氮离子注入诱导TiO2涂层在可见光下的抗菌能力
来源期刊:中国有色金属学报(英文版)2020年第1期
论文作者:郑立 钱仕 刘宣勇
文章页码:171 - 180
关键词:TiO2;微弧氧化;氮离子注入;抗菌能力
Key words:TiO2; micro-arc oxidation; nitrogen ion implantation; antibacterial capability
摘 要:为了提高钛组件的抗菌能力,通过微弧氧化(MAO)处理和进一步的氮等离子体浸没离子注入(N-PIII)处理,在钛表面制备抗菌涂层。XPS光谱测试结果表明,采用氮离子注入N-PIII法将氮掺入TiO2涂层,随着注入时间的增加,TiO2涂层表面氮含量增加。掺氮样品在可见光区域的吸光度显著增加,并且氮注入样品的光吸收峰边缘与微弧氧化样品的光吸收峰相比向红外光区移动。将大肠杆菌和金黄色葡萄球菌接种在样品表面,以评估样品的抗菌能力。细菌实验结果表明,掺氮态TiO2在可见光下可以有效降低细菌活力。由实验结果可见,微弧氧化和氮离子注入复合工艺制备的抗菌TiO2涂层在医学和海洋领域具有很大潜力。
Abstract: In order to enhance the antibacterial ability of titanium components, an antibacterial coating was fabricated on Ti surface by micro-arc oxidation (MAO) and further nitrogen plasma immersion ion implantation (N-PIII). The XPS spectra demonstrated that nitrogen was incorporated into TiO2 coatings by N-PIII and the nitrogen content on the surface of TiO2 coatings increased as the N-PIII time increased. Nitrogen-incorporated samples exhibited remarkably increased absorbance in the visible region and the light absorption edge of nitrogen-incorporated samples showed a redshift compared to MAO samples. Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus were seeded on the samples to assess their antibacterial ability. The bacterial experiment demonstrated that nitrogen-incorporated TiO2 could effectively reduce the bacterial viability in visible light. Thus, the antibacterial TiO2 coatings fabricated by MAO and further N-PIII might have large potential in the medical and marine fields.
Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 30(2020) 171-180
Li ZHENG1,2, Shi QIAN1, Xuan-yong LIU1,2
1. State Key Laboratory of High Performance Ceramics and Superfine Microstructure, Shanghai Institute of Ceramics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shanghai 200050, China;
2. College of Materials Science and Opto-Electronics Engineering, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100049, China
Received 28 March 2019; accepted 9 August 2019
Abstract: In order to enhance the antibacterial ability of titanium components, an antibacterial coating was fabricated on Ti surface by micro-arc oxidation (MAO) and further nitrogen plasma immersion ion implantation (N-PIII). The XPS spectra demonstrated that nitrogen was incorporated into TiO2 coatings by N-PIII and the nitrogen content on the surface of TiO2 coatings increased as the N-PIII time increased. Nitrogen-incorporated samples exhibited remarkably increased absorbance in the visible region and the light absorption edge of nitrogen-incorporated samples showed a redshift compared to MAO samples. Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus were seeded on the samples to assess their antibacterial ability. The bacterial experiment demonstrated that nitrogen-incorporated TiO2 could effectively reduce the bacterial viability in visible light. Thus, the antibacterial TiO2 coatings fabricated by MAO and further N-PIII might have large potential in the medical and marine fields.
Key words: TiO2; micro-arc oxidation; nitrogen ion implantation; antibacterial capability
1 Introduction
Titanium and its alloys are widely used in medical instruments and marine components because of their low density, high specific strength and excellent processability [1]. As a relatively simple and reliable technique, micro-arc oxidation (MAO) has been widely used to improve wear resistance and corrosion resistance of these titanium instruments and components [2,3]. However, conventional MAO medical instruments and marine components are lack of antibacterial ability. The bacteria on medical instruments will induce bacterial infection, ultimately leading to surgical failure. The overgrowth of bacteria will accelerate the corrosion damage of marine components, resulting in shorter service life [4]. Therefore, it is essential to enhance the antibacterial ability of medical instruments and marine components.
