高浓度镍环境中不同培养条件对浸矿微生物群落的影响
管 昊,尹华群,刘 杰,罗焱杰,刘学端,邱冠周
(中南大学 资源加工与生物工程学院,湖南 长沙,410083)
摘 要:为了解高浓度镍环境中不同能源条件对浸矿微生物群落组成的影响,以59 g/L(1 mol/L)的镍离子作为选择压力,在不同培养条件下富集酸性环境中的微生物,并通过聚合酶链式反应-限制性片段长度多态性(PCR-RFLP)技术分析微生物群落多样性。研究结果表明:在高浓度镍离子胁迫下仍存在多种微生物,分别属于变形菌门、酸杆菌和厚壁菌门。此外,研究还发现,不同的富集条件对微生物群落影响很大。当pH值为4时,以亚铁为能源的富集物中,其微生物群落主要以Acidiphilium属和Acidobacterias属为主;在以单质硫为能源的富集物中,90%的微生物属于Acidiphilium;在以硫酸亚铁、单质硫及酵母粉为能源的富集条件下,Acidiphilium和 Pseudomonas为优势种群。
关键词:生物冶金;微生物群落;镍抗性;PCR-RFLP;酸性矿坑水
中图分类号:Q939 文献标识码:A 文章编号:1672-7207(2009)03-0543-07
Effect of culture conditions on microbial community with high concentration of nickel ion
GUAN Hao, YIN Hua-qun, LIU Jie, LUO Yan-jie, LIU Xue-duan, QIU Guan-zhou
(School of Minerals Processing and Bioengineering, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China)
Abstract: The influence of energy resources on leaching microbial community was studied. AMD (Acid mine drainage) microbes was cultivated and selected. In high concentration (59 g /L) of nickel sulphate, with different energy resources, the microbial community diversity was analyzed by polymerase chain reaction-restriction fragment length polymorphism (PCR-RFLP) technique. The results show that there are several kinds of bacteria in high-concentration nickel ion, which are close to Firmicutes, Acidobacteria, and Proteobacteria in affinity respectively. Moreover, the results indicate that the different culture conditions show great impact in the microbial community. Acidiphilium and Acidobacterias are the dominant species in microfloras enriched in pH=4 media with ferrous iron as energy sources. In microfloras enriched in pH=4 media with sulfur as energy sources, about 90% of the bacterium are Acidiphilium. With the energy source including ferrous iron, sulfur and yeast extract, Acidiphilium and Pseudomonas are the dominant species.
Key words: microbial metallurgy; microbial community; nickel-resistance; PCR-RFLP; acid mine drainage
