基于容量参数的二次电池嵌入型电极材料固相扩散系数的测定方法
唐新村, 金 乐, 刘 畅
(中南大学 化学化工学院, 长沙 410083)
摘 要: 介绍了一种以容量参数为主变量的测定锂二次电池中电极材料固相扩散系数的方法。 该方法只需颗粒半径这一辅助参数, 通过球型扩散模型建立了恒流-恒压充电容量(RPG)比, 进一步发展成为容量间歇滴定技术(CITT)。 采用RPG法可在较宽的电压范围内测定嵌入型电极材料的平均固相扩散系数, 实验结果重现性好。 由RPG法测得0~1.5V时锂离子在石墨电极中的平均固相扩散系数值为1.055×10-10cm2/s。 由CITT技术测得锂离子在LiMn2O4中的固相扩散系数在3.95V和4.12V左右存在个两个极小峰, 且随着循环次数的增加, 扩散系数值逐渐增大。
关键词: 固相扩散系数; 容量参数; 嵌入型电极材料; 锂二次电池 中图分类号: O646
文献标识码: A
Determination of solid diffusion coefficient of insertion-host electrode materials based on capacity parameter
TANG Xin-Cun, JIN Le, LIU Chang
(College of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Central South University,Changsha 410083, China)
Abstract: A method of determining the solid diffusion coefficient of electrode materials in the lithium battery was introduced, where the capacity was the main variable. This method needs only one complementary parameter ( the radius of insertion-host particle, R) . Based on the ratio of potentio-charge capacity to the galvano-charge capacity(RPG) by the spherical diffusion model, the method was developed to the capacity intermittent titration technique(CITT). By RPG method, the average solid diffusion coefficient of insertion-host materials can be determined at a relativly wide range of voltage. The Li+ diffusion coefficients in graphite were determined as 1.055×10-10cm2/s in the voltage range from 0 to 1.5V. The Li+ solid diffusion coefficients in LiMn2O4 were determined at different galvano-charge currents. Results shows that the Li+ solid diffusion coefficients reach the minimum at the voltage of 3.95 and 4.12V, and the diffusion coefficients increase with the increasing circulation times. So by CITT method, the solid diffusion coefficient of electrode materials at different charge-discharge circulations can be determined conveniencely.
