
Ni(OH)2 particles synthesized by high energy ball milling
LIU Yuan-gang(刘元刚), TANG Zhi-yuan(唐致远),
XU Qiang(徐 强), ZHANG Xiao-yang(张晓阳), LIU Yong(柳 勇)
School of Chemical Engineering and Technology, Tianjin University, Tianjin 300072, China
Received 17 October 2005; accepted 6 March 2006
Abstract: High energy ball milling(HEBM) method was applied to synthesize nickel hydroxide with and without partial substitution for Ni2+ sites by such metallic ions as Al3+, Al3+Zn2+ and Al3+Zn2+Co2+. The morphologies, structures, composition and thermal stability of the prepared powders were studied by SEM, XRD, FTIR and TG. The results reveal that all the synthesized Ni(OH)2 particles agglomerate in sub-micron sizes and the non-substituted Ni(OH)2 is composed of beta phase with a crystal interlayer distance of 4.64 ?, while the Al3+, Al3+Zn2+, Al3+Zn2+Co2+ substituted products are composed of alpha phase with 8.03 ? crystal interlayer space. Absorbed water molecule is found in all the synthesized Ni(OH)2 and the non-substituted particles are more thermally stable than substituted α-Ni(OH)2. The absorption peaks of inserted crystal anions of  and
and 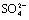 are detected for metallic ion substituted α-Ni(OH)2. The specific capacity of Al3+ substituted Ni(OH)2 is 325 mA?h/g, 5 mA?h/g higher than Al3+Zn2+ substituted and non-substituted Ni(OH)2, but 25 mA?h/g greater than Al3+Zn2+Co2+ substituted Ni(OH)2. The electrochemical mechanism of synthesized Ni(OH)2 electrodes is discussed by EIS spectrum and Al3+ substituted Ni(OH)2 electrode shows a high electrochemical cyclic stability.
are detected for metallic ion substituted α-Ni(OH)2. The specific capacity of Al3+ substituted Ni(OH)2 is 325 mA?h/g, 5 mA?h/g higher than Al3+Zn2+ substituted and non-substituted Ni(OH)2, but 25 mA?h/g greater than Al3+Zn2+Co2+ substituted Ni(OH)2. The electrochemical mechanism of synthesized Ni(OH)2 electrodes is discussed by EIS spectrum and Al3+ substituted Ni(OH)2 electrode shows a high electrochemical cyclic stability.
Key words: nickel hydroxide; Ni(OH)2 electrodes; high energy ball milling; metallic ion substitution
1 Introduction
Ni(OH)2/NiOOH has been used as positive materials in alkaline secondary batteries for more than 100 years[1-3]. The performance improvement of Ni(OH)2/NiOOH electrode is crucial for the application of these batteries as they are all positive electrode controlled. Lots of investigations[4-6] have been reported on the preparation, characterization and electrochemical behavior of nickel hydroxide. However, synthesis of metallic ion substituted Ni(OH)2 was rarely covered by high energy ball milling(HEBM) method, which is a powder processing technique[7] that allows production of homogeneous materials starting from blended powder mixtures. In the present paper, we synthesized alpha and beta phase Ni(OH)2 with and without Al3+, Al3+Zn2+ and Al3+Zn2+Co2+ partial substitution for Ni2+ ions by HEBM method and discussed their morphology, structure, composition, thermal property and electrochemical performance. SEM, XRD, TG, FTIR, EIS, charge-discharge curves and cyclic performance were applied to characterize the synthesized Ni(OH)2.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Synthesis of nickel hydroxide
A QM-1SP2-CL planetary ball mill was used together with a cylindrical agate kettle and some agate balls. For non-substituted Ni(OH)2, 10.5 g NiSO4·6H2O was mixed with 4.4 g NaOH before milling. For substituted Ni(OH)2, additive agents of 2.668 g Al2(SO4)3·18H2O, 0.576 g ZnSO4·7H2O and 0.564 g CoSO4·7H2O were demanded and the substitution styles of metallic ions were Al3+, Al3+Zn2+, and Al3+Zn2+Co2+ respectively. The ball to feed mass ratio was about 15:1 and the total milling period was 1 h, and the milling speed was 250 r/min. After milling, the precipitate was filtered and repeatedly washed with distilled water. Then the aqueous suspensions were then centrifuged and vacuum-dried at 60 ℃ for 12 h.
