文章编号:1004-0609(2005)04-0558-07
激光熔覆Fe-Ti-B复合材料涂层的组织
张维平, 刘硕
(大连理工大学 材料工程系, 大连 116023)
摘 要: 选用合适的激光工艺参数及涂层成分, 利用激光熔覆工艺在45#钢表面制备了原位析出Fe-Ti-B复合材料涂层。 远离平衡态的激光表面处理工艺使涂层中原位析出了一定数量的不同于稳定相的亚稳定相。 利用X射线衍射(XRD)、 透射电镜(TEM)等手段对涂层的显微组织及相结构进行了研究。 结果表明: 涂层中主要含有呈块状、 条状、 颗粒状或团絮状分布的Fe2B(Fe3B)/α-Fe和TiB2(TiB)/α-Fe低熔点共晶或离异共晶组织; 原位共晶相析出时与基体保持某种最合理的空间取向, 在α-Fe基体与原位析出相界面上存在隐约可见的位错堆积。
关键词: 激光熔覆; Fe-Ti-B; 原位析出; 涂层; 显微组织 中图分类号: TG113
文献标识码: A
Microstructure of Fe-Ti-B composite coating prepared by
laser cladding
ZHANG Wei-ping, LIU Shuo
(Department of Materials Engineering,Dalian University of Technology, Dalian 116023, China)
Abstract: In-situ precipitating Fe-Ti-B composite coating was fabricated on 45# steel surface by laser cladding with optimal laser parameters and coating compositions. A certain amount of metastable phases differing from the stable phases were obtained through laser surface modification which deviates from the equilibrium state. The microstructure of the coating was studied by X-ray diffractometry(XRD) and transmission electron microscopy(TEM). The results show that the coating mainly contains Fe2B(Fe3B)/α-Fe and TiB2(TiB)/α-Fe low melting point eutectic or divorced eutectic presenting block, strip, granular and wadding shape. The in-situ eutectic phases and the matrix have a certain optimal orientation relationship as they precipitate. The faint dislocation tangle lies at the interface between the matrix and the in-situ precipitating phases.
Key words: aser cladding; Fe-Ti-B; in-situ precipitating; coating; microstructure
激光熔覆技术可以得到常规工艺条件下难以得到的非平衡亚稳定相及微观组织, 在保证材料整体性能的同时最大程度地改善其表面性能[1-4]。 对一定合金成分的涂层表面, 在激光熔覆过程中原位析出亚稳相的种类、 分布形态、 形成机制及其对材料性能的影响是该工艺当前研究的热点[5-8]。 大多数研究得出的原位析出相类别都是基于X射线衍射峰的标定, 偶尔配有简单的电子显微镜分析, 一些重要析出相的标定结果可靠性较低, 这种局限性在部分研究中已有报导[9-11]。
