文章编号:1004-0609(2012)02-0496-08
Fe-P非晶合金的电沉积行为及热处理对其结构与性能的影响
王森林,宋运建
(华侨大学 材料科学与工程学院,厦门 361021)
摘 要:在以柠檬酸三钠为络合剂的酸性镀液中电沉积Fe-P非晶合金,采用差示扫描量热(DSC)、X射线衍射(XRD)和扫描电镜(SEM)研究该合金镀层的晶化行为和表面微观形貌。结果表明:镀液中加入络合剂,且随着pH值升高和温度降低时,Fe-P非晶合金共沉积的阴极极化增大。镀态Fe-P合金为非晶态结构,于330.5 ℃时开始晶化; 383.6 ℃时,α-Fe(P)固溶体大量晶化析出;472.5 ℃时,Fe3P(I-4)相大量脱溶析出。且随着热处理温度升高,合金镀层的耐蚀性能和硬度先增加后下降,450 ℃热处理所得镀层的耐蚀性能最佳且硬度最大;在400 ℃以下时,镀膜具有良好的抗热氧化能力,当温度在400 ℃以上时,抗氧化能力迅速下降。
关键词:Fe-P非晶合金镀层;电沉积行为;热处理
中图分类号:O646 文献标志码:A
Electro-deposition behaviors of Fe-P amorphous alloy and effect of heat treatment on its structure and performances
WANG Sen-lin, SONG Yun-jian
(College of Materials Science and Engineering, Huaqiao University, Xiamen 361021, China)
Abstract: The Fe-P amorphous alloy was electro-deposited from an acidic bath containing sodium citrate as a complexant. The crystallization behavior and surface micro-morphology of the alloy coating were investigated by differential scanning calorimetry (DSC), X-ray diffractometry (XRD) and scanning electron microscopy (SEM). The results show that the cathodic polarization of Fe-P amorphous alloy co-deposition increases with the increases of the complexant concentration, the bath pH value and the decrease of temperature, respectively. The structure of the as-plated Fe-P alloy coating is amorphous. The amorphous alloy begins to crystallize at 330.5 ℃, and α-Fe(P) solid solution appears at 383.6 ℃, then, lots of Fe3P(I-4) phase separate out from solid solution at 472.5 ℃. The corrosion resistance and micro-hardness of the alloy coating increase, then decrease, and the best properties appear at 450 ℃. The heat oxidation experiments show that the oxidation resistance of the coating is good bellow 400 ℃ and drops rapidly above 400 ℃.
Key words: Fe-P amorphous alloy coating; electro-deposition behavior; heat treatment
