稀土元素对Al-Cu-Mg-Ag合金显微组织影响的研究进展
来源期刊:中国有色金属学报2009年第8期
论文作者:宋旼 肖代红 贺跃辉 张福勤
文章页码:1355 - 1365
关键词:Al-Cu-Mg-Ag合金;稀土;显微组织;力学性能;
Key words:Al-Cu-Mg-Ag alloy; rare earth; microstructures; mechanical properties
摘 要:Al-Cu-Mg-Ag合金展示了比传统Al-Cu及Al-Cu-Mg合金更加优异的室温与高温力学性能,源于其主要强化相(Ω相)有较好的热稳定性。然而该合金的使用温度仍然低于200 ℃,当温度超过200 ℃时,Ω相的粗化速率急剧增加,容易发生共格失稳而转变为θ相,从而降低合金的高温力学性能。研究表明通过添加合适的稀土或过渡族元素可以有效地抑制Ω相的生长速率,提高Ω相的形核密度和热稳定性,从而提高合金的高温力学性能。综述了Ce、Yb及Sc元素对Al-Cu-Mg-Ag合金显微组织与力学性能的影响,并探讨了Ce、Yb及Sc元素提高Ω相热稳定性的机理。
Abstract: Al-Cu-Mg-Ag alloys exhibit much better mechanical properties than traditional Al-Cu and Al-Cu-Mg alloys at both room- and elevated temperatures because of the good thermal stability of the main strengthening phase (Ω phase). However, this type of alloys can only be used under 200 ℃. When the temperature is above 200 ℃, the coarsening speed of Ω phase increases dramatically, and Ω phase is very easy to lose coherent with the matrix and changes to θ phase, which substantially decreases the mechanical properties of the alloys at elevated temperature. It is shown that adding proper rare earth or transient elements can substantially inhibit the growth speed of Ω phase, increase the nucleation density and thermal stability of Ω phase, and thus improve the mechanical properties of Al-Cu-Mg-Ag alloys. The effects of Ce, Yb and Sc on the microstructures and mechanical properties of Al-Cu-Mg-Ag alloys were reviewed, and the mechanisms of the effects of Ce, Yb and Sc on the thermal stability of Ω phase were discussed.
基金信息:国家高技术研究发展专项经费资助项目
教育部留学归国人员科研启动项目资助项目
湖南省自然科学基金资助项目
文章编号:1004-0609(2009)08-1355-11
宋 旼,肖代红,贺跃辉,张福勤
(中南大学 粉末冶金国家重点实验室,长沙 410083)
摘 要:Al-Cu-Mg-Ag合金展示了比传统Al-Cu及Al-Cu-Mg合金更加优异的室温与高温力学性能,源于其主要强化相(Ω相)有较好的热稳定性。然而该合金的使用温度仍然低于200 ℃,当温度超过200 ℃时,Ω相的粗化速率急剧增加,容易发生共格失稳而转变为θ相,从而降低合金的高温力学性能。研究表明通过添加合适的稀土或过渡族元素可以有效地抑制Ω相的生长速率,提高Ω相的形核密度和热稳定性,从而提高合金的高温力学性能。综述了Ce、Yb及Sc元素对Al-Cu-Mg-Ag合金显微组织与力学性能的影响,并探讨了Ce、Yb及Sc元素提高Ω相热稳定性的机理。
关键词:Al-Cu-Mg-Ag合金;稀土;显微组织;力学性能
中图分类号:TG 111.6 文献标识码: A
SONG Min, XIAO Dai-hong, HE Yue-hui, ZHANG Fu-qin
(State Key Laboratory of Powder Metallurgy, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China)
Abstract: Al-Cu-Mg-Ag alloys exhibit much better mechanical properties than traditional Al-Cu and Al-Cu-Mg alloys at both room- and elevated temperatures because of the good thermal stability of the main strengthening phase (Ω phase). However, this type of alloys can only be used under 200 ℃. When the temperature is above 200 ℃, the coarsening speed of Ω phase increases dramatically, and Ω phase is very easy to lose coherent with the matrix and changes to θ phase, which substantially decreases the mechanical properties of the alloys at elevated temperature. It is shown that adding proper rare earth or transient elements can substantially inhibit the growth speed of Ω phase, increase the nucleation density and thermal stability of Ω phase, and thus improve the mechanical properties of Al-Cu-Mg-Ag alloys. The effects of Ce, Yb and Sc on the microstructures and mechanical properties of Al-Cu-Mg-Ag alloys were reviewed, and the mechanisms of the effects of Ce, Yb and Sc on the thermal stability of Ω phase were discussed.
