近等温锻造后TC21钛合金的显微组织及力学性能
来源期刊:中国有色金属学报(英文版)2015年第1期
论文作者:石志峰 郭鸿镇 刘 瑞 王晓晨 姚泽坤
文章页码:72 - 79
关键词:TC21钛合金;近等温锻造;显微组织;α相形貌;残留β基体;拉伸性能
Key words:TC21 titanium alloy; near-isothermal forging; microstructure; α phase morphology; residual β matrix; tensile properties
摘 要:研究经不同参数近等温锻造并固溶时效热处理后TC21钛合金的显微组织及拉伸性能。结果表明,所有试样中都存在细小片状α相强化的残留β基体,而初生等轴α相、弯曲片状α相及片状α相可能同时或单独出现在试样中。残留β基体含量的增多会增加合金中α/β相界面,从而引起合金强度增加。随着残留β基体含量的增加,细小片状α相增多,变形过程中被位错切过,导致合金的塑性有下降趋势。另外,当长轴方向与最大剪切应力平行时,粗大的片状α相也会降低合金的塑性。
Abstract: Microstructure and tensile properties of TC21 titanium alloy after near-isothermal forging with different parameters plus solution treatment and aging were investigated. It is found that the residual β matrix, which was strengthened by fine secondary α platelets forming during aging, exists in all the samples; while primary equiaxed α phase, bent lamellar α phase and α plates are simultaneously or individually present in one sample. The strength of alloy increases proportionally with increasing the content of residual β matrix, which is the result of increasing α/β interphase boundary. The plasticity of alloy has a downward trend as the content of residual β matrix increases. This attributes to the increase of fine secondary α platelets, which are cut by dislocations during the deformation. Additionally, coarse α plates with long axis parallel to the maximum resolved shear stress (MRSS) also reduce the plasticity of TC21 alloy.
Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 25(2015) 72-79
Zhi-feng SHI1, Hong-zhen GUO1, Rui LIU1, Xiao-chen WANG1,2, Ze-kun YAO1
1. School of Materials Science and Engineering, Northwestern Polytechnical University, Xi’an 710072, China;
2. School of Aeronautics, Northwestern Polytechnical University, Xi’an 710072, China
Received 12 February 2014; accepted 19 May 2014
Abstract: Microstructure and tensile properties of TC21 titanium alloy after near-isothermal forging with different parameters plus solution treatment and aging were investigated. It is found that the residual β matrix, which was strengthened by fine secondary α platelets forming during aging, exists in all the samples; while primary equiaxed α phase, bent lamellar α phase and α plates are simultaneously or individually present in one sample. The strength of alloy increases proportionally with increasing the content of residual β matrix, which is the result of increasing α/β interphase boundary. The plasticity of alloy has a downward trend as the content of residual β matrix increases. This attributes to the increase of fine secondary α platelets, which are cut by dislocations during the deformation. Additionally, coarse α plates with long axis parallel to the maximum resolved shear stress (MRSS) also reduce the plasticity of TC21 alloy.
Key words: TC21 titanium alloy; near-isothermal forging; microstructure; α phase morphology; residual β matrix; tensile properties
1 Introduction
Titanium alloys are widely used in aviation industry, especially in manufacturing aircraft structural components and aero-engine [1-3]. TC21 titanium alloy, a recently developed two-phase titanium alloy, has been received increasing attention in the last decade [4-6]. This alloy is mainly used to fabricate aircraft structural components such as frames and beams because of its high strength, high fracture toughness and low crack propagation rate [7].
It is difficult to form these components due to the high deformation resistance and complex shape, such as bulkheads with high ribs and thin webs. Isothermal forging, which can reduce the deformation load and enhance the plasticity and filling ability of alloy due to the constant temperature and lower strain rate, provides a viable way to form such components [8-11]. After isothermal forging, near net shape forgings can generally be obtained, which improves the material utilization and reduces the cost. GUO et al [12] pointed out that the material utilization of titanium alloy precise forgings manufactured by isothermal forging could reach 74.2%. Nevertheless, the dies employed for isothermal forging could badly be corroded or oxidized at high temperatures after a long reaction time. Therefore, near-isothermal forging [13], whose die temperature is slightly lower than the forging temperature (or sample temperature), is sometimes adopted to reduce these damages and prolong the lifetime of forging dies. Due to the low strain rate, the temperature depression occurs during near-isothermal forging. After near-isothermal forging, the solution treatment and aging [14,15] is usually applied to two- phase titanium alloy. The complicated thermo- mechanical processing causes the microstructure of titanium alloys to be different from that after other forging methods.
