DOI:10.19476/j.ysxb.1004.0609.2019.08.01
淬火速率对汽车用新型高强韧铝合金晶间腐蚀的影响
李承波1, 2,邓运来1,唐建国1,李建湘2,张新明1
(1. 中南大学 材料科学与工程学院,长沙 410083;
2. 广东和胜工业铝材股份有限公司,中山 528463)
摘 要:采用晶间腐蚀实验结合扫描和透射电镜分析,研究淬火速率对汽车用新型高强韧铝合金晶间腐蚀的影响。结果表明:淬火速率从960 ℃/s降低至1.8 ℃/s,晶界淬火析出相的长度及无沉淀析出带PFZ宽度分别从24.3 nm和23.7 nm增加至94.5 nm和97.8 nm,晶间腐蚀等级从3级增加至4级,最大腐蚀深度和平均腐蚀深度从71.6 μm和60.3 μm分别增加至174.2 μm和157.9 μm。随着淬火速率的减小,晶界析出相的粒径增加,晶界析出相的相间距增加,晶界PFZ宽度也相应增大,晶界析出相的Zn含量增加最快,Mg含量的增加次之,Cu含量的增加最慢,从而导致晶间腐蚀深度增加。
关键词:铝合金;淬火速率;无沉淀析出带;晶间腐蚀
文章编号:1004-0609(2019)-08-1575-08 中图分类号:TG156.32;TG174.3 文献标志码:A
在新能源汽车上应用铝合金可以达到明显的轻量化效果,实现“汽车轻量化”,达到节能减排的目的,对提高汽车使用性能和安全性具有重要意义。高强韧的7xxx系铝合金具有强度高、密度低的特点,广泛用作航空航天、轨道交通等的结构材料,可达到显著的减重效果。目前,新能源汽车行业也开始逐步采用高强韧的7xxx系铝合金来实现汽车车身的轻量化目标。7xxx系合金是可热处理强化铝合金,淬火是决定该系合金最终性能的一个关键因素,淬火速率太小会导致力学性能、腐蚀性能下降,而淬火速率太大会产生残余应力,甚至发生变形。
科研工作者在淬火速率对高强度铝合金力学性能的影响方面开展了大量的研究[1-4],但淬火速率对腐蚀性能方面的研究还比较少。一般认为,淬火速率减小会降低7xxx系合金的耐蚀性能。张新明等[5]研究发现7055铝合金薄板空气淬火的最大晶间腐蚀深度约为室温水淬火的2倍,即淬火速率减小大大降低了抗晶间腐蚀性能。张翀等[6]研究了轧制变形对7A55铝合金晶间腐蚀的淬火敏感性的影响,发现淬火速率的减小会导致该合金的抗晶间腐蚀能力降低。LIU等[7]研究表明7055-T6铝合金板材的耐腐蚀性能随淬火速率减小而显著降低,同时研究还发现[8],晶粒形貌显著影响7055铝合金的剥落腐蚀敏感性。李芳芳[9]研究了淬火介质对高强铝合金抗晶间腐蚀性能的影响,发现空气淬火时抗晶间腐蚀性能很差。李承波等[10]研究了7085铝合金的剥落腐蚀淬火敏感性,发现剥落腐蚀深度随淬火速率的减小而显著增加。