基于扩展有限元方法的齿牙疲劳断裂分析
来源期刊:中国有色金属学报(英文版)2019年第10期
论文作者:韦宇 江勇
文章页码:2099 - 2108
关键词:齿轮;疲劳;断裂;有限元法
Key words:gear; fatigue; fracture; finite element method
摘 要:齿轮传动系统主要失效形式是齿牙疲劳断裂。本文作者基于周期性边界条件建立二维双齿模型。采用扩展有限元法(XFEM)对服役过程齿牙的疲劳行为进行分析,重点研究初始裂纹和载荷因素对齿牙疲劳断裂的影响。结果表明,当最大主应力处萌生取向为0°的裂纹时,齿牙疲劳寿命最短,而靠近齿根的裂纹相对安全。同时,评价疲劳载荷情况必须综合考虑载荷比、载荷幅和平均载荷值。进一步针对材料选材开展模拟研究,为齿轮的设计提供指导。模拟结果表明,材料常数C和抗拉强度是影响齿牙疲劳寿命的最重要参数。
Abstract: Gear teeth in gear transmission systems suffer seriously from fatigue failure during service. In this work, a 2D double-tooth model was constructed with periodic boundary conditions. The fatigue fracture behavior of gear teeth was analyzed using the extended finite element method (XFEM), with emphases on the impacts of initial crack geometries and cyclic load factors. The results suggested that the shortest fatigue life is expected for 0° orientation cracks initiating at the maximum principal stress. Cracks that initiate closer to the bottom land of gear tooth are relatively safe. Moreover, to evaluate the fatigue load conditions, load ratio, load range, and mean load should be all taken into considerations. Further XFEM simulation for material selection was performed to guide the gear design. Among various material parameters, the material constant C and tensile strength are the most significant ones in determining the fatigue life.
Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 29(2019) 2099-2108
Yu WEI, Yong JIANG
State Key Laboratory of Powder Metallurgy, School of Materials Science and Engineering, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China
Received 30 January 2019; accepted 2 August 2019
Abstract: Gear teeth in gear transmission systems suffer seriously from fatigue failure during service. In this work, a 2D double-tooth model was constructed with periodic boundary conditions. The fatigue fracture behavior of gear teeth was analyzed using the extended finite element method (XFEM), with emphases on the impacts of initial crack geometries and cyclic load factors. The results suggested that the shortest fatigue life is expected for 0° orientation cracks initiating at the maximum principal stress. Cracks that initiate closer to the bottom land of gear tooth are relatively safe. Moreover, to evaluate the fatigue load conditions, load ratio, load range, and mean load should be all taken into considerations. Further XFEM simulation for material selection was performed to guide the gear design. Among various material parameters, the material constant C and tensile strength are the most significant ones in determining the fatigue life.
Key words: gear; fatigue; fracture; finite element method
1 Introduction
Gear transmission systems find wide applications in automobile, aerospace, and machinery industries, due to the combined advantages of high transmission efficiency, precise transmission ratio, high reliability, and high durability. These gears are operated under cyclic loading conditions and in harsh environments, often leading to fatigue failure. Fatigue fracture has been accounting for a considerable proportion of gear failure modes [1]. During the normal course of operation, the gear tooth is subjected to bending due to the application of load on the gear tooth. When the load is repeated for a very huge number of cycles, the fatigue of the gear induces the crack initiation at the gear tooth root which propagates with each rotational cycle of the gear and ultimately leads to the breaking of the gear tooth. A better understanding of fatigue behaviors of the gear and their dependence on the initial crack geometries, load conditions, and material parameters, can give insightful guidance on the optimal design of gear systems with extended service lives.
A typical fatigue fracture process is principally divided into two stages, i.e. crack initiation at the tooth root and crack propagation along the tooth root to ultimate failure. Both stages may last for a very long time period. For most fatigue failure cases, traditional experimental analyses turn out to be very time- consuming and cost-inefficient, and numerical simulation methods are thus more preferred for investigating the fatigue fracture behaviors of the gear. There are various numerical methods that have been applied to simulating the fatigue fracture of the gear, including the finite element method (FEM) [2][1], the boundary element method [3,4], the mesh-free methods [5-7], and the extended finite element method (XFEM) [8-10]. The traditional FEM, however, requires that the crack always coincides with the edges of elements. As the crack grows, remeshing at the crack tip and redefining the crack geometry must be performed during each iteration. Hence, the fatigue fracture simulation using FEM can be extremely cumbersome. The extended finite element method (XFEM) [11] is especially developed to address these challenges. The XFEM can model a crack independent of finite element meshes. The level set method [12] is further adopted by XFEM to localize the crack tip and track its propagation [13], and the enrichment functions are added to the standard finite element approximation to account for the presence of the crack [8].
