文章编号: 1004-0609(2006)05-0867-07
激光熔化沉积NiTi/Ni3Ti金属间化合物合金的
显微组织和耐磨性
李 昂, 李 安, 张凌云, 王华明
(北京航空航天大学 材料科学与工程学院 激光材料加工制造技术实验室, 北京 100083)
摘 要: 利用激光熔化沉积技术制备出分别以NiTi和Ni3Ti为初生相的NiTi/Ni3Ti金属间化合物耐磨合金, 采用XRD、 OM、 SEM、 EDS等手段分析合金的组织, 测试合金的室温干滑动磨损性能。 结果表明, 其室温干滑动磨损机制为软磨料磨损和氧化磨损; 对于以Ni3Ti为初生相的合金, 其室温干滑动磨损机制在中低负荷下为氧化磨损和显微切削, 在高负荷下则是Ni3Ti的显微切削; 以NiTi为初生相的NiTi/Ni3Ti金属间化合物合金具有更好的抗室温摩擦磨损性能。
关键词: 激光熔化沉积; NiTi; Ni3Ti; 磨损; 显微组织 中图分类号: TG146
文献标识码: A
Microstructure and wear resistance of
laser melting deposited NiTi/Ni3Ti intermetallic alloys
LI Ang, LI An, ZHANG Ling-yun, WANG Hua-ming
(Laboratory of Laser Materials Processing and Manufacturing,
School of Materials Science and Engineering,
Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, Beijing 100083, China)
Abstract: The wear-resistant NiTi/Ni3Ti intermetallic alloys were designed and fabricated by the laser melting deposition process. The as-solidified microstructures of the NiTi/Ni3Ti intermetallic alloys were characterized by X-ray diffraction(XRD), optical microscope(OM), scanning electron microscope(SEM) and energy dispersive spectrometer(EDS). The wear resistance of the alloys was evaluated under room-temperature dry sliding wear test condition coupling with hardened bearing steel GCr15. The results indicate that the room temperature dry-sliding wear mechanism of the NiTi/Ni3Ti intermetallic alloy with NiTi dendrite as the primary phase is soft abrasion and oxidative wear, while that of the NiTi/Ni3Ti intermetallic alloy with Ni3Ti as the primary phase is oxidative wear and micro-cutting under low/medium normal load, and micro-cutting is under high normal load; the NiTi/Ni3Ti intermetallic alloy with NiTi dendrite as the primary phase has better wear resistance under dry sliding wear test conditions than that with Ni3Ti as the primary phase.
