J. Cent. South Univ. Technol. (2007)04-0479-06
DOI: 10.1007/s11771-007-0093-1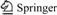
Effect of working condition on thermal stress of NiFe2O4-based cermet inert anode in aluminum electrolysis
LI Jie(李 劼) , WANG Zhi-gang(王志刚), LAI Yan-qing(赖延清), LIU Wei(刘 伟), YE Shao-long(叶绍龙)
(School of Metallurgical Science and Engineering, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China)
__________________________________________________________________________
Abstract: Based on the FEA software ANSYS, a model was developed to simulate the thermal stress distribution of inert anode. In order to reduce its thermal stress, the effect of some parameters on thermal stress distribution was investigated, including the temperature of electrolyte, the current, the anode cathode distance, the anode immersion depth, the surrounding temperature and the convection coefficient between anode and circumstance. The results show that there exists a large axial tensile stress near the tangent interface between the anode and bath, which is the major cause of anode breaking. Increasing the temperature of electrolyte or the anode immersion depth will deteriorate the stress distribution of inert anode. When the bath temperature increases from 750 to 970 ℃, the maximal value and absolute minimal value of the 1st principal stress increase by 29.7% and 29.6%, respectively. When the anode immersion depth is changed from 1 to 10 cm, the maximal value and absolute minimal value of the 1st principal stress increase by 52.1% and 65.0%, respectively. The effects of other parameters on stress distribution are not significant.
Key words: inert anode; thermal stress; working condition; aluminum electrolysis
__________________________________________________________________________
1 Introduction
Carbon is always used as anode in the process of aluminum electrolysis, which produces many problems. Inert anode that can solve the problems of using carbon anode and reduce the production cost by 30% has become the research focus of international aluminum and material field[1-3]. Inert anode has some advantages including reducing the labour intensity and avoiding the environment pollution. Additionally, oxygen is the byproduct of electrolysis, its value is about 3% of the value of aluminum produced according to some research[4-6].
At present, most researches are carried out on three types of inert anode, i.e. metal oxide ceramic anode, metal or alloy anode and cermet anode. Among cermet anodes, the research on NiFe2O4-based cermet is more than others[7-11], and the object of this paper is NiFe2O4-based cermet inert anode and the composition(mass fraction) is 17%Ni/83%(10NiO-90 NiFe2O4).
Because the inert anode is immersed in the high-temperature electrolyte, great thermal stress will be produced. In order to reduce its thermal stress, the concept of functionally graded material was introduced to the inert anode preparation. ZHANG et al[12] studied the influence of layer number(n), composition index(p) and the cone angle(θ) on the distribution of the thermal stress at the surface. The results show that the layer number(n) influences the smooth of the stress curve mainly. The composition index(p) is the key factor for the stress relax. The decrease of p results in the decrease of thermal stress. The increase of the angle is beneficial to relax the thermal stress, but its effect is less than the composition index. The research of LI et al[13] got the similar conclusions. Multi-layer graded anode has big stress between layers and its preparation is very complicated, so in this paper it was simplified and a finite element model was developed to simulate the working condition of inert anode. The effect of some major parameters was investigated including the temperature of electrolyte, the intensity of current, the anode cathode distance(L), the anode immersion depth, the surrounding temperature and the convection coefficient between anode and circumstance.
2 Model and calculation method
2.1 Solid model
A half-anode solid model was developed according to the actual dimension (see Fig.1). The model comprises of five parts, that is anode, anode rod, filling stuff, bath and crust. The initial value of anode immersion depth was set to 6 cm, i.e. half of the anode height. Taking the heat balance into consideration, the initial value of L was set to 7.5 cm, and Fig.2 shows the anode structure briefly.
