文章编号:1004-0609(2015)-07-1978-09
碳还原锌浸出渣炼铁过程的热力学分析
刘 洋1,谭 军1,刘常青1,尹周澜1,陈启元1,张平民1,廖 舟2
(1. 中南大学 化学化工学院,有色金属资源化学教育部重点实验室,长沙 410083;
2. 株洲冶炼集团股份有限公司,株洲 412000)
摘 要:对锌浸出渣熔池熔炼碳还原炼铁反应过程进行了热力学分析。结果表明:ZnFe2O4和KFe3(SO4)2(OH)6受热分解的含铁产物是Fe2O3,ZnFe2O4在300~1800 K温度范围内不能自发分解,KFe3(SO4)2(OH)6在652.25K即可分解;高pCO/pCO2、低温(但要高于炉渣熔融的温度)有利于熔体中的Fe2O3还原生成液态铁;含硫物相低温分解后的产物有金属硫酸盐K2SO4和CaSO4,两者热分解脱硫的有利条件均是高温及低硫分压、低氧分压(但氧分压要高于硫酸盐分解生成硫化物的限值),CaSO4热分解脱硫比K2SO4易于进行。锌浸出渣中碱性氧化物CaO的存在,一方面可以降低Zn2SiO4碳热还原的起始反应温度,另一方面可以提高炉渣碱度及炉渣中CaO的活度,降低硫在铁液与炉渣中的分配平衡常数。
关键词:锌浸出渣;熔池熔炼;碳还原;炼铁;热力学分析;脱硫
中图分类号:TF51 文献标志码:A
Thermodynamic analysis on iron-making process of zinc leaching residue by carbon reduction
LIU Yang1, TAN Jun1, LIU Chang-qing1, YIN Zhou-lan1, CHEN Qi-yuan1, ZHANG Ping-min1, LIAO Zhou2
(1. Key Laboratory of Resources Chemistry of Nonferrous Metals, Ministry of Education,
College of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China;
2. Zhuzhou Smelter Group Co., Ltd., Zhuzhou 412000, China)
Abstract: Iron-making of zinc leaching residue was obtained by carbon reduction in bath smelting, and the thermodynamic process was analyzed. The results show that Fe2O3 is the pyrolysis product of ZnFe2O4 and KFe3(SO4)2(OH)6. ZnFe2O4 can not decompose in the temperature range of 300-1800 K, but KFe3(SO4)2(OH)6 decomposes at 652.25K. Higher pCO/pCO2 and lower temperature that should be higher than the slag melting temperature, are favor able to the reduction of Fe2O3. The metal sulfates of K2SO4 and CaSO4 are decomposing products of sulfur-contained phases at low temperature, and the favorable desulfurization conditions of K2SO4 and CaSO4 are high temperature, low sulfur-partial pressure and low oxygen-partial pressure that must be higher than the limit of sulfates converting into sulfides. The desulfurization of CaSO4 is easier than that of K2SO4. CaO in zinc leaching residue reduces the initial reaction temperature of Zn2SiO4 reduction, improves slag basicity and activity of CaO in slag and decreases the sulfur distribution ratio between liquid iron and molten slag.
Key words: zinc leaching residue; bath smelting; carbon reduction; iron-making; thermodynamic analysis; desulfurization