Many research efforts have been devoted to endowing MAO coatings with antibacterial ability, and the following two techniques are the most investigated: (1) loading antibiotics [5,6], and (2) doping antibacterial elements such as copper, silver, and zinc [7-9]. The release of oxides of antibiotics and antibacterial elements can effectively kill most bacteria [10,11]. However, the toxicity of these biocidal coatings is under scrutiny, and the antibacterial efficiency cannot maintain over a more extended period. Therefore, it remains a challenge to design an antibacterial surface to fulfill various requirements of titanium instruments and components.
Photoactivated self-cleaning coatings have become a significant focus in recent years as environmentally friendly materials. The most commonly known photoactive material is TiO2. Under ultraviolet irradiation, TiO2 can generate electron-hole pairs and exhibits strong oxidizing abilities, which is expected to kill organisms on the surface of materials [12]. However, pure TiO2 can only undergo photocatalysis under ultraviolet light, limiting its antibacterial effect under the sunlight. Doping TiO2 with foreign atoms, such as C [13], N [14,15], and S [16], can effectively regulate the band structure of TiO2 and give TiO2 photocatalytic properties in visible light. Taking into account environmental and safety requirements, we selected nitrogen, a significant element in the atmosphere, as the doping element, looking forward to acquiring an active antibacterial surface.
Herein, we fabricated environmentally friendly antibacterial TiO2 coatings on Ti by MAO and further N-PIII without destroying the integrity of the coatings. Moreover, the effects of N-PIII on the surface composition, contact angle, gap band and antibacterial properties of TiO2 were systematically characterized. The method in this study might provide new insights into the antimicrobial surface design of medical instruments and marine components.
2 Experimental
2.1 Sample preparation
Commercial pure Ti plates (10 mm × 10 mm × 1.0 mm) were used in the experiments. Firstly, these plates were ultrasonically pretreated in a mixed acid solution (V(HF):V(HNO3):V(H2O)=1:5:4) twice, 10 min totally. Then, the samples were ultra- sonically cleaned with deionized water several times and micro-arc oxidized in 0.2 mol/L sulfuric acid solution to fabricate TiO2 coatings. The MAO process was conducted with a constant current of 1.8 A, a frequency of 800 Hz and a duty cycle of 10% and ended at 270 V. The micro-arc oxidized samples were designated as MAO.
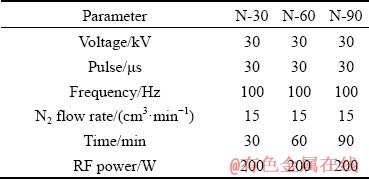
Afterward, these MAO samples were exposed to N-PIII treatment for 30, 60 and 90 min, respectively. And the obtained samples were denoted as N-30, N-60 and, N-90, accordingly. Other important processing parameters were listed in Table 1.
Table 1 Parameters of nitrogen plasma immersion ion implantation for different samples
2.2 Characterization of MAO and N-PIII samples
The surface morphologies of samples were observed by scanning electron microscope (SEM; S-4800, Hitachi, Japan). The crystalline phases of samples were analyzed by X-ray diffraction (XRD; D/max 2500PC, Rigaku, Japan). Elemental compositions and elemental chemical states were determined by X-ray photoelectron spectroscope (XPS; RBD upgraded PHI-5000C ESCA system, USA). UV-visible absorption spectra of samples were recorded by ultraviolet and visible spectro- photometer (UV-vis; Lambada 750, PerkinElmer, USA). The water contact angles of samples were measured by the contact angle instrument (SL20 0B, Solon, China).
2.3 Antibacterial tests
Escherichia coli (E. coli, ATCC 25922) and Staphylococcus aureus (S. aureus, ATCC 25923) were used to assess the antibacterial ability of the samples. A 60 μL suspension of the bacteria was dropped onto each sample, and the bacterial density was 5×106 CFU/mL. After incubated at 37 °C for 12 h in the dark and visible light, respectively, the samples attached with bacteria were stained for fluorescent observation. The LIVE/DEAD BacLight Kit (L13152, Molecular Probes, USA) was used to stain the bacteria in the dark according to the manufacturer’s instruction. Then, the samples with the bacteria were observed by the confocal laser scanning microscope (CLSM, Leica SP8, Germany).
For the SEM observation, additional samples with bacteria were cultured at 37 °C for 12 h. Then, the samples were rinsed with phosphate buffered saline (PBS) twice, and fixed with 2.5% glutaraldehyde (Sigma-Aldrich, USA) at 4 °C for 6 h. The samples were dehydrated with a series of ethanol solutions, and the bacterial morphologies were observed by SEM.