In addition, the mechanical properties of titanium alloys are sensitive to their microstructures. Several researchers have tried to establish the relationships between mechanical properties and microstructure.  [16] summarized the relationships among processing, microstructure, and mechanical properties of two-phase α+β titanium alloys, and pointed out that the α colony size was the most important microstructural parameter determining the mechanical properties. LEE [17] and TILEY et al [18] quantified the important microstructural features by rigorous stereological procedures, developed the fuzzy logic and Bayesian neural network models to predict the room temperature tensile properties of Timetal 550 and determined the individual influence of the microstructural features on tensile properties. Good understanding of relationships among processing parameters, microstructure and mechanical properties is helpful to manufacturing high quality forgings. Therefore, it is necessary to research the microstructure and mechanical properties of TC21 titanium alloy after near-isothermal forging plus solution treatment and aging.
[16] summarized the relationships among processing, microstructure, and mechanical properties of two-phase α+β titanium alloys, and pointed out that the α colony size was the most important microstructural parameter determining the mechanical properties. LEE [17] and TILEY et al [18] quantified the important microstructural features by rigorous stereological procedures, developed the fuzzy logic and Bayesian neural network models to predict the room temperature tensile properties of Timetal 550 and determined the individual influence of the microstructural features on tensile properties. Good understanding of relationships among processing parameters, microstructure and mechanical properties is helpful to manufacturing high quality forgings. Therefore, it is necessary to research the microstructure and mechanical properties of TC21 titanium alloy after near-isothermal forging plus solution treatment and aging.
In the present work, the effects of near-isothermal forging parameters, including die temperature, strain rate and forging temperature, on microstructure and mechanical properties of TC21 titanium alloy were studied. The formation of α phase with different morphologies was investigated. The effects of microstructural features on mechanical properties were analyzed.
2 Experimental
The proposed TC21 titanium alloy bar with diameter of 300 mm was used in this work. The β transus temperature was approximately 960 °C. The chemical composition of this alloy is shown in Table 1. The microstructure of as-received TC21 alloy bar consisted of primary equiaxed α phase and transformed β matrix, as shown in Fig. 1. The average diameter of equiaxed α phase was 6 μm, and the volume fraction approached to 30%.
The samples with the dimensions of 60 mm×14 mm×30 mm were machined from as-rolled TC21 bar by EDM (electric discharge machining). The near- isothermal forging parameters consisted of die temperature of 900 and 940 °C, forging temperature (sample temperature) of 900, 940, 950, 970 and 990 °C, strain rate of 5.5×10-4 s-1 and 1×10-2 s-1, and the same reduction in height of 60%. Air cooling, solution treatment and aging (900 °C, 1 h, AC+590 °C, 4 h, AC) were performed after forging. The near-isothermal forging experiments were carried out in 630 t hydraulic press which allowed samples to be forged at a constant strain rate. The heat treatments were implemented in the SX2-4-13 resistance furnace.
Table 1 Chemical composition of TC21 alloy bar (mass fraction, %)
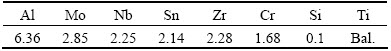
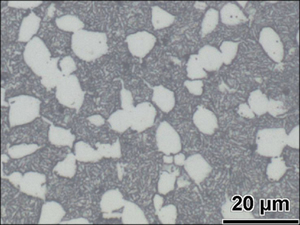
Fig. 1 Optical microstructure of as-received TC21 titanium alloy bar
The room temperature tensile properties were measured on the Instron 1196 testing machine at a strain rate of 5.0×10-4 s-1. Cylindrical samples with a gauge length of 25 mm and diameter of 5 mm were employed. The mean value of four tested samples was obtained to reduce the error.