Key words: Al-Cu-Mg-Ag alloy; rare earth; microstructures; mechanical properties
Al-Cu-Mg系合金由于有良好的综合性能而被广泛地用作航空航天结构材料。然而该合金主要用于室温,当温度超过100 ℃时,由于其强化相(θ′相,S相)发生粗化而使性能显著下降[1]。POLMEAR等[2?10]发现,在高Cu/Mg质量比例的Al-Cu-Mg合金中加入微量Ag能使合金析出一种新的时效强化相(Ω相)。相对于Al-Cu-Mg合金中的主要强化相(θ′相,S相)来说,Ω相在较高的温度下(可达200 ℃)有着优良的抗粗化性能,从而不仅改善了合金室温和高温力学性能,还提高了合金的高温抗蠕变性能。尽管目前关于Ω相的晶体结构仍然存在争议,但大量的研究均表明Ω相与Al-Cu合金中的典型平衡θ相结构类似,且成分相同[11?31]。实际上,在Ω和θ相的结构模型中其晶格常数的差别非常小,以至于在250 ℃以上的温度下长时间时效将最终使得Ω相被θ平衡相所取代[15]。研究表明:Mg和Ag在Ω相的形核过程中均起到重要的作用,其中Mg是诱发Ω相形核的主要元素,而Ag起到Ω相形核催化剂的作用[11, 32]。当在Al-Cu合金中同时加入Mg和Ag元素时,Mg和Ag元素强烈的相互作用而形成原子簇,使得Mg原子沿基体的{111}面上偏聚(Mg原子簇)。由于Mg原子比Al原子大,Mg原子簇在Al基体中将会产生负畸变区。这种负畸变区的存在,促进了Cu原子沿基体{111}面上偏聚, 以减低给基体带来的晶格畸变,从而使得Mg原子簇成为Ω相的优先形核区域, 抑制了θ′相沿基体{100}面的形核。
大量研究[33?36]表明,Si的存在对Ω相的析出存在不利影响。合金中Mg-Si 原子间的强烈交互作用抑制了Ag-Mg原子团的形成,从而抑制了Ω相的析出。在Mg元素与Si元素相对质量比高时,Ω相形核没有被抑制,但是当Si含量过高时,合金中析出了σ相,Ω相形核被抑制。RAVIPRASAD等[34]在对添加了Ag和Si 的Al-2.5Cu-1.5Mg 进行研究时发现,Ag和Si原子的添加促进了多元原子团的形成;在高温时效过程中,合金沿〈100〉方向析出了针状GPB 区,同时还有X′相和Ω相,但是Ω相不如X′相稳定,在长时间时效后溶解。
尽管Al-Cu-Mg-Ag合金展示了优于Al-Cu及Al-Cu-Mg合金的室温与高温力学性能,但其使用温度不能超过200 ℃。当温度超过200 ℃时,Ω相的粗化速率将急剧增大,使得Ω相迅速发生共格失稳而转化成平衡θ相,从而显著地降低了合金的力学性能。HUTCHINSON等[37]指出:在Ω相应变场的周围可以存在空位或间隙原子以降低弹性应变能,而空位或间隙原子的存在取决于Ω相的厚度。由于Ω相与基体共格,存在周期性的空位错配度,在200 ℃以下空位在Ω相界面的聚集将显著地提高增厚台阶的形核能。当温度超过250 ℃时,增厚台阶的形核势垒降低,原子扩散速率加快,因此Ω相的粗化速率迅速增加。
为进一步提高Al-Cu-Mg-Ag合金的高温力学性能,提高Al-Cu-Mg-Ag合金的使用温度,许多科研 工作者展开了提高Ω相热稳定性的研究。大量的研 究[38?44]表明:通过添加合适的稀土元素可以有效地 提高Ω相的抗粗化性能和热稳定性,从而提高Al-Cu-Mg-Ag合金的力学性能和使用温度。本文作者就Ce、Yb及Sc等稀土元素对Ω相高温抗粗化性能及热稳定性的影响,以及对Al-Cu-Mg-Ag合金力学性能和显微组织的影响作一综合评述。
1 Ce对Al-Cu-Mg-Ag合金显微组织的影响
在所有的稀土元素中,Ce对Al-Cu-Mg-Ag合金力学性能和显微组织影响的研究最多[38?41]。XIAO和SONG等[38?41]均指出:Ce可以有效细化Al-Cu-Mg-Ag合金铸态组织的晶粒,增加Ω相的形核率,并通过阻碍Ω相的长大而提高Ω相的热稳定性,从而提高Al-Cu-Mg-Ag合金的室温与高温力学性能。
图1所示为Ce对Al-5.3Cu-0.8Mg-0.6Ag合金铸态晶粒度的影响[40]。从图1可以看出:不含Ce的Al-Cu-Mg-Ag合金的平均晶粒大小约为100 μm,而含0.2%Ce(质量分数)的Al-Cu-Mg-Ag合金的平均晶粒大小为45 μm,含0.45% Ce的Al-Cu-Mg-Ag合金的平均晶粒大小为30 μm左右,这表明添加微量Ce有利于细化晶粒。同时从图1可看出,含Ce的合金在晶界上有一薄层析出物,背散射电子分析表明,这些析出相是在晶界上生成的复杂稀土化合物。这些化合物中除Al外,还含有Cu、Ce、Mn 和Ag 等元素。Ce细化晶粒的作用除与稀土的变质作用有关外,还可作如下解释:Ce 的原子半径较大(0.18 nm),而Al的原子半径小(0.143 nm),其原子半径差超过15%,使得 Ce 在Al中固溶度低,在共晶温度下,Ce 在纯铝中的最大固溶度低于0.1%[45]。因此,Ce 主要富集在晶界上,或以微小的稀土化合物存在晶内,这些化合物可作为非均匀形核的核心。因此,添加微量的Ce有助于提高结晶的形核数目,从而降低晶粒的尺寸。
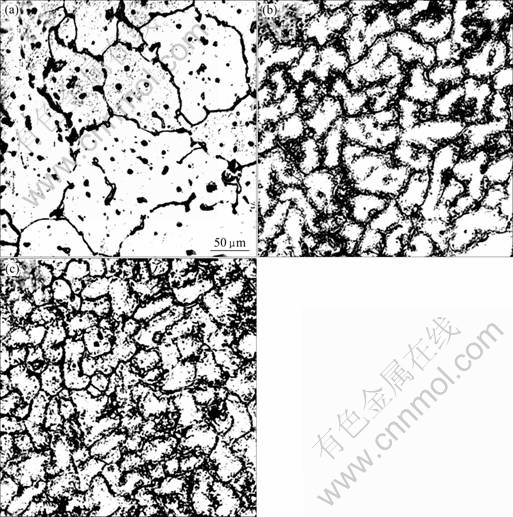
图1 Al-5.3Cu-0.8Mg-0.6Ag合金的铸态显微组织
