文章编号:1004-0609(2010)07-1309-07
小尺寸T3/35CrMnSi钢异种材料
惯性径向摩擦焊接头的特性
罗 键1, 孙 玉1, 2, 刘德佳1, 2, 吴 玮3, 徐晓菱3
(1. 重庆大学 机械传动国家重点实验室,重庆 400030;2. 重庆大学 材料科学与工程学院,重庆 400030;
3. 中国兵器工业第五九研究所,重庆 400039)
摘 要:针对小尺寸异种金属材料惯性径向摩擦焊接存在的困难,采用扫描电镜(SEM)、能谱分析(EDS)、显微硬度和剪切强度等测试方法,研究小尺寸T3/35CrMnSi异种材料惯性径向摩擦焊接头的特征。结果表明:在接头过渡区出现塑性变形层、动态再结晶、元素扩散互溶,实现了界面的冶金结合;接头界面塑性变形层的厚度随着主轴转速、摩擦力、顶锻力的变化而变化;当厚度约为5 μm时,界面结合质量最好;接头力学性能以及热影响区宽度的变化与塑性变形层、马氏体相变、材料物性有关;在主轴转速大于1 800 r/min、顶锻压力大于190 MPa的情况下,接头不容易出现缺陷。
关键词:小尺寸T3铜;35CrMnSi钢;惯性径向摩擦焊;塑性变形;显微硬度;剪切强度
中图分类号:TG4 文献标志码:A
Characteristics of inertia radial friction welding joints of small size T3/35CrMnSi dissimilar metal materials
LUO Jian1, SUN Yu1, 2, LIU De-jia1, 2, WU Wei3, XU Xiao-ling3
(1. State Key Laboratory of Mechanical Transmission, Chongqing University, Chongqing 400030, China;
2.College of Materials Science and Engineering, Chongqing University, Chongqing 400030, China;
3.No.59 Institute of China Ordnance Industry, Chongqing 400039, China)
Abstract: Based on the difficulty of inertia radial friction welding small size T3/35CrMnSi dissimilar metal materials, the characteristics of joints of T3/35CrMnSi were analyzed by SEM, EDS, microhardness test and shear strength test. The results show that plastic deformation layer, dynamic recrystallization, and diffusion and dissolution of elements occur in the joint transition region, achieving metallurgical bonding. The thickness of the plastic deformation layer changes with spindle speed, friction pressure, forging pressure; when the thickness is about 5 μm, the interface quality is the best. The joint mechanical properties and the width of heat affected zone are relative to the plastic deformation layer, martensitic transformation and material properties. In the case that the spindle speed is more than 1800 r/min, the forging pressure is more than 190 MPa, the welding joints are bonded successfully and have no local spot defects.
