轧制变形量对7A55铝合金淬火敏感性的影响
张新明,张 翀,刘胜胆,朱航飞
(中南大学 材料科学与工程学院,湖南 长沙,410083)
摘 要:为了研究轧制变形量与淬火敏感性的关系,测量了变形量为70%,80%和90%的7A55铝合金轧制板材在不同淬火条件下的拉伸力学性能。结果表明,热处理T6态下合金的强度、延伸率随着淬火速率的增加而提高;合金的淬火敏感性随着轧制变形量的增加而增大;固溶发生再结晶的过程中,与基体共格的Al3Zr粒子被大角度晶界扫过转变为非共格粒子;在缓慢淬火过程中,粗大平衡相η(MgZn2)以非共格的Al3Zr粒子作为形核位置析出,显著减弱时效强化效果,造成淬火敏感性现象;再结晶程度随着轧制变形而增大,是导致淬火敏感性提高的主要原因。
关键词:7A55铝合金;轧制变形量;淬火敏感性;Al3Zr
中图分类号:TG172.9 文献标识码:A 文章编号:1672-7207(2007)04-0589-06
Effect of rolling reduction on quench sensitivity of aluminium alloy 7A55
ZHANG Xin-ming, ZHANG Chong, LIU Sheng-dan, ZHU Hang-fei
(School of Materials Science and Engineering, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China)
Abstract: The mechanical properties of aluminium alloy 7A55 plates with different rolling reductions(70%, 80% and 90%) were investigated to obtain the relations between rolling reduction and quench sensitivity. The results show that the strength and elongation of the plates with T6 temper increase with quenching rate; the quench sensitivity of aluminium alloy 7A55 increases with rolling reduction. The migration of high angle grain boundary results in the transformation of the coherent Al3Zr particles to the incoherent in recrystallization during solution treatment at 470 ℃. Furthermore, the incoherent Al3Zr particles serve as the nucleation sites of η(MgZn2)during slow quenching, which causes a marked loss of age-hardening and quench sensitivity of the alloy. Therefore, the volume of recrystallization which increases with rolling reduction is mainly responsible for the enhanced quench sensitivity.
Key words: aluminium alloy 7A55; rolling reduction; quench sensitivity; Al3Zr