目前,我国铁精矿日趋减少,各种湿法冶金渣、化工渣(即除铁渣或沉铁渣)累积很多。这些渣常含有多种有价金属,也是一种较好的铁资源。属于火法冶金工艺的熔池熔炼法很适合回收处理各种湿法冶金渣、化工渣及用于冶炼低品位矿。
湿法锌占世界锌总产量的85%以上,至2007年,我国湿法(电解)锌的产量占全国锌总产量的65.9%[1]。传统的湿法炼锌工艺包括焙烧、浸出、净化、电积和制酸5个主要过程。湿法炼锌过程中会产生大量的锌浸出渣[2],目前,我国每年产生的锌浸出渣超过320万t。锌浸出渣的主要组成元素是铁和锌,此外还含有大量的稀贵金属铟、银及有价金属铅、镓和镉等。锌浸出渣的矿物学分析表明,渣中锌、铁的主要存在形式是铁酸锌(ZnFe2O4)[3-4],铁酸锌稳定的性质增加了锌、铁的分离回收难度。
为有效回收锌浸出渣中有价金属,前人已开发了多种工艺,如热酸浸出沉铁法[5-7]、选冶联合法[8-11]、回转窑烟化法[12]和Ausmelt熔池熔炼法[13-14]等。若使铁酸锌分解,在热酸浸出沉铁工艺中通常要采用高浓度(200~250 g/L)和高温度(90~95 ℃)的酸,虽然锌的浸出率较高,但铁同时也溶解在酸液中,后续的除铁工艺复杂;选冶联合法虽然可以降低二次资源再利用加工成本,相应提高产品的回收率,但在冶炼工艺流程中出现的问题仍未能得到解决[10];回转窑挥发铅、锌直收率近95%,但能耗高,炉衬寿命短,劳动条件差,生产效率相对较低[12]。
锌浸出渣中硫的含量大于8%(质量分数),其赋存形式多为硫酸盐,伴有少量单质硫和金属硫化物,不能直接用作炼铁原料;而采用湿法或常规选矿方法回收其中的铁难度又很大,现还没有一种方法能够综合回收利用其中的铁及其他有价金属;仅能够以少量搭配于精矿进入冶炼系统,大部分做堆存处理。
对于锌冶炼产生的锌浸出渣、沉铁渣和锌窑渣的回收利用,冶金学者做了大量的研究工作。LI[11]等采用碳还原-磁选分离工艺处理浸锌渣,该法通过在弱还原性气氛下将铁酸锌还原为氧化锌和磁性铁,再用磁选方法分离,达到分离回收铁锌的目的。虽然工艺所需要的还原温度低,成本低,但由于焙烧和磁选过程中颗粒间的相互团聚包裹严重,致使铁精矿的品位低,仅58.6%(质量分数),铁、锌的回收率也仅分别达到68.4%、86.4%,且铁精矿中硫含量高,达到1.23%(质量分数)。杨慧芬等[15]进行了煤泥对浸锌渣的直接还原研究,结果表明:锌和铅挥发率分别达到96.69%和97.65%,铁总回收率为81.19%,但是实验没有考虑生铁中危害单质硫的脱除,由1250 ℃焙烧90 min的焙砂EDS谱也能明显看到硫的衍射峰。薛佩毅等[16]采用焙烧-浸出工艺回收黄钾铁矾渣中多种有价金属,锌、铅和镉的浸出率均在95%以上,铁精矿品位提高到54%(质量分数),铁总得率在90%以上,且杂质元素含量在铁精矿标准范围之内,但是其所用铁矾渣物相单一,仅主要含黄钾铁矾一种物相,这种方法难以处理以难分解铁酸锌为主要物相组成的锌浸出渣和沉铁渣。李密[17]已报道韩国温山锌冶炼厂应用Ausmelt熔池熔炼法成功处理锌浸出渣的工业化范例,该技术搭配处理锌浸出渣、炼铅QSL炉渣和针铁矿渣,但只考虑有价金属锌、铅、银和铟的回收,未考虑铁的资源化问题。
熔池熔炼是炉料在液态熔池(熔渣、熔锍)中迅速完成气-液-固相间主要反应的熔炼方法,广泛用于炼铜、炼镍、炼铅和炼铁等[18-20]。熔池熔炼法可以实现有价金属的综合回收,相比于回转窑法具有更高的金属挥发率。用熔池熔炼法处理锌浸出渣,对易挥发金属如锌、铅、铟等以氧化物烟尘形式回收,难挥发有价金属铁可经还原熔炼直接得到生铁。锌浸出渣经直接还原熔炼虽可以实现金属锌、铅和铟的回收,但是,由于入炉原料中硫含量过高,并且硫元素主要以硫酸盐形式存在,致使产出的生铁含硫量高达3%(质量分数)以上,远远超出炼钢生铁标准(w(S)<0.07%,质量分数)。所以,在进行锌浸出渣的还原熔炼之前,应先对其做高温焙烧预处理,脱除其中的硫元素。针对湖南省某冶炼厂富铁锌浸出渣,本文作者在表征分析锌浸出渣物相组成的基础上,对锌浸出渣熔池熔炼碳还原炼铁反应过程进行热力学分析,以期对锌浸出渣碳还原炼铁,实现各种湿法冶金渣的铁资源化提供理论依据。
1 锌浸出渣成分及组成
试验用锌浸出渣取自湖南省某冶炼厂,用研钵磨细至粒径小于74 μm后于真空干燥箱中干燥3 h备用,锌浸出渣的XRF和XRD表征结果分别如表1和图1所示。
XRF表征结果显示,锌浸出渣中铁、锌含量分别达27.05%、16.26%(质量分数),具有较高的回收价值。
表1 锌浸出渣的化学成分
Table 1 Chemical composition of zinc leaching residue (mass fraction, %)
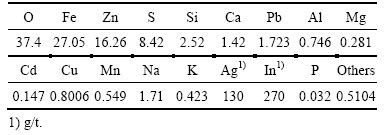
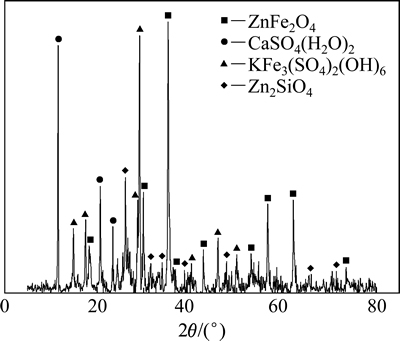
图1 锌浸出渣的XRD谱
Fig. 1 XRD pattern of zinc leaching residue
