Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 24(2014) 2839-2844
Interfacial structure and mechanical properties of hot-roll bonded joints between titanium alloy and stainless steel using niobium interlayer
Dong-sheng ZHAO1, Jiu-chun YAN2, Yu-jun LIU1, Zhuo-shang JI1
1. State Key Laboratory of Structural Analysis for Industrial Equipment, School of Naval Architecture, Dalian University of Technology, Dalian 116024, China;
2. State Key Laboratory of Advanced Welding and Joining, Harbin Institute of Technology, Harbin 150001, China
Received 8 October 2013; accepted 23 December 2013
Abstract: The hot-roll bonding was carried out in vacuum between titanium alloy and stainless steel using niobium interlayer. The interfacial structure and mechanical properties were analyzed. The results show that the plasticity of bonded joint is improved significantly. When the bonding temperature is 800 °C or 900 °C, there is not intermetallic layer at the interface between stainless steel and niobium. When the bonding temperature is 1000 °C or 1050 °C, Fe-Nb intermetallic layer forms at the interface. When the bonding temperature is 1050 °C, cracking occurs between stainless steel and intermetallic layer. The maximum strength of ~417.5 MPa is obtained at the bonding temperature of 900 °C, the reduction of 25% and the rolling speed of 38 mm/s, and the tensile specimen fractures in the niobium interlayer with plastic fracture characteristics. When the hot-roll bonded transition joints were TIG welded with titanium alloy and stainless steel respectively, the tensile strength of the transition joints after TIG welding is ~410.3 MPa, and the specimen fractures in the niobium interlayer.
Key words: hot roll bonding; titanium alloy; stainless steel; niobium
1 Introduction
Bonding joint between titanium alloy and stainless steel can be used in nuclear, chemical and aerospace industries [1,2], and the connection method contains brazing [3], diffusion bonding [4,5], explosive welding [6] and hot roll bonding [7,8] but with the problem of intermetallic compounds. The solubility between Ti, Fe and Cr is limited, and Ti is a strong carbide forming element. Therefore, the hard and brittle intermetallic compounds are easily formed at high temperatures [9]. It is the main reason to reduce the bonding strength of titanium alloy and stainless steel and even leads to cracking. To solve this problem we must improve the plasticity of bonded joint on one hand using solid state connection method to reduce the volume fraction of the intermetallic compounds, and on the other hand selecting a suitable interlayer for the titanium alloy and stainless steel to form a solid solution or low brittle intermetallic compounds, thus reducing the brittleness of bonded joint.
The vacuum hot-roll bonding is a solid state connection method by plastic deformation of the materials to achieve close contact and bonding in vacuum; the bonding temperature is low, and the bonding time is very short [10-13]. Because of the short bonding time, it is possible to reduce the volume fraction of the intermetallic compounds at bonding interface effectively. The experiment shows that using copper or nickel as the interlayer makes the strength of the hot-roll bonded joint between titanium alloy and stainless steel higher [7,8], and the volume fraction of the intermetallic compounds decrease obviously compared with diffusion bonding.
Copper, nickel, aluminum [14], silver [15], etc. can be used as the interlayer. Compared with the interlayer material, niobium has good plasticity and high- temperature resistance. Niobium does not form any intermetallic compound with Ti, and its corrosion resistance is better than titanium alloy and stainless steel, so niobium can be used as the interlayer [16].
The transition joint between titanium alloy and stainless steel is one of the main applications. So, it is necessary to study the changes in the microstructure and properties of the bonded interface after welding transition joints with titanium alloy and stainless steel respectively, so that to select a suitable welding method and process parameters to weld transition joints with titanium alloy and stainless steel. However, the research on this area is less currently.
The experiment of hot roll boning between titanium alloy and stainless steel using niobium interlayer was carried out. The effect of bonding temperature on the microstructure and the mechanical properties of bonded joints was examined. The TIG welding experiment between hot-rolled transition joints with titanium alloy and stainless steel was completed, tested and the microstructure and properties of hot roll bonded transition join after TIG welding were analyzed.