Optical microscopy (OM) was utilized to characterize the microstructures of the samples’ cross sections which were approximately 10 mm away from the tensile fracture. Scan electron microscopy (SEM) and transmission electron microscopy (TEM) were used to observe the morphology and distribution of precipitates. An image analysis software Image-ProPlus was used to quantifiably describe the microstructural features, and regression analysis was employed to establish quantitative relationship between the tensile strength and content of residual β matrix.
3 Results and discussion
3.1 Microstructure after near-isothermal forging
The microstructures of titanium alloys are usually classified according to the morphology of α phase, including equiaxed microstructure, lamellar microstructure and bi-model microstructure [2]. However, α phase exhibits many varieties of morphologies after the near-isothermal forging with a temperature depression followed by solution treatment and aging, as illustrated in Fig. 2.
Figures 2(a)-(d) show the microstructures at various forging temperatures (FT) under die temperature (DT) of 940 °C and strain rate (SR) of 1×10-2 s-1. Due to the higher strain rate, the forging is completed in 90 s, so the temperature depression is not obvious. When forging temperatures are beyond the β transus temperature (such as 990 and 970 °C), prior β grains which participated in the deformation exhibit a pancake shape [16]. In the elongated prior β grains, there are mainly coarse α plates (Figs. 2(a) and (b)), which formed during solution treatment. During the following aging, a high content of fine secondary α platelets precipitated between coarse α plates (see Fig. 3). When the forging temperature is below the β transus temperature (950 and 940 °C), there are a small amount of primary equiaxed α phases besides coarse α plates (see Figs. 2(c) and (d)), and the content of primary equiaxed α phase declines with the forging temperature rising. Similar to those beyond the β transus temperature, coarse α plates formed during the solution treatment and a high content of fine secondary α platelets precipitated during aging.
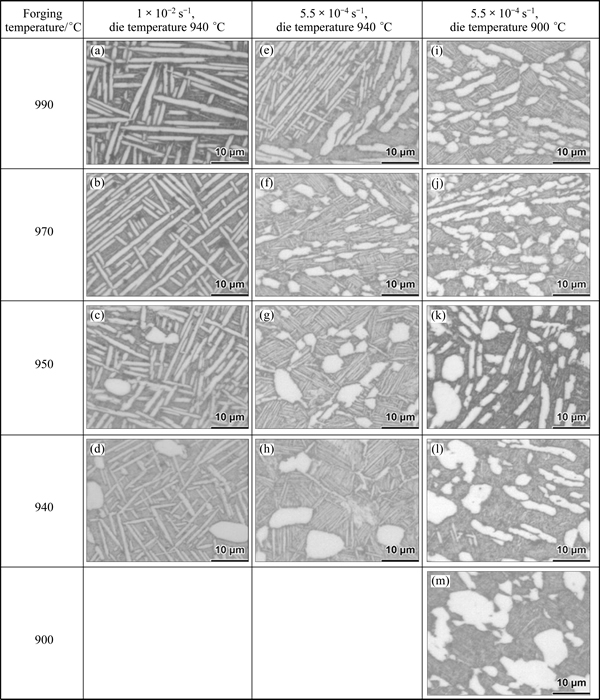
Fig. 2 Optical microstructures after near-isothermal forging with different parameters
Figures 2(e)-(h) show the microstructures at various forging temperatures under the die temperature of 940 °C and strain rate of 5.5×10-4 s-1. Under this condition, it takes approximately 28 min to complete the forging. So, there is obvious temperature depression during the deformation compared with that under strain rate of 1×10-2 s-1. If the forging temperature is above the β transus temperature, the forging-ending temperature is likely to drop to below β transus temperature, forming the through-transus forging. When the forging temperature was 990 °C (30 °C above the β transus temperature), major deformation was completed in the single β phase field, in which prior β grains participated in the deformation and formed the elongated shape. Subsequently, the forging temperature dropped to below β transus temperature, and grain boundary α layer formed along prior β grain boundary. The grain boundary α layer was then deformed in two-phase field, and finally formed equiaxed or bent lamellar α phase. As shown in Fig. 2(e), these equiaxed or bent lamellar α phases exist only along prior β grain boundaries and are not present in the interior of elongated β grains. During solution treatment, coarse α plates which are a little smaller than those under strain rate of 1×10-2 s-1 formed in the interior of elongated β grains. A high content of fine secondary α platelets precipitated from residual β phase during aging as mentioned above. When the forging