CHEN等[11]研究表明7085铝合金锻件的抗应力腐蚀性能随着淬火速率的减少呈现先提高后降低的规律。晶间腐蚀是7xxx系铝合金一种常见的局部腐蚀类型。晶间腐蚀的发生会急剧恶化材料的力学性能,大大缩短材料的使用寿命,同时对构件的安全性造成严重的威胁[12-14]。因而,高强韧7xxx系铝合金的晶间腐蚀问题一直是科研工作者关注的重点。以前的研究大多只是定性地揭示了晶界析出相跟腐蚀性能之间的关系,本文作者通过研究淬火速率对汽车用新型高强韧7xxx系铝合金晶间腐蚀的影响规律,并结合显微组织的观察结果分析和探讨影响机理,以期能够建立高强铝合金显微组织与晶间腐蚀之间的定量关系。
1 实验
材料为某企业提供的2 mm厚的新型7xxx系铝合
金冷轧薄板,其化学成分为(质量分数,%):Al-5.8Zn- 2.4 Mg-1.4Cu-0.08Cr-0.08Zr-0.05Ti,w(Fe)<0.1%, w(Si)<0.06%。样品在SX-4-10型箱式电阻炉中固溶,固溶温度为475 ℃,保温时间为15 min,然后分别在4种介质中淬火:室温水淬、沸水淬火、室温油淬和空气淬火,淬火速率分别为960、98、10.8和1.8 ℃/s[15]。淬火转移时间小于5 s。淬火冷却至室温再到油浴炉中进行时效,时效工艺为:120 ℃、24 h。根据国标GB/T 7998—2005进行晶间腐蚀浸泡实验,腐蚀液配比为57 g NaCl+10 mL H2O2+1 L蒸馏水,余量为蒸馏水(或去离子水),腐蚀液的体积与样品暴露面积之比为10 mL:1 cm2,浸泡过程温度是恒定的,采用水浴,保证腐蚀液温度为(35±2) ℃。在腐蚀液中浸泡6 h后取出并在金相显微镜下观察腐蚀形貌和腐蚀深度。
晶间腐蚀试验完成后,切取截面样品观察腐蚀情况。切取样品进行显微组织分析,金相观察采用XJP-6A型金相显微镜,腐蚀液为Keller试剂,该试剂的成分为:1 mL HF,1.5 mL HCL,2.5 mL HNO3,95 mL蒸馏水。在FEI Quanta-200扫描电镜上观察第二相形貌,并对一些第二相进行能谱分析。透射电镜分析在荷兰FEI产的Tecnai G2 F20型电镜上进行,加速电压为200 kV。样品磨成厚0.08 mm的薄片,冲成d 3 mm圆片,然后双喷减薄,电解液为20%HNO3+ 80%CH3OH(体积分数),温度控制在-20 ℃以下。
2 实验结果
2.1 晶间腐蚀
