AISI 316不锈钢和Ti6Al4V合金在 海水环境中的腐蚀与腐蚀磨损行为
来源期刊:中国有色金属学报(英文版)2014年第4期
论文作者:陈 君 张 清 李全安 付三玲 王建章
文章页码:1022 - 1031
关键词:Ti6Al4V 合金;AISI 316不锈钢;腐蚀磨损;交互作用
Key words:Ti6Al4V alloy; AISI 316 stainless steel; tribocorrosion; synergistic effect
摘 要:采用立式万能销盘腐蚀磨损试验机研究AISI 316不锈钢和Ti6Al4V合金在海水中与Al2O3 陶瓷对磨时的腐蚀与腐蚀磨损行为,重点讨论腐蚀磨损之间的交互作用。结果表明,摩擦作用使得Ti6Al4V合金和316不锈钢的开路电位大幅下降,腐蚀磨损过程中的电流密度远高于静态腐蚀时的电流密度,摩擦明显促进了合金的腐蚀。两种合金在海水中的磨损量远大于在纯水中的磨损量,腐蚀促进了磨损,并且Ti6Al4V合金的耐磨性优于316不锈钢的耐磨性,腐蚀磨损之间的交互作用是材料损失的一个重要因素。本实验所用的摩擦装置为单向滑动的面面接触方式,这使得摩擦对腐蚀的促进作用在总磨损量中所占的比例很小。
Abstract: The corrosion and tribocorrosion behaviors of AISI 316 stainless steel and Ti6Al4V alloys sliding against Al2O3 in artificial seawater using a pin-on-disk test rig were investigated. And the synergistic effect between corrosion and wear was emphatically evaluated. The results show that the open circuit potentials of both alloys drop down to more negative value due to friction. The corrosion current densities obtained under tribocorrosion condition are much higher than those under corrosion-only condition. Friction obviously accelerates the corrosion of the alloys. The wear loss for both alloys is larger in seawater than that in pure water. Wear loss is obviously accelerated by corrosion. And AISI 316 stainless steel is less resistant to sliding damage than Ti6Al4V alloy. The synergistic effect between wear and corrosion is a significant factor for the materials loss in tribocorrosion. In this surface-on-surface contact geometry friction system, the material loss is large but the ratio of wear-accelerated-corrosion to the total wear loss is very low.
Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 24(2014) 1022-1031
Jun CHEN1,2, Qing ZHANG1, Quan-an LI1, San-ling FU1, Jian-zhang WANG2
1. School of Materials Science and Engineering, Henan University of Science and Technology, Luoyang 471023, China;
2. State Key Laboratory of Solid Lubrication, Lanzhou Institute of Chemical Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Lanzhou 730000, China
Received 20 March 2013; accepted 3 January 2014
Abstract: The corrosion and tribocorrosion behaviors of AISI 316 stainless steel and Ti6Al4V alloys sliding against Al2O3 in artificial seawater using a pin-on-disk test rig were investigated. And the synergistic effect between corrosion and wear was emphatically evaluated. The results show that the open circuit potentials of both alloys drop down to more negative value due to friction. The corrosion current densities obtained under tribocorrosion condition are much higher than those under corrosion-only condition. Friction obviously accelerates the corrosion of the alloys. The wear loss for both alloys is larger in seawater than that in pure water. Wear loss is obviously accelerated by corrosion. And AISI 316 stainless steel is less resistant to sliding damage than Ti6Al4V alloy. The synergistic effect between wear and corrosion is a significant factor for the materials loss in tribocorrosion. In this surface-on-surface contact geometry friction system, the material loss is large but the ratio of wear-accelerated-corrosion to the total wear loss is very low.
Key words: Ti6Al4V alloy; AISI 316 stainless steel; tribocorrosion; synergistic effect
1 Introduction
Stainless steels and titanium alloys are the most popular corrosion-resistant materials used in various applications due to their excellent corrosion resistance and good mechanical properties. The corrosion resistance is provided by the spontaneous formation on the metallic surface of an oxide film with thickness of 1-10 nm containing mainly Cr2O3 for AISI 316 stainless steel and TiO2for Ti6Al4V alloy [1-5]. In many situations, stainless steels and titanium alloys are subjected combined corrosion and wear actions, such as marine and off-shore equipments, deep-sea submergence vehicles like underwater robots and submarine oil production systems, biomaterials used for orthopedic implants and hip and knee prostheses, cutting tools, chemical pumps, food processing and mining equipments [6-10]. These alloys are subjected to scratching, abrasion, erosion, and other forms of wear damage in a corrosive environment. Tribocorrosion can lead to the damage or even complete removal of the passive film from the contact surface, resulting in wear-accelerated-corrosion and corrosion-accelerated-wear. In most cases, the material loss caused by tribocorrosion is greater than the simple sum of pure mechanical wear and static corrosion [6,11,12].