Key words: small size T3 copper; 35CrMnSi steel; inertia radial friction welding; plastic deformation; microhardness; shear strength
近年来,由于工业生产技术的快速发展,铜或铜合金与钢的焊接应用越来越多。铜或铜合金与钢的异种接头充分发挥了材料的各自性能和作用,大大节省了材料,降低了成本。目前,铜合金与钢的焊接方法通常有手工电弧焊、埋弧焊、钎焊、电子束焊、激光焊以及扩散焊等,但这些焊接方法存在如下缺点:1) 采用常规熔化焊焊接方法,由于铜和钢的互溶性差,且铜容易发生氧化,使得接头容易形成低熔点共晶体, 产生热裂纹,从而导致生产效率不高,产品性能下降;2) 采用电子束焊、激光焊、扩散焊方法,需要使用较大功率的焊接设备,焊前准备要求苛刻,容易产生夹杂、气孔等缺陷,使得接头力学性能下降,同时工艺复杂,成本较高;3) 采用钎焊工艺,其装配比较繁琐,且接头强度不高,应用场合受到局限。而惯性径向摩擦焊技术特别适合用于性能差异较大的异种金属及难熔金属材料的连接[1-7],是解决铜合金与钢异钟材料焊接的有效方法之一。
小尺寸T3/35CrMnSi钢棒的摩擦焊接过程存在一定的技术难点。由于小尺寸T3/35CrMnSi钢棒单位长度上的曲率差别较大,使得真实微观接触面积仅为名义宏观接触面积的很小一部分。文献[8]的研究表明:在摩擦过程中,摩擦副的实际接触面积越小,表面形貌的随机性对摩擦的影响越大,越不利于摩擦能量的产生、传递和储存;焊接夹具尺度效应的影响使得工件所受应力分布难以均匀,焊接过程中工件出现偏差、错动等问题。
本文作者针对小尺寸T3/35CrMnSi细棒的焊接问题,研究惯性径向摩擦焊接头的微观组织、塑性变形层特点、力学性能和工艺适应性等问题,解释小尺寸铜环与35CrMnSi细棒惯性径向摩擦焊接的缺陷及其原因,优化焊接工艺来解决小尺寸T3/35CrMnSi的焊接问题。
1 实验
1.1 惯性径向摩擦焊的原理与设备
惯性径向摩擦焊是一种典型的固相焊接方法,其工艺原理如图1(a)所示。焊接小尺寸T3铜环与小直径35CrMnSi棒材时,装配铜环和棒料(棒料外径和铜环内径间隙为0.5~2.5 mm)在规定的位置,焊机液压系统推动圆锥形的工模,通过工模使轴向压力转化为对铜环的径向压力(F),使铜环与棒料相互摩擦,在界面产生摩擦热量,使接头加热并产生塑性变形;最后,在顶锻力的作用下,实现异种金属接头的连接[4-7]。试验设备为CT-25多功能惯性摩擦焊机,如图1(b)所示。设备主要参数有主轴转速(n(t))、轴向压力(p),摩擦压力(p1)、顶锻压力(p2)、位移(s(t))、焊接时间(t)、转动惯量等。
1.2 材料及试样尺寸
试验材料为小尺寸T3紫铜环和35CrMnSi钢棒。35CrMnSi钢棒尺寸为d 20 mm×50 mm,焊前处于调质状态;铜环尺寸为d 30 mm×3.5 mm(厚)×4.5mm(宽),铜环材料处于冷拔状态。材料的化学成分分别如表1和表2所列。
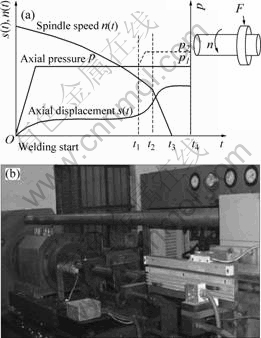
图1 惯性径向摩擦焊工艺原理示意图
Fig.1 Schematic diagram (a) and welding equipment (b) of inertia radial friction welding
表1 T3的化学成分
Table 1 Chemical composition of T3 (mass fraction, %)
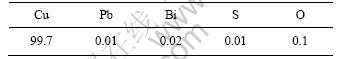
表2 35CrMnSi的化学成分