7×××铝合金存在淬火敏感性,其力学性能随淬火速率的减小而降低。大量研究结果表明[1-2],淬火敏感性的产生是缓冷时平衡相的析出降低合金的过饱和度、减弱时效强化效果造成的。影响淬火敏感性的因素有:
a. 平衡相的析出。对于7×××合金而言,缓冷淬火过程中,合金元素(Cu+Mg+Zn)的复合添加会导致平衡相的析出,增大合金的淬火敏感性[2-3]。
b. 晶粒组织形态。再结晶组织及大角度晶界的出现会增大合金的淬火敏感性[4-6]。
c. 微量元素的作用。微量Cr和Mn的添加可有效地抑制再结晶、细化晶粒,但合金的淬火敏感性大大增强。微量Zr的添加不仅可以起到上述作用,而且不会引起严重的淬火敏感性[7]。
现代航空航天工业的高速发展对7×××合金的大尺寸截面构件尤其是高性能的厚板材料的需求日趋迫切。厚板难以淬透,其心部的淬火速率很小;淬火敏感性的存在,导致厚板表层和心部性能的差异使其整体性能下降。减小合金的淬火敏感性,提高厚板的淬透性,是获取高性能合金厚板的合理途径。轧制变形是影响合金力学性能的重要因素,因为原先的晶粒经剧烈塑性变形转变成扁平、延长的变形组织,同时轧制获得的变形储能是合金再结晶的驱动力,而再结晶组织和大角度晶界的出现能提高合金的淬火敏感性。本文作者以轧制变形改变晶粒组织形态为出发点,研究了轧制变形对7A55铝合金淬火敏感性的影响,并对其影响机理进行分析和探讨。
1 实 验
本实验所研究的7A55铝合金的化学分析成分如表1所示。铸锭的尺寸为80 mm×60 mm×20 mm,均匀化处理制度为:400 ℃/5 h+465 ℃/24 h。铸锭铣面后于420 ℃预热2 h,进行轧制。轧制变形量分别为70%,80%和90%。板材经470 ℃固溶后采用20 ℃水、60 ℃水、100 ℃水和空气进行淬火,之后立即进行120 ℃/24 h人工时效。试样在CSS-44100万能拉伸实验机上进行常温拉伸测试。在7501型涡流电导仪上测量电导率。在XJP-6A型金相显微镜观察金相组织。在TecNai G220型电镜上进行TEM透射电镜观察。
表1 实验合金的化学成分
Table 1 Chemical composition of aluminium alloy 7A55

2 实验结果
2.1 固溶时间的确定
一般地,对于同一铝合金板材,变形量越大,所需的固溶时间越短[8]。将3种变形量的试样进行470 ℃的固溶处理,保温0~150 min。试样于20 ℃水淬后立即测量其电导率,电导率曲线如图1所示。电导率可反映合金中溶质的过饱和度,电导率越低,过饱和度越高[9]。图1中,3条曲线都存在着一个时间点,在该点之前曲线呈现出陡直下降,之后平缓下降。对于变形量分别为70%,80%和90%的试样,该时间点依次为90 min,90 min,75 min。这是因为此时大部分合金元素溶入基体,合金的过饱和度趋于稳定,取该时间为固溶时间最合适。
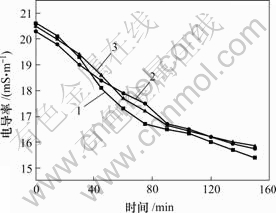
1—90%; 2—80%; 3—70%
图1 固溶处理后的电导率曲线
Fig.1 Electrical conductivity of samples after solution treatment
2.2 拉伸力学性能
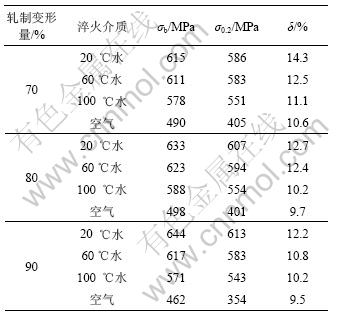
表2所示为不同淬火条件下7A55铝合金的力学性能。从表2中可以看出:在同一变形量下,从空冷到20℃水淬随着淬火速率的增大,合金的抗拉强度(σb)和屈服强度(σ0.2)增大。20 ℃和60 ℃水淬试样的抗拉强度都在610 MPa以上。100 ℃水淬试样的抗拉强度为570~590 MPa。而空冷试样的强度损失为最大,抗拉强度低于500 MPa,远低于水淬的抗拉强度。试样的延伸率从空冷到20 ℃水淬随着淬火速率的增加而增大。
表2 不同淬火条件下7A55铝合金的力学性能
Table 2 Mechanical properties of aluminium alloy 7A55 in different quenching conditions