在电沉积过程中引入类金属原子(如P、S、B和C等)与金属共沉积,这些类金属原子会夹杂在金属镀层中,当这些非金属元素在镀层中占一定比例时,合金原子呈长程无序排列,从而得到非晶态合金镀层。电沉积铁基非晶态合金具有很多优异的性能(如软磁性能[1-2]、高硬度[3]、较好的耐腐蚀性能[4]和储锂性能[5-6]等),因此倍受研究者重视,电沉积Fe-P非晶合金就是其中之一。ZE?EVI?等[7]首次采用阳极线性扫描伏安法(Anodic linear sweep voltammetry, ALSV)研究工艺条件对电沉积Fe-P非晶合金的组成及相结构的影响。结果表明:随着工艺条件的改变,合金镀层中可能出现FeP、Fe2P和Fe3P三相中的一相或几相。张远声等[8-9]研究表明,镀液的pH=1.5时,阴极效率和分散能力最佳,用铁可溶性阳极可有效防止镀液中Fe(Ⅲ)浓度增加,有利于Fe-P非晶合金镀液的稳定。由于非晶态结构属于高自由能的热力学亚稳态,受热时易向自由能低的结构转变,从而影响其性能,尤其是人们发现非晶合金基体上均匀弥散分布一定比例的晶化相时,非晶合金的性能会大幅度地提高[10-11],因此,研究热处理对非晶态合金结构和性能的影响是必要的。俞春福等[12]研究表明,由于弥散强化作用,Fe-P非晶合金经400 ℃热处理后,硬度可达1 100 HV;范云鹰等[13]也对Fe-P非晶合金镀层晶化行为进行了研究,合金在300 ℃左右开始晶化,在330 ℃左右开始转变为α-Fe(P)固溶体,370 ℃左右FexP(x=1, 2, 3)从α-Fe(P)固溶体析出,此时硬度最大。目前,大多数电沉积Fe-P非晶合金的镀液中均不加络合剂,为了保证镀层中P含量和提高镀液的分散能力,施镀的pH很低(约1.5左右),沉积过程中析氢副反应严重,导致得到的合金镀层结构缺陷(气孔、裂缝等)较多,进而影响该镀层的性能。本文作者通过在镀液在加入适量柠檬酸三钠络合剂,由于它能与Fe(Ⅱ)有效配位络合,改善了该镀液的稳定性能,因此可提高施镀pH(约2.6),较大幅度降低析氢副反应程度,提高了所得镀层的质量(缺陷较少)。研究镀液中络合剂含量、pH值和温度对Fe-P非晶合金电沉积行为的影响,重点研究了热处理对Fe-P非晶合金镀层的晶化行为、表面微观形貌、耐腐蚀性能、显微硬度的影响及其抗热氧化能力,从合金镀层的结构演化讨论了这些变化的微观因素。
1 实验
1.1 Fe-P非晶合金镀层的电沉积
实验所用电沉积Fe-P非晶合金镀液组成和沉积条件已申请专利,低碳钢作阳极(电镀时用尼龙布包裹),所用试剂均为分析纯,镀液用蒸馏水配制,pH值用为10% H2SO4(质量分数)和NaOH调节,pH计测量。采用紫铜圆盘电极研究Fe-P非晶合金电沉积行为,采用紫铜圆盘电极,Fe-P非晶合金沉积基体采用20 mm×20 mm紫铜箔(组成和表面形貌测试用)和17 mm×17 mm×2 mm(XRD结构和硬度测试用)的低碳钢(A3钢),每次实验紫铜圆盘电极、紫铜箔和碳钢均经过以下预处理:金相砂纸打磨→蒸馏水洗→酸洗→超声碱性除油→蒸馏水洗→化学抛光→去离子水洗。
1.2 测试仪器与方法
在三电极体系下采用美国普林斯顿PAR2273电化学工作站测量极化曲线和合金镀层的电化学阻 抗,辅助电极为铂片(S=3.0 cm×3.0 cm),参比电极为饱和甘汞电极(SCE)。阴极极化实验采用紫铜圆盘电 极电位扫描速度为10 mV/s。测量镀层的耐腐蚀性能时,用环氧树脂对合金镀层试样进行覆盖,中间留出1.0 cm×1.0 cm的镀层表面,以此制作成工作电极,电解液为3.5%(质量分数)的NaCl溶液。先测量体系的开路电位,然后测量镀层的电化学阻抗谱和Tafel曲线(电位扫描速度为5 mV/s),测量电化学阻抗的频率范围从0.01 Hz到100 kHz,测量信号的幅值为10 mV。
在紫铜箔上镀覆1.0 h,然后把合金镀层机械剥离下来,用美国TA公司生产的SDT-2960型差热-热重分析仪做差示扫描量热,氩气保护(测热氧化质量增加率时不需气体保护),升温速度均为10 ℃/min。合金镀层的热处理在石英管式真空炉中进行(真空度达0.67 Pa),恒温1.0 h。镀层表面微观形貌用日本Hitachi公司生产的S-4800N 场发射高分辨率扫描电镜(SEM)观察,组成分析用扫描电镜附带的ISIS-300能谱仪 (英国牛津公司生产)测定。镀层相结构分析在D/max-RC转靶衍射仪上进行,Cu的Kα射线,扫描速度5 (°)/min。合金的显微硬度在维氏硬度计上测量,载荷量1 N,保荷时间10 s,不同温度处理的镀层厚度均匀。
