不同热处理后TC21钛合金的显微组织及力学性能
来源期刊:中国有色金属学报(英文版)2013年第10期
论文作者:石志峰 郭鸿镇 韩锦阳 姚泽坤
文章页码:2882 - 2889
关键词:TC21钛合金;热处理;显微组织;力学性能
Key words:TC21 titanium alloy; heat treatment; microstructure; mechanical properties
摘 要:研究了损伤容限型TC21钛合金在不同热处理过程中的组织演化及显微组织对力学性能的影响。结果表明,锻后空冷并经(900 °C,1 h,AC)+(590 °C,4 h,AC)热处理,能获得较佳的综合性能。单相区变形,β晶粒呈盘状;单相区退火,β晶粒呈等轴状。单相区变形或退火后的冷却速率及两相高温区退火决定粗大α片的含量及形貌;经过时效或第三次退火后,细小的次生α片从残留β基体中析出。合金的抗拉强度和屈服强度随着粗大α片含量的增加而降低。低的有效滑移长度和高的裂纹扩展阻力能提高合金的室温塑性。交叉分布的粗大α片厚度的增加,有助于提高合金的断裂韧性。
Abstract: Microstructure evolutions during different heat treatments and influence of microstructure on mechanical properties of TC21 titanium alloy were investigated. The results indicate that the excellent mechanical properties can be obtained by adopting air cooling after forging followed by heat treatment of (900 °C, 1 h, AC)+(590 °C, 4 h, AC). Deformation in single β field produces pan-like prior β grains, while annealing in single β field produces equiaxed prior β grains. Cooling rate after forging or annealing in single β field and the subsequent annealing on the top of α+β field determine the content and morphology of coarse α plates. During aging or the third annealing, fine secondary α plates precipitate. Both ultimate strength and yield strength decrease with the content increase of coarse α plates. Decreasing effective slip length and high crack propagation resistance increase the plasticity. The crisscross coarse α plates with large thickness are helpful to enhance the fracture toughness.
Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 23(2013) 2882-2889
Zhi-feng SHI, Hong-zhen GUO, Jin-yang HAN, Ze-kun YAO
School of Materials Science and Engineering, Northwestern Polytechnical University, Xi’an 710072, China
Received 28 September 2012; accepted 25 April 2013
Abstract: Microstructure evolutions during different heat treatments and influence of microstructure on mechanical properties of TC21 titanium alloy were investigated. The results indicate that the excellent mechanical properties can be obtained by adopting air cooling after forging followed by heat treatment of (900 °C, 1 h, AC)+(590 °C, 4 h, AC). Deformation in single β field produces pan-like prior β grains, while annealing in single β field produces equiaxed prior β grains. Cooling rate after forging or annealing in single β field and the subsequent annealing on the top of α+β field determine the content and morphology of coarse α plates. During aging or the third annealing, fine secondary α plates precipitate. Both ultimate strength and yield strength decrease with the content increase of coarse α plates. Decreasing effective slip length and high crack propagation resistance increase the plasticity. The crisscross coarse α plates with large thickness are helpful to enhance the fracture toughness.
Key words: TC21 titanium alloy; heat treatment; microstructure; mechanical properties
1 Introduction
Over the past decades, titanium alloys have been widely used in aircraft and aircraft engines due to their high strength, relatively low density, excellent corrosion and creep resistance [1,2]. With the design criteria’s change of aero structural components, new damage tolerance design is proposed, and it requires titanium alloys to have sufficient residual strength and lifetime in the presence of fatigues, corrosion, or accidental injuries [3]. TC21 alloy (Ti-6Al-2Sn-2Zr-3Mo-1Cr-2Nb-Si), a new α+β titanium alloy, is designed to satisfy the damage tolerance. Due to the excellent balance of strength, plasticity and fracture toughness, more and more attention has been paid to TC21 alloy in the last decade [4,5].