Key words: laser melting deposition; NiTi/Ni3Ti; wear; microstructure
金属间化合物NiTi具有独特的形状记忆效应和超弹性、 优异的强韧性配合及优良的生物相容性, 在工业装备及生物工程等领域得到广泛应用。 在Ni-Ti二元合金系中, 除NiTi外, 还存在Ni3Ti、 NiTi2两种金属间化合物, 其中Ni3Ti具有六方晶系D024 型晶体结构, 被广泛用作钴基、 镍基和铁基高温合金中的沉淀析出强化相[1-12]。
近年来的研究表明, NiTi金属间化合物合金在干滑动磨损条件下还表现出很好的耐磨性能。 金嘉陵[13]对几种近等原子比NiTi合金的滑动磨损性能进行了研究, 发现高载荷下NiTi合金虽然硬度明显较低, 但其耐磨性却明显优于渗氮38CrMoAl钢和Co45钴基耐磨合金; 其独特的超弹性及高阻尼特性被认为是NiTi合金具有优异耐磨性的主要原因。 Li[14]对NiTi合金的耐磨性作了研究, 认为形状记忆效应和超弹性改变了表面接触状态, 马氏体择优取向和应力诱发马氏体相变对裂纹的钝化作用, 使NiTi具有良好的抗干滑动磨损性能。 徐久军等[15]研究了NiTi合金的砂磨损行为, 并与Cr13钢进行了对比试验研究, 结果发现NiTi合金的磨损量仅为Cr13钢的19%。
[BJ(,,,][BJ)] 第16卷第5期 李 昂, 等: 激光熔化沉积NiTi/Ni3Ti金属间化合物合金的显微组织和耐磨性 Ni3Ti只能以严格化学计量比的形式存在, 在Inconel 706和Incoloy 901等镍基和铁基高温合金中, Ni3Ti是一种重要的沉淀析出强化相。 通过共晶反应向韧性相中引入强化相是设计制备金属高耐磨材料的重要手段, 因此, 以Ni3Ti为强化相、 以NiTi为基体的金属间化合物合金可望具有优良的耐磨性能。 迄今为止, 没有发现研究单相Ni3Ti金属间化合物耐磨性能的相关文献。 本文作者设计并利用激光化沉积技术(见图1), 制得NiTi/Ni3Ti双相金属间化合物耐磨合金, 对该合金的显微组织结构以及在室温干滑动磨损实验条件下的耐磨性进行研究。
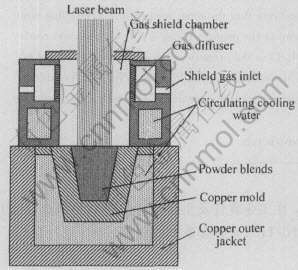
图1 合金激光熔化沉积示意图
Fig.1 Schematic illustration of laser melting deposition process
1 实验
设计了质量分数(%)分别为Ni62Ti38和Ni70.8Ti29.2的NiTi/Ni3Ti金属间化合物耐磨合金, 选用粒径小于48μm的雾化纯镍粉和粒径小于147μm雾化纯钛粉作为原材料, 粉末混合均匀后在100℃电炉下保温干燥6h。 激光熔化沉积实验在三座标四轴联动数控激光加工机床的8kW横流连续CO2激光加工系统上进行, 将混合粉末置于水冷铜模中, 实验中通氩气保护。 激光熔炼工艺参数为: 激光功率3kW、 光斑直径4mm。 采用机械抛光工序制备铸锭的金相截面, 使用体积比为1∶6∶7的HF-HNO3-H2O腐蚀液腐蚀。 用Olympus BX51M光学显微镜(OM)观察显微组织, 用Dmax-rB旋转阳极X射线衍射仪(采用CuKα, 扫描速度5(°)/min, 管压40kV)并结合Link ISIS能谱仪进行物相鉴定。 