DOI: 10.11817/j.issn.1672-7207.2019.05.015
隧道充填岩溶管道滑移失稳突水机制
黄震1, 2, 3,李仕杰1,赵奎1,吴锐1,钟文1
(1. 江西理工大学 资源与环境工程学院,江西 赣州,341000;
2. 南京大学 地球科学与工程学院,江苏 南京,210023;
3. 中国矿业大学 深部岩土力学与地下工程国家重点实验室,江苏 徐州,221116)
摘要:为探究隧道充填岩溶管道滑移失稳突水机制,将岩溶管道视为“塞子”,建立岩溶管道滑移失稳突水的地质模型和力学传递模型,推导出充填岩溶管道失稳判据及安全系数计算公式,并通过算例分析岩溶管道倾角和含水体水位对岩溶管道安全性的影响。研究结果表明:弱透水或不透水的充填岩溶管道在突水过程中的作用类似“塞子”,具有较强阻水性能,此时突水模式为岩溶管道的充填物滑移失稳突水;隧道开挖过程中,作用在岩溶管道的下滑力和抗滑力达到临界条件时,管道发生滑移失稳,最终导致突水的发生;充填岩溶管道的安全系数随着含水体水位增大而不断降低,管道倾角对安全系数的影响比水位的影响小;地下水对岩溶管道安全性的影响很大,其中渗透压力、静水压力和扬压力对管道安全性的影响较大,是触发管道发生滑移失稳、引发突水的关键因素。
关键词:隧道工程;突水机制;力学模型;岩溶管道;滑移失稳
中图分类号:U451 文献标志码:A 文章编号:1672-7207(2019)05-1119-08
Water inrush mechanism for slip instability of filled karst conduit in tunnels
HUANG Zhen1, 2, 3, LI Shijie1, ZHAO Kui1, WU Rui1, ZHONG Wen1
(1. School of Resources and Environment Engineering, Jiangxi University of Science and Technology, Ganzhou 341000, China;
2. School of Earth Sciences and Engineering, Nanjing University, Nanjing 210023, China;
3. Sate Key Laboratory for Geomechanics & Deep Underground Engineering,
China University of Mining and Technology, Xuzhou 221116, China)
Abstract: In order to investigate the water inrush mechanism for slip instability of filled karst conduit in tunnels, a fundamental geological model and the mechanical transitive model of the conduit slip were established by assuming the karst conduit as a plug. The instability criteria for the karst conduit and an equation to calculate the safety factor of the karst conduit were deduced. Influences of the conduit inclination and the water level of the aquifer on the safety of karst conduit were investigated. The results show that the karst conduit of low permeability or impermeable plays a role as a plug that has strong water blocking effects, and it leads to water inrush induced by the conduit slip. Conduit slip and then water inrush occur when the sliding force exceeds anti-sliding force. The safety factor of the karst conduit decreases with the increase of water level of the aquifer. The influence of conduit inclination on safety factor is less significant than that of the water level. The safety of karst conduit is strongly related to groundwater. Seepage pressure, hydrostatic pressure and uplift pressure are the key factors to cause conduit slip and water inrush.