2 结果与讨论
2.1 Fe-P非晶合金的共沉积行为
2.1.1 络合剂浓度对Fe-P非晶合金共沉积行为的影响
图1所示为保持镀液中其他成分浓度不变,改变络合剂柠檬酸三钠浓度时,得到Fe-P非晶合金沉积的阴极极化曲线。从图1可见,未加入络合剂时,合金的析出电位为-0.80 V(vs SCE,以下相同),镀液中加入络合剂后,合金的析出电势变为-0.85 V,合金的析出电位变负,随着络合剂的量逐渐增加,合金的起始沉积电位逐渐负移,说明在镀液中加入络合剂,可以增大镀液的阴极极化,有利于获得优良的镀层。阴极极化增大的原因主要是由于络合剂与镀液中主盐离子形成了络合物,增大了离子放电所需的活化能,因而放电速度变慢[14],镀液与镀层的性能也随之改善。但加入过多的络合剂时,Fe-P沉积的析出电位过负,电沉积过程中的析氢副反应将会变严重,从而使得阴极电流效率和镀层的质量下降。
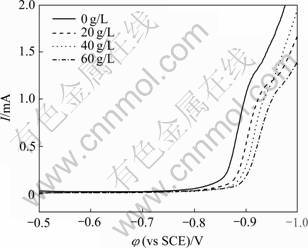
图1 络合剂浓度对Fe-P合金共沉积阴极极化的影响
Fig. 1 Influences of complexant concentration on cathodic polarization of Fe-P codeposition
2.1.2 镀液pH值对Fe-P非晶合金共沉积行为的影响
不同镀液pH值的Fe-P非晶合金共沉积阴极极化曲线如图2所示。由图2可以看出,随着pH值升高,Fe-P非晶合金的析出电位逐渐负移,阴极极化逐渐增大,合金沉积所需要的过电势逐渐增大,阴极过电势越大,电结晶成核速率越大,晶粒越细小,有利于获得光亮致密的合金镀层。镀液pH升高有利于沉积过程镀层表面形成氢氧化亚铁膜,该膜抑制合金沉积,同时有利于抑制析氢副反应。虽然pH升高有利于获得细致紧密的镀层,但pH值超过一定范围时,镀液中的Fe(Ⅱ)易被空气氧化而转变为Fe(Ⅲ),导致镀液中的Fe(Ⅲ)增加,这样镀层表面会出现发黑,镀层的质量和形貌不佳。
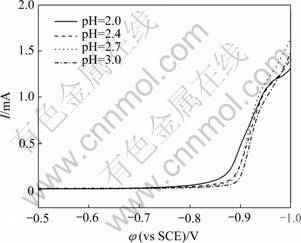
图2 镀液pH值对Fe-P合金共沉积阴极极化的影响
Fig. 2 Influences of pH on cathodic polarization of Fe-P alloy codeposition
2.1.3 温度对Fe-P非晶合金共沉积行为的影响
图3所示为不同温度下Fe-P非晶合金共沉积阴极极化曲线。由图3可知,温度对Fe-P非晶合金共沉积影响很大,随着镀液温度的升高,Fe-P非晶合金的阴极极化曲线逐渐正移,合金共沉积电位逐渐变正,阴极极化减小,易于合金共沉积。因为温度升高,Fe-P合金共沉积所需的活化能降低,从而合金的共沉积电位变正。但是,由于合金析出的过电势减小,会使电结晶成核速率下降,晶粒生长速度变快,晶粒尺寸粗大,且温度的升高将降低析氢电势、加快氢气的析出,导致镀液的电流效率下降,不利于Fe-P的共沉积,所以,温度不能过高。虽然镀液温度的降低可以增大 Fe-P合金沉积的阴极极化,但低温会使得镀液的分散能力下降,镀层的光亮区域减小,不利于获得优良的镀层,因此沉积过程要选择适当的温度。
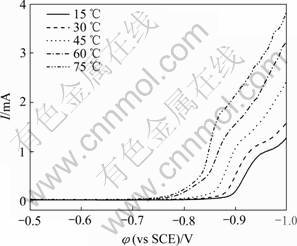
图3 温度对Fe-P合金共沉积阴极极化的影响
Fig. 3 Influences of temperatures on cathodic polarization of Fe-P alloy codeposition
2.2 热处理温度对Fe-P非晶合金镀层结构与性能的影响
2.2.1 Fe-P非晶合金镀层的晶化行为
图4所示为在理想的镀液组成和沉积条件下得到的Fe-P非晶合金的能谱,合金镀成各元素含量(摩尔分数)为Fe 76.0%和P 24.0%,以此组成的镀层进行以下研究。
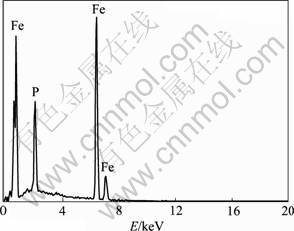
图4 Fe-P非晶合金镀层的EDS谱