temperature was 970 °C (10 °C above the β transus temperature), the forging temperature quickly dropped to below β transus temperature, and major deformation was completed in two-phase field. Besides grain boundary α layer, the lamellar α phase formed in the interior of elongated β grains, and it also participated in the deformation. Grain boundary α layer and lamellar α phase turned into equiaxed α phase because of the full spheroidization (or bent lamellar α phase due to the unfinished spheroidization), as can be seen in Fig. 2(f). The spheroidization of grain boundary α layer and lamellar α phase is associated with boundary splitting or termination migration [19]. The spheroidization fraction at 970 °C is distinctly higher than that at 990 °C, and this is because it owns the larger deformation degree and longer deformation time in two-phase field, which is favorable to the spheroidizing of lamellar α phase [20]. It is difficult to discern the α phase originating from the grain boundary α layer or lamellar α phase after spheroidization, and it uniformly distributes throughout the entire matrix. The coarse prior β grains disappear. Compared with those under strain rate of 1×10-2 s-1, the α plates formed during solution treatment become obviously smaller. Several α plates which are parallel to each other form α colonies. During aging, limited fine secondary α platelets precipitated. They are present at the triple points of α colonies or some areas between α plates in α colonies, as can be seen in Fig. 4.

Fig. 3 TEM images showing fine secondary α platelets precipitating during aging
When the forging temperature is 950 °C (10 °C below β transus temperature), primary equiaxed α phase is retained, as shown in Fig. 2(g). The forging temperature is higher than die temperature (940 °C), so there is also temperature depression during the deformation. Lamellar α phase which formed during deformation changed to equiaxed or bent lamellar α phase due to spheroidization. The equiaxed α phase caused by spheroidization is obviously smaller than primary ones. Compared with that at 970 °C, the content of equiaxed or bent lamellar α phase caused by spheroidization decreases because of the less temperature difference between dies and samples. The fine equiaxed β grains resulted from dynamic recrystallization are found, and they are pinned up by equiaxed or bent lamellar α phase. In the interior of β grains, there are α colonies composed of several α plates paralleled to each other. These α plates which have the similar size with those of sample f also formed during solution treatment. A handful of fine secondary α platelets precipitated in the way similar to that of sample f. When the forging temperature is 940 °C (see Fig. 2(h)), there are more primary equiaxed α phases, but no bent lamellar α phases compared with that at 950 °C (see Fig. 2(g)). Because the forging temperature is equal to the die temperature, there is no temperature depression.
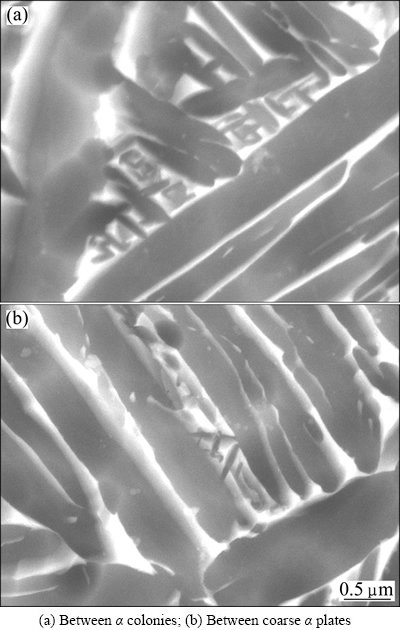
Fig. 4 SEM images showing fine secondary α platelets
Figures 2(i)-(m) show the microstructures at various forging temperatures under the die temperature of 900 °C and strain rate of 5.5×10-4 s-1. When the forging temperatures are higher than the β transus temperature (990 °C and 970 °C), the microstructures shown in Figs. 2(i) and (j) are similar to those of sample f. The die temperature of 900 °C causes the larger temperature depression. So, more equiaxed or bent lamellar α phases resulted by the spheroidization are present in the microstructures, and their content increases as the forging temperature descends. The content of finer α plates formed during solution treatment reduces as the forging temperature falls.