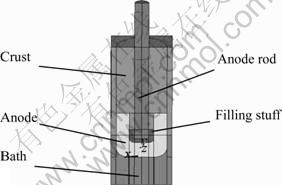
Fig.1 Solid model of NiFe2O4-based cermet inert anode
Fig.2 Brief structure of NiFe2O4-based cermet inert anode(unit: m)
2.2 Finite element model
Solid model was built first and then meshed with hexahedrons to gain a finite element model (see Fig.3). The SOLID69 element that has two degree of freedom(DOF) i.e. volt and temperature, was used to indicate the electric part of the model and SOLID70 element that has only one DOF (temperature) was used to indicate the non-electric part of the model. After thermo-electric analysis, the distribution of temperature and voltage can be gained. After saving the result of node temperature, the volume and mesh of bath would be deleted because the stress is not affected by the liquid bath. Then the whole model was transformed to the structural analysis. After reading the saved node temperature result, the stress distribution can be calculated using SOLID45 element.

Fig.3 Finite element model of NiFe2O4-based cermet inert anode
2.3 Material properties
The model comprises of five kinds of materials, in which the composition of anode rod is Cr12MoV and its material properties can be obtained from material handbook. The composition of anode is 17%Ni/83% (10NiO-90NiFe2O4), the form of volume fraction is 10.8%Ni/89.2%(10NiO-90NiFe2O4) and the resistivity of anode is from experiment data. Due to the similarity of properties between (10NiO-90NiFe2O4) and 5324(5324 is a kind of ceramic with 51.7%NiO and 48.3%Fe2O3[14]), the other parameters of anode can be calculated using the linear mixing rule based on Voight’s presumption[15],
P = P1 f1+P2 f2 (1)
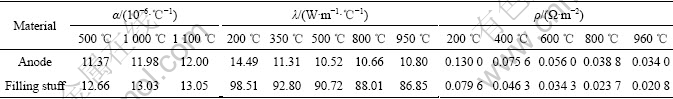
where P represents the material property; f is the volume fraction; the subscripts 1 and 2 represent the relevant materials respectively. The material properties of anode filling stuff were also calculated from the above mixing rule. Among these parameters, the thermal expansion coefficient, the heat transfer coefficient and the resistivity of anode and filling stuff are very significant, which are listed in Table 1.
Table 1 Thermal expansion coefficient, heat transfer coefficient and resistivity of anode and filling stuff at different temperatures
2.4 Boundary conditions
There are three kinds of boundary conditions, i.e. electrical, thermal and structural boundary conditions. In electrical boundary conditions, current was applied to the upper face of anode rod and the lower surface of bath was applied zero voltage. In thermal boundary conditions, the node temperature of bath was set to 960 ℃ initially, convection and radiation boundary conditions were applied on the surface between anode and surrounding air, the effect of radiation was converted to the convection coefficient. As for the structural boundary conditions, the plane of z=0 was set as symmetrical plane and the center lines on it were restricted by x=0 and z=0.
3 Results and discussion
3.1 Thermal stress distribution characteristics
Fig.4 shows the distribution of thermal stress. It is obvious in Fig.4 that there exists compressive stress on the most surface of anode, anode rod and filling surface (positive value means tensile stress while negative value means compressive stress), but it is not harmful for the anode. The anode is a kind of cermet that belongs to fragile material, and the fragile materials often have higher intensity that can resist relative large compressive stress. But from Fig.4 it can also be seen that there exists a common characteristic, that is, large tensile stress exists on the contacting surface of anode and bath (three-phase interface), which is very disadvantageous for the anode and is the major cause of the anode cracking.
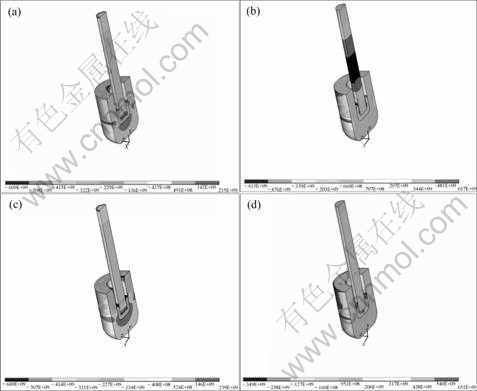
Fig.4 Stress distribution of anode, filling stuff and anode rod
(a) x-direction(radial direction); (b) y-direction(axial direction); (c) z-direction(hoop direction); (d) 1st principal stress
In this paper the structure of anode was simplified and that complicated anode structure was not adopted. According to the intensity theory and the cracking type and taking the maximal and minimal value of all direction’s stress and the 1st principal stress as the optimized goals, the effect of some parameters on the stress distribution was investigated, including the bath temperature, the current density, anode cathode distance, the anode immersion depth, the surrounding temperature and the convection coefficient between anode and circumstance.