室温干滑动磨损实验在MM-200型摩擦磨损试验机上进行, 试样尺寸为10mm×10mm×10mm, 对磨环为淬火GCr15钢环(硬度为HRC57~59), 法向载荷分别选取98、 147和196N, 对磨环转速为400r/min, 相对滑动速度为0.838m/s, 磨损时间为60min, 总滑动行程为3016m。 以淬火45#钢试样作为标样, 磨损实验前后的试样及摩擦副均采用超声波清洗, 并使用精度为0.1mg的Sartorius BS110型电子天平称取试样的磨损量, 再将清洗后的试样进行SEM观察磨损表面形貌。
2 结果与讨论
Ni62Ti38和Ni70.8Ti29.2合金粉末激光熔化沉积所得铸锭的X射线衍射谱如图2所示。 由图可知, 两合金均由金属间化合物NiTi和Ni3Ti组成; 图3和4所示分别为Ni62Ti38和Ni70.8Ti29.2合金的组织形貌。 通过EDS分析和硬度测试并结合NiTi/Ni3Ti二元共晶相图可知, Ni62Ti38合金由NiTi初生树枝晶和基体NiTi/Ni3Ti共晶组织组成, Ni70.8Ti29.2合金由大块状Ni3Ti初生相和基体NiTi/Ni3Ti共晶组织组成。
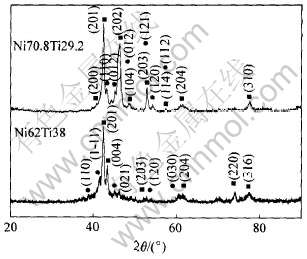
图2 NiTi/Ni3Ti金属间化合物合金的X射线衍射谱
Fig.2 XRD patterns of experimental
NiTi/Ni3Ti intermetallic alloys
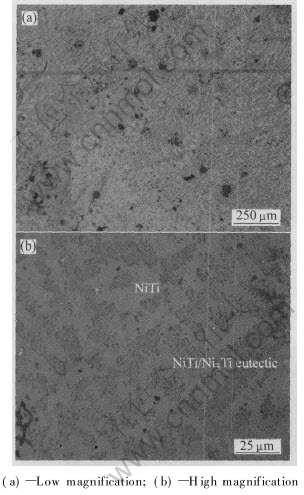
图3 Ni62Ti38金属间化合物合金显微组织
Fig.3 OM micrographs of Ni62Ti38 intermetallic alloy

图4 Ni70.8Ti29.2金属间化合物合金显微组织
Fig.4 OM micrographs of Ni70.8Ti29.2 intermetallic alloy
图5所示为Ni62Ti38、 Ni70.8Ti29.2和标样淬火45#钢的磨损质量损失结果。 由图5可见, Ni62Ti38试样在3种载荷条件下的磨损质量损失均比Ni70.8Ti29.2、 淬火45#钢要小。
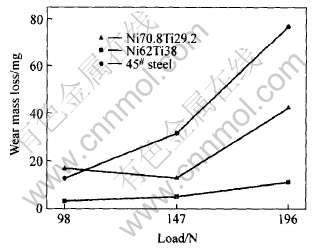
图5 Ni62Ti38及Ni70.8Ti29.2金属间化合物合金和
标样淬火45#钢的磨损质量损失随实验载荷的变化
Fig.5 Wear mass loss of Ni62Ti38 and Ni62Ti38 NiTi/Ni3Ti intermetallic alloys and hardened 0.45%C steel as function of test load
图6所示为法向载荷为98N时Ni62Ti38合金的磨损表面形貌。 其EDS结果(摩尔分数, %)为Ni6.35Ti10.15Fe46.01Cr1.06O36.43, Fe、 O元素含量很高, 表明磨屑是由从对磨环磨损下来的物质组成, 并且在随后的过程中被氧化。 由于Ni62Ti38试样以体心立方NiTi为初生相, 在磨损过程中, 磨损下来的磨屑粘附于试样表面, 在进一步的磨损中, 磨屑发生部分氧化, 表现出氧化磨损的特征; 在后续磨损过程中, 磨屑粘附层与对磨环发生磨损, 在一定程度上缓解了对磨副对试样的磨损, 因而试样的磨损质量损失小。
随着法向载荷增至147和196N时, 试样的表面磨损形貌和98N时的磨损形貌相似, 表面被大量的磨屑所遮覆; 在磨损过程中, 试样的磨损质量损失小。