The XFEM analyses on fatigue fracture have been proven very successful in many ways for various engineering systems [14-17]. RAD et al [18] predicted the fatigue life of a typical helical gear using XFEM. SINGH et al [19,20] applied the XFEM to investigate the effects of voids, inclusions, and minor cracks on fatigue life. NASRI and ZENASNI [21] employed the XFEM and Paris’ law to evaluate the fatigue life of coated materials. MARTINEZ et al [22] simulated the fatigue crack propagation in railway axle using XFEM. All these simulations are favorably compared with available experimental results. BERGARA et al [23] further demonstrated the capabilities of the XFEM-based linear elastic fracture mechanics (LEFM) approach for simulating fatigue crack growth. By integrating 3D-XFEM and LEFM, CURA et al [24,25] investigated the effects of the wheel geometric parameters (rim and web thickness) on crack propagation path under the centrifugal loading, enabling the improved design of gears.
Encouraged by these successes, in the present work, we employed the XFEM simulations based on the LEFM and Paris’ law as implemented in ABAQUS to investigate the fatigue fracture behaviors of gear teeth during normal operation. A 2D finite element model of one pair of teeth was built in the commercial soft ABAQUS. The dependence of fatigue crack propagation and fatigue life of gear on the initial crack geometries (initial crack position, orientation, and length), cyclic loading conditions (load ratio, load range, and mean load) and material factors, was intensively simulated and discussed. The knowledge obtained will provide important insights for the optimal design of gears.
2 Methods and modeling
2.1 XFEM method
Standard finite element methods describe the displacement fields using shape function and element mesh nodes, such as
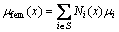 (1)
(1)
where S is the complete set of all nodes in the mesh, Ni(x) are the shape functions. The Cartesian coordinate axes are denoted by x≡(x,y) in 2D, with Latin lower case indices referring to Cartesian components. μi represent the nodal displacements of the elements. With the XFEM method, the displacement fields [9,10,26] for 2D crack modeling are written in the general form as

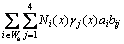 (2)
(2)
where Ni are the standard finite element shape functions. n is the number of global nodes. Wb or Ws represents the nodes of an element that is completely or partially cut by the crack, respectively. ai are the nodal enriched degrees of freedom associated with the Heaviside function H(x). bij are the nodal enriched degrees of freedom vector values associated with the crack-tip enrichment function γj(x).
The Heaviside function H(x) is a discontinuous function through the crack surface and is constant on each side of the crack. γj(x) is the crack tip enrichment function that can be written as [27]
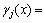
 (3)
(3)
where r and θc are local crack tip parameters, as schematically defined in Fig. 1.

Fig. 1 Local parameters r and θc defined for crack tip with crack length of a
2.2 Fatigue crack growth
To determine the crack growth direction, the maximum principal stress criterion is often taken where the crack growth direction is always presumed to be perpendicular to the maximum principle stress direction [20]. According to this criterion, at each crack tip increment (see Fig. 1), the direction of crack growth θc is obtained by setting the local shear stress to be zero, i.e.
KIsin θc±KII(3cos θc-1)=0 (4a)
Thus
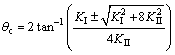 (4b)
(4b)
where KI and KII are the stress intensity factors to predict the local stress state near the crack tip caused by remote load modes I and II, respectively, according to the linear elastic fracture mechanics (LEFM). The stress intensity factors are further related to the energy dissipated during fracture per unit of newly created fracture surface area, i.e. the energy release rate G, through the elastic modulus E [28]:
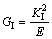 (5)
(5)
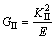 (6)
(6)
Thus, Eq. (4) can be further rewritten as
 (7)
(7)
where GI and GII are the fracture energy release rates under modes I and II, respectively. In practice, the equivalent fracture energy release rate G=2(1-ν)(GI+GII), as defined in Ref. [23], is more often adopted in ABAQUS for a two-dimensional (2D) problem. Here, ν is the Poison ratio of the material. The fatigue crack growth can be thus described using the Paris’ law which relates sub-critical crack growth rate (da/dN) to the range of the fracture energy release rate (△G) (or the stress intensity factor, △K) during the fatigue cycle as [29]
 (8)
(8)
where △G(=Gmax-Gmin) measures the varying range of the energy release rate, and Gmax or Gmin corresponds to the energy release rate when the structure is under the maximal or minimal load (Fmax or Fmin) during the cycle, respectively. C and M are material constants and can be evaluated by three-point bending tests according to the standard procedure ASTM E 399-80 [30].