A lot of researches have been done to improve the mechanical properties of TC21 alloy. QU et al [6] reported the variation of microstructure and mechanical properties of TC21 alloy bars after α+β processing and β processing, respectively. WANG et al [7] tried to improve the mechanical properties of TC21 alloy through adopting isothermal forging with low strain rate by changing forging temperature. The solution and aging treatment have been chosen to optimize the microstructure and mechanical properties of TC21 alloy by changing solution temperatures and cooling methods after solution with the same aging treatment [8-10]. Some of these thermo-mechanical processing methods can make TC21 alloy to acquire eligible mechanical properties in laboratory scale, but it is different to manufacture satisfactory forgings in industrial scale. So, some heat treatments differing from solution and aging treatment were employed to optimize the mechanical properties of TC21 alloy.
The relationships between mechanical properties and microstructural features are always the research focus of titanium alloys. Some researchers have tried to establish the quantitative relationships by fuzzy neural network [11-13] or regression analysis [14].
In this work, several heat treatments were carried out to optimize the mechanical properties of TC21 alloy. Microstructure evolution during different heat treatments was studied, and the influence of microstructural morphologies on mechanical properties of TC21 alloy was analyzed.
2 Experimental
The material in this experiment derived from the TC21 titanium alloy as-rolled bars with diameter about 300 mm. The phase transus temperature was about 960 °C by metallographic techniques. As can be seen in Fig. 1, the original microstructure consists of equiaxed primary α phase and transformed β matrix. The equiaxed α phases, with average diameter of 6 μm, uniformly distribute in the entire field of view, and there are fine α plates existing in the transformed β matrix.
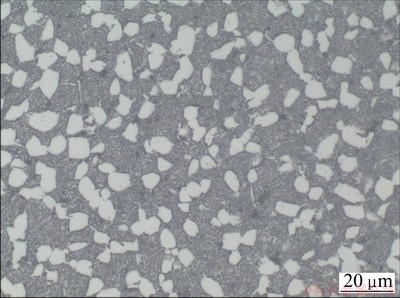
Fig. 1 Microstructure of as-rolled TC21 titanium alloy
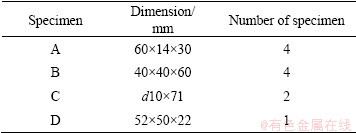
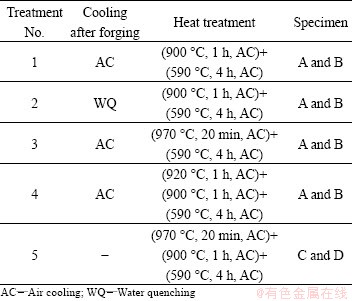
The as-rolled TC21 alloy was spark machined to various cuboid specimens, and their sizes and number are shown in Table1. Specimens A and C were prepared for tensile test, and specimens B and D for fracture toughness test. Specimen A and B were forged in J53-300 friction press at single β phase field (980 °C) with the height reduction of 60%. The specimens were heated before forging in the SX2-4-13 resistance-heated furnace, and the soaking time of specimens was calculated at 0.7 min/mm. Specimens C and D were prepared without deformation. And then these specimens were processed by different heat treatments. The cooling methods and heat treatments after forging are shown in Table 2. The heat treatments were carried out in the SX2-4-13 resistance-heated furnace.
Table 1 Dimensions and number of TC21 alloy specimens for processing
Tensile tests were performed on ENST-1196 testing machine, and the tensile specimens had gauge dimensions of 5 mm (diameter) and 25 mm (length). Fracture toughness tests were performed on CT samples with the thickness of 20 mm in Instron-1251 testing machine. The microstructures of TC21 alloy specimens at different time during entire processing were observed using OLYMPUS-PMG3 optical microscope (OM). The microstructure morphologies were quantificationally determined by Image-Pro Plus software.
Table 2 Heat treatments carried on TC21 titanium alloy
3 Results and discussion
3.1 Microstructure evolution
The schematics of every heat treatment are shown in Fig. 2. And t0, t1, t2, t3 in horizontal axis in Fig. 2 represent the time when specimens were cooled to room temperature after forging, the first annealing in triple heat treatment, solution or the secondary annealing in triple heat treatment, and aging or the third annealing in triple heat treatment, respectively.