Fig.1 As-cast microstructures of Al-5.3Cu-
0.8Mg-0.6Ag: (a) Without Ce; (b) With 0.2% Ce; (c) With 0.45% Ce[40] (with permission of original author)
图2所示为Ce对Al-5.3Cu-0.8Mg-0.6Ag合金在185 ℃下人工时效至峰值态显微组织的影响[40]。从图2可以看出,与不含Ce的Al-Cu-Mg-Ag合金相比,含Ce的Al-Cu-Mg-Ag合金中Ω相的尺寸较小、密度和体积分数较大,这表明Ce可以有效地提高Ω相的形核密度并抑制Ω相的生长速率。对于高Cu/Mg质量比例的Al-Cu-Mg-Ag合金来说,在时效的早期,基体的{111}面上分布着大量的Mg/Ag/空位簇,这些原子/空位簇是Ω相非均匀形核的中心[46]。最近的第一原理计算表明:Mg-Ag原子簇必须与Cu结合才能满足在基体的{111}面上稳定存在的力学条件[47],这种Mg-Ag-Cu原子簇即为Ω相的形核中心。当Ce元素加入到合金后,Ce原子通过置换取代基体中的Al原子。当Ce原子以置换形式存在于Al 基体中时,Ce原子周围造成较大的晶格畸变区,固溶处理后,基体中过饱和的空位在Ce 原子周围的偏聚可减小晶格畸变能和空位形成能,因此,在Ce 原子周围可能会形成空位对或空位簇。一些研究工作证实,Al基体中过饱和的空位往往优先沿着{111}密排面结合成空位盘[48],当空位盘足够大时,将塌卸成不全位错,其中包含着层错。这种不全位错在Sukuki气团的作用下,将更多地吸收周围的Mg和Ag 原子,形成更多的Mg/Ag/vacancy 聚合体,这些聚合体成为Ω相形核的核心,从而提高了Ω相的析出密度。早期的研究[38]还指出:Ce可以有效地降低Ω相的形核温度,抑制GP区的形核,从而加速Ω相的形核。

图2 Al-5.3Cu-0.8Mg-0.6Ag合金在185 ℃峰时效态的TEM像
Fig.2 TEM images of Al-5.3Cu-0.8Mg-0.6Ag alloys after aging to peak aged stage at 185 ℃: (a) Without Ce; (b) With 0.2% Ce; (c) With 0.45% Ce[40](with permission of original author)
图3所示为含与不含Ce的Al-5.3Cu-0.8Mg-0.6Ag合金在185 ℃下人工时效至峰值态后,再在300 ℃下退火处理20和100 h后的显微组织[40]。从图3可以看出,在300 ℃下继续退火处理20 h后,两种合金中的Ω相都仍然为片状,但不含Ce的合金中的Ω相远比含Ce合金中的Ω相要厚。在300 ℃下退火100 h后,不含Ce的合金中的亚稳Ω相已经被稳定的θ沉淀相所取代,而含Ce合金中的亚稳Ω相仍然存在,保持为片状,且片的厚度增加不大,但片的直径出现了显著增加。早期的研究表明:片状析出相的生长机制为台阶机制[23],而关于Ω相台阶形核势垒的研究在早期的文献中已有详细讨论[37?49],即 200 ℃下Ω相优异的抗粗化性能来源于生长台阶的缺乏,这种缺乏主要是由于台阶具有高的形核势垒。HUTCHINSON等[37]指出:在Ω相应变场的周围可以存在空位或间隙原子以降低弹性应变能,而空位或间隙原子的存在取决于Ω相的厚度。由于Ω相与基体共格,存在周期性的空位错配度,因此在250 ℃以下时空位在Ω相的聚集将显著地提高增厚台阶的形核能。当温度超过250 ℃时,增厚台阶的形核势垒降低,原子的扩散速率加快,因此Ω相的粗化速率迅速加快。这种高的粗化速率导致Ω相的尺寸迅速增加,最终与基体发生共格失稳,因此不含Ce的合金中的Ω相在300 ℃下退火100 h后转化为稳定的θ相。然而从图2可以看出,当含有Ce时,Al-Cu-Mg-Ag 合金在300 ℃下退火100 h后Ω相仍然保持为片状,与基体共格,并没有转化为稳定的θ相。这可能由两种机制造成。首先稀土元素Ce可以显著降低Cu元素在Al基体中的扩散速率[40]。由于Ω相的化学组成为Al2Cu,因此Cu元素扩散速率的降低将显著地抑制Ω相的粗化速率。其次由于稀土元素Ce在Al基体中的固溶度较低(即使在共晶温度固溶度也小于0.1%)[50],大量超过固溶度极限的Ce原子在凝固过程中聚集在晶界,而部分过饱和的Ce原子也聚集在Ω相与基体的相界面处以降低自由能。如前所述,Ce原子的半径远大于Al原子的半径,在Ce原子的周围将产生空位以降低弹性应变能,而空位在Ω相与基体界面的聚集将显著的提高增厚台阶的形核势垒,从而降低Ω相的粗化速率,提高了Ω相的热稳定性。
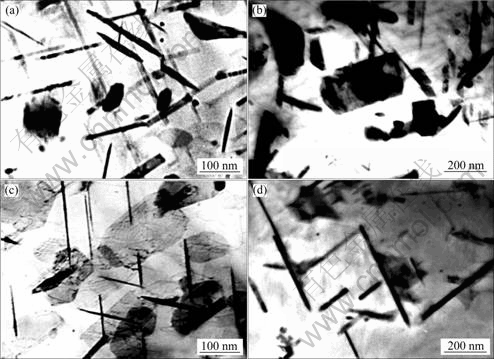
图3 Al-5.3Cu-0.8Mg-0.6Ag合金在185 ℃时效至峰值后,继续在300 ℃下退火的显微组织
Fig.3 Microstructures of Al-5.3Cu-0.8Mg-0.6Ag alloys after aging to peak-aged stage at 185 ℃ followed by annealing at 300 ℃: (a), (c) 20 h; (b), (d) 100 h; (a), (b) Without Ce; (c), (d) With 0.45% Ce[40] (with permission of original author)