采矿活动使金属硫化矿大量暴露于地表,经过自然与生物的氧化作用导致产生大量酸性矿坑水(Acid mine drainage,AMD)[1]。AMD通常含有高浓度的金属离子与硫酸盐,可利用的底物类型也非常有限。然而,在这样的极端环境中,微生物群落仍然非常丰富,至少含有11个原核生物门[2],这些微生物为生物冶金提供了重要的生物资源。这些微生物对能源的要求差异很大,由于AMD环境的营养物质缺乏,大多数嗜酸性微生物的初级生产只能依赖化能无机自养进 行,尤其是亚铁离子和低价硫的氧化,铁和硫是这些嗜酸性微生物能量代谢的重要组成部分[3]。尽管如此,AMD环境中仍然存在异养生活的嗜酸性微生物,包括兼性异养与专性异养微生物[4-6]。因此,研究不同能源条件下微生物群落的组成对浸矿微生物的分离及提高生物浸出效率具有重要的理论参考价值。就镍的生物浸出而言,其环境中镍离子的含量常常会达到 1.2 mmol/L,甚至更高,对微生物产生严重的毒害作用。此外,在镍矿浸出环境中,pH值较高(pH>4),一般浸矿微生物(一般生长最适宜pH<3.5)生长易受到抑制,且浸矿过程中耗酸量大,成本较高[7-8]。因此,如何筛选适合镍浸出的微生物或微生物种群,是目前镍生物浸出需要解决的一个关键问题。本文作者在含镍的3种富集培养基中进行微生物的选择性富集,并通过PCR-RFLP的方法对这些微生物进行群落组成分析,研究高浓度镍离子和不同培养物对微生物群落的影响,为镍浸出微生物的筛选和工业应用提供理论参考。
1 材料与方法
1.1 样品来源
原始水样取自江西德兴铜矿、江西银山矿及广西镍矿的酸性矿坑水,对各水样进行ICP全元素分析。收集的水样在40 ℃保存。
1.2 富集培养
1.2.1 培养基
基本培养基为9K无硫酸亚铁基础培养基,其组成为:(NH4)SO4 3 g,KCl 0.1 g,K2HPO4 0.5 g,MgSO4?7H2O 0.5 g,Ca(NO3)2 0.01 g,FeSO4?7H2O 44.2 g,加H2O至1 L。
在基础培养基中分别加入:44.2 g/L硫酸亚铁(以NF表示);44.2 g/L硫酸亚铁和1%单质硫(以NS表示);44.2 g/L硫酸亚铁、1%单质硫及0.1%酵母粉(以NY表示),pH值均调节至4.0。培养基经121 ℃灭菌 20 min,3类培养基中的硫酸亚铁溶液单独分开,用0.22 μm滤膜过滤除菌。
1.2.2 富集培养
首先,从3个样品中各取5 mL原始水样混合并分别加入3组富集培养基中,同时,在富集培养基中加入0.2 mol/ L Ni2+(硫酸镍)进行选择性富集,在 30 ℃摇瓶培养。待培养液富集物中微生物浓度达到107个/mL时,从第1代培养液富集物中各取5 mL接入加有0.4 mol/L硫酸镍的富集培养基中,此后,每代依次增加Ni2+浓度,其浓度分别为:0.2,0.4,0.6,0.8,1.0和1.2 mol/L。当Ni2+浓度达到1.2 mol/L时,微生物无法存活,所以,设定能够抑制微生物生长的最低抑菌浓度(Minimal inhibitory concentration,MIC)为 1.0 mol/L。以1.0 mol/L Ni2+浓度传代培养,至细菌生长稳定,过滤离心收集菌体。从加入Ni2+的3组富集培养基中获得的菌体样本分别标记为NF,NS和NY。
1.3 基因组DNA的提取以及16S rRNA基因的扩增
富集培养的3类细菌样本的基因组DNA使用细菌基因组DNA提取试剂盒(Tiangen,DP302)提取。
以基因组DNA作为模板,采用通用引物27F及1492R(上海生工生物工程技术服务有限公司生产)进行16S rRNA基因的PCR扩增。循环参数设置为:在94 ℃保温5 min;在94 ℃保温45 s;在55 ℃保温45 s;在72 ℃保温90 s,共30个循环;最后在72 ℃保温 7 min。
PCR扩增产物采用1%的琼脂糖凝胶电泳检 测,并采用E.Z.N.A Gel Extraction Kit(Omega)试剂盒回收。
1.4 16S rRNA基因的克隆、筛选与测序
PCR产物与pGEM-T克隆载体(Promega)连接,转入E.coli DH5α感受态细胞(Tiangen)构建克隆文库。每个样品随机挑选至少100个白色克隆子进行PCR扩增筛选,并进行电泳检测。对阳性克隆的PCR产物加入HinpⅠ和MspⅠ,置于37 ℃进行限制性酶切5 h。酶切产物使用EB染色的2.5%琼脂糖凝胶电泳;电泳后进行RFLP结果分析。相同带型的电泳条带被归为一种RFLP带型模式,并挑取一个代表性的对应克隆进行测序。