Over the past few years, increasing efforts have been made to study the tribocorrosion behaviors of metallic materials under combined chemical, electrochemical and mechanical actions condition. Most of these previous studies focus on the basis understanding of the complex phenomena, including identifying the synergy between corrosion and wear and quantifying the synergistic components through mathematical model [13,14]. Stainless steels and titanium alloys, which are passive materials, are by far the most frequently used materials in tribocorrosion, mostly in H2SO4 solutions[12,15,16], Ringer’s solution [17,18], Na2SO4solution [19] and NaCl solution [20,21]. Limited work has been done in seawater, where these alloys are most frequently used. Moreover, the contact model in most previous studies was ceramic ball and metallic flat system containing seriously uneven stress distribution and high maximum Hertzian pressure. Limited work on tribocorrosion focused on the surface-surface contact model, which was frequently found in practical application. Different contact models may produce different tribocorrosion results. HENRY et al [1,5] studied the tribocorrosion phenomena of 316L stainless steel and Ti6Al4V titanium alloy sliding against an alumina ball in 0.5 mol/L H2SO4 solution under different applied electrochemical potentials (cathodic, free or anodic potential) and found that the wear rate of Ti6Al4V alloy is much higher than that measured for 316L stainless steel and nickel alloy. The fundamental mechanism of wear-corrosion synergism in tribo- corrosion using surface-on-surface contact geometry has not been fully understood.
In our previous work [22], the tribocorrosion behaviors of Ti6Al4V and Monel K500 alloys sliding against 316 stainless steel were studied, but that apparatus could not monitor the corrosion process. In this work, the tribocorrosion apparatus was improved and the electrochemical instrument was linked with friction device to in-situ evaluate the tribocorrosion behavior. The corrosion and tribocorrosion phenomena of AISI 316 stainless steel and Ti6Al4V titanium alloy sliding against an alumina pin in artificial seawater and pure water were investigated. The contributions of different mechanical and corrosive components involved in material loss were determined by the potentiodynamic polarization curves and wear loss measurements.
2 Experimental
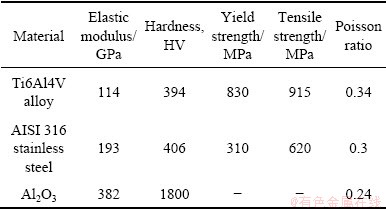
The metallic materials used in this work were AISI 316 stainless steel and Ti6Al4V alloys. Table 1 shows the mechanical properties of the two alloys. These alloys were machined into specimens of a ring (outer diameter: 54 mm, inner diameter: 38 mm). Only the upper surface was contacted with the electrolyte and other surfaces were insulated with paint. The wetted area was about 11.5 cm2. The counterpart material was Al2O3pin after machining a flat surface at one end of a cylinder (diameter: 4.7 mm, height: 13 mm). The wear track was a ring with a mean diameter of 46 mm and a width of 4.7 mm (diameter of the pin). The area of the wear track was about 6.8 cm2. The electrolyte was artificial seawater, which was prepared according to ASTM D1141-98 standard. The pH value was adjusted to 8.2 using 0.1 mol/L NaOH solution. The composition of the artificial seawater is shown in previous article [23]. Temperatures of seawater in this work were conducted at (0±1), (30±1) and (60±1) °C. The test cell was filled with about 300 mL seawater. A saturated calomel electrode (SCE) was inserted into the cell close to the metallic specimen to serve as the reference electrode and platinum wire was used as the counter electrode.
Table 1 Mechanical properties of different materials
Sliding wear tests were carried out using an MMW-1 pin-on-disk tribometer. Corrosion-wear test setup combined with in-situ electrochemical measurements is illustrated in Fig. 1. All sliding tests were carried out at a constant rotation speed of 200 r/min, which meant a linear velocity of 0.54 m/s. A normal load of 100 N was applied. The duration was 60 min. After wear tests, the metallic specimens were ultrasonically cleaned in acetone to remove corrosion products and then weighed. The gravimetric measurements before and after corrosion-wear tests were completed. The volume loss can be determined below:
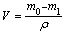 (1)
(1)
where V is the volume loss (mm3), m0 is the mass of materials before sliding wear (mg), m1 is the mass of material after sliding wear (mg), and ρ is the density. The morphologies of the worn surfaces were examined using a JEM-5600LV scanning electron microscope (SEM). All tests were repeated at least twice to check for reproducibility.
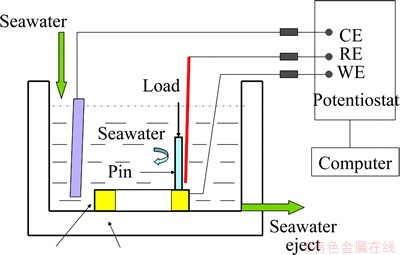
Fig. 1 Schematic diagram of tribocorrosion apparatus
In the electrochemical measurements, the ohmic resistance may affect the accuracy. An effective method to minimize the negative influence was to position the tip of the Luggin tube as close as possible to the working electrode [23,24]. To confirm the ohmic resistance, electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) technique was used to determine the ohmic resistance value. The value was about 13 Ω under this experimental condition. This small value proved that the error due to the electrolyte resistance is negligible. Several series of experiments were conducted to study the corrosion-wear: 1) Potentiodynamic test, which involved measuring the polarization curves during sliding and corrosion-only, was initiated after a stable open potential. It was performed with a potential sweep rate of 1.67 mV/s from -1 to 1 V. CHI software was used to analyze the polarization data. 2) Corrosion-wear tests were carried out under open circuit potential and the evolution of open circuit potential was measured.