Table 2 Chemical composition of 35CrMnSi (mass fraction, %)

1.3 制备与焊接工艺参数
焊前对铜环用95%的磷酸和5%的硝酸混合溶液浸泡20 min左右,用清水冲洗干净,酒精风干;35CrMnSi钢棒用丙酮清洗干净。因特殊的焊接结构要求,对焊后的接头要保证铜环的厚度适中,而合适的铜环厚度需要选择适当的焊接能量输入,因此,本试验采用3组对比试样,设计不同的工艺参数来研究小尺寸T3铜环和35CrMnSi细棒的惯性径向摩擦焊接,如表3所列。
表3 T3铜合金与35CrMnSi的惯性径向摩擦焊工艺参数
Table 3 Parameters of inertia radial friction welding for T3 and 35CrMnSi

焊后从接头中间用电火花线切割制备成金相试样。采用8% CuCl2的氨水溶液先腐蚀界面T3铜侧,用酒精风干,然后用4%的硝酸酒精溶液腐蚀35CrMnSi钢侧。试样使用KQ-100E超声波清洗仪清洗后,采用TESCAN VegaⅡ LMUSEM电子扫描显微镜(SEM)和随机携带的能谱分析仪(EDS)观察微观组织,确定界面特征。在HV-1000型显微硬度计上测试硬度。因为两种材料的硬度相差比较大,准确起见,对铜界面侧采用0.49 N档,35CrMnSi钢界面侧采用4.9 N档,分别延时20 s测量,测量距离界面相等的3点的硬度值,取其平均值为最终测试结果。把试样接头沿横向加工成2 mm厚的薄片,在QJWE型电液伺服万能材料试验机上分析剪切强度。
2 结果与分析
2.1 惯性径向摩擦焊接头的微观组织
惯性径向摩擦焊焊接异种接头分为明显的3个区域:Ⅰ区材料为35CrMnSi,Ⅱ区为接头35CrMnSi/T3过渡区,Ⅲ区材料为T3,如图2所示。由图2可见,在接头过渡区产生了塑性变形层,这种塑性变形层是在T3铜环与35CrMnSi细棒的相互摩擦过程中,由于焊接能量和外加压力的作用,材料产生大量塑性变形、动态再结晶、晶粒细化、触变而成形的一层特殊构造层。其中,产生的塑性变形层主要集中在T3铜环一侧,在35CrMnSi一侧的很少。这主要是因为两种材料的物化性质有差异,T3铜作为摩擦副面的主动摩擦面,35CrMnSi作为被动摩擦面而造成的。
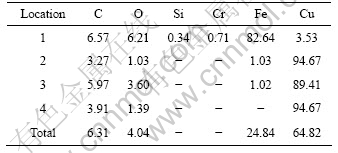
表4所列为焊接接头的能谱分析(见图2)的结果,从界面到塑性变形层中元素的过渡情况(见图2)来看,位置1的Cu含量为3.53%,而位置4的Cu含量则为94.67%;反过来,Fe元素含量从位置1的82.64%减少到位置3的1.02%。因此,可以认为在惯性径向摩擦焊的塑性变形区发生了合金元素的扩散与互溶,产生了Cu和Fe的固溶体,实现了界面的冶金结合。
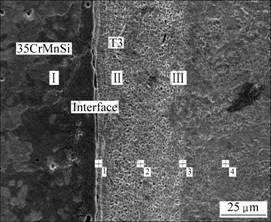
图2 焊接接头的微观组织和能谱分析位置
Fig.2 Microstructure and energy spectrum analysis of welding joints
表4 对应图2的能谱分析数据
Table 4 Corresponding data of EDS analysis in Fig.2 (molar fraction, %)
2.2 惯性径向摩擦焊接头的塑性变形层与工艺适应性
采用专用微观结构测试软件Nano Measurer测量图3所示的塑性变形层的厚度。依照如图3中箭头所标注的方法,从下到上以此测量每个试样10次以上,并且考虑界面局部塑性变形区宽度,求其平均值作为塑性变形层的厚度,统计结果如图4所示。试样1的界面塑性变形层厚度约为9 μm,试样2的约为48 μm,而试样3的仅为5 μm,塑性变形层的厚度由大到小顺序如下:试样2、试样1、试样3。
塑性变形层的厚度与主轴转速、摩擦压力、顶锻压力等主要工艺参数有密切关系。主轴转速越快,摩擦功率越大,所获得的塑性变形层越厚。因此,在顶锻焊接之前,塑性变形层的厚度从小到大依次为试 样3、试样2、试样1。但是随着顶锻压力的增大,引起塑性变形层的厚度变小、不均匀,焊接界面出现“波浪”状咬合,见图3中的试样3。塑性变形层的厚度由大到小的顺序如下:试样2、试样1、试样3。