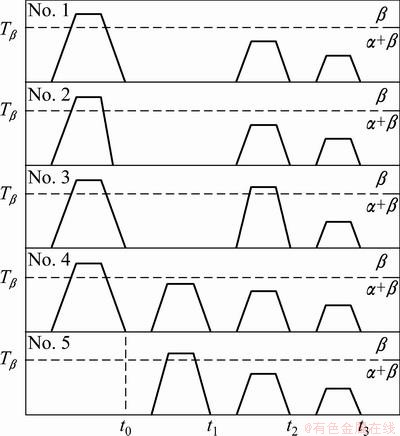
Fig. 2 Schematics of different heat treatments
Treatment 1 is also called solution and aging treatment, which is one of methods usually adopted for TC21 alloy [6-10]. Figure 3 gives the microstructures of TC21 alloy at different time during the heat treatment. As can be seen in Figs. 3(a) and (b), (c) (Figs. 3(a) and (b) parallel to the compressive direction, while Fig. 3(c) perpendicular to that), the microstructure comprises prior β grains, and the prior β grains exhibit pancake shape. During the entire processing, the morphologies of prior β grains have little change. In the “as-forged” microstructure at t0, there are coarse α plates homogeneously distributing in prior β grains (Fig. 3(d)). Due to relatively fast cooling rate, atomic diffusion was not sufficient, phase boundaries between coarse α plates and β phase are indistinct. After solution at 900 °C for 1 h (at t2), the number of α plates decreases, but the width of α plates increases at t 2 compared with those at t0 (Fig. 3(e)). So it can be inferred that parts of α plates dissolved, and the others coarsened during solution at 900 °C. After aging at 590 °C for 4 h (at t3), the residual β matrix becomes clear (Fig. 3(f)), and fine secondary α platelets (Fig. 4) precipitated during aging can be found in residual β matrix [15].
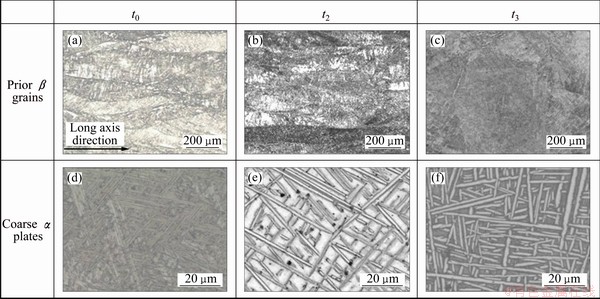
Fig. 3 Microstructures at different time during heat treatment 1

Fig. 4 Secondary α platelets precipitated during aging [15]
The water quenching was adopted after forging in treatment 2. Compared with treatment 1, the microstructure also consists of plate-like β grains at different time (Fig. 5(a), (b) and (c)). No α phase can be found in β grains at t0 (Fig. 5(d)). This is because the cooling rate was so fast that the phase transition was restricted. After solution at t2 (Fig. 5(e)), coarse α plates appeared in prior β grains, and the residual β matrix was not clear. After aging at t3, the phase boundary between coarse α plates and residual β matrix became clear (Fig. 5(f)). And during this step, the secondary α platelets precipitated in residual β phase, which is similar to that mentioned above.
Compared with treatment 1, the solution temperature in treatment 3 raises to 970 °C (10 °C above the transus), which is also called β treatment. Treatment 3 has the same as-forged microstructure with treatment 1 (at t0). But after solution treatment (at t2), the microstructure had a great change. During the solution in the single β field, the recrystallization occurred, and pan-like prior β grains were substituted by equiaxed ones (Fig. 6(a)). And almost nothing can be found in equiaxed β grains (Fig. 6(c)). After aging (at t3), equiaxed β grains had little change (Fig. 6(b)). Blurry coarse α plates precipitated in β grains, and the phase boundaries were indistinct (Fig. 6(d)).
Treatment 4 is a seldom-used heat treatment. WANG et al [7] tried to optimize the mechanical properties of TC21 alloy suffering isothermal forging by this way. According to Table 2 and Fig. 2, the specimens own the same as-forged microstructure with specimens 1 and 3. During the whole processing, pan-like prior β grains basically kept unchanged (Figs. 7(a), (b) and (c)). But the number and size of coarse α plates varied at different time. After the first annealing at 920 °C for 1 h (at t1), few coarse α plates formed (Fig. 7(d)). But after the second annealing at 900 °C for 1 h (at t2), the number and size of coarse α plates had an obvious increase (Fig. 7(e)). After the third annealing at 590 °C for 4 h (at t3), coarse α plates did not have significant changes, but the residual β matrix became clear compared with that at t2 (Fig. 7(f)).