其自身的三元碱度经计算为0.455,属酸性渣。
XRD表征结果表明,锌浸出渣的主要物相组成是铁酸锌(ZnFe2O4)、二水合硫酸钙(CaSO4(H2O)2)、硅酸锌(Zn2SiO4)和黄钾铁矾(KFe3(SO4)2(OH)6)。XRF表征结果表明,锌浸出渣铅含量约1.723%,但XRD表征并没检测到含铅物相。这一方面可能是因为含铅物相的结晶性不好,另一方面可能是因为铅含量低,接近XRD的检测限(1%)。
2 熔池熔炼的热力学分析
锌浸出渣的熔池熔炼首先是锌浸出渣的热分解过程,然后是热分解产物的碳还原过程。锌浸出渣热分解产物的碳还原过程分为非熔融状态时的金属氧化物直接碳热还原和熔融状态时的氧化物熔体还原两个阶段。
2.1 还原产物的蒸汽压
用熔池熔炼法处理锌浸出渣,能否富集其中的铅、锌、银、铟等有价金属,主要取决于有价金属的挥发性,即某一温度下的蒸汽压。有价金属铅、锌、铁等金属的蒸汽压与温度关系如图2所示。金属的蒸汽压-温度关系数据取自文献[21]。
从图2可以看出,锌、铅在高温下都具有较高的蒸汽压,这是它们易挥发进入烟气的原因。在200~1200 K温度范围内,同一温度下,锌、铅的饱和蒸汽压依次降低,即挥发度依次减小。锰、铜的饱和蒸汽压介于铅和铁之间,铁的饱和蒸汽压(p*)最低。1000 K时,铁的饱和蒸汽压不足10-8 Pa,铅的饱和蒸汽压约1.5 Pa,锌的饱和蒸汽压已高达1.145×104 Pa。1700 K时,铁的饱和蒸汽压约1.2 Pa,铅的饱和蒸汽压高达1.286×104 Pa。可见,易挥发有价金属锌、铅在熔池熔炼法处理锌浸出渣过程中,熔渣中的锌、铅化合物被还原为金属,并以气态挥发物进入气相,气相中锌、铅在炉上部空间或烟道系统再被氧化,最后成为氧化锌、氧化铅被捕集于收尘设备中。还原后不易挥发的金属铁等夹杂在熔渣中,熔池温度高于金属的熔点后成液态,与渣相分离。
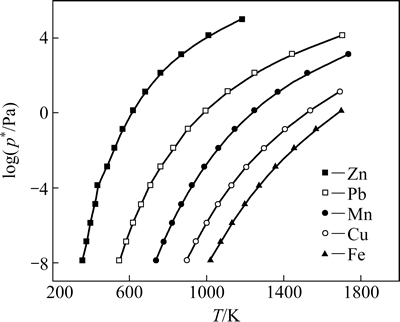
图2 金属的饱和蒸气压与温度的关系
Fig. 2 Relationship between saturated vapor of metals and temperature
2.2 碳热还原过程的热力学原理及应用
对于纯物质,其摩尔定压热容与温度的关系式为
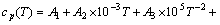
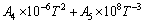 (1)
(1)
物质的吉布斯自由能是随温度变化的状态函数,其绝对值不可求,根据Kirchhoff方程,可定义温度T时纯物质i的标准焓、标准熵、标准吉布斯自由能分别为
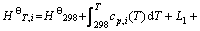
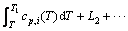 (2)
(2)
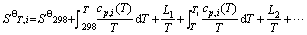 (3)
(3)
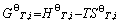 (4)
(4)
式中:L1、L2,…分别为对应温度段内物质的相变焓。
化学反应吉布斯自由能变为
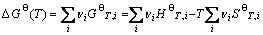 (5)
(5)
式中: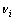 为反应的计量数,反应物为负,产物为正。
为反应的计量数,反应物为负,产物为正。
由锌浸出渣的物相分析结果可知,铁、锌主要赋存于铁酸锌、硅酸锌和黄钾铁矾中,因此,锌浸出渣的火法处理过程实质上要进行化合物的分解过程和金属氧化物的还原过程。首先是铁酸锌、硅酸锌和黄钾铁矾的分解,形成铁、锌的金属氧化物,然后经还原得到单质金属铁、锌。基于上述热力学原理,锌浸出渣中各种化合物分解反应的标准吉布斯自由能变化与温度关系,金属氧化物还原反应的标准吉布斯自由能变化与温度关系,均可根据热力学计算求得。热力学基础物性参数均来源于国际广泛引用的热力学数据库[22-23]。
锌浸出渣中铁酸锌、硅酸锌、黄钾铁矾和二水合硫酸钙的分解反应方程式见(6)~(9),其反应的ΔGΘ(kJ)-T(K)关系曲线如图3所示。
ZnFe2O4(s)=ZnO(s)+Fe2O3(s) (6)
Zn2SiO4(s)=2ZnO(s)+SiO2(s) (7)
2KFe3(SO4)2(OH)6(s)=3Fe2O3(s)+K2SO4(s)+6H2O(g)+3SO2(g)+3/2O2(g) (8)
CaSO4(H2O)2(s)=CaSO4(s)+2H2O(g) (9)
由图3知,在300~1800 K温度范围内,铁酸锌和硅酸锌的ΔGΘ受温度的影响很小,也不受气氛的影响;ΔG=ΔGΘ>0,不能自发进行。黄钾铁矾和二水合硫酸钙理论起始分解温度分别为652.25和347.37 K,分解温度低,较易分解。
虽然铁酸锌、硅酸锌在300~1800 K温度范围内的分解反应不能自发进行,但在碳还原条件下,铁酸锌的分解反应(6)分别通过与反应(10)及反应(11)耦合,硅酸锌的分解反应(7)分别通过与反应(12)及反应(13)耦合,即如反应式(14)~(17)所示,其反应的ΔGΘ(kJ)~T(K)关系曲线如图4所示。
