文章编号:1004-0609(2016)-10-2086-07
微量元素(Hf/Ta/Nb)添加对近α-Ti合金高温抗氧化性能的影响
车晋达1,姜贝贝1,王 清1,张瑞谦2,唐 睿2,陈国清1,董 闯1
(1. 大连理工大学 三束材料改性教育部重点实验室&材料科学与工程学院,大连 116024;
2. 中国核动力研究设计院 反应堆燃料及材料重点实验室,成都 610213)
摘 要:利用“团簇加连接原子”结构模型解析典型高温近α-Ti合金Ti 1100成分,进而在此基础上添加Hf、Ta和Nb元素进行合金化,形成成分通式 [Al-(Ti13.7(Zr/Hf)0.3)](Al0.69Sn0.18Si0.12(Mo/Ta/Nb)0.03)。合金组织结构分析和高温抗氧化性结果表明:Hf元素的添加并未改变合金的结构和组织,在此基础上,不同配比的Ta和Nb替代Mo时合金由片层转变β组织转变为等轴α组织;系列合金在800 ℃下,Hf替代Zr后合金的抗氧化能力显著提高,Ta和Nb进一步合金化后合金的抗氧化能力进一步增强,其100 h后的氧化质量增加约为(2.2±0.2) mg/cm2。
关键词:近α-Ti合金;成分设计;微量合金化;高温氧化
中图分类号:TG146.23 文献标志码:A
高温近α-Ti合金由于比强度高、抗高温氧化性和耐腐蚀性优异,使其在航空发动机上得到了广泛的应用[1-2]。典型合金有Ti 1100(美国)、IMI834(英国)、BT36(俄罗斯)、以及Ti600(中国)合金等[3-9],最高使用温度可达600 ℃。为满足高温工作环境,近α-Ti合金通常需要加入多种微量元素进行合金化,如Al、Sn、Zr、Mo、Si、Ta等,使得合金在HCP-α固溶体基体上存在少量BCC-β相,以保证合金的高温力学性能。但在高温长期热暴露情况下会产生α2 脆性相,将显著降低合金的塑性和热稳定性[10],高温钛合金的结构稳定性和抗氧化性是制约合金使用温度两个最重要条件。因此,为研发出使用温度高的高温钛合金,人们将Al当量法[11](w(Aleq)=1.0% w(Al)+0.33% w(Sn)+ 0.17% w(Zr)+10.0% w(O))引入到多元合金化的高温近α-Ti合金的成分设计中,研究表明,热稳定性好的近α-Ti合金的w(Aleq)=6.5%~9.0%,而当w(Aleq)>9.0%时,Ti3Al脆性相会从基体中析出[12]。d电子合金理论也常用来设计高温钛合金,根据表征合金化效应的两个参量Bo和Md,可预测β相转变温度,以此作为合金选择的判据[13];也可根据合金的电子浓度e/a控制Ti3Al脆性相的析出[14],由此确定合金元素及加入量[15]。除此以外,利用BP神经网络可建立Ti 1100等系列高温近α钛合金的本构关系模型[16-17],为钛合金开发奠定基础。以上传统的合金设计方法难以实施复杂体系的合金成分优化,要实现我国在新材料研究领域的跨越式发展,迫切需要设计方法研究,为这类合金设计提供理论指导。
多元合金化势必带来合金成分设计的复杂化,对于固溶体基的高温近α-Ti合金,还未从局域结构的短程序角度出发进行合金设计与优化。局域结构的化学短程序是固溶体合金的一个典型特征,借助此概念,提出了一个“团簇加连接原子”结构模型,其中团簇为以溶质为心的最近邻配位多面体(FCC结构中为配位数CN12立方八面体,BCC结构中为CN14菱形十二面体),通常形成于存在强交互作用溶质与基体之间,以代表化学短程序,而与基体具有弱交互作用的溶质则位于团簇之间的连接位置。根据团簇在固溶体结构中的不同堆垛模式,可给出不同的团簇与连接原子比例,由此给出的合金成分式为[团簇](连接原子)x(x为连接原子的个数)[18]。进而在FCC和BCC结构中研究了团簇的堆垛模式,发现团簇最密堆垛时对应的连接原子个数分别为x=3(FCC)和x=1(BCC)[19]。并且,对BCC β-Ti多组元合金的研究结果表明低弹性模量的多元β-Ti合金满足团簇成分式[CN14团簇](连接原子)1[20]。