Key words: tunnelling engineering; water-inrush mechanism; mechanical model; karst conduit; slip instability
为适应我国经济建设的高速发展、国家安全的需求以及中、西部国土资源开发的需要,我国地下空间开发的规模不断增大,隧道工程也相应急剧增加,尤其以各类交通(铁路、公路)、水利水电领域隧道工程建设最为显著。中国作为世界上岩溶分布面积最大的国家,岩溶已成为我国隧道建设过程中不可忽视的问题[1-3]。岩溶导致隧道工程建设过程中极易遭遇突水突泥、坍塌等地质灾害,其中突水突泥所造成的人员伤亡和经济损失在各类地质灾害中居于前列[4-9]。突水突泥灾害的有效防控已成为制约我国隧道工程建设的关键问题,突水突泥致灾机理及预警与控制研究已成为国家基础工程建设的重点。由于地质条件的复杂性及孕灾模式的不同,隧道突水往往表现出不同的类型,其中根据储藏条件和致灾构造的类型,可将突水划分为裂隙型突水、断层突水、溶洞溶腔型突水、管道和地下河型突水4类[4]。岩溶管道等充填型致灾构造为突水的优势通道,具有广泛的地下水补给网路和充足的补给水源,当附近存在大型含水体时将成为潜在的突水通道,一旦突水将造成严重的工程灾害和环境破坏[9-11]。充填岩溶管道失稳突水模式一般可分为充填介质的渗透失稳及充填体的滑移失稳突水2类[9]。目前,人们对充填岩溶管道失稳突水机制进行了大量研究:李利平[10]建立了强渗流作用下充填介质的渗透失稳力学模型;石少帅[12]采用三维可视化突水突泥模型试验系统开展了充填型裂隙蓄水构造渗透失稳模型试验,揭示了充填物渗透失稳的灾变演化机制;周毅等[13-14]利用大型可视化固液耦合试验平台研究了隧道开挖过程中充填型岩溶管道在施工扰动和地下水渗流作用下失稳突水机制,指出管道突水明显受控于其发育形态;CHU[15]建立了3种岩溶管道的力学失稳模型,得到了相应的失稳判据;周宗青[16]综合理论分析、试验、数值模拟及软件开发研究了隧道充填型致灾构造突水突泥的灾变演化机理。目前的研究主要针对充填介质的渗透失稳模式这一类型,而有关岩溶管道滑移失稳突水的研究较少。当充填岩溶管道弱透水或不透水时,充填体此时具有阻水和充水特征,其在突水过程中起到一种类似于“塞子”的作用。例如早期形成的岩溶管道充填体在历经长期的地质演化过程后,充填物呈现密实、非均质和稳定的结构状态,其渗透性较差甚至完全不透水,具有极强的阻水能力,此时充填体就起到了“塞子”的作用[9-10]。BAI等[17]假设陷落柱由围岩、塞子及塞子与围岩之间的充填物组成,采用塞子模型对破碎岩体构成的陷落柱进行了描述;孙强等[18]假设岩溶管道由刚体、泥质充填物及岩桥或锁固段组成运用突变理论对管道导通型突水进行了分析;李术才等[9-10]建立了隧道岩溶充填体滑移失稳突水模型。但在实际工程中,隧道岩溶管道滑移失稳突水演化过程十分复杂,其灾变机制尚不明确。随着大批具有“大埋深、长洞线、高应力、强岩溶、高水压、构造复杂”等特点的隧道工程的开工建设[9],岩溶管道滑移失稳突水问题也愈加突出。因此,有必要进一步研究隧道充填岩溶管道滑移失稳突水机制。本文作者在前人研究的基础上对岩溶管道滑移失稳突水机制及其稳定性判据进行研究,以期为进一步研究隧道突水灾变机理提供参考。
1 充填管道滑移失稳力学模型
结合以往研究成果,针对岩溶管道滑移失稳突水建立模型,如图1所示。图1中,a为隧道半径,b为隧道中心到损伤区距离,h为潜在含水体水位(以管道顶面为基准面),P为孔隙水压力;第i个破坏体单元的长度为li,垂高为hi,倾角为θi。视致密的充填结构为潜在破坏体,则管道由塞子状的破坏体及围岩组成。为分析管道滑移失稳突水的力学演化机理并探讨其突水灾变的条件,建立管道滑移失稳力学传递模型,如图2所示(其中D为工程扰动产生的震动力,d为管道直径,τ为剪切力,t为渗透压力产生的拖曳力)。