图3 焊接界面塑性变形层的形貌与微观结构
Fig.3 Interface morphologies and micro- structures of plastic deformation layers: (a) Sample 1; (b) Sample 2; (c) Sample 3
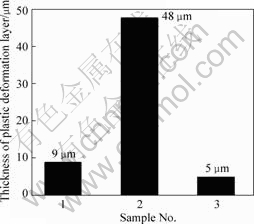
图4 接头界面塑性变形层的厚度
Fig.4 Thickness of plastic deformation layer of joints
焊接质量的好坏不一定仅仅取决于塑性变形层的厚度,塑性变形层的厚度和焊接质量之间并没有直接的对应关系。从图3所示的焊接界面塑性变形层的形貌与微观结构可见,焊接接头的结合质量从好到差依次为试样3,试样2,试样1。
根据以上的分析并结合表3的焊接工艺参数可知,摩擦阶段形成的塑性变形层的厚度必须与顶锻压力的大小匹配,过小的塑性变形层厚度达不到焊接的质量要求;过大的塑性变形层厚度,要求很大的顶锻压力。因此,塑性变形层的厚度和顶锻压力的匹配将显著影响焊接接头的结合强度。
2.3 惯性径向摩擦焊的力学性能与微观组织演变
2.3.1 显微硬度
图5所示为在不同焊接条件下接头的显微硬度。从图5可见,小尺寸T3/35CrMnSi钢棒惯性径向摩擦焊接头的显微硬度变化发生在距摩擦结合面-0.1~0.3 mm处;接头包括热影响区和塑性变形区,和熔化焊相比,惯性径向摩擦焊的焊缝宽度小得多。T3铜和35CrMnSi钢棒焊接界面附近显微硬度变化十分剧烈。在I区内,试样3的硬度变化最大,试样2的硬度曲线的斜率大于试样1的,在距界面的同样位置,硬度由大到小的顺序依次为试样3,试样2,试样1。在Ⅱ
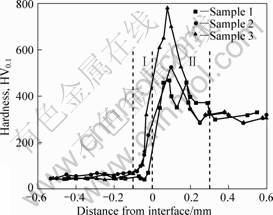
图5 焊接接头硬度曲线
Fig.5 Hardness curve of welding joints
区内,3个试样的显微硬度的变化趋势是先增大后减少,硬度由大到小的顺序依次为试样3,试样2,试样1。这种硬度的变化与表3所列的惯性径向摩擦焊接工艺参数有密切关系,并相互印证:试样1的焊接工艺是硬规范,但摩擦阶段的塑变不充分,结合不牢固,硬度较低;试样2的焊接工艺是偏软规范,顶锻压力不够,结合不太牢固,硬度其次;试样3的焊接工艺参数最佳,因此,接头摩擦变形充分,顶锻压力足够,结合牢固,硬度也较高,在焊缝中的不同区域硬度变化也最为剧烈。
该惯性径向摩擦焊接头显微硬度变化的这种特点还与材料摩擦塑性变形层的产生、动态再结晶有直接关系。惯性径向摩擦焊摩擦面的摩擦生热、界面温度的升高、塑性变形层的生成以及顶锻压强的作用导致动态再结晶的发生,出现细晶区。该细晶区在界面方向呈近似正态分布特点,因此,使得硬度也出现以界面为中心沿厚度方向的变化特征(见图5)。另外,I区的宽度为0.1 mm,而II区的宽度为0.3 mm,但是T3铜熔点低、容易发生塑性变形和动态再结晶,I区宽度应该比II区宽度大。研究表明:在T3铜侧的I区,由于T3铜的导热系数大,热膨胀系数小,摩擦界面产生的热量迅速被传导,塑性变形层在顶锻阶段容易被挤出,使得该侧焊接热影响区的宽度较小;而在35CrMnSi钢侧的II区,则与之相反,35CrMnSi钢侧热影响区较宽,加之冷却阶段形成淬火马氏体[5, 9],提高了35CrMnSi钢侧II区的硬度,因此II区的宽度比I区的大,这与图3和图4所表现出来的规律一致。
2.3.2 剪切强度
焊合程度是检测摩擦焊接头质量的主要指标之一。根据惯性径向摩擦焊焊接接头的结构特点,只能进行剪切强度试验,并且铜及铜合金的抗拉强度与剪切强度成正比,其抗拉强度是剪切强度的1.1倍[10],因此剪切强度的大小也可以作为接头质量高低的评判标准。图6所示为参考GB/T6396复合钢板力学及工艺性能试验方法所得的焊接接头剪切强度的试验数据。采用3种工艺参数所得试样的剪切强度都超过220 MPa,接头强度满足使用要求。

图6 T3/35CrMnSi钢惯性径向摩擦焊焊接头的剪切强度