Fig. 4 EDS spectrum of Fe-P amorphous alloy coating
图5所示为该非晶合金的差示扫描量热曲线(DSC)。从图5中可以看出,在210.0 ℃处有一个微弱的放热峰,在383.6和472.5 ℃处各有一个较强的放热峰,表明在热处理过程中,这3个温度下的合金可能发生了晶型转变生成新相[15-16]。根据差示扫描结果,确定真空热处理分别在350、450、500和600 ℃下进行,然后进行X射线衍射实验。
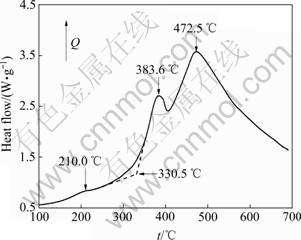
图5 Fe-P非晶合金的差示扫描量热曲线
Fig. 5 DSC curve of Fe-P amorphous alloy
图6所示为Fe-P合金镀层镀态及在不同温度热处理1.0 h后的XRD谱。由图6可看出,合金镀态时的XRD谱在2θ约为45°处出现一个弥散的宽化峰,说明合金在镀态呈非晶态结构。Fe-P非晶合金从330.5 ℃开始晶化,350 ℃热处理时析出α-Fe(P)固溶体;随着热处理温度升高,合金进一步晶化,450 ℃热处理时析出大量α-Fe(P)固溶体,同时有较多的Fe3P(I-4)相脱溶析出并弥散在合金中;经500 ℃热处理后,大量Fe3P(I-4)相颗粒从α-Fe(P)固溶体中脱溶析出并长大;经600 ℃热处理后,Fe3P(I-4)完全从α-Fe(P)固溶体中脱溶析出,合金最终晶化为α-Fe与Fe3P(I-4)两相混合物。
结合图5和6可以认为,210.0 ℃处为合金受热析出氢气时的较弱放热峰,这是由于电沉积过程中阴极析出的氢气渗入合金镀层造成的;383.6 ℃处为大量 生成α-Fe(P)固溶体的强放热峰;472.5 ℃处为大量Fe3P(I-4)相从脱溶α-Fe(P)固溶体析出的放热峰。该研究结果与文献[13]中的研究结果不同,Fe-P非晶合金晶化析出α-Fe(P)固溶体和脱溶析出Fe3P相的放热峰温度明显提高,可能是由于Fe-P非晶合金镀层组成不同,同时表明本研究所得的镀层热稳定性能较好。
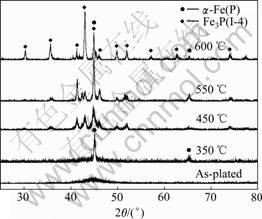
图6 Fe-P非晶合金在不同温度热处理1.0 h后的XRD谱
Fig. 6 XRD patterns of Fe-P amorphous alloy after heat treated at various temperatures for 1.0 h
2.2.2 热处理温度对Fe-P非晶合金镀膜微观形貌的影响
Fe-P非晶合金镀层在镀态和不同温度真空热处 理后的表面微观形貌如图7所示。由图7可以看出, Fe-P非晶合金在镀态时的表面比较平整致密,少量的凸凹是由于基体不平造成的,只有少许裂缝和气孔,这可能是由于电沉积时发生阴极析氢副反应,析出的氢渗入镀层形成内应力造成的。用肉眼观察非晶合金表面光亮致密呈银白色。经350 ℃真空热处理后,由于Fe-P非晶合金镀层内残留的氢气受热析出表面留下一些气孔,同时由于α-Fe(P)固溶体析出和结构驰豫作用,合金镀层变得疏松,表面较粗糙。450 ℃真空热处理镀层的表面形态明显不同于前两个镀层,此时镀层析出大量α-Fe(P)固溶体,同时有较多的Fe3P(I-4)相细小颗粒脱溶析出并弥散在合金中,镀层表面非常平整致密。经500 ℃热处理后,Fe3P(I-4)脱溶相已成为平衡相,但由于分散细小的Fe3P(I-4)颗粒使合金系统具有很高的界面能,为了降低总界面能,高密度的细小Fe3P(I-4)颗粒倾向粗化成具有较小总界面、低密度分布的较大颗粒,即发生Ostwald熟化[17],合金表面发生粗化。经600 ℃热处理后,由于Ostwald熟化作用,合金镀层继续粗化,结构完全发生转变,表面疏松有大量凹坑。
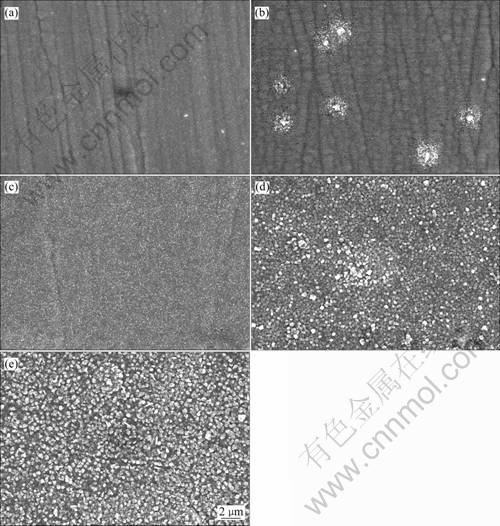
图7 Fe-P非晶合金镀层在不同温度下热处理1.0 h后的SEM像
Fig. 7 SEM images of Fe-P amorphous alloy coating after heat treated at various temperatures for 1.0 h: (a) As-plated; (b) 350 ℃; (c) 450 ℃ ; (d) 500 ℃; (e) 600 ℃