2.2 Analysis of nickel hydroxide
The morphology of synthesized Ni(OH)2 particles was determined by the JEOL JSM-6460LV scanning electronic microscopy. An Phillips X’Pert PANalytica X-ray diffractometer was applied to characterize the structure with a cobalt anode and Kα1 radiation at λ= 0.178 89 nm. Thermogravimetric measurements were carried out using NETZSCH STA409PC thermal analyzer and the heating rate was 20 ℃/min. A Nicolet Nexus 670 fourier transform infrared spectrophotometer was used to analyze the infrared spectroscopy of synthesized samp2.3 Unsealed battery preparation
9% nickel powder and 4.5% CoO were thoroughly mixed with 86% (mass fraction) synthesized nickel hydroxide. Several drops of 60% polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) were added as binder to the mixture. Then the mixture was pasted into nickel foam, dried, roll-pressed and spot welded with nickel ribbon. Two pieces of MmNi3.55Co0.75Mn0.4Al0.3 plates were used as counter electrodes. After being wrapped in separator, the nickel electrode was held tightly with two MH electrodes in 7.8 mol/L KOH alkaline solution with perforated Teflon plate.
2.4 Electrochemical property measurements
Charge-discharge and electrochemical cyclic performance were conducted with an automatic BS9380 battery-testing instrument. The sample was charged at 30 mA/g for 15 h, rested for 20 min and then discharged at 60 mA/g to 1.0 V. Electrochemical impedance spectro- scopy(EIS) was performed by GAMARY PCI4-750 electrochemical workstation with a home-made Hg/HgO reference electrode. The sinusoidal voltage was 5 mV and the frequency range was between 105 Hz and 5×10-3 Hz.
3 Results and discussion
3.1 Morphology
As the four synthesized Ni(OH)2 particles display similar microscopic appearances, only the images of Al3+ substituted Ni(OH)2 are provided. Fig.1(a) shows that the synthesized particles agglomerate greatly and grow up to big ones. It seems impossible to determine the size of single Ni(OH)2 powder. However, when Ni(OH)2 powders are dispersed in ethanol with ultrasonic vibrations, observed from Fig.1(b) and Fig.1(c), the maximum distance between the opposite edges of one powder is of typical sub-micron size. The preparing mechanism may be described as follows. During the milling process, the reagent powders are repeatedly impacted and fractured. The intimate contact between starting powder particles activates the conversion of mechanical energy into chemical energy to bring about chemical reaction. At the same time, the incessant impact reduces the size of particles and allows their fresh surface to come into further contact, proceeding the energy conversion reactions. After milling for a certain period, there is an overall tendency to drive both very fine and vary large Ni(OH)2 particles towards an intermediate size, since the fracturing impacts tend to decrease the larger particles as well as smaller particles is able to withstand fracturing deformation and welded into larger pieces.

Fig.1 Microscopic morphologies of Al3+ substituted Ni(OH)2
3.2 X-ray diffraction
Fig.2 shows that X-ray diffraction peaks of synthesized Ni(OH)2 are broadened with depressed intensity, indicating decreased crystallite size. For Al3+, Al3+Zn2+, Al3+Zn2+Co2+ substituted Ni(OH)2, their maximum diffraction peaks appear nearly 2θ=12.80?, consistent with those of standard α-Ni(OH)2. According to Bragg Formula d=1.792 9 ?/2sinθ, the d-value of metallic ion substituted α-Ni(OH)2 is 8.03 ?. The highest diffraction peak of non-substituted Ni(OH)2 occurs at 2θ=22.20? with a d value of 4.64 ?, accordant with beta phase of rhombus hexagonal structure. The reason to explain the above difference is given that water molecules can either be adsorbed or structurally bonded in nickel hydroxide lattices[8,9]. The intercalated water can alter the interplanar distances of Ni(OH)2, resulting in an expansion of c-axis from 4.6 ? for β-Ni(OH)2 to approximately 8 ? for substituted α-Ni(OH)2. Small peak shifts of synthesized α-Ni(OH)2 can be attributed to some intercalated anions, such as 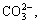
 and the stacking faults or growth faults[10-12].
and the stacking faults or growth faults[10-12].