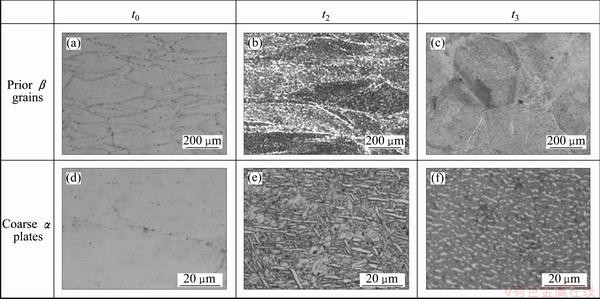
Fig. 5 Microstructures at different time during heat treatment 2
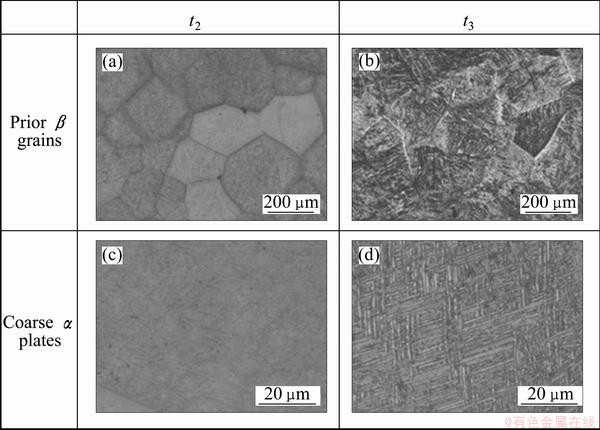
Fig. 6 Microstructures at different time during heat treatment 3
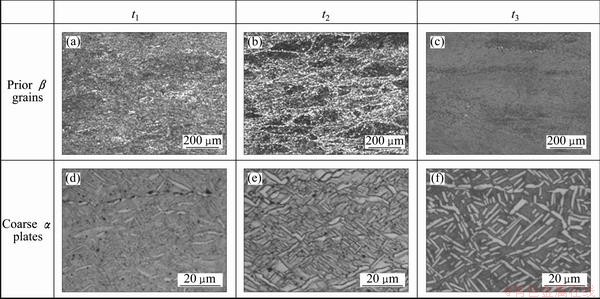
Fig. 7 Microstructures at different time during heat treatment 4
Treatment 5 is also called triple heat treatment. The specimens did not suffer deformation. Figure 8 shows the microstructure of TC21 alloy at different time during triple heat treatment. As can be seen in Figs. 8(a), (b) and (c), the coarse equiaxed β grains with diameter about 400 μm formed after the first annealing (at t1) and had little change during subsequent annealing. After the first annealing at 970 °C (10 °C above the transus), nothing can be found in prior β grains (Fig. 8(d)). After the second annealing was conducted at 900 °C for 1 h, there were coarse α plates forming in prior β grains (Fig. 8(e)). During the third annealing, the secondary α platelets would precipitate as mentioned above.
From the above results, the different steps during the whole processing have different effects on the final microstructure. Deformation or annealing in single β field mainly affects the morphology of prior β grains. In this work, single axial compression made prior β grains exhibit a pancake shape (Figs. 3(a), 5(a) and 7(a)). After annealing in single β field (the first annealing in triple heat treatment or solution in β treatment), the pan-like prior β grains would be replaced by equiaxed ones (Figs. 6(a) and 8(a)). Cooling rate after forging or annealing in single β field and the subsequent annealing in the top of α+β field determines the content, morphology and size of coarse α plates. Some coarse α plates are crisscross of each other, such as in Fig. 3(f), Fig. 6(d) and Fig. 8(f); while other coarse α plates are independent of each other, such as in Fig. 5(f) and Fig. 7(f). The distribution of coarse α plates is probably influenced by cooling rate after forging and the following solution temperature. During aging or the third annealing at 590 °C for 4 h applied to all specimens, fine secondary α plates would precipitate in the residual β matrix.