本文作者利用优化的激光工艺参数及涂层成分制备了激光熔覆Fe-Ti-B原位复合涂层, 在利用X射线衍射(XRD)分析涂层物相组成的基础上, 重点利用透射电镜(TEM)及相应的选区电子衍射花样(SADP)详细观察并分析了涂层的细微组织及相结构, 二种实验结果的较好吻合准确地说明了有关析出相的存在及其组织结构。
1实验方法
采用加工成40mm×25mm×10mm的退火态45#钢作为熔覆基体, 将待处理面磨光并清洗干净。 涂层材料选用自行配制的Fe-Ti-B合金粉。 优化的涂层成分为: 30.5Ti, 13.5B, Fe余量。 所用粉末粒径≤74μm, 为分析纯。 将上述粉末充分混合后用有机粘结剂调匀并均匀涂覆在基材表面, 厚度为0.5mm左右, 在真空中烘干。 用HJ-4型横流CO2激光器在Ar气保护下进行激光熔覆处理。 激光光斑直径为3~4mm, 透镜焦距为300mm, 输出功率为1.5~2kW, 扫描速度为1~1.5mm/s。 利用XRD-6000型X射线衍射仪和JEM-100CXⅡ型透射电镜分析涂层的显微组织和相结构。 利用线切割并研磨后进行双喷电解抛光制得TEM薄膜。
2涂层的XRD分析
图1所示为涂层表面的XRD谱。 激光处理涂层表面是由α-Fe粘接金属基体及多种原位析出硬质相组成, 其中, 室温下的稳定相TiB2、 Fe2B含量较多, 而亚稳相TiB、 Fe3B相对较少。 激光在材料表面的高能量输入诱发了原位反应 Ti+2B =TiB2+Q, 从而生成平衡态稳定相TiB2。 在远离平衡态的激光处理过程中, 亚稳相TiB的生成过程认为是TiB2+Ti =2TiB-Q, 高能量激光扫描有利于该吸热反应的进行。 TiB具有一般平衡态稳定相所不具备的一系列优异性能, 如脆性相对较小, 它的存在一定程度上有利于克服金属陶瓷涂层共有的脆性大、 开裂倾向严重的缺点[12]。 从Fe-B相图可以看出: Fe2B与FeB是平衡冶金过程中不同成分配制的合金熔体中析出的低熔点共晶相。 在上述Fe含量相对较高的涂层熔体快速冷却过程中, 涂层表面在形成Fe2B/α-Fe稳定共晶组织的同时, 还析出了亚稳Fe3B相, 它的形成是由于快速凝固过程阻碍了B原子向α-Fe基体扩散, 并且快速凝固过程在基体中产生了较大的拉应力, 引起了基体金属的晶格畸变, 从而导致B原子溶入基体金属八面体间隙的阻力增大, 所以, 快速凝固更有利于亚稳相Fe3B的生成。
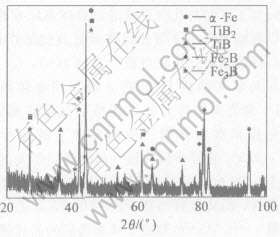
图1涂层表面X射线衍射谱
Fig.1XRD pattern of coating surface
标定X射线衍射峰可知: 经激光处理后, 涂层表面所有物相的衍射峰位相对于标准衍射峰均稍向左移, 这产生于点阵参数变大而引起的相同衍射晶面间距的变大(由Bragg公式: 2dsinθ=λ可以说明)。 点阵参数的增加归因于两个方面: 1) 激光熔覆快速凝固过程造成了金属基体内的固溶扩展, 引起了相关相更大的点阵畸变; 2) 快速凝固过程在涂层内部造成了很大的拉应力, 拉应力畸变也增加了点阵参数的变化[10, 13]。 衍射峰的整体偏移不影响物相标定结果的可靠性。 此外, 由于涂层中某些物相的衍射晶面间距非常接近, 实验结果发现有几种物质的较强衍射线由于靠得很近而重叠在一起, 从而难以分辨单个物质的衍射强度, 如: 在2θ=43.92°与44.30°之间的强衍射峰重叠处, 通过与标准衍射数据比较, 发现有3种物质的有关晶面发生了衍射, 这种重叠峰的标定结果可靠性较低。 激光熔覆非平衡过程使涂层表面析出了大量亚稳相, 其中还存在晶格畸变等晶体缺陷, 所以, 用标准衍射谱对涂层表面进行定性分析有一定困难, 需配以TEM实验及电子衍射谱的详细标定。