2 Experimental
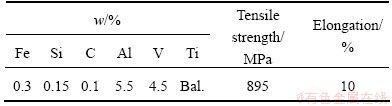
The dimensions of Ti-6Al-4V alloy and 0Cr18Ni10Ti stainless steel were 100 mm × 70 mm × 19 mm and 120 mm × 70 mm × 19 mm, respectively. The dimensions of pure niobium foil used as interlayer were 110 mm × 80 mm × 0.5 mm. The chemical composition and tensile properties of Ti-6Al-4V and 0Cr18Ni10Ti used are given in Tables 1 and 2, respectively.
Table 1 Chemical composition and properties of stainless steel (0Cr18Ni10Ti)
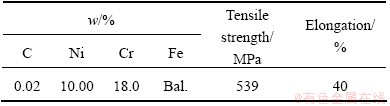
Table 2 Chemical composition and properties of titanium alloy (Ti-6Al-4V)
Ti-6Al-4V alloy was etched with an aqueous solution containing HF and H2O (volume ratio 1:5) for 2 min before bonding. A mixture of HF, HNO3 and H2O (volume ratio 1:1:8) solution was used as etchant for 0Cr18Ni10Ti stainless steel for 2-3 min after being heated to 40-50 °C. Niobium foil was etched with an aqueous solution containing HF and HNO3 (volume ratio 1:3) for 1 min. The front of two metal plates was fixed with two rivets of d12.9 mm×45 mm by CSS-WEW1000 hydraulic universal testing machine.
The assembled samples were put in a vacuum furnace with a pressure (1-3)×10-3 Pa, heated up to temperature 800-1050 °C with a heating rate of 400 °C/h, and then heated preservation for 45 min. And then the samples were pushed into rollers by a machine hand. The reduction was 25%. The rolling speed was 38 mm/s. The samples were put in a vacuum chamber and cooled down after rolling.
The tensile strength of joints was measured using an electronic testing machine (Instron-5569). Figure 1 shows that the sheet tensile specimens were machined in the vertical rolling direction with cross-sectional area of 10 mm×3 mm and length of ~30 mm. The Nb interlayer was at the centre of the gauge length. Tensile strength of the rolling joints was evaluated using a tensile testing machine set at a crosshead speed of 1 mm/min at room temperature. Three samples were tested at each process parameter to check the reproductive results.
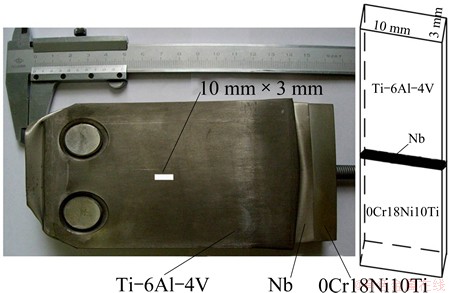
Fig. 1 Cutting location of tensile specimen
The microstructure at interface was observed by a scanning electron microscope (HITACHIS-4700). The chemical composition of the intermetallic layers was detected by energy spectrum (EDAX), and the presence of the intermetallic phases in the reaction zone was confirmed by X-ray diffraction study (D/max-rB) on the fracture surfaces of the couples using Cu target.
Figure 2 shows the schematic diagram of TIG weld of hot-roll bonded joint to titanium alloy and stainless steel. The dimensions of the hot-roll bonded transition joint (the bonding temperature of 800 °C, the reduction of 25%, and the rolling speed of 38 mm/s) were 70 mm × 30 mm × 3 mm, which was machined in the perpendicular rolling direction. The stainless steel side of the transition joint was TIG welded with 0Cr18Ni10Ti stainless steel whose dimensions were 70 mm × 50 mm × 3 mm, while the titanium side of the transition joint was TIG welded with titanium alloy whose dimensions were 70 mm × 50 mm × 3 mm. The welding current of the TIG welding was 120 A and the gas flow was 8 L/min.