After being cultured at 37 °C for 12 h, samples attached with bacteria were put into the sterilized centrifugal tube, which contained 4 mL of physiological saline. The tube was agitated vigorously for 30 s by a vortex mixer to separate bacteria from the surface of samples. After being diluted 10, 100, and 1000 times by sterile physiological saline, 100 μL of the diluted suspension was dropped on the standard Luria- Bertani (LB, Sigma, USA) or Nutrient Broth (NB, Oxoid, UK) agars. All plates were incubated at 37 °C for another 18 h and the colonies were counted according to the National Standard of China (GB/T 4789.2 protocol).
2.4 Statistical analysis
All data were presented as the mean ± standard deviation. Statistically significant differences (P) between different groups were assessed via one-way analysis of variance and Turkey’s multiple comparison tests.
3 Results and discussion
3.1 Material characterization
The surface morphologies of MAO samples before and after N-PIII were shown in Fig. 1. The microporous structures were formed on the surface of MAO samples by micro-arc oxidation treatment. After nitrogen ion implantation treatment for 30, 60 and 90 min, respectively, the original surface topographies of MAO samples have not been altered, indicating that the incorporation of nitrogen by N-PIII had no influence on the structure of TiO2 coatings.
The XRD patterns of MAO and N-PIII samples are shown in Fig. 2(a). From the XRD spectra of MAO samples, strong diffraction peaks at 2θ values of 25.2° and 48.0° corresponded to (101) and (200) crystal planes of anatase TiO2 (JCPDS No.21-1272), respectively. And diffraction peaks at 2θ values of 27.4°, 36.0°, 41.2° and 54.3° corresponded to (110), (101), (111) and (211) crystal planes of rutile TiO2 (JCPDS No.21-1276), respectively. After N-PIII, the diffraction peaks of crystalline anatase and rutile could also be observed at the same position, indicating that N-PIII did not induce the formation of new crystal phases on the surface of MAO samples.
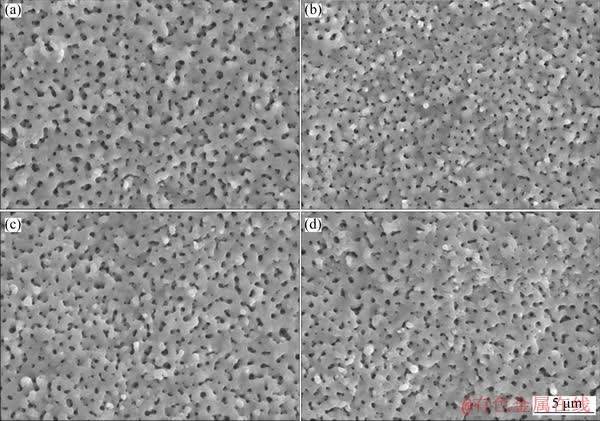
Fig. 1 SEM images of MAO (a), N-30 (b), N-60 (c) and N-90 (d) samples
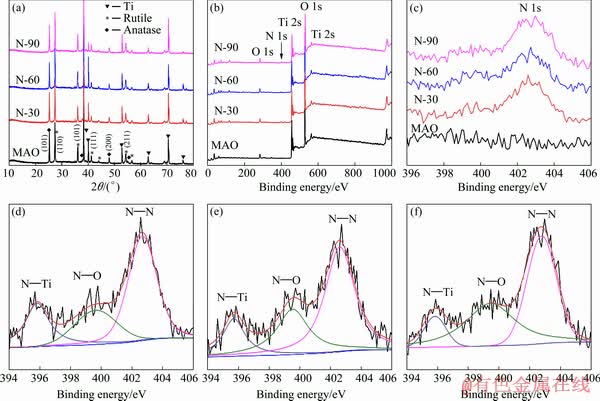
Fig. 2 XRD patters (a), XPS spectra (b) and XPS N 1s spectra (c) of MAO, N-30, N-60, and N-90, and XPS spectra of N in N-30 (d), N-60 (e) and N-90 (f) samples
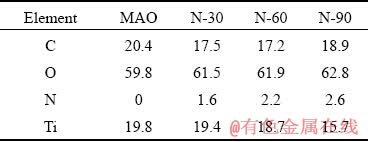
The elemental compositions and elemental chemical states on the surface of all samples were determined by XPS. As shown in Figs. 2(b) and (c), the presence of nitrogen on the surface of N-30, N-60 and N-90 samples was confirmed, while there was no nitrogen on the surface of MAO samples. From the surface elemental compositions (Table 2) detected by XPS, it is known that the nitrogen content on the surface of N-PIII samples increased as the nitrogen ion implantation time increased, which meant that incorporated nitrogen content could be controlled by nitrogen ion implantation time.