3 Results and discussion
3.1 Corrosion-only polarization curves
The potentiodynamic polarization curves in artificial seawater without sliding are shown in Fig. 2. The electrochemical tests were conducted while the Al2O3 pin rotated at 200 r/min to minimize concentration polarization effects. The pin and ring were detached to avoid any wear. The aim of this test was to investigate the chemical stability of passive films without any mechanical damage. Typical passivation behavior was clearly observed for both alloys. The cathodic domain included potentials below about -0.5 V where the current was determined by the reduction of water and, partially, of dissolved oxygen. The narrow domain characterized by the transition from cathodic to anodic current appeared at the vicinity of corrosion potential. Then a large passive zone was found, where the current density remained approximately constant [17,25]. Interesting, after the transpassivity zone, at the potential above 0.5 V, the secondary passivation appeared for AISI 316 stainless steel. Secondary passivation of AISI 316 stainless steel was also reported by BETOVA et al [26]. The secondary passivation was due to the structural re-arrangement of the passive film and incorporation of iron in the outer passive layer at high potentials. Current density measured for the secondary passivation region was higher compared with the primary passivation current density [24].
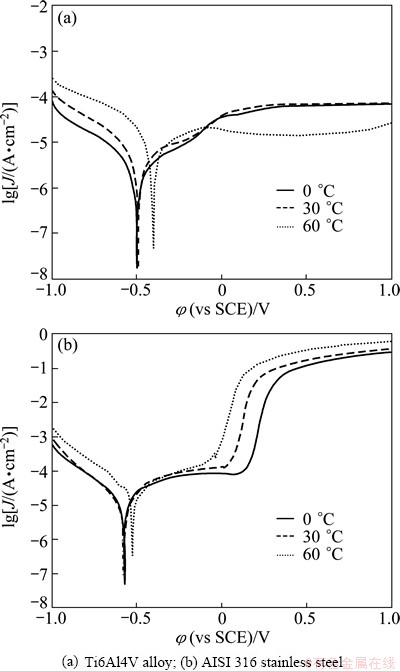
Fig. 2 Potentiodynamic polarization curves of different alloys at different temperatures without concurrent sliding
3.2 Polarization curves with sliding
Polarization curves obtained from metallic samples abraded by Al2O3pins can be used to analyze the repassivating ability when the passive film is mechanically destroyed or removed. The polarization curves with sliding are shown in Figs. 3(a) and (b). For comparison, the polarization curves without sliding are shown in Figs. 3(c) and (d) together with the smoothed curves with sliding. Since the contact area of the friction couples is constant during tests, the calculation of current density is based on the area of the wear scar. The polarization curves shown in Figs. 3(a) and (b) are plotted using raw data and exhibit significant current oscillations. The oscillations indicate the interaction between instantaneous removal and recovery of the passive film due to sliding. Moreover, the position of contact points between the pin and the metallic samples changes continuously, which is contributed to variation in oscillations and instabilities on the polarization curves also [24]. To facilitate the data analysis and comparison, the polarization curves shown in Figs. 3(c) and (d) are smoothed using least square method in the CHI software.
Two alloys were passive-characterized under both corrosion-only and tribocorrosion states. This implies that both alloys have self-healing capabilities when the passive film is damaged. It can be seen from Figs. 3(c) and (d) that the sliding action affects the shape and position of the potentiodynamic polarization curves. In the curves with sliding, the corrosion potential shifts to lower and more active potentials by about 0.2 V compared with the curves without sliding. The decrease of potential is due to the mechanical damage of the passive film. The polarization curves with sliding show that the corrosion current changes obviously to higher currents compared with the corrosion-only curves. This indicates that a rapid dissolution occurs in the wear track compared with the unworn area.
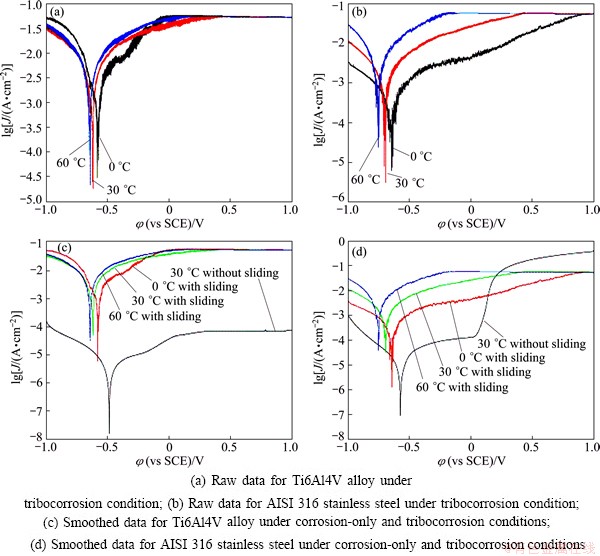
Fig. 3 Polarization curves of both alloys under different conditions in artificial seawater
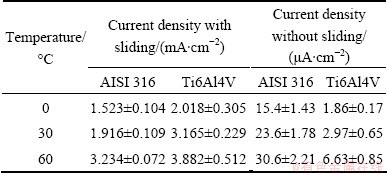
The corrosion current densities of both alloys under two conditions at different temperatures are summarized in Table 2. It can be seen that both alloys show low anodic current density due to the effective protection of passivation in artificial seawater. However, the current density of the order of 10-3 A/cm2 is obtained when the passive film is damaged. Interesting, the corrosion current density obtained under tribocorrosion condition is three orders of magnitude higher than that under passive condition. Moreover, temperature is an important factor for the corrosion behaviors of two alloys from 0 to 60 °C.