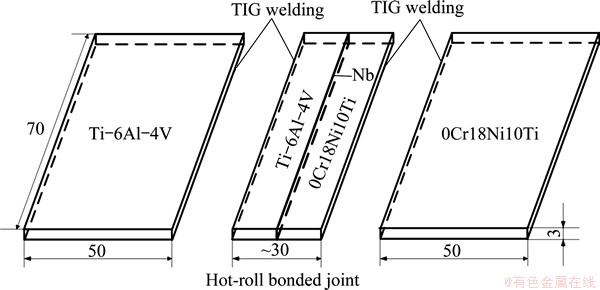
Fig. 2 Schematic diagram of TIG welding of hot-roll bonded joint to titanium alloy and stainless steel (unit: mm)
3 Results and discussion
Figure 3 shows the SEM-back scattered electron (BSE) images of the interface of stainless steel/ niobium at the bonding temperature of 800-1050 °C. Figures 3(a) and (b) show that the interface bonds well, and there are no holes or cracks, and no obvious intermetallic layers, when the bonding temperature is 800 °C or 900 °C, respectively. When the bonding temperature is 800 °C or 900 °C, the material achieves close contact and is bonded by plastic deformation. Due to the low bonding temperature, short bonding time (hot-roll speed of 38 mm/s), and slow diffusion speed of atoms, the bonding cannot be achieved by the element diffusion, but only by plastic deformation of material to achieve close contact and bonding [17]. So, it is bonded well with no obvious intermetallic layer at the interface.
Figures 3(c) and (d) show that, when the bonding temperature is 1000 °C or 1050 °C, the intermetallic layer is formed at the interface between stainless steel and niobium. When the bonding temperature is 1000 °C, a small number of holes appear between the stainless steel and intermetallic layer. The thickness of the intermetallic layer is 0.3-0.4 μm with the composition of Fe (~21.78%, mass fraction) and Nb (~62.22%, mass fraction), and the results tested by energy spectrum (EDAX) and Fe-Nb binary phase diagram show that the possible phase is Fe6Nb7+Nb. When the bonding temperature is 1050 °C, the cracks appear between the stainless steel and intermetallic layer. The thickness of the intermetallic layer is ~0.5 μm with the composition of Fe (~36.19%) and Nb (~47.16%), and the results tested by energy spectrum (EDAX) and Fe-Nb binary phase diagram show that the possible phase is Fe2Nb+Fe6Nb7. This shows that intermetallic layer is formed at the interface between stainless steel and niobium after the hot-roll bonding process because of the diffusion of elements. Cracking occurs between the stainless steel and intermetallic layer. This is because the intermetallic compound is hard and brittle, and also the concentration of stress is easily formed under the thermal stress which leads to cracking. So, it is necessary to reduce the volume fraction of the intermetallic compounds to improve the plasticity of joints.
Figure 4 shows the secondary electron images of the fracture surface of joint bonded at 900 °C, and the tensile specimen fractured in the niobium interlayer with ductile fracture characteristics. At that time, the plasticity of bonded joints improved significantly. When the bonding temperature was 800 °C, the tensile specimen fractured at the interface between niobium and titanium alloys with brittle fracture characteristics. When the bonding temperature was 1000 °C, the tensile specimen fractured at the interface between niobium and stainless steel with brittle fracture characteristics.