3.2 Mechanical properties
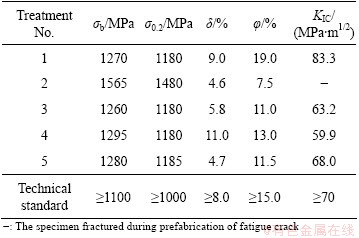
The room temperature mechanical properties of TC21 titanium alloy after different heat treatments are shown in Table 3. As can be seen in Table 3, both of ultimate strength and yield strength of all specimens after different heat treatments are high. The highest ultimate strength and yield strength, reaching 1565 MPa and 1480 MPa, respectively, are obtained after treatment 2, but at the same time it owns the lowest elongation, reduction of area and fracture toughness. TC21 alloy reveals weak plasticity and fracture toughness, and only the specimens after treatment 1 can satisfy the technical standards. According to the above results, the better comprehensive mechanical properties of TC21 alloy can be obtained after treatment 1.
3.3 Influence of microstructure on mechanical properties
The mechanical properties of titanium alloys are strongly influenced by their microstructures. The content, size and distribution of α phase or prior β grains determine the mechanical properties of TC21 alloy.
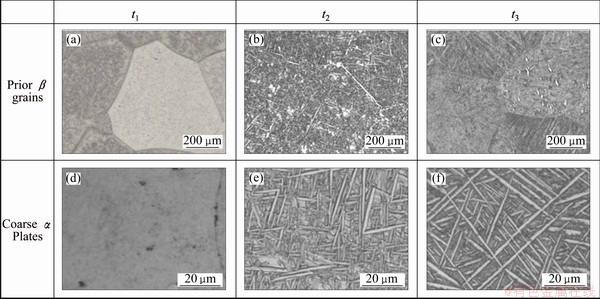
Fig. 8 Microstructures at different time during heat treatment 5
Table 3 Mechanical properties of TC21 alloy after different heat treatments
3.3.1 Influence of content of coarse α plates on strength of TC21 alloy
Except No.3 processing, any other processing includes the steps of (900 °C, 1 h, AC) + (590 °C, 4 h, AC). During these steps, the secondary α platelets precipitated from the supersaturated β phase. Before the solution or the second annealing of (900 °C, 1 h, AC), the deformation and first annealing mainly change the morphology of coarse α plates. So the final microstructure of TC21 alloy mainly consists of coarse α plates and residual β matrix.
The relationships between tensile strength and content of coarse α plates (Table 4) of TC21 titanium alloy are shown in Fig. 9. As can be seen in Fig. 9, both ultimate strength and yield strength have a trend of decrease with the content increase of coarse α plates. During (900 °C, 1 h, AC) + (590 °C, 4 h, AC), the secondary α platelets precipitated from the supersaturated β phase, which is regarded as the main reason to strengthen α+β titanium alloy [16]. This is because that the precipitating of the secondary α platelets will increase the α/β phase boundary. During deformation, dislocation slip would be blocked by α/β phase boundary, formed dislocation pile-up (Fig. 10) [17], and finally caused the strengthening of TC21 titanium alloy. So with the decrease of coarse α plates content (or content increase of residual β matrix strengthened by the secondary α platelets), the α/β phase boundaries increase, and the ultimate strength and yield strength of TC21 alloy also increase. In Fig. 9, the four sets of data (excluding data of specimen 3) are linearly fitted. It can be found that both of ultimate strength and yield strength own liner relationships with the content of coarse α plates, and the correlation coefficients are about 0.97.