Fig.6 Shear strengths of joints of T3/35CrMnSi by inertia radial friction welding
2.4 焊接缺陷及成因分析
在惯性径向摩擦焊接过程中能量输入的多少和顶锻压力的选择对摩擦焊能否形成优良的焊缝起到至关重要的作用。若能量输入过小,或者顶锻压力过小容易造成界面摩擦不充分,塑性变形层厚度较小,没有形成飞边,结合强度不够;若压力过大,则容易造成瞬时摩擦扭矩过大,损坏焊接夹具,焊缝出现裂纹等缺陷,焊缝成形不均匀,影响焊缝的力学性能[11-12]。
图7所示为在主轴转速1 800 r/min,顶锻压力190 MPa的情况下,未焊合试样的宏观缺陷照片和SEM微观组织照片。从图7(b)可见,小尺寸的T3铜环与35CrMnSi细棒并没有形成良好的焊接接头,仅在局部出现了点焊合;T3铜侧金属只出现了一层很薄的亮白色金属塑性变形层(厚度约为6 μm),而35CrMnSi钢一侧几乎没有形成塑性变形区。
上述未连接缺陷是小尺寸结构材料惯性径向摩擦焊容易出现的典型缺陷之一,也是其比较难焊的主要原因,具体分析如下。
惯性径向摩擦焊的能量来源于摩擦表面的微凸体之间的摩擦磨损、粘结和断裂以及材料塑性变形产生的热量[13-15]。摩擦界面之间微凸体的摩擦磨损、粘结和断裂等对摩擦焊能量的影响很大;在摩擦压力和摩
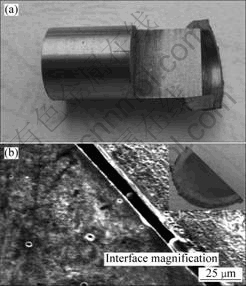
图7 在主轴转速1 800 r/min和顶锻压力190 MPa的情况下未焊合试样的形貌
Fig.7 Morphologies of sample without joining at spindle speed of 1 800 r/min and forging pressure of 190 MPa: (a) Macrostructure; (b) Microstructure
擦扭矩的作用下,摩擦表面的金属质点沿工件圆周方向做高速摩擦运动,在摩擦界面形成塑性变形层。该塑性变形层把摩擦机械能转变成热能的发热源,也构成焊接热源。在最佳的焊接工艺参数条件下,焊接能量的转换过程是:在焊接界面稳定的径向摩擦状态建立后,随着摩擦时间的推移,塑性变形体沿T3铜环从中间向两边流动,实际的塑性摩擦剪切面不断向T3铜环转移,使T3铜环产生大量的塑性变形,T3铜环以塑性变形体的形式把能量储存起来。其结果是摩擦热以内能形式储存在塑性变形体中,为后续的顶锻焊接过程做准备。
由于异种金属T3铜和35CrMnSi钢的物理性能有较大差异,在T3铜和35CrMnSi钢惯性径向摩擦焊接界面出现热阻效应,热阻效应在摩擦初始阶段最显著。
图8所示为T3铜和35CrMnSi接触界面热流变化情况,在微观上粗糙不平的T3铜和35CrMnSi接触面,热量从T3铜向35CrMnSi传导,热流线在界面间隙处有阻断情况发生,流线密度发生变化[16]。在界面首先接触处,接触面积较大,热流密度大,热量传递效率较高;而在接触面积较小处,热流密度小,热量传递效率较低。分析认为:惯性径向摩擦焊在初始摩擦时间段内,处于点接触阶段,界面接触面积较小,热阻较大,热量传递较小,仅仅在铜侧产生微量的塑性变形,在后期的顶锻焊接过程中,由于顶锻压力也较小,没有形成良好的焊缝。因此,界面出现类似凸焊的点焊状况;同时,这也和主轴转速较小、摩擦阶段的摩擦压力不够、摩擦塑变不充分、界面元素的扩散[17]等因素有关。

图8 T3铜和35CrMnSi接触面的热流效应
Fig.8 Heat flow effect at interface between T3 and 35CrMnSi
3 结论
1) 在小尺寸T3铜环和35CrMnSi钢细棒惯性径向摩擦焊的接头过渡区产生塑性变形层、动态再结晶、元素扩散互溶,实现了冶金结合。顶锻成型后,当接头塑性变形层的厚度约为5 μm时,界面结合质量最好。
2) T3铜环和35CrMnSi惯性径向摩擦焊的焊接接头显微硬度的变化在界面两侧各有特点。在T3铜侧发生动态再结晶,晶粒细化并强化;35CrMnSi侧有淬火马氏体形成。3组焊合试样的剪切强度都超过220 MPa,满足使用性能的要求。