3层的TEM分析
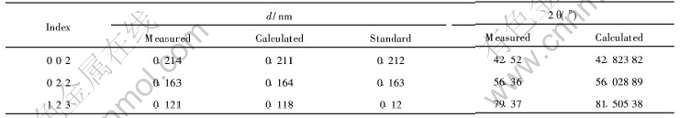
图2所示为Fe3B/α-Fe共晶组织和分布于α-Fe基底上的呈聚集状态的团絮状相TiB的透射电镜明场像(BF-TEM)以及相应的选区电子衍射谱(SADP)。 图2(a)中可见大量生长方向基本相同的细小层片状共晶组织, 层片间距非常小, 即为前述快速凝固熔体中形成的亚稳Fe3B/α-Fe低熔点共晶组织。 为了对黑色条状共晶相P1(Fe3B)的存在进行验证及表征, 在进行选区电子衍射时, 利用倒易空间旋转法得到3幅不同旋转角度的SADP, 然后利用在衍射谱中测得的相关电子衍射参数, 根据倒易空间与正空间的几何关系进行晶体点阵重构, 从而可以粗略测得相应物相晶格常数及倒易点指数, 以便与标准值进行比较对照[14]。 图2(b), (c), (d)即为层片状共晶相Fe3B的3幅不同旋转角度的SADP。 细箭头所指方向为倒易空间旋转轴方向。 旋转角度依次为在第一幅的基础上顺时针旋转17.7°, 9.3°。 平行于旋转轴方向的固定不变的面间距da=0.53nm, 它可能正好为选区物相晶体的某一个基矢, 而又恰好与正交结构的Fe3B的一个晶格常数a=0.543nm接近。 从重构后的晶体倒易点阵可以得到另外2个基矢长度b*=0.70nm, c*=0.49nm, 这与Fe3B的另外2个晶格常数也非常接近, 而且重构的晶体点阵亦为正交结构, 从而验证了Fe3B的存在。 3幅不同的SADP晶带轴方向分别为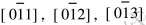 。 上述SADP指数化结果(粗箭头所示, 以下同)与正交结构晶体面间距计算理论及R之间的夹角都能严格自洽。 利用该SADP计算得出了Fe3B相应晶面间距d及衍射角2θ, 并与XRD测量值进行对照(如表1所示)。 可见, 晶面间距d的测量值、 计算值都能与标准值在一定范围内较好地对应。 d的测量值、 计算值与标准值的微小偏差除与测量和计算中的误差有关外, 主要是由前述激光熔覆快速凝固过程引起的晶格畸变造成的。 图2(a)中另一种形态的相P2将在下面进行详细分析。
。 上述SADP指数化结果(粗箭头所示, 以下同)与正交结构晶体面间距计算理论及R之间的夹角都能严格自洽。 利用该SADP计算得出了Fe3B相应晶面间距d及衍射角2θ, 并与XRD测量值进行对照(如表1所示)。 可见, 晶面间距d的测量值、 计算值都能与标准值在一定范围内较好地对应。 d的测量值、 计算值与标准值的微小偏差除与测量和计算中的误差有关外, 主要是由前述激光熔覆快速凝固过程引起的晶格畸变造成的。 图2(a)中另一种形态的相P2将在下面进行详细分析。
图3所示为图2(a)中典型共晶组织上部较大区域内的SADP以及其中两种不同衍射斑所对应[CM(22]的暗场像(DF-TEM)。 图3(a)所示为典型的强弱不同衍射斑相间分布。 SADP指数化结果表明: 强斑点对应于涂层中基体金属α-Fe, 晶带轴为[01[TX-]1]; 弱斑点为基体中另一种正交结构的原位析出相TiB, 晶带轴为[100]。 表2表明α-Fe和TiB的d与2θ的测量值、 计算值和标准值亦能较好地吻合。 为了确定α-Fe和TiB在图2(a)中的具体分布位置, 利用上述强弱两种衍射斑拍摄了α-Fe和TiB的DF-TEM, 如图3(b), (c)所示。 显然, 对应于图2(a), 其中连续分布的灰白色组织即为涂层基体α-Fe, 团絮状聚集相P2即为原位析出相TiB。 在该处的BF-TEM中看不到前述那样明显的层片状共晶组织, 而是TiB颗粒聚集沉淀在晶界处并长大, 形成的是一种离异共晶组织。 这是因为在激光熔覆快速凝固低熔点共晶析出过程中, 由于合金成分偏离共晶点很远, 共晶α-Fe依附于初晶α-Fe生长的倾向取代了其在析出相TiB上生长的倾向。 从上述基体与析出相衍射斑的交叉均匀分布规律可以预测: TiB在α-Fe基体上原位析出时必然与基体金属保持某一确定的空间取向。 由SADP指数化结果得知: 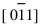 α-Fe∥[100]TiB, (011)α-Fe∥(002)TiB。 共晶组织Fe3B/α-Fe中的两共晶相也存在类似的空间取向关系。