Table 4 Microstructure parameters of TC21 alloy after different heat treatments
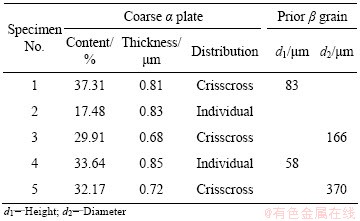

Fig. 9 Relationship between tensile strength and content of coarse α plates
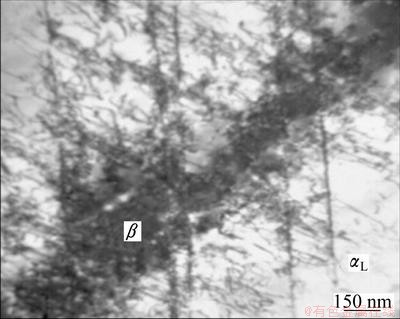
Fig. 10 Dislocation pile-up at phase boundaries [17]
3.3.2 Influence of prior β grains on plasticity of TC21 alloy
According to the microstructures in Figs. 3, 5-8 and the height and diameter of prior β grains in Table 3, it can be found that the plasticity of TC21 alloy is affected by prior β grains. In specimens 1 and 4, prior β grains exhibit pan-like shape, and TC21 alloy has better tensile plasticity in L direction (Fig. 3(a)) of prior β grains. In specimens 3 and 5, prior β grains are equiaxed, and the plasticity of TC21 alloy is lower than that in specimen 1 or 4. SAUER and LUTJERING [16] showed similar results. This phenomenon can be explained by the effective slip length parallel to the grain boundary α layers, which is thought as a soft zone. The maximum resolved shear stress has an angle about 45° with respect to the applied stress, so the distance marked D1 in Fig. 11 represents the effective slip length in the L direction in specimens 1 and 4, while D2 represents the effective slip length in specimens 3 and 5. From Table 4, it is obviously that D1 is smaller than D2. The increase of effective slip length makes the crack form easily, and drops the plasticity of metal materials. So the plasticity of specimen 1 or 4 is better than that of specimen 3 or 5.
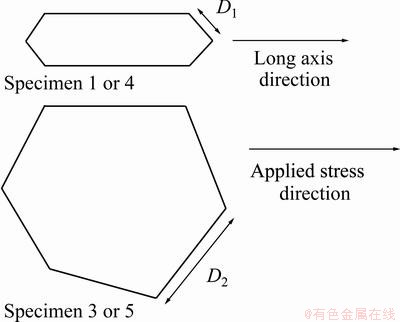
Fig. 11 Effective slip lengths in different specimens
Specimen 2 possesses pan-like prior β grains, but the elongation and reduction of area are the weakest. This can be explained by the crack propagation resistance, which is another factor affecting the alloy plasticity [16]. If alloys have enough crack propagation resistance, crack propagation will be restrained during the following deformation, and the alloy plasticity will be enhanced. The fracture toughness can reflect the alloys’ capability to resist crack propagation. From Table 3, the fracture toughness of specimen 2 is so weak that the specimen fractures during the fatigue crack prefabrication. Once the crack formed, the specimen quickly fractured. So the plasticity of specimen 2 is weak.
3.3.3 Influence of distribution and thickness of coarse α plates on fracture toughness of TC21 alloy
According to Tables 3 and 4, specimen 1 with crisscross coarse α plates has high fracture toughness, while specimens 2 and 4 with individual ones have low values. The α phase is generally considered tough phase [12]. Once the crack forms in the alloy, it will propagate under the action of imposed stress. The coarse α plates are individual in specimen 2 or 4, and the crack almost propagates along the residual β matrix, and seldom passes through α plates (Fig. 12(a)). However, in specimen 1, coarse α plates are crisscross each other, so the crack cannot avoid to meeting α plates during propagation (Fig. 12(b)). Then a plastic deformation zone in α phase, which will form nearby the crack tip, is bigger than that in β matrix [18]. The plastic deformation zone will consume some plastic deformation work, which will impede the crack to propagate. So, crisscross α plates are helpful to enhance the fracture toughness of titanium alloy compared with individual α plates.
The thickness of coarse α plates is another factor affecting fracture toughness of titanium alloy. As can be seen in Fig. 13, the fracture toughness increases with thickness increase of coarse α plates, and the similar results have been reported by many researchers [19-21]. This is because with the thickness increase of the coarse α plates, the size of the plastic deformation zone increases, the stress intensity required to cause crack propagation becomes greater, the crack propagation will be restrained, and finally the fracture toughness of TC21 alloy increases [21].
