文章编号: 1004-0609(2005)03-0404-06
铸态Ti-Sc二元合金的组织特征、 相结构和显微硬度
刘会群1, 易丹青1, 肖来荣1, 王 斌1,
卢 斌1, 黄道远1, 杨 胜1, 魏鎏英2
(1. 中南大学 材料科学与工程学院, 长沙 410083;
2. School of Technology and Society, Malm University, Malm 20506, Sweden)
摘 要: 采用真空电弧熔炼技术制备了4种成分的Ti-Sc二元合金, 并借助金相显微镜(OM)、 扫描电子显微镜(SEM)、 能谱分析(EDS)、 X射线衍射(XRD)技术及显微硬度测试, 对合金的组织形貌、 相成分以及不同形貌相的显微硬度进行了分析。 结果表明: 合金铸态组织形貌为螺旋状、 团簇状片层、 双相组织; 金属Sc对合金的组织有着明显的细化作用, 在合金中Sc与Ti形成了固溶体, 不同形貌的相, 其显微硬度差别较大; 当Sc含量为2%~3%时, Ti-Sc二元合金的显微硬度达到最高值, Sc含量高于2%~3%时, 合金基体硬度高于片层组织硬度, Sc含量低于2%~3%时, 合金基体硬度低于片层组织硬度, 少量Sc对合金性能有所提高, 对α相片层组织有强化作用。
关键词: Ti-Sc二元合金; 显微组织; 相结构; 显微硬度
中图分类号: TG113.12 文献标识码: A
Microstructure, phase structure and microhardness of as-cast Ti-Sc binary alloys
LIU Hui-qun1, YI Dan-qing1, XIAO Lai-rong1, WANG Bin1,
LU Bin1, HUANG Dao-yuan1, YANG Sheng1, WEI Liu-ying2
(1. School of Materials and Science Engineering, Central South Universtity,
Changsha 410083, China;
2. School of Technology and Society, Malm University, Malm 20506, Sweden)
Abstract: Four kinds of Ti-Sc binary alloys were prepared by vaccum arc melting technique. Microstructure, phase components and microhardness of different phases were analyzed by optical microscopy(OM), scanning electron microscope(SEM), X-ray diffraction(XRD) and microhardness tester. The results show that scandium plays a significant role on refinement of the microstructure. Solid solution forms in Ti-Sc binary alloys. The measured microhardness of different phases are in significant discrepancy. Microhardness of Ti-Sc binary alloys reaches the maximum value with 2%-3% Sc. When Sc content is higher than 2%-3%, microhardness of matrix is higher than that of plate-like phases, contrary tendency can be seen when Sc content is lower than 2%-3%. Small content of scandium can improve the properties of alloys and strengthen the α plate-like phases.
