DOI:10.19476/j.ysxb.1004.0609.2017.08.04
Cu-Sn-Bi合金在球磨和烧结过程中的组织演变
曾美琴1, 3,邢继权1, 3,何秋梅4,胡仁宗1, 3,朱 敏1, 3,鲁忠臣2, 3
(1. 华南理工大学 材料科学与工程学院,广州 510640;
2. 华南理工大学 机械与汽车工程学院,广州 510640;
3. 广东省先进储能材料重点实验室,广州 510640;
4. 广东水利电力职业技术学院,广州 510925)
摘 要:采用机械合金化法制备出Cu-10%Sn-5%Bi合金粉末,然后将其压制成型并进行烧结,制备成合金块体;利用X射线衍射(XRD)和扫描电镜(SEM)等分析手段,研究Cu-Sn-Bi合金在高能球磨和烧结过程中组织结构的变化。结果表明:高能球磨可以扩展Cu-Bi互不溶体系的固溶度,且在球磨过程中形成的Cu6Sn5相为亚稳定相,随着球磨时间延长会先形成而后发生分解,分解后的Sn将固溶到Cu中;同时在450 r/min球磨40 h后,Sn、Bi基本完全融入Cu中,形成Cu的过饱和固溶体。在烧结过程中,Bi从Cu中脱溶,细小弥散分布在Cu基体中。在700 ℃二次烧结后,Cu-Sn-Bi合金显微组织良好,具有相对较好的力学性能。
关键词:机械合金化;粉末烧结;Cu-Sn-Bi合金;过饱和固溶体
文章编号:1004-0609(2017)-08-1563-09 中图分类号:TG135 文献标志码:A
现代工业的快速发展,对于滑动轴承材料的性能提出了更高的要求。铜基轴承合金由于具有高的承载能力及疲劳强度,使其在高速度、重载荷发动机领域得到广泛的应用[1]。然而,传统的铜基轴承合金中含有有毒元素铅,对人及环境会造成危害,因而对于无铅铜基轴承合金的研究成为各国热点[2-3]。
从目前国内外的发展趋势来看,实现铜基轴承材料无铅化的的主要途径是通过寻找合适组元来替代铅元素在合金中的作用。目前已有研究[4-6]发现:通过添加石墨、MoS2、WS2和Bi等润滑组元替代铅可以实现轴承合金的去铅化,且已初步取得一定的研究进展。石墨的化学稳定性高,通常不与铜基体发生反应,工作时在摩擦热的作用下,能够形成稳定的润滑膜提高合金的减摩性能。MoS2、WS2在铜基轴承合金中的润滑机制与石墨不同,其在烧结过程中会发生分解,分解的硫与铜可以形成具有润滑特性的铜硫化合物,这些化合物具有层状结构,可以降低合金的摩擦因数,从而提高合金的耐磨减摩性能。无毒低熔点金属元素Bi与Pb一样,在固态下均与铜不互溶,且不形成化合物,基本以游离态存在于铜基体中[7]。可见,Bi与Pb具有相似的物理及化学性质,具有替代铅的可行性。张随[8]采用Bi替代Pb研究CuSn10Bi10合金替代CuSn10Pb10合金的可行性;结果表明,在腐蚀环境下,含铋铜基轴承合金较传统铜铅合金具有更好的抗咬合性能,但其延展性能有待提高。尹延国等[9-10]对无铅含铋的锡青铜轴承合金进行了探索性研究,同时将制备的铜基合金与传统的CuSn10Pb10轴承合金进行了力学及摩擦学性能对比;结果表明,在摩擦磨损过程中,Bi析出到铜基轴承合金表面,既减少了润滑油膜损伤又降低了接触点的剪切强度,起到了较好的减摩和抗粘着性能。但研究也发现,在合金组织中Bi易在铜合金晶界处偏聚,割裂合金基体的完整性,同时发现Bi的脆性较大,易于从合金磨损表面脱落,因而对铜铋轴承合金需要做进一步的研究。
目前工业上通常采用雾化方法制备合金粉末,再经过粉末烧结复合工艺[11]制备成合金带材,其制备工艺为:“铺粉-松装烧结-初轧-复烧-复轧”。辉门公司已经开发出CuSn10Bi3牌号的无铅轴承合金,其抗拉强度、疲劳强度及耐腐蚀性能均优于传统CuSn10Pb10轴承合金的[12],但所制备的铜基含铋轴承合金中Bi相组织较粗大且易于在铜合金基体晶界偏聚的问题没有得到很好的解决。机械合金化法[13](简称MA法)对于制备细小弥散分布的第二相合金有着成功的应用[14],且采用MA法制备Cu-Sn-Bi轴承合金还鲜有报道,因此,本文作者尝试采用MA法制备Cu-Sn-Bi合金,研究不同的球磨、压制及烧结工艺对合金组织结构及性能的影响。