1.5 系统发育分析
在RFLP图谱的基础上,共挑选29个具有代表性的16S rRNA基因序列进行测序分析。序列先采用NCBI的BLASTN工具进行分类鉴定,然后,采用Neighbor-Joining法对所有可用的核酸序列的系统发育情况进行分析。基于初步的系统发育分析结果,适当的16S rRNA基因序列子集被挑选出来并使用CLUSTAL W程序构建系统发育树。
2 结果与分析
2.1 富集物中16SrRNA基因克隆文库分析
从3个富集物的基因组DNA中成功扩增出正确长度的16SrRNA基因(约1.5 kb),经T-A克隆后共获得233个16S rRNA基因阳性克隆,并对这些克隆进行RFLP分析,归为29个可操作分类单元(OTU)。RFLP结果表明,NY富集物中OTU的数量明显高于其他2个富集物样品(NS和NF)的数量。3个富集物样品的16S rRNA基因克隆文库分析表明,在各个样品中都存在一些占主要优势的OTU。在NF样品中,OUT的NF-1和NF-2含量分别为克隆文库总数的51%和27%。在NS样品中,NS01,NS02和NS04是优势的可操作分类单元,分别为NS克隆文库总数的52%,13%和17%。而NY样品中的5个主要OTU NY1,NY3,NY4,NY7和NY8分别为该样品克隆文库总数的10%,26%,14%,10%和14%(图1)。
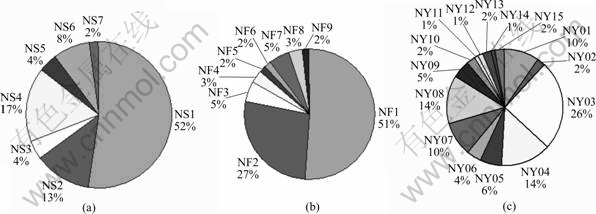
(a) NS; (b) NF; (c) NY
图1 3个富集样品中16S rRNA基因克隆文库中的OUT分布图
Fig.1 OTU distribution of 16S rRNA clone libraries taken from three enrichment samples
2.2 16S rRNA基因系统发育分析
系统发育分析结果如图2~4所示。可见,29个16S rRNA基因序列所对应的细菌分属于3个门5个属的微生物。其中,大部分OTU(NF01,NF05,NS01,NS04,NS06,NY02,NY03,NY07)属于变形菌门(Proteobacteria)的嗜酸杆菌属(Acidiphilium),其相似性为98%~99%。在变形菌门中,有7个 OTU(NF08,NS05,NY01,NY04,NY05,NY08,NY10)属于假单胞菌属(Pseudomonas),相似性为92.7%~99.3%;还有5个OTU(NF03,NS03,NY09,NY13和NY15)属于嗜酸硫杆菌属(Acidithiobacillus),其相似性约为99%;只有1个OTU(NS07)与柠檬酸杆菌属(Citrobacter)细菌有较近亲缘性,其相似性约为94%。此外,有2个OTU分属于酸杆菌门(Acidobacteria)和厚壁菌门(Firmicutes)(见图2)。在NF富集物中,分属于Acidiphilium和 Acidobacteria的微生物是16S rRNA系统发育树上的优势种群,它们的比率分别为总克隆数的55%和27%(表1),而在浸矿中常用的氧化亚铁硫杆菌(Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans)仅占7%。此外,一些分属于Strepococcus sp.和Pseudomonas sp. 的微生物也被检测到(图2(a)),分别为整个微生物群落的3%和8%。与富集物NF相比,NS样品中Acidiphilium菌的含量明显提高,其约为整个NS群落的90%。在NS富集物中,有5条序列(NS01,NS02,NS04,NS05和NS07)归于这个属(图3)。同样,属于Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans菌的微生物仅占很少一部分,约为NS 16S rRNA克隆文库的4%(表1)。在NS富集物中,有2%的微生物隶属于柠檬酸杆菌属(Citrobacter)的细菌,但其相似性仅为94%。而在NF富集物中检测到的Strepococcus sp.,在NS富集物中没有被发现。在NY富集物中,隶属于Pseudomonas 的细菌是最优势的种群,约为NY 16S rRNA克隆文库的47%。其次是Acidiphilium的细菌,为整个克隆文库的37%。与前2种富集物相比,NY样品具有较高含量的Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans克隆,约占NY 16S rRNA克隆文库的10%(表1)。
