沥青路面动水压力计算及其影响因素分析
周长红1,陈静云1,王哲人1, 2,乔英娟1
(1. 大连理工大学 土木水利学院道路研究所,辽宁 大连,116023;
2. 哈尔滨工业大学 交通科学与工程学院,黑龙江 哈尔滨,150090)
摘 要:为了分析沥青混凝土路面在循环车辆荷载作用下的孔隙水压力反应,针对饱水情况,利用变温粘弹性理论和Biot动力固结理论,由Galerkin加权余量法,形成以节点位移及节点孔隙水压力为状态参数的有效应力有限元格式;并选取常用的双圆荷载计算模型,对饱水沥青路面孔隙水压力的空间和时间分布进行计算。计算结果表明:有效应力及孔隙水压力均与外荷载具有相似的波形,只是在不同空间位置出现不同的峰值大小和相位滞 后。通过分析可以得出:渗透系数和加载速率是影响孔隙水压力峰值的2个关键参数,它们对后者具有负指数影响效果。
关键词:沥青路面;动水压力;有限元;Biot动力固结理论
中图分类号:U416.217 文献标识码:A 文章编号:1672-7207(2008)05-1100-05
Dynamic numerical method of pore water pressure and
its influence parameters for asphalt pavement
ZHOU Chang-hong1, CHEN Jing-yun1, WANG Zhe-ren1, 2, QIAO Ying-juan1
(1. School of Civil and Hydraulic Engineering, Dalian University of Technology, Dalian 116023, China;
2. School of Science and Engineering on Communication, Harbin Institute of Technology, Harbin 150090, China)
Abstract: In order to analyze dynamical response of pore water pressure in asphalt concrete pavement under the cyclical vehicle load, a dynamic finite element method (FEM) was derived by Galerkin weighted residual method based on Biot’s consolidation theory and viscoelastic incremental constitutive equations, whose variable parameter was given including displacement as well as water pressure. Furthermore, an instance of double disk load model was adopted to numerate the spatial and time distribution of pore water pressure. As a result, effective stress and pore water pressure show the same waveform as the cyclical load, except their different peak values and lagged phases in different locations. So, it can be proved with these results that permeability coefficient and loading speed are two key parameters to influence the maximal pore water pressure, and they all work with the rule of negative exponent.
Key words: asphalt concrete pavement; dynamical pore water pressure; finite element method; Biot’s consolidation theory
水损害是沥青路面早期损坏的关键因素,反复的动水压力促使了沥青集料间的剥离[1-3]。为了了解动水压力的影响程度,人们进行了很多试验研究,如孙立军等[4]通过理论分析和现场测定,认为动水压力随车速的提高呈几何级数增长。我国对动水压力的计算研究很少,只有Hoven[5]利用Terzaghi固结理论建立了动载下的孔隙水压力有限差分格式;而彭永恒等[6]利用层状体系理论建立了轴对称条件下的孔隙水压力计算公式。
针对沥青混合料的计算方法主要有层状体系力学和有限元计算方法[7-8]。由于层状体系力学方法适应性较差,而且积分逆变换困难,所以,人们试图利用有限元方法解决路面力学计算问题。目前,沥青混合料有限元方法均未考虑孔隙水压力作用,无法模拟车辆荷载作用下骨料变形和孔隙水压的瞬间或短期反 应,从而在处理含水路面受力问题时较实际有很大误差。为此,本文作者利用Galerkin弱势有限元法,以作用荷载为动力荷载,采用变温粘弹性本构关系,建立沥青路面饱和水状态下的有效应力(或动水压力)计算格式。
1 数值计算控制方程
1.1 骨架本构方程
沥青混合料为变温性粘弹性材料体,从0到t时间的变温过程后,t时刻应变满足以下记忆积分公式[9]:

1.2 Biot动力固结方程[10]:

2 流固耦合有限元格式
2.1 骨架本构方程的时间离散
将时间区间[0,t]分成N等分,则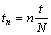 ,此时,单元节点位移和孔隙水压力分别为
,此时,单元节点位移和孔隙水压力分别为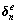 和
和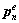 ;令时段
;令时段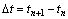 内的单元节点位移和孔隙水压力增量分别为
内的单元节点位移和孔隙水压力增量分别为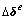 和
和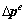 。对式(1)进行离散,由Euler积分公式,可得矩阵形式的增量本构方程:
。对式(1)进行离散,由Euler积分公式,可得矩阵形式的增量本构方程:
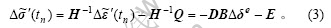
其中: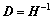 ;
;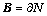 ;
;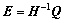 ;
;
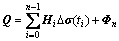 ;
;
 ;
;
 ;
;
 ;
;
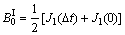 ;
;
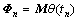 ;
;
 。
。
2.2 Biot方程的空间离散
取常见边界条件:

为了简便,将 ,
,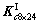 ,
,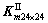 和
和 分割为8×8个子阵,记每个子阵为
分割为8×8个子阵,记每个子阵为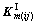 ,
, ,
, 和
和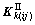 ;
;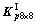 和
和 也分割为8×8个子阵,记每个子阵为
也分割为8×8个子阵,记每个子阵为 和
和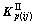 ;而
;而 和
和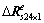 可分割为8×1个子阵,记每个子阵为
可分割为8×1个子阵,记每个子阵为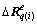 和
和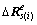 。
。
合并式(5),然后,将单元控制方程组成动力问题的增量式有限元整体控制方程:
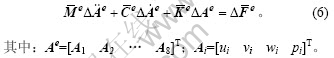
每个单元的系数矩阵 ,
,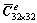 ,
,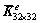 和
和 可由子阵表示为:
可由子阵表示为:
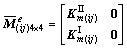 。
。
 。
。
 。
。
 。
。
3 算 例
选取道路工程中常用的双圆荷载计算模型,假设沥青混凝土面层厚度为20 cm。由于荷载和结构的对称性,此处仅取模型的1/4进行计算(见图1)。
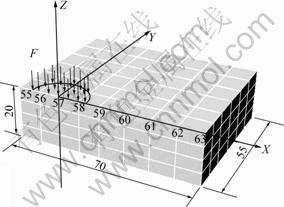
图1 计算模型 (单位:cm)
Fig.1 Computational model
采用Burgers粘弹性本构:E1=1 664 MPa,η1= 1.795×106 N?s/m,E2=1 0877 MPa,η2=9.576×104 N?s/m,泊松比为0.3。圆面内施加峰值为0.7 MPa的均布荷载(见图2)。
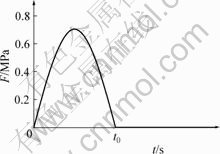
图2 半正弦均布荷载
Fig.2 Semi-sinusoid moving load
取常见边界:沥青面层与基层间不透水,即模型底面不透水,而顶面除双圆面外均透水。由于面层施工时骨料的离析以及压实的不均匀往往会造成孔隙率不均匀,因此,假定模型侧面(除去2个对称面)不透水具有一定的合理性。
因为渗透系数和加载速率是影响动水压力最主要的2个因素,所以,此处选半正弦荷载历时(t0)分别为0.005,0.01,0.1和1 s 4种情况,而渗透系数(kx= ky= kz)分别取0.000 1,0.001和0.01 cm/s,共12种组合计算。结果见表1和图3~6。
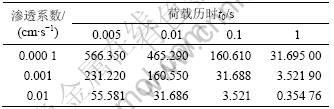
表1 不同渗透系数和加载速率组合下的孔隙水压力峰值
Table 1 Peak values of pore water pressure with different permeability coefficients and loading speeds kPa