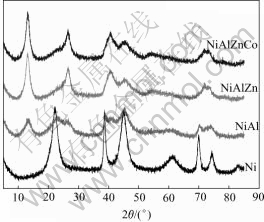
Fig.2 X-ray diffraction patterns of synthesized Ni(OH)2
3.3 FTIR spectroscopy
Fig.3 shows that all the synthesized Ni(OH)2 products have similar IR absorption spectra. However, Al3+ or Al3+Zn2+ substituted Ni(OH)2 possesses a higher absorption intensity than the other one. The bands at 3 640 cm-1 refer to specific stretching vibration of hydroxyl group in the synthesized Ni(OH)2 lattice[13] and 3 430 cm-1 to hydroxyl group of adsorbed water. The absorption peaks at 1 630 cm-1 and 530 cm-1 correspond to angular deformation of water molecules and its crystal plane respectively. The above suggests[14, 15] that some amount of water molecules are absorbed in synthesized Ni(OH)2 particles. Fig.3 also displays characteristic bands of  and
and  at 1 360 cm-1 or around 1 110 cm-1 and 600 cm-1[16], which are inserted to compensate excess positive charges of substituted metallic ions. These anions originate from the mother reagents or CO2 participation in preparation process. According to the crystal interlayer space of synthesized Ni(OH)2, these anions are mainly inserted in the interstratified planes of substituted powders.
at 1 360 cm-1 or around 1 110 cm-1 and 600 cm-1[16], which are inserted to compensate excess positive charges of substituted metallic ions. These anions originate from the mother reagents or CO2 participation in preparation process. According to the crystal interlayer space of synthesized Ni(OH)2, these anions are mainly inserted in the interstratified planes of substituted powders.
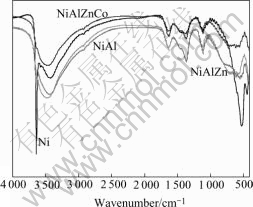
Fig.3 FTIR spectra of synthesized Ni(OH)2
3.4 TG analysis
The thermal-gravimetric curves of synthesized Ni(OH)2 powders are shown in Fig.4. For non- substituted β-Ni(OH)2, the sharp mass decrease appears between 240 ℃ and 330 ℃, and for substituted α- Ni(OH)2, a delayed and stronger mass loss occurs from 260 ℃ to 400 ℃. The total 23% mass loss is observed for β-Ni(OH)2 while it is almost 31% for Al3+ substituted α-Ni(OH)2 and 33% for Al3+Zn2+ and Al3+Zn2+Co2+ substituted α-Ni(OH)2. For non-substituted Ni(OH)2, it reveals two mass loss regions: the first region of no more than 5% from 50 ℃ to 240 ℃, and the second sharp loss between 240 ℃ and 330 ℃, where no less than 15% mass loss takes place. For substituted Ni(OH)2, it is observed that mass decrease starts sharply from 50 ℃ and continues to 400 ℃ with about 30% mass loss. Obviously, it holds a higher decomposition rate and less thermal stability. Two categories of chemical reactions are postulated according to the observed mass loss steps of synthesized Ni(OH)2[5, 17]. The first is ascribed to dehydration process (Eqn.(1)), which is the loss of water molecules associated with Ni(OH)2, and the second is attributed to Ni(OH)2 decomposition (Eqn.(2)), which is coincident with the second sharp mass loss above 240 ℃.