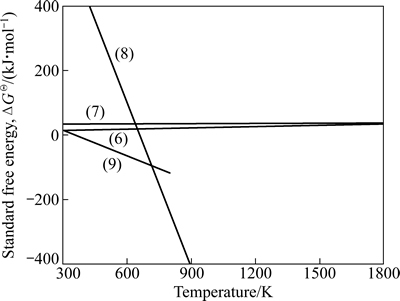
图3 反应式(6)~(9)的ΔGΘ与温度的关系
Fig. 3 Relationship between standard free energy (ΔGΘ) and temperature of reactions (6)-(9)
3Fe2O3(s)+C(s)=2Fe3O4(s)+CO(g) (10)
3Fe2O3(s)+CO(g)=2Fe3O4(s)+CO2(g) (11)
ZnO(s)+C(s)=Zn(g)+CO(g) (12)
ZnO(s)+CO(g)=Zn(g)+CO2(g) (13)
3ZnFe2O4(s)+C(s)=3ZnO(s)+2Fe3O4(s)+CO(g) (14)
3ZnFe2O4(s)+CO(g)=3ZnO(s)+2Fe3O4(s)+CO2(g) (15)
Zn2SiO4(s)+2C(s)=2Zn(g)+SiO2(s)+2CO(g) (16)
Zn2SiO4(s)+2CO(g)=2Zn(g)+SiO2(s)+2CO2(g) (17)
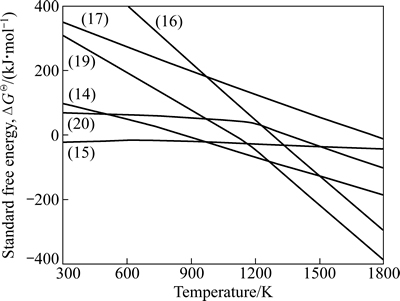
图4 反应式(14)~(17)和(19)~(20)的ΔGΘ与温度的关系
Fig. 4 Relationship between standard free energy (ΔGΘ) and temperature of reactions (14) - (17) and (19)-(20)
由图4知,碳还原铁酸锌与硅酸锌的理论(标准状态下)起始反应温度分别为868.31和1277.79 K,CO还原硅酸锌的理论起始反应温度为1749.21 K;在300~1800 K温度范围内,CO还原铁酸锌的反应能自发进行(ΔG=ΔGΘ<0 )。这些结果同LEE等[24]以碳粉为还原剂,在800~1200 ℃温度范围内对铁酸锌的还原过程所得的结论一致。
由锌浸出渣的组成分析知,其三元碱度仅0.455,属酸性渣。锌浸出渣中添加一定量的造渣剂CaO时,CaO在高温下与SiO2发生反应,生成硅酸钙(CaSiO3),反应方程式为
CaO(s)+SiO2(s)=CaSiO3(s,l) (18)
在高温下,硅酸锌的还原反应(16)、(17)分别与反应(18)发生耦合反应,反应方程式如下:
Zn2SiO4(s)+CaO(s)+2C(s)=2Zn(g)+CaSiO3(s,l)+2CO(g) (19)
Zn2SiO4(s)+CaO(s)+2CO(g)=2Zn(g)+CaSiO3(s,l)+2CO2(g) (20)
由图4知,反应(19)、(20)的理论反应起始温度分别为1099.09 K、1346.45 K。相比于反应(16)、(17)可知,添加造渣剂CaO后,C、CO还原硅酸锌的理论反应起始温度分别降低了178.7 K、402.76 K,反应起始温度大幅降低,升温阶段锌的直接还原率提高。
2.3 含铁氧化物熔体还原的热力学分析
在熔池熔炼中,含铁氧化物熔体实际上是以氧化铁为溶质,炼铁炉渣为熔剂所形成的高温溶液。此溶液中含铁氧化物可以是Fe2O3、FeO和Fe3O4等。作为含铁氧化物熔体还原反应而论,无论取用何物种都应该用其浓度或用活度来表示。因锌浸出渣含铁物相分解产物为Fe2O3,计算过程以Fe2O3表示,则反应式应写为
Fe2O3(sol)+3CO(g)=2Fe(l)+3CO2(g) (21)
式中:Fe2O3(sol)为溶解在熔渣中的Fe2O3。
当反应式中的Fe2O3的活度参考态和化学势的标准态均取纯态时,其标准反应吉布斯自由能变化和标准平衡常数为
ΔGΘ (J)=-9356.91-5.52*T(K)
(1373.15~1773.15K,拟合系数R=0.9966) (22)
ΔGΘ=-RTlnK (23)
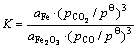 (24)
(24)
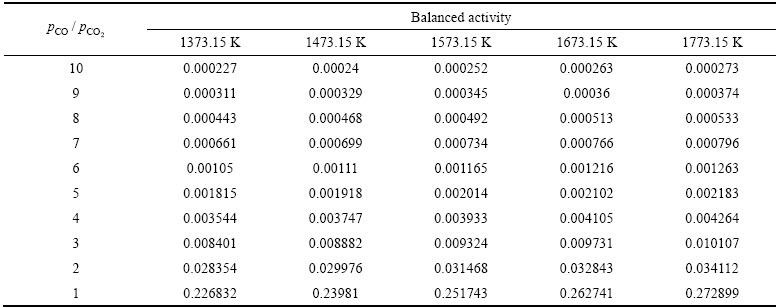
基于标准平衡常数的表达式,在给定温度和CO与CO2分压比值的条件下,含铁氧化物熔体还原反应达到平衡时,熔体中Fe2O3的浓度或活度可以通过热力学计算求得,从而可推知含铁氧化物熔体还原的极限程度。设反应产物液态铁的活度为1(即纯铁),当温度分别取为1373.15、1473.15、1573.15、1673.15和1773.15 K时,CO与CO2分压比分别为10、9、8、7、6、5、4、3、2和1时,计算所得炼铁熔体中Fe2O3的平衡活度如表2所列。
从表2可见,无论在何种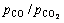 下,随着温度的升高,反应平衡时,炼铁熔体中Fe2O3的活度均增大;无论在何种温度下,随着