因此,本文作者将利用团簇结构模型解析典型多元近α钛合金Ti 1100的成分,并在此基础上设计微量Hf、Nb和Ta元素添加的系列成分合金,从而研究微量元素添加对系列合金高温抗氧化性能的影响。
1 成分解析与设计
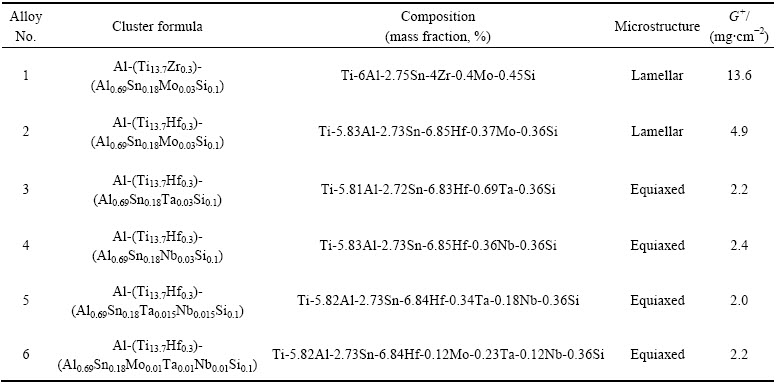
Ti 1100合金是1988年美国研制的具有良好高温蠕变性能高温近α型钛合金,其成分为Ti-6Al-2.75Sn- 4Zr-0.4Mo-0.45Si (质量分数,%),对应的摩尔分数为Ti85.36Al10.52Sn1.10Zr2.07Mo0.2Si0.76 (摩尔分数,%)。尽管该合金在室温下表现为HCP基体上存在少量β相,但从二元相图和组织演变可以看出,在高温下这类合金仍为BCC-β单一固溶体结构,这与团簇结构模型描述的结构状态相吻合,即高温下的单一固溶体结构,由此,可利用BCC固溶体中的团簇成分式解析Ti 1100合金成分。合金化元素与基体Ti之间的相互作用强弱由混合焓ΔH大小来表征,由此可确定合金化元素在团簇成分式中的占位:Al、Si和Sn由于和Ti具有大的负ΔH,优先占据团簇心部;而与Ti具有弱相互作用的Mo、Nb和Ta占据连接原子位置;Zr由于与Ti为同族元素,占据团簇壳层。固定(Ti+Zr)总量在团簇成分式中为14个原子,则利用各合金化元素含量与(Ti+Zr)总量的比值就可确定其在团簇式中的原子个数,为Al1.69Sn0.18Si0.12(Ti13.7Zr0.3)Mo0.03= [Al-(Ti13.7Zr0.3)] (Al0.69Sn0.18Si0.12Mo0.03),此时多余的Al与其他元素一起都位于连接位置,且连接原子总数为1.02,恰对应BCC固溶体连接原子x=1的情形,其基础成分式为[Al-(Ti,Zr)14]M1,M为连接原子。在此团簇成分式基础上,利用相似元素替代方法,即添加Hf元素替代Zr,添加Ta或Nb元素替代Mo元素,形成新合金系列[Al-(Ti13.7Hf0.3)](Al0.69Sn0.18Si0.12(Mo/Ta/Nb)0.03)。表1给出了该系列合金的团簇成分式及质量分数,Ti 1100作为参比合金,即No.1合金;固定其他元素不变,Hf0.3替代Zr0.3时形成No.2合金;在此基础上,Ta0.03和Nb0.03分别替代Mo0.03时形成No.3和No.4合金;Ta0.015Nb0.015等比例替代时为No.5合金,Mo0.01- Ta0.01Nb0.01等比例替代时为No.6合金,此处微量合金化元素的等比例替代采用了高熵合金化的原理[21-22]。
2 实验