3.2 Effect of electrolyte temperature
The temperature of electrolyte was changed from 750 to 970 ℃. Fig.5 shows the relevant change of thermal stress with the increase of temperature, where σmax, σmin, σx, σy, σz and σ1 mean the maximum stress, the minimum stress, x-direction stress, y-direction stress, z-direction stress and the 1st principal stress, respectively.
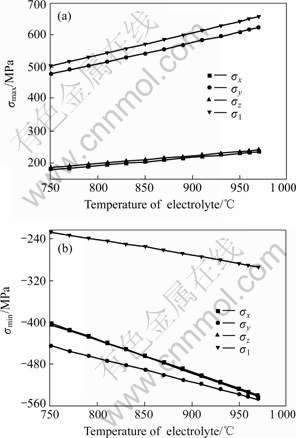
Fig.5 Effect of temperature on maximum and minimum stress
(a) Maximum stress; (b) Minimum stress
From Fig.5 it can be seen that with the increase of temperature, the maximum stress increases rapidly while the minimum (negative value means compressive stress) reduces obviously. The maximum of the 1st principal stress increases by 29.7% (from 505 to 655 MPa). The absolute minimum stress of the 1st principal stress increases by 29.6% (from 226 to 293 MPa). The absolute stress of y-direction is bigger than that in other directions. The maximum stress in y-direction increases by 30.0% (from 480 to 624 MPa) and the absolute minimum stress of it increases by 22.9% (from 446 to 548 MPa). The development trend of stress in x-direction and z-direction is similar. These pictures also show the significance of low-temperature electrolysis.
3.3 Effect of current
Fig.6 shows the change of thermal stress with the increase of current from 20 to 100 A.
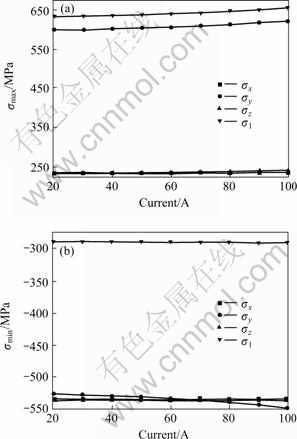
Fig.6 Effect of current on maximum and minimum stress
(a) Maximum stress; (b) Minimum stress
From Fig.6(a) it can be seen that with the increase of current, the maximum stress is increased but not significantly. The maximum stress of the 1st principal increases only by 3.5% (from 633 to 655 MPa). It is obvious that the tensile stress of y-direction is much bigger than that in other directions, which increases by 3.8% (from 599 to 622 MPa). From Fig.6(b) it can be seen that the change of minimum stress is small, the absolute minimum stress of y-direction stress increases only by 4.0% (from 526 to 547 MPa). The development trend of x-direction and z-direction stress is still similar.
3.4 Effect of anode cathode distance
Anode cathode distance is a very important parameter in the process of aluminum electrolysis, but its effect on the stress distribution is estimated to be small. The increase or decrease of L will change the whole heat balance but have little effect on the electric and temperature distribution of anode(Fig.7). When the L increases from 0.03 m to 0.10 m, the maximum and minimum stress are almost constant, which indicates that the aspect of anode stress may not be taken into account when a reasonable L wants to be determined.