下,随着温度的升高,反应平衡时,炼铁熔体中Fe2O3的活度均增大;无论在何种温度下,随着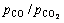 的减小,反应平衡时,炼铁熔体中Fe2O3的活度均增大。因此,高
的减小,反应平衡时,炼铁熔体中Fe2O3的活度均增大。因此,高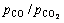 、低温(但要高于用作溶剂的炉渣熔融的温度)均有利于熔体中Fe2O3还原生成液态铁,降低熔渣(渣铁分离,熔体即是熔渣)中Fe2O3的活度。
、低温(但要高于用作溶剂的炉渣熔融的温度)均有利于熔体中Fe2O3还原生成液态铁,降低熔渣(渣铁分离,熔体即是熔渣)中Fe2O3的活度。
对于Fe2O3-CaO-SiO2-MgO-Al2O3五元渣系,根据锌浸出渣组成,添加CaO使二元碱度R调至1.8,熔体中Fe2O3的摩尔浓度为0.455169。T=1673.15 K,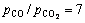 ,熔体中Fe2O3的平衡浓度X=0.000766 (取活度系数γ=1),反应(21)达到热力学平衡时铁的金属化率为99.908%。
,熔体中Fe2O3的平衡浓度X=0.000766 (取活度系数γ=1),反应(21)达到热力学平衡时铁的金属化率为99.908%。
3 铁中的含硫问题
锌浸出渣还原制铁成功与否关键在于铁中的硫含量是否符合要求,一方面取决于造氧化物熔体时含硫化合物分解的脱硫过程是否彻底,另一方面取决于硫及硫化物在液态铁中和炼铁炉渣中的分配情况。
表2 不同温度及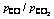 条件下熔体中Fe2O3的平衡活度
条件下熔体中Fe2O3的平衡活度
Table 2 Balanced activity of ferric oxide in melt under different temperatures and 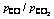
3.1 硫酸盐的分解脱硫反应
根据XRF表征结果,锌浸出渣硫含量高达8%以上,为实现铁、锌分离同时得到合格的生铁,熔融还原阶段液态铁中的硫含量必须经过处理满足生铁的要求。由物相分析知,硫元素主要赋存在黄钾铁矾和二水合硫酸钙中。根据黄钾铁矾的分解反应式,黄钾铁矾在较低温度下分解生成SO2和K2SO4,SO2挥发逸出。二水合硫酸钙(生石膏CaSO4(H2O)2)先脱除1.5分子水生成熟石膏(CaSO4(H2O)0.5),熟石膏再脱除0.5分子水生成无水硫酸钙。从理性上考虑,K2SO4和CaSO4 应熔融于炼铁炉渣中,不会转入液态铁中。它们的存在对液态铁的硫含量不会有直接影响。但在还原性气氛下,无机盐K2SO4、CaSO4能继续分解和还原得K2S、CaS和S。这些产物则有可能转入液态铁中。因此,锌浸出渣在加碳还原之前,要考虑金属硫酸盐K2SO4、CaSO4的热分解脱硫问题。
K2SO4、CaSO4分属K-S-O和Ca-S-O体系,为深入了解K2SO4、CaSO4热分解脱硫条件,根据K-S-O和Ca-S-O体系各反应物的热力学数据,分别绘制了K-S-O和Ca-S-O体系的优势区图如图5和6所示。
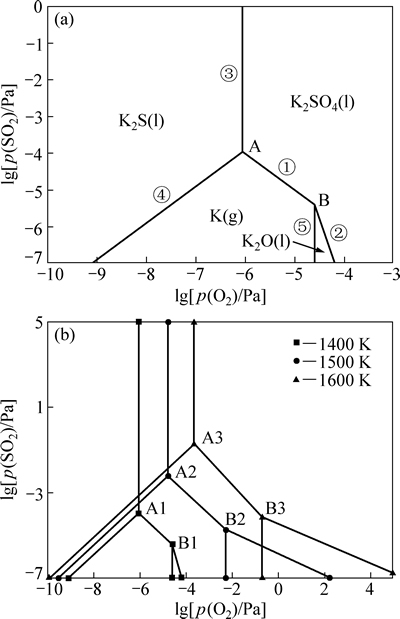
图5 K-S-O系的优势区图
Fig. 5 Predominance diagrams of K-S-O system
在K-S-O体系的优势区图中,单变线上平衡反应式分别为
K2SO4(l)=2K(g)+SO2(g)+2O2(g) (25)
K2SO4(l)=K2O(l)+SO2(g)+1/2O2(g) (26)
K2SO4(l)=K2S(l)+2O2(g) (27)
K2S(l)+O2(g)=2K(g)+ SO2(g) (28)
K2O(l)=2K(g)+1/2O2(g) (29)
为使K2SO4(l)分解不产生K2S(l),应控制分解条件避免K2SO4(l)向K2S(l)稳定区域转化,而使其向 K(g)、K2O(l) 稳定区域转化。从图5(a)可知,当温度在1400 K时,氧分压高于10-6.0578 Pa的条件下,K2SO4(l)不会产生K2S(l),只可能保持原状,或在二氧化硫分压降低的情况下产生K(g)、K2O (l)。从图5(b)可知,当温度高于1400 K时,相应的氧分压和二氧化硫分压提高。
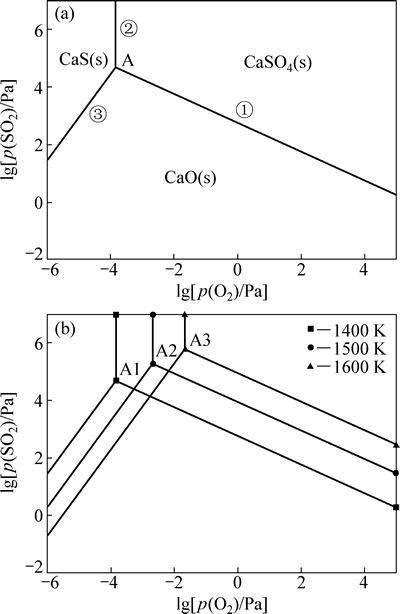
图6 Ca-S-O系(局部)的优势区图
Fig. 6 Part predominance diagrams of Ca-S-O system
在Ca-S-O体系的局部优势区图中,单变线上平衡反应式分别为
CaSO4(s)=CaO(s)+SO2(g)+1/2O2(g) (30)
CaSO4(s)=CaS(s)+2O2(g) (31)
CaS(s)+3/2O2(g)=CaO(s)+SO2(g) (32)