图1所示为4种淬火速率下样品的晶间腐蚀后截面金相照片。纵截面上的腐蚀深度如图2所示。由图1可见,淬火速率越小,晶间腐蚀深度越大。淬火速率为960 ℃/s的腐蚀等级为3级,最大腐蚀深度和平均腐蚀深度分别为71.6 μm和60.3 μm;淬火速率为98 ℃/s的腐蚀等级为3级,最大腐蚀深度和平均腐蚀深度分别为84.9 μm和72.4 μm;淬火速率为10.8 ℃/s的腐蚀等级为4级,最大腐蚀深度和平均腐蚀深度分别为125.3 μm和114.2 μm;淬火速率为1.8 ℃/s的腐蚀等级为4级,最大腐蚀深度和平均腐蚀深度分别为174.2 μm和157.9 μm。淬火速率为1.8 ℃/s的最大腐蚀深度约为淬火速率为960 ℃/s的最大腐蚀深度的2.5倍。
2.2 显微组织
图3所示为不同淬火速率下试样的纵截面金相照片。由图3可见,晶粒呈长条状沿铝合金轧制方向生长。在淬火速率为960 ℃/s时晶粒形貌清晰可见,在淬火速率为1.8 ℃/s时晶粒形貌不清晰,因为淬火过程中大量平衡相析出,导致腐蚀后的晶粒形貌不明显。
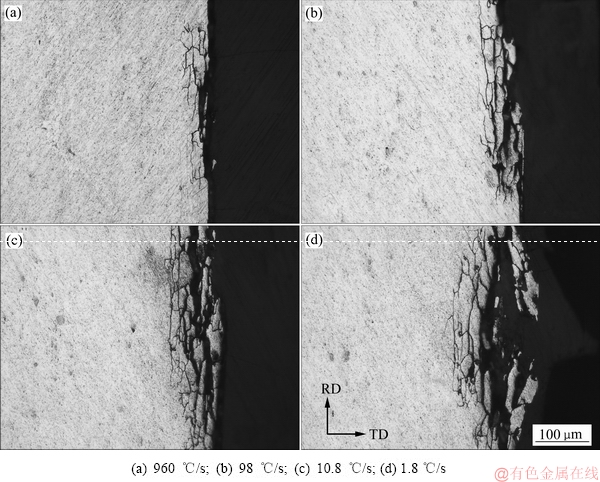
图1 不同淬火速率下样品的晶间腐蚀形貌
Fig. 1 Intergranular corrosion morphologies of samples at different quenching rates
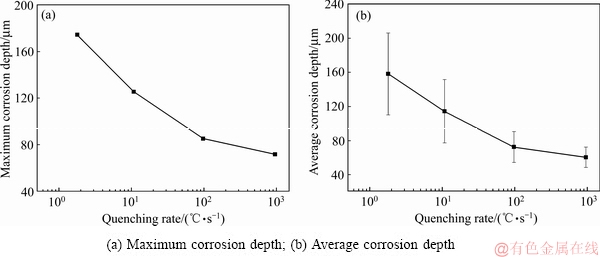
图2 不同淬火速率下样品的晶间腐蚀深度
Fig. 2 Intergranular corrosion depth of samples at different quenching rates
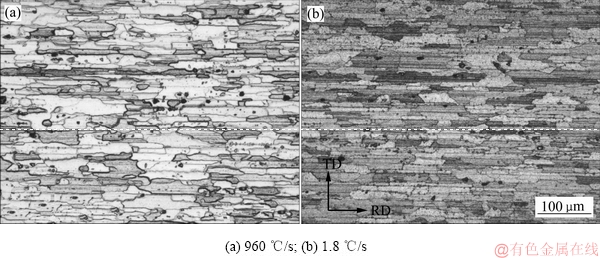
图3 不同淬火速率下样品的金相照片
Fig. 3 OM images of samples at different quenching rates
图4所示为不同淬火速率下的SEM像。从图4可以看到许多白色的初生相,这些相尺寸粗大,尺寸不均匀且分布也不均匀。对图4(b)箭头A所示的初生相进行能谱分析(见图4(e)),该相的成分为Al-7.79Fe- 16.66Cu-0.95Mg(摩尔分数,%),因此,粗大的不规则的白色相为含Fe相。淬火速率为960 ℃/s的SEM像中,基体除了白色初生相,未观察到其他相。淬火速率为1.8 ℃/s的SEM像中可以观察到很多沿晶界分布的细小白色的淬火析出相,如图4(d)箭头B所示,由此可以看出,淬火速率减小,导致晶界处大量平衡相的析出。晶界处能量高,淬火速率低时,有利于平衡相在晶界上形核并长大。
图5所示为淬火速率对晶界析出相的影响。从图5可以看出,随着淬火速率的减小,晶界析出相的尺寸增加,晶界析出相的相间距增加,晶界无沉淀析出带(Precipitate free zone, PFZ)宽度也相应增大,晶界处的这些析出相是η平衡相。当淬火速率为960 ℃/s时,合金中晶界上的第二相尺寸比较均匀,分布较连续,呈链条状。当淬火速率为98 ℃/s时,晶界上的第二相尺寸有所增加,分布不连续,晶界PFZ宽度有所增加。