2.2.3 热处理温度对Fe-P非晶合金镀层耐腐蚀性能的影响
热处理对电沉积Fe-P非晶合金的晶化行为和硬度强化机理研究较多,热处理对其耐腐蚀性能影响还鲜见报道。图8和9所示分别为Fe-P非晶合金经过不同温度热处理后的Nyquist谱图和Tafel曲线(均在各自的开路电位下测量)。
从图8可以看出,Fe-P非晶合金镀态和经过不同温度热处理1.0 h后,Nyquist谱图只有一个时间常数,由单一容抗弧组成,对应着合金镀层的腐蚀反应[18]。相应的等效电路图如图8右上方所示,Rs是溶液电阻,Cd和Rt分别代表局部腐蚀区域的双电层电容和电化学反应电荷转移阻力。随着热处理温度的升高,合金镀层的容抗弧半径变化明显,说明热处理对合金镀层的耐腐蚀性能影响较大。450 ℃之前,随热处理温度升高,容抗弧半径增大,这表明电荷传递的阻力增大,镀层的耐蚀性能提高;450 ℃热处理时,阻抗达到最大,约1 400 Ω/cm2左右,此时耐蚀性最佳;之后,热处理温度继续升高,容抗弧半径逐渐变小,合金镀层耐蚀性能下降。
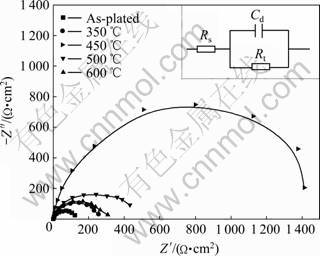
图8 Fe-P非晶合金经不同温度热处理1.0 h后的Nyquist谱
Fig. 8 Nyquist plots of Fe-P amorphous alloy after heat treated at different temperatures for 1.0 h
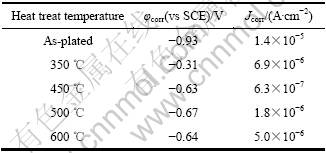
由图9知,以镀态Fe-P非晶合金为参照,随热处理温度升高,合金镀层的自腐蚀电位明显正移,腐蚀电流密度先减小后增加,耐腐蚀性能明显增强。表1是根据图9得到的Fe-P非晶合金经不同温度热处理后的电化学腐蚀参数。由表1可知,经450 ℃热处理后,合金镀层的腐蚀电流密度由镀态时的1.4×10-5 A/cm2迅速减小到6.3×10-7 A/cm2,此时耐腐蚀性能最佳;之后,随热处理温度升高,合金镀层的腐蚀电流密度不断增加,耐腐蚀性能变差,这与图8得到的结果一致。这主要是由于低温热处理时有利于消除合金镀层中的氢,同时促使原子不断扩散,减小了合金薄膜内应力与结构缺陷,镀层变得更加致密,耐腐蚀性能有所改善;450 ℃热处理时,非晶合金晶化析出了大量亚稳相α-Fe(P)固溶体,同时析出大量Fe3P(I-4)细小晶粒,引起残余非晶基体的P含量和结构变化,使得合金镀层的表面具有较高的反应活性,当镀层浸入NaCl溶液中后,合金元素在介质中具有强烈的钝化倾向,镀层表面的钝化膜能快速形成,电化学阻抗最大,腐蚀电流最小,此时合金镀层的耐腐蚀性能最佳。且随着热处理温度的升高,合金镀层在介质中所形成钝化膜的致密性和稳定性降低,耐腐蚀性能变差。
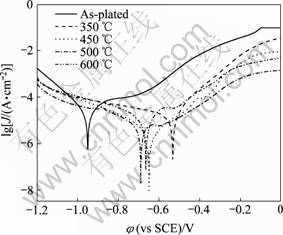
图9 Fe-P非晶合金经不同温度热处理1.0 h的Tafel曲线
Fig. 9 Tafel curves of Fe-P amorphous alloy after heat treated at different temperatures for 1.0 h
表1 Fe-P非晶合金经不同温度热处理1.0 h后的电化学腐蚀参数
Table 1 Electrochemical corrosion parameters for Fe-P amorphous alloy heated at different temperatures for 1.0 h
2.2.4 热处理温度对Fe-P非晶合金的显微硬度影响