The chemical states of nitrogen on the surface of N-PIII samples were further analyzed by the XPS N 1s spectra (Figs. 2(d-f)). The N 1s spectra of N-PIII samples exhibited several broad peaks ranging from 395 to 405 eV, indicating that nitrogen had multiple bonding states in TiO2. Moreover, the N 1s curves could be divided into three peaks centered at ~395.6, 399.5 and 402.7 eV, correlated to the chemical bonding of N—Ti, N—O and N—N, respectively [17]. Among these chemical bonds, N—Ti was thought to be mainly responsible for the enhanced visible light absorption of TiO2 [18].
Table 2 Surface elemental compositions of different samples acquired by XPS (at.%)
The ultraviolet and visible spectrophotometer was used to study the optical properties of MAO samples and N-PIII samples (Fig. 3(a)). The light absorption edge of MAO sample was situated at ~440 nm, which was in accordance with the band gap of a mixture of anatase and rutile TiO2 (2.8 eV). A broader absorption ranging from 400 to 550 nm occurred in N-30, N-60 and N-90 samples, revealing a wider distribution of local energy levels in the band gap. More importantly, N-PIII samples showed significantly increased absorbance in the visible region compared to MAO samples. From the relationship between the Kubelka-Munk function and the absorbed light energy [19] (as shown in Fig. 3(b)), the optical gaps of N-30, N-60 and N-90 samples were reduced to ~2.52, 2.45 and 2.39 eV, respectively, showing a redshift compared to MAO samples.
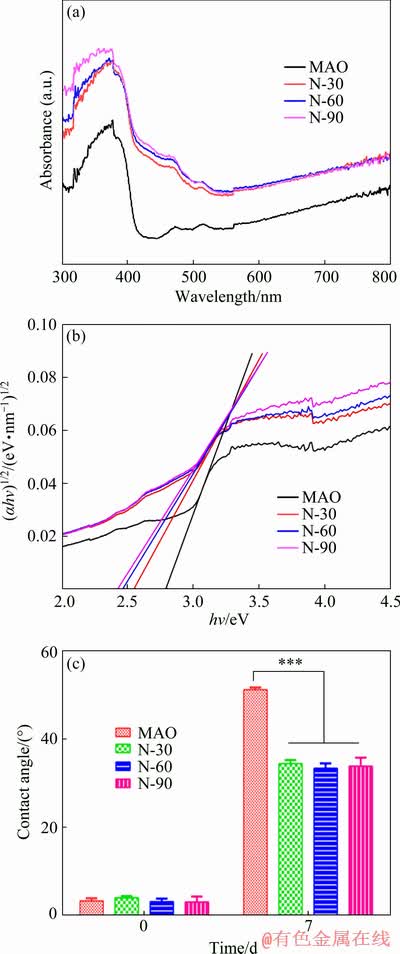
Fig. 3 UV-visible spectra (a), plot of transformed Kubelka-Munk function versus light energy (b) and contact angles (c) of MAO, N-30, N-60 and N-90 samples
The reduction of the optical gaps of N-PIII samples might be due to the formation of the local intermediate band gap (N 2p) level above the O 2p valence band of TiO2 [18]. The intermediate band gap (N 2p) energy level was slightly higher than the top of the O 2p valence band and the visible light irradiation could stimulate electrons from the N 2p valence band to the conduction band, forming positive holes in the N 2p valence band [20]. Electrons in the conduction band and holes in the N 2p valence band exhibited high reducing and oxidizing power, respectively [21]. The electrons reacted with oxygen, leading to the formation of superoxide radicals 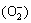 [21]. Meanwhile, the holes reacted with water, producing hydroxyl radicals (·OH) [21]. Hydroxyl radicals and superoxide radicals could react with the organic compounds to form H2O and CO2 [22], which was beneficial to improving the hydrophilicity and antibacterial properties of the surface.