本文假设如下:1) 管道与潜在含水体和隧道联通,且管道由n个规则圆柱体(塞子)组成,第i个单元体直径为di,重力为Wi (见图2(a));2) 管道内的破坏体在滑移过程中不发生变形破坏,仅与管道壁之间发生剪切破坏,且剪切带均匀分布;3) 地下水水位低于隧道水位且不承压,围岩及管道中的渗流遵循Darcy定律。需要指出的是,虽然本文将致密的充填结构视为塞子,但实际上并不是完全不透水,故地下水将对充填管道(破坏体)产生力的作用。水对破坏体产生的作用有:物理化学作用(降低滑动面的抗剪强度)、静水压力作用和渗透压力作用[19]。其中,静水压力可分为作用在破坏体上的静水压力和管道下滑面上的扬压力;渗透压力指水的渗流对破坏体产生的作用力,其最终表现为沿着渗流方向作用在滑动面的拖曳力,其分布和大小取决于其中的水力梯度分布[20-21]。
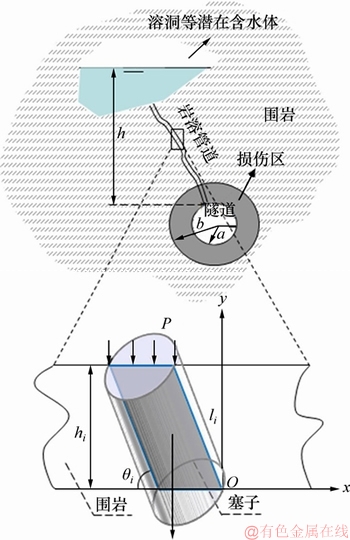
图1 充填管道滑移地质模型
Fig. 1 Geological model of filled conduit slip
对于岩体结构,无论是否存在充填物,水的渗流都会对周围骨架产生渗透压力作用[20-21]。为了分析作用在破坏体上的渗透压力,沿渗流方向取1个微圆柱体,其受力示意图如图 3 所示。微圆柱体长△l,面积为△A,孔隙率为φ,则沿渗流方向作用在微圆柱体上的力如下。
1) 孔隙水压力。设微圆柱体2个端面所受的孔隙水压力分别为P和P+△P,差量△P表达式为
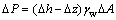 (1)
(1)
式中:△h和△z分别为微圆柱体两端面的水位差和高度差;γw为水的重度。
2) 水的重力沿渗流方向分力。微圆柱体中地下水的重力沿渗流方向的分力△Gw为
 (2)
(2)
3) 微圆柱体产生浮力的反作用力沿渗流方向的分力△F为
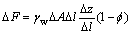 (3)
(3)
4) 渗透压力。微圆柱体骨架对水产生阻力,其反作用力即是水对微圆柱体的渗透压力,设f为水受到的单位阻力,则渗透压力△S为
 (4)
(4)
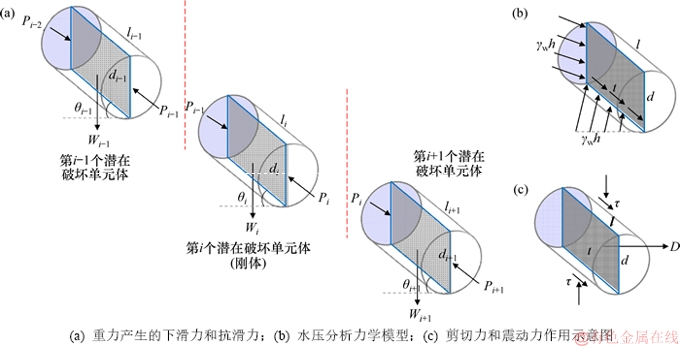
图2 管道滑移失稳力学传递模型
Fig. 2 Mechanical transitive model of slip instability for karst conduit
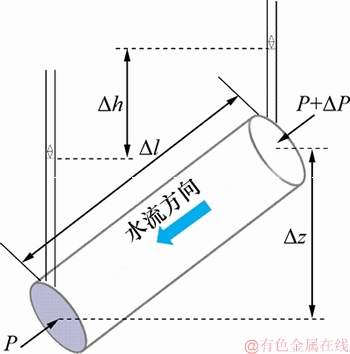
图3 管道微圆柱体受力示意图
Fig. 3 Diagram of hydrodynamic pressure of micro cylinder of karst conduit
忽略水渗流时的惯性力,根据微圆柱体的水流的静力平衡关系:
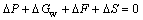 (5)
(5)
即
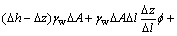
 (6)
(6)
由式(6)可求出水对微圆柱体的单位渗透压力fs为
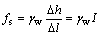 (7)
(7)
式中:I为沿渗流方向的水力梯度。
精确计算水对破坏体的渗透压力即拖曳力比较困难,较符合工程实际的做法是将此拖曳力近似取总拖曳力的一半[20-22]。设t0为总拖曳力,R为抗滑力,则作用在破坏体上的拖曳力t(见图2(b))为
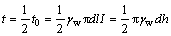 (8)
(8)
此外,作用在管道与潜在含水体接触端的静水压力Pw1为
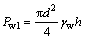 (9)
(9)
管道滑动面上的扬压力作用方向沿着下滑面法向(见图 2(b)),增加了破坏体的下滑力,扬压力Pw2可表示为
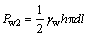 (10)
