
J. Cent. South Univ. (2018) 25: 3052-3061
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-018-3973-7
Comparative experiments on electro-osmotic treatment effect of polluted soil using EKG and iron electrodes
ZANG Jun-chao(臧俊超)1, 2, ZHENG Ling-wei(郑凌逶)1, 2, XIE Xin-yu(谢新宇)1, 2,WANG Heng-yu(王恒宇)2, LIU Yi-min(刘亦民)1, 2, PANG Jie(庞杰)1, 2
1. Research Center of Coastal and Urban Geotechnical Engineering, Zhejiang University,Hangzhou 310058, China;
2. Ningbo Institute of Technology, Zhejiang University, Ningbo 315100, China
 Central South University Press and Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer Nature 2018
Central South University Press and Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer Nature 2018
Abstract: This study presents a comprehensive comparison of the electro-osmosis treatments of heavy metal contaminated soil using electrokinetic geosynthetics (EKG) and iron electrodes in terms of both theoretical analysis and experimental research. The variation in the electrical parameters was analyzed, and the results show linear relationships between temperature and conductivity and between the soil and pore water conductivities. The average cathode contact resistance of iron is 60% smaller than that of EKG, whereas the average anode contact resistance of EKG is 56% smaller than that of iron. The values of the power consumption per unit mass of contaminants for EKG and iron are 1.895 and 1.989 kJ/g, respectively. After electro-osmosis, the number of soil pores increased, but the average area decreased, with an average area of 0.9100–1.0504 μm2. Based on microstructure analysis, we obtained higher electroosmotic efficiency and realized the effective analysis and utilization between macroscopic and microscopic parameters.
Key words: EKG; contaminated soil; electrical conductivity; ion transport; microstructure
Cite this article as: ZANG Jun-chao, ZHENG Ling-wei, XIE Xin-yu, WANG Heng-yu, LIU Yi-min, PANG Jie. Comparative experiments on electro-osmotic treatment effect of polluted soil using EKG and iron electrodes [J]. Journal of Central South University, 2018, 25(12): 3052–3061. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-018-3973-7.
1 Introduction
With accelerated urbanization, human activities have an increasing impact on the environment. Pollutants such as domestic waste, waste from the chemical industry and sewage irrigation have certain impacts on soil. As these soils have been developed for particular uses, their reinforcement characteristics significantly differ from those of ordinary soil. The electro-osmotic method is based on the movement of moisture in a porous capillary medium under the action of an electric field [1–3]. KANIRAJ et al [4] performed a series of electro-osmotic consolidation experiments on organic soil and found that it was considerably different from normal clay.
The ionic compositions in contaminated soil are complex and often contain some heavy metal ions. Some previous studies focused on reducing the content of heavy metal ions using electro- osmotic treatment [5–7]. MULLIGAN et al [8] studied technologies for the heavy metal remediation of dredged sediments. Most of the previous studies used metal electrodes, so that some of the soils underwent a chemical reaction with the metal electrode which disturbed the results of ion transport studies and causing poor heavy metal ion reduction. HU et al [9] studied the effect of electric geosynthetic reinforcement of a soft soil foundation. The existing conductive geosynthetics are mostly drainage board attached to copper wire, which has a relatively high contact resistance and potential loss.
To study the heavy metal contaminated soil migration laws more clearly and effectively, this work used stainless steel fiber spunlace nonwovens as the electrode material which will not undergo ion reaction with contaminated soil.
This research studied the properties of electrokinetic geosynthetics (EKG) and metal electrodes, the relationship between soil electrical conductivity and temperature, and the microstructure of soil and EKG materials. The research results of new EKG materials are of great significance to the drainage consolidation theory and applications of contaminated soil [10, 11].
2 Test preparation
2.1 Soil and electrode material
Soil samples were collected from the foundation pits at Shangtang Road and Huzhou Street, Hangzhou, China. The original soil samples were saturated mucky clay with a little organic matter. The depth of the soil was about 2 m. The clay was dried, crushed and ground into powder, and the concentration of heavy metals (analytical pure of Cu(NO3)2·3H2O) was 3000 mg/kg (the ratio of heavy metal to dry soil mass). The mixtures were homogenized and allowed to stand for 24 h.
