不同种泥和运行方式对启动厌氧氨氧化反应器的影响
董景,陈滢,文林,刘敏
(四川大学 建筑与环境学院,四川 成都,610065)
摘要:采用6个相同的序批式反应器(SBR),以好氧硝化-厌氧氨氧化和直接厌氧氨氧化2种运行方式,分别以河岸带污泥、好氧污泥和厌氧污泥为接种污泥启动厌氧氨氧化反应器。研究结果表明,采用好氧硝化-厌氧氨氧化方式时,接种河岸带污泥和好氧污泥的反应器分别在第110天和165天实现了厌氧氨氧化反应;接种河岸带污泥的反应器启动更快,对氨氮和亚硝酸盐氮的去除率分别可达94%和99%,接种好氧污泥的反应器对氨氮和亚硝酸盐氮的去除率最高仅为53%和67%;接种厌氧污泥的反应器并未发生明显的厌氧氨氧化反应。直接以厌氧氨氧化方式运行的反应器,3类种泥都培养了190 d,没有出现厌氧氨氧化现象。
关键词:厌氧氨氧化;河岸带污泥;好氧污泥;厌氧污泥
中图分类号:X703 文献标志码:A 文章编号:1672-7207(2014)05-1740-06
Effect of different kinds of seed sludge and operation modes on start-up of anaerobic ammonia oxidation reactors
DONG Jing, CHEN Ying, WEN Lin, LIU Min
(College of Architecture and Environment, Sichuan University, Chengdu 610065, China)
Abstract: Inoculated with riparian sediments, aerobic sludge and anaerobic sludge respectively, six sequencing batch reactors (SBR) were started-up with two operation modes, aerobic nitrification-anammox and direct anammox. The results show that using the way of aerobic nitrification-anammox, reactors inoculated with riparian sediments and aerobic sludge, respectively, achieve the anaerobic ammonia oxidation reaction after operation for 110 d and 165 d. The reactor inoculated with riparian sediments is started-up more rapidly than that for the aerobic sludge, and its NH4+-N and NO2--N removal efficiencies reach 94% and 99%, respectively. The NH4+-N and NO2--N removal efficiencies of aerobic sludge reactor are just 53% and 67% at most. However, the reactor inoculated with anaerobic sludge fails to start-up. Under the condition of direct anammox, three reactors are not able to culture anammox bacteria after operation for 190 d.
Key words: anaerobic ammonia oxidation (Anammox); riparian sediments; aerobic sludge; anaerobic sludge