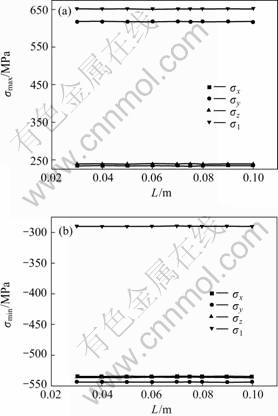
Fig.7 Effect of L on maximum and minimum stress
(a) Maximum stress; (b) Minimum stress
3.5 Effect of anode immersion depth
Fig.8 shows the change of thermal stress with the increase of anode immersion depth from 0.01 to 0.1 m.
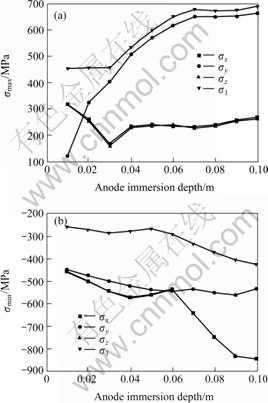
Fig.8 Effect of anode immersion depth on maximum and minimum
(a) Maximum stress; (b) Minimum stress
From Fig.8 it can be seen that the stress distribution becomes worse when the anode immersion depth increases. The change of x-direction stress is quite similar with that of z-direction stress, and the tensile stress of y-direction is still the biggest among all directions. Fig.8 has a inflexion at 0.03 and 0.06 m anode immersion depth respectively, which may be due to different precisions of mesh, but it will not affect the total evolution trend. The maximum of the 1st principal stress increases by 52.1% (from 453 to 689 MPa) and the maximum stress of y-direction increases by 447.9% (from 121 to 663 MPa). The absolute minimum of the 1st principal stress increases by 65.0% (from 257 to 424 MPa) and the absolute minimum stress of y-direction increases by 19.0% (from 448 to 533 MPa). Considering its effect and other factors synthetically, the reasonable value of anode immersion depth is in the range of 0.03 - 0.06 m.
3.6 Effect of surrounding temperature and convection coefficient between anode and circumstance
When the surrounding temperature is changed from 50 to 150 ℃, the change of stress is shown in Fig.9.
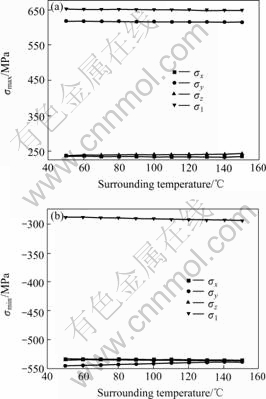
Fig.9 Effect of surrounding temperature on maximum and minimum stress
(a) Maximum stress; (b) Minimum stress
The maximum and minimum stresses almost keep constant when the surrounding temperature is increased. The y-direction tensile stress is still the biggest and most important. The evolution trend of x-direction and z-direction is quite analogous.
The convection coefficient was changed from 80 to 200 W/(m2·℃), Fig.10 shows its effect on stress distribution.
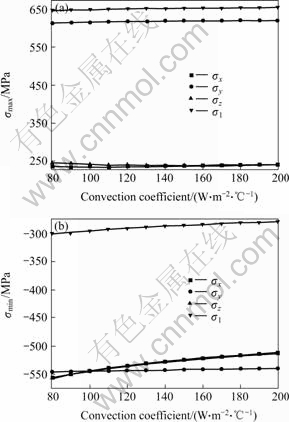
Fig.10 Effect of convection coefficient on maximum and minimum stress
(a) Maximum stress; (b) Minimum stress
From Fig.10 it can be seen that the effect of convection coefficient on maximum stress is smaller than that on minimum stress. With increasing convection coefficient, the absolute minimum stress reduces a little, which means the stress distribution becomes better. However, in total, the effect of convection coefficient is not remarkable.
4 Conclusions
1) Compressive stress exists on most surface of anode, a large tensile stress exists at the solid-liquid-air three-phase contact line, which is the major cause of the crack of the anode. In the tensile stresses, the y-direction(axial direction) stress is much bigger than x-direction and z-direction stress. The stress distributions of x-direction and z-direction are very similar.
2) The temperature of electrolyte affects the thermal stress remarkably. With the increase of electrolyte temperature, the maximum stress increases rapidly while the minimum stress decreases obviously. Low- temperature electrolysis is helpful to the stress distribution of inert anode.