[21]. Meanwhile, the holes reacted with water, producing hydroxyl radicals (·OH) [21]. Hydroxyl radicals and superoxide radicals could react with the organic compounds to form H2O and CO2 [22], which was beneficial to improving the hydrophilicity and antibacterial properties of the surface.
The water contact angles of all samples were shown in Fig. 3(c). The surfaces of fresh MAO samples and N-PIII samples were very hydrophilic. However, after 7 d of storage under the same conditions, the contact angles of all samples increased largely due to the unavoidable accumulation of hydrocarbons on the surfaces of these samples [23]. Hydroxyl radicals and super- oxide radicals produced by N-PIII samples could reduce the C content on the surfaces (Table 2) and hydroxyl radicals could also increase the hydrophilicity of the surfaces. Thus, the contact angles of N-PIII samples were approximately 16° lower than that of MAO samples after 7 d of storage.
3.2 Antibacterial ability

Fig. 4 Fluorescent images of E. coli (a) and S. aureus (b) on different samples in dark and light conditions (50 μm)
S. aureus and E. coli were used to examine the antibacterial ability of the samples. The Live/Dead assay was performed on all samples, and the nucleic acid of both living and dead bacteria could be stained by SYTO 9 to produce green fluorescence while only the nucleic acid of dead bacteria could be stained by PI to produce red fluorescence [24]. The fluorescent images of E. coli and S. aureus were shown in Fig. 4. For E. coli cultured in the dark (Fig. 4(a)), there were no obvious reduction in green fluorescence among N-30, N-60 and N-90 samples relative to MAO samples and no obvious visible red fluorescence. It was suggested that N-PIII samples did not display significant anti- bacterial ability in the dark condition. Interestingly, in the light condition, a significant reduction of the green fluorescence on N-PIII samples was found. Additionally, a significant increase of the red fluorescence was observed on N-PIII samples. These results indicated that N-PIII samples could effectively inhibit the adhesion of E. coli and destroy E. coli on the sample surfaces, and the antibacterial ability of N-PIII samples increased with the increase of nitrogen content in visible light. The similar trend was found in the S. aureus culture experiments as shown in Fig. 4(b).
The morphology and membrane integrity of E. coli and S. aureus were observed by SEM as shown in Fig. 5. Large amounts of E. coli were seen on all samples in the dark (Fig. 5(a)) and the cytoplasmic membranes of E. coli were intact and smooth, which indicated that E. coli could grow well on all samples and N-PIII samples had no significant negative effects on the growth of E. coli in the dark. After cultured for 12 h in visible light (Fig. 5(a)), there was less E. coli on the surface of N-PIII samples compared with MAO samples. The bacteria on MAO samples could keep the typical rod-like shape while partial bacteria on N-30, N-60 and N-90 samples appeared to be disrupted in shape and lose the integrity of cell membrane, which suggested that N-PIII samples could inhibit the adhesion of E. coli and exhibit good antibacterial ability in visible light. S. aureus also grew well on all samples and had a spherical shape with a smooth surface in the dark (Fig. 5(b)). After being cultured for 12 h in visible light (Fig. 5(b)), a decrease of the bacteria number on N-PIII samples could be observed while some S. aureus on N-PIII samples was distorted in shape.
To further investigate the antibacterial performance of N-PIII samples, the bacteria were detached from the samples and cultured on agar plates for 18 h, and the results were shown in Fig. 6.