厌氧氨氧化技术是目前废水处理领域最经济、最简洁的生物脱氮技术[1]。与传统生物脱氮技术相比,厌氧氨氧化具有更好的经济效益和可持续性[2]。它在厌氧或缺氧条件下,微生物以CO2或CO3-为碳源,以NH4+为电子供体,以NO2-或NO3-为电子受体,将NH4+,NO2-或NO3-转变为氮气,无需供氧,也不需外加有机碳源,可以大幅度降低能耗成本,同时污泥量小,不会产生二次污染,独特的优势使其成为近年来国内外的研究热点。目前,已有一些厌氧氨氧化的实际工程投入运行,其主要用于处理生活污水、养猪废水、污泥消化液以及垃圾渗滤液等[3]。厌氧氨氧化反应最初是在污水处理工艺(反硝化流化床)中发现的[4],而目前已被广泛发现于各种自然生态系统中,如人工湿地[5]、河口[6-7]、湖底[8]、海洋沉积物[9-11]等。海洋中33%~65%的氮气产生自大陆架和斜坡底泥中的厌氧氨氧化反应[12]。厌氧氨氧化菌属于严格自养菌,生长速度缓慢,倍增时间长,易受外界环境因子影响,富集培养较困难。厌氧氨氧化反应器一般启动较慢,第1个生产性厌氧氨氧化反应器启动时间长达1 250 d[13],唐崇俭等[14]经过255 d才成功启动中试Anammox反应器。李祥等[15]经研究发现:接种厌氧氨氧化污泥后,可以加速反应器的启动,在第72天启动成功。但是,厌氧氨氧化技术在实践中受到种泥来源的限制,获得经济、易得的种泥有助于厌氧氨氧化技术的推广和应用。本文作者采用不同种泥、不同运行方式启动厌氧氨氧化反应器,以便为厌氧氨氧化反应器的快速启动提供借鉴。
1 实验材料与方法
1.1 实验装置
实验采用6个相同的SBR反应器(如图1),反应器由遮光纸包裹,有效容积为2.2 L。运行周期为24 h,其中进水10 min,生化反应23 h,静止40 min,排水10 min,排水比为50%。
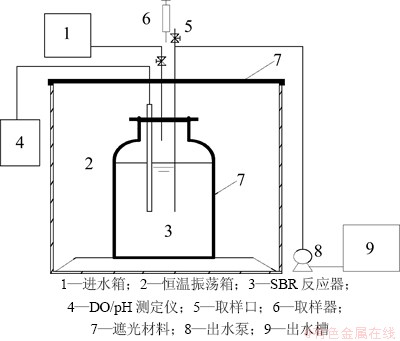
图1 实验装置示意图
Fig. 1 Schematic diagram of experimental system
1.2 接种污泥与实验进水
分别以河岸带污泥、好氧污泥和厌氧污泥作为接种污泥培养厌氧氨氧化菌。河岸带污泥取自成都市某河流的岸边带污泥,其混合液悬浮固体(MLSS)质量浓度为64.58 g/L,混合液挥发性悬浮固体(MLVSS)质量浓度为18.43 g/L,挥发份物质含量w(VSS)/w(SS)为0.13,该污泥无机物含量较高;好氧污泥取自成都某污水处理厂好氧曝气池,接种的污泥量MLSS为21.01 g/L,MLVSS为13.31 g/L,w(VSS)/w(SS)为0.63;厌氧污泥取于同一污水处理厂,接种的污泥量MLSS为19.39 g/L,MLVSS为12.23 g/L,w(VSS)/w(SS)为0.63。
实验用水为人工配水,用NH4Cl模拟含氮废水,好氧阶段进水氨氮质量浓度为70~140 mg/L;厌氧阶段进水氨氮质量浓度为70 mg/L,同时投加NaNO2模拟亚硝酸盐,质量浓度为70 mg/L。另外,还投加微量元素,如KH2PO4,KHCO3,MgSO4·7H2O,CaCl2,CoC12·6H2O,CuSO4·5H2O,NiC12·6H2O,Na2SeO4· 10H2O,H3BO3和EDTA。
1.3 测定项目与方法
氨氮采用纳氏试剂光度法,亚硝酸盐氮采用N-(1-萘基)-乙二胺光度法,硝酸盐氮采用麝香草酚分光光度法,COD采用5B-3(D)型COD快速测定仪测定,MLSS和MLVSS采用标准重量法[16]。pH,DO和氧化还原电位采用WTW-pH/oxi340i型便携式测量仪测定。微生物相采用Olympus Dp70型光学显微镜和四川大学分析测试中心的JSM-5900LV型电子显微镜观察。
1.4 实验方案