2 Yb对Al-Cu-Mg-Ag合金显微组织的影响
XIAO等[42]研究了稀土元素Yb对Al-Cu-Mg-Ag合金力学性能和显微组织的影响,他们指出:与Ce类似,少量的Yb可以有效地细化Al-Cu-Mg-Ag合金铸态组织的晶粒,增加Ω相的形核率,并通过阻碍Ω相的长大而提高Ω相的热稳定性,从而提高Al-Cu-Mg-Ag合金的室温与高温力学性能。
图4所示为Yb对Al-5.3Cu-0.8Mg-0.6Ag-0.5Mn合金铸态晶粒度的影响[42]。从图4可以看出:不含Yb的Al-Cu-Mg-Ag合金的平均晶粒大小约为75 μm,而含0.15%(质量分数)Yb的Al-Cu-Mg-Ag合金的平均晶粒大小为25 μm,含0.25% Ce的Al-Cu-Mg-Ag合金的平均晶粒大小为20 μm左右,这表明添加微量Yb有利于细化晶粒。背散射电子分析表明,在含Yb的合金在晶界上还将形成复杂含Yb的稀土化合物。Yb细化晶粒的机制与Ce相同,即Yb 的原子半径较大,在Al 中固溶度低,主要富集在晶界或以微小的稀土化合物存在晶内,这些化合物可作为非均匀形核的核心。因此,添加微量的Yb有助于提高结晶的形核数目,从而降低晶粒的尺寸。

图4 Al-5.3Cu-0.8Mg-0.6Ag-0.5Mn合金的铸态显微组织
Fig.4 As-cast microstructures of Al-5.3Cu- 0.8Mg-0.6Ag-0.5Mn: (a) Without Yb; (b) With 0.15% Yb; (c) With 0.25% Yb[42] (with permission of original author)
图5所示为Yb对Al-5.3Cu-0.8Mg-0.6Ag-0.5Mn合金在185 ℃下人工时效至峰值态显微组织的影响[42]。从图5可以看出,与不含Yb的Al-Cu-Mg-Ag合金相比,含Yb的Al-Cu-Mg-Ag合金中Ω相的尺寸较小、密度和体积分数较大,这表明Yb可以有效地提高Ω相的形核密度并抑制Ω相的生长速率。同时图5还表明,Yb含量的适当提高可以有效地增加Ω相的形核密度。Yb提高Ω相的形核密度并抑制Ω相生长速率的机制与Ce类似,即当Yb元素加入到合金后,Yb原子通过置换取代基体中的Al原子,在周围造成较大的晶格畸变区。固溶处理后,基体中过饱和的空位在Yb原子周围的偏聚可减小晶格畸变能和空位形成能。空位团聚集到一定尺寸后将塌卸为不全位错,在Sukuki气团效应下,不全位错将更多地吸收周围的Mg和Ag 原子,形成更多的Mg/Ag/vacancy 聚合体,成为Ω相形核的核心,从而提高了Ω相的析出密度。

图5 Al-5.3Cu-0.8Mg-0.6Ag-0.5Mn合金在185 ℃峰时效态的TEM像
Fig.5 TEM images of Al-5.3Cu-0.8Mg- 0.6Ag-0.5Mn alloys after aging to peak aged stage at 185 ℃: (a) Without Yb; (b) With 0.15% Yb; (c) With 0.25% Yb[42] (with permission of original author)
图6所示为含Yb与不含Yb的Al-5.3Cu-0.8Mg- 0.6Ag-0.5Mn合金在300 ℃下人工时效120 h后的显微组织[42]。从图6可以看出,在300 ℃下退火处理120 h后,不含Yb的合金中的亚稳Ω相已经被稳定的θ沉淀相所取代,而含Yb合金中的亚稳Ω相仍然保持为片状。这表明Yb可以有效地提高Ω相的热稳定性和抗粗化速率。Yb提高Ω相的热稳定性和抗粗化速率的机制与Ce类似,即Yb在Al基体中的固溶度较低,大量超过固溶度极限的Yb原子在凝固过程中聚集在晶界,而部分过饱和的Yb原子也聚集在Ω相与基体的相界面处以降低自由能。如前所述,Yb原子的半径远大于Al 原子的半径,在Yb原子的周围将产生空位以降低弹性应变能,而空位在Ω相与基体界面的聚集将显著地提高增厚台阶的形核势垒,从而降低Ω相的粗化速率,提高了Ω相的热稳定性。
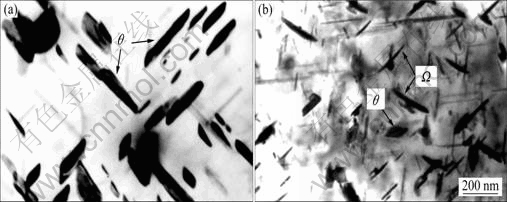
图6 Al-5.3Cu-0.8Mg-0.6Ag-0.5Mn合金在300 ℃时效120 h后的显微组织
Fig.6 Microstructures of Al-5.3Cu-0.8Mg-0.6Ag-0.5Mn alloys after aging for 120 h at 300 ℃: (a) Without Yb; (b) With 0.15% Yb[42] (with permission of original author)
3 Sc对Al-Cu-Mg-Ag合金力学性能和显微组织的影响XIAO等[43]最近研究了稀土元素Sc对Al-Cu-Mg- Ag合金力学性能和显微组织的影响,他们指出:适量的Sc可以有效地细化Al-Cu-Mg-Ag合金铸态组织的晶粒,增加Ω相的形核率,并通过阻碍Ω相的长大而提高Ω相的热稳定性,并抑制合金的动态再结晶,从而提高Al-Cu-Mg-Ag合金的室温与高温力学性能。
