文章编号:1004-0609(2011)09-2182-08
316L不锈钢/Cu梯度复合材料的残余热应力分布
胡 锐, 刘 涛, 薛祥义, 常 辉, 寇宏超, 李金山
(西北工业大学 凝固技术国家重点实验室,西安 710072)
摘 要:为了得到合理的316L不锈钢/Cu 梯度复合材料结构,基于316L不锈钢/Cu复合材料的微观组织与宏观结构建立相应的单胞模型和复合材料模型,并采用有限元软件ANSYS对两种模型进行残余热应力的数值模拟,分析复合材料内的等效应力和主应力的分布规律。结果表明:对于单胞模型,残余热应力分布形态不仅与不锈钢球溶解程度相关,而且与其溶解形态也有关系,并且随着不锈钢的溶解,平均等效应力的大小分布发生了转移,较大的平均应力从基体转移到了增强体。对于复合材料模型,随着不锈钢球的溶解,梯度复合区内的等效应力呈梯度减小分布,表现为平滑的应力过渡,因此,可以在复合区与铜相接连处得到缓和的热应力分布。
关键词:梯度复合材料;微观组织;热应力;有限元分析
中图分类号:TB331;TG141 文献标志码:A
Distribution of residual thermal stress
in 316L stainless steel/Cu graded composite material
HU Rui, LIU Tao, XUE Xiang-yi, CHANG Hui, KOU Hong-chao, LI Jin-shan
(State Key Laboratory of Solidification Processing, Northwestern Polytechnical University, Xi’an 710072, China)
Abstract: In order to get a reasonable 316L stainless steel /Cu graded composite structure, the cell and composite finite element models based on the actual microstructure and macrostructure of 316L stainless steel/Cu composite material were established to analyse the residual thermal stress. This analysis was based on the commercial finite element software ANSYS. The distributions of von Mises effective stress and principal stress in composite were presented. The results show that, in the cell model, the distribution of residual thermal stress in composite material is not only concerned with the dissolution degree, but also with the morphology of stainless steel balls, and the distribution of average von Mises effective stress shifts and the reinforcement sustains the larger stress than the matrix with the dissolution of stainless steel balls. In the composite model, the von Mises effective stress is gradually reduced in graded areas of composite material, showing a relatively smooth transition of stress, so the thermal stress between composite material and copper can be released by the gradient of dissolved stainless steel balls.