实验采用6个完全一样的SBR反应器,分别记为R1~R6。其中R1和R4接种河岸带污泥,R2和R5接种好氧污泥,R3和R6接种厌氧污泥。R1,R2和R3采用好氧硝化-厌氧氨氧化的运行方式,其运行过程分为好氧硝化阶段、厌氧阶段Ⅰ和厌氧阶段Ⅱ 3个阶段;R4、R5和R6采用直接厌氧氨氧化的运行方式,运行过程分为厌氧阶段Ⅰ和厌氧阶段Ⅱ。好氧阶段反应器敞口,由恒温振荡器低速振荡供氧以维持溶解氧质量浓度(DO)在2~2.5 mg/L之间,并保持污泥处于完全混合状态,温度控制为30 ℃;厌氧阶段反应器密闭,温度控制为35 ℃,厌氧阶段Ⅰ反应前用氮气(>99.9%)以0.2 L/min的流速对反应器充气排氧3 min;厌氧阶段Ⅱ不再开盖换水,当氨氮或亚硝酸盐氮质量浓度降低到20 mg/L时,用进样器少量高浓度进药。
2 结果与讨论
2.1 以好氧硝化-厌氧氨氧化方式启动反应器
2.1.1 好氧硝化阶段
好氧硝化阶段的运行情况如图2所示。从图2可以看出,3个反应器进水氨氮质量浓度均从70 mg/L逐渐提高至140 mg/L。当进水氨氮质量浓度为70 mg/L,运行14 d后,3个反应器的氨氮去除率均可接近100%。进一步提高氨氮质量浓度至140 mg/L,氨氮去除率并未受到明显影响。与R2和R3反应器相比,R1达到高效脱氮的时间较短,第9天的氨氮去除率就已接近100%,而此时R2和R3的氨氮去除率只有60%左右。
接种河岸带污泥的反应器R1抗冲击能力较强。在第12天受到环境条件的冲击后,R2和R3的氨氮去除率迅速降低到20%左右,至少需要3 d才能恢复。R1受到冲击后,氨氮去除率只降低到80%左右,而且在第2天即恢复至原来水平。
在硝化培养初期,R2和R3反应器中便发生了硝化反应,而R1中并未发现亚硝酸盐氮和硝酸盐氮的积累,但氨氮却得到了去除,这可能是因为河岸带污泥中的某些自然物质,对其发生了物理吸附作用。
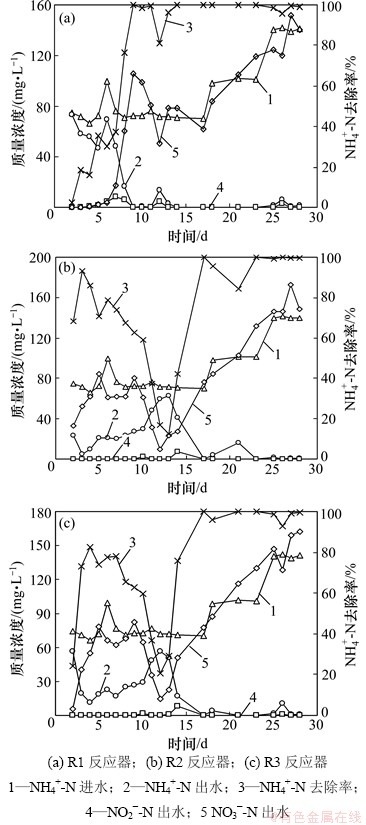
图2 3个反应器好氧硝化阶段的运行情况
Fig. 2 Operation of three reactors during aerobic nitration phase
2.1.2 厌氧氨氧化阶段
当反应器R1,R2和R3的氨氮去除率稳定在100%左右时,在第29天对其进行厌氧阶段Ⅰ的培养,控制进水氨氮和亚硝酸盐氮质量浓度为70 mg/L,并对进水进行脱氧处理。3个反应器厌氧阶段氨氮和亚硝酸盐氮的去除率如图3所示。氨氮与亚硝酸盐氮同时得到去除是厌氧氨氧化反应的特征之一[17]。但是R1,R2和R3反应器并未出现出水氨氮与亚硝酸盐氮浓度都明显降低的时期,说明该时期内厌氧氨氧化反应并未成为3个反应器中的主导反应。
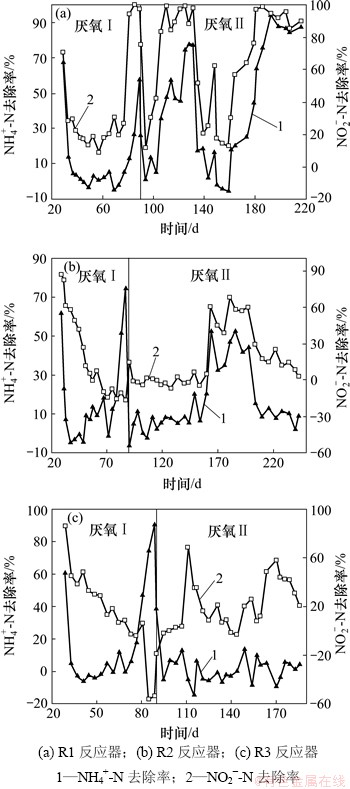
图3 3个反应器厌氧阶段的运行情况
Fig. 3 Operation of three reactors during anaerobic phase
R1,R2和R3反应器中的种泥均先经过好氧硝化培养,再转为厌氧环境。条件改变导致有些细菌无法适应而死亡。3个反应器中的亚硝酸盐氮在厌氧阶段Ⅰ初期都有所去除,这是因为异养菌以死亡细菌为有机碳源进行了厌氧反硝化反应。从R1反应器中的亚硝酸盐氮去除率比R2和R3反应器中的低,可看出R1反应器中发生的反硝化反应强度较弱,说明从好氧转为厌氧条件时R1反应器中死亡的细菌较少,即用河岸带污泥培养的细菌对环境的适应能力更强。
在第81天和第82天,对3个反应器进行基质刺激实验,保持进水氨氮质量浓度70 mg/L不变,将进水亚硝酸盐氮质量浓度提高至140 mg/L。在受到基质冲击后,R1反应器中的氨氮和亚硝酸盐氮均得到了去除,且其去除率均呈上升趋势,在第89天分别达到了58%和97%,但其氨氮去除量、亚硝酸盐氮去除量和硝酸盐氮生成量之比并不符合厌氧氨氧化反应的经验值1:1.32:0.26[18]。R2和R3反应器的氨氮去除率均大幅度上升,分别达到75%和91%,而亚硝酸盐氮却并没有得到去除,R2反应器中的亚硝酸盐氮去除率降为负值。在第83天,将进水亚硝酸盐氮质量浓度恢复到70 mg/L。