Table 2 Corrosion current densities of AISI 316 stainless steel and Ti6Al4V alloys at different temperatures
3.3 Open circuit potential
The open circuit potential recorded during tribocorrosion is a mixed potential reflecting the state of both unworn surface and wear track surface. The evolution of the open circuit potential for both alloys under tribocorrosion at 30 °C is shown in Fig. 4.
At the start of sliding, the open potential drops sharply down to more negative potential value. The passive film can be damaged in the contact area. A galvanic coupling between the passive surface and the active surface forms [8,12]. As a consequence, a quickly local dissolution of the active area occurs. Since the open circuit potential of the active surface is more negative compared with the passive surface, the open circuit potential shifts towards negative. Once the sliding is ended, the open circuit potential starts to increase (anodic shift) with a high speed and reaches the initial open circuit potential back after some time. This indicates the re-establishment of passive state on the surface in the wear track. In addition, the open circuit potential in the tribocorrosion condition is lower for AISI 316 stainless steel compared with Ti6Al4V alloy. It may be due to the lower corrosion current densities of AISI 316 stainless steel compared with Ti6Al4V alloy (Table 2). This results in low electron release and low polarization effect for AISI 316 stainless steel. Thus, Ti6Al4V alloy exhibits lower open circuit potential compared with AISI 316 stainless steel [27].
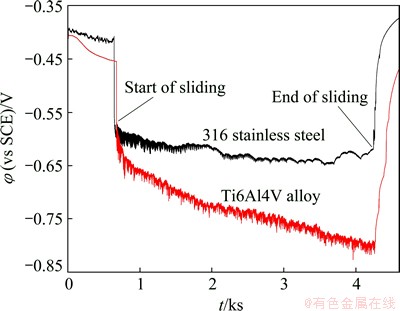
Fig. 4 Evolution of open potential for both alloys under tribocorrosion at 30 °C
3.4 Wear behaviors
The typical evolution of friction coefficient for both alloys with time is shown in Fig. 5. The friction coefficient rapidly reaches a steady state exhibiting some peaks at fairly regular time intervals. Such fluctuations are attributed to the formation and ejection of wear debris. Friction coefficient is larger in pure water compared with that in seawater. This indicates that the remarkable antifriction effect of seawater is significant. Moreover, the AISI 316 stainless steel exhibits larger friction coefficient compared with Ti6Al4V alloy.
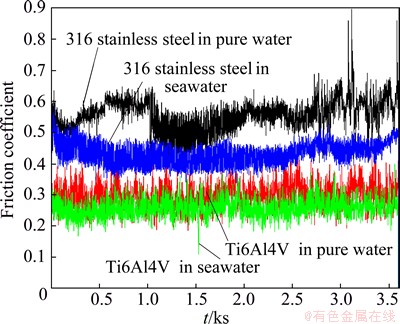
Fig. 5 Evolution of friction coefficient for both alloys in different media
Figure 6 shows the wear loss in artificial seawater and pure water. It can be seen from Fig. 6 that the wear loss is much greater in seawater than that in pure water, and Ti6Al4V alloy shows smaller wear loss compared with AISI 316 stainless steel. This indicates that corrosion can reduce wear resistance. And AISI 316 stainless steel is less resistant to sliding damage than Ti6Al4V alloy. The wear loss of Ti6Al4V alloy changes slightly at different temperatures. And with the increase of temperature from 0 to 60 °C, the wear loss of AISI 316 stainless steel slightly decreases in both media. Temperature is not an important factor for the wear performance of both alloys from 0 to 60 °C. The wear loss of the counterpart material Al2O3 pin is shown in Fig. 7, which shows that the damage of Al2O3can be negligible when it slides against Ti6Al4V alloy. However, the wear loss of Al2O3 sliding against AISI 316 stainless steel is very large.