1 实验
将平均粒度为74μm的Cu粉(纯度99.9%)、Sn粉(纯度99.5%)以及Bi粉(纯度99.9%)按Cu-10%Sn- 5%Bi、Cu-5%Bi(质量分数)比例配成混合粉,然后利用QM-3SP2球磨机进行高能球磨,球罐容量为0.4 L,钢球与粉末的球料比为15:1,球磨工艺采用450 r/min不同时间球磨,球磨过程在氩气保护下进行。将球磨40 h后的合金粉末在800 MPa压力下冷压成若干个d 24 mm×3 mm的圆块,然后采用CVD(G)-07/50/2高温管式炉在高纯氩气保护下,以5 ℃/min的加热速率升温至指定温度,保温20 min后随炉冷却,来研究不同烧结温度对合金组织结构及性能的影响。
采用Philips X’Pert MPD X射线衍射仪(XRD)和Zeiss super 40场发射扫描电子显微镜分析合金的相结构和显微组织结构,其中XRD的主要参数为:辐射源为Cu Kα,电压为40 kV,电流为40 mA,发散狭缝DS为0.5°,抗发散狭缝AS为1°,扫描步长为0.02°,每步停留时间20 s。测试前采用Si标样对设备进行角度校正。采用GB 5163-85(可渗性烧结金属材料密度的测试)进行密度的测量以及致密度的计算,每个数值是由5个样品的测试平均值获得,每组数据的误差范围是±0.5。用HVS-1000型数字显微硬度计测量合金硬度,载荷为4.9 N,保压时间为10 s,每个样品取5个点的平均值。将上述合金块体线切割成拉伸试样(标距9 mm,宽3 mm,厚3 mm),用Instron5900型电子万能材料试验机测试合金的拉伸强度,拉伸速率为0.6 mm/min。
2 结果与分析
2.1 球磨对Cu-Sn-Bi合金粉末组织结构的影响
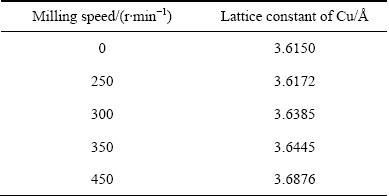
图1所示为经450 r/min球磨不同时间后Cu- 10%Sn-5%Bi合金粉末的XRD谱。由图1可见,球磨1 h后,合金粉末由Cu、Sn、Bi、Cu6Sn5等4相组成,表明球磨过程中,由于外界机械能的作用,促进了Cu、Sn间的扩散而形成了Cu6Sn5中间相;球磨5h后,合金中Sn相的衍射峰明显减弱而Cu6Sn5相的衍射峰则明显升高,表明球磨时间的延长进一步促进了Sn与Cu之间反应生成Cu6Sn5相;当球磨时间达到10 h后,合金中Bi相的衍射峰明显减弱并宽化,Sn的衍射峰消失,而Cu的衍射峰发生宽化且略微向低角偏移;当球磨时间达到20 h后,合金中仅存在宽化的Cu的衍射峰,且其衍射峰进一步向低角偏移。有研究表明[15],球磨形成的Cu6Sn5相在高能球磨的作用下会先形成而后发生分解出分解的Sn原子固溶到Cu晶格中;再进一步增加球磨时间,衍射峰变化不明显。利用柯亨最小二乘法[15]计算出经450 r/min球磨不同时间后Cu-10%Sn-5%Bi合金中Cu的晶格常数,结果如表1及图2所示。可见,球磨时间小于10 h时,Cu的晶格常数变化不明显,未能形成大量的Cu固溶体相,这可能因为一方面Bi相未固溶于Cu,另一方面Sn和Cu主要形成了Cu6Sn5相;球磨时间在10~20 h时,Cu的晶格常数急剧增加,这应该与这段时间Cu6Sn5相及Bi相的消失有关,高能球磨在该阶段积累了一定的能量使Cu6Sn5相发生分解,分解后的Sn再固溶到Cu中,同时球磨使Cu晶格畸变产生大量的位错等缺陷,使Bi可能也固溶到Cu中,从而导致Cu的晶格常数变大;之后随着球磨时间的进一步增加,合金中Cu的晶格常数增加变缓,表明其逐渐达到饱和状态,残留的少量Sn、Bi继续固溶在Cu中形成过饱和固溶体。为证实这一推论的正确性,对比计算出250、300、350和450 r/min条件下,球磨40 h的Cu-10%Sn-5%Bi合金中Cu的晶格常数,如表2所列。可见,随着球磨转速的增加,合金粉末XRD谱中Cu6Sn5相衍射峰逐步减弱,并在450 r/min时消失,其Cu的晶格常数也伴随着Cu6Sn5相衍射峰的减弱而增加。这也证明了Cu6Sn5相在高转速条件下可能发生分解,形成了Cu(Sn)的固溶体相。