图7所示为Ni70.8Ti29.2合金在法向载荷为98N时的磨损表面形貌。 由图可见, 磨损表面上磨屑粘附很少, 磨损表面和显微组织特征十分相似, 特别值得注意的是, 在Ni3Ti块状初生相区域及共晶Ni3Ti上都几乎没有粘着磨屑, 也没有塑性变形特征, 说明具有D024晶体结构的Ni3Ti具有十分优异的抗金属粘着性能。 在磨损过程中, 粘附磨屑层对该区域起到类似于Ni62Ti38的作用, 而光滑的Ni3Ti区域由于没有磨屑层的保护, GCr15对磨环上的微凸体与试样发生直接磨损。
图8所示为Ni70.8Ti29.2金属间化合物在法向载荷为196N时的表面磨损形貌。 由图可见, 当法向载荷增加到196N时, Ni70.8Ti29.2合金试样磨损表面发生粘着的程度仍比较轻, 表层有类似切削的痕迹, 说明在高转速、 高载荷磨损实验条件下, 磨损机制主要是以显微切削方式进行的二体磨料磨损。 当法向载荷由98N增加至196N时, 在磨损过程中, 高接触应力导致产生大量摩擦热, 从而使磨损表面温度升高; 初始粘着的磨屑由于具有大的表面积, 在高温下迅速地氧化, 降低磨屑与试样表面的粘附强度从而迅速地被磨损下来; 同时在高温下, 试样的表面发生软化, 而对磨副GCr15由于高速转动, 其表面微凸体的摩擦热在脱离试样/对磨环接触区域后可迅速地散发到周围环境中, 因而其软化程度不大, 仍保持较高的硬度, 在接下来的磨损中, 较硬的GCr15微凸体作为磨料以切削方式直接磨损试样表面。
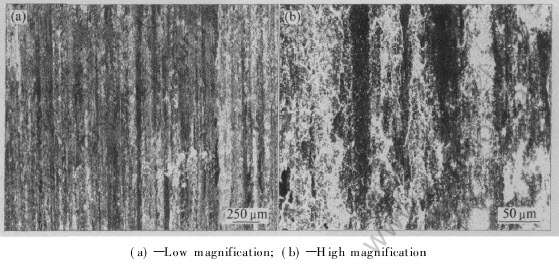
图6 Ni62Ti38金属间化合物合金在法向载荷为98N时的表面磨损形貌
Fig.6 Worn surface morphologies of NiTi/Ni3Ti intermetallic alloy (Ni62Ti38) under normal load of 98N

图7 Ni70.8Ti29.2金属间化合物合金在法向载荷为98N时的表面磨损形貌
Fig.7 Worn surface morphologies of NiTi/Ni3Ti intermetallic alloy (Ni70.8Ti29.2) under normal load of 98N

图8 Ni70.8Ti29.2 金属间化合物合金在法向载荷为196N时的表面磨损形貌
Fig.8 Worn surface morphologies of NiTi/Ni3Ti intermetallic alloy (Ni70.8Ti29.2) under normal load of 196N
尽管Ni62Ti38和Ni70.8Ti29.2合金试样的磨损表面形貌特征相差很大, 但其在磨损过程中所产生的磨屑形貌都很相似(如图9所示), 均以粉末状、 块状和长条状的形式存在。
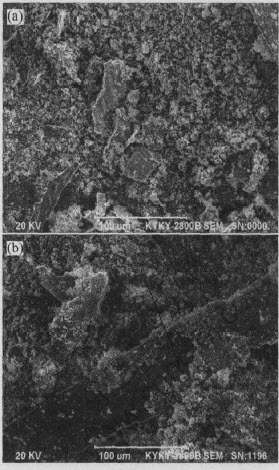
图9 Ni62Ti38在法向载荷147N时(a)和
Ni70.8Ti29.2在法向载荷98N时(b)的磨屑形貌
Fig.9 Worn debris morphologies of Ni62Ti38 under 147N normal load(a) and Ni70.8Ti29.2 under 98N normal load(b)
EDS分析结果表明, 粉末状磨屑的化学成分(摩尔分数, %)约为Ti0.59Ni1.38Fe63.73-Cr1.03O33.27, 主要为来自对磨环的铁的氧化物; 对磨环表层氧化膜厚度增长到一定值时, 在高的接触应力下, 基体/氧化膜界面分离, 氧化膜脱落, 在对磨环的高速离心力作用下氧化物质脱离对磨环/试样接触区域。
图9(a)中的块状磨屑中EDS分析结果(摩尔分数, %)为Ti0.48Fe85.33Cr1.35O12.85, 与粉末状磨屑的成分接近, 其形成机理为一种“机械合金化”的效应。 在法向载荷的情况下, 高速转动的对磨副对试样表面的粘附粉末进行反复辗压, 最终形成块状磨屑。