2.3 淬火敏感性比较
为了比较各变形量试样的淬火敏感性,定义如下公式:

Q越大,则因淬火速率下降而造成的强度损失越严重。试样的淬火敏感性如图2所示。由图2可见,变形量为70%,80%和90%的试样从20 ℃水淬到空冷的抗拉强度降幅为20%,21.3%和28.3%,而变形量为70%和80%的试样在 100 ℃水淬和空冷条件下的降幅很接近。图2所示结果表明,随着变形量的增大,抗拉强度下降的幅度更大,淬火速率对试样的力学性能的影响增大,即淬火敏感性增大。综合考虑力学性能、淬火敏感性,变形量80%的试样性能最优。
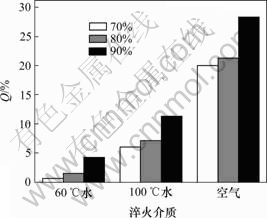
图2 各变形量试样的淬火敏感性
Fig.2 Quench sensitivity of samples with various rolling reductions
2.4 淬火态与时效态电导率比较
图3所示为合金经470 ℃固溶处理在不同淬火介质中淬火后的电导率以及随后经120 ℃/24 h时效后的电导率。从图3可以看出,空冷试样的电导率较大,在19.5 mS/m以上。这是因为固溶处理过程中,合金中的η(MgZn2)和T(AlZnMgCu)等第二相相继溶解[10],合金元素充分溶入基体。而合金元素在基体中的固溶度会随温度的降低而显著减小,在空冷条件下,有足够的时间从基体中缓慢析出,使合金在室温下获得极低的过饱和度。而20 ℃水淬的试样电导率降至16.5 mS/m左右,下降幅度比较空冷的大得多。因为在快速淬火条件下,合金元素来不及扩散、析出,故合金获得很高的过饱和度。

图3 淬火态与时效态的电导率
Fig.3 Electrical conductivity of quenched samples and aged samples
经过120 ℃/24 h时效,合金元素将会以η′(MgZn2)的形式从基体中脱溶、析出,合金的过饱和度会降低,因此,时效态的电导率比淬火态的电导率高。从两者的差值可大致反映出时效析出的程度,空冷条件下电导率差小于0.3 mS/m,几乎丧失时效强化能力。
2.5 金相组织比较
合金固溶时发生部分再结晶,而在120 ℃时效时由于温度较低,晶粒组织基本没有变化。时效态的试样用Graff Seagent试剂腐蚀,20 ℃水淬试样的时效态组织如图4所示,其中白色区域为再结晶组织,黑色区域为未再结晶组织。这是由于Graff Seagent试剂优先腐蚀晶界和亚晶界,未再结晶部分由于有大量亚结构被腐蚀而呈黑色[11]。从图4可见,在纵截面上,再结晶晶粒沿轧向呈长条纤维状。图4(a)中,变形量为70%的试样的再结晶组织分布最少,随着变形量的增大,再结晶组织增多。

变形量:(a) 70%; (b) 80%; (c) 90%
图4 20 ℃水淬试样的时效态组织
Fig.4 Optical morphologies of samples quenched at 20 ℃ water and aged at 120 ℃
3 分析与讨论
合金固溶处理过程中,在轧制变形所获得的变形储能的驱动下,主要通过PSN机制[12]发生再结晶。首先在Al3Zr沉淀相密度较低的区域发生再结晶,再结晶晶粒的晶界(大角度晶界)逐步向Al3Zr沉淀相密度高的区域迁移。图5所示为Al3Zr和η′(MgZn2)粒子的形态和分布。从图5(a)可见,反映Al3Zr粒子呈圆球状,粒子间距λ<1 μm,粒子直径d<0.3 μm,完全满足阻碍晶界迁移的条件,所以Al3Zr会对晶界的移动产生阻滞作用,阻碍再结晶的进行。当大角度晶界扫过Al3Zr粒子时,会使与基体共格的Al3Zr转变为非共格[5-6]。非共格的Al3Zr与基体间存在高界面能,可作为η(MgZn2) 的非均匀形核位置[6]。此外,随机大角度晶界增多,也成为非均匀形核的有利位置。

(a) 20 ℃水淬后暗场下的Al3Zr; (b) 20 ℃水淬、120 ℃/24 h时效后析出的η′(MgZn2)