Key words: solid diffusion coefficient; capacity parameter; insertion-host electrode materials; secondary lithium battery
离子嵌入型化合物(ion insertion-host compound)作为电极活性材料, 如LiCoO2、 LiMn2O4、 LixC6等锂离子嵌入型化合物和LaNi5储氢合金、 Ni(OH)2等氢离子嵌入型化合物, 分别在锂离子电池、 镍氢电池等高能二次电池中得到了成功的应用[1-4]。 由于离子(如Li+、 H+)在嵌入型化合物内部的脱出/嵌入是实现能量存储与输出的关键步骤, 因此在离子这些材料中的固相扩散系数成为一个非常重要的电极动力学参数[5]。 目前最常见的固相扩散系数测定方法大多是直接建立在基于电压、 电流和时间参数之间的响应关系基础之上的, 如: 电化学阻抗法(EIS)、 电流间歇滴定法(GITT)、 电位间歇滴定法(PITT)、 电流脉冲驰豫法(CPR)[6-16]。 本文作者介绍了一种以充/放电容量参数作为主变量测定离子嵌入型电极材料固相扩散系数的新方法。 该方法所需要仪器即为普通的电池充放电测试仪, 仅需确定电极材料颗粒半径一个辅助参数。 采用该方法可以简单方便地测定不同电压、 不同循环次数下的固相扩散系数值。
1 理论模型
由于恒流充电过程中不可避免地存在极化效应, 导致部分的极化容量损失, 这部分损失的容量可以通过进一步的恒压充电得到补偿。 因此, 恒流-恒压充电不但在实践中可补偿单纯的恒流充电所存在的极化容量损失问题, 而且由于恒压充电所补偿的容量反映了研究体系的动力学特征, 在理论上也可应用于二次电池的动力学性能分析。 在建立恒流-恒压充电理论模型过程中, 主要的核心思想有以下两点[17, 18]:
1) 组成整个多孔电极的每一个颗粒都相当于一个独立的微电极, 通过球形扩散模型求出单一颗粒的恒流充放电容量和恒压充电容量的数学表达式, 即

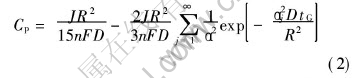
式中 D为电极材料的固相扩散系数, cm2/s; R为材料颗粒半径, cm; tG为恒流充电时间, s。
2) 利用容量的加和性质(即电极总容量等于每一个独立微电极容量的加和), 通过引入恒压-恒流容量比值的概念, 建立描述多孔电极的容量性质的数学模型。 按照上述思想得到RPG方程:
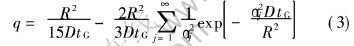
式中 q为恒压充电容量与恒流充电容量的比值, 无量纲; n为嵌入离子的电荷数(如Li+、 H+, n=1), αj为已知常数数列, 由方程tanα=α解得。 引入无量纲参数ξ, ξ=R2/DtG, 将方程在不同q值范围内通过最小二乘法对ξ进行线性化匹配, 最终得到的D=f(q)的系列方程, 结果列于表1。 根据这系列方程, 只要测出颗粒半径R、 恒压-恒流充电比值q和恒流充电时间tG, 即可得到扩散系数D。
2 RPG法测定平均固相扩散系数
恒压-恒流充电容量比值法(ratio of potentio-charge capacity to galvano-charge capacity, RPG)可在宽的电压范围下测定嵌入型电极材料的平均固相扩散系数[17, 18]。 RPG法所采用D=f(q)方程为

由于恒流充电的电压范围较宽, q值的范围通常小于0.50。 图1所示为RPG法测定锂离子在石墨中平均固相扩散系数的测试曲线。 从图1(a)中的电压—时间曲线和图1(b)中的电流—时间曲线可以得到恒流充电时间t的值(204min)。 从图1(a)和
表1 不同q 和ξ范围下式(3)最小方差线性化方程
Table 1 Equations fitted by linear least-square fits of Eqn.(3) for different ranges of q or ξ
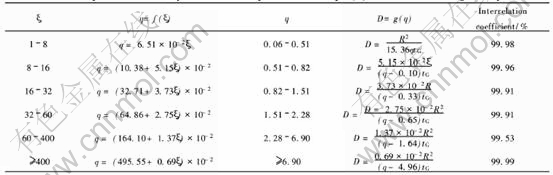
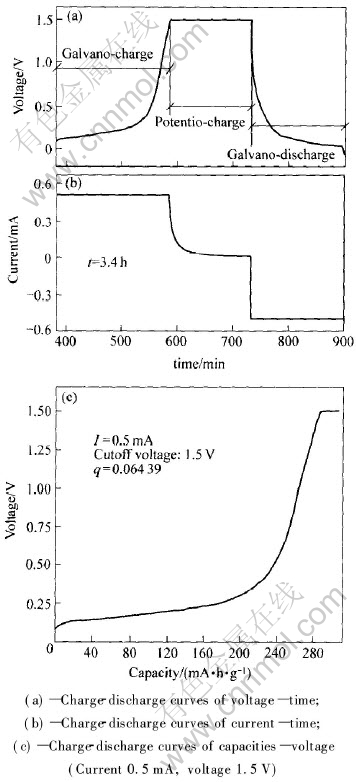
图1 石墨电极的恒流—恒压充放电曲线
Fig.1 Curves of galvano-potentio-charge vs galvano-discharge of graphite