Key words: Ti-Sc binary alloy; microstructure; phase structure; microhardness
钛是20世纪50年代发展起来的一种重要的结构金属[1], 钛具有两种同素异晶体, 分别以α和β表示, 钛的同素异晶转变温度为882.5℃, 其低温晶体α具有密排六方结构, 在882.5℃以上, 稳定的β晶体为体心立方结构。 钪有两种晶型: 在标准状态下为六方密排晶格(hcp)的α-Sc, 在高温1337℃以上转变为体心立方晶格(bcc)的β-Sc。 若要形成完全可溶混的固溶体, 组分的结晶结构必须相同, 因此只有具有六方晶格(hcp)和体心立方晶格(bcc)的金属才能与钪完全溶混。 钛能与钪形成连续的固溶体[2]。 钛和钪的金属原子半径分别为0.145、 0.163nm[3], 其相对差值小于14%, 所以钛钪固溶体类型为置换式固溶体[4]。 目前, 国内外对微量金属Sc对铝合金组织与性能的影响已作了很多研究, 这些研究表明[5-9]: 微量Sc添加到铝合金中有细化组织、 提高强度、 提高再结晶温度等作用, 因其在铝合金中形成Al3Sc相, 与基体共格, 产生了显著的共格强化作用。 但有关金属 Sc对钛合金组织与性能的影响报道很少, 金属Sc加入到钛合金中对合金的组织与性能的影响目前尚不清楚, 对Ti-Sc二元相图的研究也还不充分。 所以本文作者从基础工作着手, 选择Ti-Sc二元系中若干有代表性的成分, 研究其铸态组织, 以及对Ti-Sc二元系的某些不确定方面进行实验研究。
1 实验
根据Ti-Sc二元合金相图(见图1), 用真空电弧熔炼方法制备了Ti-37Sc(1号)、 Ti-25Sc(2号)、 Ti-5Sc(3号)及Ti-2Sc(4号)(质量分数, %)4个合金成分的钮扣锭, 并重熔了工业纯钛TA1铸锭, 铸锭随炉冷却。 实验原料采用工业纯钛TA1及纯金属钪(99.983%)。 采用光学金相显微镜(OM)、 扫描电子显微镜(SEM)、 能谱仪(EDS)及X射线衍射(XRD)观察分析了合金的组织特征、 相组成。 用SHIMADZU HMV显微硬度计测量了合金的显微硬度, 压头类型为维氏, 136°角锥压头, 载荷0.1N, 加载时间10s。
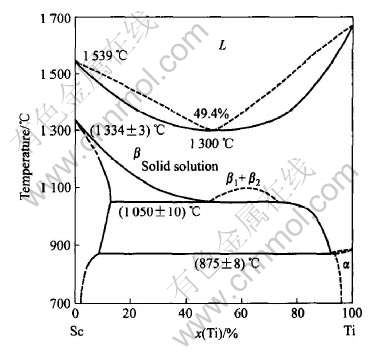
图1 Ti-Sc二元合金相图
Fig.1 Phase diagram of Ti-Sc binary alloy[10]
2 结果及分析
2.1 组织形貌及相分析
图2所示为铸态Ti-Sc二元合金的显微组织。 图3所示为合金的SEM组织形貌。 Ti-37Sc合金的显微组织与其他Ti-Sc合金的组织有着明显的不同, 这是Sc含量高所致。 由图2及图3可知, Ti-37Sc合金β晶界内的组织由尺寸约3μm的螺旋状的相组成, 此类相的成分由表1能谱分析结果可知为n(Ti)∶n(Sc)=8∶1;在Ti-25Sc合金中, 结合Ti-Sc二元相图, 其铸态组织中存在β与α相, 沿β晶界分布着向晶内生长的α片层组织, 片层宽度约为2μm, β晶界内的组织具有双相组织的形貌特征, 其相的成分和β晶界处α片层相的成分均为n(Ti)∶n(Sc)=8∶1, 与Ti-37Sc合金的相成分相同;在Ti-5Sc合金中存在着明显的晶界偏析, 其β晶界内的组织具有双相组织的形貌特征, 即存在着β基体和转变的β相(块状α相)及初生的α片层相, 由于溶质元素在晶界相对高的含量, 所以在晶界两侧还存在初生α片层组织[11]。 由能谱分析的结果可知, 晶界偏析相的Sc含量比β晶内双相组织的相的Sc含量略低, 其成分均接近于n(Ti)∶n(Sc)=19∶1, 合金成分接近于名义成分;Ti-2Sc合金的组织类似于Ti-5Sc合金的组织, 但要比其细小的很多, 其β晶内为双相组织, 由α片层与块体组织组成, 其片层相与基体成分为n(Ti)∶n(Sc)=49∶1, 合金质量比接近于名义成分;从能谱分析的结果看, 4种合金中金属Sc均固溶于Ti中。 由图2(e)和2(f)与其他二元合金组织对比可见, 重熔后工业纯钛TA1中的α片层组织比其他Ti-Sc合金的片层要粗大的多, 可见少量的金属Sc对合金组织的细化比较明显。