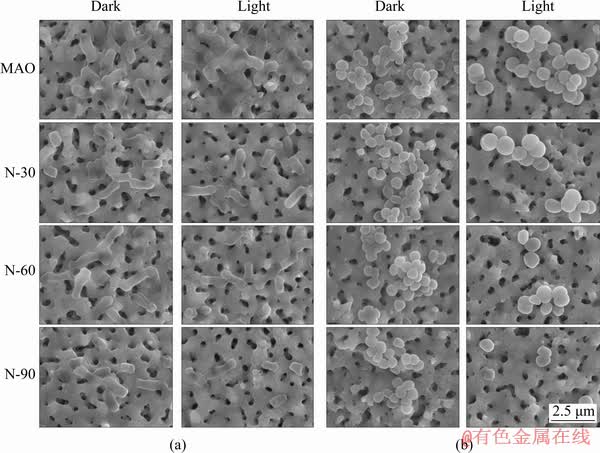
Fig. 5 SEM morphologies of E. coli (a) and S. aureus (b) on different samples in dark and light conditions
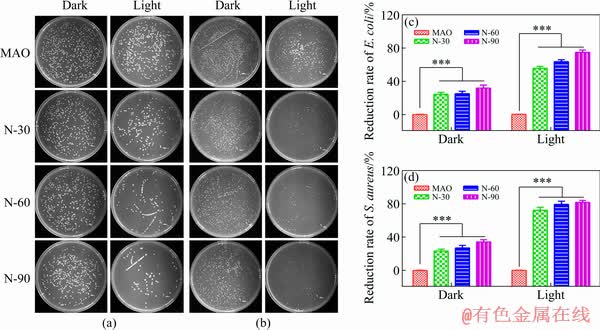
Fig. 6 Images of recultivated E. coli (a) and S. aureus (b) colonies on agar culture plates and reduction rates of E. coli (c) and S. aureus (d) colonies
For the dark group, there was no significant difference in the amounts of E. coli and S. aureus on all samples. However, for the lighting group, a dramatic decrease of the bacteria number was found on the plates corresponding to N-PIII samples compared with that of MAO samples. The bactericidal rates of N-30, N-60 and N-90 samples against E. coli were 56%, 66% and 75%, respectively. Meanwhile, the bactericidal rates of those samples against S. aureus were 73%, 78% and 81%, respectively, exhibiting a similar trend.
From these results of bacterial experiments, it could be concluded that the bacteria on N-PIII samples could grow well in the dark, while the viability of the bacteria on N-PIII samples was reduced in visible light. It was proposed that the antibacterial ability of N-PIII in visible light was due to the incorporation of nitrogen, which narrowed the optical gaps of N-PIII samples. Reactive oxygen species (ROS, including superoxide radicals and hydroxyl radicals) could be produced by photocatalysis of N-PIII samples with narrowed gaps in visible light [18], as shown in Fig. 7. Hydroxyl radicals were a strong and nonselective oxidant [20], which could virtually damage all types of organic biomolecules, including carbohydrates, nucleic acids, lipids, proteins, DNA, and amino acids [25]. Aqueous reactions of superoxide radicals could produce singlet oxygen (1O2) [20], which was the main mediator of phototoxicity and could irreversibly damage the treated tissues [26], causing biomembrane oxidation and degradation [25]. Critical bacteria functions could be damaged by ROS and the bacteria eventually died [27,28]. Thus, N-PIII samples exhibited good antibacterial properties in visible light.
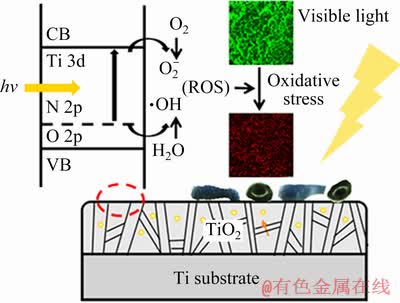
Fig. 7 Schematic illustration of antibacterial mechanism of N-PIII samples
4 Conclusions
(1) Nitrogen-incorporated TiO2 coatings were produced by MAO and N-PIII. The SEM and XRD results demonstrated that nitrogen could be successfully incorporated into TiO2 coatings by N-PIII without destroying the surface topographies and phase compositions of the coatings.
(2) Nitrogen-incorporated samples exhibited remarkably increased absorbance in the visible region and the light absorption edge of nitrogen- incorporated samples showed a redshift compared with MAO samples.
(3) The bacterial experiment demonstrated that nitrogen-incorporated TiO2 coating did not exhibit significant antibacterial property in the dark, while it could effectively reduce the bacterial viability in visible light.
References
[1] YAN Shao-kun, SONG Guang-Ling, LI Zheng-xian, WANG Hao-nan, ZHENG Da-jiang, CAO Fu-yong, HORYNOVA M, DARGUSCH M S, ZHOU Lian. A state-of-the-art review on passivation and biofouling of Ti and its alloys in marine environments [J]. Journal of Materials Science & Technology, 2018, 34: 421-435.