As can be seen in Figs. 2(k)-(m), primary equiaxed α phase still exists in the microstructure since the forging temperature is below the β transus temperature. The content of primary equiaxed α phase reduces as the forging temperature increases. Bent lamellar α phase is present due to the temperature depression during the deformation, and their content decreases as forging temperature falls. When the forging temperature is 900 °C, which is equal to the die temperature, there is no bent lamellar α phase (see Fig. 2(m)). In Figs. 2(k)-(m), few α plates are found. The reason is that the forging-ending temperature has dropped to 900 °C, which is the same with the solution temperature. So, the α plates which nucleated or further grew during cooling after forging dissolved during solution treatment.
After near-isothermal forging with different parameters plus solution treatment and aging, four types of α phases with different morphologies can be found: primary equiaxed α phase, bent lamellar (or equiaxed) α phase, α plates and fine secondary α platelets. The four types of α phases form in different stages of the thermo-mechanical processing. The primary equiaxed α phase exists when the forging temperature is below the β transus temperature, while it disappears when forging temperature is above the β transus temperature. The bent lamellar (even equiaxed) α phase will form if there are obvious temperature depressions during the deformation in two-phase field. If the solution temperature is lower than that at the end of forging, α plates form during solution treatment; otherwise, they don not form. Finally, the fine secondary α platelets precipitated during aging. The primary equiaxed α phase, bent lamellar (or equiaxed) α phase and α plates are present simultaneously or individually in one sample. They can be seen in optical figures, so they are called “visible α phase” here. Fine secondary α platelets together with residual β phase are called “residual β matrix strengthened by fine secondary α platelets” (“residual β matrix” for short).
3.2 Mechanical properties after near-isothermal forging
The room temperature tensile properties of TC21 alloy after near-isothermal forging with different parameters followed by solution treatment and aging are shown in Table 2. It can be seen that near-isothermal forging parameters have obvious influences on the tensile properties of TC21 alloy. For instance, the ultimate strength (UTS), yield strength (YS), elongation (El) and reduction of area (RA) change in the range of 1140-1255 MPa, 1095-1200 MPa, 8.25%-14.5% and 22.5%-40%, respectively. Under die temperature of 940 °C and strain rate of 1×10-2 s-1, the alloy has high strength, but low plasticity. The tensile properties have little change when forging temperature changes from 940 °C to 990 °C, e.g. the changes are just 20 MPa for ultimate strength, 50 MPa for yield strength, 1% for elongation and 8% for reduction of area. When the strain rate drops to 5.5×10-4 s-1, the strength has a downward trend, the plasticity obviously increases and tensile properties exhibit a greater variation compared with those at the higher strain rate of 1×10-2s-1.
Table 2 Mechanical properties of TC21 alloy after near- isothermal forging
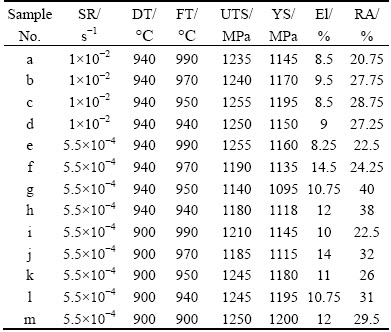
Table 3 Content of residual β matrix for different samples
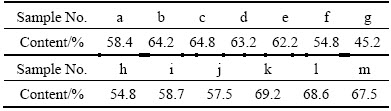
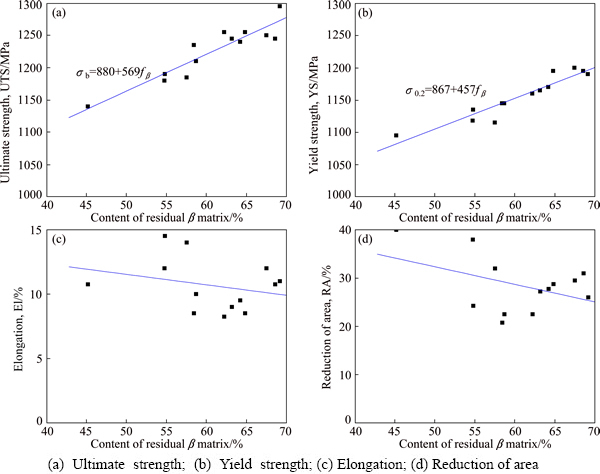
Fig. 5 Relationships between tensile properties and content of residual β matrix
3.3 Relationship between mechanical properties and microstructural features
In spite of the same solution treatment and aging, the residual β matrix exhibits different contents due to different isothermal-forging parameters, as shown in Table 3. The content of residual β matrix has a great influence on the tensile strength. As can be seen in Figs. 5(a) and (b), both ultimate strength and yield strength show rising trend as the content of residual β matrix increases. This phenomenon was also found by SRINIVASU et al [21]. The strength models as a function of the content of residual β matrix are set up by experimental data fitting, and the following equations can be obtained:
σb=880+569fβ (1)
σ0.2=867+475fβ (2)
where σb and σ0.2 represent ultimate strength and yield strength, respectively, and fβ represents the content of residual β matrix. The correlation coefficients for ultimate strength and yield strength are 0.925 and 0.942, respectively, which indicates that both ultimate strength and yield strength have good linear correlations with the content of residual β matrix.