Key words: functional graded material; microstructure; thermal stress; finite element analysis (FEM)
应用于热交换器的高导热纯铜管与316L不锈钢隔板之间存在着热膨胀系数的差异,因此,在冷热循环过程中,316L不锈钢/Cu界面上会产生较大结构应力和热应力[1],制约了交换器管件的使用寿命。采用316L不锈钢/Cu梯度复合材料,通过成分与结构的梯度变化使复合材料物理性能呈渐变状态,从而使两种材料之间因膨胀系数差而产生的热应力得到很好的缓释[2-4]。这种具有梯度结构设计特点的非均质复合材料,在化工、核能热交换器上可望获得广泛的应用。
目前,梯度材料的结构设计主要集中在改变组分之间从增强体到基体的比例分布上[5-9],但这些方法并不改变增强体与基体的界面形貌。当增强体和基体均为金属时,通过增强体在基体中的溶解,改变其溶解界面的成分与微结构变化,来获得一种具有特殊宏观梯度特征、良好的界面结合和避免粉末冶金缺陷[10-12]的梯度复合材料不失为一种有效的方法。本研究以316L不锈钢球与铜两种可溶解的金属材料为研究对象,分析在制备过程中不锈钢的溶解行为与残余热应力的关系。
对于复合材料的热应力分析,使用有限元法对单胞模型的分析是最有效的一种[13],但是,这种以一些规则图形作为嵌入颗粒的单胞模型无法准确地描述实际的应力分布情况。因此,本文作者以316L不锈钢/Cu 梯度复合材料的实际微观组织为模板,建立基于视场的胞元模型,对材料从加工温度到室温的残余热应力进行了深入分析,为316L不锈钢/Cu 梯度复合材料的应用提供依据。
1 实验
图1所示为梯度复合材料使用位置及其结构。
材料的制备方法为无压浸渗法,通过纯铜(Cu含量由Cu:316L不锈钢=1:1确定)浸渗自由堆垛的316L不锈钢球而得到。材料的基体为具有不锈钢析出的Cu合金,增强体为316L不锈钢。316L/Cu复合区的微观组织如图2所示。从图2中可以看出,316L不锈钢的溶解程度随着距离铜端的增大而减小。复合区中的316L不锈钢的形态及分布演变特征为:从靠近不锈钢端边缘溶解的树枝状形态(见图2(b)),演变为大量树枝与部分颗粒的混合形态(见图2(c)), 最后演变为靠近铜端的完全溶解的颗粒形态(见图2(d))。因此,可以由不锈钢在铜中逐渐溶解来实现复合材料的结构变化梯度和成分变化梯度,从而得到一种新的自然梯度结构。
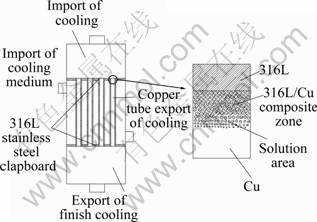
图1 梯度复合材料使用位置及其结构
Fig.1 Structure and location of graded composite material

图2 316Lp/Cu复合材料在不同溶解情况下的形貌
Fig.2 Microstructures of 316Lp/Cu composite material with different stainless steel dissolved: (a) 4-5 mm from interface of composite zone and copper; (b) 3-4 mm from interface of composite zone and copper; (c) 2-3 mm from interface of composite zone and copper; (d) 1-2 mm from interface of composite zone and copper
2 以微观组织为模板的有限元分析
2.1 胞元模型
模拟所选的金相样本分别为图2中各个位置所选的单个不锈钢球溶解形貌,其位置为线框所选处。
胞元模型是以图2形貌为基础画出1/4钢球模型,基体部分将采取平均化处理如,结果图3所示。
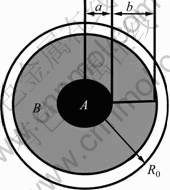
图3 平均化处理示意图
Fig.3 Schematic diagram of average method
根据图3所示结构,由
 (1)
(1)
解得R0=1.105(a+b)。