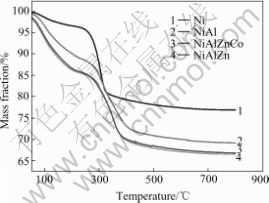
Fig.4 Thermo-gravimetric analysis of synthesized Ni(OH)2
Ni(OH)2?XadsH2O→Ni(OH)2+XH2O (1)
Ni(OH)2→NiO+H2O (2)
3.5 Electrochemical performance
Fig.5(a) and Fig.5(b) show the charge and discharge curves of synthesized Ni(OH)2 electrodes. The β- Ni(OH)2 electrode possesses lower charging and discharging potential platform than that of substituted α-Ni(OH)2. According to the relationship between crystal structure and electrochemical performance, for β- Ni(OH)2, the interlayer spacing and the crystal defects increase after HEBM, resulting in an easy oxidation and low charging potential. While for substituted α-Ni(OH)2, besides favorable effects of special crystal structure for proton diffusion, those anions, such as  and
and 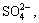 obstruct proton movement by intercalating into Ni(OH)2 interlayer planes and generate a higher charging potential. The specific capacity of Al3+ substituted α-Ni(OH)2 is 325mA?h/g and non- substituted Ni(OH)2 exhibits an identical value of 320 mA?h/g with that of Al3+Zn2+Co2+ substituted Ni(OH)2, 20 mA?h/g greater than that of Al3+Zn2+ substituted electrode. Fig.5(c) shows the electrochemical impedance spectroscopy of synthesized Ni(OH)2 electrodes. The Nyquist plots of all experimental electrodes are divided into three parts: one inductive loop in high frequency, one depressed semicircle in intermediate frequency and one inclined straight line in low frequency. This suggests that high frequency loop has a characteristic of the charge-transfer process at the electrode/electrolyte interface, and the linear response in the low frequency is a indication of semi-infinite hydrogen diffusion process in the solid electrode[18-22]. It is obvious that, compared with substituted α-Ni(OH)2, non-substituted β-Ni(OH)2 shows a higher proton diffusion coefficient and a larger capacitive arc diameter as well as a transition from an angle 13.5? with the real axis toward 59.5? through the lower frequency region. But with the increase of metallic ions, the Warburg linear slopes firstly rise and then gradually decrease, for example, an angle of 82.8? with the real axis is calculated for Al3+ substituted α-Ni(OH)2, 82.1? for Al3+Zn2+ substituted α-Ni(OH)2 and 69.8? for Al3+Zn2+Co2+ α-Ni(OH)2. The reasons might be that substituted metallic ions can reduce the reaction resistance of α-Ni(OH)2 and increase their electro- chemical performance[23,24]. Usually, α-Ni(OH)2 has an unstable structure in alkaline solution and reverts to β-Ni(OH)2 gradually. Fig.5(d) displays the variation of the discharging capacity with cycle number for Al3+ substituted Ni(OH)2. The discharging capacity remains more than 81% of its highest value over 130 cycles, indicating that the α-Ni(OH)2 stabilization is improved after Al3+ substitution for Ni2+ in the nickel hydroxide lattice.
obstruct proton movement by intercalating into Ni(OH)2 interlayer planes and generate a higher charging potential. The specific capacity of Al3+ substituted α-Ni(OH)2 is 325mA?h/g and non- substituted Ni(OH)2 exhibits an identical value of 320 mA?h/g with that of Al3+Zn2+Co2+ substituted Ni(OH)2, 20 mA?h/g greater than that of Al3+Zn2+ substituted electrode. Fig.5(c) shows the electrochemical impedance spectroscopy of synthesized Ni(OH)2 electrodes. The Nyquist plots of all experimental electrodes are divided into three parts: one inductive loop in high frequency, one depressed semicircle in intermediate frequency and one inclined straight line in low frequency. This suggests that high frequency loop has a characteristic of the charge-transfer process at the electrode/electrolyte interface, and the linear response in the low frequency is a indication of semi-infinite hydrogen diffusion process in the solid electrode[18-22]. It is obvious that, compared with substituted α-Ni(OH)2, non-substituted β-Ni(OH)2 shows a higher proton diffusion coefficient and a larger capacitive arc diameter as well as a transition from an angle 13.5? with the real axis toward 59.5? through the lower frequency region. But with the increase of metallic ions, the Warburg linear slopes firstly rise and then gradually decrease, for example, an angle of 82.8? with the real axis is calculated for Al3+ substituted α-Ni(OH)2, 82.1? for Al3+Zn2+ substituted α-Ni(OH)2 and 69.8? for Al3+Zn2+Co2+ α-Ni(OH)2. The reasons might be that substituted metallic ions can reduce the reaction resistance of α-Ni(OH)2 and increase their electro- chemical performance[23,24]. Usually, α-Ni(OH)2 has an unstable structure in alkaline solution and reverts to β-Ni(OH)2 gradually. Fig.5(d) displays the variation of the discharging capacity with cycle number for Al3+ substituted Ni(OH)2. The discharging capacity remains more than 81% of its highest value over 130 cycles, indicating that the α-Ni(OH)2 stabilization is improved after Al3+ substitution for Ni2+ in the nickel hydroxide lattice.
