DOI: 10.11817/j.issn.1672-7207.2019.09.027
油菜秆热解过程中重金属形态研究
朱明伟,蒋绍坚,付国富,蔡攀,王凯,王浩
(中南大学 能源科学与工程学院,湖南 长沙,410083)
摘要:采用BCR连续提取法研究修复植物油菜秆和生物炭中重金属形态,并利用风险评估指数对重金属的环境污染风险进行评估。研究结果表明:随热解温度的升高,各重金属残渣态质量分数增大,Cd,Cu,Mn和Pb的稳定性增强,生物有效性降低,而Zn由于酸溶态质量分数增大,稳定性减弱;随热解时间的延长,Cd和Cu的可氧化态质量分数减小,残渣态质量分数增大,Zn的可还原态质量分数减小,可氧化态与残渣态总质量分数增大,Mn和Pb的各形态质量分数保持相对稳定;热解可有效降低重金属的污染风险。
关键词:修复植物;热解;重金属形态;生物有效性
中图分类号:TK6 文献标志码:A 文章编号:1672-7207(2019)09-2304-06
Morphology of heavy metals in process of pyrolysis of rape stalk
ZHU Mingwei, JIANG Shaojian, FU Guofu, CAI Pan, WANG Kai, WANG Hao
(School of Energy and Engineering, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China)
Abstract: BCR sequential extraction was performed to analyze the morphology of heavy metals(HMs) in rape straw and biochar prepared under different pyrolysis temperature and time, and the environmental potential risk of HMs was evaluated by risk assessment code. The results show that a significant portion of HMs is embodied in the residue with the rising temperature, and the stability of Cd, Cu, Mn and Pb is enhanced, which indicates lower bioavailability. However, with the increase of temperature, the stability of Zn is weakened due to the increase of acid soluble fraction. With the prolongation of pyrolysis time, the proportion of oxidizable fraction of Cd and Cu decreases,while residual fraction increases. The percentage of reducible fraction of Zn decreases, but the total percentages of oxidizable and residual fraction increase. However, there was no remarkable change in the speciation of Mn and Pb. According to risk assessment code, the environmental potential risk of HMs is markedly mitigated.
Key words: phytoremediating plants; pyrolysis; morphology of heavy metal; bioavailability