图7所示为Sc对Al-5.3Cu-0.8Mg-0.6Ag-0.2Zr合金铸态晶粒度的影响[43]。从图7可以看出:不含Sc及含0.1% Sc的Al-Cu-Mg-Ag合金铸态晶粒很大,超过200 μm,而当Sc的含量超过0.3%时,Al-Cu-Mg-Ag合金的晶粒尺寸急剧下降,约30 μm,这表明添加足够量的Sc可以有效地细化晶粒。对比图1、4和7可知,Sc细化晶粒的作用远大于Ce和Yb。实际上,Sc细化Al-Cu-Mg-Ag-Zr合金的机理与Sc细化其他铝合金的机理相同,即Sc与Zr在凝固过程中与Al结合形成稳定的Al3(Sc, Zr)弥散相,该相具有LI2结构,能抑制晶界迁移,从而显著地细化晶粒。值得注意的是,与Ce和Yb不同,Sc只有达到一定的浓度才能起到细化晶粒的作用,主要是因为Sc在Al基体中有较大的固溶度,只有含量超过固溶度并形成弥散相后才对合金的铸态晶粒起到明显的细化作用。
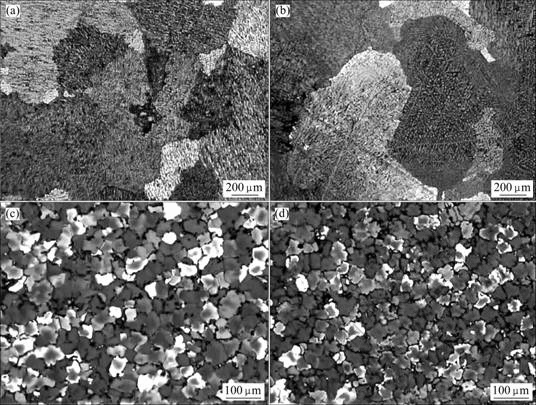
图7 Al-5.3Cu-0.8Mg-0.6Ag-0.2Zr合金的铸态显微组织
Fig.7 As-cast microstructures of Al-5.3Cu-0.8Mg-0.6Ag-0.2Zr: (a) Without Sc; (b) With 0.1% Sc; (c) With 0.3% Sc; (d) With 0.5% Sc[43] (with permission of original author)
图8所示为不含Sc以及含0.3% Sc的Al-5.3Cu-0.8Mg-0.6Ag-0.2Zr合金在185 ℃下人工时效至峰值态以及在300 ℃下时效50 h后的显微组 织[43]。从图8(a)和8(b)可以看出,在185 ℃下人工时效至峰值态,与不含Sc的Al-Cu-Mg-Ag合金相比,含0.3% Sc的Al-Cu-Mg-Ag合金中Ω相的尺寸较小、密度和体积分数较大,这表明Sc可以有效地提高Ω相的形核密度并抑制Ω相的生长速率。目前关于Sc提高Ω相的形核密度并抑制Ω相生长速率的机制还不清楚,但从含Sc的Al-Cu-Mg-Ag合金的时效硬化曲线[43]可知:Sc通过提高Ω相早期原子偏聚区的形核密度,从而提高了Ω相的形核密度。从图8(c)和8(d)可以看出,在300 ℃下时效50 h后,不含Sc的合金中的亚稳Ω相已经转变为平衡的θ相,而含0.3%Sc的合金中的Ω相仍然保持为片状,没有发生共格失稳,但已经发生了明显的长大,这表明Sc可以有效地提高Ω相的热稳定性。值得指出的是:Sc对Al-Cu-Mg-Ag合金显微组织更重要的影响是时效过程中在基体中析出了Al3(Sc, Zr)弥散相(如图8(b)所示),这种相在高温下比Ω相更加稳定,粗化速率更小,在合金的热变形过程中可以抑制晶界与亚晶界的迁移,从而抑制动态再结晶的发生。
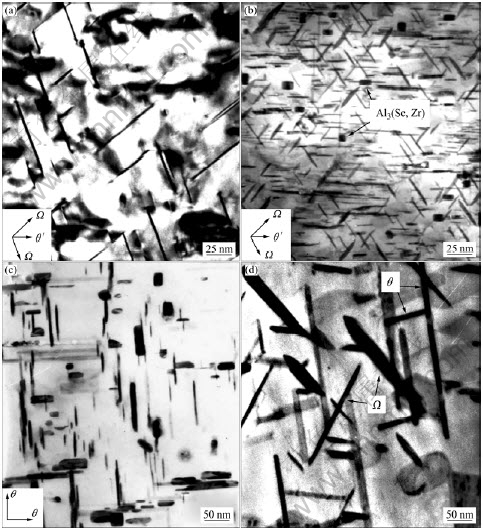
图8 Al-5.3Cu-0.8Mg-0.6Ag-0.2Zr合金在185 ℃峰时效态及300 ℃时效50 h的TEM像
Fig.8 TEM images of Al-5.3Cu-0.8Mg-0.6Ag-0.2Zr alloys after aging to peak aged stage at 185 ℃ and aging for 50 h at 300 ℃: (a) At 185 ℃, without Sc; (b) At 185 ℃, with 0.3%Sc; (c) At 300 ℃, without Sc; (d) At 300 ℃, with 0.3%Sc[43] (with permission of original author)
4 稀土元素对Al-Cu-Mg-Ag合金力学性能的影响
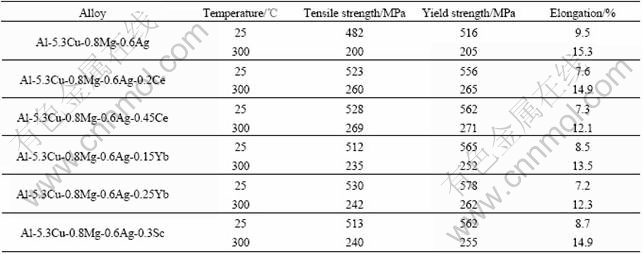
稀土元素Ce、Yb及Sc对Al-Cu-Mg-Ag合金力学性能的影响见表1[38, 42, 43]。从表1可以看出,在没有明显降低伸长率的情况下,Ce、Yb及Sc均能显著地提高Al-Cu-Mg-Ag合金室温和高温的屈服强度和抗拉强度。如前所述,Ce、Yb及Sc均能显著地提高Ω相的形核密度并抑制Ω相的生长速率,因此在含Ce、Yb及Sc的Al-Cu-Mg-Ag合金中,Ω相的密度更大、尺寸和间距更小,可以更有效地阻碍位错的运动,从而提高合金的室温力学性能。而高温下Ce、Yb及Sc可以有效地抑制Ω相的粗化速率,提高Ω相的热稳定性,从而提高Al-Cu-Mg-Ag合金的高温力学性能。值得注意的是,Sc对Al-Cu-Mg-Ag合金力学性能的影响不仅体现在提高Ω相的形核密度及热稳定性,还体现在Sc在基体中形成弥散相,抑制Al-Cu-Mg-Ag合金晶界与亚晶界的迁移、位错的运动以及动态再结晶过程,使得基体保持变形组织,这种强化机制与Sc强化其他铝合金的机制相同。XIAO等[43]还指出,尽管Sc强化效果明显,但含量不能太高,否则Sc与其他合金元素将在晶界形成较大尺寸的弥散相或结晶相,在变形过程中容易在晶界诱发微裂纹的产生,从而降低Al-Cu-Mg-Ag合金的室温与高温强度。
表1 稀土对Al-Cu-Mg-Ag合金力学性能的影响[38, 42, 43]
Table 1 Effects of rare earth on mechanical properties of Al-Cu-Mg-Ag alloy[38, 42, 43]