Fe-P非晶合金具有较高的硬度,镀态时硬度达5 606 MPa,可作耐磨材料使用,但在使用过程中难免会受到环境温度的影响,因此,研究热处理温度对 Fe-P非晶合金的显微硬度影响是必要的。图10所示为热处理温度对Fe-P非晶合金显微硬度的影响。由图10可知,热处理温度对合金镀层的硬度影响很大,这是因为热处理改变了合金的微观结构,从而导致硬度不断变化。随热处理温度升高,合金镀层硬度呈现先增加后下降趋势,经450 ℃热处理后,合金硬度达到最大值11 554 MPa。从上述热处理对合金镀层结构的影响可知,经250 ℃热处理后,由于合金镀层内部氢气逐渐析出和原子扩散改善了镀层的内部缺陷,改善了合金镀层的致密度,但是由于氢气的析出在合金镀层表面留下较多气孔,合金镀层硬度增加不大;350 ℃热处理时,α-Fe(P)固溶体开始析出,合金镀层的硬度进一步增加;经400 ℃热处理后,由于α-Fe(P)固溶体大量析出,同时有少量的硬脆相Fe3P(I-4)颗粒析出呈弥散分布,合金镀层硬度迅速增加;经450 ℃热处理后,由于大量的硬脆相Fe3P(I-4)颗粒析出并弥散分布在合金中,与位错发生交互作用,阻碍了位错的运动,提高了合金的抗塑性变形能力[19],合金镀层硬度达到最大值;经500和600 ℃热处理后,由于发生Ostwald熟化作用,合金镀层的硬度逐渐下降。
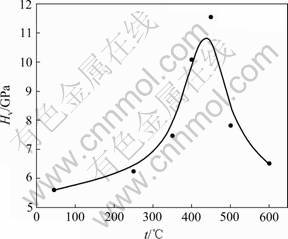
图10 热处理温度对Fe-P非晶合金显微硬度的影响
Fig. 10 Effect of heat treatment temperature on micro- hardness of Fe-P amorphous alloy
2.2.5 Fe-P非晶合金镀膜的抗热氧化能力
电沉积Fe-P非晶合金主要成分是铁,在温度较高的环境中使用会发生氧化,生成铁的氧化物,影响合金镀层的硬度和耐腐蚀性能,因此,有必要研究Fe-P非晶合金在高温下的热氧化行为。图11所示为Fe-P非晶合金在空气中的差示扫描量热和热重曲线(DSC-TG)。由TG曲线知,在400 ℃之前,氧化质量增加率很低,这是因为在此温度范围内,合金镀层主要以非晶态存在,非晶合金由于不存在长程有序,没有晶界、位错等缺陷,与晶态合金相比具有较强的抗氧化能力;400 ℃之后,氧化质量增加率急剧增大,原因是脱溶析出大量弥散分布的Fe3P(I-4)相颗粒,造成合金镀层组织结构的不均匀性,合金镀层的抗氧化能力明显下降。由DSC曲线知,Fe-P非晶合金在 392.8 ℃处有一很强的放热峰,表明合金镀层在此处发生了结构转变,这与TG曲线结果一致。
图12所示为Fe-P非晶合金在空气中不同温度热处理后的XRD谱。由图12可看出,Fe-P非晶合金在空气中经300 ℃热处理后的结构基本不变,仍为非晶态结构;在400 ℃时,合金结构开始发生转变,α-Fe(P)固溶体大量生成,同时Fe3P(I-4)相开始生成,只有微量的Fe2O3生成;400 ℃以后,由于Fe3P(I-4)相大量生成,造成合金镀层不均匀,合金迅速氧化,Fe2O3和FeO大量生成,合金的质量迅速增加。因此,Fe-P非晶合金在不经任何处理的情况下,不能在400 ℃以上的有氧环境中使用,否则会由于氧化作用失去其使用价值。
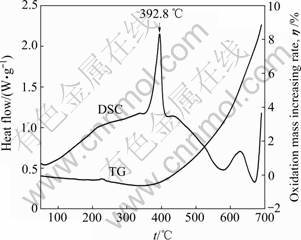
图11 Fe-P非晶合金在空气中的差示扫描量热和热重曲线
Fig. 11 DSC-TG curves of Fe-P amorphous alloy in air
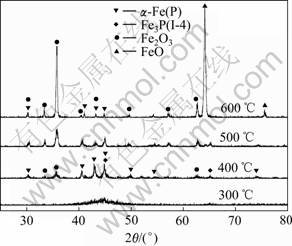
图12 Fe-P非晶合金在空气中经不同温度热处理后的 XRD谱
Fig. 12 XRD patterns of Fe-P amorphous alloy after heat treated at various temperatures in air
3 结论
1) 镀液的 pH值升高,温度降低,柠檬酸三钠络合剂浓度增大,均会增加Fe-P非晶合金共沉积的阴极极化,同时有利于获得致密镀层。
2) 镀态Fe-P合金镀膜为非晶态结构。随着热处理温度升高,镀膜在330.5 ℃开始晶化;383.6 ℃时,α-Fe(P)固溶体大量晶化析出;483.7 ℃时,Fe3P(I-4)相大量脱溶析出。
3) 随着真空热处理温度升高,合金镀层的耐蚀性能和硬度先增加后下降,经450 ℃热处理后,合金镀层的耐蚀性能最佳且硬度最大。
4) 400 ℃以下时,Fe-P非晶合金镀层具有良好的耐热氧化能力;而当温度高于400 ℃时,镀层耐热氧化能力迅速下降。
致谢:
诚挚感谢厦门大学杨防祖副教授提供的显微硬度测试。
REFERENCES
[1] 王森林, 陈志明. 电沉积条件对Fe-Co-P合金结构和磁性能的影响[J]. 稀有金属材料与工程, 2007, 36(s3): 5-8.