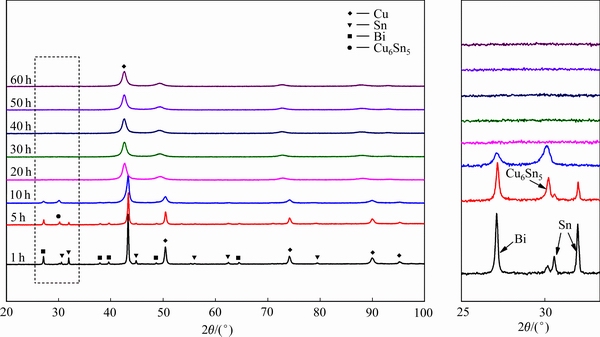
图1 经450 r/min球磨不同时间后Cu-10%Sn-5%Bi合金粉末XRD谱
Fig. 1 XRD patterns of Cu-10%Sn-5%Bi alloy after milling with 450 r/min for different milling time
此外,在图1中还发现,随球磨时间的增加,Cu的衍射峰发生宽化,这与其晶粒细化及晶格畸变有关。图3所示为利用VOIGT函数法[16]计算得到,经不同时间球磨后Cu-10%Sn-5%Bi合金粉末中Cu的晶粒尺寸随球磨时间的变化。从图3可以看出,随着球磨时间的增加,Cu的晶粒尺寸逐渐减小。当球磨时间在5~10 h时,Cu晶粒细化最明显,之后当球磨时间达到20 h后,其晶粒尺寸变化不明显,基本稳定在20 nm左右。
表1 经450 r/min球磨不同时间后Cu-10%Sn-5%Bi合金中Cu的晶格常数
Table 1 Lattice constant of Cu in Cu-10%Sn-5%Bi alloy with 450 r/min milling speed for different milling time
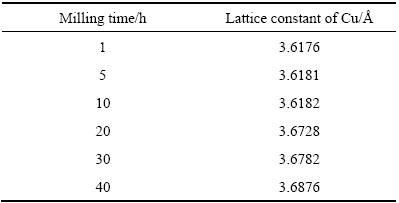
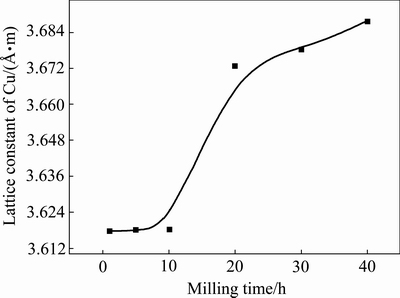
图2 经450 r/min球磨不同时间后Cu-10%Sn-5%Bi合金中Cu的晶格常数的变化
Fig. 2 Change of lattice constant of Cu in Cu-10%Sn-5%Bi alloy after milling with 450 r/min for different time
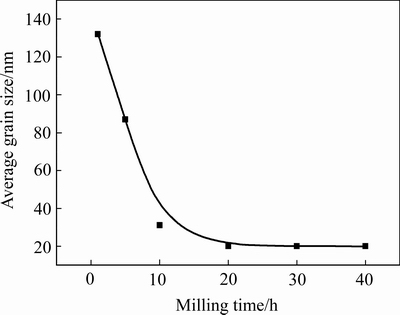
图3 经450 r/min球磨不同时间后Cu-10%Sn-5%Bi合金中Cu晶粒尺寸的变化
Fig. 3 Change of grain size of Cu in Cu-10%Sn-5%Bi alloy after milling with 450 r/min for different time
表2 经不同球磨转速40 h后Cu-10%Sn-5%Bi合金中Cu的晶格常数
Table 2 Lattice constant of Cu in Cu-10%Sn-5%Bi alloy after milling for 40 h with different milling speeds
通常Cu-Bi为固态二元互不溶体系,但在图1中发现,随着球磨时间的增加,Bi的衍射峰逐渐减弱并消失,推测其是固溶到Cu中。也有文献报道[18],采用塑性变形等条件,低混合热的互不溶体系极其容易出现扩展固溶等现象。为了验证高能球磨能够扩展Bi在Cu中的固溶度,采用不同球磨转速球磨40 h制备Cu-5%Bi合金粉末,并对其进行XRD分析,结果如图4所示。从图4中可以看出,当球磨转速达到450 r/min后,Bi相衍射峰消失,合金中仅存在宽化的Cu的衍射峰,且其随转速增加而向低角度偏移,利用柯亨最小二乘法计算Cu的晶格常数,结果如表3所列。从表3可以看出,Cu-5%Bi合金粉末球磨后Cu的晶格常数变大,且随着球磨转速的增加,Cu的晶格常数增大更明显。在本实验的二元Cu-Bi合金体系中,Cu的晶格常数产生变化只能是由于Bi元素固溶造成的,且Bi的原子半径比Cu的大,其固溶到Cu中,将导致Cu的晶格常数增大;而球磨转速增大,Bi几乎全部固溶,这也与Cu的晶格常数随球磨转速增大的结果相符合。由此证明,高能球磨可以扩展Cu-Bi互不溶体系的固溶度,使Bi固溶到Cu中。
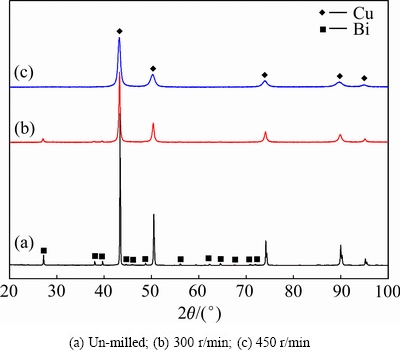