Table 1 Basic properties of silt clay

The EKG electrode used in the experiment was made of stainless steel fiber spunlace. The surface density was 155.7 g; the thickness was 0.835 mm; the maximum pore size was 244.83 μm; the average pore diameter was 51.76 μm; and the resistivity was 0.012 Ω·m. The microstructure of the EKG electrode was analyzed using scanning electron microscopy before the experiment [12].
2.2 Installation and test procedures
As shown in Figure 1, the plexiglass cylinder had a diameter and height of 28.5 cm and 14.1 cm, respectively [13]. The bottom of the cylinder had a drilled hole to connect the cylinder to the water bottle through a bolt and catheter, which was used to collect the water discharged from the cathode. During the test, the water discharged from the cathode was sampled with a needle tube and filtered to prepare the samples that were used to test the conductivity and content of heavy metal ions. During the test, we replaced the water-collecting flask under the drainpipe at regular intervals and measured the conductivity of the pore water using the LAQUA conductivity meter. The real-time temperature data of the anodes, cathodes and middle of the soils were collected using temperature sensor.
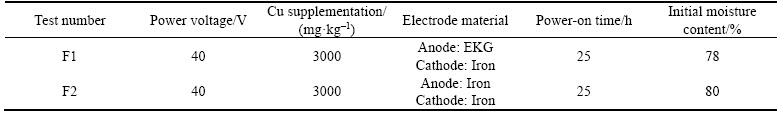
For EKG electrode testing, the improved geotextile placed on the inside of the plexiglass box acted as the anode, and the metal tube fixed in the middle of the cylinder acted as the cathode. For iron electrode testing, an iron sheet with a height of 14.1 cm and a length of 91 cm was placed on the inside of the plexiglass box as the anode. After the soil was placed into the cylindrical test device layer by layer and the plexiglass cover was attached, six fine wire probes were inserted into the potential test holes. The basic experimental conditions of the EKG and iron specimens are shown in Table 2.
After the test, soil samples were collected from the anode, cathode and middle area. The soil element sampling points are shown in Figure 1. The moisture in the soil samples was removed by freeze drying, and small specimens were prepared for microstructure observation in a liquid nitrogen atmosphere. The surface of each sample was treated by depositing a thin layer of gold and teach sample was placed into a scanning electron microscope for observation and analysis. Quantitative studies of the microstructure were conducted using Image J [14].
3 Test results analysis
3.1 Comparison of basic electrical parameters of electro-osmosis
In practical engineering, the energy consumption of electro-osmosis is used as the most important evaluation index that accounts for the cost because this energy consumption will vary widely under different conditions. The contact resistance, energy consumption coefficient and unit displacement energy consumption were studied to obtain the electrical characteristics of the different electrode materials.
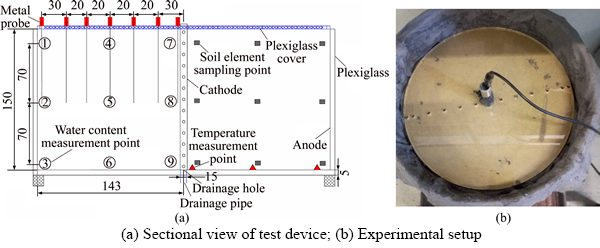
Figure 1 Photos of test device:(Unit: mm)
Table 2 Basic experiment conditions of EKG and iron
3.1.1 Contact resistance
This study found that the cathode average contact resistances of iron and EKG are 4.2–10.3 Ω and 7.3–32 Ω, respectively, showing that the contact resistance of iron is 60% smaller than that of EKG. The current of the EKG electrode is smaller than that of the iron electrode in the late stage because the EKG had a larger contact resistance. This study found that the anode average contact resistance of EKG is 56% smaller than that of iron, with values of 2.5–5.8 Ω and 4.9–21 Ω for EKG and iron, respectively. The EKG electrode is composed of stainless steel fiber spunlace nonwovens that are in full contact with the soil. In the future, by using a hollow cylindrical cathode to reduce the cathode contact resistance, we can increase the contact area between the cathode and the soil of F1 test group to improve the electro- osmosis efficiency.