(10)
管道自重力产生的下滑力和抗滑力可采用基于刚体极限平衡理论的传递系数法进行分析和计算(见图 2(a)),另外,工程扰动产生的震动力(爆破等)对岩溶管道也会产生影响(其中震动力D为水平作用力,见图2(c)),则抗滑力R和下滑力T可表示为
 (11)
(11)
式中:Ri为第i个破坏体单元的抗滑力;Ti为第i个破坏体单元的下滑力;ri为第i个破坏体单元与单元管道壁产生的摩擦力;ψi为第i个破坏体(充填体)单元传递给第i+1个破坏体(充填体)单元的传递系数。
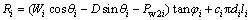 (12)
(12)
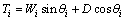 (13)
(13)
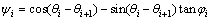 (14)
(14)
式中:φi和ci分别为第i个破坏体单元的滑面摩擦角和内聚力;Pw2i为第i个破坏体单元受到的扬压力。
在第i个破坏体单元任一深度z位置取高为△z的微圆柱体,由库仑强度理论计算该点的抗剪强度τfi为
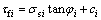 (15)
(15)
式中:σsi为第i个破坏体单元受到的法向应力。单元与单元管道壁产生的摩擦力为
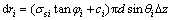 (16)
(16)
对式(16)积分得:
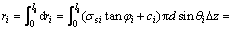
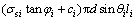 (17)
(17)
管道滑移失稳突水的安全系数可定义为管道抗滑力和下滑力的比值。根据以上分析与计算,整理可得管道滑移失稳突水的安全系数Fk为
 (18)
(18)
当管道滑移失稳突水的安全系数Fk为1时,管道抗滑力等于下滑力,此时管道处于临滑极限状态,因此,当Fk>1时,管道能够维持稳定,不会发生突水事故;当Fk<1时,岩溶管道将发生滑移失稳,进而诱发突水。
2 算例分析
2.1 工程背景
为验证式(18)的有效性并分析管道倾角和含水体水位对岩溶管道安全性的影响,本文基于圆梁山隧道的地质力学条件建立简化的管道滑移失稳突水模型并对其安全性进行评估。
圆梁山隧道为渝怀铁路全线最难的控制性工程全长11.068 km,岩溶发育,溶洞成群,并穿越长约 7.1 km的可溶性灰岩地层,属于特长深埋隧道,具有高水压、强岩溶等特点。圆梁山隧道建设过程中先后揭露5个深埋充填型溶洞,分别编号为K1~K5,施工过程中先后发生大规模突水突泥70余次[23],最高水压达 4.6 MPa,最大涌水量达72 000 m3/h(2002-09-11),造成9人死亡和巨大的经济损失。
按溶洞突水次数计算,隧道施工过程中K1溶洞共发生7次突水,K2溶洞发生13次突水,K3溶洞发生1次突水,K4溶洞发生5次突水,K5溶洞发生6次突水。通过对溶洞管道内充填物的介质成分进行测试分析,可将上述5个溶洞充填类型分为泥砾型、细砂型和黏土型[22-25],其中K1,K2和K3溶洞充填物特征如图 4 所示。
K1,K4和K5溶洞为泥砾型充填岩溶,充填物中各组分(黏土、砂、砾石和水)所占的比例基本相同,其级配曲线基本呈直线状(见图 4(a)),表明岩溶管道充填物未突出前,其级配良好,呈现较致密结构。

图4 岩溶管道充填物特征[23]
Fig. 4 Characteristics of infill materials in karst conduits[23]
K2溶洞为细砂型充填岩溶,充填介质大都为粉细砂,颗粒均匀,级配不均(见图 4(a)),此类型充填岩溶易透水,因此,容易发生突水涌砂问题。
K3溶洞为黏土型充填岩溶。由图4 (b)可知:K3溶洞充填物中黏土质量分数达70%以上,为典型的黏土型充填,由于黏土弱透水或不透水,因此在工程扰动和水压的作用下,此类充填岩溶管道容易发生滑移失稳,常造成爆喷型突水突泥。