However, the increase of the alloy strength is associated with the increase of α/β interphase boundary. After solution treatment and aging, the microstructure of TC21 alloy mainly consisted of visible α phase and residual β matrix. The width of the fine secondary α platelets is from 0.1 to 0.2 μm (see Figs. 3 and 4), and they are far smaller than those of visible α phase (see Fig. 2). The α/β interphase boundary increases when visible α phase is replaced by fine secondary α platelets with the same content. Because of the same solution treatment and aging, the total content of α phase for different samples is approximatively constant. Therefore, the more the residual β matrix of the samples has, the more the α/β interphase boundary is. The plastic deformation of metal or alloys at room temperature is realized by means of dislocation slip. The fine secondary α platelets is semicoherent with the residual β phase [22-24]. The elastic stress field around fine secondary α platelets and the elasticity modulus difference between fine secondary α platelets and residual β phase hinder the dislocation motion [25]. The more the α/β interphase boundary is, the more obvious the inhibition effect is. So, the strength of TC21 alloy increases as the content of residual β matrix increases.
The content of residual β matrix has also an influence on tensile plasticity. As shown in Figs. 5(c) and (d), with the content of residual β matrix increasing, both elongation and reduction of area exhibit a downward trend. This phenomenon is related to fine secondary α platelets. During the tensile deformation, fine secondary α platelets were cut by the dislocation along a crystal plane (see Fig. 6), which reduces the resistance of subsequent dislocations through this crystal plane. Dislocations collectively slip along the same crystal plane, forming the coplanar slip, which easily causes the microcrack. With the increase of fine secondary α platelets, the probability for microcracks increases, and finally the plasticity of alloy decreases. But the elongation and reduction of area are scattered with respect to the content of residual β matrix. This indicates that the content of residual β matrix is only one of the factors that influence the plasticity of TC21 alloy, and there are other factors affecting the plasticity of TC21 alloy.
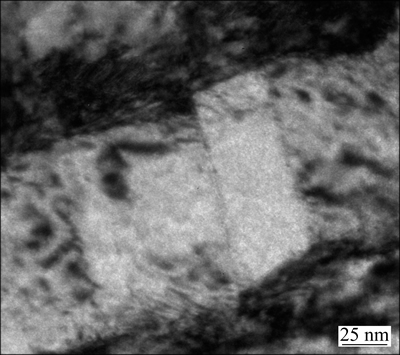
Fig. 6 TEM image showing dislocation cutting through fine secondary α platelets
The size and distribution of α plates are the other factors that influence the plasticity of TC21 alloy. As can be seen in Fig. 2 and Table 3, the alloys forged under die temperature of 940 °C and strain rate of 1×10-2s-1 have coarse α plates and simultaneously own the weaker elongation compared with that under other conditions. This phenomenon can be explained as follows. Compared with the residual β matrix strengthened by fine secondary α platelets, the α plates are thought as soft zones [17]. The plastic deformation of titanium alloy preferentially occurs in these areas. The maximum resolved shear stress has an angle of 45° with respect to the applied stress. When the long axis of these α plates is parallel to or overlaps with direction of the maximum resolved shear stress, the effective slip length is maximum, as can be seen in Fig. 7. This easily causes the crack to form, and drops the plasticity of the materials.