将球体间隙的基体体积等效为内径为a+b、外径为R0的一个球壳,未溶解区为A区域,溶解区为B区域,并以面心排布计算。然后,依据图2所示不锈钢的溶解形貌建立胞元模型,如图4 (a)~(c)所示。对比分析表明,316L不锈钢球的溶解形貌轮廓与金相照片中的形貌是非常相似的。在设置有限元单元类型时,采用平面应力单元,其网格模型如图4 (e)~(g)所示。本研究中材料的真实表面残余应力是利用X射线衍射法对所制备的316Lp/Cu复合材料测试得到。首先确定试样测试区域尺寸为10 mm×10 mm×10 mm,其次对试样进行预处理、进行研磨、抛光、去除表面应力,最后进行X射线应力测试。

图4 胞元模型及网格模型
Fig.4 Cell model and meshed model for simulation: (a) Zone 1, for cell model; (b) Zone 2, for cell model; (c) Zone 3, for cell model; (d) Zone 1, for meshed model; (e) Zone 2, for meshed model; (f) Zone 3, for meshed model
2.2 边界条件
作为1/4球形模型,其在膨胀变形时,扇形的两个直角边在各自的垂直方向的位移为零,而其外弧边为自由边界。由于在铜凝固前基体与增强体不产生热应力,因此所加载荷的温度范围选为25~1 080 ℃。
2.3 材料参数
复合材料由316L不锈钢和具有不锈钢析出的Cu合金组成,在计算中两者均视为弹塑性体。由于常温下不锈钢的主要元素Fe和Cr在Cu中固溶度几乎为零,因此,可以将铜合金中析出物以原不锈钢成分计算。根据Fe-Cu二元相图在浸渗温度1 200 ℃下的溶解度得出溶解于Cu中Fe的含量,从而由316L不锈钢化学式计算出常温下析出的316L含量。从而铜合金的物性参数可利用Reuss法则[14]计算,如下所示:
E (z) = Cg{ECuφCu+E316L(1-φCu)}+
(1-Cg)/{φCu/ECu+(1-φCu)/E316L} (2)
α(z) = (αCu KCuφCu +α316L K316Lφ316L)/
(KCuφCu+K316Lφ316L) (3)
λ (z) = (λCu KCuφCu+λ316LK316Lφ316L)/
(KCuφCu+K316Lφ316L) (4)
v (z) = v316Lφ316L+vCuφCu
K=E/[2(1-v)] (5)
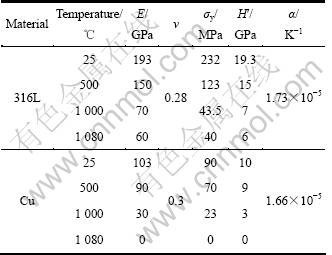
式中:E(z)、α(z)、λ(z)、v (z)和K 分别为弹性模量、线膨胀系数、热导率、泊松比和体弹性模量,Cg 为经验常数,取0.5;φ为体积分数;E为弹性模量;ν为泊松比;α为热膨胀系数。材料的其他参数如表1所列,其中σy为屈服强度;H′为硬化模量。
表1 材料参数
Table 1 Material parameters
2.4 数据处理
为了更宏观地描述复合材料的平均应力,采用如下公式[12]对所得到的模拟数据进行处理:
 (6)
(6)
式中:σ为平均应力;V为胞元单元体积;V k为胞元中的第k个单元体积;σk为第k个单元的平均应力;N为胞元总单元数。下标c代表复合材料,m代表基体,p代表增强体。
3 模拟结果及其分析
3.1 等效应力及其分布规律
根据图2建立不同溶解情况的单胞模型,如图3所示,计算材料由1 080 ℃降到25 ℃时的等效应力分布规律并将计算结果分为基体与增强体两部分列出。图5所示为基体Cu合金的等效应力分布,图6所示为增强体316L的等效应力分布。
从图5中可以看出,基体的等效应力分布并不均 匀,其较大应力主要集中在基体与增强体的界面周围。1区和2区的较大应力区域较广且呈梯度形式分布,3区的较大应力并没有像1区和2区那样在基体内形成大面积的较大应力区,而只是在基体与溶解增强体的界面处形成较小的梯度分布。从图6可以看出,高应力的区域主要集中在不锈钢溶解的部位,最大应力 同样出现在界面处,且主要集中在不锈钢球间接触区以及边界曲线的曲率半径较小处。根据式(6)计算基体、增强体和复合材料整体的平均应力,结果如图7 所示。
从图7可以看出,基体的平均等效应力随着不锈钢球溶解程度的增加而减小,而增强体与复合材料的平均等效应力随着不锈钢的溶解而增加,但复合材料的增幅范围并不大。