当淬火速率为10.8 ℃/s时,晶界上的第二相尺寸明显增加,其周围有明显的无沉淀析出带,且大小不均匀,分布也不连续,尺寸较大的相是淬火后就析出的,而尺寸很小的是时效时析出的。此处冷却强度低,因此,冷却过程中晶界上已有大量的第二相析出,时效后这些相继续长大。当淬火速率为1.8 ℃/s时,晶界第二相的尺寸最大,尺寸相差很大且分布不连续,且离晶界越近,晶内沉淀相的数量越少,晶界附近很宽的范围内均没有沉淀强化相析出。
图6所示为淬火速率对晶界析出相尺寸的影响,图7所示为淬火速率对晶界PFZ宽度的影响。从图6和图7可以发现,随着淬火速率的减小,晶界处平衡相的长度和厚度尺寸均增加,晶界PFZ宽度也相应增大。当淬火速率为960 ℃/s时,晶界上基本看不到平衡相析出。测得时效后晶界处析出相的长度约为24.3 nm,这些析出相应该是时效析出的,此时晶界PFZ宽度为23.7 nm。当淬火速率为98 ℃/s时,晶界平衡相尺寸较大且不连续,晶界处平衡相的长度和厚度平均尺寸分别为43.8 nm和15.6 nm,最大长度可达52 nm,最大厚度可达20 nm,此时晶界PFZ宽度增加,为40.5 nm。当淬火速率为10.8 ℃/s时,晶界处平衡相的长度和厚度平均尺寸分别为79.4 nm和28.3 nm,最大的长度可达115 nm,最大厚度为60 nm,此时晶界PFZ宽度为75.8 nm。当淬火速率为1.8 ℃/s时,晶界处η平衡相尺寸大且不连续,晶界处平衡相的长度和厚度平均尺寸分别为94.5 nm和41.7 nm,最大长度可达150 nm,最大厚度可达80 nm,此时晶界PFZ宽度最大,为97.8 nm。
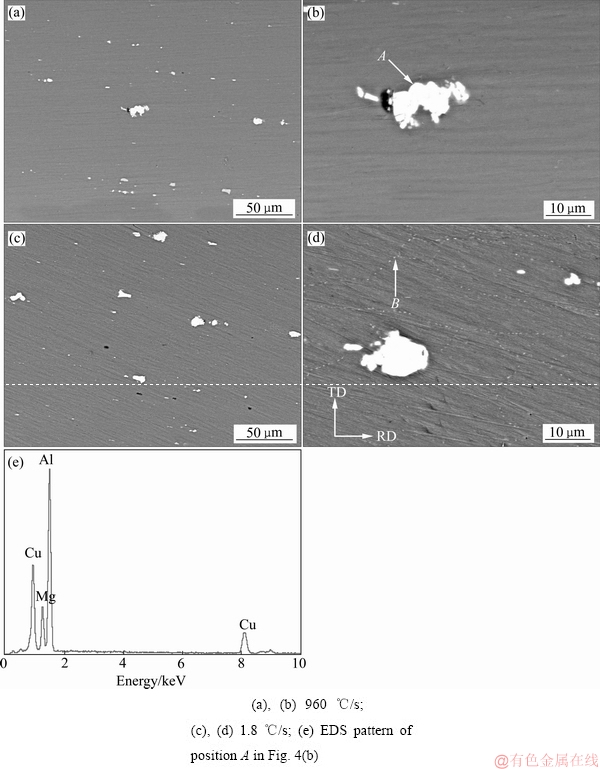
图4 不同淬火速率下样品的SEM像和EDS谱
Fig. 4 SEM images of different quenching rates
图8所示为淬火速率对晶界析出相成分的影响。晶界析出相成分的结果如图9所示。从图8和图9可以看出,当淬火速率为960 ℃/s时,晶界析出相的Zn、Mg、Cu含量很低;当淬火速率为1.8 ℃/s时,Zn和Mg的含量显著增加,Cu含量也有所增加。可以发现,随着淬火速率减小,晶界析出相的Zn含量增加最快,Mg含量次之,Cu含量的增加最慢。
3 分析与讨论
图10所示为晶界析出相的尺寸及PFZ的宽度对晶间腐蚀深度的影响。从图10可以看出,随着晶界析出相的尺寸及PFZ宽度的增加,晶间腐蚀深度增加,当晶界淬火析出相的尺寸及PFZ宽度分别为24.3 nm和23.7 nm,最大晶间腐蚀深度为71.6 μm。当晶界淬火析出相的尺寸及PFZ宽度分别为94.5 nm和97.8 nm,最大晶间腐蚀深度为174.2 μm。