从X射线衍射结果(图5)可见, 合金中存在的主要是α-Ti, 由于Sc与Ti形成了固溶体, 所以未见有金属Sc的衍射峰, 未形成Ti-Sc金属间化合物。 随着Sc含量的降低, 在Ti-5Sc(3号)和Ti-2Sc (4号)合金中出现了少量的β-Ti, 可见在其铸态的组织中还存在残留的体心立方结构的β-Ti。

图2 Ti-Sc二元合金的铸态显微组织
Fig.2 As-cast microstructures of Ti-Sc binary alloys
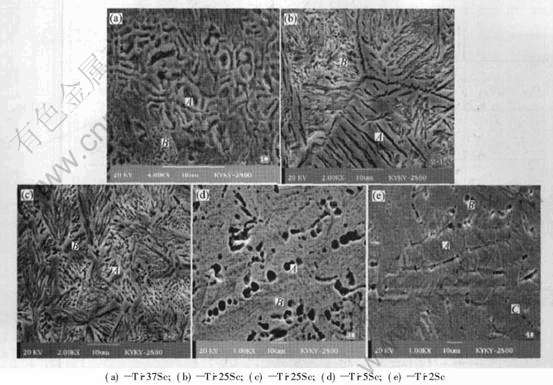
图3 铸态Ti-Sc二元合金的SEM形貌
Fig.3 SEM morphologies of as-cast Ti-Sc binary alloys
表1 Ti-Sc二元合金的能谱分析结果
Table 1 EDS results of Ti-Sc binary alloys
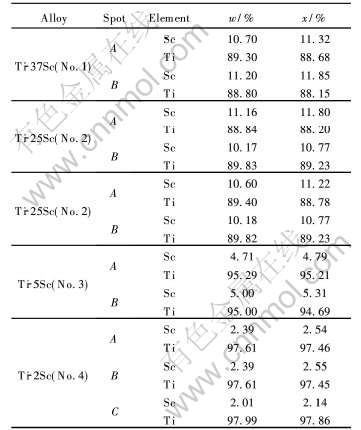
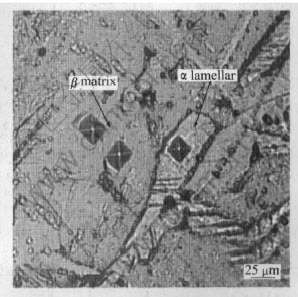
图4 Ti-25Sc合金的显微硬度测量示意图
Fig.4 Schematic sketch of measurement of microhardness in Ti-25Sc alloy
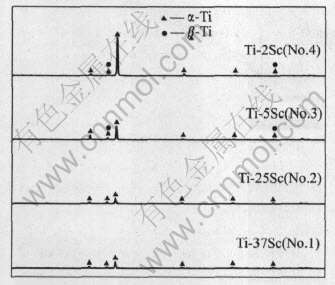
图5 Ti-Sc二元合金的X射线衍射谱
Fig.5 XRD patterns of Ti-Sc binary alloys
2.2 显微硬度分析
表2列出了Ti-Sc二元合金的显微硬度值, 图6所示为Sc含量对Ti-Sc二元合金显微硬度的影响。 Sc含量为2%时, Ti-Sc二元合金的显微硬度达到最高值, Sc含量高于2%时, 合金基体硬度高于片层组织硬度, 低于2%时, 合金基体硬度低于片层组织硬度, 同时由表2可知, 微量Sc使合金显微硬度有所提高, 对片层α相有强化作用, 这与其组织有着密切的关系。 Sc含量高的合金中, 如Ti-37Sc合金, 由于金属Sc质地柔软、 硬度低以及多数Sc固溶于钛中, 使得其硬度值比其他Ti-Sc二元合金以及纯钛的硬度值低很多; 在Ti-25Sc合金中, 其基体硬度明显高于其晶界两侧的片层组织的硬度, 据Sauer等[11]的研究, 晶界两侧的α片层簇组织形成了合金中的“软区域”, 此区域是导致片层簇组织硬度低的原因。 随着Sc含量的减少, 合金中基体和片层组织的硬度比较接近。 合金中片层组织的形貌、 尺寸及分布状态对其性能有着重要的影响[12-14]。
表2 Ti-Sc二元合金的显微硬度
Table 2 Measured microhardness of Ti-Sc binary alloys
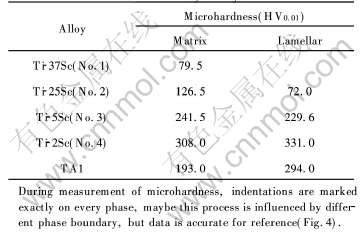
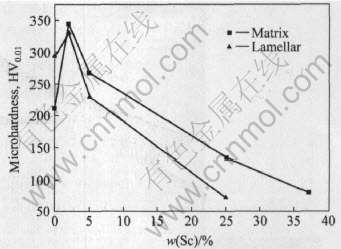
图6 Sc含量对Ti-Sc二元合金显微硬度的影响
Fig.6 Effects of Sc content on microhardness of Ti-Sc binary alloys
3 结论
1) 在Ti-Sc二元合金中, 不同Sc含量的Ti-Sc二元合金的组织变化非常明显。 随着Sc含量的减少, 合金组织由螺旋状、 片层簇状组织逐渐变为典型的双相组织, 与工业纯钛组织比较可见, 金属Sc对合金的组织有着明显的细化作用。 由SEM结果可见, 沿晶界向晶内生长的片层组织宽度约为2μm。 从EDS以及XRD结果可知, 在4种成分的Ti-Sc二元合金中, 金属Sc均固溶于Ti中, 形成了固溶体, 未形成Ti-Sc金属间化合物。
2) Sc含量为2%~3%时, Ti-Sc二元合金的显微硬度达到最高值; Sc含量高于2%~3%时, 合金基体硬度高于片层组织硬度; Sc含量低于2%~3%时, 合金基体硬度低于片层组织硬度, 少量Sc使合金显微硬度有所提高, 对α相片层有强化作用, 这与其组织有密切的关系。
REFERENCES
[1]刘静安, 吴煌良. 钛合金手册[M]. 重庆: 科学技术文献出版社重庆分社, 1982. 3.