近年来,全球土壤重金属污染日益严重,目前修复重金属污染土壤的方法主要有物理、化学和生物修复法等[1],其中植物修复法在重金属污染土壤修复治理方面得到广泛关注。修复植物吸收土壤中的重金属,将重金属转移、贮存于体内,从而降低土壤中重金属的含量,植物修复法具有成本低廉、治理效果稳定、能大规模原位治理和保持土壤生产力等优点,被认为是最有应用前景的修复方法[2]。然而,采用植物修复法会产生大量富集重金属的生物质,处置不当容易造成重金属二次污染,因此,对修复植物收获物进行有效的后续处理是治理土壤重金属污染的重要环节。目前,国内外处置修复植物的方法主要有焚烧法、灰化法和热解法等[3],采用焚烧法和灰化法处置含重金属生物质均存在较大的重金属二次污染风险[4]。有研究表明:热解法可以使重金属富集在产物炭中降低二次污染风险,具有较好的应用情景。STALS等[5]通过快速热解修复植物发现,产物油中Cu和Zn质量分数均低于0.000 5%,Cd和Pb质量分数均低于0.000 1%,重金属几乎全部富集在生物炭中;LIEVENS等[6]利用管式炉反应器对富集Cd,Cu,Pb和Zn的柳树枝叶进行了热解处理,发现重金属大部分残留在固体产物中。然而,重金属在环境中的迁移性、生物有效性、活性取决于其赋存形态[7-8],因此,研究生物炭中重金属的化学形态对其环境化学行为有重要的意义。本文作者采用BCR连续提取法对油菜秆和产物炭中重金属形态进行研究,研究热解温度和时间对重金属形态的影响,并采用环境风险评估指数对重金属的环境污染风险进行评估,为修复植物的无害化处理和资源化利用提供理论依据。
1 实验部分
1.1 实验原料
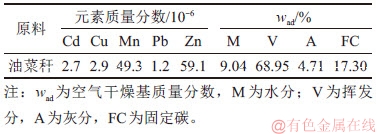
实验油菜秆源自湘潭某受重金属污染的农田试验基地,自然晒干切段,粉碎后选择直径小于0.9 mm的油菜秆颗粒。油菜杆工业分析和重金属元素分析结果如表1所示。
表1 油菜秆的元素分析和工业分析
Tabel 1 Elemental analysis and proximate analysis of rape stalk
1.2 热解实验
通过TCGC-1200型真空管式炉制备生物炭,选择N2作为实验气氛,升温速率为15 ℃/min,制备方案如表2所示。
实验步骤如下:
1) 称取油菜秆原料(20.00±0.01) g,装入100 mL称好质量的瓷坩埚中并加盖;
2) 将瓷坩埚放入管式炉,通保护气体,根据表2设定升温程序;
3) 待热解反应温度达到设定温度并停留预定时间后,停止加热;
4) 待坩埚冷却至室温,收取并称量坩埚和热解残渣。
表2 N2气氛下热解油菜秆制备生物炭实验方案
Table 2 Experimental scheme of pyrolysis of rape stalk under N2 atmosphere

1.3 BCR连续提取
欧盟标准物质局(BCR)连续提取法,将重金属形态分为酸溶态、可还原态、可氧化态与残渣态[9-10]。其中,酸溶态重金属包括水溶态重金属、可交换态重金属和碳酸盐结合态重金属,易迁移转化,对环境危害最大;可还原态重金属主要与无定形的铁锰氧化物、水化氧化物结合,在还原条件下较易释放;可氧化态重金属主要与有机质、硫化物结合,当环境氧化还原电位较高时,有机质分子可能发生降解,重金属被释放,被认为是较稳定的形态,对环境危害较小;残渣态重金属主要与硅酸盐、结晶铁镁氧化物等结合,其稳定性较强,能够长期稳定存在。
采用BCR连续提取法对油菜秆和生物炭中各重金属的酸溶态、可还原态、可氧化态与残渣态依次进行提取,提取液中重金属的浓度通过全谱直读等离子体发射光谱仪(ICP-OES:德国斯派克分析仪器公司)测定。BCR连续提取过程如图1所示。
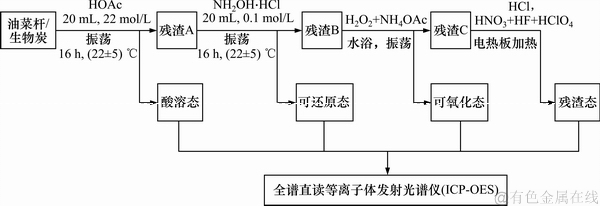
图1 BCR连续提取实验流程图
Fig. 1 Flow chart of BCR continuous extraction method
1.4 环境风险评估
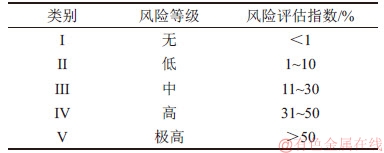
在重金属各形态中,酸溶态具有较强的生物有效性,在自然环境中最容易被植物直接吸收利用,可还原态与可氧化态虽可被植物间接利用,但需要在一定的理化条件下才释放生物有效性,残渣态中的重金属元素因其主要赋存于化学性质稳定的硅酸盐等矿物质中,故几乎不被生物利用[11]。在各重金属形态中,酸溶态可直接被植物吸收利用,具有较大的环境污染风险,为了评估油菜秆和生物炭中重金属的环境污染风险,引入风险评估指数(RAC),该指数已被广泛应用于环境科学领域的重金属毒性评估[12],计算式为
R=CF1/CHM×100% (1)
式中,R为风险评估指数,%;CF1为重金属酸溶态质量分数;CHM为重金属各形态总质量分数。