As shown in Figure 2, in the process of electro-osmosis, the temperature of the contact surface between the electrode and soil is always high. The average temperatures of the soil at the cathode and anode for the iron electrode are 48.47 and 26.98 °C, respectively, and those for the EKG electrode are 39.75 and 27.15 °C, respectively. Comprehensive analysis of the contact resistance shows that the contact resistance at the cathode is greater than that at the anode for both EKG and iron. During the test, the soil temperatures at the anode and cathode are proportional to the resistance data analyzed above because of the large amount of energy consumed by heat production.
3.1.2 Coefficient of energy consumption
As shown in Figure 3, the EKG electrode has a lower coefficient of energy consumption than the iron electrode, which increases greatly at approximately 18 h. The growth rate of the energy consumption for the iron electrode is 73% with a final displacement of 91.3%. In contrast, the growth rate of the energy consumption for the EKG electrode is 60% with a final displacement of 94.6%, which indicates a decrease in the electro-osmotic efficiency. In an actual project, the electro-osmotic time must be controlled to achieve the best reinforcement effect.
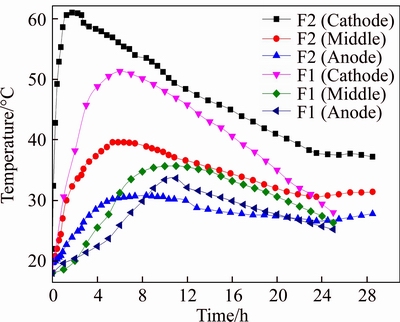
Figure 2 Temperature change versus time during electro- osmosis

Figure 3 Comparison chart of coefficient of energy consumption
Total energy consumption:
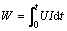 (1)
(1)
Unit drainage energy consumption:
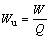 (2)
(2)
where t is the power-on time (h); u is power supply output voltage (V); i is the current in the circuit (A); Q is the total test displacement of each group (mL); W is the total energy consumption (kW·h); Wu is the unit drainage energy consumption (kW·h/L).
3.2 Conductivity relationship derivation
The contact resistance, energy consumption coefficient and unit drainage energy consumption are important electrical parameters that are very closely related to the change in conductivity [15, 16]. Conductivity is one of the most important input parameters for finite element analysis. Thus, the understanding of the conductivity in the process of electro-osmosis has considerable practical significance.
It is assumed that the electrodes are in the form of a circular axially symmetrical arrangement, where ra and rc are the electrode radii of the anode and the cathode, respectively [17]. The soil is assumed to be homogeneous before energization. Assuming that the anode radius is ra, the cathode radius is rc, the cathode field strength is Ec and the electric field strength at a distance from the cathode at the center of r is Er, we obtain the following equation:
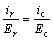 (3)
(3)
where ir and ic are the current density at r and the cathode, respectively. According to the principle of current continuity:
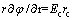 (4)
(4)
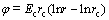 (5)
(5)
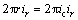 (6)
(6)
These equations indicate that the potential distribution between the cathode and the anode is linearly related to the distance between the cathode poles in the semi-logarithmic coordinates. If the applied voltage is U:
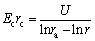 (7)
(7)
 (8)
(8)
Combining Eqs.(7) and (5):
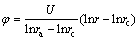 (9)
(9)
The electric current is:
 (10)
(10)
where h is the length of the electrode or the height of the soil:
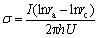 (11)
(11)
In this work, the experimental design indicators are U=40 V, h=0.1 m, ra=0.143 m and rc=0.015 m; substituting these values into the above formula, we obtain σ=0.089I.
3.2.1 Relationship between conductivities of pore water and soil
The conductivity of pore water is one of the main factors that affect the soil conductivity. In the process of electro-osmosis, the electrical conductivity of soil decreases as the pore water in discharged [18]. The pore water conductivity and the soil conductivity are assumed to have a linear relationship.