图4 经不同转速球磨40 h后Cu-5%Bi合金的XRD谱
Fig. 4 XRD patterns of Cu-5%Bi alloy after milling with different milling speeds for 40 h
表3 经不同转速球磨40 h后的Cu-5%Bi合金中Cu的晶格常数
Table 3 Lattice constant of Cu in Cu-5%Bi alloy after milling with different milling speeds for 40 h

将450 r/min球磨40 h后的Cu-10%Sn-5%Bi合金粉末压制成块体,再将其抛光后进行SEM形貌观察及能谱分析,结果如图5所示。从图5可以看出,压制后的合金块体中存在较多的孔洞,粉末颗粒轮廓形貌清晰,相互之间通过机械咬合结合在一起。对合金生坯高倍观察(见图5(b))没有出现第二相的衬度,这也与图1中球磨40 h后的XRD结果一致,即此时合金仅由单相Cu的过饱和固溶体组成。另外,从合金低倍下能谱面扫面结果(见图5(a)中插图)可以看出,合金中Sn、Bi元素较为均匀弥散分布在铜合金基体中。
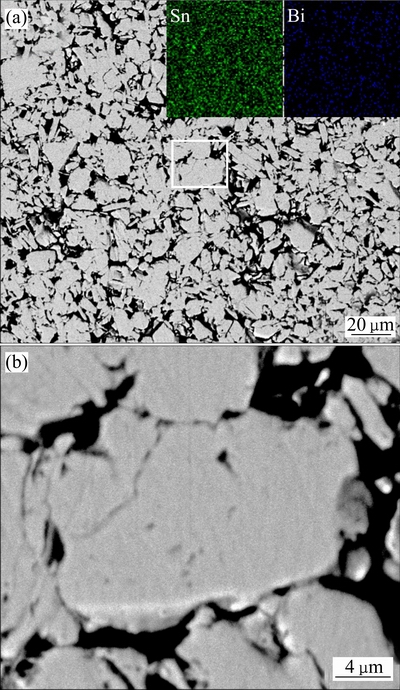
图5 Cu-10%Sn-5%Bi合金生坯SEM背散射形貌图及能谱分析结果
Fig. 5 Back scattering SEM, EDS(a) and high magnification(b) images of Cu-10%Sn-5%Bi green
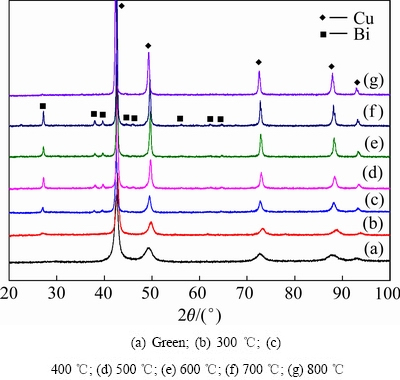
图6 经不同温度一次烧结后Cu-10%Sn-5%Bi合金的XRD衍射谱
Fig. 6 XRD patterns of Cu-10%Sn-5%Bi alloy after primary sintering at different temperatures
2.2 Cu-Sn-Bi合金在烧结过程中组织演变
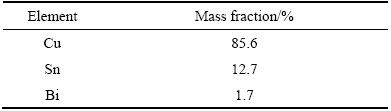
由图5可见,一次压制后的生坯中存在较多的孔洞,为此,将采用“复压复烧”工艺制备合金块体,两次压制及烧结温度均相同,以此来研究合金组织结构及性能的变化。图6所示为经不同温度一次烧结后的Cu-10%Sn-5%Bi合金的XRD谱。可见,Cu-10%Sn- 5%Bi合金经压制加一次烧结后,Bi开始从Cu的过饱和固溶体中析出,但在300 ℃烧结时,Bi相的衍射峰十分微弱;当烧结温度提高到400 ℃时,Bi相出现明显的衍射峰;之后随着烧结温度的提高,Bi相的衍射峰逐渐增强,表明Bi的脱溶量逐渐增多。而Cu相的衍射峰则随着温度的提高而逐渐变得尖锐,这是由于Cu的晶粒长大导致的,且在700 ℃烧结后Bi相的衍射峰相对最强,表明该温度下Bi的脱溶量最大。因为采用“复压复烧”工艺,故对经不同温度两次烧结后的Cu-10%Sn-5%Bi合金也进行了XRD分析,结果如图7所示。与图6对比可以看出,经过不同温度两次烧结后,合金中的Bi相衍射峰强度均比一次烧结后的强度高,这是由于经过相同温度两次烧结后Bi的析出量增多,且其晶粒发生长大引起的。且经过两次700 ℃烧结后,合金中Bi相衍射峰数量最多,强度较高,表明在该温度下Bi已基本从Cu中脱溶出来。两次烧结后Cu的晶粒发生长大使其衍射峰也较一次烧结后的更为尖锐。而且从图6及7中还发现,经不同温度烧结后的合金中均未发现Sn相的衍射峰,表明其可能并未发生脱溶。此外,当烧结温度提高到800 ℃时,一次烧结及两次烧结后的合金中仅存在尖锐的Cu相的衍射峰,而Bi相的衍射峰则十分不明显。为了确定800 ℃烧结后合金中Bi是否流失,对该温度两次烧结后合金块体进行SEM及能谱分析,结果如图8及表3所示。由图8可见,合金中仅存在少许白亮色Bi相,能谱分析(见表3)表明,Bi的含量只有1.7%(质量分数),这较原始添加量5%偏差较大。由于本实验的“复压复烧”工艺采用随炉升温及冷却,当烧结温度达到800 ℃后,已融化的低熔点金属元素Bi(熔点为271.3℃)在液态停留时间较长,且合金中存在较多的孔洞,易使Bi从合金基体中流失,导致合金成分发生改变,因此采用“复压复烧”工艺制备Cu-10%Sn-5%Bi合金的烧结温度不能在800 ℃以上。
