化学气相沉积法改性ACFs及其去除溶液中甲基橙的应用
来源期刊:中国有色金属学报(英文版)2013年第2期
论文作者:王丽平 黄柱成 张明瑜
文章页码:530 - 537
关键词:粘胶基活性碳纤维;化学气相沉积;改性;甲基橙;吸附等温线;动力学;热力学
Key words:viscose activated carbon fiber; chemical vapor deposition; modification; methyl orange; adsorption isotherm; kinetics; thermodynamics
摘 要:通过化学气相沉积法(CVD)对粘胶基活性炭纤维(ACFs)进行表面改性,利用比表面积、SEM、孔径分布和红外光谱等分析方法对样品进行表征。通过吸附实验研究改性ACFs对溶液中甲基橙的吸附行为。结果表明,吸附数据较符合Langmuir等温线模型;准二级动力学方程能够较好地反映改性ACFs对溶液中甲基橙的吸附动力学;颗粒间扩散为控制步骤,但并非唯一控制步骤。经计算获得的热力学参数包括ΔG、ΔH和ΔS,表明吸附为自发的放热物理吸附过程。从红外光谱分析可知,氢键作用是改性ACFs吸附甲基橙的主要吸附机理。
Abstract: Viscose activated carbon fibers (ACFs) were modified with chemical vapor deposition (CVD). The samples were characterized using specific surface area, scanning electron microscopy (SEM), pore size distribution and Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR). Batch adsorption experiments were carried out to investigate the adsorption behavior of modified ACFs for methyl orange(MO) from its aqueous solutions. The results show that the adsorption isotherms of MO onto modified ACFs well follows the Langmuir isotherm equation. The adsorption kinetics of MO can be well described by the pseudo second-order kinetic model. The adsorption process involves the intra-particle diffusion, but is not the only rate-controlling step. Thermodynamic parameters including ΔG, ΔH and ΔS were calculated, suggesting that the adsorption of MO onto modified ACFs is a spontaneous, exothermic and physisorption process. FTIR result indicates that the major adsorption mechanism of modified ACFs for MO is hydrogen bond.
Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 23(2013) 530-537
Li-ping WANG1,2, Zhu-cheng HUANG2, Ming-yu ZHANG3
1. Department of Bioengineering and Environmental Science, Changsha University, Changsha 410003, China;
2. School of Minerals Processing and Bioengineering, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China;
3. State Key Laboratory of Powder Metallurgy, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China
Received 19 November 2011; accepted 4 June 2012
Abstract: Viscose activated carbon fibers (ACFs) were modified with chemical vapor deposition (CVD). The samples were characterized using specific surface area, scanning electron microscopy (SEM), pore size distribution and Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR). Batch adsorption experiments were carried out to investigate the adsorption behavior of modified ACFs for methyl orange(MO) from its aqueous solutions. The results show that the adsorption isotherms of MO onto modified ACFs well follows the Langmuir isotherm equation. The adsorption kinetics of MO can be well described by the pseudo second-order kinetic model. The adsorption process involves the intra-particle diffusion, but is not the only rate-controlling step. Thermodynamic parameters including ΔG, ΔH and ΔS were calculated, suggesting that the adsorption of MO onto modified ACFs is a spontaneous, exothermic and physisorption process. FTIR result indicates that the major adsorption mechanism of modified ACFs for MO is hydrogen bond.
Key words: viscose activated carbon fiber; chemical vapor deposition; modification; methyl orange; adsorption isotherm; kinetics; thermodynamics
1 Introduction
Dyes are being used in many industries including textile, cosmetic, papermaking, leather, medicine and food processing. Among them, azo-dye is the most important class of synthetic organic dyes and accounts for half of the total dyes. Azo-dye wastewater has been considered a wastewater to be treated urgently because azo-dye wastewater is not only highly chromatic and strongly noxious, but also difficult to degrade and easy to decompose to carcinogenic aromatic amine under deoxidization condition. Nowadays, main treatment methods for azo-dye wastewater include photocatalytic degradation [1-3], biodegradation [4,5], electrochemical oxidation [6,7] and adsorption [8-10].