由于在厌氧阶段Ⅰ没有成功实现厌氧氨氧化反应,因此,为了严格控制系统为厌氧条件,在第90天对3个反应器采用厌氧阶段Ⅱ的培养方式。不再开盖换水,当氨氮或亚硝酸盐氮质量浓度降低到20 mg/L时,用进样器投加少量高浓度进水,使反应初始氨氮和亚硝酸盐氮质量浓度为70 mg/L左右。R1反应器在采用厌氧阶段Ⅱ的培养方式后,立即观察到明显的厌氧氨氧化反应特性,氨氮去除量、亚硝酸盐氮去除量和硝酸盐氮生成量之比在第110天就达到稳定,其平均值为1:1.29:0.17,基本符合1:1.32:0.26。R2反应器在厌氧阶段Ⅱ初期,氨氮和亚硝酸盐氮基本没有得到去除,其出水浓度大致等于进水浓度。直到第165天,R2反应器开始出现氨氮与亚硝酸盐氮同时脱除,硝酸盐氮升高的现象。其氨氮去除量、亚硝酸盐氮去除量和硝酸盐氮生成量之比平均值为1:1.6:0.15,因此,可以断定,R2反应器中发生了明显的厌氧氨氧化反应。在该阶段,R3反应器中的亚硝酸盐氮虽有所去除,但是,氨氮却基本没有得到去除,同时,其三态氮的变化量比值也不符合厌氧氨氧化反应的特征值,说明接种厌氧污泥的R3反应器并没有成功启动。
为了更好地检测厌氧氨氧化过程中各参数的动态变化,在第131天将R1反应器中的污泥转接到可以在线监测并记录的SBR中,转接过程中因少量溶解氧的混入,物质变化波动变大。经过34 d,运行趋于稳定。接种河岸带污泥的反应器中再次观察到明显的厌氧氨氧化反应。系统氨氮和亚硝酸盐氮初始质量浓度在70 mg/L左右时,R1反应器的氨氮和亚硝酸盐氮去除率分别可达94%和99%,而R2反应器的氨氮和亚硝酸盐氮去除率的最高值仅为53%和67%。由此可以说明,河岸带污泥和好氧污泥都可作为接种污泥启动厌氧氨氧化反应器,而接种河岸带污泥的反应器脱氮效果更好。这是因为河岸带是陆地和水层的交汇处,厌氧好氧条件交替变化,在较高浓度氨氮存在时,会发生部分硝化和不完全反硝化反应,成为亚硝酸盐的积累区,为厌氧氨氧化反应提供了充足的基质NH4+和NO2-。因为河岸带污泥具有适合厌氧氨氧化菌生活的环境条件,所以,其中的厌氧氨氧化细菌数量大且种类繁多[19]。因此,接种河岸带污泥的反应器更易培养出厌氧氨氧化菌。
2.2 以直接厌氧氨氧化方式启动反应器
R4,R5和R6反应器采用直接厌氧氨氧化的培养方式,共历时190 d,其中厌氧阶段Ⅰ89 d,厌氧阶段Ⅱ101 d。在厌氧阶段Ⅰ,3个反应器的氨氮出水浓度大于进水浓度,且部分亚硝酸盐氮通过反硝化作用得到去除,这是因为死亡细菌蛋白质水解,导致氨氮浓度升高,同时为反硝化反应提供碳源。在转入厌氧阶段Ⅱ的运行条件后,3个反应器立即观察到氨氮和亚硝酸盐氮同时去除的现象,推测其发生了微弱的厌氧氨氧化反应。但是补充反应基质后,厌氧氨氧化反应迹象均立即消失,长时间无法恢复。本实验采用该方法并未成功启动厌氧氨氧化反应器,与曹雨佳等[20]的研究结果不同,可能是因为其运行时间不够或实验条件不同。
2.3 微生物相观察
在接种前和好氧硝化-厌氧氨氧化方式的厌氧阶段Ⅱ,对河岸带污泥和好氧污泥进行光学显微镜和电子显微镜观察,结果如图4和图5所示。
河岸带污泥接种时为黑色,微生物量和种类都较少,还含有透明的晶体状物质,无机成分较多。经过好氧培养,污泥颜色由黑色转为土黄色,出现密实菌胶团。进入厌氧阶段Ⅰ后,菌胶团开始解体。厌氧阶段Ⅱ出现大量圆形或椭圆形的细菌,成簇聚生。
好氧污泥接种时为土黄色,菌胶团较密实,微生物种类丰富;厌氧阶段Ⅰ,菌胶团开始解体,原型动物消失;厌氧阶段Ⅱ同时观察到大量成蔟生长的细菌,呈圆形或椭圆形。
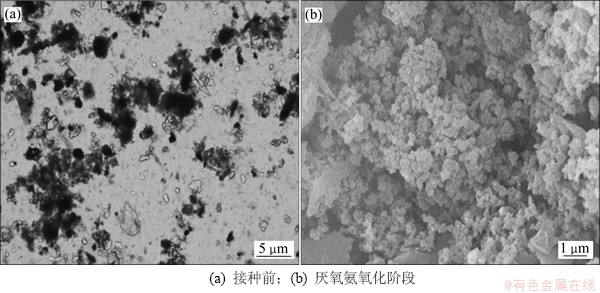
图4 河岸带污泥接种前及厌氧阶段Ⅱ微生物相
Fig. 4 Microbial morphology of riparian sediments before inoculation and during anaerobic phaseⅡ

图5 好氧污泥接种前及厌氧阶段Ⅱ微生物相