5 研究展望
到目前为止,稀土元素对Al-Cu-Mg-Ag合金显微组织和力学性能的影响已经得到了相应的研究。研究表明添加合适的Ce、Yb及Sc元素可以有效地抑制Ω相的生长速率,提高Ω相的形核密度和热稳定性,从而提高合金室温和高温力学性能。目前关于稀土对Al-Cu-Mg-Ag合金力学性能影响的研究均以瞬时拉伸为手段,由于Al-Cu-Mg-Ag合金主要应用于航空航天结构材料,通常需要在室温或高温下长时间使用,因此抗蠕变和抗疲劳性能是Al-Cu-Mg-Ag合金更加重要的性能指标。目前国内外关于稀土元素对Al-Cu-Mg-Ag合金室温及高温抗蠕变和抗疲劳性能影响的研究很少,未来研究的发展方向是进一步研究稀土元素对Al-Cu-Mg-Ag合金抗蠕变和抗疲劳性能的影响,从而拓展该合金的使用范围。
[1] POLMEAR I J, COUPLE M J. Design development of an experimental wrought aluminum alloy for use at elevated temperatures[J]. Metall Trans A, 1988, 19(4): 1027?1034.
[2] POLMEAR I J. The effects of small additions of silver on the aging of some aluminum alloy[J]. Trans Met Soc AJME, 1964, 230: 1331?1338.
[3] POLMEAR I J, CHESTER R J. Abnormal age hardening in an Al-Cu-Mg alloy containing silver and lithium[J]. Scripta Metall, 1989, 23: 1213?1217.
[4] POLMEAR I J. Recent development in light alloys[J]. Mater Trans JIM, 1996, 37(1): 12?31.
[5] SONG Min, CHEN Kang-hua, HUANG Lan-ping. Effects of Ag addition on mechanical properties and microstructures of Al-8Cu-0.5Mg alloy[J]. Trans Nonferrous Met Soc China, 2006, 16(4): 776?771.
[6] YU Ri-cheng, LIU Zhi-yi, LIU Yan-bin, XU Min, YAN Kuan, MA Fei-yue. Hot working process of a high strength heat resisting Al-Cu-Mg-Ag alloy[J]. Heat Treatment of Metals, 2006, 31(5): 75?79.
[7] SCULLY J R, LITTLE D A, CONNOLLY B J. An electrochemical framework to explain the intergranular stress corrosion behavior in two Al-Cu-Mg-Ag alloys as a function of aging[J]. Corrosion Science, 2007, 49(2): 347?372.
[8] LUMLEY R N, POLMEAR I J. The effect of long term creep exposure on the microstructure and properties of an underaged Al-Cu-Mg-Ag alloy[J]. Scripta Materialia, 2004, 50(9): 1227?1231.
[9] CHANG C H, LEE S L, LIN J C, YEH M S, JENG R R. Effect of Ag content and heat treatment on the stress corrosion cracking of Al-4.6Cu-0.3Mg alloy[J]. Materials Chemistry and Physics, 2005, 91(2/3): 454?462.
[10] SCULLY J R, LITTLE D A, CONNOLLY B J. An electrochemical framework to explain the intergranular stress corrosion behavior in two Al-Cu-Mg-Ag alloys as a function of aging[J]. Corrosion Science, 2007, 49(2): 347?372.
[11] MUDDLE B C, POLMEAR I J. The precipitate Ω phase in Al-Cu-Mg-Ag alloys[J]. Acta Metall Mater, 1989, 37(3): 777?789.