The conductivity of the pore water was measured using a LAQUA conductivity meter. The soil conductivities in the first 10 h for the specimens with the iron electrode and the EKG electrode were selected in the test. Figures 4 and 5 show the data fitting results of the iron electrode and the EKG electrode, respectively. In these figures, the line is the data fitting result, and the points are the measured conductivity values.

Figure 4 Relationship between conductivity of pore water and soil (iron electrode)
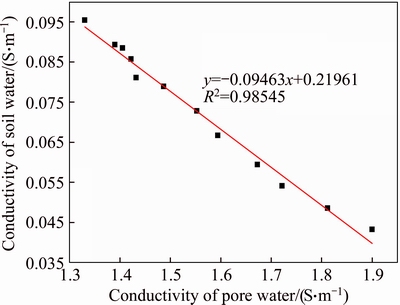
Figure 5 Relationship between conductivity of pore water and soil (EKG electrode)
As shown in Figures 4 and 5, as the heavy metal copper ions were removed, the pore water conductivity gradually increased for both the iron electrode and the EKG electrode. As the water discharge and the contact resistance increased over time, the soil conductivity gradually decreased. The fitting results show that the pore water conductivity and the soil conductivity have a linear relationship and that the R2 values for the EKG and iron electrodes are 0.98545 and 0.97947, respectively. The fitting results can be used to estimate the relationship between the pore water conductivity and soil conductivity.
In this work, the content of copper in the electro-osmotic effluent was measured using inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry (ICP-MS), and the variation rule was consistent with the changes in the conductivity. The final copper content was 0.3 mg/L.
3.2.2 Relationship between soil conductivity and temperature
In this work, the temperature and soil conductivity data over the first 10 h were selected to plot the relationship between soil temperature and soil conductivity. A linear relationship was obtained for the EKG and iron electrodes through piecewise linear fitting using Origin software.
As shown in Figures 6 and 7, in the absence of an electric field, the electrical conductivity in the soil tends to gradually increase with increasing temperature. However, under the action of an electric field, the electrical conductivity gradually decreases. The results show that the content of copper ions in the pore water gradually increased as the water content in the soil gradually decreased over time. These changes resulted in a gradual decrease in the thickness of the electric double layer and a reduction in soil conductivity.
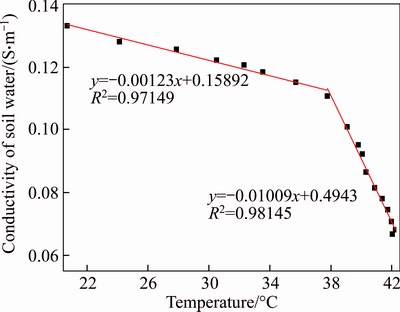
Figure 6 Fitting curve of temperature and conductivity for iron electrode

Figure 7 Fitting curve of temperature and conductivity for EKG electrode
The results show linear fitting relationships between soil temperature and conductivity and between the soil conductivity and pore water conductivity in the process of electro-osmosis. The results are helpful for understanding the change trend of the conductivity under multi-field coupling, which provides a reference regarding the variation in the electrical parameters during electro-osmosis.
3.3 Micro-mechanism analysis of electro-osmosis process
The process of electro-osmosis consists of multi-field coupling of the electric field, seepage field and temperature field. Thus, research on the microcosmic mechanism of electro-osmosis is beneficial for understanding the macroscopic phenomena.
In this work, the ion change in the soil was studied along with the microstructures of the soil and the EKG electrode, and the relationship between microstructure changes and macroscopic characteristics was explored.
Analysis of micro-structural changes can explain the change in conductivity, which is helpful to understand the relationship between temperature and conductivity of soil and pore water. Based on this, we obtain higher electroosmotic efficiency and realize the effective analysis and utilization between macroscopic and microscopic parameters.