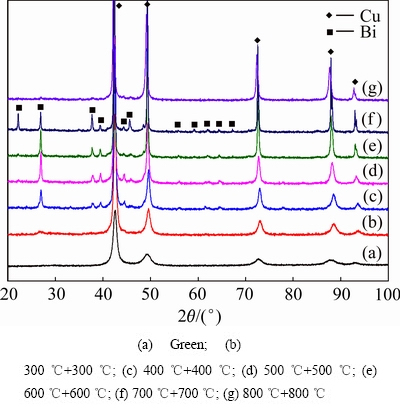
图7 经不同温度两次烧结后Cu-10%Sn-5%Bi合金的XRD衍射谱
Fig. 7 XRD patterns of Cu-10%Sn-5%Bi alloy after twice sintering at different temperatures

图8 Cu-10%Sn-5%Bi合金经800℃两次烧结后SEM背散射像
Fig. 8 Back scattering SEM images of Cu-10%Sn-5%Bi alloy after twice sintering at 800℃
表3 经800 ℃烧结两次后Cu-10%Sn-5%Bi合金中的元素含量
Table 3 Element content of Cu-10%Sn-5%Bi alloy after twice sintering at 800 ℃
对不同温度两次烧结后的Cu-10%Sn-5%Bi合金块体进行SEM分析,如图9所示,图像均为背散射电子像,其中白亮色的点状区域对应的是原子序数较大的Bi相,灰色区域对应的是原子序数较小的Cu基体。从图9中可以看出,在300 ℃烧结时,合金中孔洞较粗大,粉末颗粒之间边界清晰可见,表明其基本没有形成冶金结合,仅通过机械咬合作用而结合在一起。但对该合金进行高倍观察,如图9(a)中插图所示,则发现合金这些大颗粒中已经析出细小弥散分布的纳米级Bi相。Cu-Bi为二元不互溶体系,通过高能球磨的作用使Bi固溶到Cu中,而在随后的加热及冷却过程中,Bi相再脱溶析出,但由于温度较低时,新形成的Bi相还未长大,因而呈纳米晶弥散分布于Cu基体中。由图9(b)和(c)可见,随着烧结温度的提高,加快了合金粉末间原子的扩散,同时熔融的Bi填补了少量的孔洞,使合金颗粒间彼此粘合成一个整体,但是由于烧结温度较低,合金中低熔点Bi熔融状态时间较短,不足以填补Cu基体的间隙,且合金粉末间原子扩散较慢导致其冶金结合效果不好。当烧结温度提高到700 ℃时,部分熔融的Bi相填补了铜基体中的孔洞,提高了合金的致密度,同时温度的提高加快了合金原子间的扩散速度,使得合金粉末间产生良好的冶金结合,且此时Bi相较为均匀的分布在Cu基体中。由于在这些不同温度烧结后的合金组织中均没有观察到Sn相的存在,为了确定合金成分是否发生了变化,进一步对经不同温度两次烧结后的Cu-10%Sn-5%Bi合金进行能谱分析(见表4)。结果表明,合金中Sn相的含量接近原来的成分配比,表明Sn并未脱溶,而是固溶在Cu中,这与图6及图7合金经不同温度烧结后的XRD中没有Sn相的衍射峰的结果相一致,同时在700 ℃烧结后合金中的Bi含量也接近原来的成分配比,并没有流失。
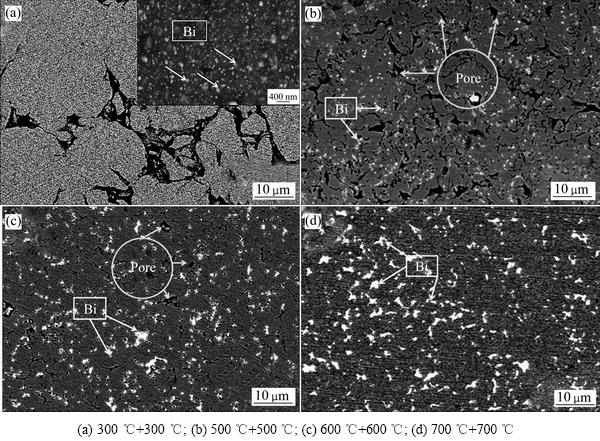
图9 经不同温度两次烧结后Cu-10%Sn-5%Bi合金的SEM背散射像
Fig. 9 Back scattering SEM images of Cu-10%Sn-5%Bi alloy after twice sintering at different temperatures
表4 经不同温度两次烧结后Cu-10%Sn-5%Bi合金的能谱分析
Table 4 EDS analysis of Cu-10%Sn-5%Bi alloy after twice sintering at different temperatures
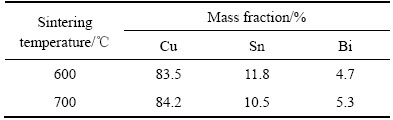
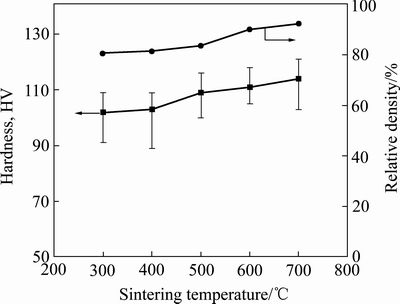
图10 经不同温度两次烧结后Cu-10%Sn-5%Bi合金的致密度及显微硬度随温度的变化