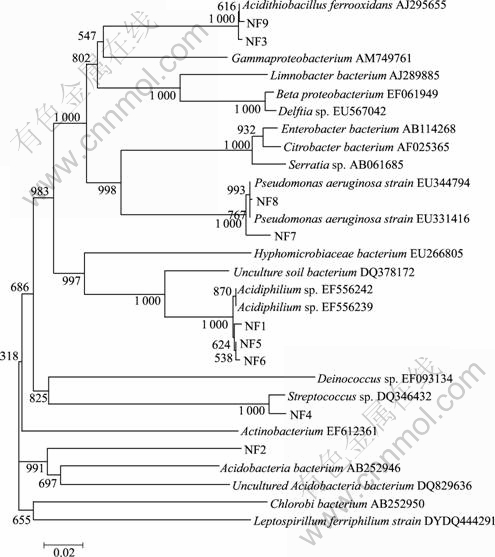
图2 微生物群落的16S rRNA系统发育分析(NF)
Fig.2 Phylogenetic analysis of microbial community based on 16S rRNA gene(NF)
表1 不同富集条件下微生物群落的组成
Table 1 Microbial community composition under different richness conditions w/%
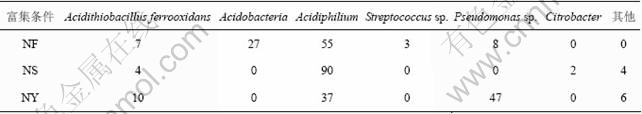
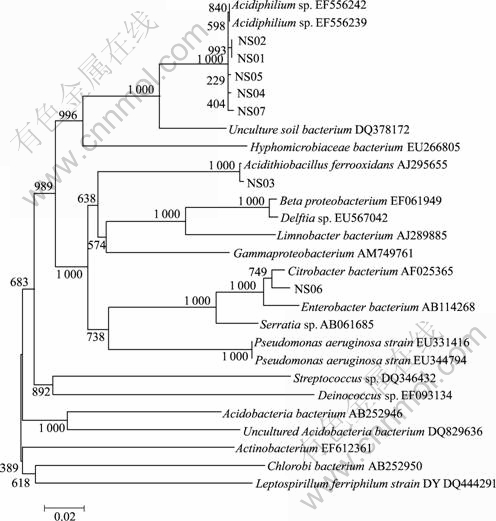
图3 微生物群落的16S rRNA系统发育分析(NS)
Fig.3 Phylogenetic analysis of microbial community based on 16S rRNA gene(NS)
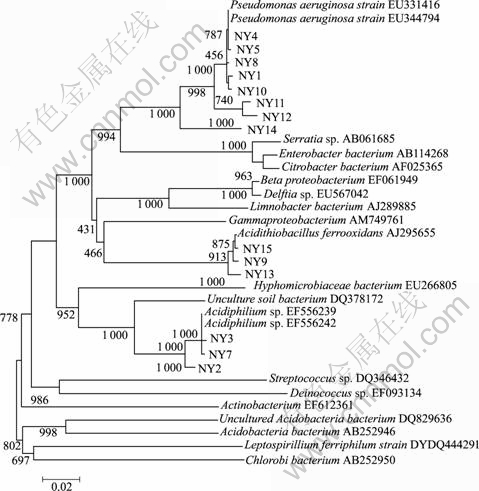
图4 微生物群落的16S rRNA系统发育分析(NY)
Fig.4 Phylogenetic analysis of microbial community based on 16S rRNA gene(NY)
2.3 讨 论
Acidiphilium属在各含镍培养体系中均占有较高丰度,Acidithiobacillus属虽被检测出,但所占丰度 较低。Kenneth等的研究发现,兼性异养Acidiphilium属不仅能够利用硫和亚铁营自养生活,同时,还能 够利用葡萄糖和酵母提取物进行异养生活[9-10]。Acidiphilium属微生物是一类能够进行铁呼吸作用,利用有机物或者H还原三价铁而获得能量进行化能异养生长的细菌[11-12]。该属的成员主要存在于酸性矿水中,能够适应pH值为1.5~6.0的环境,相对于Acidithiobacillus属来说适应性更强。因此,在pH值为4.0的培养条件下,其为主要的优势种群。
此外,在镍选择压力的不同富集条件下,Acidithiobacillus属的细菌也普遍存在。Acidithiobacillus属的细菌大多数属于嗜酸好氧的化能自养革兰氏阴性菌[13-15],其中,氧化亚铁硫杆菌(Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans)以亚铁、元素硫或金属硫化矿作为能量来源,吸收氮、磷等无机营养物质,以空气中的二氧化碳为碳源生长[16-17]。在多种金属硫化矿的生物冶金研究中,氧化亚铁硫杆菌被认为是主要的浸矿菌种之一。研究表明:在氧化亚铁硫杆菌与氧化硫硫杆菌混合浸出低品位镍铜硫化矿的过程中,在25%的矿浆浓度下,浸出14 d后,镍的浸出率达到80.2%[18]。
在抗镍的微生物群落中还检测到假单胞菌属细菌,其在酵母粉存在的培养体系中丰度较高。另外,在亚铁加硫粉培养体系中检测到柠檬酸杆菌属细菌,这可能与这些微生物利用有机物作为能源有关。一些研究者也发现,假单胞菌类对重金属的抗性机制主要是对金属的胞外吸附,而柠檬酸杆菌属细菌的有机代谢物如柠檬酸同样具有络合吸附金属离子的能力, 这些特性可能是这2种菌群得以在含镍培养体系中生存的原因[19]。此外,氧化亚铁硫杆菌等铁氧化菌都对有机酸和其他小分子的有机物敏感,这些菌类在代谢和休眠期间都释放有机物进入培养基中,到一定程度将抑制细菌的生长,而异养菌可通过代谢这些有机物解除抑制,这可能是氧化亚铁硫杆菌丰度较少而一些异养菌如Acidiphilium丰度较高的原因。铁氧化菌和异养菌混合培养,可能会比纯培养微生物表现出更强的重金属抗性和更好的浸矿效果[20]。
含镍培养物中还有一类重要的微生物属于酸杆菌门。在以往微生物生态学研究中,经常发现这类微生物存在于一些生物浸出系统的酸性环境中[21]。但是,这类微生物是否具有生物浸出功能,还有待进一步证实。此外,还发现少量属于厚壁菌门链球菌属的微生物,其在群落中的功能也有待于进一步研究。
3 结 论