3.3.1 Ion transport
The changes in the elemental contents in the soil and the electro-osmotic drainage water were analyzed using ICP-MS; the main conclusions are as follows:
The calcium ion content decreased by 97%, whereas the sodium and potassium ion contents increased by 104% and 262%, respectively. Exchange occurred between different ions, with the following exchange order: Na+++2+< Ca2+2+3+3+. As the sodium ions between the double electric layer and the internal inter-crystal layer are replaced by other ions, the physical properties of the soil change significantly. The results show a consistent distribution pattern of Mg2+/Ca2+ in the soil after the electro-osmosis test, which is higher at the cathode than at the anode.
The removal efficiency and energy consumption of heavy metals in the soil are calculated using the following formula:
1) Calculation of the removal rate
Because the metal ions are accumulated around the cathode eventually, the soil near the cathode will be treated centrally; the copper content in this region would not be taken into account in the final calculation.
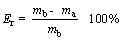 (12)
(12)
where Er is the final removal rate of heavy metals; mb is the quality of heavy metals in the soil added before the test (g); ma is the mass of heavy metals remaining in the soil after the test (g);
2) Calculation of the energy consumption
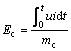 (13)
(13)
where Ec is the energy consumption per unit mass of contaminants (kJ/g); mc is the final removal quality of the contaminants/g;The final removal rates of copper for the EKG and iron electrodes are 38.3% and 33.3%, respectively. According to the measurement data of iron ions, the Fe3+/Fe2+ produced in the anode gather near the anode and a small number of ions migrate to the cathode to form precipitates in the alkaline environment. Combined with the data analysis of the ion test data, some of the copper ions in the soil underwent the following precipitation reaction, with the copper ions gradually concentrating near the cathode:
Cu2++2OH–(aq)→Cu(OH)2↓ (14)
The copper ion content measured in electro- osmotic drainage water at the end of the test is 0.16 mg/L. The migration ability of Fe3+/Fe2+ is weak and has a smaller contribution to the effect of electro-osmosis. Low-order and small ions have stronger migration abilities, resulting in the migration of water molecules, which is the key factor for determining the effect of electro-osmosis [19, 20]. The values of power consumption per unit mass of contaminants for EKG and iron are 1.895 and 1.989 kJ/g, respectively.
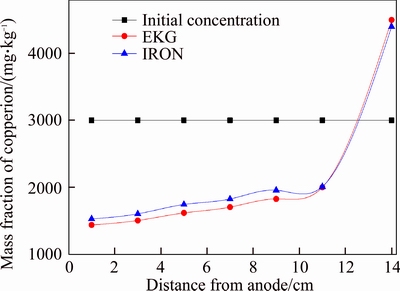
Figure 8 Distribution of copper ion mass fraction in soil
3.3.2 Change of soil microstructure
Quantitative analysis of the porosity distribution and fractal dimension of soil in different positions after electro-osmosis were analyzed [21]. The microcosmic mechanism and the change in the electrical properties of heavy metal contaminated soils are further explored to provide a reference for establishing the relationship between microstructure changes and macroscopic electrical properties. The main parameters selected are apparent porosity (the ratio of the pore area to the total area) and the degree of roundness R0 (which describes the proximity of the object’s trait to a circle) [22].
Image J software is used to denoise the image and to divide the threshold value. After obtaining the binarized image, the main analysis data are shown in Table 3.
The data show that the cohesive clay in the undisturbed soil is mostly characterized by an empty honeycomb structure. The connections between the clay particles are mostly edge-side and edge-face. The pore volume is small without directional arrangement, but the average area is larger with an average of 1.6231 μm2. Under the action of an electric field, the soil after electro- osmosis showed a clump-like structure, and the cementing condition between the soils was obviously improved with the surface-to-surface contact and embedded contact.
After electro-osmosis, the number of pores increased, however, the average area decreased, with an average area value in the range of 0.9100–1.0504 μm2. The roundness of the pores in the soil tended to increase after electro-osmosis, and the apparent porosity decreased by 27%, with some minor differences between the soil microstructure of the EKG and iron electrode.