WANG Sen-lin, CHEN Zhi-ming. Influence of the electro-deposition conditions and heat treatment on the structure and magnetic performances of the Fe-Co-P alloy[J]. Rare Materials and Engineering, 2007, 36(s3): 5-8.
[2] SULITANU N, BR?NZ? F. Electrodeposited Ni-Fe-S films with high resistivity for magnetic recording devices[J]. Journal of Optoelectronics and Advanced Materials, 2004, 6(2): 641-645.
[3] 李庆伦, 俞春福, 崔永植. 电镀Fe-P非晶合金研究现状[J]. 表面技术, 1999, 28(1): 4-5.
LI Qing-lun, YU Chun-fu, CUI Yong-zhi. The present research situation for electrodeposition Fe-P amorphous alloy[J]. Surface Technology, 1999, 28(1): 4-5.
[4] 傅静缘, 罗泾源. Fe-P非晶合金电沉积镀层的制备及其腐蚀性能[J]. 北京钢铁学院学报, 1987, 9(1): 98-104.
FU Jing-yuan, LUO Jing-yuan. The elecrodeposition coating of Fe-P amorphous alloy and the study of corrosive behavior of the alloy[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Iron and Steel Technology, 1987, 9(1): 98-104.
[5] ZHENG X M, HUANG L, WU Y S, XUE L J, KE F S, SUN S G. Electrodeposition and lithium storage performance of amorphous Fe-P alloy electrodes[J]. Chinese Journal of Inorganic Chemistry, 2009, 25(2): 317-320.
[6] HUANG L, ZHENG X M, WU Y S, XUE L J, KE F S, WEI G Z, SUN S G. Electrodeposition and lithium storage performance of novel three-dimensional porous Fe-Sb-P amorphous alloy electrode[J]. Electrochemistry Communication, 2009, 11: 585-588.
[7] ZE?EVI? S K, ZOTOVI? J B, GOJKOVI? S L J, RADMILOVI? V. Electrochemically deposited thin films of amorphous Fe-P alloy: Part Ⅰ. Chemical composition and phase structure characterization[J]. Journal of Electroanalytical Chemistry, 1998, 448: 245-252.
[8] 张远声, 龚 敏, 郑莉丽. Fe-P非晶合金电镀液的基本性能[J]. 表面技术, 1998, 27(3): 3-5.
ZHANG Yuan-sheng, GONG Min, ZHENG Li-li. The base property of Fe-P amorphous alloy solution[J]. Surface Technology, 1998, 27(3): 3-5.