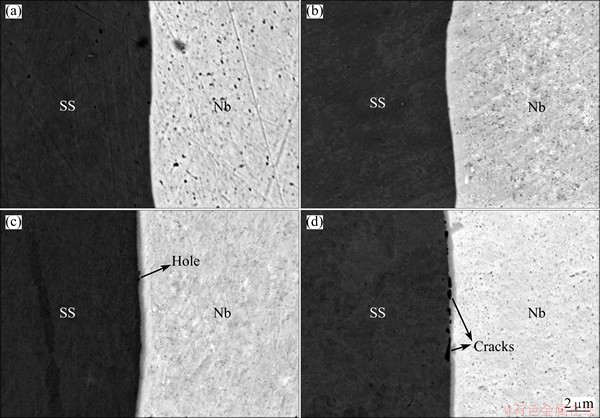
Fig. 3 SEM-BSE images of interface of stainless steel (SS)/ niobium at bonding temperatures of 800 °C (a), 900 °C (b), 1000 °C (c) and 1050 °C (d)
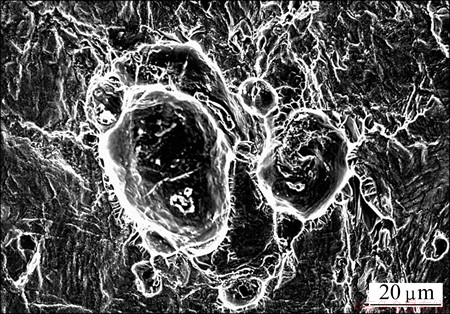
Fig. 4 Secondary electron image of fracture surface of bonded joint at bonding temperature of 900 °C
Figure 5 shows the XRD analysis results of the fracture surfaces. Figure 5(a) shows that Nb, Ti, and NbTi4 are found on the fracture surface when the bonding temperature is 800 °C. This shows that the plastic deformation resistance of the material is good when the hot-roll bonding temperature is low, so a connection surface of the niobium and titanium fails to achieve a complete contact and bonding, and tensile specimen fractures at the interface between the niobium and titanium alloy. Figure 5(b) shows the XRD results of the tensile fracture surfaces when the bonding temperature is 900 °C. Fracture surface shows the ductile fracture characteristics with niobium on the surface. This shows that when the bonding temperature is 900 °C, it is bonded well between the stainless steel and niobium; although the Fe-Nb intermetallic compound is formed, the volume fraction is small, so it has little effect on the plasticity of joints, and also the plastic deformation of niobium and titanium alloy is enough to achieve a close contact and bonding. It is well bonded between the stainless steel/niobium, niobium/titanium alloy, and the volume fraction of the intermetallic compounds is effectively controlled, so the plasticity of the hot-roll bonded joint is significantly improved. Figure 5(c) shows that the Fe6Nb7 is found on the fracture surface when the bonding temperature is 1000 °C. This indicates that when the bonding temperature is increased, the volume fraction of the Fe-Nb intermetallic compounds increases; hard and brittle intermetallic compounds cause bonded joint to fracture at the interface between stainless steel and intermetallic layer.
Table 3 shows the result of the tensile strength of the hot-roll bonded joint. It can be seen that when the bonding temperature is 800 °C or 900 °C, the maximum tensile strengths of the hot-roll bonded joint are ~424.1 MPa and ~417.5 MPa, respectively, and the tensile strength is significantly higher compared with the niobium interlayer. As the hot-roll bonding temperature continues rising, the tensile strength decreases. When the bonding temperature is 1050 °C, the tensile strength is ~121.2 MPa. When the bonding temperature is 800 °C or 900 °C, it is bonded well between stainless steel and niobium without an obvious intermetallic layer, so the bonding strength has little difference. But as the bonding temperature continues rising, the volume fraction of the intermetallic compounds increases and brittleness of the joint increases even causing a crack at the bonding interface, therefore, the tensile strength of the specimen decreases.