从上述分析可知,随着不锈钢球的溶解,平均等效应力的大小分布发生了转移,较大的平均应力逐渐从基体转移到增强体上。因此,在材料强度的薄弱处(复合区与铜端的界面即钢球溶解程度最大处),大应力集中在较高强度的增强体上,从而减小了材料的失效概率。
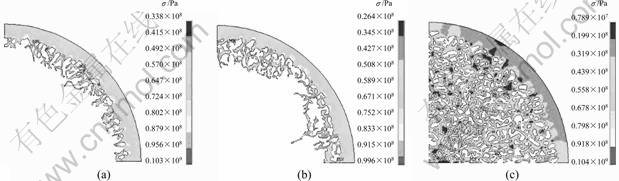
图5 基体的等效应力
Fig.5 von Mises effective stresses of matrix: (a) Zone 1; (b) Zone 2 ; (c) Zone 3

图6 增强体的等效应力
Fig.6 von Mises effective stresses of reinforcement: (a) Zone 1; (b) Zone 2; (c) Zone 3
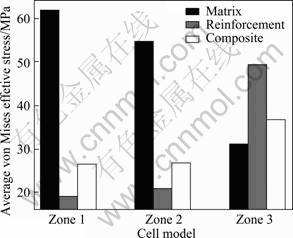
图7 基体、增强体和复合材料整体的等效平均应力
Fig.7 Average von Mises effective stress of matrix, reinforcement and composite
3.2 整体结构的等效应力及热应力分布规律
由于胞元模型不能从宏观上反映316L/Cu复合材料内部的应力分布情况,因此,需要建立一个与复合材料结构相似的整体模型来分析。根据试验所得到的真实复合材料结构,建立有限元模型,其中上端为未溶解部位,下端为完全溶解端,中间为溶解过渡区,在此分析中,为了简化计算将发生溶解的不锈钢球外圆部分使用Reuss法则等效为一个整体。等效部分的材料参数是通过将图4中胞元模型溶解部分以整体替换,改变316L不锈钢与铜合金比例并结合前面单胞模型计算结果来近似确定。图8所示为其整体模型及网格模型。
图9所示为316L/Cu复合区从1 080 ℃降到25 ℃时的等效应力分布规律。由图9可见,溶解区的钢球内部整体上表现为较低的应力状态,而未溶解区的钢球内部,其应力呈梯度分布,最大应力出现在接触区。在溶解区的基体内应力同样整体较小,而未溶解区的基体内部在钢球之间间隙较大处应力值较小,间隙较小处应力值较大并在钢球接触处出现最大应力值。与不考虑钢球溶解的情况相比,在从溶解区到铜端的过渡部位,钢球内部的应力和钢球之间铜基体的应力得到降低。这种低应力分布能够使得复合区与铜端呈现更为平滑的应力过渡,从而保证了铜端与复合区的良好结合。
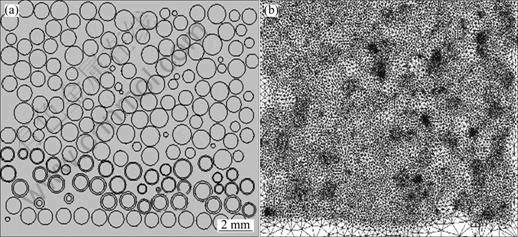
图 8 复合材料模型和网格模型
Fig.8 Composite model (a) and mesh model for simulation (b)
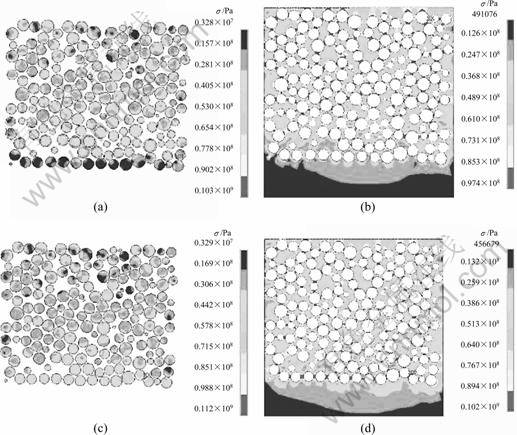
图9 复合材料基体的等效应力
Fig.9 von Mises effective stresses of copper and stainless steel in composite: (a) Copper with stainless steel dissolved, (b) Stainless steel with stainless steel dissolved; (c) Copper with stainless steel undissolved, (d) Stainless steel with stainless steel undissolved
图10所示为316L/Cu复合区的主应力σ22和σ11。从图10可以看出,热应力在钢球与钢球接触处出现最大值,表现为拉应力或压应力。对复合区中σ22的观察可以发现,铜基体内部与钢球内部的应力都表现为拉应力。根据式(6),计算此时铜基体内的σ22平均应力为8.6 MPa,同理,计算钢球内的σ22平均值为30.43 MPa。而对于σ11,发现其分布与σ22的不同,σ11在铜基体内部主要表现为压应力,而在钢球内部主要表现为拉应力。计算铜基体内σ11的平均值为-4.5 MPa,钢球内σ11的平均值为8.87 MPa。根据静水应力的计算公式可知,铜基体的静水应力为2.05 MPa,表现为拉应力,钢球的静水应力为19.65 MPa,也表现为拉应力。由于应力三轴度是静水应力与等效应力的比值,因此,静水应力所表现的拉压性质就决定了三轴度的拉压性质,从而决定了材料的潜在失效危险[15]。从上面分析可知,材料失效的潜在危险主要集中在强度较高的钢球内,这有助于避免材料内部裂纹的萌生,从而减小材料失效的概率。