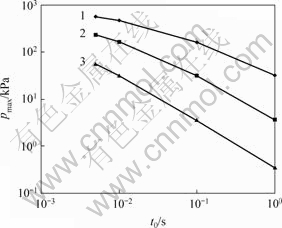
渗透系数/(cm?s-1): 1—0.000 1; 2—0.001; 3—0.01
图3 动水压力峰值随渗透系数和半正弦历时变化曲线图
Fig.3 Peak value curves of pore water pressure
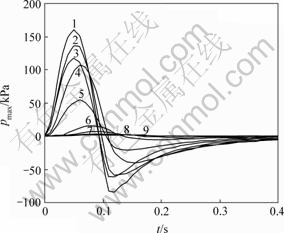
点号:1—57;2—56;3—58;4—55;5—59;6—60;7—61;8—62;9—63
图4 节点55~63处孔隙水压力随时间变化图
Fig.4 Graph of pore water pressure on nodes (55 to 63) varying with time
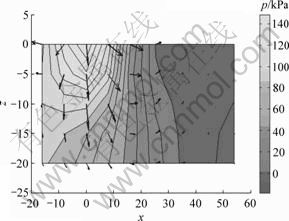
图5 0.05 s时刻y=0竖直面水压力云图与流速场
Fig.5 Contour of pore water pressure & quiver of water velocity on vertical section (y=0) at 0.05 s
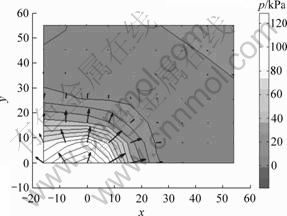
图6 0.05 s时刻z=-5 cm水平面处水压力云图与流速场
取Y=ln pmax,K=ln kw,T=ln t0,对表1中数据进行拟合,可得:
a. 双线性关系方程,
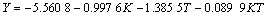 。(7)
。(7)
b. 双二次关系方程,
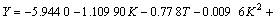
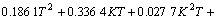
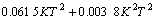 。 (8)
。 (8)
此处只列举渗透系数为0.000 1 cm/s,半正弦荷载历时0.1 s情况下动水压力随时间变化图,以及达到峰值时的水压力云图和流速场,如图4~6所示。
由图4可以看出,在半正弦荷载作用下,沥青混凝土内动水压力也呈现出相似的波动状态,不同的是,外荷载撤除以后,动水压力并未立即消失,而是相应地延迟一段时间后,逐渐消散至0(因为本文以1×105 Pa作为水压力基准,所以,允许出现负的水压力,同时,此处指的0水压力实际上是1×105 Pa)。另外,计算区域内的动水压力峰值出现在外荷载作用点处,并且在此点附近,水压力反应与外力的波动几乎同时。而与荷载作用点越远的地方,水压力越小,相位越滞后,
Fig.6 Contour of pore water pressure & quiver of water velocity on horizontal section (z=-5 cm) at 0.05 s
表现为曲线更加平缓,具有明显的波动状态。
由图5和图6还可以看出,荷载作用下方压力梯度和水流速度最大,而边缘处由于不排水限制,水压力略有增大。
另外,由图3及式(7)和(8)可以看出,渗透系数和半正弦荷载历时对动水压力峰值的影响具有相似性。
若假定它们都可以近似表示为: (x为kw或t0,b>0),则
(x为kw或t0,b>0),则
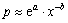 。
。
即每种因素是近似于负指数影响的。
许永等[13-14]认为当孔隙率为5%~8%时,渗透系数的数量级为0.000 1 cm/s,若考虑行车速度为80 km/h,可得出水压力为400~600 kPa,与文献[15]中的结论一致,可以间接证明此方法的有效性。
4 结 论
a. 利用Biot固结方程和水渗流方程,结合热粘弹性理论,耦合形成的动水压力有限元格式,对模拟动载作用下的沥青混凝土受力状态和水压力变化行之 有效。
b. 沥青路面在饱水状态时,其应力、应变及动水压力随着外荷载的波动而呈周期性地波动。并且距荷载作用处越远的点,这种波动的振幅越小,相位越滞后。
c. 沥青混凝土的渗透系数和车轮荷载作用时间是影响孔隙水压力峰值的2个主要因素,它们与水压力峰值间的关系均近似为负指数关系。
参考文献:
[1] 沙庆林. 高速公路沥青路面早期破坏与对策[J]. 长沙理工大学学报: 自然科学版, 2006, 3(3): 1-6.
SHA Qing-lin. The premature damage of bituminous pavement on expressway and the countermeasures[J]. Journal of Changsha University of Science and Technology: Natural Science, 2006, 3(3): 1-6.
[2] 王端宜, 邹桂莲, 韩传岱. 对沥青路面水损害早期破坏的认识[J]. 东北公路, 2001, 24(1): 23-25.
WANG Duan-yi, ZOU Gui-lian, HAN Chuan-dai. Early realization for water damage of asphalt pavement[J]. Northeastern Highway, 2001, 24(1): 23-25.
[3] Stuart K D. Moisture damage in asphalt mixtures—A state-of-the-art[R]. Georgetown: Department of Transportation, 1990.