3) T3铜和35CrMnSi钢惯性径向摩擦焊接接头出现的未焊合、局部点焊等焊接缺陷的原因是在摩擦焊初始阶段存在界面热阻效应、摩擦热输入不足、界面塑性变形不充分以及顶锻压力不够。在主轴转速大于1800 r/min,顶锻压力大于190 MPa的情况下,接头不容易出现缺陷。
REFERENCES
[1] LUO Jian, YE Yan-hong, XU Jun-jie, LUO Jin-yao, WANG Xiao-chuan. A new mixed-integrated approach to control welded flashes forming process of damping tube-gland in continuous drive friction welding[J]. Materials & Design, 2009, 30(2): 353- 358.
[2] 赵熹华, 冯吉才. 压焊方法及设备[M]. 北京: 机械工业出版社, 2005.
ZHAO Xi-hua, FENG Ji-cai. Pressure welding methods and equipment[M]. Beijing: China Machine Press, 2005.
[3] LUO J. A new measure technique and model for friction torque in continuous drive friction welding: Engineering oriented voltage-current floating evaluation measurement method and exponential function model of friction torque[J]. Science and Technology of Welding and Joining, 2001, 6(4): 209-212.
[4] XU Xiao-ling, WU Wei, XU Yuan-ze. The research of radial friction welding[J]. Welding in the World, 2005, 1(1/2): 12-15.
[5] 刘小文, 史永高, 毛信乎, 杜随更. TC4钛合金摩擦焊接头的力学性能及显微组织[J]. 焊接学报, 2001, 22(6): 77-80.
LIU Xiao-wen, SHI Yong-gao, MAO Xin-hu, DU Sui-geng. Mechanical properties and microstructure of titanium alloy friction welded joint[J].Transactions of the China Welding Institution, 2001, 22(6): 77-80.
[6] 李亚江, 王 娟, 刘 鹏, 等. 异种难焊材料的焊接及应用[M]. 北京: 化学工业出版社, 2004.
LI Ya-jiang, WANG Juan, LIU Peng, et al. Application and welding of difficulty to weld dissimilar materials[M]. Beijing: Chemical Industry Press, 2004.
[7] 徐晓菱. 紫铜与高碳合金钢的摩擦焊焊接性[J]. 焊接, 1995(6): 17-18.
XU Xiao-ling. Weldability of friction welding between copper and high carbon alloy steel[J]. Welding & Joining, 1995(6): 17-18.
[8] 葛世荣, 朱 华. 摩擦学的分形[M]. 北京: 机械工业出版社, 2005.
GE Shi-rong, ZHU Hua. The fractal of tribology[M]. Beijing: China Machine Press, 2005.