图5 Al3Zr和MgZn2粒子的形态和分布
Fig.5 Shape and distribution of Al3Zr and η′(MgZn2) particles
从图1和图3可知,在快速淬火(水淬)后,合金的电导率与未固溶处理的试样的电导率相比有显著的下降,获得了室温下的过饱和固溶体。合金元素充分溶入基体,为时效析出强化相η′(MgZn2)提供了物质基础和驱动力。在随后的时效过程中,Al3Zr可以促进强化相η′的析出,且η′(MgZn2)易于在Al3Zr周围非均匀析出[13]。如图5(b)所示,强化相η′(MgZn2)很细小,在基体中呈弥散分布,这有利于力学性能的提高。
值得注意的是,在缓慢淬火条件下,合金元素在基体中的固溶度会随着温度的下降而显著降低,并且会发生新相析出。如图6(a)所示,空冷过程中会析出大量的粗大平衡相η(MgZn2)。其形态多为条状、盘状;析出相的尺寸达到几百纳米,主要密集分布在再结晶晶粒内。如图6(b)所示,条状析出相为η(MgZn2),箭头所指的黑点为圆球状的Al3Zr粒子。有大量的平衡相η在Al3Zr粒子上非均匀形核析出,这类位于再结晶晶粒内的Al3Zr粒子是非共格[2, 6]。另一方面,如图6(c)所示,在亚晶组织中平衡相η的数量稀少,且尺寸相对较小;相应地,其对强度损失造成的影响也很小。这是因为亚晶组织中缺乏理想的非均匀形核位置。图6(d)所示为空冷试样经120 ℃/24 h时效后的微观组织,箭头所指的粉末状物质为强化相η′。由于平衡相η的析出导致基体中溶质的贫乏,故强化相η′的析出量很小,与图5(b)形成明显的对比。这反映出时效析出效果的显著降低。未添加Zr的合金,缓冷时只有极少的平衡相η于基体中析出,对合金性能的影响很小,未表现出显著的淬火敏感性[2]。可见,合金的淬火敏感性与微量Zr的添加密切相关。淬火敏感性现象的本质是溶质原子的去向;缓冷时,再结晶组织内平衡相η的析出是造成淬火敏感性的主因。
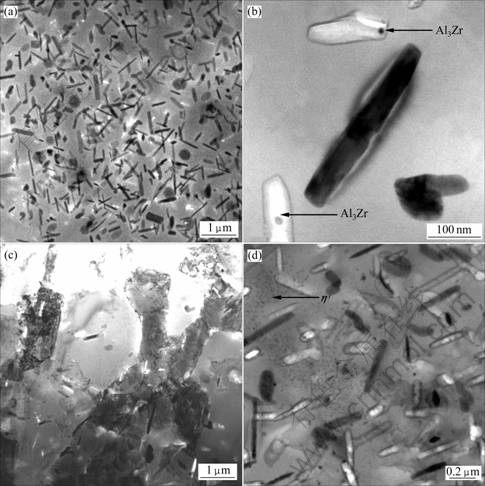

(a) 粗大平衡相η(MgZn2); (b) Al3Zr作为粗大平衡相η(MgZn2)形核位置;
(c) 平衡相η在亚晶组织中的析出; (d)平衡相η对时效相η′析出的影响
图6 空冷后的合金组织
Fig.6 TEM images of air quenched sample
轧制变形量大的试样变形储能高,晶粒单位体积内的界面自由能较高,再结晶驱动力大,在固溶过程中,再结晶的程度较大(如图4所示),出现更多的大角度晶界,这样,就有更多与基体共格的Al3Zr粒子被大角度晶界扫过而转变为非共格的粒子,从而具有更多的非均匀形核位置。缓冷淬火过程中有更多的粗大平衡相η(MgZn2)借助非共格的Al3Zr粒子非均匀形核析出,消耗更多的溶质原子,大大降低合金的过饱和度,导致合金时效后的强度损失更大,所以,增大变形量可提高合金的淬火敏感性。
4 结 论
a. 从拉伸力学性能看,合金的强度、延伸率随着淬火速率的增加而增大;随着轧制变形量的增大,合金的淬火敏感性增大。综合考虑力学性能、淬火敏感性,变形量80%的试样性能最优。
b. 轧制变形量大的试样变形储能高,在固溶处理过程中,再结晶程度较大,获得更多的非共格Al3Zr作为缓冷时的非均匀形核位置,这促进缓冷时粗大平衡相η的形核析出,导致时效后合金的强度损失更大,所以,合金的淬火敏感性随轧制变形量的增加而增大。
参考文献:
[1] Robinsona J S, Cudd R L, Tanner D A, et al. Quench sensitivity and tensile property inhomogeneity in 7010 forgings[J]. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 2001, 119(1/3): 261-267.