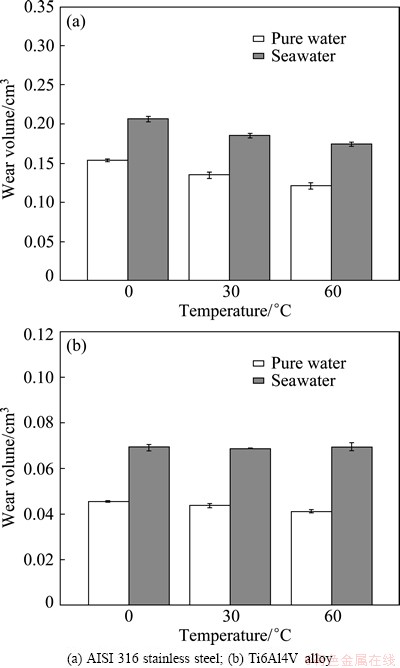
Fig. 6 Wear loss of both alloys in seawater and pure water under tribocorrosion
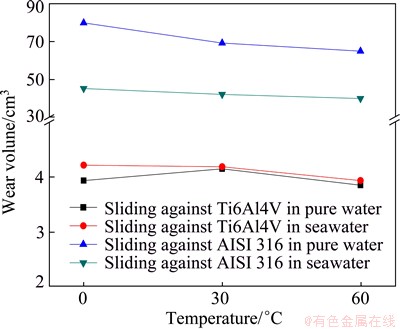
Fig. 7 Wear loss of counterpart material Al2O3
It should be pointed out that the relative wear loss of AISI 316L stainless steel and Ti6Al4V alloys under tribocorrosion was studied by researchers [1,6,18]. They found that the wear rate of Ti6Al4V alloy is much higher than that of 316L stainless steel. Ti6Al4V alloy is a harder material compared with 316L stainless but suffers severe wear. This is due to the poor resistance to wear of the passive film TiO2. However, the wear loss of Ti6Al4V alloy is smaller compared with AISI 316 stainless steel in this work. This is attributed to different wear mechanisms of two alloys. SEM observations of the wear track on AISI 316 stainless steel show significant amount of wear debris and severe rough surface (Fig. 8). Sharp cracks and thin flakes are found also. The wear track on Ti6Al4V alloy observed by SEM shows smooth surface and very few wear debris (Fig. 9). To distinguish the wear mechanism more clearly, the SEM images of wear debris for two alloys in seawater are shown in Fig. 10. It can be seen that the shapes of wear debris are banded for Ti6Al4V alloy and thin sheet for AISI 316 stainless steel. This corresponds to the analysis of wear worn surfaces. Therefore, the wear mechanism of Ti6Al4V alloy is severe adhesion wear and furrow wear, and the wear mechanism of AISI 316 stainless steel is fatigue wear. Meanwhile, large wear of Al2O3 may create abrasive third bodies and cause the high wear loss of AISI 316 stainless steel. In this unidirectional surface-on-surface contact geometry tribocorrosion system, different wear mechanisms cause large wear loss of AISI 316 stainless steel compared with Ti6Al4V alloy. Different contact geometries of friction system may cause different wear mechanisms and behaviors for AISI 316 stainless steel and Ti6Al4V alloys.
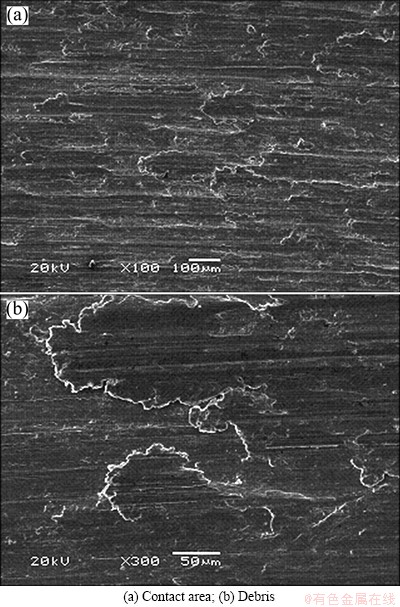
Fig. 8 SEM images of wear track on AISI 316 stainless steel after friction test
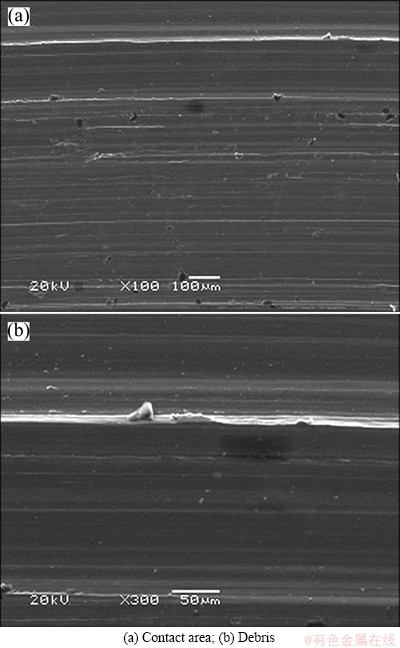
Fig. 9 SEM images of wear track on Ti6Al4V alloy after friction test

Fig. 10 SEM images of wear debris in seawater
3.5 Synergistic effect
Tribocorrosion is the complex phenomenon combined with simultaneous action of corrosion and wear. The synergistic effect between mechanical action and corrosion may lead to an acceleration of the degradation of passive metals in sliding contacts [13,18]. Therefore, the wear loss under tribocorrosion (V) is normally written as the summation of pure mechanical wear (Vm), static corrosion volume (Vc) and synergistic factor (△V):
 (2)
(2)
Moreover, the term △V can be further split into two more terms: the effect of corrosion on wear Vcm and the effect of wear on corrosion Vmc. Then, Eq. (2) becomes
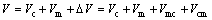 (3)
(3)
The dissolution volume (Vcorr) occurs in the wear track region, and the passive area is given by Faraday’s equation as
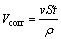 (4)
(4)
 (5)
(5)
where v is the corrosion rate; S is the corrosion area; t is the corrosion time; ρ is the density of the material; M is the relative atomic mass of alloy; Jcorr is the current density; n is the electrochemical equivalent of the material. In this work, Eqs. (4) and (5) were applied to the estimate of Vc and Vmc. Here, the problem is how to calculate Jcorr and S. Jcorr can be obtained from polarization curves. And S is equal to the wear scar area. There are many methods to determine the material loss caused by pure mechanical effect. One of them, which is adopted in this work, is to suppose that in pure water there is no electrochemical corrosion and the oxidation effect can be ignored because of its low oxidation speed. Therefore, in this work, Vm can be obtained in pure water with quite low electric conductivity [18,28]. As a result, V and Vm can be obtained from the experiment in pure water and seawater. Vcm cannot be obtained directly, but it can be estimated from Eq. (3).