α-Fe∥[100]TiB, (011)α-Fe∥(002)TiB。 共晶组织Fe3B/α-Fe中的两共晶相也存在类似的空间取向关系。
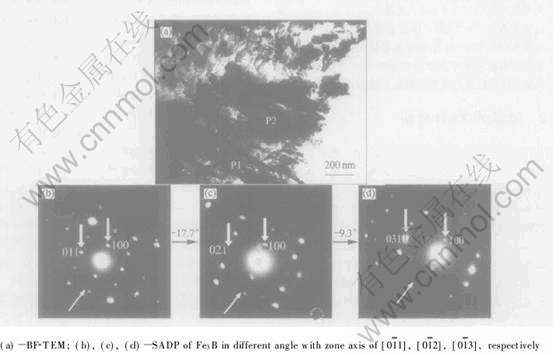
图2 Fe3B/α-Fe共晶组织和团絮状TiB相形貌以及相应的SADP
Fig.2 Morphology of Fe3B/α-Fe eutectic structure and wadding-like TiB and corresponding SADP
表1利用Fe3B相SADP计算得到的d及2θ与XRD测量结果的对照
Table 1Contrasting of d and 2θ obtained from SADP of Fe3B and XRD measurement
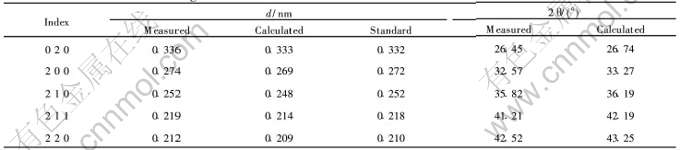
图4(a), (b)所示分别为弥散分布于α-Fe基体中的小块状或颗粒状Fe3B相以及相应的SADP。 对衍射斑强弱相间分布的SADP进行标定可知: 强斑点对应α-Fe基体, 晶带轴为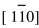 ; 弱斑点对应为Fe3B, 晶带轴为
; 弱斑点对应为Fe3B, 晶带轴为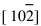 。 二者的空间取向关系为:
。 二者的空间取向关系为: 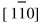 α-Fe∥
α-Fe∥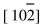 Fe3B, (002)α-Fe∥(060)Fe3B。 该区域的BF-TEM所显示出的也是两种共晶相独立生长的离异共晶组织, 共晶相Fe3B在晶界或相界处呈块状或颗粒状生长。
Fe3B, (002)α-Fe∥(060)Fe3B。 该区域的BF-TEM所显示出的也是两种共晶相独立生长的离异共晶组织, 共晶相Fe3B在晶界或相界处呈块状或颗粒状生长。
以上对前述X射线衍射谱中物相鉴定较困难、 与标准衍射数据有一定偏差的原位析出亚稳定相Fe3B和TiB进行了形貌观察及SADP标定, 配合X射线衍射分析说明了这两种亚稳定相的存在, 而且, 上述SADP中同种物相最强衍射斑对应的晶面[CM(22]指数与标准PDF卡片中相应物相最强衍射线的指数能够吻合, 这也从另一角度验证了SADP标定的可靠性。 下面将对稳定析出相TiB2和Fe2B进行TEM观察及SADP标定。
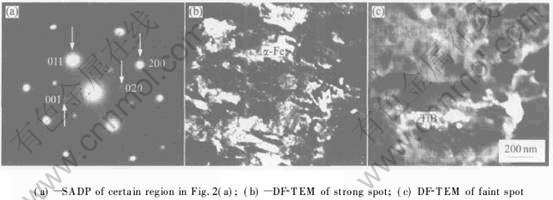
图3图2(a)中共晶组织上部较大区域内的SADP以及强弱两种不同衍射斑所对应的暗场像
Fig.3 SADP of large region above eutectic structure in Fig.2(a) and
corresponding DF-TEM of strong and faint spots
表2α-Fe和TiB的d值与2θ的测量值、 计算值和标准值对照
Table 2Contrasting of measured, calculated and standard values of d and 2θ of α-Fe and TiB
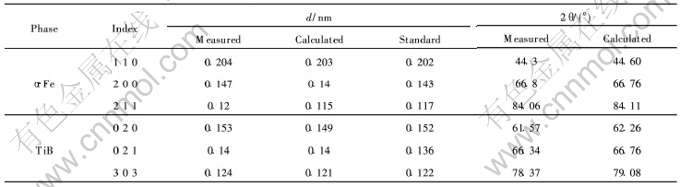