3.3.3 Change in EKG microstructure
To evaluate the degree of overlap between the stainless steel fibers and analyze the conductive structure of EKG materials quantitatively, this study used the microstructure analysis of cohesive soils as a reference and defined the area of overlap between stainless steel fibers as the “lap joint”.
According to the geotextile fiber conductive model, each stainless steel fiber in the EKG electrode is assumed to have a small resistance. According to the basic electrical principle, if all the resistances are connected in parallel, then the resistance is calculated as follows:
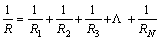 (15)
(15)
After the test, EKG electrodes were cut at different positions on the anode, and the distances from the bottom edge were 1 cm (S2), 7 cm (S3), and 13 cm (S4), respectively. Then, scanning electron microscopy analysis was performed using the QUANTAFEG650 field emission scanning electron microscope.
Table 3 Summary of quantitative analysis of soil micro-parameters
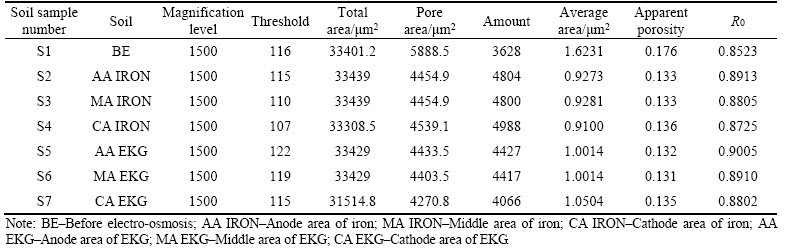
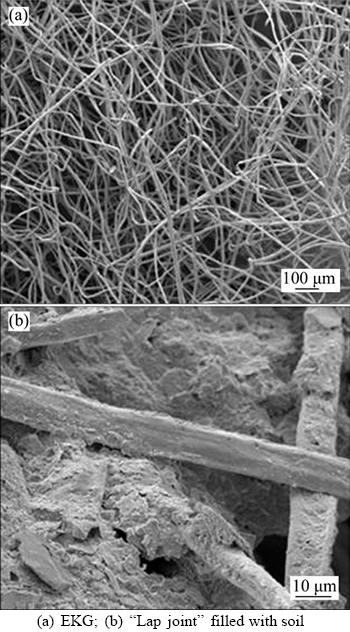
Figure 9 SEM images:
To determine the optimal magnification for the microstructural analysis of EKG electrode materials, this study used the relationship between the soil pores and the geotextile “lap joint” along with the existing research results of the microstructures of cohesive soils. The best magnification for analyzing the EKG electrodes was found to be approximately 200 times based on the inverse ratio of the pore area. Image J software was used to obtain the binarized image, the main analysis data obtained are shown in Table 4.
According to the data analysis and microstructure analysis, the stainless steel fibers are arranged in parallel in the EKG electrode before the electro-osmosis process. The main conductive modes of the stainless steel fibers are in accordance with parallel connections, and the different stainless steel fibers have less overlap with each other.
Compared with the arrangement of the stainless steel fibers and the conductive structure before electro-osmosis, the number of “lap joints” increased. Thus, with more overlap between the stainless steel fibers, the electrical conductivity of the EKG electrode decreased with time. The numbers of “lap joints” in samples S2, S3 and S4 are 514, 267 and 69, respectively, indicating that the conductivity at the bottom of the anodic geotextile significantly decreased. This result is also consistent with the change trend of the soil water content. According to the microstructural analysis, the soil is partially filled with “lap joints” of stainless steel fibers during the electro-osmosis process, forming an agglomerated structure.
4 Conclusions
A comprehensive comparison of the electro-osmosis treatments of heavy metal contaminated soil using EKG materials and iron electrodes is presented in terms of both theoretical analysis and experimental research. The main conclusions of this study are as follows.
1) This study found that the average cathode contact resistance of iron is 60% smaller than that of EKG, whereas the average anode contact resistance of EKG is 56% smaller than that of iron.
2) The average temperatures of the soil at the cathode and anode of the iron electrode are 48.47 °C and 26.98 °C, respectively. The EKG electrode has a lower coefficient of energy consumption than the iron electrode, which increases greatly at approximately 18 h.