The values of V, Vm, Vc, Vmc, Vcm and ΔV for Ti6Al4V alloy and AISI 316 stainless steel are listed in Tables 3 and 4, respectively. And Fig. 11 shows the fraction of each factor under tribocorrosion. It can be seen that the static corrosion volume (Vc) is obviously negligibly small for both alloys. In addition, the contribution of pure mechanical wear to total wear (Vm/V) is about 60% for Ti6Al4V alloy and about 70% for AISI 316 stainless steel. This indicates that pure mechanical wear is the dominated factor. Moreover, the synergistic factor (△V) between wear and corrosion is also high. The ratios of △V/V for Ti6Al4V alloy and AISI 316 stainless steel at 30 °C are about 36% and 27%, respectively. Therefore, Ti6Al4V alloy is more sensitive to the synergistic effect than AISI 316 stainless steel. The ratios of Vm/V for both alloys decrease slightly with the increase of temperature. This means that the high temperature decreases the mechanical wear but increases the synergistic effect. Although the electrochemical dissolution process of both alloys is significantly promoted and the corrosion rates increase by hundreds of times because of the mechanical effect, the ratio of wear-accelerated-corrosion to the total wear loss Vmc/V is not very large. Actually, they are only 3.2% and 0.92% for Ti6Al4V alloy and AISI 316 stainless steel at 30 °C, respectively. Contrarily, the ratios of corrosion- accelerated-wear to the total wear loss Vcm/V are very large, and they are 33.1% and 26.3% for Ti6Al4V alloy and AISI 316 stainless steel at 30 °C, respectively.
Table 3 Contribution of synergistic effect for Ti6Al4V alloys under tribocorrosion

Table 4 Contribution of synergistic effect for AISI 316 stainless steel under tribocorrosion

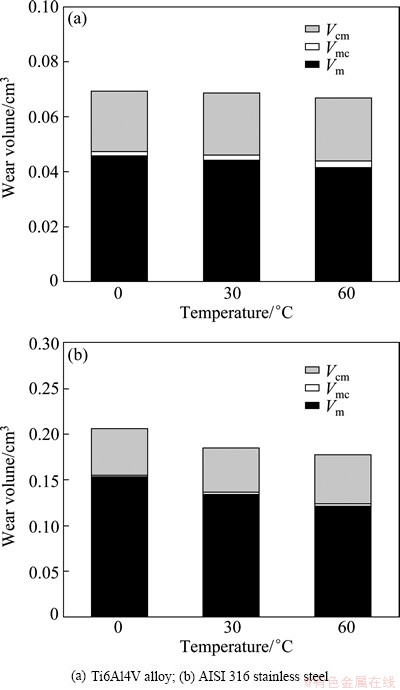
Fig. 11 Fraction of each factor under tribocorrosion
Wear can highly accelerate corrosion current density due to the following reasons. 1) The passive or adsorptive film is damaged or removed by wear. Consequently, bare surfaces exposed to electrolyte suffer large metal dissolution. 2) Wear causes plastic deformation in wear track and increases the densities of point defects, cracks and dislocations, which make the surface more active and cause high corrosion rate. The corrosion-accelerated-wear obviously increases the material loss. According to the model proposed by JIANG et al [14] and STACK [29], wear under tribocorrosion can be treated as a low cycle fatigue process, which involves crack initiation and propagation. The tip of cracks has high-density of point defects and dislocations due to the plastic deformation, which have high activity and are prone to dissolution. The effect of artificial seawater contributed to wear is to promote the growth and propagation of micro-cracking. This process can be considered stress corrosion [14,21].