实验所用原料为纯度99.99%的Ti、Al和Zr,99.95%(质量分数)的Mo、Ta、Nb、Si和Sn。在高纯Ar保护下用电弧炉熔炼方法制备系列合金的母合金锭,利用真空铜模吸铸快冷技术制备直径为6 mm的合金棒,质量损失不超过0.1%。将合金棒在950 °C固溶处理保温1 h后水淬,并在560 ℃进行时效处理保温6 h。采用Bruker D8 Focus X型射线衍射仪(XRD)检测系列合金的相结构组成;利用OLYMPUS金相显微镜(OM)观察合金组织形貌,金相腐蚀液成分为10%HF+20% HNO3+70% H2O (体积分数),利用Zeiss Supra55型扫描电子显微镜观测样品氧化层形貌及厚度;采用HVS-1000型维氏硬度仪测试合金硬度,加载载荷为3 N,加载时间为10 s,每个合金测量10次取平均值;高温抗氧化实验在马弗炉(KSL-1400X-A2) 型中进行,实验温度分别为650 ℃和800 ℃,圆棒样品尺寸为d 6 mm×12 mm,每隔25 h取出测试样品质量,氧化实验时间总长为100 h。
表1 [Al-(Ti13.7Hf0.3)](Al0.69Sn0.18Si0.12(Mo/Ta/Nb)0.03)系列合金成分及显微组织和抗氧化性能(800 ℃, 100 h)
Table 1 Compositions, microstructure, and oxidation mass G+ (800 ℃, 100 h) of designed [Al-(Ti13.7Hf0.3)](Al0.69Sn0.18Si0.12- (Mo/Ta/Nb)0.03) alloy series
3 结果与讨论
图1所示为时效后系列合金的XRD谱,可以看出No.3、No.4、No.5和No.6合金均表现为单一HCP-α相,而在No.1和No.2合金中,在α基体上存在少量BCC-β相((110)衍射峰)析出,表明强β稳定元素Mo的存在提高了合金的β结构稳定性,故在热处理后仍有有少量β相保留。
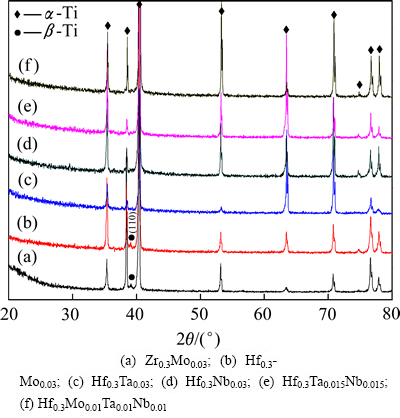
图1 时效后系列合金[Al-(Ti13.7Hf0.3)](Al0.69Sn0.18Si0.12- (Mo/Ta/Nb)0.03)的XRD谱
Fig. 1 XRD patterns of aged [Al-(Ti13.7Hf0.3)](Al0.69Sn0.18- Si0.12(Mo/Ta/Nb)0.03) alloy series
图2所示为该系列合金相应的金相组织形貌,参比合金No.1为片层β转变组织,当Hf0.3替代Zr0.3后,合金No.2仍保持相似的片层组织,如图2(a)、(b)所示;在此基础上,当用Nb、Ta替代Mo时,合金组织形貌如图2(c)~(f)所示,合金No.3~No.6均表现为等轴α组织。研究表明[23-24],等轴α组织的蠕变强度相对较差,但热稳定性能优异;而片层β转变组织则具有较高的蠕变强度和断裂韧性,但塑性和热稳定性较差。Zr元素被视为β结构稳定的中性元素,即不对BCC-β结构稳定性产生影响[25],Hf元素与Zr作用相同,对比No.1与No.2合金可知,Hf为β结构稳定的中性元素。然而,弱β结构稳定的Nb和Ta元素替代强β稳定的Mo元素时,合金组织发生了改变,变为等轴α组织,且未再有残余β相。
图3所示为该系列合金时效后的硬度变化图,可以看出Hf0.3替代Zr0.3后,No.2合金的硬度与参比合金No.1的硬度相当,约为340HV,这是由于这两个合金具有相同的片层β转变组织;Ta和Nb逐步替代Mo时会使得合金的硬度略有降低,尤其当Mo0.01Ta0.01Nb0.01等比例添加时,合金硬度降至323HV。不同的显微组织对合金硬度值有所影响,但影响程度不大,整体来说,该系列合金硬度值处于320~360 HV之间。