1(b)还可以看出, 在恒压充电过程中电流随时间而逐渐减小到零, 表明通过恒压充电使锂离子在石墨颗粒中的径向浓度梯度逐渐减小, 直至达到均匀分布。 图1(c)所示为恒流—恒压充电的电压对容量曲线, 从该图可得到恒流充电容量和恒压充电容量的数据, 分别为290.4和18.7mA·h/g。
由此可算得q值为6.439×10-2, 并满足式(4)中q〈0.51的要求。 因此, 锂离子在石墨电极中的平均固相扩散系数D可按式(4)求出。 通过激光粒度分析仪和扫描电镜, 测出石墨平均颗粒半径R(11.3μm), 即可得到的0~1.5V下锂离子在石墨电极中的平均固相扩散系数值为1.055×10-10cm2/s。
3 CITT法测定不同电压和不同循环次数下的固相扩散系数
在RPG法基础上, 本文作者进一步将其发展成为容量间歇滴定技术(CITT, capacity intermittent titration technique)[18]。 图2所示为典型的CITT测试曲线。 由图2可以看出, CITT技术实际
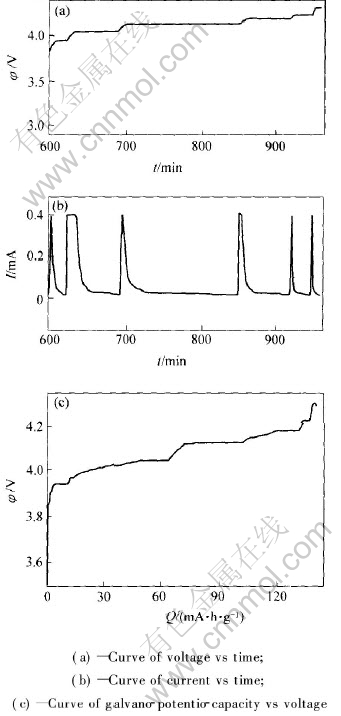
图2 尖晶石LiMn2O4在0.4mA恒流充电电流下测得的一次CITT曲线
Fig.2 CITT curves of LiMn2O4 at galvano-charge current of 0.4mA
上是在小的电压范围下连续地进行多个RPG测试, 从而达到通过一次实验测定不同电压下的扩散系数值的目的。 如果进行多个循环的CITT测试, 则可获得不同电压和不同循环次数下的固相扩散系数。 因此, 采用CITT技术可以非常方便地检测不同充放电循环次数下电极材料的固相扩散系数。
图3所示为尖晶石LiMn2O4/Li电池的前20次循环的CITT曲线及前20次充放电过程中锂离子在LiMn2O4中的扩散系数。 由图3可知, 锂离子在LiMn2O4中的固相扩散系数不但与电压(或锂离子在Mn2O4晶格中的浓度, 或充电深度DOC)有关, 而且随循环次数发生变化。 随着电压的变化, 在3.95V和4.12V左右存在两个极小峰, 整个扩散系数值—电压曲线呈扭曲的“W”形状, 这一结果与其它文献报道的基本一致[16]。 然而, 一个有趣的现象是这两个极小峰随着循环次数的增加, 都在逐
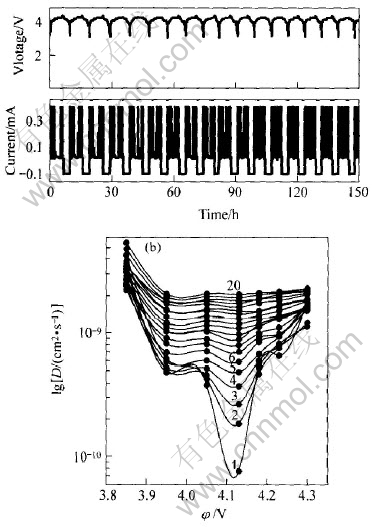
图3 尖晶石LiMn2O4/Li电池前20次的CITT循环曲线和lgD-φ曲线
Fig.3 First 20th CITT cycling curves(a) and lgD-φ curves(b) of LiMn2O4/Li battery at galvano-charge current 0.4mA and galvano-discharge current 0.1mA
渐地趋向于平坦化。 在第17次循环时, 这两个极小峰已经变得很不明显, 尤其是在4.12V处的极小峰随着循环次数的增加变化值非常快。 从图3还可以看出, 随着循环次数的增加, 锂离子在LiMn2O4中的固相扩散系数整体上在增大, 但随着循环次数的增多, 扩散系数增大的速率逐渐变小。 这一结果表明锂离子在LiMn2O4中重复脱/嵌时, 整个体系具有自我增强扩散的能力。
4 结论
1) RPG法测锂离子的平均固相扩散系数, 具有重现性好的特点。 采用RPG法测得在1.0~2.5V电压范围内, 锂离子的石墨中的固相扩散系数为4.292×10-10~10219×10-10cm2/s。
2) 容量间歇滴定技术(CITT)能够方便地测定不同电压、 不同循环次数下嵌入粒子在嵌入电极材料中固相扩散系数。
3) 锂离子在尖晶石LiMn2O4正极材料中的固相扩散系数在3.95和4.12V左右存在两个极小峰。 随着循环次数的增加, 这两个峰逐渐平坦, 并且整体固相扩散系数值呈增大趋势, 表明锂离子在LiMn2O4中重复脱/嵌时具有自我增强扩散的能力。
REFERENCES
[1]Yazami R. High performance LiCoO2 positive electrode material[J]. J Power Sources, 1995, 54: 389-392.