2.2 计算分析
以圆梁山隧道为工程背景,采用前面建立的管道滑移导通突水模型对泥砾型及黏土型充填管道安全性进行评估。由于实际工程的条件过于复杂,为简化计算,将管道考虑为单一滑体,并且忽略工程扰动产生的爆破震动力的影响,管道直径为d,管道长度为l,管道倾角为θ。根据式(18),管道滑移失稳突水模型的安全系数Fk可表示为
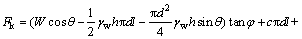
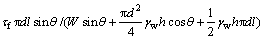 (19)
(19)
式中:τf可根据管道受到的垂直和水平应力计算求得。
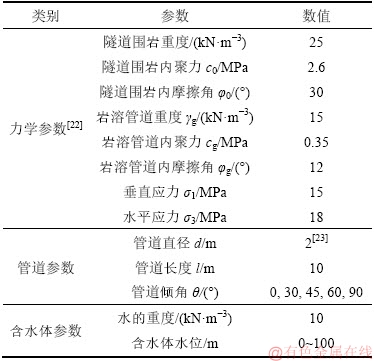
本次计算的力学参数主要参考文献[22]中圆梁山隧道围岩和管道的基本力学参数选取;根据文献[23],将管道直径d取为 2 m,管道长度l取为10 m,管道倾角θ分别取0°,30°,45°,60°和90°;岩溶含水体水位取0~100 m,计算所需的参数如表 1 所示。
表1 计算参数
Table 1 Calculation parameters
利用式(19)对计算得到在岩溶含水体作用下岩溶管道滑移失稳安全系数与管道倾角及含水体水位的关系,如图 5所示。从图 5可以看出:岩溶管道的安全系数随着岩溶含水体水位的增加而不断降低。对比含水体水位为 0 m和10 m的结果可知:含水体引起的渗透压力、静水压力和扬压力使岩溶管道安全系数降低 87.4%~93.7%(未考虑管道倾角为0°的情况);相较而言,管道倾角对安全系数的影响较小,以含水体水位为10 m为例,管道倾角由0°变为90°时,安全系数仅降低 5.2%。此外,根据图 5(c)可知:管道发生滑移失稳导通突水的临界水位约为 55 m,当含水体水位低于55 m时,充填岩溶管道较稳定,不会诱发突水。

图5 安全系数与含水体水位及管道倾角的关系
Fig. 5 Relationships among safety factor, water level of aquifer and conduit inclination
为了进一步分析含水体特征对充填岩溶管道稳定性的影响,本文研究当管道倾角θ=60°时,考虑所有水压力、不考虑水压力的影响、不考虑渗透压力(动水压力)的影响以及不考虑静水压力和扬压力4种不同情况下,水压力对安全系数的影响如图6所示。由图 6可知:不考虑含水体的水压力影响时,岩溶管道安全系数Fk约为54.21,管道十分稳定,不会发生突水;水压力的作用对管道安全性的影响很大,管道安全系数在水压力的作用下随着含水体的水位增加而不断降低。此外,渗透压力对管道安全性影响显著,其曲线基本与考虑所有水压力的曲线重合;静水压力和扬压力对管道安全性的影响也较大,以含水体水位为 20 m为例,所有水压力使管道安全系数降低 94.6%,渗透压力使安全系数降低 93.9%,静水压力和扬压力使安全系数降低 47.2%。因此,渗透压力、静水压力和扬压力对管道安全性的影响较大,是触发管道发生滑移失稳,进而引发导通突水的关键因素。

图6 水压力对安全系数的影响
Fig. 6 Influence of water pressure on safety factor
3 结论
1) 充填岩溶管道滑移失稳突水多发生在充填体呈密实、非均质和稳定结构状态的弱透水或不透水的充填岩溶管道中,其在突水过程中的作用类似“塞子”,具有强阻水能力。
2) 地下水在岩溶管道滑移时将对充填体施加静水压力、扬压力和渗透压力;在隧道开挖过程中,作用在充填岩溶管道的下滑力和抗滑力达到临界条件时,岩溶管道将发生滑移失稳突水。
3) 致密泥砾型及黏土型充填管道会发生岩溶管道的滑移失稳突水;岩溶管道的安全系数随着岩溶含水体水位的增加而不断降低,含水体引起的渗透压力、静水压力和扬压力将造成岩溶管道安全系数下降;地下水对岩溶管道安全性的影响很大,是触发管道发生滑移失稳,引发突水的关键因素。