根据RAC对重金属的环境风险进行分级,重金属环境污染风险等级划分[13]如表3所示。
表3 重金属环境污染风险等级划分
Table 3 Classification of heavy metal environmental pollution risk
2 结果与分析
2.1 热解温度对重金属形态分布的影响
油菜秆原料标记为RS,在400,500和600 ℃条件下制备的生物炭分别标记为BCT400,BCT500和BCT600。油菜秆与BCT400,BCT500和BCT600中重金属形态分布如图2所示。
由图2(a)可知:Cd在油菜秆中主要以可还原态和可氧化态存在,分别占37.5%和39.7%,残渣态仅为4.6%;随热解温度的升高,可氧化态和残渣态逐渐增加,可还原态逐渐减少,稳定性增强,这与夏娟娟等[10]的研究结论一致,但考虑到Cd元素易挥发,因此,热解温度不宜太高。
由图2(b)可知:Cu在油菜秆中主要以可氧化态存在,占64.6%;生物炭中仅有可氧化态和残渣态,且当热解温度从400 ℃升高至600 ℃过程中,可氧化态由64.0%减少至42.6%,残渣态由36.0%增加至57.4%,说明热解可有效降低Cu的酸溶态和可还原态,热解温度升高促进可氧化态向残渣态的转化,进一步降低了Cu的污染风险。
由图2(c)可知:Mn在油菜秆中主要以酸溶态存在,占51.8%,可氧化态和残渣态之和不足20.0%;生物炭中Mn的可氧化态明显增加,随热解温度的升高,生物炭中残渣态逐渐增加,酸溶态和可还原态逐渐减少,降低了Mn的生物有效性。
据图2(d)可知:油菜秆和生物炭中Pb的可氧化态和残渣态总质量分数均在87.5%以上;生物炭中未检测到酸溶态,随热解温度的升高,生物炭中可氧化态Pb逐渐减少,残渣态逐渐增加,可还原态基本不变。说明热解可促进可氧化态向残渣态的转化,原因是热解温度升高使得可氧化态Pb随生物炭中有机质的分解与转化不断被释放,并与残渣态中某些难提取的物质结合,形成化学性质稳定的残渣态[14]。
据图2(e)可知:Zn在油菜秆中的酸溶态和可还原态总质量分数高达69.8%;热解后,酸溶态和可还原态大幅降低,但酸溶态Zn随热解温度的升高而增加,热解温度升高使Zn的稳定性减弱,这与SHAO等[15]的研究结果一致。
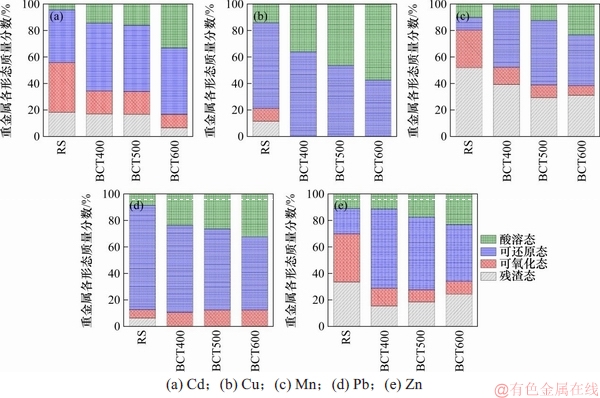
图2 不同热解温度条件下重金属形态分布
Fig. 2 Distribution of heavy metals at different pyrolysis temperatures
2.2 热解时间对重金属形态分布的影响
热解时间分别为10,30和50 min条件下制备的生物炭分别被标记为BCt10,BCt30和BCt50,油菜秆与BCt10,BCt30和BCt50中重金属形态分布如图3所示。
由图3可知:重金属Cd,Mn和Zn在油菜秆、BCt10、BCt30和BCt50生物炭中均存在酸溶态、可还原态、可氧化态和残渣态,但可氧化态与残渣态的总质量分数分别从油菜秆中的44.2%,19.7%和30.2%增加到生物炭中的64.9~72.2%,55.3%~67.2%和51.7%~68.9%;Cu和Pb在生物炭中不存在酸溶态。这说明热解过程使重金属的稳定性增强,生物有效性降低。
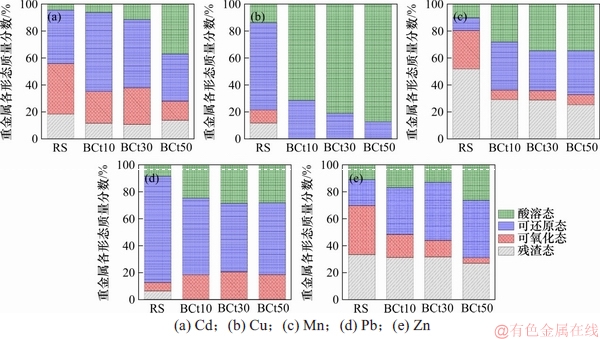
图3 不同热解时间条件下重金属形态分布
Fig. 3 Distribution of heavy metals at different pyrolysis time conditions
Cd,Mn和Zn在3种生物炭中的形态分布呈现了一定的差异性:随热解时间的延长,Cd的残渣态明显增加,可氧化态快速减小,但可还原态和酸溶态总质量分数变化不大,说明热解时间的延长主要促进了Cd的可氧化态向残渣态的转化;随着热解时间延长,Mn的各形态保持相对稳定,Zn的酸溶态基本保持不变,可还原态快速减小,可氧化态快速增加,说明Zn的可还原态主要转化成可氧化态。
由图3(b)可知:Cu在生物炭中以可氧化态和残渣态存在,当热解时间从10 min增加到30 min过程中,可氧化态质量分数由28.4%减少到12.6%,残渣态质量分数由71.6%增加到87.4%,说明热解时间延长促进可氧化态转化为残渣态,与图2(b)表现出了一致的变化趋势,但可氧化态转化程度明显大于残渣态,这可能是由于可氧化态的热解温度更高的原因,说明温度是影响热解过程重金属形态的主因子,这与王君等[16]的研究结论一致。由图3(d)可知:Pb在生物炭中以可还原态、可氧化态和残渣态存在,可还原态质量分数仅为20.0%左右,热解时间变化过程中,Pb各形态质量分数保持相对稳定。