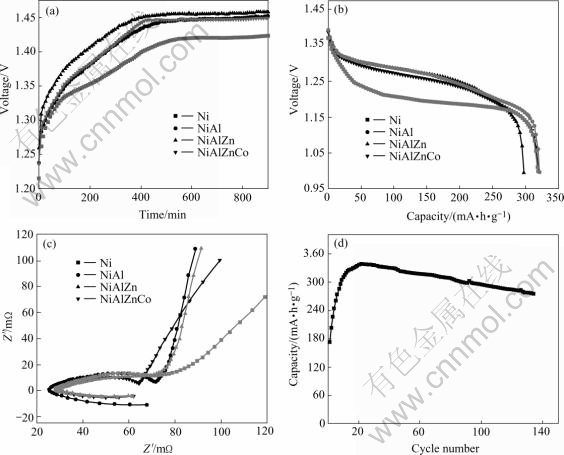
Fig.5 Electrochemical performance of synthesized Ni(OH)2: (a) Charging curves of synthesized Ni(OH)2; (b) Discharging curves of synthesized Ni(OH)2; (c) EIS spectra of synthesized Ni(OH)2; (d) Cycle life of Al3+ substituted Ni(OH)2
4 Conclusions
The study demonstrates that high energy ball milling(HEBM) method is a simple and effective way to synthesize Ni(OH)2 powders with and without metallic ions substitution for Ni2+ sites in the lattice, such as Al3+, Al3+Zn2+ and Al3+Zn2+Co2+. The synthesized Ni(OH)2 particles are in sub-micron size and agglomerate seriously. Turbostratic α-Ni(OH)2 is obtained by metallic ion substitution with a 8.03 ? crystal interlayer distance, while non-substituted Ni(OH)2 displays a low crystalline β-phase with 4.64 ? interlayer space. From FTIR spectra, the absorption peaks of inserted anions as 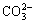 and
and  are detected for substituted α-Ni(OH)2 as well as stretching vibration bands of absorbed water. When metallic ions as Al3+, Al3+Zn2+ and Al3+Zn2+Co2+ are intercalated into Ni(OH)2 lattice, the synthesized Ni(OH)2 gets less thermal stability and its decomposition speed increases gradually. Compared with substituted α-Ni(OH)2, non-substituted β-Ni(OH)2 has higher proton diffusion rate. Moreover, with the increase of substituted metallic ions, diffusion resistances of substituted α-Ni(OH)2 gradually decrease. The specific discharging capacity of Al3+ substituted Ni(OH)2 reaches 325 mA?h/g, 5 mA?h/g higher than that of Al3+Zn2+ substituted and non-substituted Ni(OH)2 and 25 mA?h/g greater than that of Al3+Zn2+Co2+ substituted α-Ni(OH)2. After being cycled more than 130 times, Al3+ substituted Ni(OH)2 electrode remains over 81% of its highest specific capacity.
are detected for substituted α-Ni(OH)2 as well as stretching vibration bands of absorbed water. When metallic ions as Al3+, Al3+Zn2+ and Al3+Zn2+Co2+ are intercalated into Ni(OH)2 lattice, the synthesized Ni(OH)2 gets less thermal stability and its decomposition speed increases gradually. Compared with substituted α-Ni(OH)2, non-substituted β-Ni(OH)2 has higher proton diffusion rate. Moreover, with the increase of substituted metallic ions, diffusion resistances of substituted α-Ni(OH)2 gradually decrease. The specific discharging capacity of Al3+ substituted Ni(OH)2 reaches 325 mA?h/g, 5 mA?h/g higher than that of Al3+Zn2+ substituted and non-substituted Ni(OH)2 and 25 mA?h/g greater than that of Al3+Zn2+Co2+ substituted α-Ni(OH)2. After being cycled more than 130 times, Al3+ substituted Ni(OH)2 electrode remains over 81% of its highest specific capacity.
References
[1] NAGARAJAN G S, VAN ZEE J W. Characterization of the performance of commercial Ni/MH batteries [J]. Journal of Power Sources, 1998, 70: 173-180.
[2] YAN De-yi, WANG Jian-guo. Preparation of an improved positive electrode and its application in Ni/MH batteries [J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 1999, 293-295: 775-779.
[3] ZHAN F, JIANG L J, WU B R, XIA Z H, WEI X Y, QIN G R. Characteristics of Ni/MH power batteries and its application to electric vehicles [J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 1999, 293-295: 804-808.
[4] DEABATE S, FOURGEOT F, HENN F. X-ray diffraction and micro-Raman spectroscopy analysis of new nickel hydroxide obtained by electrodialysis [J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2000, 87: 125-136.
[5] SONG Quan-sheng, TANG Zhi-yuan, GUO He-tong, CHAN S L I.. Structural characteristics of nickel hydroxide synthesized by a chemical precipitation route under different pH values [J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2002, 112: 428-434.