图9(b)中的块状磨屑的EDS分析结果(摩尔分数, %)为Ti0.02Ni0.58Fe96.53Cr1.26O1.61, 实质上是从GCr15对磨环上切削下来的切屑。
为分析NiTi/Ni3Ti金属间化合物合金的室温干滑动磨损机理, 对磨损的亚表层组织进行了分析。 Ni62Ti38和Ni70.8Ti29.2金属间化合物合金试样在法向载荷为196N时, 亚表层材料无断裂, 均未发生明显的局部塑性形变(如图10所示)。

图10 NiTi/Ni3Ti金属间化合物合金
干滑动摩擦磨损的亚表层形貌
Fig.10 Worn subsurface morphologies of NiTi/Ni3Ti intermetallic alloys
图11所示为NiTi/Ni3Ti金属间化合物合金及标样淬火45#钢在室温干滑动磨损实验条件下的摩擦因数随时间变化曲线。 由图可以看出, Ni62Ti38合金的平均摩擦因数约为0.43, Ni70.8Ti29.2的平均摩擦因数约为0.38, 而标样的平均摩擦系数为0.65左右。 Ni70.8Ti29.2的摩擦系数比Ni62Ti38略小, 其原因是Ni3Ti为六方晶体结构, 摩擦系数比bcc结构的NiTi要小。
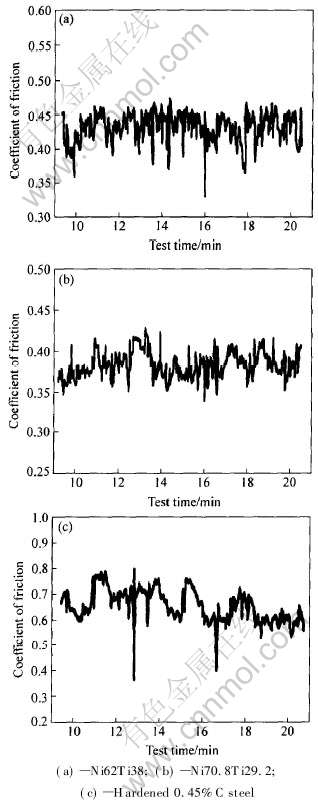
图11 激光熔炼NiTi/Ni3Ti金属间化合物合金及淬火45#钢在室温干滑动磨损实验条件下的摩擦因数随时间的变化曲线
Fig.11 Friction coefficient of laser-melted NiTi/Ni3Ti intermetallic alloys and hardened 0.45%C steel under dry sliding wear test conditions
与体心立方金属相比, 密堆六方金属由于滑移系少, 塑韧性较差。 尽管具有六方D024晶体结构Ni3Ti的硬度为HV600左右, 比bcc结构NiTi(HV200~500左右)的硬度高, 但是在室温干滑动磨损条件下, Ni3Ti的严重脆性导致其不能发挥高强度优势。 由于Ni3Ti属于六方结构, 它的抗金属粘着能力较强, 在磨损过程中, 磨损表面缺乏粘附磨屑层的保护, 硬的GCr15微凸体作为磨料直接切削Ni3Ti, 导致其质量损失较大。 而NiTi具有优异的韧性, 在磨损过程的初始阶段, 接触发生在少数微凸体上, 在这些接触面上产生很高的应力, 使微凸体发生变形, 部分由于接触应力高而被磨损脱落形成磨屑。 GCr15的原子以金属键结合, 表面的微凸体由于高的接触应力和摩擦力作用脱落形成磨屑。 这些磨屑在随后的磨损过程中部分转移到NiTi/Ni3Ti金属间化合物复合材料表面, 遮覆在试样表面。 在随后的磨损过程中, 这些遮覆层不仅可以起到一定的润滑作用, 而且可以保护复合材料表面, 避免其与对磨环直接接触。 因此Ni62Ti38试样在后续的磨损过程中大部分时间可避免高硬度的GCr15钢对磨副对其进行磨损切削, 从而磨损质量损失小。
3 结论
1) 采用激光熔化沉积方法分别制备出了以树枝状NiTi为初生相和以块状Ni3Ti为初生相的NiTi/Ni3Ti金属间化合物耐磨合金。
2) 对于以NiTi为初生相的合金, 其室温干滑动磨损机制为软磨料磨损和氧化磨损。
3) 对于以Ni3Ti为初生相的合金, 其室温干滑动磨损机制在中低负荷下为氧化磨损和显微切削, 在高负荷下是显微切削。
4) 以NiTi为初生相的合金的抗室温干滑动摩擦磨损性能比以Ni3Ti为初生相的合金的要好一些。
REFERENCES
[1]杨杰, 吴月华. 形状记忆合金及其应用[M]. 合肥: 中国科学技术大学出版社, 1993.