2.3 重金属环境风险分析
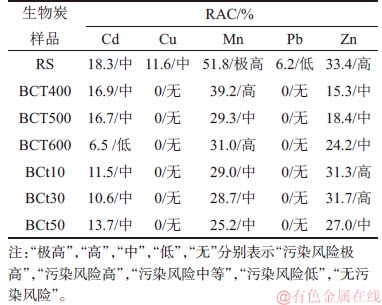
油菜秆与生物炭中的重金属生态风险评估结果如表4所示。从表4可知:Cu和Pb在油菜秆中分别表现出中和低污染风险,说明在生态环境中具有一定的生物毒性,但热解后生物炭中的Cu和Pb对环境不再具有污染性,表明热解可以降低油菜秆中的Cu和Pb生物毒性;油菜秆和生物炭中的Cd和Zn对环境都具有一定的污染风险;油菜秆中Mn具有极高的污染风险,但在生物炭中污染风险降低。整体而言,热解过程降低了油菜秆中重金属的环境污染风险,削弱了重金属的生物有效性,但如果将生物炭应用于土壤修复或污水处理等领域,则还需做进一步的处理,避免其中的Mn,Cd和Zn对生态环境造成“二次污染”。
表4 油菜秆与生物炭的重金属RAC
Table 4 RAC of heavy metal in rape stalk and biochar
3 结论
1) 油菜秆中的Cd主要以酸溶态和可还原态形态存在,其质量分数分别为37.5%和39.7%,Cu以可氧化态为主,占64.6%,Mn以酸溶态为主,占51.8%,Pb以可氧化态和残渣态为主,二者总质量分数占97.5%,Zn则以酸溶态和可还原态为主,二者总质量分数占69.8%;通过热解处置油菜秆,生物炭中各重金属的酸溶态或可还原态质量分数显著减小,有效降低了重金属的活性。
2) 随热解温度的升高,各重金属残渣态质量分数增大,Cd,Cu,Mn和Pb逐渐从不稳定的形态向相对稳定的形态转化,重金属稳定性增强,生物有效性降低;Zn由于其酸溶态质量分数随温度升高而增加,其稳定性减弱。
3) 随热解时间的延长,生物炭中Cd和Cu的可氧化态质量分数显著减小,残渣态质量分数快速增大;Zn的可还原态质量分数显著减小,可氧化态与残渣态总质量分数快速增大;然而,Mn和Pb的各形态质量分数保持相对稳定。
4) 油菜秆中的Cd,Cu,Mn,Pb和Zn均具有不同程度的环境污染风险,通过热解处置后,Cu和Pb不再具有污染性和毒性,其他重金属的污染风险和生物毒性降低,因此,生物炭应用于土壤修复、污水处理等领域之前还应做进一步的处理,以避免其中的Mn,Cd和Zn对生态环境造成二次污染。
参考文献:
[1] 樊霆, 叶文玲, 陈海燕, 等. 农田土壤重金属污染状况及修复技术研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2013, 22(10): 1727-1736.
FAN Ting, YE Wenling, CHEN Haiyan, et al. Review on contamination and remediation technology of heavy metal in agricultural soil[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2013, 22(10): 1727-1736.
[2] DILKS R T, MONETTE F, GLAUS M. The major parameters on biomass pyrolysis for hyper accumulative plants: a review[J]. Chemosphere, 2016, 146: 385-395.
[3] DELPLANQUE M, COLLET S, DEL GRATTA F, et al. Combustion of Salix used for phytoextraction: the fate of metals and viability of the processes[J]. Biomass and Bioenergy, 2013, 49: 160-170.
[4] 邢前国, 潘伟斌. 富含Cd、Pb植物焚烧处理方法的探讨[J]. 生态环境, 2004, 13(4): 585-586, 600.
XING Qianguo, PAN Weibin. On incineration of plants with high concentration of cadmium and lead[J]. 2004, 13(4): 585-586, 600.