分别在650 ℃和800 ℃下对时效后的系列合金进行了抗高温氧化性能测试,氧化时间总计100 h,每25 h记录一次氧化质量增加,图4分别给出了系列合金在这两个温度下氧化质量增加曲线。可以看出,在650 ℃氧化100 h后,No.1~No.6合金的氧化质量增加G+值均小于1.0 mg/cm2,其中参比合金的氧化质量增加最大为0.9 mg/cm2,Hf、Nb和Ta合金化的合金的氧化质量增加G+仅为0.2~0.3 mg/cm2。然而,系列合金在800 ℃下的高温抗氧化性能显著优异于参比合金No.1的,参比Ti 1100合金氧化100 h后的氧化质量增加G+=13.6 mg/cm2,而Hf替代Zr后,合金No.2的抗氧化能力显著提高,氧化质量增加为G+=4.9 mg/cm2,约为参比合金的1/3;在此基础上,Nb和Ta替代Mo的合金No.3~No.6的抗氧化能力进一步提高,但提高幅度没有前者高,氧化质量增加约为(2.2±0.2) mg/cm2,与添加Ta、Nb元素的合金抗氧化能力相当。
图5所示为该系列合金800 ℃氧化100 h后外观形貌图。可以看出,参比合金No.1表面存在厚金黄色氧化皮,并伴有大片氧化皮剥落,如图5(a)所示,氧化程度严重。Hf替代Zr后,No.2合金表面为浅黄色氧化皮,并有小片状氧化皮剥落,如图5(b)所示。Ta、Nb不同比例替代Mo元素的合金No.3~No.6氧化层为白蓝色,只有少量片状氧化皮剥落,如图5(c)所示。进而,根据表面氧化层的扫描电镜形貌图测出氧化层厚度,其中参比合金的氧化最严重,氧化层厚度约为150 μm,并有分层和剥落现象,如图6(a)所示。Hf替代Zr后合金Hf0.3Mo0.03(No.2)的氧化层厚度显著降低,约为18 μm,且氧化层分布均匀,如图6(b)所示。在此基础Ta、Nb不同比例的合金化会使得氧化层厚度略有降低,约为15 μm,且氧化层分布更为均匀,如图6(c)所示。
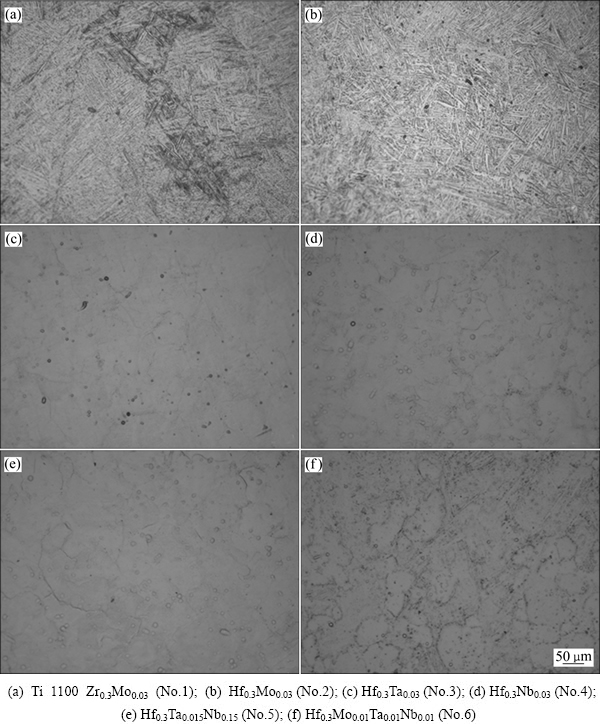
图2 时效后系列合金 [Al-(Ti13.7Hf0.3)](Al0.69Sn0.18Si0.12(Mo/Ta/Nb)0.03)的金相显微组织
Fig. 2 Micrographs of aged [Al-(Ti13.7Hf0.3)](Al0.69Sn0.18Si0.12(Mo/Ta/Nb)0.03) alloy series
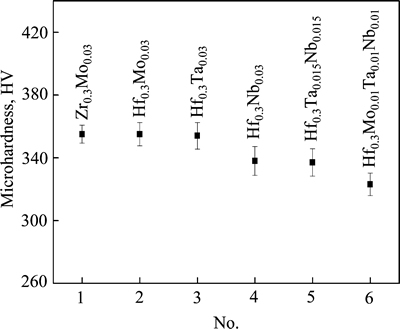
图3 系列合金[Al-(Ti13.7Hf0.3)](Al0.69Sn0.18Si0.12(Mo/Ta/Nb)0.03)时效后的硬度
Fig. 3 Microhardness of aged [Al-(Ti13.7Hf0.3)](Al0.69Sn0.18- Si0.12(Mo/Ta/Nb)0.03) alloy series
高温合金对温度十分敏感,在650 ℃长时间暴露下,参比合金和Hf/Ta/Nb合金化的系列合金均具有较高的抗氧化能力,均未出现氧化层剥落现象,且氧化质量增加为同一数量级,这是由于650 ℃时O原子扩散速率较慢造成的。而在高温下(800 ℃),由于O的扩散能力提高,且O在Ti中的固溶度较大(最大溶解度为14.3%(质量分数)),故需要添加合金化元素对O扩散产生阻碍作用。但不同的合金化元素会对O的扩散产生不同的阻碍作用,进而使得合金的抗氧化能力发生改变[26]。Hf0.3替代Zr0.3后合金的氧化质量增加值发生陡降,表明Hf元素能够很大程度地提高合金抗氧化能力,Ta和Nb进一步合金化会使得合金的抗氧化能力继续提高,如图6所示,Hf、Ta和Nb元素的共同添加会使合金表面产生一层致密且薄的TiO2及Al2O3氧化层,阻止合金进一步被氧化。故Hf相对Zr元素、Ta与Nb相对Mo元素在合金高温抗氧化性上均有提升,且No.6合金在650 ℃和800 ℃条件下均具有十分优异的高温抗氧化性能。