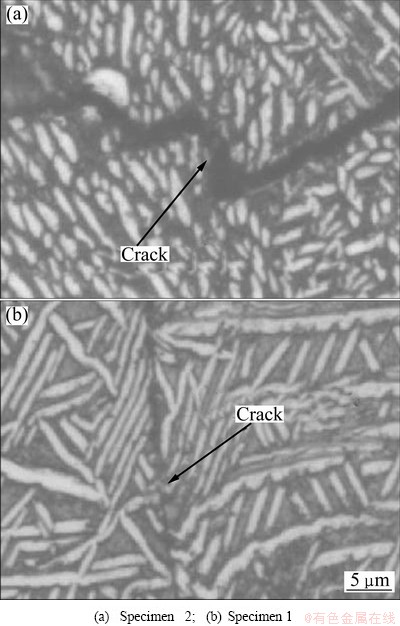
Fig. 12 Crack propagation routes
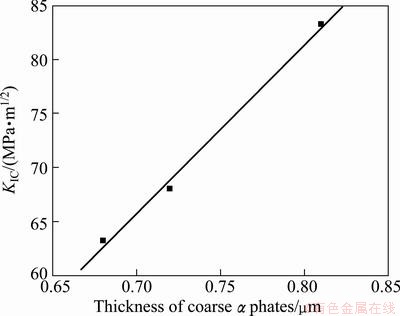
Fig. 13 Relationship between fracture toughness and thickness of coarse α plates
4 Conclusions
1) Deformation in single β field produces pan-like prior β grains, while annealing in single β field produces equiaxed prior β grains. Cooling rate after forging or annealing in single β field and the subsequent annealing in the top of α+β field determine the content and morphology of coarse α plates. During aging or the third annealing, fine secondary α plates precipitate from residual β matrix.
2) The microstructure of TC21 alloy mainly comprises coarse α plates and residual β matrix strengthened by the secondary α platelets. And both ultimate strength and yield strength decrease with the increase of coarse α plates.
3) The plasticity of TC21 alloy is influenced by prior β grains. The plasticity in the L direction of the specimen with pan-like prior β grains is better than that with equiaxed prior β grains. Moreover, low crack propagation resistance (i.e. low fracture toughness) also drops the plasticity of TC21 alloy.
4) The fracture toughness of TC21 alloy is influenced by the distribution and thickness of coarse α plates. Crisscross α plates with a large thickness are helpful to enhance the fracture toughness.
References
[1] van BOHEMAN S M C, KAMP A, PETROV R H, KESTENS L A I, SIETSMA J. Nucleation and variant selection of secondary α plates in a β Ti alloy [J]. Acta Mater, 2008, 56: 5907-5914.
[2] BOYER R R. An overview on the use oftitaniumin the aerospace industry [J]. Mater Sci Eng A, 1996, 213: 103-114.
[3] ZHAO Yan-lei, LI Bo-long, ZHU Zhi-shou, NIE Zuo-ren. The high temperature deformation behavior and microstructure of TC21 titanium alloy [J]. Mater Sci Eng A, 2010, 527: 5360-5367.
[4] LIU Hui-jie, FENG Xiu-li. Microstructures and interfacial quality of diffusion bonded TC21 titanium alloy joints [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2011, 21: 58-64.
[5] ZHU Zhi-shou, WANG Xin-nan, GU Wei, CHEN Ming-he. Study on high temperature deformation behaviors of new type TC21 titanium alloy [J]. Materials China, 2009, 28: 51-55.
[6] QU Heng-lei, ZHOU Yi-gang, ZHOU Lian, ZHAO Yong-qing, ZENG Wei-dong, FENG Liang, YANG Yan-qing, CHEN Jun, YU Han-qing, LI Hui, ZHANG Ying-nan, GUO Hong-chao. Relationship among forging technology, structure and properties of TC21 alloy bars [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2005, 15: 1120-1124.
[7] WANG Xiao-chen, GUO Hong-zhen, SHI Zhi-feng, WANG Yan-wei, YAO Ze-kun. Study on isothermal forging temperature of high damage-tolerant titanium alloy [J]. Forging & Stamping Technology, 2010, 35: 20-23.
[8] MA Shao-jun, WU Xue-ren, LIU Jian-zhong, WANG Li-fa. Influence of microstructures on mechanical properties for TC21 titanium alloy [J]. Journal of Aeronautical Materials, 2006, 26: 22-25.