图5所示为灰白色α-Fe基体中原位析出的方块状相的BF-TEM及其SADP。 图5(a)中原位析出相呈方块状镶嵌在灰白色基体上, 由高能密度激光促成的原位反应保证了相结合界面的牢固性。 然而, 单次激光熔覆涂层中的某些区域组织不太均匀, 图5(a)所示TiB2相明显比前述其它析出相粗大, 这种情况可以用激光二次重熔来解决[15-17]。 灰色α-Fe基体中存在有隐约可见的位错条纹。 由图5(b)所示块状相SADP可见: 衍射斑接近六方点阵。 图中细箭头所指为选取该块状晶体相倒易空间点阵时旋转轴方向, 该方向面间距d=0.257nm, 由于d≈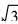 /2)aTiB2(aTiB2=0.303nm), 所以, 该方向正好对应于TiB2晶体点阵中一个基矢的方向, 因此判断其为密排六方结构的TiB2相。 该倒易晶向所对应的晶面间距d以及标定出的晶面指数与TiB2标准PDF卡片中次强衍射峰的相应值基本对应。 该衍射谱晶带轴为
/2)aTiB2(aTiB2=0.303nm), 所以, 该方向正好对应于TiB2晶体点阵中一个基矢的方向, 因此判断其为密排六方结构的TiB2相。 该倒易晶向所对应的晶面间距d以及标定出的晶面指数与TiB2标准PDF卡片中次强衍射峰的相应值基本对应。 该衍射谱晶带轴为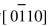 。 TiB2相的d和2θ的计算值、 测量值和标准值对照如表3所示。 TiB2是激光处理过程中数量最多的一种重要的稳定态原位析出相。
。 TiB2相的d和2θ的计算值、 测量值和标准值对照如表3所示。 TiB2是激光处理过程中数量最多的一种重要的稳定态原位析出相。
图6(a), (b)所示分别为α-Fe基体中另一种析出相的BF-TEM及其SADP。 图6(a)中在灰白色基体上均匀弥散分布着细颗粒状析出相。 在基体内部的两相界面上, 分布着比较明显的位错缠结, 这是基体内的运动位错在相界面处受阻堆积的结果。 图6(b)所示SADP亦为典型的强弱衍射斑相间分布。 SADP指数化结果表明: 强斑点与图3(a)所示强斑点的指数及点阵参数是一致的, 即为α-Fe基体; 弱斑点标定为具有四方结构的Fe2B, 晶带轴为[010]。 表4所列为Fe2B相的d和2θ的计算值、测量值和标准值对照。 Fe2B相在α-Fe基体上原位析出时二者空间取向关系为: 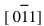 α-Fe∥[010]Fe2B,
α-Fe∥[010]Fe2B, 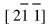 α-Fe∥[003]Fe2B。 BF-TEM显示Fe2B/α-Fe稳定态低熔点共晶组织也具有离异共晶的特点。
α-Fe∥[003]Fe2B。 BF-TEM显示Fe2B/α-Fe稳定态低熔点共晶组织也具有离异共晶的特点。

图4α-Fe基体中的小块状或颗粒状Fe3B相形貌及相应的SADP
Fig.4 Morphology of little block-like and granular Fe3B dispersing in
α-Fe matrix and corresponding SADP

图5灰白色α-Fe基体中原位析出的方块状相形貌及其SADP
Fig.5Morphology of diamond phase in-situ precipitated from
gray α-Fe matrix and corresponding SADP
表3TiB2的d与2θ的测量值、 计算值和标准值对照
Table 3Contrasting of measured, calculated and standard values of d and 2θ of TiB2
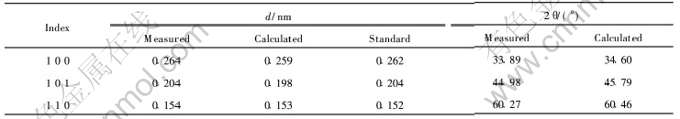
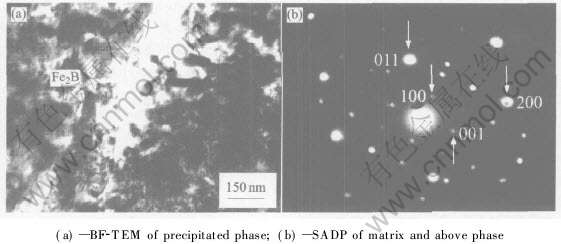