Among the proposed methods, adsorption is regarded as one of the competitive methods because of low cost, high efficiency and easy operation. The most common adsorbents include zeolite [11], molecular sieve [12,13], activated aluminium oxide [14] and activated carbon [15,16]. Activated carbon fibers (ACFs) have been a high efficient adsorption material since 1960s because of high specific surface area, developed microporous structure, small and narrow pore size distribution, great adsorption capacity, fast desorption rate and easy regeneration [17,18]. Generally, adsorption efficiency is decided by specific surface area, pore size distribution and surface functional group of the adsorbent and properties of the adsorbate. However, HUANG et al [19] studied the pore structure of viscose ACFs mainly consisting of micropores (pore diameter <2 nm), which results in low adsorption efficiency of ACFs for macromolecule dyes. In order to improve the adsorption efficiency of ACFs for dyes, modification is important, which can transform micropores to mesoporous. YAO et al [20] proposed that carbon nonotubes (CNTs) easily adsorb dye molecules due to its mesoporous and similar aromatic ring structure.
In this work, MO, one kind of azo-dyes was selected to investigate the adsorption properties of modified ACFs. Firstly, ACFs were modified with CNTs growing on these surfaces by CVD. Secondly, the samples were characterized using specific surface area, SEM, pore size distribution and FTIR. And finally, the adsorption behavior of modified ACFs for MO from its aqueous solutions was investigated.
2 Experimental
2.1 Materials
Viscose-based ACFs mat was adopted. Purities of nitrogen, hydrogen and acetylene were 99.99%, 99.99% and 99.9%, respectively. Absolute ethyl alcohol and 65%-68% HNO3 (mass fraction) were used. All chemicals used in this study were of analytical- laboratory grade. Molecule structure of MO is shown in Fig. 1.
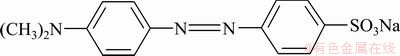
Fig. 1 Molecular structure of MO
2.2 Modifying methods
At first, Ni(NO3)2 was loaded by soaking the viscose-based ACFs. Then, the treated ACFs were dried in a vacuum oven at 75 °C to evaporate ethanol solvent. After that, the reduction of Ni(NO3)2 on the dried ACFs was carried out at 550 °C under hydrogen atmosphere. With acetylene as carbon source, hydrogen as diluent gas and nitrogen as inert protection gas, CNTs were grown on the surface of ACFs in a quartz flow reactor by a home-made tube furnace for 60 min. In the end, the reactor was cooled down to the room temperature under nitrogen atmosphere.
2.3 Characterization methods
The specific surface areas were measured by automatic specific surface analyzer (Quantachrome Autosorb-1) and pore size distribution was determined by automated pore size analyzer (QUDRASORB SI). The surface functional groups were analyzed by Fourier transform infrared spectrometer (NEXUS670). JSM-6700F was used to characterize the morphology of samples. MO concentrations were determined by spectrometry at the wavelength of maximum absorbance, 475 nm, using UV-759 ultraviolet and visible spectrophotometer.
2.4 Adsorption experiment
Batch adsorption experiments were carried out using 250 mL glass bottles with addition of 0.1 g modified ACFs and 100 mL MO solution with different concentrations. The glass bottles were sealed and put in a bathing constant temperature vibrator and then shaken for a time. The pH of solutions was tested with a pH meter. The adsorption amount of MO at equilibrium qe (mg/g) was calculated by
 (1)
(1)
where ρ0 and ρe are the concentrations of MO at initial and equilibrium states, respectively; V is the volume of the solution; and m is the mass of adsorbent used; and qe is the adsorption capacity at equilibrium.
3 Results and discussion
3.1 Morphology and specific surface area
The specific surface area of modified ACFs reached 531.95 m2/g. The morphologies of ACFs before and after modification by SEM are shown in Fig. 2. As shown in Fig. 2(a), the smooth surface is clearly observed. However, the rough surface and the uniformly distributed CNTs are presented in Fig. 2(b).