The present work aimed to simulate the fatigue fracture behavior of the gear teeth during operation using XFEM. We firstly employed the commercial finite element soft ABAQUS to construct a two-dimensional gear model with a preset crack at the tooth root. The material parameters are referred to Ref. [1] and tabulated in Table 1. To simulate the operation course, the displacement and rotation of the boundary nodes are fully constrained. A cyclic load with Fmin=0 kN and Fmax=36 kN (see Fig. 2) is applied on the contact point, being perpendicular to the tooth profile. The gear model structure, along with the mesh and boundary conditions, are shown in Fig. 3. The mesh shape may have strong influence on the crack growth path, and also, to help reduce the computational time, a common meshing method with a local mesh refinement scheme is adopted as suggested by CURA et al in Ref. [25].
Table 1 Material parameters used [1]
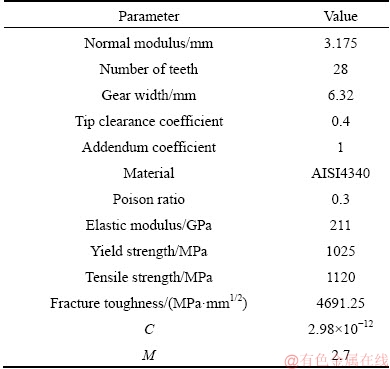
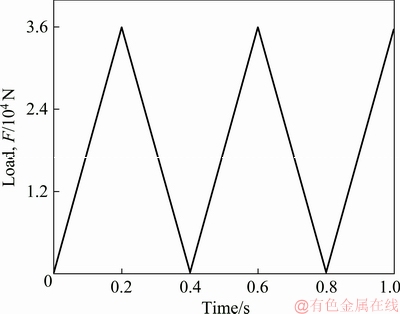
Fig. 2 Applied cyclic loading for XFEM fatigue simulation
3 Results and discussion
3.1 Initial crack geometries
3.1.1 Crack initiation location
Cracks are often found to occur at the gear tooth root where the principle stress is the maximum during the phase of engagement [25]. To confirm the maximum principle stress (psmax)at the tooth root, a gear model without the preset crack was firstly built and simulated under a static concentrated load in Fig. 3. The geometrical dimension and material parameters of the gear followed exactly one experimental sample previously reported in Ref. [1]. A static concentrated load of Fmax=36 kN was applied to the contact point between a pair of gear teeth during the course of operation. The calculated von Mises stress distribution of the gear is shown in Fig. 3. Here, the von Mises stress was employed as a measure of equivalent tensile stress on each element of the gear body. Very clearly, upon the static concentrated load, the psmax occurs at the tooth root position in Fig. 3 where the gear is the most vulnerable to crack. Therefore, we were able to preset an initial crack at the position where the maximum von Mises stress is located, and aligned it to be perpendicular to the profile of the gear tooth root for the subsequent fatigue fracture simulation.

Fig. 3 Gear double-teeth model with settings of meshes and boundary conditions, and simulated von Mises stress field under static concentrated load of Fmax=36 kN
With the same mesh and boundary condition settings in Fig. 3, the cycle load was then applied to the simulation of fatigue crack propagation. Figure 4 shows how the fatigue crack propagates with the load cycles. Under the given load conditions, the preset crack with an initial length of 0.5 mm opened immediately during the first cycle, and then propagated continuously through the whole tooth. After 48375 load cycles, the whole tooth broke from the gear body. The simulated crack propagation path was found to be perfectly consistent with the common fracture failure of gear tooth induced by fatigue loads as observed in Refs. [1,31] (see Fig. 5). We thus felt comfortable to employ the same model and settings for further XFEM simulations, to investigate the effects of geometrical factors (such as the initial crack position, orientation, and length), loading factor (such as the load ratio, mean stress, and stress range), and material parameters, on fatigue fracture behaviors of the gear.
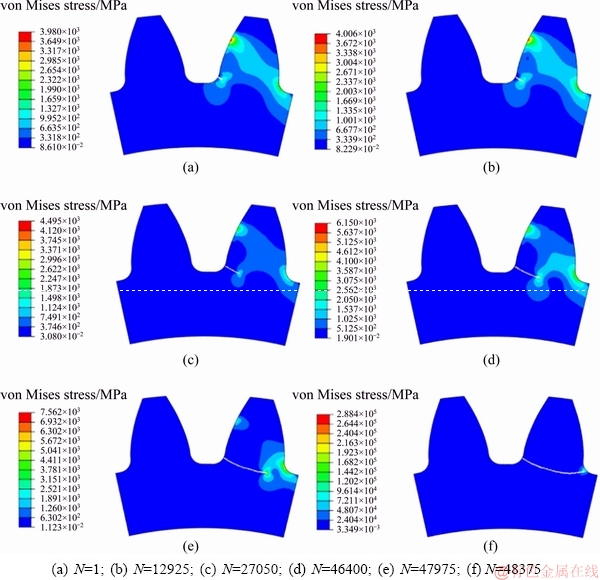
Fig. 4 Fatigue crack propagation versus load cycles (Preset crack with initial crack length of 0.5 mm was positioned at point of gear tooth root where maximum principle stress was located)

Fig. 5 Commonly observed fatigue-induced fractures of gear teeth [1,31]
To assess the effects of crack initiation location on the fatigue fracture behaviors, the initial crack was preset at several different positions of the gear tooth root, including the maximum principal stress position (Pm) and four other neighboring positions (P1-P4) distributed along the tooth profile, as denoted in Fig. 6(a). All initial cracks had the same initial length of 0.5 mm and were positioned perpendicularly to the tooth profile. The loading, meshing and boundary conditions were taken as the same as above. The XFEM predicted fatigue lives are compared in Fig. 6(a). Here fatigue life is defined as the number of cycles for an initial crack to propagate through the whole tooth and cause the complete tooth breaking from the gear. Clearly, the shortest fatigue life was predicted for the crack initiation at Pm. The fatigue lives for crack initiation at P2, Pm and P3 are all comparable, about four- or eight-fold lower than that at P1 or P4, respectively. The crack initiation location does influence the exact growth path of the crack, although all the predicted paths look likely the same as commonly observed in Fig. 5.