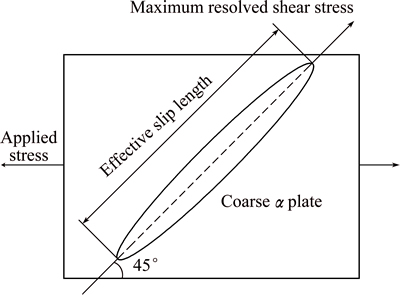
Fig. 7 Schematic diagram of effective slip length
4 Conclusions
1) After near-isothermal forging with different parameters plus solution treatment and aging, α phase exhibits four types of morphologies: primary equiaxed α phase, bent lamellar α phase, α plates and fine secondary α platelets. Fine secondary α platelets and residual β phase form residual β matrix.
2) The strength of TC21 alloy increases as the content of residual β matrix increases, and it exhibits good linear correlations between them. The strengthening of TC21 alloy is associated with the increase of α/β interphase boundary, which hinders the dislocation motion.
3) The plasticity of TC21 alloy has a downward trend with the content of residual β matrix increasing. This phenomenon is caused by the fine secondary α platelets, which are cut through tensile deformation.
4) Coarse α plates, whose long axis is parallel to the maximum resolved shear stress, reduce the plasticity of TC21 alloy.
References
[1] BANERJEE D, WILLIAMS J C. Perspectives on titanium science and technology [J]. Acta Mater, 2013, 61: 844-879.
[2] LUTJERING G, WILLIAMS J C. Titanium [M]. 2nd ed. Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer-Verlag, 2007.
[3] LEYENS C, PETERS M. Titanium and titanium alloys [M]. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH, 2003.
[4] ZHAO Yan-lei, LI Bo-long, ZHU Zhi-shou, NIE Zuo-ren. The high temperature deformation behavior and microstructure of TC21 titanium alloy [J]. Mater Sci Eng A, 2010, 527: 5360-5367.
[5] ZHU Y C, ZENG W D, LIU J L, ZHAO Y Q, ZHOU Y G, YU H Q. Effect of processing parameters on the hot deformation behavior of as-cast TC21 titanium alloy [J]. Mater Des, 2012, 33: 264-272.
[6] SHI Zhi-feng, GUO Hong-zhen, HAN Jin-yang, YAO Ze-kun. Microstructure and mechanical properties of TC21 titanium alloy after heat treatment [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2013, 23(10): 2882-2889.
[7] QU Heng-lei, ZHOU Yi-gang, ZHOU Lian, ZHAO Yong-qing, ZENG Wei-dong, FENG Liang. Relationship among forging technology, structure and properties of TC21 alloy bars [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2005, 15(5): 1120-1124.
[8] PETROV P, PEFILOV V, STEBUNOV S. Prevention of lap formation in near net shape isothermal forging technology of part of irregular shape made of aluminium alloy A92618 [J]. J Mater Process Technol, 2006, 177: 218-223.
[9] SHI K, SHAN D B, XU W C, LU Y. Near net shape forming process of a titanium alloy impeller [J]. J Mater Process Technol, 2007, 187-188: 582-585.
[10] JONES N G, DASHWOOD R J, DYE D, JACKSON M. Thermomechanical processing of Ti-5Al-5Mo-5V-3Cr [J]. Mater Sci Eng A, 2008, 490: 369-77.
[11] XIA Xiang-sheng, CHEN Ming, LU Yong-jin, FAN Fu-you, ZHU Chun-hua, HUANG Jing, DENG Tian-quan, ZHU Shi-feng. Microstructure and mechanical properties of isothermal multi-axial forging formed AZ61 Mg alloy [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2013, 23(11): 3186-3192.
[12] GUO H Z, YAO Z K, ZHAO Z L, GUO Y G, TANG J, LI Y C. The application of isothermal neat net-shape forming technology on titanium complicated load-bearing structures [C]//Proceedings of the 12th World Conference on Titanium, Beijing: Science Press, 2011: 1744-1747.
[13] HE Wei-wei, TANG Hui-ping, LIU Hai-yan, JIA Wen-peng, LIU Yong, YANG Xin. Microstructure and tensile properties of containerless near-isothermally forged TiAl alloys[J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China,2011, 21(12): 2605-2609.