[2] Conserva M, Fiorini P. Interpretation of quench-sensitivity in Al-Zn-Mg-Cu alloys[J]. Metall Trans, 1973, 4(3): 857-861.
[3] Eto T, Nakai M. New aspect of development of high strength aluminum alloy for aerospace applications[J]. Materials Science and Engineering, 2000, 285(1/2): 62-68.
[4] Dorward R C, Beerntsen D J. Grain structure and quench-rate effects on strength and toughness of AA7050 Al-Zn-Mg-Cu-Zr alloy plate[J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A, 1995, 26(9): 2481-2484.
[5] Deschamps A, Brechet Y. Influence of quench and heating rates on the ageing response of an Al-Zn-Mg-(Zr) alloy[J]. Materials Science and Engineering, 1998, A251(1/2): 200-207.
[6] Deschamps A, Brechet C. Nature and distribution of quench-induced precipitation in an Al-Zn-Mg-Cu alloy[J]. Scripta Materialia, 1998, 39(11): 1517-1522.
[7] 谢优华, 杨守杰, 戴圣龙, 等. 锆元素在铝合金中的应用[J]. 航空材料学报, 2002, 22(4): 56-61.
XIE You-hua, YANG Shou-jie, DAI Sheng-long, et al. Application of element Zr in aluminum alloys[J]. Journal of Aeronautical Materials, 2002, 22(4): 56-61.
[8] 李松瑞, 周善初. 金属热处理[M]. 长沙: 中南大学出版社, 2003.
LI Song-rui, ZHOU Shan-chu. Heat treatment of metals[M]. Changsha: Central South University Press, 2003.
[9] 张 茁, 陈康华. 固溶处理对Al-Zn-Mg-Cu铝合金电导率的影响[J]. 粉末冶金材料科学与工程, 2004, 9(1): 79-83.
ZHANG Zhuo, CHEN Kuang-hua. Effect of solution heat-treating on electrical conductivity of Al-Zn-Mg-Cu aluminum alloy[J]. Materials Science and Engineering of Powder Metallurgy, 2004, 9(1): 79-83.
[10] 陈康华, 刘红卫, 刘允中. 强化固溶对Al-Zn-Mg-Cu系铝合金力学性能和断裂行为的影响[J]. 中南工业大学学报: 自然科学版, 2000, 31(4): 339-341.
CHEN Kang-hua, LIU Hong-wei, LIU Yun-zhong. The effect of promotively-solutionizing treatment on the mechanical properties and fracture of ultra high strength 7055 aluminum alloys[J]. Journal of Central South University of Technology: Science and Technology, 2000, 31(4): 339-341.
[11] Robson J D, Prangnell P B. Predicting the recrystallized volume fraction in AA7050 hot rolled plate[J]. Materials Science and Technology, 2002, 18(6): 607-619.
[12] Engler O, Sachot E, Ehrstrom J C. Recrystallization and texture in hot deformed aluminium alloy 7010 thick plates[J]. Materials Science and Technology, 1996, 12(9): 717-729.
[13] 杨守杰, 谢优华, 陆 政, 等. Zr对超高强铝合金时效过程的影响[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2002, 12(2): 226-230.
YANG Shou-jie, XIE You-hua, LU Zhen, et al. Influence of zirconium on ageing process in super-high strength aluminum alloy[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2002, 12(2): 226-230.
收稿日期:2006-10-17
基金项目:国家重点基础研究发展计划资助项目(2005CB623700)
作者简介:张新明(1946- ),男,湖南常德人,教授,博士,从事材料科学与工程研究
通讯作者:张新明,男,教授,博士;电话:0731-8830265; E-mail: xmzhang@mail. csu. edu. cn