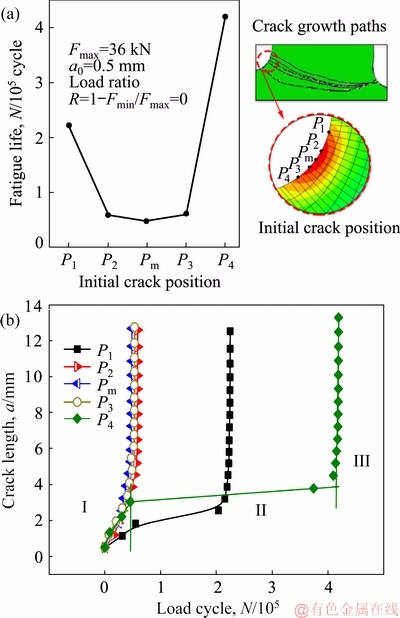
Fig. 6 Fatigue lives versus initial crack positions at gear tooth (a) and crack growth process for different crack initiation locations at tooth root (b)
Fatigue life does not reflect all the details of crack growth process, such as the growth rate. In Fig. 6(b), we further evaluated the crack growth rates as the crack length versus the number of cycles for all the crack initiation locations. Please note that a fatigue crack never grows in a consistent speed but follows a typical three-stage process of crack initiation, crack growth, and finally ultimate failure. To be more specific, the crack propagates slowly during the first stage of crack initiation until it reaches a critical size. Once reaching the critical size, it propagates quickly during the crack growth in a direction perpendicular to the maximum principle stress, and eventually leads to the ultimate failure of the material, often in a brittle catastrophic fashion. As seen in Fig. 6(b), the initiation location of crack significantly affects its growth rate. For crack initiation at P2, Pm, or P3, the first initiation stage is nearly absent, which should be attributed to the resulted high stress intensity factor △K. The initial crack begins to become instable, and its length increases quickly from the initial value of 0.5 mm to its critical size of 1-2 mm, within about the first 1×104 cycles. The growth stage is also short, during which the crack propagates rapidly to the complete breaking of gear tooth, within only a few tens of thousands of cycles. While for crack initiation at P1 or P4, the first initiation stage lasts for two or four hundreds of thousands of cycles, being accompanied with an increased critical size of ~2 or 4 mm, respectively. Among all the cracks, the P4 crack which is close to the bottom land of gear tooth is the safest. As seen in Fig. 6, different crack initiation locations also lead to different fracture paths of the gear. Nevertheless, in practice, the exact crack initiation location is difficult to predict, for it is sensitive to the manufacturing process of gear which may cause various initial crack positions [32].
3.1.2 Initial crack orientation
To assess the effects of initial crack orientation on the fatigue fracture behaviors, the initial crack was preset at the position Pm with different orientations, including 0° (which is perpendicular to the tooth profile), -5°, 5°, -15°, 15°, and -20°, 20°, as denoted in Fig. 7(a). The loading, meshing, and boundary conditions were taken as the same as above. The XFEM predicted fatigue lives are compared in Fig. 7(a). Certainly, the shortest fatigue life was found for the initial crack orientation of 0° at Pm. The fatigue lives for initial crack orientations of 0°, -5°, and 5° are still comparable, but are three- or five-fold lower than that for -20° or 20°, respectively.