[14] WEISS I, SEMIATIN S L. Thermomechanical processing of beta titanium alloys—An overview [J]. Mater Sci Eng A, 1998, 243: 46-65.
[15] SAUER C, LUTJERING G. Thermo-mechanical processing of high strength β-titanium alloys and effects on microstructure and properties [J]. J Mater Process Technol, 2001, 117: 311-317.
[16]  G. Influence of processing on microstructure and mechanical properties of (α+β) titanium alloys [J]. Mater Sci Eng A, 1998, 243: 32-45.
G. Influence of processing on microstructure and mechanical properties of (α+β) titanium alloys [J]. Mater Sci Eng A, 1998, 243: 32-45.
[17] LEE E. Microstructure evolution and microstructure/mechanical properties relationships in α+β titanium alloys [D]. Columbus: The Ohio State University, 2004.
[18] TILEY J, SEARLES T, LEE E, KAR S, BANERJEE R, RUSS J C, FRASER H L. Quantification of microstructural features in α/β titanium alloys [J]. Mater Sci Eng A, 2004, 372: 191-198.
[19] ZHEREBTSOV S, MURZINOV M, SALISHCHEV G, SEMIATIN S L. Spheroidization of the lamellar microstructure in Ti-6Al-4V alloy during warm deformation and annealing [J]. Acta Mater, 2011, 59: 4138-4150.
[20] XU Bin, WANG Xiao-yin, ZHOU Jian-hua, WANG Kai-xuan, ZENG Wei-dong. Microstructure evolvement regularity of TC17 titanium alloy in hot deformation [J].The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2010, 20(S1): 167-172. (in Chinese)
[21] SRINIVASU G, NATRAJ Y, BHATTACHARJEE A, NANDY T K, NAGESWARA Rao G V S. Tensile and fracture toughness of high strength β Titanium alloy, Ti-10V-2Fe-3Al, as a function of rolling and solution treatment temperatures [J]. Mater Des, 2013, 47: 323-330.
[22] FURUHARA T, OGAWA T, MAKI T. Atomic structure of interphase boundary of an α precipitate plate in a β Ti-Cr alloy [J]. Philos Mag Lett, 1995, 72: 175-183.
[23] BHATTACHARYYA D, VISWANATHAN G B, DENKENBERGER R, FURRER D, FRASER H L. The role of crystallographic and geometrical relationships between α and β phases in an α/β titanium alloy [J]. Acta Mater, 2003, 51: 4679-4691.
[24] BHATTACHARYYA D, VISWANATHAN G B, FRASER H L. Crystallographic and morphological relationships between β phase and the Widmanstatten and allotriomorphic α phase at special β grain boundaries in an α/β titanium alloy [J]. Acta Mater, 2007, 55: 6765-6778.
[25] LI B Q, WAWNER F E. Dislocation interaction with semicoherent precipitates (Ω phase) in deformed Al-Cu-Mg-Ag alloy [J]. Acta Mater, 1998, 46: 5483-5490.
石志峰1,郭鸿镇1,刘 瑞1,王晓晨1,2,姚泽坤1
1. 西北工业大学 材料学院,西安 710072;
2. 西北工业大学 航空学院,西安 710072
摘 要:研究经不同参数近等温锻造并固溶时效热处理后TC21钛合金的显微组织及拉伸性能。结果表明,所有试样中都存在细小片状α相强化的残留β基体,而初生等轴α相、弯曲片状α相及片状α相可能同时或单独出现在试样中。残留β基体含量的增多会增加合金中α/β相界面,从而引起合金强度增加。随着残留β基体含量的增加,细小片状α相增多,变形过程中被位错切过,导致合金的塑性有下降趋势。另外,当长轴方向与最大剪切应力平行时,粗大的片状α相也会降低合金的塑性。
关键词:TC21钛合金;近等温锻造;显微组织;α相形貌;残留β基体;拉伸性能
(Edited by Xiang-qun LI)
Foundation item: Projects (51205319, 51101119) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China
Corresponding author: Zhi-feng SHI; Tel: +86-29-88493744, Fax: +86-29-88492642; E-mail: titansmith@163.com
DOI: 10.1016/S1003-6326(15)63580-4