图6α-Fe基体中的另一种析出相形貌及其SADP
Fig.6Morphology of another precipitated phase in α-Fe matrix and corresponding SADP
表4Fe2B的d与2θ的测量值、 计算值和标准值对照
Table 4 Contrasting of measured, calculated and standard values of d and 2θ of Fe2B
4结论
选用合适的激光工艺参数及涂层成分, 在45#钢基体表面得到了激光熔覆Fe-Ti-B复合材料涂层。 涂层中包含均匀连续分布的粘结金属基体α-Fe以及大量原位析出稳定相与亚稳相, 主要是呈块状、 条状、 颗粒状或团絮状分布的Fe2B(Fe3B)/α-Fe和TiB2(TiB)/α-Fe低熔点共晶或离异共晶组织。 利用XRD, TEM及相应的SADP可以完整地标定出原位复合涂层中的这些物相, 而且可知原位共晶相在α-Fe基体上析出时与基体保持某种最合理的空间取向。 在α-Fe基体与原位析出相界面上存在隐约可见的位错堆积。
REFERENCES
[1]Conde A, Zubiri F, de Damborenea J. Cladding of Ni-Cr-B-Si coatings with a high power diode laser[J]. Mater Sci Technol, 2002, 34: 233-238.
[2]WANG X B, LIANG Y, YANG S L. Formation of TiB2 whiskers in laser cladding Fe-Ti-B coatings[J]. Surf Coat Technol, 2001, 137(3): 209-216.
[3]王春敏, 蔡良续, 王华明. 激光熔覆Ni-Si金属硅化物复合材料涂层显微组织与耐蚀性[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2002, 12(1): 183-187.
WANG Chun-min, CAI Liang-xu, WANG Hua-ming. Microstructure and corrosion resistance of laser cladding Ni-Si metal-silicate composite coatings[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2002, 12(1): 183-187.
[4]尚丽娟, 贺春林, 才庆魁, 等. 应用稀土及激光熔覆工艺制备钴基合金梯度涂层[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2002, 12(4): 653-657.
SHANG Li-juan, HE Chun-lin, CAI Qing-kui, et al. Formation of gradient coating of Co-based alloy with rare earth by laser cladding[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2002, 12(4): 653-657.
[5]Hadji L. Morphological instability prior to particle engulfment by a solidifying interface[J]. Scripta Materialia, 2003, 48: 665-669.
[6]杨森, 钟敏霖, 刘文今. 激光熔覆制备原位自生TiC颗粒强化Ni基合金复合涂层的研究[J]. 航空材料学报, 2002, 22(1): 26-29.
