氏体晶粒长大的影响[J]. 材料热处理学报, 2016, 37(7): 117-122.
LI Yongliang, WANG Fuming, LI Changrong, et al. Effect of Ti on austenite grain growth behavior of automobile beam steel with yield strength of 700 MPa[J]. Transactions of Materials and Heat Treatment, 2016, 37(7): 117-122.
[11] 兰鹏, 杜辰伟, 张家泉, 等. 送装工艺对板坯再加热过程奥氏体晶粒细化的影响[J]. 工程科学学报, 2017, 39(12): 1835-1843.
LAN Peng, DU Chenwei, ZHANG Jiaquan, et al. Effect of charging processes on the austenite grain refinement of continuously cast slabs during reheating[J]. Chinese Journal of Engineering, 2017, 39(12): 1835-1843.
[12] UHM S, MOON J, LEE C, et al. Prediction model for the austenite grain size in the coarse grained heat affected zone of Fe-C-Mn steels: considering the effect of initial grain size on isothermal growth behavior[J]. ISIJ International, 2004, 44(7): 1230-1237.
[13] 齐亮, 赵爱民, 赵征志, 等. 铌对高钢级管线钢中碳氮化物析出热力学影响[J]. 材料科学与工艺, 2012, 20(6): 29-34.
QI Liang, ZHAO Aimin, ZHAO Zhengzhi, et al. Effect of niobium on the carbonitride complex precipitation in high-grade pipeline steels[J]. Materials Science and Technology, 2012, 20(6): 29-34.
[14] 雍岐龙, 马鸣图, 吴宝熔. 微合金钢——物理和力学冶金[M].北京: 机械工业出版社, 1989: 254.
YONG Qilong, MA Mingtu, WU Baorong. Microalloyed steels—physical and mechanical metallurgy[M]. Beijing: China Machine Press, 1989: 254.
[15] 惠亚军, 潘辉, 李文远, 等. 1000MPa级Nb-Ti微合金化超高强度钢加热制度研究[J]. 金属学报, 2017, 53(2): 129-139.
HUI Yajun, PAN Hui, LI Wenyuan, et al. Study on heating schedule of 1000 MPa grade Nb-Ti microalloyed ultra-high strength steel[J]. Acta Metallurgica Sinica, 2017, 53(2): 129-139.
[16] 雍岐龙.钢铁材料中的第二相[M].北京: 冶金工业出版社, 2006: 68.
YONG Qilong. The second phase in steel materials[M].Beijing: Metallurgical Industry Press, 2006: 68.
[17] FU Junwei, NIE Qiangqiang, QIU Wenxiu, et al. Morphology, orientation relationships and formation mechanism of TiN in Fe-17Cr steel during solidification[J]. Materials Characterization, 2017, 133: 176-184.
[18] 傅杰, 朱剑, 迪林, 等. 微合金钢中TiN的析出规律研究[J]. 金属学报, 2000, 36(8): 801-804.
FU Jie, ZHU Jian, DI Lin, et al. Study on the precipitation behavior of TiN in the microalloyed steels[J]. Acta Metallrugica Sinica, 2000, 36(8): 801-804.
[19] DU J, STRANGWOOD M, DAVIS C L. Effect of TiN particles and grain size on the charpy impact transition temperature in steels[J]. Journal of Materials Science & Technology, 2012, 28(10): 878-888.
[20] YAN W, SHAN Y Y, YANG K. Effect of TiN inclusions on the impact toughness of low-carbon microalloyed steels[J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A, 2006, 37(7): 2147-2158.
[21] 薛润东, 赵志毅, 王明侠, 等. 均热时间对含Ti、Nb微合金元素高强钢固溶规律的影响[J]. 北京科技大学学报, 2007, 29(9): 907-910.
XUE Rundong, ZHAO Zhiyi, WANG Mingxia, et al. Effect of soaking time on the dissolution of microalloyed elements in high-strength steel containing Ti and Nb[J]. Journal of University of Science and Technology Beijing, 2007, 29(9): 907-910.
[22] GLADMAN T. On the theory of the effect of precipitate particles on grain growth in metals [J]. Proceedings of the Royal Society, 1966, 294: 298-309.
(编辑 赵俊)
收稿日期: 2019 -01 -02; 修回日期: 2019 -04 -10
基金项目(Foundation item):国家自然科学基金资助项目(51771139) (Project(51771139) supposed by the National Natural Science Foundation of China)
通信作者:梁文,博士,高级工程师,从事热轧汽车用钢等研究;E-mail:15972996369@163.com