[2] SHI P, NG W F, WONG M H, CHENG F T. Improvement of corrosion resistance of pure magnesium in Hanks’ solution by microarc oxidation with sol-gel TiO2 sealing [J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2009, 469: 286-292.
[3] LIN Xiu-zhou, ZHU Min-hao, ZHENG Jian-feng, LUO Jun, MO Ji-liang. Fretting wear of micro-arc oxidation coating prepared on Ti6Al4V alloy [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2010, 20: 537-546.
[4] DETTY M R, CIRIMINNA R, BRIGHT F V, PAGLIARO M. Environmentally benign sol-gel antifouling and foul- releasing coatings [J]. Accounts of Chemical Research, 2014, 47: 678-687.
[5] ITO M, MOCHIDA K, ITO K, ONDUKA T, FUJII K. Induction of apoptosis in testis of the marine teleost mummichog Fundulus heteroclitus after in vivo exposure to the antifouling biocide 4,5-dichloro-2-n-octyl-3(2H)- isothiazolone (Sea-Nine 211) [J]. Chemosphere, 2013, 90: 1053-1060.
[6] KAZEMZADEH N M, LAI B F L, DING Chuan-fan, KIZHAKKEDATHU J N, HANCOCK R E W, WANG R Z. Multilayered coating on titanium for controlled release of antimicrobial peptides for the prevention of implant- associated infections [J]. Biomaterials, 2013, 34: 5969-5977.
[7] HEUSER M, CARDENAS G. Chitosan-copper paint types as antifouling [J]. Journal of the Chilean Chemical Society, 2014, 59: 2415-2419.
[8] LAGERSTROM M, LINDGREN J F, HOLMQVIST A, DAHLSTROM M, YTREBERG E. In situ release rates of Cu and Zn from commercial antifouling paints at different salinities [J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2018, 127: 289-296.
[9] JURCZYK K, KUBICKA M M, RATAJCZAK M, JURCZYK M U, NIESPODZIANA K, NOWAK D M, GAJECKA M, JURCZYK M. Antibacterial activity of nanostructured Ti-45S5 bioglass–Ag composite against Streptococcus mutans and Staphylococcus aureus [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2016, 26: 118-125.
[10] BRYAN G W, LANGSTON W J. Bioavailability, accumulation and effects of heavy-metals in sediments with special reference to United Kingdom estuaries—A review [J]. Environmental Pollution, 1992, 76: 89-131.
[11] TURNER A. Marine pollution from antifouling paint particles [J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2010, 60: 159-171.
[12] FOSTER H A, DITTA I B, VARGHESE S, STEELE A. Photocatalytic disinfection using titanium dioxide: Spectrum and mechanism of antimicrobial activity [J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2011, 90: 1847-1868.
[13] KHAN S U M, AL-SHAHRY M, INGLER W B. Efficient photochemical water splitting by a chemically modified n-TiO2 [J]. Science, 2002, 297: 2243-2245.
[14] WANG He-feng, SHU Xue-feng, LI Xiu-yan, TANG Bin. Photocatalytic activities of N doped TiO2 coatings on 316L stainless steel by plasma surface alloying technique [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2012, 22(S): s120-s126.
[15] DONG Lin, CAO Guo-xi, MA Ying, JIA Xiao-lin, YE Guo-tian, GUAN Shao-kang. Enhanced photocatalytic degradation properties of nitrogen-doped titania nanotube arrays [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2009, 19: 1583-1587.
[16] UMEBAYASHI T, YAMAKI T, ITOH H, ASAI K. Band gap narrowing of titanium dioxide by sulfur doping [J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2002, 81: 454-456.
[17] WANG Jin, TAFEN D N, LEWIS J P, HONG Zhang-lian, MANIVANNAN A, ZHI Ming-jia, LI Ming, WU Nian-qiang. Origin of photocatalytic activity of nitrogen-doped TiO2 nanobelts [J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2009, 131: 12290-12297.
[18] ASAHI R, MORIKAWA T, OHWAKI T, AOKI K, TAGA Y. Visible-light photocatalysis in nitrogen-doped titanium oxides [J]. Science, 2001, 293: 269-271.
[19] STENGL V, BAKARDJIEVA S, MURAFA N, HOUSKOVA V, LANG K. Visible-light photocatalytic activity of TiO2/ZnS nanocomposites prepared by homogeneous hydrolysis [J]. Microporous and Mesoporous Materials, 2008, 110: 370-378.