η平衡相(MgZn2) 是高强韧铝合金淬火过程中主要析出相,无沉淀析出带(PFZ)基本可以当作纯铝。前期的研究表明[12],晶界平衡η相的电位为-1.05 V,PFZ为-0.85 V,晶内基体的电位为-0.75 V,高强韧铝合金在腐蚀环境中η平衡相作为阳极相而优先溶解。当淬火速率较低时,大量的η平衡相在晶界析出,造成高强韧铝合金腐蚀非常明显。同时在腐蚀的过程中PFZ也作为阳极相被腐蚀,促使晶间腐蚀的产生,腐蚀裂纹会沿着大角度晶界继续扩展。
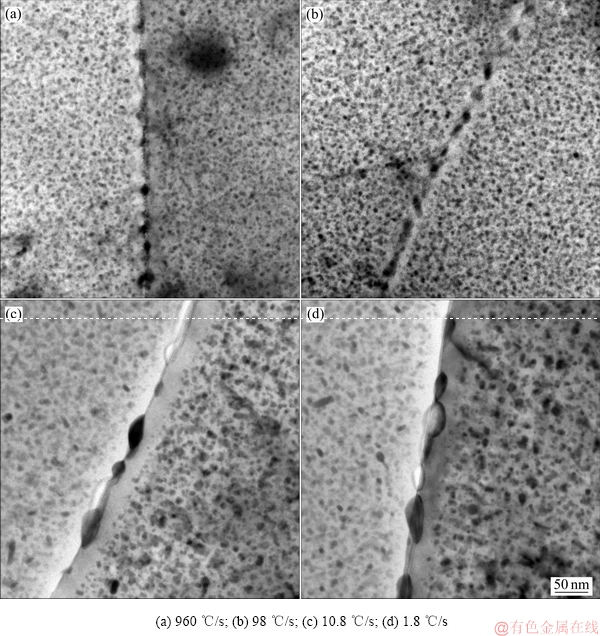
图5 不同淬火速率下的晶界析出相
Fig. 5 Precipitates of grain boundary at different quenching rates
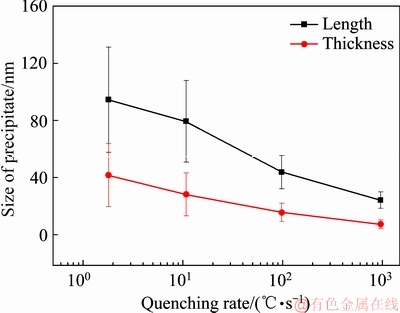
图6 淬火速率对晶界析出相尺寸的影响
Fig. 6 Effect of quenching rates on size of precipitate in grain boundary
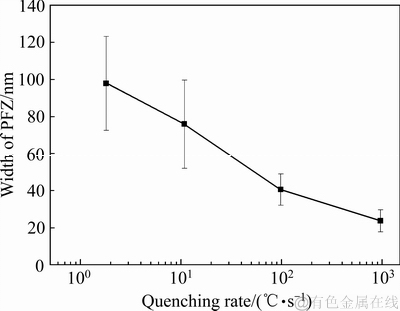
图7 淬火速率对晶界PFZ宽度的影响
Fig. 7 Effect of quenching rates on width of PFZ in grain boundary
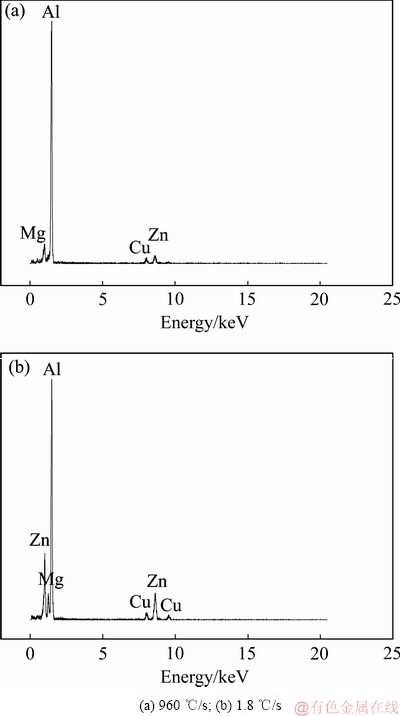
图8 淬火速率对晶界析出相成分的影响
Fig. 8 Effect of quenching rates on composition of precipitate at grain boundary
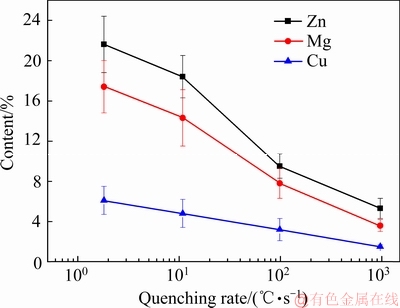
图9 不同淬火速率的晶界析出相成分
Fig. 9 Precipitate components of grain boundary in different quenching rates
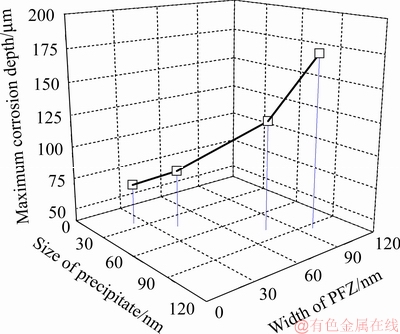
图10 晶界析出相的尺寸及PFZ的宽度对晶间腐蚀深度的影响
Fig. 10 Effect of size of precipitate at grain boundary and width of PFZ on intergranular corrosion depth
高强韧7xxx系铝合金腐蚀主要是沿着晶界发生的,因此,晶界状态是影响腐蚀的主要因素。前期课题组的大量研究发现[5-8, 16-18],高强铝合金的腐蚀性能与再结晶程度、晶粒形态、晶界析出情况息息相关。淬火过程对合金中的晶粒形态影响不明显。