Fig. 5 Microbial morphology of aerobic sludge before inoculation and during anaerobic phaseⅡ
3 结论
(1) 采用好氧硝化-厌氧氨氧化运行方式,接种河岸带污泥和好氧污泥的反应器分别在第110天和第165天培养出具有厌氧氨氧化活性的污泥。接种厌氧污泥和采用直接厌氧氨氧化方式的反应器没有培养出厌氧氨氧化污泥。
(2) 接种河岸带污泥的反应器能更快地实现厌氧氨氧化反应,培养的厌氧氨氧化菌活性更好,氨氮与亚硝酸盐氮的去除率分别可达94%和99%;而接种好氧污泥的反应器对氨氮和亚硝酸盐氮的去除率最高值仅为53%和67%。
(3) 接种价廉、易得的河岸带污泥,采用好氧硝化-厌氧氨氧化方式启动厌氧氨氧化反应器,启动相对较快,处理效果好,有利于最经济、最简洁的生物脱氮技术——厌氧氨氧化工艺的广泛推广。
参考文献:
[1] 刘杰, 杨洋, 左剑恶, 等. 亚硝化与厌氧氨氧化串联工艺处理高氮低碳废水的研究进展[J]. 中国沼气, 2009, 27(3): 13-18.
LIU Jie, YNAG Yang, ZUO Jiane, et al. A review on process of anaerobic ammonium oxidation (anammox) combined with short-cut nitrification for treating wastewater containing high strength ammonium[J]. China Biogas, 2009, 27(3): 13-18.
[2] Kartal B, Kuenen J G, Van Loosdrecht M C M. Sewage treatment with anammox[J]. Science, 2010, 328(5979): 702-703.
[3] 丁英翠. 利用序批式生物膜反应器实现厌氧氨氧化脱氮的研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学市政环境工程学院, 2011: 3-10.
DING Yingcui. Anerobic ammonium oxidation in a sequencing batch biofilm reactor[D]. Harbin: Harbin Institute of Technology. School of Municipal and Environmental Engineering, 2011: 3-10.
[4] Mulder A, Van de Graaf A A, Robertson L A, et al. Anaerobic ammonium oxidation oxidation discovered in a denitrifying fluidized bed reactor[J]. FEMS Microbiology Ecology, 1995, 16(3): 177-183.
[5] Zhu G B, Jetten M S M, Kuschk P, et al. Potential roles of anaerobic ammonium and methane oxidation in the nitrogen cycle of wetland ecosystems[J]. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol, 2010, 86(4): 1043-1055.
[6] Dale O R, Tobias C R, Song B. Biogeographical distribution of diverse anaerobic ammonium oxidizing (anammox) bacteria in CapeFear River Estuary[J]. Environ Microbiol, 2009, 11(5): 1194-1207.