[9] ZHANG Li-jun, TIAN Jun-qiang, ZHOU Zhong-bo, KOU Hong-chao, ZHU Zhi-shou. Effects of heat treatment on microstructures and mechanical performances of TC21 titanium alloy forgings [J]. Materials China, 2009, 28: 84-87.
[10] LEI Wen-guang, MAO Xiao-nan, HOU Zhi-min, LU Ya-feng, QU Heng-lei, ZHOU Yi-gang, XI Zheng-pin. Effect of heat treatment on microstructures and mechanical properties of TC21 alloy large bar [J]. Titanium Industry Process, 2010, 27: 28-31.
[11] TILEY J, SEARLES T, LEE E, KAR S, BANERJEE R, RUSS J C, FRASER H L. Quantification of microstructural features in α/β titanium alloys [J]. Mater Sci Eng A, 2004, 372: 191-198.
[12] LEE Eunha. Microstructure evolution and microstructure/ mechanical properties relationships in α+β titanium alloys [D]. Columbus, USA: The Ohio State University, 2004.
[13] SHA Wei, MALINOV Savko. Titanium alloys: Modelling of microstructure, properties and applications [M]. Cambridge: Woodhead Publishing, 2009.
[14] WANG Tao, GUO Hong-zhen, WANG Yan-wei, YAO Ze-kun. Influence of processing parameters on microstructure and tensile properties of TG6 titanium alloy [J]. Mater Sci Eng A, 2010, 528: 736-744.
[15] LIU Dong-sheng. The heat treatment and phase transformation of a high strength and high toughness titanium alloy [D]. Beijing: Tsinghua University, 2005. (in Chinese)
[16] SAUER C, LUTJERING G. Influence of α layers at β grain boundaries on mechanical properties of Ti-alloys [J]. J Mater Process Technol, 2001, 117: 311-317.
[17] WANG Tao, GUO Hong-zhen, WANG Yan-wei, PENG Xiao-na, ZHAO Yan, YAO Ze-kun. The effect of microstructure on tensile properties, deformation mechanisms and fracture models of TG6 high temperature titanium alloy [J]. Mater Sci Eng A, 2011, 528: 2370-2379.
[18] ZHONG Qun-peng, ZHAO Zi-hua. Fractography [M]. Beijing: Higher Education Press, 2006. (in Chinese)
[19] WOOD J R, RUSSO P A, WELTER M F, CRIST E M. Thermomechanical processing and heat treatment of Ti–6Al–2Sn– 2Zr–2Cr–2Mo–Si for structural applications [J]. Mater Sci Eng A, 1998, 243: 109-118.
[20] LUETJERING G, WILLIAMS J C. Titanium [M]. 2nd ed. Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer-Verlag, 2007.
[21] RICHARDS N L, BARNBY J T. The relationship between fracture toughness and microstructure in alpha-beta titanium alloys [J]. Mater Sci Eng, 1976, 26: 221-229.
石志峰,郭鸿镇,韩锦阳,姚泽坤
西北工业大学 材料学院,西安 710072
摘 要:研究了损伤容限型TC21钛合金在不同热处理过程中的组织演化及显微组织对力学性能的影响。结果表明,锻后空冷并经(900 °C,1 h,AC)+(590 °C,4 h,AC)热处理,能获得较佳的综合性能。单相区变形,β晶粒呈盘状;单相区退火,β晶粒呈等轴状。单相区变形或退火后的冷却速率及两相高温区退火决定粗大α片的含量及形貌;经过时效或第三次退火后,细小的次生α片从残留β基体中析出。合金的抗拉强度和屈服强度随着粗大α片含量的增加而降低。低的有效滑移长度和高的裂纹扩展阻力能提高合金的室温塑性。交叉分布的粗大α片厚度的增加,有助于提高合金的断裂韧性。
关键词:TC21钛合金;热处理;显微组织;力学性能
(Edited by Xiang-qun LI)
Foundation item: Project (51101119) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China
Corresponding author: Zhi-feng SHI; Tel: +86-29-88493744; Fax: +86-29-88492642; E-mail: titansmith@163.com
DOI: 10.1016/S1003-6326(13)62810-1