Fig. 10 Variation of relative density and microhardness of Cu-10%Sn-5%Bi alloy after twice sintering at different temperatures
2.3 烧结后Cu-Sn-Bi合金的力学性能
由于在“复压复烧”过程中,当烧结温度达到800 ℃后,Cu-10%Sn-5%Bi合金中的Bi相流失较多,为此后面的致密度及性能测试,不再分析800 ℃烧结的样品。对其他不同温度两次烧结后的Cu-10%Sn-5%Bi合金块体采用排水法测量其致密度,并对其显微硬度进行测试,结果如图10所示。从图10中可以看出,Cu-10%Sn-5%Bi合金的致密度及硬度均随着烧结温度的提高而逐渐增大。当烧结温度达到700 ℃后,合金的致密度达到92%以上,显微硬度可达114 HV。这是由于在700 ℃下,第一次烧结过程中,固溶到Cu中的Bi脱溶析出弥散分布在Cu基体中,填补了合金中较小的孔隙,通过复压工艺,使合金中较大孔隙变小,再通过复烧的过程,使合金中低熔点组元熔融得以填补合金中细小的孔隙,从而提高合金的致密度,同时在该温度下烧结有利于合金粉末中原子的扩散,使合金间形成更好的冶金结合。在700 ℃条件下,合金中晶粒还没有完全长大而发生粗化,从图9(d)也可以看出,软质的第二相Bi弥散分布在Cu基体中,这也有利于提高合金整体的硬度。
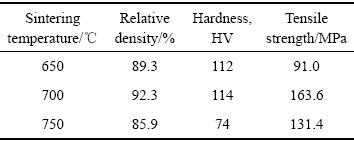
为了确定700 ℃是否为本“复压复烧”工艺制备合金块体的最佳烧结温度,进一步尝试采用650 ℃及750 ℃温度对合金块体进行烧结,并与700 ℃烧结后的合金块体进行力学性能对比,如表5所列。从测试结果来看,经700 ℃烧结后的合金块体的致密度、硬度均相对较高。此外,还可通过测试合金块体的拉伸强度来判断合金的烧结性能。从拉伸强度测试结果(见表5)来看,经700 ℃烧结的合金块体拉伸强度高达 163 MPa,表明在该温度下制备的合金具有最优的力学性能。
表5 经不同温度烧结后的Cu-10%Sn-5%Bi合金的力学性能
Table 5 Mechanical test of Cu-10%Sn-5%Bi alloy sintered at different temperature
3 结论
1) 高能球磨可以扩展互不溶Cu-Bi体系的固溶度,使Bi固溶到Cu中;经450 r/min球磨40 h,Sn和Bi相基本全部固溶于Cu基体中,形成仅有的Cu的过饱和固溶体,其晶粒尺寸在20 nm左右。
2) 在球磨初期,Cu-Sn间会形成亚稳定的Cu6Sn5相,该相随球磨时间的增加先形成而后发生分解,在球磨后期,分解后的Sn又会固溶到Cu基体中。
3) 高能球磨制备的Cu-10%Sn-5%Bi合金粉末,在烧结过程中,Bi相从Cu的过饱和固溶体中析出,而Sn则继续保持固溶在Cu中,最终获得较细小的Bi相均匀分布在Cu(Sn)基体上。
4) 在保证Bi相不发生流失的前提下,两次700 ℃烧结所制备的Cu-10%Sn-5%Bi合金,其Bi相较为均匀分布在Cu基体中,烧结致密度达到了92.3%,硬度和拉伸强度分别达到114 HV和163.6 MPa。
REFERENCES
[1] ITO H, KAMIYA S, KUMADA Y. The transition of plain bearing materials[J]. Journal of Japanese Society of Tribologists, 2003, 48(3): 172-177.
[2] 蒋玉琴. 国内外汽车滑动轴承材料发展现状及趋势[J]. 汽车工艺与材料, 2009(3): 10-13.
JIANG Yu-qin. The development and trend of automobile sliding bearing materials[J]. Automobile Technology & Material, 2009(3): 10-13