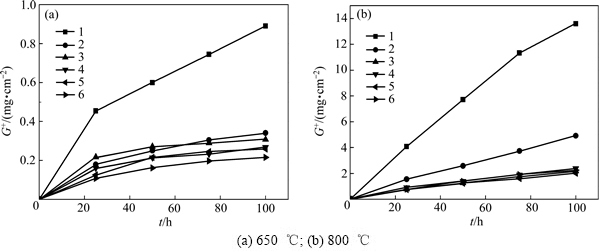
图4 系列合金[Al-(Ti13.7Hf0.3)](Al0.69Sn0.18Si0.12(Mo/Ta/Nb)0.03)时效后的高温氧化质量增加曲线
Fig. 4 Oxidation mass gains curves of aged [Al-(Ti13.7Hf0.3)](Al0.69Sn0.18Si0.12(Mo/Ta/Nb)0.03) alloy series at elevated temperatures
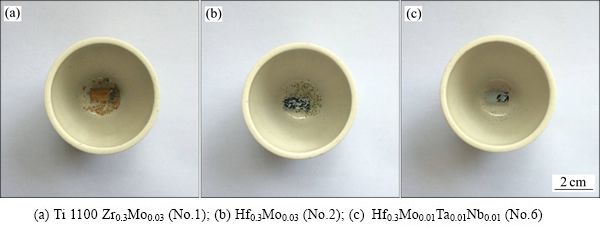
图5 典型系列合金800 ℃氧化100 h表面外观形貌图
Fig. 5 Appearances of typical alloys after oxidation at 800 ℃ for 100 h

图6 典型系列合金800 ℃氧化100 h SEM背散射形貌图
Fig. 6 SEM back-scattering images of typical alloys after oxidation at 800 ℃ for 100 h
4 结论
1) 以近α-Ti 1100合金作为参比合金,利用团簇结构模型确定了[Al-(Ti,Zr)14]M1为基础成分式,并用相似组元替换方法设计了Hf、Nb、Ta微合金化的系列合金,其团簇成分式为[Al-(Ti13.7(Zr/Hf)0.3)](Al0.69Sn0.18- Si0.12(Mo/Ta/Nb)0.03)。
2) 组织与结构结果表明Hf0.3替代Zr0.3时,与参比合金Ti 1100具有相同的组织结构,为片层β转变组织,在α基体上存在少量BCC-β相;在此基础上,不同组合的Ta和Nb替代Mo时合金组织转变为等轴α组织,无BCC-β相出现。系列合金的硬度差别不大,约为320~360 HV。
3) 高温抗氧化实验结果表明系列合金和参比合金在650 ℃下均具有较高的抗氧化能力,而在800 ℃下,和Ti 1100相比,Hf替代Zr后合金的抗氧化能力显著提高,Ta和Nb进一步合金化后合金的抗氧化能力进一步增强,其100 h后的氧化质量增加从Ti 1100的13.6 mg/cm2降低至(2.2±0.2) mg/cm2,氧化层厚度也由150 μm降低至15 μm。
REFERENCES
[1] 朱知寿. 我国航空用钛合金技术研究现状及发展[J]. 航空材料学报, 2014, 34(4): 44-50.
ZHU Zhi-shou. Recent research and development of titanium alloys for aviation application in China[J]. Journal of Aeronautical Materials, 2014, 34(4): 44-50.
[2] WILLIAMS J C, STRAKE E A. Progress in structural materials for aerospace systems[J]. Acta Materialia, 2003, 51(19): 5775-5799.