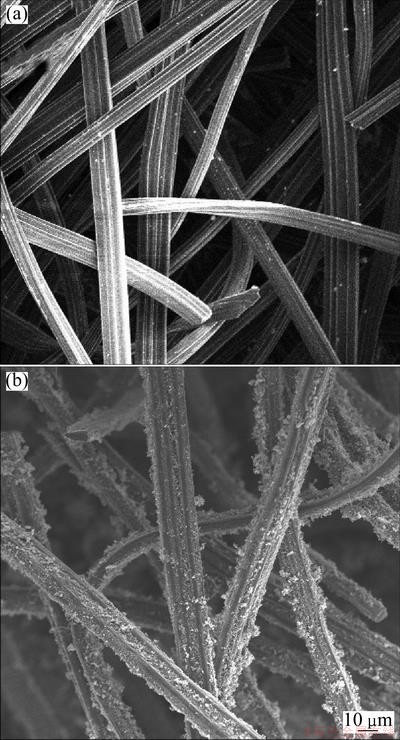
Fig. 2 SEM images of unmodified (a) and modified (b) ACFs
3.2 Pore size distribution
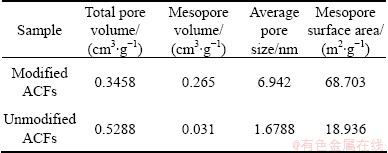
Figure 3 shows the pore size distribution of unmodified and modified ACFs. As seen from Fig. 3, the pore sizes of ACFs are mostly less than 1 nm, while micropores and mesoporous play a leading role in the pore structure of modified ACFs and a few macropores still exist. The pore structure parameters are listed in Table 1, indicating that modification enlarges the mesopore volume and mesopore surface area of material and accordingly increases the adsorption capacity of ACFs for big molecule dyes from aqueous solution.
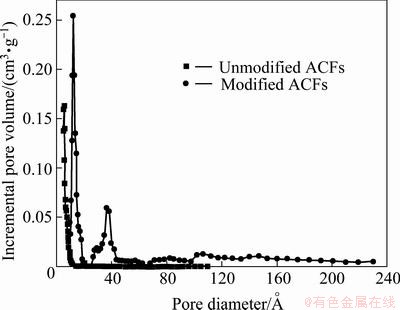
Fig. 3 Pore size distribution of modified and unmodified ACFs
Table 1 Pore structure parameters of modified and unmodified ACFs
3.3 FTIR spectrum
FTIR spectra of samples are shown in Fig. 4. Figure 4 clearly shows that the positions of characteristic absorption peaks go little change after adsorption, but the intensities of some absorption peaks change. The viscose-based activated carbon fibers reported in Ref. [14] are made up of carbon, oxygen, nitrogen and hydrogen. Therefore, the peaks at 3400, 3465 and 3500 cm-1 are due to the stretch vibration of —OH, —NH2 and —NH and the intensity of these peaks sharply increases, demonstrating that these functional groups participate in the adsorption process and hydrogen bond is the most important adsorption mechanism. The peak at 1630 cm-1 is attributed to the stretching vibration of C=C and —C=O. The peak at 1630 cm-1 moderately increases, which also results from adsorbing MO.
3.4 Contrast of adsorption efficiencies of modified and unmodified ACFs
When the solution temperature is 25 °C, MO concentration is 10 mg/L, adsorbent mass is 0.1 g, solution volume is 100 mL and rotate speed is 120 r/min, the adsorption efficiencies of modified and unmodified ACFs are shown in Fig. 5. It is seen from Fig. 5 that the efficiency of unmodified ACFs is 89.35%, while the efficiency of modified ACFs reaches 100%, which indicates that modifying greatly strengthens the adsorptivity of ACFs.
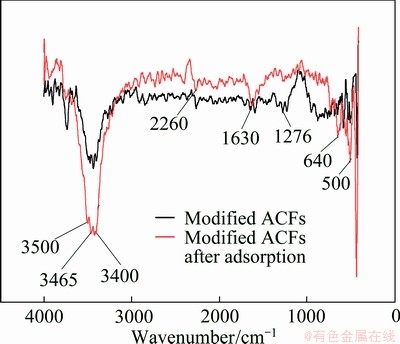
Fig. 4 FTIR spectra of modified ACFs and modified ACFs after adsorption
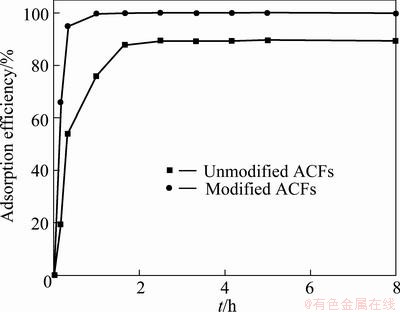
Fig. 5 Adsorption efficiencies of modified and unmodified ACFs
3.5 Adsorption behavior of modified ACFs
3.5.1 Adsorption isotherms
Figure 6(a) presents the adsorption isotherm of modified ACFs for MO from aqueous solution at different temperatures. From Fig. 6(a), it is seen that the adsorption capacity increases with increasing adsorption equilibrium concentration in the range of experimental concentration at a certain temperature, which is due to the increase in the driving force from the concentration gradient when the initial MO concentration increases, which results in the increased adsorption capacity. Moreover, the adsorption capacity decreases with increasing adsorption temperature, which suggests that adsorption is exothermic.