实验结果显示淬火速率对时效态合金的组织结构,包括基体的析出相尺寸、晶界析出相大小与连续分布以及PFZ宽度,都产生了明显的影响,见图4和图5。因为晶界处能量高,Zn和Mg在铝基体中的扩散速度快,而Cu在铝基体中的扩散速度慢。在慢速淬火过程中,基体中大量的Zn和Mg原子扩散到晶界处富集,从而在晶界处形成尺寸较大的η平衡相(MgZn2),而晶界附近的Zn和Mg原子贫化,导致时效后形成很宽的PFZ,如图5(c)和(d)所示。淬火速率越小,扩散至晶界处的Zn和Mg原子越多,晶界处析出的η平衡相尺寸越大(见图6),析出相的Zn和Mg含量越高(见图8和图9),而晶界附近的Zn和Mg原子贫化越严重,造成晶界PFZ宽度增加(见图7)。
晶界析出相及PFZ与基体电化学行为存在明显差异。由实验结果可知,淬火速率减小,合金抗腐蚀能力降低。结合组织观察结果认为,这主要与淬火速率减小时晶界析出相的尺寸和间距增加、晶界析出相的Zn和Mg含量增加及PFZ宽化有关。高强韧7xxx系铝合金在腐蚀介质中,晶界区域各相与基体固溶体的腐蚀电位不同导致电偶腐蚀的发生,使合金产生沿晶界的腐蚀现象。晶界析出相(主要为η相)、PFZ及晶粒内部相互间会形成腐蚀微电池,而晶界析出相和无沉淀析出带往往成为阳极而优先溶解,从而形成沿晶界的阳极溶解通道[17-18]。随淬火速率减小,粗大平衡相在晶界析出,尺寸增加且不均匀,析出相的Zn和Mg含量增加,同时PFZ宽化,这亦会促进晶界溶解的发生,导致晶间腐蚀的发生,降低合金的抗晶间腐蚀能力。
4 结论
1) 随着淬火速率的减小,晶间腐蚀深度增加,淬火速率从960 ℃/s减小至1.8 ℃/s,腐蚀等级从3级增加至4级,最大腐蚀深度和平均腐蚀深度从71.6 μm和60.3 μm分别增加至174.2 μm和157.9 μm。
2) 随着淬火速率的减小,晶界析出相的尺寸增加,晶界析出相的相间距增加,晶界PFZ宽度也相应增大,晶界析出相的Zn含量增加最快,Mg含量的增加次之,Cu含量的增加最慢。淬火速率从960 ℃/s减小至1.8 ℃/s,晶界淬火析出相的尺寸及PFZ宽度从24.3 nm和23.7 nm分别增加至94.5 nm和97.8 nm,从而导致晶间腐蚀深度增加。
REFERENCES
[1] LIU S D, LI C B, ZHANG X M. Effect of natural aging on quench-induced inhomogeneity of microstructure and hardness in high strength 7055 aluminum alloy[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2015, 625(3): 34-43.