[12] REICH L, MURAYAMA M, HONO K. Evolution of Ω phase in an Al-Cu-Mg-Ag alloy—A three dimensional atom probe study[J]. Acta Mater, 1998, 46(17): 6053?6062.
[13] KERRY S, SCOTT V D. Structure and orientation relation of precipitates formed in Al-Cu-Mg-Ag alloys[J]. Metal Sci, 1984, 18(6): 289?294.
[14] AULD J H. Structure of metastable precipitate in some Al-Cu-Mg-Ag alloys[J]. Mater Sci Technol, 1986, 2(7): 784?787.
[15] SCOTT V D, KERRY S, TRUMPER R L. Nucleation and growth of precipitates in Al-Cu-Mg-Ag alloys[J]. Mater Sci Technol, 1987, 3(10): 827?835.
[16] GARG A, HOWE J M. Convergent-beam electron diffraction analysis of the Ω phase in an Al-4.0Cu-0.5Mg-0.5Ag alloy[J]. Acta Metall Mater, 1991, 39(8): 1939?1946.
[17] KNOWLES K M, STOBBS W M. The structure of {111} age-hardening precipitates in Al-Cu-Mg-Ag alloys[J]. Acta Crystallogr B, 1988, 44(3): 207?227.
[18] 李世晨, 郑子樵. 计算机模拟Al-Cu-(Mg)-(Ag)时效初期原子分布状态[J]. 中南工业大学学报: 自然科学版, 2000, 31(5): 441?444.
LI Shi-chen, ZHENG Zi-qiao. Computer simulation of distribution of the solutes in Al-Cu-(Mg)-(Ag) on initial aging stages[J]. J Cent South Univ Technol: Natural Science, 2000, 31(5): 441?444.
[19] 李世晨, 郑子樵, 刘组耀, 李 剑, 杨培勇, 殷顺高. Al-Cu-Li-xMg 合金时效初期微结构演变的Monte Carlo 模拟[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2005, 15(9): 1376?1383.
LI Shi-chen, ZHENG Zi-qiao, LIU Zu-yao, LI Jian, YANG Pei-yong, YIN Shun-gao. Monte Carlo simulation of microstructural evolution of Al-Cu-Li-xMg alloys during initial aging stage[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2005, 15(9): 1376?1383.
[20] 陈志国, 李世晨, 刘组耀, 郑子樵. 微合金化Al-4.0Cu-0.3Mg 合金时效初期微结构演变的计算机模拟[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2004, 14(8): 1274?1280.
CHEN Zhi-guo, LI Shi-chen, LIU Zu-yao, ZHENG Zi-qiao. Computer simulation of microstructural evolution of microalloyed Al-4.0Cu-0.3Mg alloys[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2004, 14(8): 1274?1280.
[21] 陈大钦, 郑子樵, 李世晨, 陈志国, 刘祖耀. 外加应力对Al-Cu 及Al-Cu-Mg-Ag 合金析出相生长的影响[J]. 金属学报, 2004, 40(8): 799?804.
CHEN Da-qin, ZHENG Zi-qiao, LI Shi-chen, CHEN Zhi-guo, LIU Zu-yao. Effect of external stress on the growth of precipitates in Al-Cu and Al-Cu-Mg-Ag alloys[J]. Acta Metall Sinica, 2004, 40(8): 799?804.
[22] FONDA R W, CASSADA W A, SHIFLET G J. Accommodation of the misfit strain surrounding {111} precipitates (Ω) in Al-Cu-Mg-(Ag)[J]. Acta Metall Mater, 1992, 40: 2539?2546.
[23] 宋 旼, 陈康华, 黄兰萍. Al-Cu-Mg-(Ag)合金中时效析出相的生长动力学研究[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2006, 16(8): 1313?1319.
SONG Min, CHEN Kang-hua, HUANG Lan-ping. Precipitation and growth dynamics of precipitates in Al-Cu-Mg-(Ag) alloy during aging[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2006, 16(8): 1313?1319.
[24] POLMEAR I J, PONS G, OCTOR H, SANCHEZ C, MORTON A, BORBIDGE W, ROGERS S. After concorde: Evaluation of an Al-Cu-Mg-Ag alloy for use in the proposed European SST[J]. Materials Science Forum, 1996, 217/222(part 3): 1759?1764.
[25] AULD J H. Structure of a metastable precipitate in an Al-Cu-Mg-Ag alloy[J]. Acta Crystallogr A, 1972, 28: S98.
[26] TAYLOR J A, PARKER B A, POLMEAR I J. Precipitation in Al-Cu-Mg-Ag casting alloy[J]. Metal Science, 1978, 12(10): 478?482.
[27] CHESTER R J, POLMEAR I J. Precipitation in Al-Cu-Mg-Ag alloys[J]. Institution of Metallurgists (Course volume), 1983, 3(20): 75?81.
[28] KERRY S, SCOTT V D. Structure of precipitate in Al-Cu-Mg-Ag alloy[J]. Archiwum Naukio Materialach, 1985, 6(2): 79?86.
[29] MUKHOPADHYAY A K, GUNTHER E, BIRGIT S. Nucleation of Ω phase in an Al-Cu-Mg-Mn-Ag alloy aged at temperatures below 200 ℃[J]. Scripta Materialia, 2001, 44(4): 545?551.
[30] HONO K, SANO N, BABU S S, OKANO R, SAKURAI T. Atom probe study of the precipitation process in Al-Cu-Mg-Ag alloys[J]. Acta Metallurgica et Materialia, 1993, 41(3): 829?838.
[31] CHESTER R J, POLMEAR I J. TEM investigation of precipitates in Al-Cu-Mg-Ag and Al-Cu-Mg alloys[J]. Micron, 1980, 11(3/4): 311?312.
[32] CHESTER R J, POLMEAR I J. The metallurgy of light metals[M]. London: Institute of Metals, 1983: 69?75.