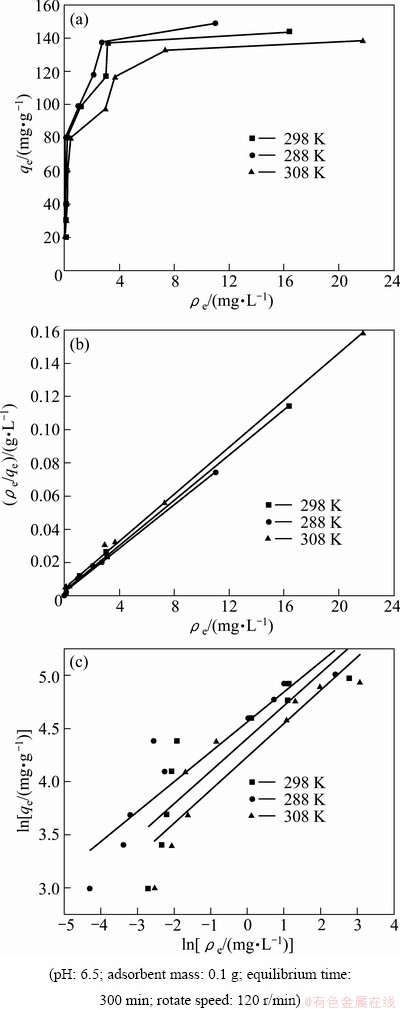
Fig. 6 Adsorption isotherms (a), Langmuir plots (b) and Freundlich plots (c) for MO onto modified ACFs at different temperatures
Langmuir and Freundlich adsorption models were widely applied to researching adsorption process characteristic [20-22]. The Langmuir model postulates that the adsorption is supposed to a monolayer adsorption. Langmuir isotherm equation is presented as follows:
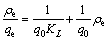 (2)
(2)
where q0 and KL are the Langmuir constants.
The Freundlich isotherm model assumes that the surface of adsorbent is heterogenous and adsorption is considered polymolecular layer adsorption. Its linearized form can be written as
 (3)
(3)
where KF and n are the Freundlich constants.
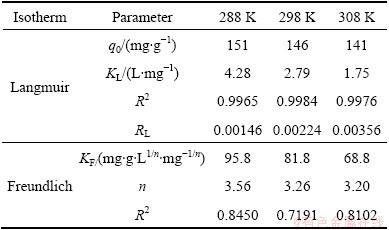
The isotherm adsorption data were analyzed using Langmuir and Freundlich adsorption models and the results are shown in Fig. 6(b) and Fig. 6(c). The isotherm constants and correlation coefficients were calculated from the linear Langmuir plots by plotting ρe/qe vs ρe in Fig. 6(b) and listed in Table 2. Furthermore, RL referred to as separation factor can be predicted whether an adsorption system is favorable or unfavorable [23,24].
 (4)
(4)
where KL is the Langmuir constant and ρ0 is the highest dye concentration.
RL values calculated are listed in Table 2 at all temperatures. The adsorption capacity decreases from 151 mg/g to 141 mg/g with increasing temperature from 15 °C to 35 °C, which specifies an exothermic nature of the adsorption process. KL decreases with an increase in temperature. As can be seen from Table 2, at all temperatures the RL values are between 0 and 1.0, indicating that the adsorption of MO onto modified ACFs is favorable [23]. Figure 6(c) shows the Freundlich adsorption plot. According to regression analysis, n and KF are calculated and listed in Table 2. By comparing R2, it can be deduced that the experimental equilibrium adsorption data are well described by the Langmuir equation compared with Freundlich model.