Fig. 7 Fatigue lives versus initial crack orientations at gear tooth (a) and crack growth process for different orientations of initial crack at position Pm (b)
We further evaluated the crack growth rates for all the initial crack orientations. As seen in Fig. 7(b), the crack growth rate can also be affected by the initial crack orientation. The orientation of 0° is perpendicular to the direction of maximum principle stress, and thus has the highest stress intensity factor △K and the least number of load cycles for crack initiation. The crack initiation phase periods for the orientations of -5°, 0°, and 5° are comparable. Other orientations deviate much from the perpendicular direction, leading to the greatly reduced stress intensity factors and hence the elongated crack initiation phase periods. This is especially true for the -20° and 20° orientations, where the first initiation stage lasts for more than 1×105 or 2×105 cycles, as compared to just a few tens of thousands of cycles for the -5°, 0°, and 5° orientations. It is worth noting that the initial crack orientation has only a little influence on the critical size of crack, which is 1-2 mm for all the considered orientations, not comparable to the effect of the crack initiation location. This suggests that even with different initial orientations, the cracks at Pm can be more easily to adjust their orientation during the initiation stage and propagate along the same path during growth until the final ultimate failure. Consequently, the initial crack orientation does not affect much the crack growth path, consisting with other findings for thin rim gears [24] and also for coated materials [21].
3.1.3 Initial crack length
Fatigue crack growth rate can depend sensitively on the critical size of the crack. In this sense, the initial crack length may play decisive role in fatigue fracture behaviors of gears. To manifest this, six initial cracks with different lengths, including 0.2, 0.5, 0.8, 1.0, 2.0, and 2.5 mm, were preset at position Pm and aligned perpendicularly to the tooth profile. The loading, meshing, and boundary conditions were taken as the same as above.
Figure 8(a) shows the fatigue lives and crack growth paths for different initial crack lengths of gears, and Fig. 8(b) compares the crack growth rates. Clearly, the fatigue life decreases consistently with increasing the initial crack length. For the cracks with an initial length above 2.0 mm, the crack initiation stage was not obvious, and the crack grew quickly to reach the final failure stage. This agrees the predicted critical size of 1-2 mm for fatigue crack initiation at position Pm with various orientations. Please note that the fatigue life was reduced to only a couple of thousands of cycles for an initial length of 2.0 or 2.5 mm. Please also note that the initial crack length does not affect the crack growth path. Combining the results in Figs. 7 and 8, one may conclude that, once a crack initiates at Pm, the crack growth path is almost determined and the fatigue cracks of gears always propagate along the gear root bottom, ending up at the opposite end of the tooth root.
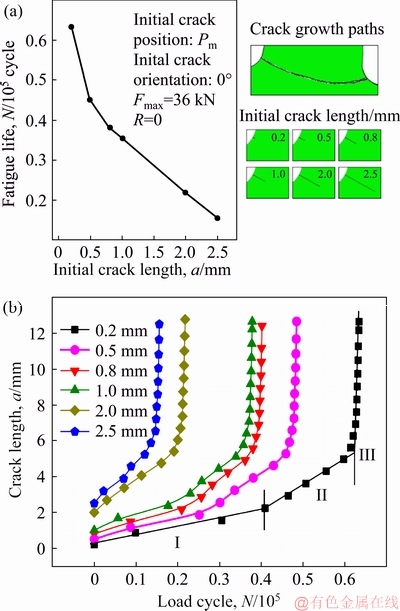
Fig. 8 Fatigue lives versus initial crack lengths at gear tooth (a) and crack growth process for different lengths of initial crack at position Pm (b)
3.2 Cyclic loading condition
In Section 3.1, we have investigated fatigue fracture behaviors of the gear under a given cyclic loading. With a given load frequency, the cyclic loading condition is determined by load ratio (or load range) and mean load. Fatigue performance is often evaluated using an S-N curve, which plots the magnitude of a cyclic stress (S) versus the logarithmic scale of cycles to final failure (N). Here, we evaluated the fatigue performance by plotting the number of cycles to final failure versus the magnitude of load ratio R. Generally, for a given Fmax, the greater the applied load ratio is and the higher the mean load is, the shorter the fatigue life will be. For instance, KRüGER et al [33] performed a three-point bending test to investigate the effects of stress range on the fatigue behaviors of a Ti-6-22-22-S alloy, showing that fatigue crack growth rate increases with increasing the load ratio. In our XFEM simulations, two approaches for increasing the load ratio were made by (1) fixing Fmax (=36 kN) and decreasing Fmin to 0, and (2) fixing Fmin (=7.2 kN) and increasing Fmax to 36 kN. The simultaneous consideration of the two approaches is advantaged: either approach can achieve an increasing load range, but the first one results in a decreasing mean load while the second one results in an increasing mean load. Therefore, both the individual and combinational effects of the stress range and mean stress can be possibly discussed. Figure 9 and Table 2 show all our XFEM simulation results. Again, the initial crack length was preset as 0.5 mm at position Pm with 0° orientation. The cycle frequency and boundary conditions were also taken as the same as above.