3) The results show linear fitting relationships between temperature and conductivity and between the soil and pore water conductivities in the process of electro-osmosis. The values of the power consumption per unit mass of contaminants for EKG and iron are 1.895 and 1.989 kJ/g, respectively. These results are helpful for understanding the change trend of the conductivity under multi-field coupling, which provides a reference for the variation in the electrical parameters during electro-osmosis.
Table 4 Summary of quantitative analysis of EKG micro-parameters
4) The data show that the cohesive clay in the undisturbed soil primarily has an empty honeycomb structure. The connections between the clay particles are mostly edge-side and edge-face. The pore volume is small without directional arrangement, but the average area is larger with an average of 1.6231 μm2. After electro-osmosis, the number of soil pores increases, but the average area decreases, with an average area of 0.9100–1.0504 μm2. The roundness of pores in the soil shows an increasing trend after electro-osmosis, and the apparent porosity decreases by 27%.
5) Compared with the arrangement of stainless steel fibers and the conductive structure before electro-osmosis, the number of “lap joints” increases after electro-osmosis, indicating greater overlap between the stainless steel fibers. As a result, the soil is partially filled with “lap joints” of stainless steel fibers during the electro-osmosis process, forming an agglomerated structure. These changes affect the overall conductivity of the EKG material. To improve the conductivity of the EKG material, textile technology can be improved and researched; further study is required to improve the EKG electrode.
References
[1] IWATA M, TANAKA T, JAMI M S. Application of electro-osmosis for sludge dewatering—A review [J].Drying Technology, 2013, 31(2): 170–184.
[2] MAHMOUD A,OLIVIERJ, VAXELAIRE J, HOADLEYA F A. Electrical field: A historical review of its application and contributions in wastewater sludge dewatering [J].Water Research,2010, 44(8): 2381–2407.
[3] TUAN P A, MIKA S,PIRJOI. Sewage sludge electro- dewatering treatment—A review [J].Drying Technology, 2012,30(7): 691–706.
[4] KANIRAJ S R, YEE J H S. Electro-osmotic consolidation experiments on an organic soil [J]. Geotechnical and Geological Engineering, 2011, 29(4): 505–518.
[5] RISCO C, LOPEZ-VIZCAINO R, SAEZ C, YUSTRES A, CANIZARES P, NAVARRO V, RODRIGO M. Remediation of soils polluted with 2,4-D by electrokinetic soil flushing with facing rows of electrodes: A case study in a pilot plant [J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2016, 285: 128–136.
[6] FIGUEROA A, CAMESELLE C, GOUVEIA S, HANSEN H K. Electrokinetic treatment of an agricultural soil contaminated with heavy metals [J]. Journal of Environmental Science and Health, Part A: Toxic/Hazardous Substances and Environmental Engineering, 2016, 51(9): 691–700.
[7] HE F, GAO J, PIERCE E, STRONG P J, WANG H, LIANG L. In situ remediation technologies for mercury- contaminated soil [J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2015, 22(11): 8124–8147.
[8] MULLIGAN C N, YONG R N, GIBBS B F. An evaluation of technologies for the heavy metal remediation of dredged sediments [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2001, 85(1, 2): 145–163.
[9] HU Yu-chen, WANG Zhao, ZHUANG Yan-feng. Experimental studies on electro-osmotic consolidation of soft clay using EKG electrodes [J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2005, 27(5): 709–714. (in Chinese)
[10] JONES C J F P, LAMONT-BLACK J, GLENDINNING S. Electrokinetic geosynthetics in hydraulic applications [J]. Geotextiles and Geomembranes, 2011, 29(4): 381–390.
[11] GLENDINNING S, JONES C J F P, PUGH R C. Reinforced soil using cohesive fill and electrokinetic geosynthetics (EKG) [J]. International Journal of Geomechanics, ASCE, 2005, 5(2): 138–146.