Table 2 Isotherm parameters for removal of MO by modified ACFs at different temperatures
3.5.2 Adsorption kinetics
The effect of contact time on the adsorption capacity is shown in Fig. 7(a). Figure 7(a) indicates that the adsorption rate changed from fast to slow with the contact time increasing, perhaps because there were a great deal of adsorption active sites on the surface of modified ACFs during the initial time which caused the great diffusion driving force of MO molecules, while when the contact time extended, the diffusion driving force of MO molecules diminished due to the adsorption active sites lessened and thus the adsorption rate decreased. The adsorption reached equilibrium after 300 min.
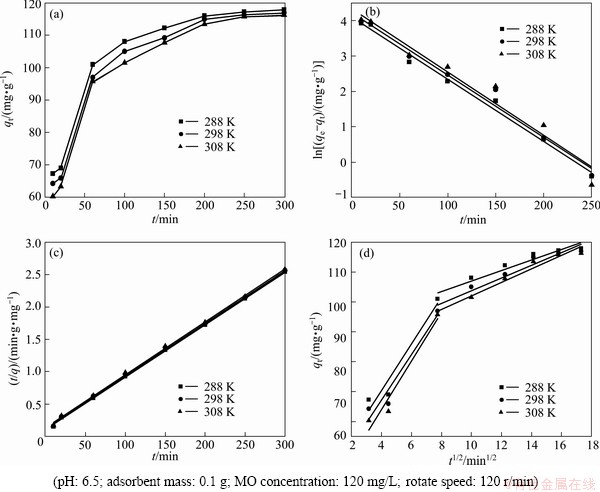
Fig. 7 Kinetic analysis(a), pseudo-first order kinetics plots(b), pseudo-second order kinetics plots(c) and intra-particle diffusion kinetics plots(d) of MO onto modified ACFs at different temperatures
In order to investigate MO adsorption rate, the kinetics of MO adsorption onto modified ACFs was modeled using the pseudo first-order, pseudo-second order and intra-particle diffusion kinetics equations. The pseudo first-order kinetic model of Lagergren is represented by
 (5)
(5)
where qt is the adsorption capacity at time t, and k1 is the rate constant of the pseudo first-order equation.
The pseudo second-order kinetic model is expressed as
 (6)
(6)
where k2 is the rate constant of the pseudo second-order model.
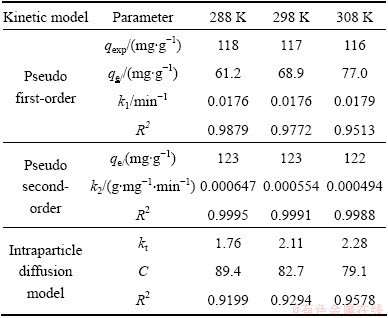
The pseudo first-order kinetic plot and the pseudo second-order kinetic plot are shown in Figs. 7(b) and (c), respectively, and the relevant parameters obtained by regression analysis are listed in Table 3. Table 3 shows clearly that the values of R2 are larger than 0.99, which indicates that MO adsorption data on modified ACFs were successfully described by pseudo second-order model because the values of R2 were greater and the equilibrium adsorption capacities were more similar to the experimental data calculated by the pseudo first-order kinetics model.
In order to elucidate the diffusion mechanism, the adsorption experimental data were plotted by the intra-particle diffusion model and its equation is expressed as
 (7)
(7)
where kt is the intra-particle diffusion rate constant [mg/(g·min1/2)] and C is the constant relating to the thickness of boundary.
The plots for qt against t1/2 are drawn by the intra-particle diffusion model. The regression is linear and the plot passes through the origin, suggesting intra-particle diffusion is only rate-controlling step. The regression is linear, but the plot does not pass through the origin, indicating that adsorption involves the intra-particle diffusion, but it is not the only rate- controlling step [25]. If the regression is not linear, it is suggested that a step or a few steps may control the absorption rate. Figure 7(d) shows that the regression plots are multistage linear. The first stage meant external boundary diffusion and the second stage expressed intra-particle diffusion. The regression parameters were also calculated and listed in Table 3. Table 3 demonstrates the adsorption process is controlled by not only intra-particle diffusion, but also film diffusion because the second stage regression is linear but not passed through the origin.