[3] 李 鹏. 国外内燃机滑动轴承材料无铅化及其应用[J]. 汽车工艺与材料, 2009(7): 1-3.
LI Peng. Lead free and its application in internal combustion engine sliding bearing material[J]. 2009(7): 1-3
[4] YOKOTA H, DESAKI T, HAYAKAWA H, HASHIZUME K, ITO H, INAYOSHI N, MURAKAMI Y, NOZU T, SUZUKI M. Newly development lead free copper alloy bushing for fuel injection pump[C]// Proceeding of SAE World Congress. Michigan, 2006: 6-11.
[5] Kouji Zushi, Kenji Sakai, Hiroyuki Sugawara, Hideo Ishikawa. Development of lead free copper based alloy for piston pin bushing under higher load engines[C]// Proceeding of SAE World Congress. Michigan, 2006: 20-21.
[6] KATO H, TAKAMA M, IWAI Y, WASHIDA K, SASAKI Y. Wear and mechanical properties of sintered copper–tin composites containing graphite or molybdenum disulfide[J]. Wear, 2003, 255(1): 573-578.
[7] YIN Y G, LI Y Y, ZHANG G T, YIN L, JIAO X N. Study on mechanical properties of Cu-Bi bearing materials[C]// Advanced Materials Research. Trans Tech Publications, 2013: 89-92.
[8] 张 随. 滑动轴承用Cu-Sn-Bi合金的性能[J]. 汽车工艺与材料, 2011(7): 58-61.
ZHANG Sui. The properties of Cu-Sn-Bi sliding bearing alloy[J]. Automobile Technology & Material, 2011(7): 58-61
[9] YIN Y G, LIN F D, YAO W, XIE T, YU J W. Tribological properties of the surface bonded self-lubricating coating[C];; Advanced Materials Research. Trans Tech Publications, 2011: 583-587.
[10] 尹延国, 林福东, 俞建卫, 焦明华, 解 挺, 田 明. 无铅铜铋轴承合金的摩擦学特性[J]. 材料热处理学报, 2012(S1): 1- 6.
YINYan-guo, LINFu-dong, YUJian-wei, JIAOMing-hua, XIETing. Tribological properties of lead-free copper bismuth bearing alloys[J]. Transactions of Materials and Heat Treatment, 2012(S1): 1-6.
[11] 高铁堆, 栗联娣. 粉末冶金铅青铜高密度轴承材料的研制[J]. 粉末冶金技术, 1993, 11(4): 311-312.