It can be observed in Fig. 9 that the load ratio significantly affects the fatigue performance of the gear. A same general trend is observed for both approaches, i.e. the fatigue life decreases with the increase of load ratio. The increasing load ratio leads to the increasing fracture energy release rate or stress intensity factor range (△G or △K), and thus the fatigue crack growth rate is increased, according to Eq. (8). The comparison between A3 and B5 also confirms that under the same mean stress, a larger stress range leads to a larger load ratio and thus a smaller fatigue life. Further comparisons between A1 and B2 (A3 and B3) suggest that under the same stress range, the higher the mean stress is, the longer the reduced fatigue life is. Based on our limited data, it is clear that the cyclic loading conditions have nonlinear and complex impacts on fatigue behaviors, and load ratio does not solely determine the fatigue life. Load ratio, load range, and mean load must be closely combined to evaluate the fatigue loading conditions. Other loading factors such as service environmental conditions [34,35] can also be important, which are, however, beyond the scope of this study. To achieve a more quantitative understanding on the effects of loading conditions, sophisticated experimental design with nonlinear regression analysis can be resorted to.

Fig. 9 Predicted gear fatigue lives with increasing load ratio R
Table 2 Parameters for Fig. 9

3.3 Material parameters
To evaluate the fatigue dependence on material parameters, three commercial steels were selected for XFEM simulations. The material properties are compared in Table 3, where C and m are defined in Eq. (8). For XFEM simulations, the loading, meshing, and boundary conditions were taken as the same as in Section 3.1. The initial crack length was preset as 0.5 mm at position Pm with 0° orientation.
Figure 10(a) compares the crack propagation at the tooth root as the number of load cycles during the whole fatigue life for different gear steels (AISI4130, AISI4340, and AISI9310). The fatigue life can be measured as 1648 cycles only for the AISI4130, 41666 cycles for the AISI4340, or up to 215576 cycles for the AISI9310 gear, respectively. According to in Eq. (8), for a given relative energy release rate △G, the sub-critical crack growth rate is dictated by the material constants of C and M. The reduced C and M shall be in favor of a lower crack growth rate and thus an enhanced fatigue life. However, these three steels are majorly differentiated by C, according to Table 2. Consequently, one can see clearly from Fig. 10 that the crack growth rate decreases and the fatigue life increases constantly with decreasing the material constant C. The higher tensile strength also contributes to the promoted fatigue life, perhaps due to its stronger prevention effects on fatigue crack initiation, while the elastic modulus and fracture toughness have no obvious impact on fatigue life. We can thus conclude that, among various material parameters, the material constant C and the tensile strength stand out to be the most significant factors in determining the fatigue life of the gear teeth. These findings offer important guidance on material selection of the gear.
Table 3 Material parameters of three commercial steels

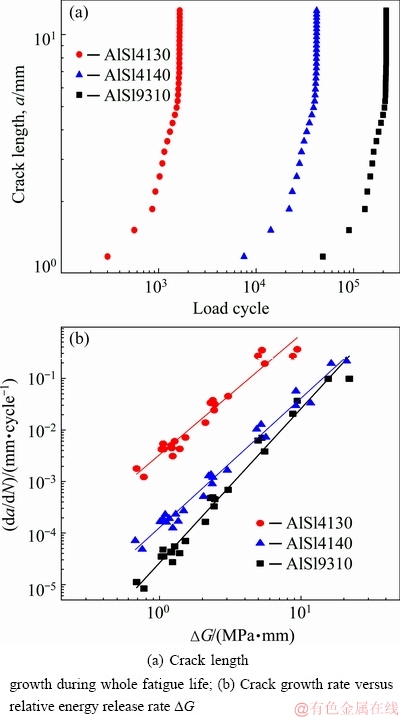
Fig. 10 XFEM predicted crack propagation for different gear steels (AISI4130, AISI4340, and AISI9310)
4 Conclusions
(1) The crack initiation location does affect the propagation path of fatigue cracks along the gear tooth root. The shortest fatigue life is predicted for crack initiation at the maximum principal stress position Pm. Cracks that initiate closely to the bottom land of gear tooth turn out to be relatively safe.
(2) The crack growth rate can also be affected by the initial crack orientation. The 0° orientation leads to the highest stress intensity factor △K and thus requires the least number of load cycles to crack initiation. The initial crack orientation does not affect much the crack growth path.
(3) Fatigue crack growth rate sensitively depends on the initial crack length, and consequently, the fatigue life decreases consistently with increasing the initial crack length. Once a crack initiates at Pm, the crack propagation path is almost determined. It always propagates along the gear root bottom until reaching the opposite end of the gear root.
(4) Loading conditions have nonlinear, complex impacts on the fatigue performance of the gear. Load ratio does not solely determine the fatigue life. Load range and mean load must be closely combined to evaluate the fatigue loading conditions.