3) The effect of anode immersion depth on thermal stress cannot be ignored. The total trend is that with the increase of anode immersion depth, the stress distribution becomes worse. The reasonable immersion depth is 0.03-0.06 m.
4) Current has small effect on stress distribution while other parameters’ effect is not significant including the anode cathode distance, the surrounding temperature and the convection coefficient between anode and circumstance.
References
[1] LIU Ye-xiang. Advance on the research and development of inert anode and wettable cathode in the aluminum electrolysis[J]. Light Metals, 2001(5): 26-29. (in Chinese)
[2] PAWLEK R P. Inert anodes: An update[C]// SCHNEIDER W. Light Metals. Warrendale: TMS, 2002: 449-456.
[3] de NORA V. Aluminium electrowinning—The future[J]. Aluminium, 2000, 76(12): 998-999.
[4] ZHOU Wei-ming, GUO Zhong-cheng.Present status of materials of inert anode for electrolysising aluminium[J]. Metallurgical Collections, 2004 (1): 1-3. (in Chinese)
[5] CHEN Xi-ping, LIU Feng-qin. Present studying situation of inert anodes in aluminum electrolysis cells[J]. Nonferrous Metals (Extractive Metallurgy), 2002 (4): 23-26. (in Chinese)
[6] WU Xian-xi. Conditions of investigation on the inert anodes in aluminium electrolysis[J]. Light Metals, 2000(1): 41-43. (in Chinese)
[7] ZHANG Lei, ZHOU Ke-chao, LI Zhi-you, et al. Effect of atmosphere on densification in sintering nickel ferrite ceramic for aluminum electrolysis[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2004, 14(6): 1002-1006. (in Chinese)
[8] ZHANG Gang, LAI Yan-qing, TIAN Zhong-liang, et al. Preparation of nickel ferrite based cermets for aluminum electrolysis[J]. Journal of Materials Science & Engineering, 2003, 21(4): 510-513. (in Chinese)
[9] TIAN Zhong-liang, LAI Yan-qing, ZHANG Gang, et al. Preparation of NiFe2O4-Cu based cermet inert anodes in aluminum electrolysis[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2003, 13(6): 1540-1545. (in Chinese)
[10] JIAO Wan-li, ZHANG Lei, YAO Guang-chun, et al. Sintering process of NiFe2O4 spinel with and without TiO2 adding[J]. Journal of the Chinese Ceramic Society, 2004, 32(9): 1150-1153. (in Chinese)
[11] LAI Yan-qing, LI Jie, TIAN Zhong-liang, et al. On the corrosion behaviour of NiFe2O4-NiO based cermets as inert anodes in aluminum electrolysis[C]// McNeil J. Light Metals. Warrendale: TMS, 2006: 495-500.
[12] ZHANG Xiao-yong, ZHOU Ke-chao, LI Zhi-you, et al. Design for the relax of thermal stress in the surface of 2-D functionally graded model[J]. Journal of Materials Science and Engineering, 2003, 21(5): 697-702. (in Chinese)
[13] LI J, ZHANG Q S, LAI Y Q, et al. Thermal stresses relaxation design of Ni/NiFe2O4 system functionally graded cermet inert anode[J]. Acta Metallurgica Sinica, 2005, 18(5): 635-641.
[14] WEYAND J D, DEYOUNG D H, RAY S P, et al. Inert Anodes for Aluminum Smelting[R]. Washington D C: Aluminum Company of America, 1986.
[15] WANG Bao-lin, HAN Jie-cai, ZHANG Xing-hong. Uneven Material Mechanics[M]. Beijing: Science Press. 2003. (in Chinese)
_____________________
Foundation item: Project (2005CB623703) supported by the National Basic Research and Development Program of China; Project (50474051) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China
Received date: 2006-11-11; Accepted date: 2007-03-27
Corresponding author: WANG Zhi-gang, Doctoral candidate; Tel: +86-731-8830474; E-mail: wzg03@163.com
(Edited by ZHAO Jun)