参考文献:
[1] SOROCHAN E A, TOLMACHEV V V. A base for building codes and construction methods in karst-prone regions[J]. Soil Mechanics and Foundation Engineering, 2006, 43(6): 216-220.
[2] 钱七虎. 地下工程建设安全面临的挑战与对策[J].岩石力学与工程学报, 2012, 31(10): 1945-1956.
QIAN Qihu. Challenges faced by underground projects construction safety and counter measures[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2012, 31 (10): 1945-1956.
[3] LI Xiaodong, LIU Congqiang, HARUE M, et al. The use of environmental isotopic (C, Sr, S) and hydrochemical tracers to characterize anthropogenic effects on karst groundwater quality: a case study of the Shuicheng Basin, SW China[J]. Applied Geochemistry, 2010, 25(12): 1924-1936.
[4] ZHAO Yong, LI Pengfei, TIAN Siming. Prevention and treatment technologies of railway tunnel water inrush and mud gushing in China[J]. Journal of Rock Mechanics and Geotechnical Engineering, 2013, 5(6): 468-477.
[5] HUANG Fu, ZHAO Lianheng, LING Tonghua, et al. Rock mass collapse mechanism of concealed karst cave beneath deep tunnel[J]. International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences, 2017, 91: 133-138.
[6] 李术才, 刘斌, 孙怀凤, 等. 隧道施工超前地质预报研究现状及发展趋势[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2014, 33(6): 1090-1113.
LI Shucai, LIU Bin, SUN Huaifeng, et al. State of art and trend of advanced geological prediction in tunnel construction[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2014, 33(6): 1090-1113.
[7] LI Liping, ZHOU Zongqing, LI Shucai, et al. An attribute synthetic evaluation system for risk assessment of floor water inrush in coal mines[J]. Mine Water and the Environment, 2015, 34: 288-294.