YANG Sen, ZHONG Min-lin, LIU Wen-jin. Research on the fabrication of in-situ synthesized TiC particles reinforced Ni-based alloy composite coating by laser cladding[J]. J Aero Mater, 2002, 22(1): 26-29.
[7]花国然, 黄因慧, 赵剑峰, 等. 激光熔覆纳米Al2O3等离子喷涂陶瓷涂层[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2004, 14(2): 199-203.
HUA Guo-ran, HUANG Yin-hui, ZHAO Jian-feng, et al. Plasma sprayed ceramic coating by laser cladding of Al2O3 nano-particles[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2004, 14(2): 199-203.
[8]Sexton L, Lavin S, Byrne G, et al. Laser cladding of aerospace materials[J]. J Mater Pro Techno, 2002, 122: 63-68.
[9]Pinkerton A J, Lin L. The effect of laser pulse width on multiple-layer 316L steel cladding microstructure and surface finish[J]. Appl Surf Sci, 2003, 208-209, 411-416.
[10]李强, 雷廷权, 孟庆昌, 等. 激光熔覆Ni-Cr-B-Si-C合金涂层显微组织的透射电镜研究[J]. 中国激光, 1999, 26(4): 374-377.
LI Qiang, LEI Ting-quan, MENG Qing-chang, et al. Study of laser cladding Ni-Cr-B-Si-C alloy coatings microstructure by TEM[J]. Chinese J Laser, 1999, 26(4): 374-377.
[11]张维平, 刘硕, 马玉涛. 激光熔覆原位生成TiB2及其组织结构研究[J].大连理工大学学报, 2004, 44(3): 402-406.
ZHANG Wei-ping, LIU Shuo, MA Yu-tao. Study of in-situ synthesis of TiB2 by laser cladding and its microstructure[J]. J Dalian Univ of Technol, 2004, 44(3): 402-406.
[12]Kooi B J, Pei Y T, de Hosson J Th M. The evolution of microstructure in a laser clad TiB-Ti coating[J]. Acta Mater, 2003, 51: 831-845.
[13]张维平, 刘硕, 邹龙江. TiB2-TiB/Fe金属陶瓷复合涂层原位合成及显微分析[J]. 大连理工大学学报, 2004, 44(6): 798-801.
ZHANG Wei-ping, LIU Shuo, ZOU Long-jiang. In-situ synthesis and microanalysis of TiB2-TiB/Fe metal-ceramics composite coating[J]. J Dalian Univ of Technol, 2004, 44(6): 798-801.
[14]Woldan A, Kusinski J, Tasak E. The microstructure of plain carbon steel laser-alloyed with silicon carbide[J]. Materials Chemistry and Physics, 2003, 81: 507-509.
[15]LIU Shuo, ZHANG Wei-ping, MA Yu-tao. Research on the formation of metal-ceramic surface composite coating by wide-band laser cladding[J]. Trans of Metal and Heat Treatment, 2004, 25(5): 1025-1028.
[16]Socola G, Torricellib P, Bracci B, et al. Biocompatible nanocrystalline octacalcium phosphate thin films obtained by pulsed laser deposition[J]. Biomaterials, 2004, 25: 2539-2545.
[17]金云学, 张虎, 曾松岩, 等. Ti-Al-B合金中铝含量对硼化物的存在方式和形态的影响[J]. 材料科学与工艺, 2001, 9(3): 287-290.
JIN Yun-xue, ZHANG Hu, ZENG Song-yan, et al. Influence of Al content on constitutes and morphologies of borides in Ti-Al-B alloys[J]. Mater Sci & Technol, 2001, 9(3): 287-290.
基金项目: 国家自然科学基金资助项目(59701001)
收稿日期: 2004-08-31; 修订日期: 2004-12-26
作者简介: 张维平(1964-), 男, 博士, 副教授.
通讯作者: 刘硕; 电话: 0411-84706206; E-mail: shuo-l@163.com
(编辑袁赛前)