[3] KHANNA N, DAVIM J P. Design-of-experiments application in machining titanium alloys for aerospace structural components[J]. Measurement, 2015, 61: 280-290.
[4] JAYAPRAKASH M, KOMATSU D, OKAZAKI M, MIYASHITA Y, OTSUKA Y, MUTOH Y. High temperature fretting fatigue behavior of IMI 834 titanium alloy[J]. Transactions of the Indian Institute of Metals, 2016, 69(2): 439-444.
[5] KOSAKA Y, FOX S P, FALLER K, REICHMAN S H. Properties and processing of TIMETAL LCB[J]. Journal of Materials Engineering and Performance, 2005, 14(6): 792-798.
[6] 蔡建明, 李臻熙, 马济民, 黄 旭, 曹春晓. 航空发动机用600 ℃高温钛合金的研究与发展[J]. 材料导报, 2005, 19(1): 50-53.
CAI Jian-ming, LI Zhen-xi, MA Ji-min, HUANG Xu, CAO Chun-xiao. Research and development of 600 ℃ high temperature titanium alloys for aeroengine[J]. Materials Review, 2005, 19(1): 50-53.
[7] CHANDRAVANSHI V, SARKAR R, KAMAT S V, NANDY T K. Effects of thermomechanical processing and heat treatment on the tensile and creep properties of boron-modified near alpha titanium alloy Ti-1100[J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A, 2013, 44(1): 201-211.
[8] 魏寿庸, 何 瑜, 王青江, 刘羽寅. 俄航空发动机用高温钛合金发展综述[J]. 航空发动机, 2005, 31(1): 52-58.
WEI Shou-yong, HE Yu, WANG Qing-jiang, LIU Yu-yin. Development of the areo-engine heat-resisting titanium alloys in Russia[J]. Aeroengine, 2005, 31(1): 52-58.
[9] 张文婧, 宋晓云, 惠松骁, 叶文君, 王永玲, 王小翔, 王韦琪. 单级退火对BTi-6431S合金组织和力学性能的影响[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2013, 23(6): 1530-1535.