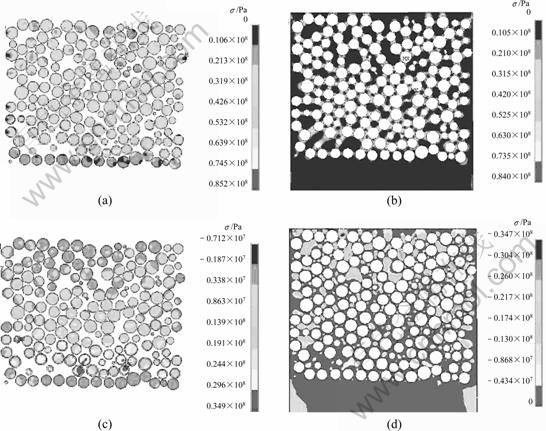
图10 复合材料的主应力σ22和σ11
Fig.10 Principal stress in composite: (a) σ22 of stainless steel; (b) σ22 of copper; (c) σ11of stainless steel; (d) σ11 of copper
3.3 复合区残余应力的测定与模拟验证
试验是通过测定X射线衍射峰2θ角相对位移来测算材料内部的应力大小。所测试对象为Cu的[420]晶面,扫射偏移角度分别为0°、15°、30°和45°。
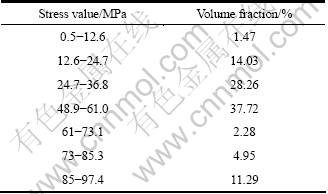
检测的sin2Ψ与衍射角2θ关系如图11所示。 通过数据处理,得出铜内的平均应力为71.32 MPa。而对于模拟的316L/Cu复合区,基体平均应力值分布如表2所列。
根据式(6)计算其平均应力为47.9 MPa。计算的平均应力值比检测的平均应力值71.32 MPa小23.66 MPa。而从应力值分布最多的48.9~61 MPa来看,其数值与所检测的数值比较接近。这是因为在分布面积较大的应力值范围内,其X衍射线强度较高,而在分布面积较小的应力值范围内,其X衍射线强度较弱,不能很好地体现出来,因而导致检测数值相对计算值较大。通过以上分析,说明计算模拟的数值是可信的。
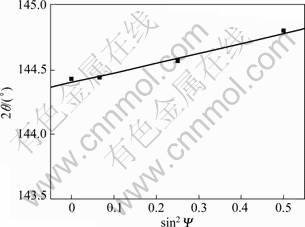
图11 sin2Ψ和衍射角2θ的关系
Fig.11 Relationship between sin2Ψ and 2θ
表2 复合区基体等效应力值分布
Table 2 Distribution of average von Mises effective stresses in matrix of composite zone
4 结 论
1) 复合材料内部残余应力分布形态不仅与不锈钢球的溶解程度有关,而且与不锈钢球的溶解形态有关;随着不锈钢球的溶解,平均等效应力的大小分布发生了转移,较大平均应力从基体转到了增强体。
2) 316L/Cu复合材料内部不仅存在拉应力区,而且存在不同程度和不同范围的压应力区,失效的潜在危险主要集中在强度较高的钢球上。
3) 随着不锈钢球的溶解,从与纯铜连接的末端界面处开始,梯度复合区内的等效应力呈梯度减小分布,呈现较为平滑的应力过渡,钢球的梯度溶解可实现复合区与单相铜之间的热应力缓释。
REFERENCES
[1] 汪建平, 金伟娅, 汪秀敏, 高增梁. 基于有限元分析管壳式换热器拉脱力的研究[J]. 核动力工程, 2008, 29(6): 58-61.
WANG Jian-ping, JIN Wei-ya, WANG Xiu-min, GAO Zeng-liang. Study on pull-out force in tube-and-shell heat exchangers with finite element method[J]. Nuclear Power Engineering, 2008, 29(6): 58-61.
[2] TOKITA M. Development of large-size ceramic/metal bulk FGM fabricated by spark plasma sintering [J]. Materials Science Forum, 1999, 308: 83-88.
[3] LIEW K M, HE X Q, KITIPORNCHAI S. Finite element method for the feedback control of FGM shells in the frequency domain via piezoelectric sensors and actuators[J]. Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering, 2004, 193(3): 257-273.