[4] 孙立军, 张宏超, 刘黎萍, 等. 沥青路面初期损坏特点和机理分析[J]. 同济大学学报, 2002, 30(4): 416-421.
SUN Li-jun, ZHANG Hong-chao, LIU Li-ping, et al. Characteristics and mechanism of initial failures on asphalt pavement[J]. Journal of Tongji University, 2002, 30(4): 416-421.
[5] Hoven J M. Measurement and analysis of pore water pressure in thawing pavement structures subjected to dynamic loading[D]. Minneapolis: The University of Minnesota, 1997: 7-1-7-8.
[6] 彭永恒, 任瑞波, 宋凤立, 等. 轴对称条件下层状弹性体超孔隙水压力的求解[J]. 工程力学, 2004, 21(4): 204-208.
PENG Yong-heng, REN Rui-bo, SONG Feng-li, et al. An axisymmetric solution of multi-layered elastic body super-pressure in small opening water[J]. Engineering Mechanics, 2004, 21(4): 204-208.
[7] 钟 阳, 陈静云, 王 龙, 等. 求解动荷载作用下多层粘弹性半空轴对称问题的精确刚度矩阵法[J]. 计算力学学报, 2003, 20(6): 749-755.
ZHONG Yang, CHEN Jing-yun, WANG Long, et al. Explicit solution for dynamic response of axisymmetrical problems in multilayered viscoelastic half space by exact stiffness matrix method[J]. Chinese Journal of Computational Mechanics, 2003, 20(6): 749-755.
[8] 任瑞波, 谭忆秋, 钟岱辉. 沥青路面粘弹性问题的理论分析[J]. 四川建筑科学研究, 2004, 30(1): 76-79.
REN Rui-bo, TAN Yi-qiu, ZHONG Dai-hui. The theoretical analysis of visco-elastic question on asphalt pavement[J]. Sichuan Building Science, 2004, 30(1): 76-79.
[9] 张义同. 热粘弹性理论[M]. 天津: 天津大学出版社, 2002: 19-21.
ZHANG Yi-tong. Theory of thermo-viscoelasticity[M]. Tianjin: Tianjin University Press, 2002: 19-21.
[10] Biot M A. Theory of propagation of elastic waves in a fluid saturated porous solid[J]. The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 1956, 28(2): 166-191.
[11] 王勖成. 有限单元法[M]. 北京: 清华大学出版社, 2003: 14-28.
WANG Xu-cheng. Finite element method[M]. Beijing: Tsinghua University Press, 2003: 14-28.
[12] 李 宁, 陈飞熊. 饱和土体固-液两相介质动力耦合问题有限元解析[J]. 西安公路交通大学学报, 1999, 19(4): 6-10.
LI Ning, CHEN Fei-xiong. FEM modeling of dynamic consolidation and liquefaction in the saturated soil[J]. Journal of Xi’an Highway University, 1999, 19(4): 6-10.
[13] 许 永, 赵鸿铎. 沥青混凝土路面渗水规律研究[J]. 城市道桥与防洪. 2005, 7(4): 123-124.
XU Yong, ZHAO Hong-duo. Study on penetration rule of bituminous concrete pavement[J]. Urban Roads Bridges and Flood Control, 2005, 7(4): 123-124.
[14] 张宏超, 孙立军. 沥青路面早期损坏的现象与试验分析[J]. 同济大学学报: 自然科学版, 2006, 34(3): 331-334.
ZHANG Hong-chao, SUN Li-jun. Development and analysis of premature failures of the asphalt pavements[J]. Journal of Tongji University: Natural Science, 2006, 34(3): 331-334.
[15] 罗志刚, 周志刚, 郑健龙, 等. 沥青路面水损害分析[J]. 长沙交通学院学报, 2005, 21(3): 35-36.
LUO Zhi-gang, ZHOU Zhi-gang, Zheng Jian-long, et al. Analysis of the moisture damage in asphalt pavement[J]. Journal of Changsha Communications University, 2005, 21(3): 35-36.
收稿日期:2007-12-04;修回日期:2008-03-20
基金项目:国家自然科学基金资助项目(50578031)
通信作者:周长红(1980-),男,山东肥城人,博士,从事沥青路面水损害研究及其数值计算;电话:13124115580;E-mail: zch_sdu@sohu.com