YANG Jie, WU Yue-hua. Shape Memory Alloy and Its Application[M]. Hefei: University of Science and Technology of China Press, 1993.
[2]张永刚, 韩雅芳, 陈国良, 等. 金属间化合物结构材料[M]. 北京: 国防工业出版社, 2001.
ZHANG Yong-gang, HAN Ya-fang, CHEN Guo-liang, et al. Structural Intermetallics[M]. Beijing: National Defence Industry Press, 2001.
[3]Miyazaki S, Imai T, Igo Y, et al. Effect of cyclic deformation on the pseudoelasticity characteristics of Ti - Ni alloys[J]. Metall Trans A, 1986, 17A: 115-120.
[4]Miyazaki S, Otsuki Y, Suzuki Y. Transformation pseudoelasticity and deformation behavior in a Ti -50.6at% alloy[J]. Scripta Metallurgica, 1981, 15(3): 287-292.
[5]Singhal L K, Martin J W. The mechanism of tensile yield in an age-hardened steel containing γ′(ordered Ni3Ti) precipitates[J]. Acta Metallurgica, 1968, 16(6): 947-953.
[6]Chester T S, William C H. The Superalloys[M]. Toronto: John Wiley & Sons, Inc, 1972.
[7]Betteridge W, Heslop J. The Nimonic Alloys and Other Nickel-Base High-Temperature Alloys[M]. Britain: J.W.Arrowsmith Ltd, 1974.
[8]Sheffler K D, Hertzberg R W, Kraft R W. Elevated-temperature mechanical properties and fracture behavior of a Ni-Ni3Ti eutectic alloy[J]. Transaction of the ASM, 1969, 62: 105-116.
[9]Liu R, Li D Y. Experimental studies on tribological properties of pseudoelastic TiNi alloy with comparison to stainless steel 304[J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions, 2000, 31A(11): 2773-2783.
[10]阎小军, 杨大智, 刘黎明. 超弹性NiTi合金丝激光点焊接头的组织和性能[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2005, 15(1): 19-23.
YAN Xiao-jun, YANG Da-zhi, LIU Li-ming. Microstructure and properties of laser spot-welded joint of superelastic NiTi alloy wire[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2005, 15(1): 19-23.
[11]赵连城, 郑玉峰. 形状记忆与超弹性镍钛合金的发展与应用[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2004, 14(S1): 323-326.
ZHAO Lian-cheng, ZHENG Yu-feng. Development and applications of nickel - titanium alloys with shape memory effect and superelasticity[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2004, 14(S1): 323-326.
[12]Garay J E, Anselmi-Tamburini U, Munir Z A. Enhanced growth of intermetallic in the Ni-Ti system by current effects[J]. Acta Materialia, 2003, 51: 4487-4495.
[13]金嘉陵, 王宏亮. NiTi合金耐磨性研究[J]. 金属学报, 1988, 24(1): 66-69.
JIN Jia-ling, WANG Hong-liang. Wear resistance of the NiTi alloy[J]. Acta Metallurgica Sinica, 1998, 24(1): 66-69.
[14]Li D Y. Wear behaviour of NiTi shape memory alloys[J]. Scripta Mater, 1996, 34: 195-200.
[15]徐久军, 严立, 朱新河, 等. NiTi形状记忆合金砂石磨损的机敏行为[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2000, 10(S1): 188-191.
XU Jiu-jun, YAN Li, ZHU Xin-he, et al. Smart behavior of NiTi shape memory alloy under sand-erosion wear[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2000, 10(S1): 188-191.
基金项目: 国家自然科学基金重点资助项目(50331010); 航空基础科学基金资助项目(05H51009)
收稿日期: 2005-11-22; 修订日期: 2006-03-06
通讯作者: 王华明, 教授, 博士; 电话: 010-82338131; E-mail: wanghm@buaa.edu.cn; wanghuaming@263.net
(编辑何学锋)