[4] 王 豫, 姚凯伦. 功能梯度材料研究的现状与将来发展[J] . 物理, 2000, 29 (4): 206-211.
WANG Yu, YAO Kai-lun. State of the art and future development of functionally graded materials[J]. Physics, 2000, 29(4): 206-211.
[5] ZHANG Guo-bing, GUO Quan-gui, WANG Kun-jie, ZHANG Hua, SONG Yan, SHI Jing-li, LIU Lang. Finite element design of SiC/C functionally graded materials for ablation resist ance application [J]. Mater Sci Eng A, 2008, 488: 45-49.
[6] 徐金富, 张学彬, 费有静, 张亚非, 吴海飞, 叶以富. MoSi2/不锈钢连接梯度过渡层的残余应力[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2007, 17(6): 934-939.
XU Jin-fu, ZHANG Xue-bin, FEI You-jing, ZHANG Ya-fei, WU Hai-fei, YE Yi-fu. Residual stress in graded interla- yer of MoSi2/316L stainless steel joining[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2007, 17(6): 934-939.
[7] CANNILLO V, MONTORSI M, SILIGARDI C, SOLA A, de PORTU G, MICELE L, PEZZOTTI G. Microscale computational simulation and experimental measurement of thermal residual stresses in glass–alumina functionally graded materials [J]. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2006, 26: 1411-1419.
[8] XU Jin-fu, WU Hai-fei, ZHANG Xue-bin, FEI You-jin, YE Yi-fu, LI Wen. Simulation and analysis of residual stress in the graded interlayer of MoSi2 composite/316L stainless steel joint[J]. Journal of Materials Engineering and Performance, 2008, 17(6): 802-807.
[9] CHEN Fu-yi, JIE Wan-qi. Finite element design of MgO/Ni system functionally graded materials [J]. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 2007, 182: 181-184.
[10] 杨中民, 田 丰, 张联盟. 有连续组分的Ti2Mo系梯度材料的制备[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2002, 12( S1): 214 -217.
YANG Zhong-min, TIAN Feng, ZHANG Lian-meng. Fabrication of Ti2Mo functionally graded material with smoothly varying composition[J].The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2002, 12( S1): 214 -217.
[11] 方海生, 陈义良, 杜卓林, 章明宇, 黄 庆. 功能梯度材料制备过程影响因素的数值研究[J]. 材料科学与工程学报, 2003, 21(4): 469- 474.
FANG Hai-sheng, CHEN Yi-liang, DU Zhuo-lin, ZHANG Ming-yu, HUANG Qing. Numerical study on influencing factors of functionally graded material during casting[J]. Journal of Materials Science and Engineering, 2003, 21(4): 469-474.
[12] 胡昌义, 邓建国, 高逸群. CVD铱涂层/Re基复合喷管研究进展宇航[J]. 材料工艺, 1998(3): 7-10.
HU Chang-yi, DENG De-guo, GAO Yi-qun. The development of CVD iridium-coated rhenium thruster[J]. Aerospace Materials and Technology, 1998(3): 7-10.
[13] 张 鹏, 李付国. SiC颗粒增强铝基复合材料的热循环行为研究[J]. 稀有金属材料与工程, 2009, 38(9): 1929-1934.
ZHANG Peng, LI Fu-guo. Thermal cycling behavior of aluminum matrix composites reinforced with SiC particles[J]. Rare Metal Materials and Engineering, 2009, 38(9): 1929-1934.
[14] GASIK M M. Micromechanical modeling of functionally graded materials [J]. Computational Materials Science, 1998, 13: 42-55.
[15] SHEN H, LISSENDEN C J. 3D finite element analysis of particle-reinforeced aluminum[J]. Mater Sci Eng A, 2002, 338: 271-281.
(编辑 何学锋)
基金项目:教育部新世纪优秀人才计划资助项目(NCET-07-0690);高等学校学科创新引智计划资助项目(B08040)
收稿日期:2010-08-27;修订日期:2011-04-01
通信作者:胡 锐,教授,博士; 电话:029-88491764;E-mail: rhu@nwpu.edu.cn