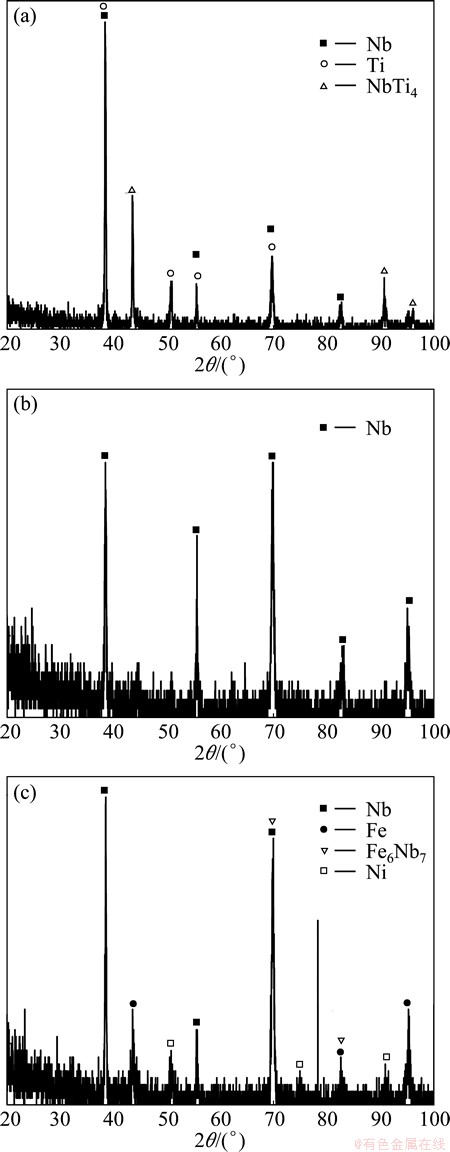
Fig. 5 XRD patterns of fracture surfaces of couples bonded at 800 °C (a), 900 °C (b) and 1000 °C (c)
Table 3 Tensile strength of hot-roll bonded joints at different bonding temperatures
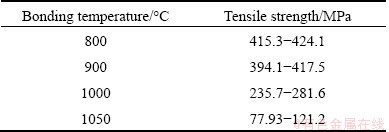
Figure 6 shows the SEM-BSE image and element distribution profile of the interface between stainless steel and niobium which is formed after TIG welding of hot-roll bonded transition joints with titanium alloy and stainless steel. Figure 6(a) shows that there is no obvious difference at the interface between stainless steel and niobium before (Fig. 3(a)) and after TIG welding. Figure 6(b) shows that, element diffusion is not obvious after TIG welding. The welding of hot-rolled transition joints with titanium alloy and stainless steel has little effect at the bonding interface, and there is no obvious intermetallic layer at the interface between stainless steel and niobium. The tensile specimen after TIG welding fractured in niobium interlayer and the tensile strength was ~410.3 MPa which has little difference from that before TIG welding.
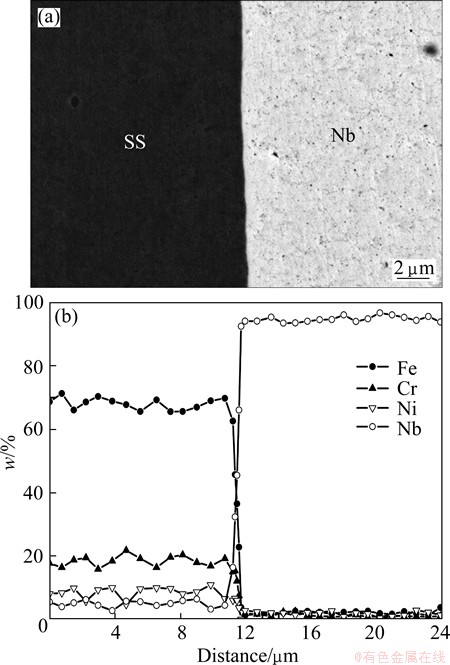
Fig. 6 SEM-BSE image (a) and element distribution profile (b) of interface between stainless steel and niobium after TIG welding
Figure 7 shows the SEM-BSE image of the TIG welded joint tensile fracture surface, which presents obvious ductile fracture characteristics. The experimental results show that the hot-roll bonded transition joints of titanium alloy and stainless steel with niobium interlayer have good heat resistance.