ZHANG Wen-jing, SONG Xiao-yun, HUI Song-xiao, YE Wen-jun, WANG Yong-ling, WANG Wei-qi. Effect of single annealing on microstructure and mechanical properties of BTi-6431S titanium alloy[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2013, 23(6): 1530-1535.
[10] GHONEM H. Microstructure and fatigue crack growth mechanisms in high temperature titanium alloys[J]. International Journal of Fatigue, 2010, 32(9): 1448-1460.
[11] BOYER R R. An overview on the use of titanium in the aerospace industry[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 1996, 213(1): 103-114.
[12] WEISS I, SEMIATIN S L. Thermomechanical processing of alpha titanium alloys: An overview[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 1999, 263(2): 243-256.
[13] 张济山, 崔 华, 胡壮麒. d电子合金理论及其在合金设计中的应用[J]. 材料科学与工程, 1993, 11(3): 1-10.
ZHANG Ji-shan, CUI Hua, HU Zhuang-qi. d-electrons alloy theory and its applications in alloy design[J]. Journal of Materials Science and Engineering, 1993, 11(3): 1-10.
[14] 李 东, 万晓景. 钛合金热稳定性研究Ⅲ. 热稳定性判据及其应用[J]. 金属学报, 1984, 20(6): 391-397.
LI Dong, WAN Xiao-jing. On the thermal stability of Ti alloys Ⅲ. The criterion for thermal stability and its application[J]. Acta Metallurgica Sinica, 1984, 20(6): 391-397.
[15] 魏宝敏, 台立民. Ti-Al-Sn-Zr-Mo-Si系高温钛合金的研究进展[J]. 特种铸造及有色合金, 2013, 33(5): 424-428.
WEI Bao-min, TAI Li-min. Progress in Ti-Al-Sn-Zr-Mo-Si high temperature titanium alloy[J]. Special Casting & Nonferrous Alloys, 2013, 33(5): 424-428.
[16] 孙 宇, 曾卫东, 赵永庆, 戚运莲, 韩远飞, 邵一涛, 马 雄. 基于BP神经网络Ti600合金本构关系模型的建立[J]. 稀有金属材料与工程, 2011, 40(2): 220-224.
SUN Yu, ZENG Wei-dong, ZHAO Yong-qing, QI Yun-lian, HAN Yuan-fei, SHAO Yi-tao, MA Xiong. Modeling of constitutive relationship of Ti600 alloy using BP artificial neural network[J]. Rare Metal Materials and Engineering, 2011, 40(2): 220-224.
[17] CAI An-hui, XIONG Xiang, LIU Yong, AN Wei-ke, ZHOU Guo-jun, LUO Yun, LI Tie-lin, LI Xiao-song, TAN Xiang-fu. Compositional optimization of glass forming alloys based on critical dimension by suing artificial neural network[J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2014, 24(5): 1458-1466.
[18] 刘恩雪, 王 清, 马仁涛, 查前锋, 冀春俊, 董 闯. 低Nb含量Ti-Mo-Nb-Zr-Sn BCC低弹性模量固溶体合金的成分设计[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2013, 22(12): 3378-3385.
LIU En-xue, WANG Qing, MA Ren-tao, ZHA Qian-feng, JI Chun-jun, DONG Chuang. Composition design of Ti-Mo-Nb-Zr-Sn BCC solid solution alloys with low elastic modulus and low Nb content[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2013, 22(12): 3378-3385.
[19] PANG Chang, JIANG Bei-bei, SHI Yao, WANG Qing, DONG Chuang. Cluster-plus-glue-atom model and universal composition formulas [cluster](glue atom)x for BCC solid solution alloys[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2015, 652: 63-69.
[20] WANG Qing, JI Chun-jun, WANG Ying-min, QIANG Jian-bing, DONG Chuang. β-Ti alloys with low Young’s moduli interpreted by cluster-plus-glue-atom model[J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A, 2013, 44(4): 1872-1879.
[21] SANTODONATO L J, ZHANG Y, FEYGENSON M, PARISH C M, GAO M C, WEBER R J K, NEUEFEIND J C, TANG Zhi, LIAW P K. Deviation from high-entropy configurations in the atomic distributions of a multi-principal-element alloy[J]. Nature Communications, 2015, 6: 5964-5976.