It should be pointed out that the relative contribution of wear-accelerated-corrosion and corrosion-accelerated-wear to the total material loss in the tribocorrosion of stainless steels and titanium alloys was investigated by several investigators [6,13,14,21,30]. IWABUCHI et al [18,19,31] found that the ratios of wear-accelerated-corrosion to the total wear loss of stainless steel and titanium alloy sliding against an alumina ball in seawater were in the range of 27.2%-68.3%. The synergistic effect was mainly due to wear-accelerated-corrosion. Others [21,32] also observed that wear-accelerated-corrosion was a dominate factor for stainless steels and titanium alloys. However, the ratio of wear-accelerated-corrosion to the total wear loss (Vmc/V) is very small in this work. These different conclusions can be attributed to the contact geometry. In these ball-on-surface contact geometry systems, the wear rate is in the range of 10-6 mm3/(N·m). The wear rate is in the range of 10-3 mm
4 Conclusions
1) The wear loss is greater in seawater than that in pure water for AISI 316 stainless steel and Ti6Al4V alloy, which is due to the synergistic factor between corrosion and wear. In addition, AISI 316 stainless steel exhibits larger wear loss compared with Ti6Al4V alloy.
2) The open circuit potential is obviously lower under the tribocorrosion condition compared with that in the passive state, which is due to removal of passive film by sliding action. The corrosion current density obtained under tribocorrosion condition is three orders of magnitude higher than that at passive state.
3) Temperature can influence the corrosion rate for both alloys in seawater. With the increase of temperature from 0 to 60 °C, the corrosion current densities of both alloys under sliding and corrosion-only conditions rapidly increase. However, with the change of temperature from 0 to 60 °C, the wear loss for both alloys changes slightly.
References
[1] HENRY P, TAKADOUM J, BERCOT P. Tribocorrosion of 316L stainless steel and TA6V4 alloy in H2SO4 media [J]. Corrosion Science, 2009, 51(6): 1308-1314.
[2] MISCHLER S, PONTHIAUX P. A round robin on combined electrochemical and friction tests on alumina/stainless steel contacts in sulphuric acid [J]. Wear, 2001, 248: 211-225.
[3] HSU R W W, YANG C C, HUANG C A, CHEN Y S. Investigation on the corrosion behavior of Ti-6Al-4V implant alloy by electrochemical techniques [J]. Materials Chemistry and Physics, 2004, 86(2-3): 269-278.
[4] LEE H, MALL S, ALLEN W Y. Fretting fatigue behavior of shot-peened Ti-6Al-4V under seawater environment [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2006, 420(1-2): 72-78.
[5] HENRY P, TAKADOUM J, BERCOT P. Depassivation of some metals by sliding friction [J]. Corrosion Science, 2011, 53(1): 320-328.
[6] LANDOLT D, MISCHLER S, STEMP M. Electrochemical methods in tribocorrosion: A critical appraisal [J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2001, 46(24-25): 3913-3929.
[7] WOOD R J K. Erosion-corrosion interactions and their effect on marine and offshore materials [J]. Wear, 2006, 261(9): 1012-1023.
[8] PONTHIAUX P, WENGER F, DREES D, CELIS J P. Electrochemical techniques for studying tribocorrosion processes [J]. Wear, 2004, 256: 459-468.
[9] YANO A, HIRAYAMA Y, SAKANISHI A, SHIRAI S, UCHIDA Y, FUJITA K, KIKKAWA F, FUJIOKA K, KAWAZOE T, SAKI K, YAMAMOTO Y. Corrosive wear of bronze propeller shaft sleeve. Part 1: Investigation of the sleeve used and fundamental corrosive wear test [J]. Tribology Transactions, 2007, 50(1): 1-12.
[10] YANO A, SAKANISHI A, TAKAHASHI F, SHIRAI S, UCHIDA Y, FUJITA K, KIKKAWA F, FUJIOKA K, KAWAZOE T, SAKI K, YAMAMOTO Y. Corrosive wear of bronze propeller shaft sleeve. Part 2: Wear control by cathodic protection and application to an actual ferry [J]. Tribology Transactions, 2007, 50(1): 13-24.
[11] MISCHLER S. Triboelectrochemical techniques and interpretation methods in tribocorrosion: A comparative evaluation [J]. Tribology International, 2008, 41(7): 573-583.
[12] DIOMIDIS N, CELIS J P, PONTHIAUX P, WENGER F. Tribocorrosion of stainless steel in sulfuric acid: Identification of corrosion-wear components and effect of contact area [J]. Wear, 2010, 269(1-2): 93-103.
[13] WATSON S W, FRIEDERSDORF F J, MADSEN B W, CRAMER S D. Methods of measuring wear-corrosion synergism [J]. Wear, 1995, 181-183: 476-484.
[14] JIANG J, STACK M M, NEVILLE A. Modelling the tribocorrosion interaction in aqueous sliding conditions [J]. Tribology International, 2002, 35(10): 669-679.
[15] DIOMIDIS N, CELIS J P, PONTHIAUX P, WENGER F. A methodology for the assessment of the tribocorrosion of passivating metallic materials [J]. Lubrication Science, 2009, 21(2): 53-67.
[16] DIOMIDIS N, GOCKAN N, PONTHIAUX P, WENGER F, CELIS J P. Assessment of the surface state behaviour of Al71Cu10Fe9Cr10 and Al3Mg2 complex metallic alloys in sliding contacts [J]. Intermetallics, 2009, 17(11): 930-937.
[17] MUNOZ A I, JULIAN L C. Influence of electrochemical potential on the tribocorrosion behaviour of high carbon CoCrMo biomedical alloy in simulated body fluids by electrochemical impedance spectroscopy [J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2010, 55(19): 5428-5439.