[2] LI C B, LIU S D, ZHANG X M. Effect of Zener-Hollomon parameter on quench sensitivity of 7085 aluminum alloy[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2016, 688(12): 456-462.
[3] ZHANG X M, LIU W J, LIU S D. Effect of processing parameters on quench sensitivity of an AA7050 sheet[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2011, 528(3): 795-802.
[4] ZHANG Y. Quench sensitivity of 7xxx series aluminium alloys[D]. Melbourne: Monash University, 2014.
[5] 张新明, 刘胜胆, 刘 瑛. 淬火速率和锆含量对7055型铝合金晶间腐蚀的影响[J]. 中南大学学报(自然科学版), 2007, 38(2): 181-185.
ZHANG Xin-ming, LIU Sheng-dan, LIU Ying. Influence of quench rate and zirconium content on intergranular corrosion of 7055 type aluminum alloy[J]. Journal of Central South University (Science and Technology), 2007, 38(2): 181-185.
[6] 张 翀, 张新明, 刘胜胆. 轧制变形对7A55铝合金晶间腐蚀的淬火敏感性的影响[J]. 矿冶工程, 2007, 27(6): 69-71.
ZHANG Chong, ZHANG Xin-ming, LIU Sheng-dan. Effect of rolling deformation on quench sensitivity relative to intergranular corrosion of 7A55 aluminum alloy[J]. Mining and Metallurgical Engineering, 2007, 27(6): 69-71.
[7] LIU S D, CHEN B, LI C B. Mechanism of low exfoliation corrosion resistance due to slow quenching in high strength aluminium alloy[J]. Corrosion Science, 2015, 91(11): 203-212.
[8] LIU S D, LI C B, ZHANG X M. Influence of grain structure on quench sensitivity relative to localized corrosion of high strength aluminum alloy[J]. Materials Chemistry and Physics, 2015, 167(10): 320-329.
[9] 李芳芳. 预变形及淬火介质对高强铝合金抗晶间腐蚀性能的影响[J]. 湖南冶金职业技术学院学报, 2009, 9(4): 22-25.
LI Fang-fang. Effect of pre-deformation and quenching agent on intergranular corrosion resistance of high-strength aluminum alloys[J]. Journal of Hunan Metallurgical Professional Technology College, 2009, 9(4): 22-25.
[10] 李承波, 张新明, 刘胜胆. 7085铝合金剥落腐蚀的淬火敏感性[J]. 材料研究学报, 2013, 27(5): 454-460.
LI Cheng-bo, ZHANG Xin-ming, LIU Sheng-dan. Quench sensitivity relative to exfoliation corrosion of 7085 aluminum alloy[J]. Chinese Journal of Materials Research, 2013, 27(5): 454-460.
[11] CHEN S Y, CHEN K H, PENG G S. Effect of quenching rate on microstructure and stress corrosion cracking of 7085 aluminum alloy[J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2012, 22(1): 47-52.