Table 3 Kinetic parameters for removal of MO by modified ACFs at different temperatures
3.5.3 Thermodynamic
Adsorption thermodynamics must be taken into account in order to make clear if the adsorption process will occur spontaneously. Values of thermodynamic parameters can be calculated by the following equations:
 (8)
(8)
 (9)
(9)
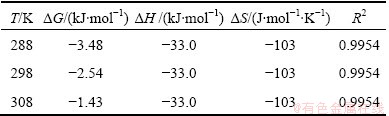
where R is the gas constant; T is the thermodynamic temperature; KL is the Langmuir constant. The plot for ΔG against T is shown in Fig. 8(a) and the values of ΔH and ΔS were calculated by linear regression analysis according to Eqs. (9). The calculated thermodynamic parameters are listed in Table 4. Table 4 presents that the values of ΔG were negative which suggests the adsorption process was spontaneous and the values of ΔG increased with an increase in temperature, indicating that the adsorption process became more favorable at lower temperatures. The value of ΔH is -33.0 kJ/mol, proving that the adsorption reaction was exothermic. The negative value of ΔS was considered the decreasing randomness at the solid–solution interface during the adsorption process and the similar results were reported in Refs. [26,27].
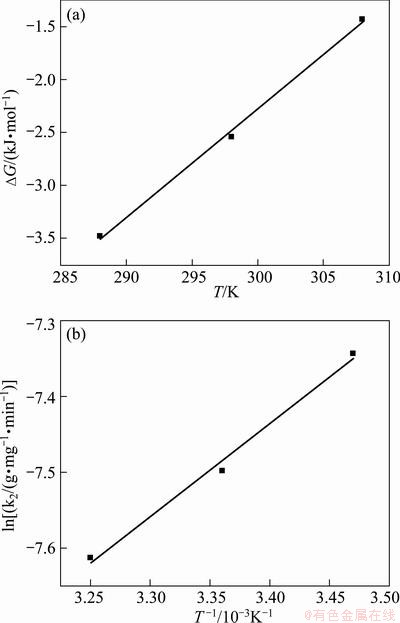
Fig. 8 Thermodynamic regression for MO adsorption onto modified ACFs
Table 4 Thermodynamic parameters for MO adsorption onto modified ACFs
The relationship between the rate constants k2 of the pseudo-second-order model and the temperatures can be depicted by the changed Arrhenius equation as follows:
 (10)
(10)
where k0 is the constant and Ea is the activation energy. The plot for ln k2 to 1/T is shown in Fig. 8(b). The activation energy of adsorption was determined as -10.20 kJ/mol by the slope of the plot. The activation energy was less than 40 kJ/mol, indicating that the adsorption was called fast physisorption [23].
4 Conclusions
1) CNTs are well distributed on the surface of unmodified ACFs and modification transformed pore structure of ACFs. Furthermore, hydrogen bond is the most important adsorption mechanism according to FTIR analysis.
2) The experimental equilibrium adsorption data are well fitted by the Langmuir equation.
3) The dynamics study demonstrates that the adsorption process can be well described with the pseudo second-order kinetic model and the adsorption rate is controlled by intra-particle diffusion and film diffusion together.
4) The values of ΔG, ΔH and ΔS indicate that the adsorption process is spontaneous, exothermic and the decreasing randomness at the solid–solution interface. The calculated activation energy of adsorption is -10.20 kJ/mol, suggesting that the adsorption is a fast physisorption.
References
[1] AGUEDACH A, BROSILLON S, MORVAN J, LHADI E K. Photocatalytic degradation of azo-dyes reactive black 5 and reactive yellow 145 in water over a newly deposited titanium dioxide [J]. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2005, 57(1): 55-62.