[18] IWABUCHI A, LEE J W, UCHIDATE M. Synergistic effect of fretting wear and sliding wear of Co-alloy and Ti-alloy in Hanks’ solution [J]. Wear, 2007, 263: 492-500.
[19] IWABUCHI A, TSUKAMOTO T, TATSUYANAGI Y, KAWAHARA N, NONAKA T. Electrochemical approach to corrosive wear of SKD61 die steel in Na2SO4 solution [J]. Wear, 1992, 156: 301-313.
[20] DING H Y, DAI Z D, ZHOU F, ZHOU G H. Sliding friction and wear behavior of TC11 in aqueous condition [J]. Wear, 2007, 263(1-6): 117-124.
[21] SUN Y, RANA V. Tribocorrosion behaviour of AISI 304 stainless steel in 0.5 M NaCl solution [J]. Materials Chemistry and Physics, 2011, 129(1-2): 138-147.
[22] CHEN Jun, YAN Feng-yuan. Tribocorrosion behaviors of Ti-6Al-4V and Monel K500 alloys sliding against 316 stainless steel in artificial seawater [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2012, 22(6): 1356-1365.
[23] CHEN J, WANG J Z, CHEN B B, YAN F Y. Tribocorrosion behaviors of Inconel 625 alloy sliding against 316 steel in seawater Tribology Transactions, 2011, 54(4): 514-522.
[24] SALASI M, STACHOWIAK G B, STACHOWIAK G W. New experimental rig to investigate abrasive-corrosive characteristics of metals in aqueous media [J]. Tribology Letters, 2010, 40(1): 71-84.
[25] BARRIL S, MISCHLER S, LANDOLT D. Electrochemical effects on the fretting corrosion behaviour of Ti6Al4V in 0.9% sodium chloride solution [J]. Wear, 2004, 259: 282-291.
[26] BETOVA I, BOJINOV M, LAITINEN T, MAKELA K, POHJANNE P, SAARIO T. The transpassive dissolution mechanism of highly alloyed stainless steels I: Experimental results and modelling procedure [J]. Corrosion Science, 2002, 44(12): 2675-2697.
[27] TEKIN K C, MALAYOGLU U. Assessing the tribocorrosion performance of three different nickel-based superalloys [J]. Tribology Letters, 2010, 37(3): 563-572.
[28] DING H Y, ZHOU G H, DAI Z D, BU Y F, JIANG T Y. Corrosion wear behaviors of 2024Al in artificial rainwater and seawater at fretting contact [J]. Wear, 2009, 267(1-4): 292-298.
[29] STACK M M. Mapping tribocorrosion processes in dry and in aqueous conditions: Some new directions for the new millennium [J]. Tribology International, 2002, 35(10): 681-689.
[30] WATERHOUSE R B, TAYLOR D E. Fretting debris and the delamination theory of wear [J]. Wear, 1974, 29: 337-344.
[31] IWABUCHI A, SONODA T, YASHIRO H, SHIMIZU T. Application of potential pulse method to the corrosion behavior of the fresh surface formed by scratching and sliding in corrosive wear [J]. Wear, 1999, 225-229: 181-189.
[32] BELLO J O, WOOD R J K, WHARTON J A. Synergistic effects of micro-abrasion-corrosion of UNSS30403, S31603 and S32760 stainless steels [J]. Wear, 2007, 263: 149-159.
陈 君1,2,张 清1,李全安1,付三玲1,王建章2
1. 河南科技大学 材料科学与工程学院,洛阳 471023;
2. 中国科学院 兰州化学物理研究所 固体润滑国家重点实验室,兰州 730000
摘 要:采用立式万能销盘腐蚀磨损试验机研究AISI 316不锈钢和Ti6Al4V合金在海水中与Al2O3 陶瓷对磨时的腐蚀与腐蚀磨损行为,重点讨论腐蚀磨损之间的交互作用。结果表明,摩擦作用使得Ti6Al4V合金和316不锈钢的开路电位大幅下降,腐蚀磨损过程中的电流密度远高于静态腐蚀时的电流密度,摩擦明显促进了合金的腐蚀。两种合金在海水中的磨损量远大于在纯水中的磨损量,腐蚀促进了磨损,并且Ti6Al4V合金的耐磨性优于316不锈钢的耐磨性,腐蚀磨损之间的交互作用是材料损失的一个重要因素。本实验所用的摩擦装置为单向滑动的面面接触方式,这使得摩擦对腐蚀的促进作用在总磨损量中所占的比例很小。
关键词:Ti6Al4V 合金;AISI 316不锈钢;腐蚀磨损;交互作用
(Edited by Wei-ping CHEN)
Foundation item: Project (LSL-1310) supported by the Open Project of State Key Laboratory of Solid Lubrication, Collaborative Innovation Center of Nonferrous Metals of Henan Province, China; Project (51171059) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China
Corresponding author: Jun CHEN; Tel: +86-15225508091; E-mail: chenjun318822200@163.com
DOI: 10.1016/S1003-6326(14)63157-5