[6] LIU Xiao-hong, YU Lan. Synthesis of nanosized nickel hydroxide by solid-state reaction at room temperature [J]. Materials Letters, 2004, 58: 1327-1330.
[7] CHEN H, WANGA J M, PAN T, XIAO H M, ZHANG J Q, CAO C N. Effects of high-energy ball milling (HEBM) on the structure and electrochemical performance of nickel hydroxide [J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2003, 28: 119-124.
[8] DELAHAYE-VIDAL A, FIGLARZ M. Textural and structural studies on nickel hydroxide electrodes(II): Turbostratic nickel(II) hydroxide submitted to electrochemical redox cycling [J]. J Appl Electrochem, 1987, 17: 589-599.
[9] INDIRA L, DIXIT M, KAMATH P V. Electrosynthesis of layered double hydroxides of nickel with trivalent cations [J]. Journal of Power Sources, 1994, 52(1): 93-97.
[10] WANG C Y, ZHONG S, KONSTANTINOV K, WALTER G, LIU H K. Structural study of Al-substituted nickel hydroxide [J]. Solid State Ionics, 2002, 148: 503-508.
[11] CARPENTER1 G J C, WRONSKI Z S. Nanocrystalline NiO and NiO-Ni(OH)2 composite powders prepared by thermal and mechanical dehydroxylation of nickel hydroxide [J]. NanoStructured Materials, 1999, 1(11): 67-80.
[12] WANG Xian-you, LUO He-an, PARKHUTIK P V, MILLAN A C, MATVEEVA E. Studies of the performance of nanostructural multiphase nickel hydroxide [J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2003, 115: 153-160.
[13] FREITAS M B J G. Nickel hydroxide powder for NiO·OH/Ni(OH)2 electrodes of the alkaline batteries [J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2001, 93: 163-173.
[14] ACHARYA R, SUBBAIAH T, ANAND S, DAS R P. Effect of preparation parameters on electrolytic behaviour of turbostratic nickel hydroxide [J]. Materials Chemistry and Physics, 2003, 81: 45-49.
[15] RAMESH T N, JAYASHREE R S, VISHNU KAMATH P. The effect of the moisture content on the reversible discharge capacity of nickel hydroxide [J]. J Electrochem. Soc, 2003, 150: A520-524.
[16] ACHARYA R, SUBBAIAH T, ANAND S, DAS R P. Effect of precipitating agents on the physicochemical and electrolytic characteristics of nickel hydroxide [J]. Materials Letters, 2003, 57: 3089-3095.
[17] AKINC M, JONGEN N, LEMAITRE J, HOFMANN H. Synthesis of nickel hydroxide powders by urea decomposition [J]. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 1998, 18: 1559-1564.
[18] MANCIER V, M?TROT A, WILLMANN P. AC impedance modelling of nickel hydroxide electrodes viewed as mixed protonic-electronic conductors [J]. Electrochimica Acta, 1996, 41(7/8): 1259-1265.
[19] LU Zhang. AC impedance studies on sealed nickel metal hydride batteries over cycle life in analog and digital operations [J]. Electrochimica Acta, 1998, (43)21-22: 3333-3342.
[20] CHENG Shao-an, ZHANG Jian-qing, ZHAO Min-hua, CAO Chu-nan. Electrochemical impedance spectroscopy study of Ni/MH batteries [J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 1999, 293-295: 814-820.
[21] YANG Chun-chen. Synthesis and characterization of active materials of Ni(OH)2 powders [J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2002, 27: 1071-1081.
[22] LIU Bing, YUAN Hua-tang, ZHANG Yun-shi. Impedance of Al-substituted α-nickel hydroxide electrodes [J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2004, 29: 453-458.
[23] WU M S, HUANG C M, WANG Y Y, WAN C C. Effects of surface modification of nickel hydroxide powder on the electrode performance of nickel/metal hydride batteries [J]. Electrochimica Acta, 1999, 44: 4007-4016.
[24] SUSANA I, C?RDOBA DE TORRESI, KELLIE PROVAZI, et al. Effect of additives in the stabilization of the α phase of Ni(OH)2 electrodes[J]. J Electrochem Soc, 2001, 148: 1179.
Corresponding author: LIU Yuan-gang; Tel: +86-769-83015363; Fax: +86-769-83195372; E-mail: lyg_fjj@163.com
(Edited by YANG Bing)