[12] FOURIE A B, JONES C J F P. Improved estimates of power consumption during dewatering of mine tailings using electrokinetic geosynthetics (EKGs) [J]. Geotextiles and Geomembranes, 2010, 28(2): 181–190.
[13] KALUMBAD,GLENDINNING S,ROGERS C D F, TYRER M, BOARDMAN D I. Dewatering of tunneling slurry waste using electrokinetic geosynthetics [J].Journal of Environmental Engineering, ASCE, 2009, 135(11): 1227– 1236.
[14] PAPADOPULOS F, SPINELLI M, VALENTE S, FORONI L, ORRICO C, ALVIANO F. Common tasks in microscopic and ultrastructural image analysis using Image J [J]. Ultrastructural Pathology, 2007, 31(6): 401–407.
[15] FRIEDMAN S P. Soil properties influencing apparent electrical conductivity: A review [J]. Computer and Electronics in Agriculture, 2005, 46(1–3): 45–70.
[16] FETZER C A. Electro-osmotic stabilization of West Branch dam [J]. Journal of the Soil Mechanics and Foundation Division, ASCE, 1967, 93(4): 85–106.
[17] TAO Yan-li, ZHOU Jian, GONG Xiao-nan, HU Ping-chuan. Electro-osmotic dehydration of hangzhou sludge with selected electrode arrangements [J]. Drying Technology, 2016, 34(1): 66–75.
[18] NIU Q F, FRATTA D, WANG Y H. The use of electrical conductivity measurements in the prediction of hydraulic conductivity of unsaturated soils [J]. Journal of Hydrology, 2015, 522: 475–484.
[19] SADEGHALVAD B, AZADMEHR A R, MOTEVALIAN H. Statistical design and kinetic and thermodynamic studies of Ni(II) adsorption on bentonite [J]. Journal of Central South University, 2017, 24(7): 1529–1536.
[20] ZHOU Zi-long, DU Xue-ming, CHEN Zhao, ZHAO Yun-long. Grouting diffusion of chemical fluid flow in soil with fractal characteristics [J]. Journal of Central South University, 2017, 24(5): 1190–1196.
[21] LIU Chun, SHI Bin, TANG Chao-sheng. Quantification and characterization of microporosity by image processing, geometric measurement and statistical methods: application on SEM images of clay materials [J]. Applied Clay Science, 2011, 54(1): 97–106.
[22] DATHE A, EINS S, NIEMEYER J, GEROLD G. The surface fractal dimension of the soil–pore interface as measured by image analysis [J]. Geoderma, 2001, 103(1, 2): 203–229.
(Edited by FANG Jing-hua)
中文导读
EKG和铁电极加固修复污染土对比研究
摘要:本文从理论分析和实验研究两方面综合比较了EKG(Electrokinetic Geosynthetics)电极和铁电极对重金属污染土壤的电渗处理效果。采用电学参数评价加固效果,结果显示温度和电导率之间以及温度与土壤和孔隙水电导率之间具有一定的线性关系。铁电极试验组阴极的平均阴极接触电阻比 EKG电极试验组的小60%,而EKG试验组的平均阳极接触电阻比铁电极试验组的小56%。EKG电极试验组和铁电极试验组单位质量污染物的能耗分别为1.895 kJ/g和1.989 kJ/g。电渗后土壤孔隙数量增加,但平均面积减少,平均面积为0.9100~1.0504 μm2。通过微观结构分析,获得了较高的电渗效率,实现了宏观和微观参数间的有效分析和利用。
关键词:EKG;污染土;电导率;离子运移;微观结构
Foundation item: Project(51378469) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China; Project(2017C33034) supported by the Application Research of Public Welfare Technology in Zhejiang Province, China; Project(LQ18E080001) supported by the Zhejiang Provincial Natural Science Foundation, China; Project(12017A610304) supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Ningbo City, China
Received date: 2017-12-22; Accepted date: 2018-06-21
Corresponding author: XIE Xin-yu, PhD, Professor; Tel: +86-13362105001; E-mail: xiexinyu@zju.edu.cn; ORCID: 0000-0001-8582- 0857