GAO Tie-dui, LI Lian-di. Preparation of powder metallurgy lead bronze bearing material with high density[J]. Powder Metallurgy Technology, 1993, 11(4): 311-312.
[12] SAXTON D M. Lead-free replacements for SAE 792 in bushing applications[C]// Proceeding of SAE World Congress. Michigan, 2006: 1-5.
[13] 朱 敏, 曾美琴, 欧阳柳章, 吴志方, 刘 辛. 机械合金化制备的 Al 基轴承合金的结构与性能[J]. 华南理工大学学报(自然科学版), 2007, 35(10): 37-43.
ZHU Min, ZENG Mei-qin, OUYANG Liu-zhang, WU Zhi-fang, LI Xin. Microstructure and wear properties of al-based bearing alloys fabricated by mechanical alloying[J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Nature Science Edition), 2007, 35(10): 37-43.
[14] 叶 新, 鲁忠臣, 曾美琴, 胡仁宗, 朱 敏. Si 添加量对机械合金化Al-12%Sn合金组织与摩擦性能的影响[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2014, 24(1): 53-60.
YE Xin, LU Zhong-chen, ZENG Mei-qin, HU Ren-zong, ZHU Min. Effect of Si addition concentration on the microstructure and wear properties of MA Al-12%Sn[J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2014, 24(1): 53-60.
[15] 张志佳. 发动机滑动轴承用无铅铜基复合材料的研究[D]. 天津: 天津大学, 2012.
ZHANG Zhi-jia. Research on Pb free Cu-based composite used by bearing materials of engine[D]. Tianjin: Tianjin University, 2012.
[16] 范 雄. 金属X射线学[M]. 北京: 机械工业出版社, 1989.
FAN Xiong. Metallic X-ray physics[M]. Beijing: China Machine Press, 1989.
[17] LANGFORD J I. A rapid method for analysing the breadths of diffraction and spectral lines using the Voigt function[J]. Journal of Applied Crystallography, 1978, 11(1): 10-14.
[18] REN F, ARSHAD S N, BELLON P, AVERBACK R S, POURYAZDAN M, HAHN H. Sliding wear-induced chemical nanolayering in Cu-Ag, and its implications for high wear resistance[J]. Acta Materialia, 2014, 72: 148-15.
Microstructure evolution of Cu-Sn-Bi alloy in ball milling and sintering
ZENG Mei-qin1, 3, XING Ji-quan1, 3, HE Qiu-mei4, HU Ren-zong1, 3, ZHU Min1, 3, LU Zhong-chen2, 3
(1. School of Materials Science and Engineering, South China University of Technology, Guangzhou 510640, China;
2. School of Mechanical & Automotive Engineering, South China University of Technology, Guangzhou 510640, China;
3. Key Laboratory of Advanced Energy Storage Materials of Guangdong Province, Guangzhou 510640, China;
4. Guangdong Polytechnic of Water Resources and Electric Engineering, Guangzhou 510925, China)
Abstract: The mechanical alloying (MA) was used to prepare Cu-10%Sn-5%Bi alloy powders. Then the bulk alloy was obtained by a combination of cold pressing and conventional powder sintering. The microstructure evolutions of Cu-10%Sn-5%Bi alloy during ball milling and sintering were investigated by XRD and SEM. The results show that high-energy milling can extend solid solubility of Cu-Bi immiscible system, and the metastable Cu6Sn5 phase successively happens to formation and decomposition with milling time. Meanwhile, the decomposition Sn is dissolved into Cu matrix. After milling with 450 r/min for 40 h, both Sn and Bi are completely dissolved into Cu matrix and a supersaturated solid solution of Cu(Sn, Bi) is formed. During sintering, Bi precipitates from Cu(Sn, Bi) supersaturated solid solution, are fine and dispersed homogeneously in Cu(Sn) matrix. The Cu-Sn-Bi alloy twice sintered at 700 ℃ exhibits an excellent microstructure and mechanical properties.
Key words: mechanical alloying; powder sintering; Cu-Sn-Bi alloy; supersaturated solid solution
Foundation item: Project(51501065) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China; Project (2014A030310395) supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province, China; Project(2014ZB0020) supported by the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities, China
Received date: 2016-07-05; Accepted date: 2016-12-29
Corresponding author: LU Zhong-chen; Tel: +86-20-87112762;E-mail: mezclu@scut.edu.cn
(编辑 王 超)
基金项目:国家自然科学基金资助项目(51501065);广东省自然科学基金资助项目(2014A030310395);中央高校基本科研业务费资助项目(2014ZB0020)
收稿日期:2016-07-05;修订日期:2016-12-29
通信作者:鲁忠臣,讲师,博士;电话:020-87112762;E-mail: mezclu@scut.edu.cn