a. 不同能源富集培养条件下微生物群落主要由变形菌门、酸杆菌和厚壁菌门的多类细菌组成。其中,Acidiphilium属和Acidithiobacillus属在不同能源培养条件下均存在,而Acidiphilium属细菌丰度最高,这些微生物可能在镍生物浸出中发挥重要作用,特别是针对于一些pH值较高(pH>4)的环境中镍被浸出。另外Pseudomonas属、Citrobacter属、Acidobacteria属等细菌也被检测到,然而,其是否具有生物浸出功能还有待进一步研究。
b. 不同的富集培养条件对微生物群落影响很大。在pH值为4时,以亚铁为能源的富集物中,微生物群落主要以Acidiphilium属和Acidobacteria属为主;在以单质硫为能源的富集物中,其90%的微生物属于Acidiphilium;以硫酸亚铁、单质硫及酵母粉为能源的富集条件下,Acidiphilium和 Pseudomonas为优势 种群。
参考文献:
[1] Olson G J, Brierley J A, Brierley C L. Bioleaching review part B: Progress in bioleaching: Applications of microbial processes by the minerals industries[J]. Applied Microbiology Biotechnology, 2003, 63(3): 249-257.
[2] 杨显万, 沈庆峰, 郭玉霞. 微生物湿法冶金[M]. 北京: 冶金工业出版社, 2003: 46-51.
YANG Xian-wan, SHEN Qing-feng, GUO Yu-xia. Microbial hydrometallurgy[J]. Metallurgical Industry Press, 2003: 46-51.
[3] Rohwerder T, Sand W. The sulfane sulfur of persulfides is the actual substrate of the sulfur-oxidizing enzymes from Acidithiobacillus and Acidiphilium spp.[J]. Microbiology, 2003, 149(7): 1699-1709.
[4] Suzuki I. Microbial leaching of metals from sulfide minerals[J]. Biotechnology Advances, 2001, 19(2): 119-132.
[5] Bond P L, Druschel G K, Banfield J F, et al. Comparison of acid mine drainage microbial communities in physically and geochemically distinct ecosystems[J]. Appl Environ Microbiol, 2000, 66(11): 4962-4971.
[6] 刘新星, 霍 强, 刘学端, 等. 古矿井区域酸性矿坑水微生物群落的多样性[J]. 中南大学学报: 自然科学版, 2007, 38(3): 415-418.
LIU Xin-xing, HUO Qiang, LIU Xue-duan, et al. Diversity of microbial community in acid mine drainage in ancient mine area[J]. Journal of Central South University: Science and Technology, 2007, 38(3): 415-418.
[7] 陈泉军, 方兆珩. 生物浸出低品位镍铜硫化矿中的镍、铜、钴[J]. 过程工程学报, 2001, 1(4): 369-403.
CHEN Quan-jun, FANG Zhao-heng. Bioleaching of Ni, Cu and Co from a low-grade Ni, Cu sulfide Ore[J]. The Chinese Journal of Process Engineering, 2001, 1(4): 369-403.
[8] 温建康, 阮仁满, 孙雪南. 金川低品位镍矿资源微生物浸出研究[J]. 矿冶, 2002, 11(1): 55-58.