[9] 张远声, 龚 敏, 凌厉为. 非晶态Fe-P合金电镀液稳定性研究[J]. 电镀与涂饰, 1999, 21(1): 10-12.
ZHANG Yuan-sheng, GONG Min, LING Li-wei. The stability of Fe-P amorphous alloy solution[J]. Plating and Finishing, 1999, 21(1): 10-12.
[10] WANG S L, HONG L L. Effect of the heat treatment on the structure and the properties of the electroless Co-Fe-B alloy[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2007, 429(1/2): 99-103.
[11] 王 玉, 郭金彪, 俞宏英, 李辉勤, 孙东柏. 镍磷非晶纳米晶复合镀层的制备及其耐腐蚀性[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2007, 17(9): 1481-1485.
WANG Yu, GUO Jin-biao, YU Hong-ying, LI Hui-qin, SUN Dong-bai. Preparation and corrosion resistance of Ni-P amorphous-nanocrystalline composite coatings[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2007, 17(9): 1481-1485.
[12] 俞春福, 崔永植, 李庆伦. 电沉积Fe-P非晶合金镀层强化机理研究[J]. 材料保护, 1999, 32(9): 3-5.
YU Chun-fu, CUI Yong-zhi, LI Qing-lun. Strengthening mechanism of amorphous Fe-P alloy deposit[J]. Materials Protection, 1999, 32(9): 3-5.
[13] 范云鹰, 张英杰, 罗少林. 电沉积Fe-P非晶镀层受热转变[J]. 材料热处理学报, 2008, 29(4): 140-142.
FAN Yun-ying, ZHANG Ying-jie, LUO Shao-lin. Transformation of electrodeposited Fe-P amorphous coatings during process of heat-treatment[J]. Transactions of Material and Heat Treatment, 2008, 29(4): 140-142.
[14] 张志凯, 郭红霞, 王 群. Fe-Ni合金电沉积的电化学行为[J]. 功能材料, 2010, 41(9): 1595-1599.
ZHANG Zhi-kai, GUO Hong-xia, WANG Qun. Electrochemical behaviors of electrodeposited Fe-Ni alloy[J]. Journal of Fuctional Materials, 2010, 41(9): 1595-1599.
[15] 杨元政, 赵德强, 温敦古, 陈小祝, 谢致薇, 白晓军. Fe61Co10Zr5W4B20块体非晶合金的晶化行为与力学性能研究[J]. 材料热处理学报, 2006, 27(6): 29-33.
YANG Yuan-zheng, ZHAO De-qiang, WEN Tun-gu, CHEN Xiao-zhu, XIE Zhi-wei, BAI Xiao-jun. Crystallization characteristics and mechanical properties of Fe61Co10Zr5W4B20 bulk amorphous alloy[J]. Transactions of Material and Heat Treatment, 2006, 27(6): 29-33.
[16] 党淑娥, 郑晓华, 闫志杰, 胡 勇, 郝维新. 非晶合金的晶化动力学与初生相的内在联系[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2007, 17(2): 296-302.
DANG Shu-e, ZHENG Xiao-hua, YAN Zhi-jie, HU Yong, HAO Wei-xin. Correlation between crystallization kinetics of amorphous alloys and primary phases during crystallization[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2007, 17(2): 296-302.
[17] 高诚辉. 非晶态合金镀及其镀层性能[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2004: 174-188.
GAO Cheng-hui. The electroplating and property of amorphous alloy[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2004: 174-188.
[18] 张 杰, 于振花, 李 焰. Zn-55%Al-Si合金镀层钢丝在海水中的耐蚀性能[J]. 材料研究学报, 2008, 22(4): 347-352.
ZHANG Jie, YU Zhen-hua, LI Yan. Corrosion behavior of hot-dipped Zn-55%Al-Si coated steel wires in seawater[J]. Chinese Journal of Materials Research, 2008, 22(4): 347-352.
[19] 罗少林. 电沉积Fe-P非晶镀层工艺及机理研究[D]. 昆明: 昆明理工大学, 2007: 48-49.
LUO Shao-lin. Research on Fe-P amorphous alloy electrodeposition and mechanism[D]. Kunming: Kunming University of Science and Technology, 2007: 48-49.
(编辑 李艳红)
收稿日期:2011-01-18 ;修订日期:2011-06-07
通信作者:王森林,教授,博士;电话:18906993609;E-mail: slwang@hqu.edu.cn