LIU Jing-an, WU Huang-liang. Titanium Alloys Handbook[M]. Chongqing: Science and Technology Literature Press Chongqing Branch Press, 1982. 3.
[2]易宪武, 黄春辉. 钪稀土元素[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1998. 26.
YI Xian-wu, HUANG Chun-hui. Rare Earth Element Scandium[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 1998. 26.
[3]潘道皑, 赵成大, 郑载兴. 物质结构[M]. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 1989. 622.
PAN Dao-ai, ZHAO Cheng-da, ZHENG Zai-xing. Structure of Material[M]. Beijing: Higher Education Press, 1989. 622.
[4]胡赓祥, 钱苗根. 金属学[M]. 上海: 上海科学技术出版社, 1980. 32-33.
HU Geng-xiang, QIAN Miao-gen. Physical Metallurgy[M]. Shanghai: Shanghai Science and Technology Press, 1980. 32-33.
[5]Davydov V G, Rostova T G, Zakharov V V, et al. Scientific principles of making an alloying a-ddition of scandium to aluminium alloys[J]. Mater Sci Eng A, 2000, A280: 30-36.
[6]Fuller C B, Krause A R, Dunand D C, et al. Microstructure and mechanical properties of a 5754 aluminum alloy modified by Sc and Zr additions[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2002, A338: 8-16.
[7]Kending K L, Miracle D B. Strengthening mechanisms of an Al-Mg-Sc-Zr alloy[J]. Acta Materialia, 2002, 50: 4165-4175.
[8]张德尧. Al-Zn-Mg-Sc系热强可焊铝合金[J]. 稀有金属快报, 2001(1): 11-14.
ZHANG De-rao. Thermal strength and weldable Al-Zn-Mg-Sc aluminium alloys[J]. Rare Metal Research Bulletin, 2001(1): 11-14.
[9]余琨, 李松瑞, 黎文献, 等. 微量Sc和Zr对2618铝合金再结晶行为的影响[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 1999, 9(4): 709-713.
YU Kun, LI Song-rui, LI Wen-xian, et al. Effect of trace Sc and Zr on recrystallization behavior of 2618 alloy[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 1999, 9(4): 709-713.
[10]虞觉奇, 易文质, 陈邦迪, 等. 二元合金状态图集[M]. 上海: 上海科学技术出版社, 1987. 551.
YU Jue-qi, YI Wen-zhi, CHEN Bang-di, et al. Constitution of Binary Alloys[M]. Shanghai: Shanghai Science and Technology Press, 1987. 551.
[11]Sauer C, Lütjering G. Influence of α layers at β grain boundaries on mechanical properties of Ti-alloys[J]. Mater Sci Eng A, 2002, A319-321: 393-397.
[12]Ding R, Guo Z X, Wilson A, et al. Microstructural evolution of a Ti-6Al-4V alloy during thermomechanical processing[M]. Mater Sci Eng A, 2002 , A327: 233-245.
[13]Flower H M. Microstructural development in relation to hot working of titanium alloys[J]. Materials Science and Technology, 1990, 6: 1082-1092.
[14]Ahmed T, Rack H J. Phase transformations during cooling in α+β titannium alloys[J]. Mater Sci Eng A, 1998, A243: 206-211.
(编辑陈爱华)
基金项目: 中瑞政府间科技合作资助项目
收稿日期: 2004-03-17; 修订日期: 2004-12-22
作者简介: 刘会群(1978-), 男, 博士研究生.
通讯作者: 刘会群; 电话: 0731-8830263; E-mail: lhq_234@163.com