(5) Among various material parameters, the material constant C and tensile strength are the most significant ones in determining the fatigue life, while the elastic modulus and fracture toughness have no obvious impact on the fatigue life of gear tooth during operation.
References
[1] ZHANG X, LI L, QI X, ZHANG J, ZHANG X, CHEN B, FENG J, DUAN S. Experimental and numerical investigation of fatigue crack growth in the cracked gear tooth [J]. Fatigue & Fracture of Engineering Materials & Structures, 2017, 40(7): 1037-1047.
[2] CHEUNG S, LUXMOORE A R. A finite element analysis of stable crack growth in an aluminium alloy [J]. Engineering Fracture Mechanics, 2003, 70(9): 1153-1169.
[3] YAN A M, NGUYEN-DANG H. Multiple-cracked fatigue crack growth by BEM [J]. Computational Mechanics, 1995, 16(5): 273-280.
[4] YAN X. A boundary element modeling of fatigue crack growth in a plane elastic plate [J]. Mechanics Research Communications, 2006, 33(4): 470-481.
[5] BELYTSCHKO T, LU Y Y, GU L. Crack propagation by element- free Galerkin methods [J]. Engineering Fracture Mechanics, 1995, 51(2): 295-315.
[6] DUFLOT M, NGUYEN H. Fatigue crack growth analysis by an enriched meshless method [J]. Journal of Computational & Applied Mathematics, 2004, 168(1): 155-164.
[7] BELYTSCHKO T, GU L, LU Y Y. Fracture and crack growth by element free Galerkin methods [J]. Modelling & Simulation in Materials Science & Engineering, 1994, 2(3A): 519-534.
[8] BELYTSCHKO T, BLACK T. Elastic crack growth in finite elements with minimal remeshing [J]. International Journal for Numerical Methods in Engineering, 2015, 45(5): 601-620.
[9] MOES N, DOLBOW J, BELYTSCHKO T. A finite element method for crack growth without remeshing [J]. International Journal for Numerical Methods in Engineering, 2015, 46(1): 131-150.
[10] SUKUMAR N, CHOPP D L, MOES N, BELYTSCHKO T. Modeling holes and inclusions by level sets in the extended finite-element method [J]. Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics & Engineering, 2001, 190(46): 6183-6200.
[11] MELENK J M, BABUSKA I. The partition of unity finite element method: Basic theory and applications [J]. Computer Methods in Applied Mechanic & Engineering, 1996, 139(1-4): 289-314.
[12] OSHER S, SETHIAN J A. Fronts propagating with curvature- dependent speed: Algorithms based on Hamilton-Jacobi formulations [J]. Journals of Computational Physics, 1988, 79(1): 12-49.
[13] STOLARSKA M, CHOPP D L, MOES N, BELYTSCHKO T. Modelling crack growth by level sets in the extended finite element method [J]. International Journal for Numerical Methods in Engineering, 2001, 51(8): 943–960.
[14] GINER E, NAVARRO C, SABSABI M, TUR M, DOMINGUEZ J, FUENMAYOR F J. Fretting fatigue life prediction using the extended finite element method [J]. International Journal of Mechanical Sciences, 2011, 53(3): 217–225.
[15] PATHAK H, SINGH A, SINGH I V. Fatigue crack growth simulations of homogeneous and bi-material interfacial cracks using element free Galerkin method [J]. Applied Mathematical Modelling, 2014, 38(13): 3093–3123.
[16] BHATTACHARYA S, SINGH I V, MISHRA B K. Fatigue life simulation of functionally graded materials under cyclic thermal load using XFEM [J]. International Journal of Mechanical Sciences, 2014, 82(5): 41–59.
[17] HACHI B E K, RECHAK S, HABOUSSI M, TAGHITE M B, MAURICE G. Fatigue growth of embedded elliptical cracks using Paris-type law in a hybrid weight function approach [J]. Comptes Rendus Mécanique, 2008, 336(4): 390–397.
[18] RAD A A, FOROUZAN M R, DOLATABADI A S. Three-dimensional fatigue crack growth modelling in a helical gear using extended finite element method [J]. Fatigue & Fracture of Engineering Materials & Structures, 2014, 37(6): 581–591.
[19] SINGH I V, MISHRA B K, BHATTACHARYA S, PATIL R U. The numerical simulation of fatigue crack growth using extended finite element method [J]. International Journal of Fatigue, 2012, 36(1): 109–119.
[20] KUMAR S, SINGH I V, MISHRA B K. A homogenized XFEM approach to simulate fatigue crack growth problems [J]. Computers & Structures, 2015, 150: 1–22.
[21] NASRI K, ZENASNI M. Fatigue crack growth simulation in coated materials using X-FEM [J]. Comptes Rendus Mécanique, 2017, 345(4): 271–280.