同理,为使CaSO4(s)分解不产生CaS (s),应控制分解条件避免CaSO4(s)向CaS (s)稳定区域转化,而使其向CaO (s)转化。由图6(a)可见,当温度在1400K时,氧分压高于10-3.8413 Pa的条件下,CaSO4(s) 不会产生CaS(s),只可能保持原状,或在二氧化硫分压降低的情况下产生CaO (s)。由图6(b)可见,当温度高于1400 K时,相应的氧分压和二氧化硫分压也提高。
3.2 K2SO4、CaSO4的碳还原反应
在硫酸盐中K2SO4、CaSO4是最难分解的, 在有还原剂碳存在的高温条件下,其还原反应式可以写为如下形式:
K2SO4+3C=K2O+0.5S2(g)+3CO(g) (33)
K2SO4+3CO(g)=K2O+0.5S2(g)+3CO2(g) (34)
CaSO4+3C=CaO+0.5S2(g)+3CO(g) (35)
CaSO4+3CO(g)=CaO+0.5S2(g)+3CO2(g) (36)
根据热力学计算,这些反应的标准吉布斯自由能变化与温度的关系如下表3所示。
表3 反应式(33)~(36)的ΔGΘ
Table 3 Standard free energy of reactions (33)-(36)
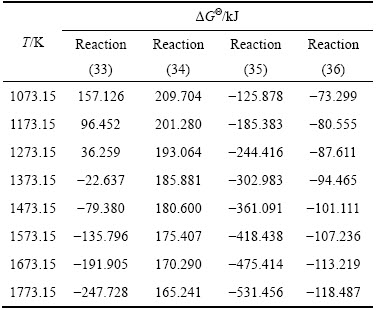
从表3可知,反应(35)、(36)比较容易实现,反应(34)最难实现;由于有碳的气化反应存在,上述4个反应中的反应(34)和反应(36)最为关键。在有还原剂碳存在的高温条件下,依据反应(36),单质硫则有可能生成,同时也可以得到氧化钙,有利于提高炼铁炉渣中氧化钙的活度。在熔池熔炼中,如果考虑到K2SO4、CaSO4 很可能融进炼铁炉渣中,这样K2SO4、CaSO4 的活度将大大降低,而炼铁炉渣中CaO的活度原本就比较高,因此,从热力学角度讲,这都不利于单质硫的生成,即使生成,其量也会很小。
3.3 硫在炼铁炉渣与铁液间的分配(平衡)问题
生铁中的含硫量决定于硫在炼铁炉渣与铁液间的分配,从本质上分析也可以认为,生铁中的含硫量是决定于硫化铁在炼铁炉渣与铁液间的分配。
基于气-固相的锌浸出渣热分解脱硫反应不能彻底脱除硫,少量未分解的K2SO4、CaSO4可能形成少量硫化物,在还原熔炼过程中也可能会形成单质硫,它们都可能进入铁液,也都可能进入炼铁炉渣。单质硫进入铁液属合成反应,比较容易,可用反应(37)表示;单质硫进入炉渣与氧离子发生置换反应,则比较难,可用反应(38)表示;硫化物(CaS)进入铁液属置换反应,比较难,可用反应(39)表示;硫化物(CaS)进入炼铁炉渣属溶解反应,比较容易,可用反应(40)表示;铁液中的硫(FeS)进入炉渣与氧化钙发生置换反应,比较容易,可用反应(41)表示。这些可能过程的反应趋势大小可用这些反应的标准吉布斯自由能变化来表示,实际上也可以用它们的标准平衡常数来表示。
S+Fe=FeS (ΔrG1Θ) (37)
S+CaO=CaS+O (ΔrG2Θ) (38)
CaS+Fe=FeS+Ca (ΔrG3Θ) (39)
CaS+CaO=CaS·CaO (ΔrG4Θ) (40)
FeS+CaO=CaS+FeO (ΔrG5Θ) (41)
这些可能过程的总效果就相当于硫在铁液和炼铁炉渣中进行了分配,其分配平衡常数(Kd)可表示为
Kd=ST,i/ST,s (42)
式中:ST,i是指铁液中的总硫含量;ST,s是指炼铁炉渣中的总硫含量。
由于单质硫进入炉渣的反应(38)和硫化物(CaS)进入铁液的反应(39)难于进行,由此产生的S2,i(反应(38)中产生的铁液中的硫)和S3,s(反应式(39)中炼铁炉渣中的硫)忽略不计,铁液中的总硫量ST,i≈S1,i(S1,i为反应式(37)中产生的铁液中的硫);炉渣熔体中的总硫量ST,s≈S5,s(S5,s为反应式(41)中产生的炼铁渣中的硫),则
S1,i∝ΔrG1Θ∝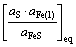 (43)
(43)
S5,s∝ΔrG5Θ∝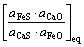 (44)
(44)
Kd∝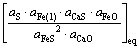 ∝
∝ (45)
(45)
由式(45)可知,硫在铁液与炉渣熔体中的分配平衡常数与硫压、液态铁的活度、炉渣中CaS和FeO的活度呈正相关,与炉渣熔体中FeS和CaO的活度呈负相关。实际上炉渣中CaS、FeO和FeS的活度都比较小,而CaO的活度却比较大。所以,当硫压一定时,决定硫在铁液与炉渣熔体中的分配平衡常数大小的主要因素是铁的活度和炉渣中CaO的活度。铁液中碳、硅、铜和锰等杂质的存在,降低了液态铁中铁的活度,使分配平衡常数减小。在有还原剂碳存在的高温条件下,有可能生成CaO,有利于提高炼铁炉渣中的活度,也使硫的分配平衡常数减小。
从热力学角度讲,硫的分配平衡常数减小则有利于液态铁中含硫量降低。应该强调的是,液态铁中的含硫量不仅决定于热力学因素,还密切地与动力学因素有关。
4 结论
1) ZnFe2O4和KFe3(SO4)2(OH)6受热分解的含铁产物是Fe2O3。这表明含铁尖晶石和低铁硫酸盐渣可以作熔池熔炼制铁造氧化物熔体的原料。