[2]Larcher D. Electrochemically active LiCoO2 and LiNiO2 made by cationic exchange under hydrothermal conditions[J]. J Electrochem Soc, 1997, 144: 408-417.
[3]Yamada S. Synthesis and properties of LiNiO2 as cathode material for secondary batteries[J]. J Power Sources, 1995, 54: 209-213.
[4]Masahiro K, Yoshinori T. Material for lithium battery positive electrode and production thereof[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 1998, 70: 140-141.
[5]王先友, 朱启安, 张允什, 等. 锂离子扩散系数的测定方法[J]. 电源技术, 1999, 23(12): 335-338.
WANG Xian-you, ZHU Qi-an, ZHANG Yun-shi, et al. Measurement of chemical diffusion coefficient of lithium-ion in cathode and anode materials of Li-ion batteries[J]. Chinese Journal of Power Sources, 1999, 23(12): 335-338.
[6]Rhoa Y H, Kanamura K. Li+ ion diffusion in Li4Ti5O12 thin film electrode prepared by PVP sol–gel method[J]. Journal of Solid State Chemistry, 2004, 177: 2094-2100.
[7]Deiss E. Spurious chemical diffusion coefficients of Li+ in electrode materials evaluated with GITT[J]. Electrochimica Acta. 2005, 50: 2927-2932.
[8]Piao T, Park S M, Doh C H, et al. Intercalation of lithium ions into graphite electrodes studied by AC impedance measurements [J]. J Electrochem Soc, 1999, 146: 2794-2798.
[9]Haran B S, Popov B N, White R E. Determination of the hydrogen diffusion coefficient in metal hydrides by impedance spectroscopy [J]. Power Sources, 1998, 75: 56-63.
[10]Uchina T, Marikaua Y, lkuta H, et al. Chemical diffusion coefficient of lithium in carbon fiber[J]. J Electrochem Soc, 1996, 143: 2606-2610.
[11]Zhang D, Popov B N, White R E. Electrochemical investigation of CrO2.65 doped LiMn2O4 as a cathode material for lithium-ion batteries [J]. J Power Sources, 1998, 76: 81-90.
[12]Zhang W, Kunar M P S, Srinivasan S, et al. AC impedance studies on metal hydride electrodes[J]. J Electrochem Soc, 1995, 142: 2935-2943.
[13]Levi M D, Aurbach D. Frumkin intercalation isotherm - a tool for the description of lithium insertion into host materials: a review [J]. Electrochimica Acta, 1999, 45: 167-185.
[14]唐致远, 薛建军, 刘春燕, 等. 锂离子在石墨负极材料中扩散系数的测定[J]. 物理化学学报, 2001, 17: 385-388.
TANG Zhi-yuan, XUE Jian-jun, LIU Chun-yan, et al. The determination of Li+ diffusion coefficient of carbon anode[J]. Acta Physico-Chimica Sinica, 2001, 17: 385-388.
[15]Wang Q, Li H, Huang X J, et al. Determination of chemical diffusion coefficient of lithium ion in graphitized mesocarbon microbeads with potential relaxation technique[J]. J Electrochem Soc, 2001, 148: A737-A741.
[16]Deiss E. Spurious potential dependence of diffusion coefficients in Li+ insertion electrodes measured with PITT[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2002, 47: 4027-4034.
[17]唐新村, 何莉萍, 陈宗璋, 等. 恒压-恒流充电容量比值法测定石墨电极中的锂离子扩散系数[J]. 物理化学学报, 2002, 18: 705-709.
TANG Xin-cun, HE Li-ping, CHEN Zong-zhang, et al. Determination of the Li+ diffusion coefficient in graphite by the method of the ratio of potentio-charge capacity to galvano-charge capacity[J]. Acta Physico-Chimica Sinica, 2002, 18: 705-709.
[18]Tang X C, Pan C Y, He L P, et al. A novel technique based on the ratio of potentio-charge capacity to galvano-charge capacity (RPG) for determination of the diffusion coefficient of intercalary species within insertion-host materials: theories and experiments[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2004, 49: 3113-3119.
(编辑龙怀中)
基金项目: 国家自然科学基金资助项目(20406024); 中南大学博士后基金资助项目(7600)
收稿日期: 2005-05-12; 修订日期: 2005-07-01
作者简介: 唐新村(1972-), 男, 副教授, 博士.
通讯作者: 金 乐; 电话: 0731-8836848; E-mail: angelinaking@sina.com.cn