[22] MARTINEZ J C, USECHE L V V, WAHAB M A. Numerical prediction of fretting fatigue crack trajectory in a railway axle using XFEM [J]. International Journal of Fatigue, 2017, 100: 32–49.
[23] BERGARA A, DORADO J I, MARTIN-MEIZOSO A, MARTINEZ- ESNAOLA J M. Fatigue crack propagation in complex stress fields: Experiments and numerical simulations using the extended finite element method (XFEM) [J]. International Journal of Fatigue, 2017, 103: 112–121.
[24] CURA F M, MURA A, ROSSO C. Investigation about crack propagation paths in thin rim gears [J]. Frattura ed IntegritA Strutturale, 2014, 30(30): 446–453.
[25] CURA F, MURA A, ROSSO C. Influence of high speed on crack propagation path in thin rim gears: Influence of high speed on crack propagation path in thin rim gears [J]. Fatigue & Fracture of Engineering Materials & Structures, 2017, 40(1): 120–129.
[26] MOHAMMADI S. Extended finite element method: For fracture analysis of structures [M]. Oxford: Blackwell, 2008.
[27] BORDAS S, NGUYEN P V, DUNANT C, GUIDOUM A, NGUYEN H. An extended finite element library [J]. International Journal for Numerical Methods in Engineering, 2010, 71(6): 703–732.
[28] IRWIN G R. Onset of fast crack propagation in high strength steel and aluminum alloys [M]. Washington: Naval Research Laboratory, 1956.
[29] PARIS P, ERDOGAN F. A critical analysis of crack propagation laws [J]. Journal of Basic Engineering, 1963, 85(4): 528–533.
[30] American Society for Testing and Materials. 1983 annual book of ASTM standards [M]. Philadelphia: ASTM, 1983.
[31] TOWNSEND D P. Surface fatigue life of high temperature gear materials [C]// Proceedings of the 30th Joint Propulsion Conference and Exhibit. Cleveland, Ohio, 1994: 3078.
[32] PEHAN S, KRAMBERGER J, FLASKER J, ZAFOSNIK B. Investigation of crack propagation scatter in a gear tooth’s root [J]. Engineering Fracture Mechanics, 2008, 75(5): 1266–1283.
[33] KRüGER L, GRUNDMANN N, TRUBITZ P. Influence of microstructure and stress ratio on fatigue crack growth in a Ti-6-22-22-S alloy [J]. Materials Today: Proceedings, 2015, 2(S): s205–s211.
[34] SURESH S, RITCHIE R O. On the influence of environment on the load ratio dependence of fatigue thresholds in pressure vessel steel [J]. Engineering Fracture Mechanics, 1983, 18(4): 785–800.
[35] XIE Xing, YI Hong, XU Jian, GEN Li-ming, CHEN Lu-yun. Effect of load ratio and saltwater corrosive environment on the initiation life of fatigue of 10Ni5CrMoV steel [C]// Proceedings of the IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering. London: IOP Publishing, 2017: 012141.
[36] URAL A, HEBER G, WAWRZYNEK P A, INGRAFFEA A R, LEWICKI D G, NETO J B C. Three-dimensional, parallel, finite element simulation of fatigue crack growth in a spiral bevel pinion gear [J]. Engineering Fracture Mechanics, 2005, 72(8): 1148–1170.
[37] ABERSEK B, FLASKER J. Experimental analysis of propagation of fatigue crack on gears [J]. Experimental Mechanics, 1998, 38(3): 226–230.
韦 宇,江 勇
中南大学 粉末冶金国家重点实验室 材料科学与工程学院, 长沙 410083
摘 要:齿轮传动系统主要失效形式是齿牙疲劳断裂。本文作者基于周期性边界条件建立二维双齿模型。采用扩展有限元法(XFEM)对服役过程齿牙的疲劳行为进行分析,重点研究初始裂纹和载荷因素对齿牙疲劳断裂的影响。结果表明,当最大主应力处萌生取向为0°的裂纹时,齿牙疲劳寿命最短,而靠近齿根的裂纹相对安全。同时,评价疲劳载荷情况必须综合考虑载荷比、载荷幅和平均载荷值。进一步针对材料选材开展模拟研究,为齿轮的设计提供指导。模拟结果表明,材料常数C和抗拉强度是影响齿牙疲劳寿命的最重要参数。
关键词:齿轮;疲劳;断裂;有限元法
(Edited by Wei-ping CHEN)
Foundation item: Project (2018YFE0306100) supported by the National MCF Energy R&D Program of China; Project supported by the State Key Laboratory of Powder Metallurgy, Central South University, China
Corresponding author: Yong JIANG; Tel: +86-731-88836320; E-mail: yjiang@csu.edu.cn
DOI: 10.1016/S1003-6326(19)65116-2