2) 根据对炼铁熔体中Fe2O3平衡活度的计算,高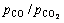 、低温(但要高于用作溶剂的炉渣熔融的温度)有利于熔体中Fe2O3还原生成液态铁,降低熔渣中Fe2O3的活度。在熔炼条件下(取T=1673.15 K,
、低温(但要高于用作溶剂的炉渣熔融的温度)有利于熔体中Fe2O3还原生成液态铁,降低熔渣中Fe2O3的活度。在熔炼条件下(取T=1673.15 K,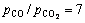 ),熔体中Fe2O3的平衡浓度X=0.000766(取活度系数γ=1),对于含铁较低的锌浸出渣(wFe为20~ 30%),铁的金属化率达99.908%,故低品位含铁渣熔池熔炼制铁是可行的。
),熔体中Fe2O3的平衡浓度X=0.000766(取活度系数γ=1),对于含铁较低的锌浸出渣(wFe为20~ 30%),铁的金属化率达99.908%,故低品位含铁渣熔池熔炼制铁是可行的。
3) 金属硫酸盐K2SO4、CaSO4热分解脱硫的有利条件均是高温及低硫、低氧,维持氧分压大于某一限值,可避免硫化物(K2S、CaS)生成,从而降低硫化物在炉渣中的活度,减小硫在铁液与炉渣中的分配平衡常数。
4) 对于高硫含量的锌浸出渣,控制分解条件使金属硫酸盐尽可能充分分解、避免硫化物生成、减少含硫物种进入氧化物熔体的量以及提高炉渣中CaO的含量均有利于降低硫在铁液与炉渣中的分配平衡常数,可降低液态铁中的硫含量。因此,经过相应处理后,锌浸出渣熔池熔炼制铁产物(生铁)硫含量可达到炼钢生铁标准。
REFERENCES
[1] 王吉坤, 冯桂林. 铅锌冶炼生产技术手册[M]. 北京: 冶金工业出版社, 2012: 293-294.
WANG Ji-kun, FENG Gui-lin. Handbook of lead and zinc smelting production technology[M]. Beijing: Metallurgical Industry Press, 2012: 293-294.
[2]  A, ERDEM M. Environmental risk assessmentandstabilization/solidificationofzinc extraction residue: Ⅰ. Environmental risk assessment[J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2010, 100(3/4): 103-109.
A, ERDEM M. Environmental risk assessmentandstabilization/solidificationofzinc extraction residue: Ⅰ. Environmental risk assessment[J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2010, 100(3/4): 103-109.
[3] ZHANG Y L, YU X J, LI X B. Zinc recovery from franklinite by sulphation roasting[J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2011, 109: 211-214.
[4] CHEN T T, DUTRIZAC J E. Mineralogical changes occurring during the fluid-bed roasting of zinc sulfide concentrates[J]. Journal of the Minerals, Metals, and Materials Society, 2004, 56(12): 46-51.
[5] ELGERSMA F, WITKAMP G J, van ROSMALEN G M. Incorporation of zinc in continuous jarosite precipitation[J]. Hydrometallurgy, 1993, 33(3): 313-339.
[6] ELGERSMA F, WITKAMP G J, VAN ROSMALEN G. Simultaneous dissolution of zinc ferrite and precipitation of ammonium jarosite[J]. Hydrometallurgy, 1993, 34(1): 23-47.
[7] DUTRIZAC J E. Effect of seeding on the rate of precipitation of ammonium jarosite and sodium jarosite[J]. Hydrometallurgy, 1996, 42(3): 293-312.