[22] REN Ming-xin, LI Bang-sheng, FU Heng-zhi. Formation condition of solid solution type high-entropy alloy[J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2013, 23(4): 991-995.
[23] HU Liang, GUO Shun, MENG Qing-kun, ZHAO Xin-qing. Effect of thermo-mechanical treatment on microstructure and mechanical property in metastable beta titanium alloys[J]. Rare Metal Materials and Engineering, 2015, 44(1): 146-151.
[24] 贾蔚菊, 曾卫东, 张尧武, 周义刚. 热处理对Ti60合金组织及性能的影响[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2010, 20(11): 2136-2141.
JIA Wei-ju, ZENG Wei-dong, ZHANG Yao-wu, ZHOU Yi-gang. Effects of heat treatment on microstructure and properties of Ti60 alloy[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2010, 20(11): 2136-2141.
[25] 魏寿庸, 石卫民, 王鼎春, 王清江, 陈志勇, 刘建荣. 600 ℃时高温钛合金(Ti60)的组织与力学性能[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2010, 20(S): s801-s806.
WEI Shou-yong, SHI Wei-min, WANG Ding-chun, WANG Qing-jiang, CHEN Zhi-yong, LIU Jian-rong. Microstructure and mechanical properties of high temperature titanium alloy Ti60 at 600 ℃[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2010, 20(S): s801-s806.
[26] HAN Gui-hong, JIANG Tao, ZHANG Yuan-bo, HUANG Yan-fang, LI Guang-hui. High-temperature oxidation behavior of vanadium, titanium-bearing magnetite pellet[J]. Journal of Iron and Steel Research, International, 2011, 18(8): 14-19.
Effects of minor Hf/Ta/Nb additions on high-temperature oxidation-resistant properties of near α-Ti alloys
CHE Jin-da1, JIANG Bei-bei1, WANG Qing1, ZHANG Rui-qian2, TANG Rui2, CHEN Guo-qing1, DONG Chuang1
(1. Key Laboratory of Materials Modification by Laser, Ion and Electron Beams, Ministry of Education,
School of Materials Science and Engineering, Dalian University of Technology, Dalian 116024, China;
2. Science and Technology on Reactor Fuel and Materials Laboratory, Nuclear Power Institute of China,
Chengdu 610213, China)
Abstract: The composition characteristics of near α-Ti alloy Ti 1100 with the guidance of a cluster-plus-glue-atom model were investigated. A new alloy series with the cluster formula of [Al-(Ti13.7(Zr/Hf)0.3)](Al0.69Sn0.18Si0.12- (Mo/Ta/Nb)0.03) was designed by adding minor Hf, Ta, and Nb. The structures of alloys were characterized, and the oxidation resistance properties were measured. The results show that the Hf substitution for Zr doesn’t influence the β transition lamellar microstructure. While that various combinations of Ta and Nb to substitute for Mo could form equiaxed α microstructure. The oxidation-resistant capacities of designed alloys are enhanced obviously at 800 ℃ in comparison with that of Ti 1100. The oxidation mass gains of the designed alloys with Hf, Nb and Ta co-alloying after 100 h at 800 ℃ are about (2.2±0.2) mg/cm2.
Key words: near α-Ti alloys; composition design; minor alloying; high-temperature oxidation
Foundation item: Projects(51171035, 51131002) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China; Project(2015DFR60370) supported by the National Science and Technology Cooperation of China; Project(2015020202) supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Liaoning Province of China
Received date: 2015-11-23; Accepted date: 2016-04-10
Corresponding author: WANG Qing; Tel: +86-411-84708615; E-mail: wangq@dlut.edu.cn
(编辑 王 超)
基金项目:国家自然科学基金资助项目(51171035,51131002);国家国际科技合作专项(2015DFR60370);辽宁省自然科学基金资助项目(2015020202)
收稿日期:2015-11-23;修订日期:2016-04-10
通信作者:王 清,教授,博士;电话:0411-84708615;E-mail: wangq@dlut.edu.cn