[20] BRUNET L, LYON D Y, HOTZE E M, ALVAREZ P J J, WIESNER M R. Comparative photoactivity and antibacterial properties of C60 fullerenes and titanium dioxide nanoparticles [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2009, 43: 4355-4360.
[21] LIN H F, LIAO S C, HUNG S W. The DC thermal plasma synthesis of ZnO nanoparticles for visible-light photocatalyst [J]. Journal of Photochemistry and Photobiology A- Chemistry, 2005, 174: 82-87.
[22] WU T X, LIU G M, ZHAO J C, HIDAKA H, SERPONE N. Photoassisted degradation of dye pollutants: V. Self- photosensitized oxidative transformation of Rhodamine B under visible light irradiation in aqueous TiO2 dispersions [J]. Journal of Physical Chemistry B, 1998, 102: 5845-5851.
[23] ZHAO G, SCHWARTZ Z, WIELAND M, RUPP F, GEIS- GERSTORFER J, COCHRAN D L, BOYAN B D. High surface energy enhances cell response to titanium substrate microstructure [J]. Journal of Biomedical Materials Research: Part A, 2005, 74: 49-58.
[24] QIU Jia-jun, WANG Dong-hui, GENG Hao, GUO Jing-shu, QIAN Shi, LIU Xuan-yong. How oxygen-containing groups on graphene influence the antibacterial behaviors [J]. Advanced Materials Interfaces, 2017, 4: 1700228.
[25] LI Yang, ZHANG Wen, NIU Jun-feng, CHEN Yong-sheng. Mechanism of photogenerated reactive oxygen species and correlation with the antibacterial properties of engineered metal-oxide nanoparticles [J]. ACS Nano, 2012, 6: 5164-5173.
[26] WANG S Z, GAO R M, ZHOU F M, SELKE M. Nanomaterials and singlet oxygen photosensitizers: Potential applications in photodynamic therapy [J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry, 2004, 14: 487-493.
[27] DEMIREL C S U, BIRBEN N C, BEKBOLET M. A comprehensive review on the use of second generation TiO2 photocatalysts: Microorganism inactivation [J]. Chemosphere, 2018, 211: 420-448.
[28] CARRE G, BENHAMIDA D, PELUSO J, MULLER C D, LETT M C, GIES J P, KELLER V, KELLER N, ANDRE P. On the use of capillary cytometry for assessing the bactericidal effect of TiO2: Identification and involvement of reactive oxygen species [J]. Photochemical & Photobiological Sciences, 2013, 12: 610-620.
郑 立1,2,钱 仕1,刘宣勇1,2
1. 中国科学院 上海硅酸盐研究所 高性能陶瓷和超微结构国家重点实验室,上海 200050;
2. 中国科学院大学 材料科学与光电技术学院,北京 100049
摘 要:为了提高钛组件的抗菌能力,通过微弧氧化(MAO)处理和进一步的氮等离子体浸没离子注入(N-PIII)处理,在钛表面制备抗菌涂层。XPS光谱测试结果表明,采用氮离子注入N-PIII法将氮掺入TiO2涂层,随着注入时间的增加,TiO2涂层表面氮含量增加。掺氮样品在可见光区域的吸光度显著增加,并且氮注入样品的光吸收峰边缘与微弧氧化样品的光吸收峰相比向红外光区移动。将大肠杆菌和金黄色葡萄球菌接种在样品表面,以评估样品的抗菌能力。细菌实验结果表明,掺氮态TiO2在可见光下可以有效降低细菌活力。由实验结果可见,微弧氧化和氮离子注入复合工艺制备的抗菌TiO2涂层在医学和海洋领域具有很大潜力。
关键词:TiO2;微弧氧化;氮离子注入;抗菌能力
(Edited by Wei-ping CHEN)
Foundation item: Projects (51831011, 31670980) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China; Project (51525207) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation for Distinguished Young Scholars of China; Projects (18YF1426900, 18410760600) supported by the Science and Technology Commission of Shanghai Municipality, China
Corresponding author: Xuan-yong LIU, Tel: +86-21-52412409, E-mail: xyliu@mail.sic.ac.cn;
Shi QIAN, E-mail: qianshi@mail.sic.ac.cn
DOI: 10.1016/S1003-6326(19)65189-7