[8] LI Liping, LEI Ting, LI Shucai, et al. Dynamic risk assessment of water inrush in tunnelling and software development[J]. Geomechanics and Engineering, 2015, 9(1): 57-81.
[9] 李术才, 王康, 李利平, 等. 岩溶隧道突水灾害形成机理及发展趋势[J]. 力学学报, 2017, 49(1): 22-30.
LI Shucai, WANG Kang, LI Liping, et al. Mechanical mechanism and development trend of water-inrush disasters in karst tunnels[J]. Chinese Journal of Theoretical and Applied Mechanics, 2017, 49 (1): 22-30.
[10] 李利平. 高风险岩溶隧道突水灾变演化机理及其应用研究[D]. 济南: 山东大学土建与水利学院, 2009: 79-86.
LI Liping. Study on catastrophe evolution mechanism of karst water inrush and its engineering application of high risk karst tunnel[D]. Jinan: Shandong University. School of Civil Engineering, 2009: 79-86.
[11] 吴兴杰. 隧道充填型岩溶管道渗流突水灾变机理研究[D]. 徐州: 中国矿业大学力学与土木工程学院, 2017: 1-2.
WU Xingjie. Study on mechanism of seepage and water-inrush from filled karst conduit in tunnel[D]. Xuzhou: China University of Mining and Technology. School of Mechanics and Civil Engineering, 2017: 1-2.
[12] 石少帅. 深长隧道充填型致灾构造渗透失稳突涌水机理与风险控制及工程应用[D]. 济南: 山东大学土建与水利学院, 2014: 1-4.
SHI Shaoshuai. Study on seepage failure mechanism and risk control of water inrush induced by filled disaster struture in deeep-long tunnel and engineering application[D]. Jinan: Shandong University. School of Civil Engineering, 2014: 1-4.
[13] 周毅, 李术才, 李利平, 等. 地下工程流-固耦合试验新技术及其在充填型岩溶管道突水模型试验中的应用[J]. 岩土工程学报, 2015, 37(7): 1232-1240.
ZHOU Yi, LI Shucai, LI Liping, et al. New technology for fluid-solid coupling tests of underground engineering and tts application in experimental simulation of water inrush in filled-type karst conduit[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical and Engineering, 2015, 37(7): 1232-1240.
[14] 周毅, 李术才, 李利平, 等. 隧道充填型岩溶管道渗透失稳突水机制三维流-固耦合模型试验研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2015, 34(9): 1739-1749.
ZHOU Yi, LI Shucai, LI Liping, et al. 3D fluid-solid coupling model test on seepage failure water-inrush mechanism of filled-type karst conduit in deep large tunnel[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2015, 34 (9): 1739-1749.
[15] CHU Vietthuc. 公路隧道充填型岩溶管道突水灾变机理及演化过程数值分析[J]. 中南大学学报(自然科学版), 2016, 47(12): 4173-4180.
CHU Vietthuc. Mechanism on water inrush disaster of filling karst piping and numerical analysis of evolutionary process in highway tunnel[J]. Journal of Central South University (Science and Technology), 2016, 47(12): 4173-4180.
[16] 周宗青. 隧道充填型致灾构造突水突泥灾变演化机理及工程应用[D]. 济南: 山东大学土建与水利学院, 2016: 79-168.
ZHOU Zongqing. Evolutionary mechanism of water inrush through filling structures in tunnels and engineering applications[D]. Jinan: Shandong University. School of Civil Engineering, 2016: 79-168.
[17] BAI Haibo, MA Dam, CHEN Zhanqing. Mechanical behavior of groundwater seepage in karst collapse pillars[J]. Engineering Geology, 2013, 164: 101-106.
[18] 孙强, 朱术云, 张蕊. 管道导通型突水特性分析[J]. 应用基础与工程科学学报, 2013, 21(3): 463-470.