[2] LI Ai-chang, WANG Li-na, FAN Hong-xian. Silver modification of TiO2/SnO2 thin films and their photocatalytic activity for methyl orange [J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2009, 19(6): 511-516. (in Chinese)
[3] LIU Shao-you, WU Lin-dong, ZHAO Zhong-xing, FENG Qing-ge, WANG Xiang, YANG Chao-de. Synthesis of Ni-doped TiO2 mesoporous material via solid-state reaction at low temperature and its kinetics of methyl orange photodegradation [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2009, 24(5): 902-908. (in Chinese)
[4] LI T, GUTHRIE J T. Colour removal from aqueous solutions of metal-complex azo dyes using bacterial cells of Shewanella strain J18 143 [J]. Bioresource Technology, 2010, 101(12): 4291-4295.
[5] van der ZEE F P, VILLAVERDE S. Combined anaerobic–aerobic treatment of azo dyes—A short review of bioreactor studies [J]. Water Research, 2005, 39(8): 1425-1440.
[6] GHONEIM M M, EL-DESOKY H S, ZIDAN N M. Electro-fenton oxidation of sunset yellow FCF azo-dye in aqueous solutions [J]. Desalination, 2011, 274(1-3): 22-30.
[7] KONG Yong, WANG Zhi-liang, WANG Yu, YUAN Jia, CHEN Zhi-dong. Degradation of methyl orange in artificial wastewater through electrochemical oxidation using exfoliated graphite electrode [J]. New Carbon Materials, 2011, 26(6): 459-464. (in Chinese)
[8] HAQUE E, LEE J E, JANG I T, HWANG Y K, CHANG J S, JEGAL J, JHUNG S H. Adsorptive removal of methyl orange from aqueous solution with metal-organic frameworks, porous chromium- benzenedicarboxylates [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2010, 181(1-3): 535-542.
[9] LIU Zhuan-nian, ZHOU An-ning, JIN Qi-ting. Mechanism of aniline adsorption on ultrafine coal powder [J]. Journal of Fuel Chemistry and Technology, 2006, 34(1): 20-24. (in Chinese)
[10] SUI Kun-yan, XIE Dan, GAO Song, WU Zhi-ming, WU Wen-wen, XIA Yan-zhi. Preparation and adsorption properties of sodium alginate/multiwalled carbon nanotubes complex gel beads [J]. Journal of Functional Materials, 2010, 41(2): 268-270. (in Chinese)
[11] DELGADO M R, AREAN C O. Carbon monoxide, dinitrogen and carbon dioxide adsorption on zeolite H-Beta: IR spectroscopic and thermodynamic studies [J]. Energy, 2011, 36(8): 5286-5291.
[12] HUANG H Y, YANG C L, ZHANG H X, LIU M C. Preparation and characterization of octyl and octadecyl-modified mesoporous SBA-15 silica molecular sieves for adsorption of dimethyl phthalate and diethyl phthalate [J]. Microporous and Mesoporous Materials, 2008, 111(1-3): 254-259.
[13] LOZANO-CASTELLO D, ALCANIZ-MONGE J, CAZORLA- D, LINARES-SOLANO A, ZHU W, KAPTEIJN F, MOULIJN J A. Adsorption properties of carbon molecular sieves prepared from an activated carbon by pitch pyrolysis [J]. Carbon, 2005, 43(8): 1643-1651.
D, LINARES-SOLANO A, ZHU W, KAPTEIJN F, MOULIJN J A. Adsorption properties of carbon molecular sieves prepared from an activated carbon by pitch pyrolysis [J]. Carbon, 2005, 43(8): 1643-1651.
[14] GENZ A,  A, JEKEL M. Advanced phosphorus removal from membrane filtrates by adsorption on activated aluminium oxide and granulated ferric hydroxide [J]. Water Research, 2004, 38(16): 3523-3530.
A, JEKEL M. Advanced phosphorus removal from membrane filtrates by adsorption on activated aluminium oxide and granulated ferric hydroxide [J]. Water Research, 2004, 38(16): 3523-3530.
[15] FOO K Y, HAMEED B H. Microwave-assisted preparation of oil palm fiber activated carbon for methylene blue adsorption [J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2011, 166(2): 792-795.
[16] MOHAMAD ALI F. Determining the resistance of mass transfer for adsorption of the surfactants onto granular activated carbons from hydrodynamic column [J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2011, 166(3): 832-840.
[17] ZHANG X P, ZHAO X, HU J Q, WEI C H, BI H T. Adsorption dynamics of trichlorofluoromethane in activated carbon fiber beds [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2011, 186(2-3): 1816-1822.