[12] 宋丰轩. 7050铝合金厚板局部腐蚀敏感性研究[D]. 长沙: 中南大学, 2014.
SONG Feng-xuan. Investigation on susceptibility to the localized corrosion of aluminium 7050 thick plate[D]. Changsha: Central South University, 2014.
[13] HHUANG L P, CHEN K H, LI S. Influence of high- temperature pre-precipitation on local corrosion behaviors of Al-Zn-Mg alloy[J]. Scripta Materialia, 2007, 56(4): 305-308.
[14] KNIGHT S P, BIRBILIS N, MUDDLE B C. Correlations between intergranular stress corrosion cracking, grain- boundary microchemistry, and grain-boundary electrochemistry for Al-Zn-Mg-Cu alloys[J]. Corrosion Science, 2010, 52(12): 4073-4080.
[15] 刘文军. Al-Zn-Mg-Cu 铝合金淬火析出行为及淬火敏感性研究[D]. 长沙: 中南大学, 2011.
LIU Wen-jun. The research about the quench induced precipitation and quenching sensitivity of Al-Zn-Mg-Cu alloys[D]. Changsha: Central South University, 2011.
[16] LI C B, LIU S D, ZHANG X M. Response of microstructure in high strength aluminum alloy to Graff Sargent etchant[J]. Material Science Forum, 2016, 877(11): 508-513.
[17] SONG F X, ZHANG X M. The effect of quench rate and overageing temper on the corrosion behavior of AA7050[J]. Corrosion Science, 2014, 78(1): 276-286.
[18] SONG F X, ZHANG X M. The effect of quench transfer time on microstructure and localized corrosion behavior of 7050-T6 Al alloy[J]. Materials and Corrosion, 2014, 65(10): 1007-1016.
Influence of quenching rate on intergranular corrosion of novel high strength and toughness automobile aluminum alloys
LI Cheng-bo1, 2, DENG Yun-lai1, TANG Jian-guo1, LI Jian-xiang2, ZHANG Xin-ming1
(1. School of Materials Science and Engineering, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China;
2. Guangdong Hoshion Industrial Aluminium Co., Ltd., Zhongshan 528463, China)
Abstract: The influence of quenching rate on intergranular corrosion of novel high strength and toughness automobile aluminum alloys was investigated by intergranular corrosion experiments, scanning electron microscopy(SEM) and transmission electron microscopy(TEM). The results show that, when the quenching rate decreases from 960 ℃/s to 1.8 ℃/s, the size of the precipitates on the grain boundary and the width of precipitate free zone (PFZ) increase from 24.3 nm to 94.5 nm and 23.7 nm to 97.8 nm, respectively. In addition, the corrosion grade increases from 3 grade to 4 grade. The maximum corrosion depth and average corrosion depth increase from 71.6 μm to 174.2 μm and 60.3 μm to157.9 μm, respectively. The element contents of grain boundary precipitates are also altered during the quenching rate changing. That is to say, the increasing of Zn content is the fastest, followed by Mg content, and the increase of Cu content is the slowest, which results in the deepening of intergranular corrosion depth.
Key words: aluminum alloy; quenching rate; precipitate free zone; intergranular corrosion
Foundation item: Project(2016YFB0300900) supported by the National Key Research and Development Plan of China; Project(51474240) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China; Project(2016A1001) supported by the Zhongshan City Science and Technology Bureau Major Special Project, China
Received date: 2018-05-20; Accepted date: 2018-07-19
Corresponding author: LI Cheng-bo; Tel: +86-731-88830265; E-mail: csulicb@qq.com
(编辑 龙怀中)
基金项目:国家自然科学基金资助项目(51474240);国家重点研发计划资助项目(2016YFB0300900);中山市科技局重大专项项目(2016A1001)
收稿日期:2018-05-20;修订日期:2018-07-19
通信作者:李承波,讲师,博士;电话:0731-88830265;E-mail:csulicb@qq.com