[33] GAO X, NIE J F, MUDDLE B C. Effects of Si additions on the precipitation hardening response in Al-Cu-Mg(-Ag) alloys[J]. Materials Science Forum, 1996, 217/222(part 2): 1251?1256.
[34] RAVIPRASAD K, HUTCHINSON C R, SAKURAI T, RINGER S P. Precipitation processes in an Al-2.5Cu-1.5Mg(%) alloy microalloyed with Ag and Si[J]. Acta Materialia, 2003, 51(17): 5037?5050.
[35] BARLOW I C, RAINFORTH W M, JONES H. Role of silicon in the formation of the Al5Cu6Mg2 phase in Al-Cu-Mg alloys[J]. Journal of Materials Science, 2000, 35(6): 1413?1418.
[36] GABLE B M, SHIFLET G J, STARKE E A Jr. The effect of Si additions on omega precipitation in Al-Cu-Mg-(Ag) alloys[J]. Scripta Materialia, 2004, 50(1): 149?153.
[37] HUTCHINSON C R, FAN X, PENNYCOOK S J, SHIFLET G J. On the origin of the high coarsening resistance of Ω plates in Al-Cu-Mg-Ag alloys[J]. Acta Metall, 2001, 49(14): 2827?2841.
[38] XIAO D H, WANG J N, DING D Y, CHEN S P. Effect of rare earth Ce addition on the microstructure and mechanical properties of an Al-Cu-Mg-Ag alloy[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2003, 352: 84?88.
[39] 肖代红, 王健农, 陈世朴, 丁冬雁. 铈对高Cu/Mg比率Al-Cu-Mg合金组织和耐热性能的影响[J]. 中国稀土学报, 2003, 21(5): 564?567.
XIAO Dai-hong, WANG Jian-nong, CHEN Shi-pu, DING Dong-yan. Effect of Ce addition on microstructure and elevated temperature properties in Al-Cu-Mg alloy with high Cu/Mg ratio[J]. Journal of the Chinese Rare Earth Society, 2003, 21(5): 564?567.
[40] 肖代红, 陈康华, 宋 旼. 铈对Al-Cu-Mg-Ag合金时效析出与显微组织的影响[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2007, 17(5): 669?675.
XIAO Dai-hong, CHEN Kang-hua, SONG Min. Effect of cerium addition on precipitation and microstructure of Al-Cu-Mg-Ag alloys[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2007, 17(5): 669?675.
[41] SONG M, CHEN K H, HUANG L P. Effects of Ce and Ti on the microstructures and mechanical properties of an Al-Cu-Mg-Ag alloy[J]. Rare Metals, 2007, 26(1): 28?32.
[42] XIAO D H, SONG M, CHEN K H, HUANG B Y. Effect of rare earth Yb addition on mechanical properties of Al-5.3Cu-0.8Mg-0.6Ag alloy[J]. Materials Science and Technology, 2007, 23(10): 1156?1160.
[43] XIAO D H, SONG M, HUANG B Y, YI J H, HE Y H, LI Y M. Effect of Sc addition on microstructure and mechanical properties of Al-Cu-Mg-Ag-Zr alloy[J]. Materials Science and Technology, 2009, 25(6): 747?752.
[44] 肖代红, 黄伯云, 宋 旼, 陈康华. Al-Cu-Mg-(Ag, La)合金的显微组织与力学性能[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2008, 18(4): 571?576.
XIAO Dai-hong, HUANG Bai-yun, SONG Min, CHEN Kang-hua. Microstructures and mechanical properties of Al-Cu-Mg-(Ag, La) alloys[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2008, 18(4): 571?576.
[45] 孙伟成, 张淑荣, 侯爱芹. 稀土在铝合金中的行为[M]. 北京: 兵器工业出版社, 1992: 46?82.
SUN Wei-cheng, ZHANG Shu-rong, HOU Ai-qin. Behaviors of RE elements in aluminum alloys[M]. Beijing: Weapon Industry Press, 1992: 46?82.
[46] 宋 旼, 肖代红. Mg和Ag元素对二元Al-Cu合金时效析出的影响[J]. 中国科学E辑, 2006, 36(11): 1283?1290.
SONG Min, XIAO Dai-hong. Effects of Mg and Ag elements on the aging precipitation of binary Al-Cu alloy[J]. Science in China: Series E, 2006, 49(5): 582?589.
[47] ZHU A, STARKE E A SHIFLET G J, An FP-CVM calculation of pre-precipitation clustering in Al-Cu-Mg-Ag alloys[J]. Scripta Mater, 2005, 53(1): 35?40.
[48] 冯 端. 金属物理(第一卷: 结构与缺陷)[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1998: 310?315.
FENG Duan. Metal physics (Vol.1): Microstructure and defect[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 1998: 310?315.
[49] LUMLEY R N, POLMEAR I J. Enhanced creep performance in an Al-Cu-Mg-Ag alloy through underageing[J]. Acta Mater,2002, 50(18): 3597?3608.
[50] 肖代红, 王健农, 丁东雁. 稀土Ce对铸态AlCuMgAg合金耐热性能的影响[J]. 特种铸造与有色合金, 2004, 24(4): 20?22.
XIAO Dai-hong, WANG Jian-nong, DING Dong-yan. Effects of minor Ce addition on the heat resistance of as-cast AlCuMgAg alloy[J]. Special Casting & Nonferrous Alloys, 2004, 24(4): 20?22.
基金项目:湖南省自然科学基金资助项目(07JJ3117),教育部留学归国人员科研启动项目资助项目;国家高技术研究发展专项经费资助项目(2006AA03Z567)
收稿日期:2008-09-26;修订日期:2008-12-18
通讯作者:宋 旼,副研究员,博士;电话:0731-88877880;E-mail: msong@mail.csu.edu.cn