[9] 李付国, 张敏聪, 段立宇, 张田仓. GH4169合金摩擦焊接规范与成形性能[J]. 焊接学报, 2001, 22(4): 43-46.
LI Fu-guo, ZHANG Min-cong, DUAN Li-yu, ZHANG Tian-cang. On thermo-mechanical specification and deformability of IN-718 alloy in friction welding[J]. Transaction of the China Welding Institution, 2001, 22(4): 43-46.
[10] 陈榕林. 机械设计手册[M]. 北京: 科学技术文献出版社,1995: 197-201.
CHEN Rong-lin. Mechanical design handbook[M]. Beijing: Science and Technology Literature Press, 1995: 197-201.
[11] 王艳芳, 王忠平, 毛 明. 顶锻速度vd对摩擦焊合区金属组织的影响[J]. 航空精密制造技术, 2006, 42(6): 39-41.
WANG Yan-fang, WANG Zhong-ping, MAO Ming. Main factors of forge rate vd on friction welding metal[J]. Aviation Precision Manufacturing Technology, 2006, 42(6): 39-41.
[12] 王快社, 王训宏, 徐可为. 搅拌摩擦焊接头摩擦摩损性能研究[J]. 润滑与密封, 2007, 32(2): 114-116.
WANG Kuai-she, WANG Xun-hong, XU Ke-wei. Research on friction and wear properties of joint by friction stir welding[J]. Lubrication Engineering, 2007, 32(2): 114-116.
[13] 傅 黎,杜随更,白建红. TC4钛合金与LD10铝合金感性摩擦焊接头的组织与性能[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2007, 17(2): 54-58.
FU Li, DU Sui-geng, BAI Jian-hong. Microstructures and properties of induction friction welded joint of TC4 Ti alloy and LD10 Al alloy[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2007, 17(2): 54-58.
[14] 蔺永城, 陈明松, 钟 掘. 形变温度对42CrMo 钢塑性成形与动态再结晶的影响[J]. 材料热处理学报, 2009, 30(1): 70-74.
LIN Yong-cheng, CHEN Ming-song, ZHONG Jue. Effects of deformation temperatures on plastic formation and microstructure evolution of 42CrMo steel[J]. Transactions of Materials and and Heat Treatment, 2009, 30(1): 70-74.
[15] 周仲荣, 雷源忠, 张嗣伟. 摩擦学发展前沿[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2006.
ZHOU Zhong-rong, LEI Yuan-zhong, ZHANG Si-wei. The development of cutting-edge tribology[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2006.
[16] 朱德才, 张立文, 斐继斌, 张国梁, 韦荣选. 固态塑性成形过程中界面接触换热的实验研究[J]. 塑性工程学报, 2008, 15(2): 92-93.
ZHU De-cai, ZHANG Li-wen, PEI Ji-bin, ZHANG Gou-liang, WEI Rong-xuan. Experiment research on the thermal contact conductance during the solid plastic forming[J]. Journal of Plasticity Engineering, 2008, 15(2): 92-93.
[17] 罗 键, 赵国际, 罗 乾, 王向杰, 徐晓凌. 35CrMnSi/T3惯性径向摩擦焊接复合界面的元素扩散[J]. 西安交通大学学报, 2010, 44(3): 63-67.
LU0 Jian, ZHAO Guo-ji, LUO Qian, WANG Xiang-jie, XU Xiao-ling. Element diffusion on interface of 35CrMnSi/T3 intertial radial friction weld[J]. Journal of Xi’an Jiaotong University, 2010, 44(3): 63-67.
(编辑 杨 华)
基金项目:教育部新世纪优秀人才支持计划资助项目(NCET-08-0607); 教育部博士点基金资助项目(20070611030);重庆市自然科学基金资助项目(CSTC2008BB3303);重庆市自然科学基金资助项目(CSTC2009BA3026);重庆大学大型仪器设备开放基金资助项目
收稿日期:2009-06-19;修订日期:2010-04-06
通信作者:罗 键, 教授, 博士; 电话:023-65105721; E-mail: luojian_cn_2005@163.com