[18] XIE Z Y, LI J P, ZHAO N, WANG F, PENG W C, MAO B Y, XIAO F K, WEI W, SUN Y H. The adsorption of carbon disulfide on activated carbon fibers [J]. Carbon, 2010, 48(1): 315-316.
[19] HUANG H C, YE D Q, HUANG B C. Nitrogen plasma modification of viscose-based activated carbon fibers [J]. Surface and Coatings Technology, 2007, 201(24): 9533-9540.
[20] YAO Y J, BING H, XU F F, CHEN X F. Equilibrium and kinetic studies of methyl orange adsorption on multiwalled carbon nanotubes [J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2011, 170(1): 82-89.
[21] HOSSEINI S, KHAN M A, MALEKBALA M R, CHEAH W, CHOONG T S Y. Carbon coated monolith, a mesoporous material for the removal of methyl orange from aqueous phase: Adsorption and desorption studies [J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2011, 171(3): 1124-1131.
[22] LIU Z N, ZHOU A N, WANG G R, ZHAO X G. Adsorption behavior of methyl orange onto modified ultrafine coal powder [J]. Chinese Journal of Chemical Engineering, 2009, 17(6): 942-948.
[23] ALMEIDA C A P, DEBACHER N A, DOWNS A J, COTTET L, MELLO C A D. Removal of methylene blue from colored effluents by adsorption on montmorillonite clay [J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2009, 332(1): 46-53.
[24]  I, SENER S. Adsorption of methylene blue onto sonicated sepiolite from aqueous solutions [J]. Ultrasonics Sonochemistry, 2010, 17(1): 250-257.
I, SENER S. Adsorption of methylene blue onto sonicated sepiolite from aqueous solutions [J]. Ultrasonics Sonochemistry, 2010, 17(1): 250-257.
[25] AL-GHOUTI M A, KHRAISHEH M A M, AHMAD M N M, ALLEN S. Adsorption behaviour of methylene blue onto Jordanian diatomite: A kinetic study [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2009, 165(1-3): 589-598.
[26] RAWAJFIH Z, MOHAMMAD H A, NSOUR N, IBRAHIM K. Study of equilibrium and thermodynamic adsorption of α-picoline, β-picoline, and γ-picoline by Jordanian zeolites: Phillipsite and faujasite [J]. Microporous and Mesoporous Materials, 2010, 132(3): 401-408.
[27] ZHAO G X, LI J X, WANG X K. Kinetic and thermodynamic study of 1-naphthol adsorption from aqueous solution to sulfonated graphene nanosheets [J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2011, 173(1): 185-190.
王丽平1,2,黄柱成2,张明瑜3
1. 长沙学院 生物工程与环境科学系,长沙 410003;
2. 中南大学 资源加工与生物工程学院,长沙 410083;
3. 中南大学 粉末冶金国家重点实验室,长沙 410083
摘 要:通过化学气相沉积法(CVD)对粘胶基活性炭纤维(ACFs)进行表面改性,利用比表面积、SEM、孔径分布和红外光谱等分析方法对样品进行表征。通过吸附实验研究改性ACFs对溶液中甲基橙的吸附行为。结果表明,吸附数据较符合Langmuir等温线模型;准二级动力学方程能够较好地反映改性ACFs对溶液中甲基橙的吸附动力学;颗粒间扩散为控制步骤,但并非唯一控制步骤。经计算获得的热力学参数包括ΔG、ΔH和ΔS,表明吸附为自发的放热物理吸附过程。从红外光谱分析可知,氢键作用是改性ACFs吸附甲基橙的主要吸附机理。
关键词:粘胶基活性碳纤维;化学气相沉积;改性;甲基橙;吸附等温线;动力学;热力学
(Edited by Xiang-qun LI)
Foundation item: Project (50802115) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China; Project (2010FJ4075) supported by Science and Technology Planning Project of Hunan Province, China; Project (CDJJ-10010205) supported by the Science Foundation of Changsha University, China; Project supported by the Construct Program of the Key Discipline in Hunan Province, China
Corresponding author: Li-ping WANG; Tel: +86-13787313004; E-mail: misswlp@163.com
DOI: 10.1016/S1003-6326(13)62495-4