SUN Qiang, ZHU Shuyun, ZHANG Rui. Analysis on water inrush mechanism of pipeline conduction[J]. Journal of Basic Science and Engineering, 2013, 21(3): 463-470.
[19] BRAY J W, HOEK E. Rock slope engineering[M]. 3rd ed. London, UK: Institution of Mining and Metallurgy, 1981: 358.
[20] 刘才华, 徐健, 曹传林, 等. 岩质边坡水力驱动型顺层滑移破坏机制分析[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2005, 24(19): 3529-3533.
LIU Caihua, XU Jian, CAO Chuanlin, et al. Analysis of bedding-slip failure mechanism of rock slope due to hydraulic drive[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2005, 24(19): 3529-3533.
[21] 胡其志, 周辉, 肖本林, 等. 水力作用下顺层岩质边坡稳定性分析[J]. 岩土力学, 2010, 31(11): 3594-3598.
HU Qizhi, ZHOU Hui, XIAO Benlin, et al. Analysis of stability of rock bedded slope under hydraulic pressure[J]. Rock and Soil Mechnice, 2010, 31 (11): 3594-3598.
[22] 刘招伟, 何满潮, 王树仁. 圆梁山隧道岩溶突水机理及防治对策研究[J]. 岩土力学, 2006, 27(2):228-232.
LIU Zhaowei, HE Manchao, WANG Shuren. Study on karst waterburst mechanism and prevention countermeasures in Yuanliangshan Tunnel[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2006, 27(2): 228-232.
[23] 刘招伟. 圆梁山隧道岩溶突水机理及其防治对策[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学工程技术学院, 2004: 30-41.
LIU Zhaowei. Karst waterburst mechanism and prevention countermeasures in Yuanliangshan Tunnel[D]. Beijing: China University of Geoscience. School of Engineering and Technology, 2004: 30-41.
[24] 张民庆, 刘招伟. 圆梁山隧道岩溶突水特征分析[J]. 岩土工程学报, 2005, 27(4): 422-426.
ZHANG Minqing, LIU Zhaowei. The analysis on the features of karst water burst in the Yuanliangshan tunnel[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical and Engineering, 2005, 27(4): 422-426.
[25] 王树仁, 何满潮, 刘招伟. 岩溶隧道突水灾变过程分析及控制技术[J]. 北京科技大学学报, 2006, 28(7): 613-618.
WANG Shuren, HE Manchao, LIU Zhaowei. Analysis on the process of water burst catastrophe and it’s prevention countermeasures in a karst tunnel[J]. Journal of University of Science and Technology Beijing, 2006, 28(7): 613-618.
(编辑 伍锦花)
收稿日期:2018-05-25;修回日期:2018-08-25
基金项目(Foundation item):国家重点基础研究发展规划(973计划)项目(2013CB036001);国家自然科学基金资助项目(41702326, 41602294);博士后创新人才支持计划项目(BX201700113);国家博士后科学基金资助项目(2017M620205);江西省自然科学基金资助项目(20171BAB206022);中国矿业大学深部岩土力学与地下工程国家重点实验室开放基金资助项目(SKLGDUEK1703);江西省教育厅科学技术研究资助项目(GJJ160675)(Project(2013CB036001) supported by the National Basic Research Development Program(973 Program) of China; Projects (41702326, 41602294) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China; Project(BX201700113) supported by the Postdoctoral Innovative Talent Support Program of China; Project(20171M620205) supported by the National Science Foundation for Post-doctoral Scientists of China; Project(20171BAB206022) supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Jiangxi Province; Project(SKLGDUEK1703) supported by the Open Fund of State Key Laboratory for Geomechanics and Deep Underground Engineering of China University of Mining & Technology; Project(GJJ160675) supported by the Science and Technology Program of the Education Department of Jiangxi Province)
通信作者:赵奎,博士,教授,从事岩石力学与采矿工程研究;E-mail: yglmf_zk@163.com