WEN Jian-kang, RUAN Ren-man, SUN Xue-nan. Study on bioleaching of low-grade nickel ores in Jinchuan[J]. Mining& Metallurgy, 2002, 11(1): 55-58.
[9] Kelly D P, Wood A P. Reclassification of some species of Thiobacillus to the newly designated general Acidithiobacillus gen. nov., Halothiobacillus gen. nov. and Thermithioballus gen. nov.[J]. International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology, 2000, 50(2): 511-516.
[10] Jiao Y. Physiological and mechanistic studies of phototropic Fe(Ⅱ) oxidation in purple non-sulfur bacteria[EB/OL]. http://resolver.caltech.edu/CaltechETD: edt-01242007-141030, 2008-05-01.
[11] Rohwerder T, Gehrke T K, Kinzler W S, et al. Bioleaching review part A: Progress in bioleaching: fundamentals and mechanisms of bacterial metal sulfide oxidation[J]. Applied Microbiology Biotechnology, 2001: 63(3): 239-248.
[12] Yang Y, Campbell C D, Clark L, et al. Microbial indicators of heavy metal contamination in urban and rural soils[J]. Chemosphere, 2005, 63(11): 1942-1952.
[13] Wakao N. Acidiphilium multivorum sp. nov., an acidophilic chemoorganotrophic bacterium from pyritic acid mine drainage[J]. Gen Appl Microbiol, 1994, 40(5): 143-159.
[14] Dees P M, Ghiorse W C. Microbial diversity in hot synthetic compost as revealed by PCR-amplified rRNA sequences from cultivated isolates and extracted DNA[J]. FEMS Microbiology Ecology, 2000, 35(2): 207-216.
[15] Golyshina O V, Kenneth N. Timmis Ferroplasma and relatives, recently discovered cell wall-lacking archaea making a living in extremely acid, heavy metal-rich environments[J]. Environmental Microbiology, 2005, 7(9): 127-133.
[16] Foucher S, Brunet F B, Hugues P, et al. Evolution of the bacterial population during the batch bioleaching of a cobaltiferous pyrite in a suspended-solids bubble column and comparison with a mechanically agitated reactor[J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2003, 71(3): 5-12.
[17] 北京有色金属研究总院. 金川低品位镍矿资源微生物浸出探索试验研究[R]. 北京: 北京有色金属研究总院, 2000: 101.
General Research Institute for Nonferrous Metals. Study on bioleaching of low-grade nickel ores in Jinchuan[R]. Beijing: General Research Institute for Nonferrous Metals, 2000: 101.
[18] 方兆珩, 柯家骏, 李洪枚, 等. 生物浸出低品位镍铜硫化矿[J]. 有色金属(冶炼部分), 2002(4): 2-20.
FANG Zhao-heng, KE Jia-jun, LI Hong-mei, et al. Bioleaching of low-grade Ni-Cu sulfide ore[J]. Nonferrous Metals(Extractive Metallurgy), 2002(4): 2-20.
[19] 康 健, 高 健, 吴学玲, 等. 混合菌群诱变及诱变菌群对闪锌矿浸出的影响[J]. 中南大学学报: 自然科学版, 2007, 38(3): 440-445.
KANG Jian, GAO Jian, WU Xue-ling, et al. Mutagenesis of mixed bacteria and influence on bioleaching of sphalerite with the mutagenized bacterial admixture[J]. Journal of Central South University: Science and Technology, 2007, 38(3): 440-445.
[20] 陈泉军, 方兆珩. 硫杆菌浸出低品位镍铜硫化矿[J]. 过程工程学报, 2001, 1(1): 49-53.
CHEN Quan-jun, FANG Zhao-heng. Bioleaching of the low-grade Ni-Cu sulfide ore from Jinchuan Mine by Thiobacillus[J]. Chinese Journal of Process Engineering, 2001, 1(1): 49-53.
[21] Goebel B M, Stackebrandt E. Cultural and phylogenetic analysis of mixed microbial populations found in natural and commercial bioleaching environments[J]. Appl Environ Microbiol, 1994, 60(5): 1614-1621.
收稿日期:2008-06-10;修回日期:2008-09-28
基金项目:国家“973”计划项目(2004CB619204);国家自然科学基金资助项目(40646029)
通信作者:刘学端(1964-),男,湖南湘乡人,博士,教授,从事微生物生态学和生物冶金研究;电话:0731-8830546;E-mail: xueduanliu@yahoo.com