[5] STALS M, THIJSSEN E, VANGRONSVELD J, et al. Flash pyrolysis of heavy metal contaminated biomass from phytoremediation: influence of temperature, entrained flow and wood/leaves blended pyrolysis on the behaviour of heavy metals[J]. Journal of Analytical and Applied Pyrolysis, 2010, 87(1): 1-7.
[6] LIEVENS C, CARLEER R, CORNELISSEN T, et al. Fast pyrolysis of heavy metal contaminated willow: influence of the plant part[J]. Fuel, 2009, 88(8): 1417-1425.
[7] 孙军, 邓四化, 徐俊, 等. 土壤重金属形态分析方法及其与环境风险的关系[J]. 上海电气技术, 2017, 10(2): 50-54.
SUN Jun, DENG Sihua, XU Jun, et al. Morphological analysis of heavy metals in soil and its relationship with environmental risk[J]. Journal of Shanghai Electric Technology, 2017, 10(2): 50-54.
[8] 赵述华, 陈志良, 张太平, 等. 稳定化处理对矿渣中重金属迁移转化的影响研究[J]. 环境科学, 2014, 35(4): 1548-1554.
ZHAO Shuhua, CHEN Zhiliang, ZHANG Taiping, et al. Effects of stabilization treatment on migration and transformation of heavy metals in mineral waste residues[J]. Environmental Science, 2014, 35(4): 1548-1554.
[9] RAURET G, L PEZ-S
PEZ-S NCHEZ J F, SAHUQUILLO A, et al. Improvement of the BCR three step sequential extraction procedure prior to the certification of new sediment and soil reference materials[J]. Journal of Environmental Monitoring, 1999, 1(1): 57-61.
NCHEZ J F, SAHUQUILLO A, et al. Improvement of the BCR three step sequential extraction procedure prior to the certification of new sediment and soil reference materials[J]. Journal of Environmental Monitoring, 1999, 1(1): 57-61.
[10] 夏娟娟, 赵增立, 李海滨, 等. 修复植物热解半焦中重金属形态分布研究[J]. 环境污染与防治, 2011, 33(1): 57-60.
XIA Juanjuan, ZHAO Zengli, LI Haibin, et al. Study on heavy metal speciation in char from pyrolysis of phytoremediating plants[J]. Environmental Pollution & Control, 2011, 33(1): 57-60.
[11] 刘晶晶, 杨兴, 陆扣萍, 等. 生物质炭对土壤重金属形态转化及其有效性的影响[J]. 环境科学学报, 2015, 35(11): 3679-3687.
LIU Jingjing, YANG Xing, LU Kouping, et al. Effect of bamboo and rice straw biochars on the transformation and bioavailability of heavy metals in soil[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2015, 35(11): 3679-3687.
[12] LI Lei, XU Z R, ZHANG Chunlei, et al. Quantitative evaluation of heavy metals in solid residues from sub- and super-critical water gasification of sewage sludge[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2012, 121: 169-175.
[13] HUANG Huajun, YUAN Xingzhong, ZENG Guangming, et al. Quantitative evaluation of heavy metals’ pollution hazards in liquefaction residues of sewage sludge[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2011, 102(22): 10346-10351.
[14] YUAN Xingzhong, HUANG Huajun, ZENG Guangming, et al. Total concentrations and chemical speciation of heavy metals in liquefaction residues of sewage sludge[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2011, 102(5): 4104-4110.
[15] SHAO Jianguang, YUAN Xingzhong, LENG Lijian, et al. The comparison of the migration and transformation behavior of heavy metals during pyrolysis and liquefaction of municipal sewage sludge, paper mill sludge, and slaughterhouse sludge[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2015, 198: 16-22.
[16] 王君, 陈娴, 桂丕, 等. 污泥炭化温度和时间对重金属形态及作物累积的影响[J]. 华南农业大学学报, 2015, 36(5): 54-60.
WANG Jun, CHEN Xian, GUI Pi, et al. Effects of pyrolysis temperature and time on the speciation and bioaccumulation of heavy metals derived from sludge[J]. Journal of South China Agricultural University, 2015, 36(5): 54-60.
(编辑 赵俊)
收稿日期: 2018 -11 -03; 修回日期: 2019 -01 -21
基金项目(Foundation item):国家自然科学基金资助项目(21577176) (Project (21577176) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China)
通信作者:蒋绍坚,教授,硕士生导师,从事低碳能源技术研究;E-mail:sjjiang@mail.csu.edu.cn