[8] PENG Ning, PENG Bing, CHAI Li-yuan, LI Mi, WANG Ji-ming, YANG Huan, YUAN Yuan. Recovery of iron from zinc calcines by reduction roasting and magnetic separation[J]. Minerals Engineering, 2012, 35: 56-60.
[9] SATOSHI ITOH, AKIRA TSUBONE, KAZUYO MATSUBAE-YOKOYAMA, KENICHI NAKAJIMA, TETSUYA NAGASAKA. New EAF dust treatment process with the aid of strong magnetic field[J]. ISIJ International, 2008, 48(10): 1339-1344.
[10] 王纪明, 彭 兵, 柴立元, 李 密, 彭 宁. 锌浸出渣还原焙烧-磁选回收铁[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2012, 22(5): 1455-1461.
WANG Ji-ming, PENG Bing, CHAI Li-yuan, LI Mi, PENG Ning. Recovery of iron from zinc leaching residue by reduction roasting and magnetic separation[J]. The Chinese Journal of NonferrousMetals, 2012, 22(5): 1455-1461.
[11] LI Mi, PENG Bing, CHAI Li-yuan, PENG Ning, YAN Huan, HOU Dong-ke. Recovery of iron from zinc leaching residue by selective reduction roasting with carbon[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2012, 237/238: 323-330.
[12] 蒋继穆. 我国铅锌冶炼现状与持续发展[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2004, 14(S1): s52-s62.
JIANG Ji mu. Status and sustainable development of lead and zinc smelting industry in China[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2004, 14(S1): s52-s62.
[13] STREET S, BROOKS G, REILLY L, WORNER H K. Environment and other bath smelting processes for treating organic and ferrous wastes[J]. Journal of the Minerals, Metals, and Materials Society, 1998, 50(4): 43-47.
[14] 周建光. 采用AUSMELT技术处理常规湿法炼锌浸出渣的探讨[C]//第八届全国铅锌冶金生产技术及产品应用学术年会论文集. 韶关: 中国有色金属学会, 2001: 133-137.
ZHOU Jian-guang. Discussion of dealing with the conventional wet smelting zinc leaching residue by AUSMELT technology[C]//Academic Essays of the Eighth National Annual Meeting of Lead and Zinc Metallurgical Production Technology and Product Application, Shaoguan: Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2001: 133-137.
[15] 杨慧芬, 蒋蓓萍, 王亚运, 苑修星, 张莹莹. 煤泥对浸锌渣的直接还原作用[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2015, 25(1): 250-257.
YANG Hui-fen, JIANG Bei-ping, WANG Ya-yun, YUAN Xiu-xing, ZHANG Ying-ying. Direct reduction effect of coal slime on zinc-leaching residue[J]. TheChinese Journal of NonferrousMetals, 2015, 25(1): 250-257.
[16] 薛佩毅, 巨少华, 张亦飞, 王新文. 焙烧-浸出黄钾铁矾渣中多种有价金属[J]. 过程工程学报, 2011, 11(1): 56-60.
XUE Pei-yi, JI Shao-hua, ZHANG Yi-fei, WANG Xin-wen. Recovery of valuable metals by leaching of roasted jarosite residue[J]. The Chinese Journal of Process Engineering, 2011, 11(1): 56-60.
[17] 李 密. 锌焙砂选择性还原与铁锌分离的基础研究[D]. 长沙: 中南大学, 2013: 5-13.
LI Mi. Fundamental research on selective reduction of zinc calcine and separation of zinc and iron[D]. Changsha: Central South University, 2013: 5-13.
[18] MACKEY P J, CAMPOS R. Modern continuous smelting and concerting by bath smelting technology[J]. Canadian Metallurgical Quarterly, 2001, 40(3): 355-376.
[19] 彭容秋. 铅冶金[M]. 长沙: 中南大学出版社, 2004: 71-86.
PENG Rong-qiu. Metallurgy of lead[M]. Changsha: Central South University Press, 2004: 71-86.
[20] 刘 群. 熔池熔炼处理铅锌冶炼渣的高温脱硫及碳热还原研究[D]. 长沙: 中南大学, 2014.
LIU Qun. Research on high-temperature desulfurization and carbon-thermal reduction of lead-zinc metallurgical slags for metals recovery by bath smelting[D]. Changsha: Central South University, 2014.
[21] 戴永年. 有色金属真空冶金[M]. 北京: 冶金工业出版社, 1998: 305-311.
DAI Yong-nian. Vacuum metallurgy of non-ferrous metals[M]. Beijing, Metallurgical Industry Press, 1998: 305-311.
[22] BARIN I, PLATZKI G. Thermochemical data of pure substances[M]. Weinheim: VCH Verlags Gesellschaft, 1995.
[23] KNACKE O, KUBASCHEWSKI O, HESSELMAN K. Thermochemical properties of inorganic substances[M]. 2nd ed. Berlin: Springer-Verlag, 1991: 1114-2412.
[24] LEE J J, LIN C J, CHEN H K. Carbothermal reduction of zinc ferrite[J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transaction B-Process Metallurgy and Materials Processing Science, 2001, 32(6): 1033-1040.
(编辑 李艳红)
基金项目:国家高技术研究发展计划资助项目(2011AA061003)
收稿日期:2014-11-04;修订日期:2015-05-07
通信作者:谭 军,副教授,博士;电话:0731-88877364;E-mail:yytanjun@163.com