[7] 郑艳玲, 侯立军, 陆敏, 等. 崇明东滩夏季沉积物厌氧氨氧化菌群落结构与空间分布特征[J]. 环境科学, 2012, 33(3): 992-998.
ZHENG Yanling, HOU Lijun, LU Min, et al. Community structure and spatial distribution of anaerobic ammonium oxidation bacteria in the sediments of Chongqing Eastern Tidal Flat in summer[J]. Environmental Science, 2012, 33(3): 992-998.
[8] 沈李东, 胡宝兰, 郑平, 等. 西湖底泥中厌氧氨氧化菌的分子生物学检测[J]. 环境科学学报, 2011, 31(8): 1609-1615.
SHEN Lidong, HU Baolan, ZHENG Ping, et al. Molecular detection of anammox bacteria in the sediment of West Lake, Hangzhou[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2011, 31(8): 1609-1615.
[9] Ward B B. Significance of anaerobic ammonium oxidation in the ocean[J]. Trends in Microbiology, 2003, 11(9): 408-410.
[10] Molina V, Farias L. Aerobic ammonium oxidation in the oxycline and oxygen minimum zone of the eastern tropical South Pacific off morthern Chile(~20°S)[J]. Deep-Sea Research, 2009, 56(16): 1032-1041.
[11] Kawagoshi Y, Nakamura Y, Kawashima H, et al. Enrichment culture of marine anaerobic ammonium oxidation (anammox) bacteria from sediment of sea-based waste disposal site[J]. Journal of Bioscience and Bioengineering, 2009, 107(1): 61-63.
[12] Trimmer M, Nicholls J C. Production of nitrogen gas via anammox and denitrification in intact sediment cores along a continental shelf to slope transect in the North Atlantic[J]. Limnol Oceanogr, 2009, 54(2): 577-589.
[13] van der Star W R L, Abma W R, Blommers D, et al. Startup of reactors for anoxic ammonium oxidation: Experiences from the first full-scale anammox reactor in Rotterdam[J]. Water Research, 2007, 41(18): 4149-4163.
[14] 唐崇俭, 郑平, 陈建伟, 等. 中试厌氧氨氧化反应器的启动与调控[J]. 生物工程学报, 2009, 25(3): 406-412.
TANG Chongjian, ZHENG Ping, CHEN Jianwei, et al. Start-up and process control of a pilot-scale Anammox bioreactor at ambient temperature[J]. Chinese Journal of Biotechnology, 2009, 25(3): 406-412.
[15] 李祥, 黄勇, 袁怡, 等. 不同泥源对厌氧氨氧化反应器启动的影响[J]. 环境工程学报, 2012, 6(7): 2143-2148.
LI Xiang, HUANG Yong, YUAN Yi, et al. Effect of different sources of sludge on start-up of ANAMMOX reactor[J]. Chinese Journal Environmental Engineering, 2012, 6(7): 2143-2148.
[16] 国家环境保护总局. 水和废水监测分析方法[M]. 4版. 北京: 中国环境科学出版社, 2002: 105-284.
State Environmental Protection Administration. The water and wastewater monitoring method[M]. 4th ed. Beijing: China Environmental Science Press, 2002: 105-284.
[17] Wang L, Li T. Anaerobic ammonium oxidation in constructed wetlands with bio-contactoxidation as pretreatment[J]. Ecological Engineering, 2011, 37(8): 1225-1230.
[18] Strous M, Kuenen J G, Jetten S M S. Key physiology of anaerobic ammonium oxidation[J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 1999, 65(7): 3248-3250.
[19] Wang S Y, Zhu G B, Peng Y Z, et al. Anammox bacterial abundance, activity, and contribution in riparian sediments of the Pearl River Estuary[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2012, 46(16): 8834-8842.
[20] 曹雨佳, 胡翔, 王建龙. 接种污泥对厌氧氨氧化反应器启动特性的影响[J]. 中国给水排水, 2008, 24(15): 7-14.
CAO Yujia, HU Xiang, WANG Jianlong. Start-up performance of anaerobic ammonia oxidation reactors[J]. China water& wastewater, 2008, 24(15): 7-14.
(编辑 赵俊)
收稿日期:2013-05-16;修回日期:2013-08-06
基金项目:国家高技术研究发展计划(“863”计划)项目(2011AA060905);国际科技合作与交流专项(2012DFG91520)
通信作者:刘敏(1972-),男,四川峨眉山人,副教授,从事水污染控制工程等研究;电话:13880762097;E-mail: liuminscu@163.com