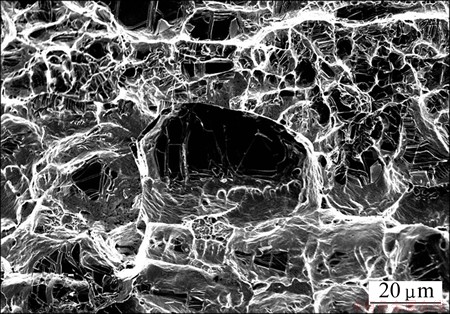
Fig. 7 SEM-BSE image of TIG welded joint tensile fracture surface
4 Conclusions
1) Hot-roll bonding of Ti-6Al-4V and 0Cr18Ni10Ti stainless steel has been performed in vacuum using a niobium interlayer. When the reduction is 25%, the rolling speed is 38 mm/s, and the boding temperature is 800 °C or 900 °C, there is no intermetallic layer at the interface between stainless steel and niobium. The thickness of the intermetallic layer at the interface between stainless steel and niobium increases with bonding temperature, and cracks appear between the intermetallic layer and stainless steel at the bonding temperature of 1050 °C.
2) When the reduction is 25%, the rolling speed is 38 mm/s, and the bonding temperature is 900 °C, the tensile strength of hot-roll bonded joints is ~417.5 MPa, and the tensile specimen fractures on the niobium side with ductile fracture characteristics.
3) The tensile strength of the transition joints (the reduction is 25%, the rolling speed is 38 mm/s, and the bonding temperature is 800 °C) after TIG welding with titanium alloy and stainless steel is ~410.3 MPa, and the tensile specimen fractures on the niobium side with ductile fracture characteristics.
References
[1] KUNDU S, CHATTERJEE S. Interfacial microstructure and mechanical properties of diffusion-bonded titanium-stainless steel joints using a nickel interlayer [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2006, 425: 107-113.
[2] GHOSH M, CHATTERJEE S. Diffusion bonded transition joints of titanium to stainless steel with improved properties [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2003, 358(1-2): 152-158.
[3] CHUNG T, KIM J, BANG J, RHEE B, NAM D. Microstructures of brazing zone between titanium alloy and stainless steel using various filler metals [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2012, 22(3): 639-644.
[4] LEE M K, LEE J G, LEE J K, HONG S M, LEE S H, PARK J J, KIM J W, RHEE C K. Formation of interfacial brittle phases sigma phase and IMC in hybrid titanium-to-stainless steel joint [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2011, 21(S1): s7-s11.
[5] KUNDU S, SAM S, CHATTERJEE S. Interfacial reactions and strength properties in dissimilar titanium alloy/Ni alloy/microduplex stainless steel diffusion bonded joints [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2013, 560: 288-295.
[6] AKBARI M S, SARTANGI P F. Effect of post-weld heat treatment on the interface microstructure of explosively welded titanium-stainless steel composite [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2008, 494: 329-336.
[7] ZHAO D S, YAN J C, WANG C W, WANG Y, YANG S Q. Interfacial structure and mechanical properties of hot roll bonded joints between titanium alloy and stainless steel using copper interlayer [J]. Science and Technology of Welding and Joining, 2008, 13: 765-768.
[8] YAN J C, ZHAO D S, WANG C W, YANG S Q. Vacuum hot roll bonding of titanium alloy and stainless steel using nickel interlayer [J]. Materials Science and Technology, 2009, 25: 914-918.
[9] ORHAN N, KHAN T I, EROGLU M. Diffusion bonding of a microduplex stainless steel to Ti-6Al-4V [J]. Scripta Mater, 2001, 45: 441-446.
[10] ZHAO D S, YAN J C, WANG Y, YANG S Q. Relative slipping of interface of titanium alloy to stainless steel during vacuum hot roll bonding [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2009, 499: 282-286.
[11] ZHAO D S, YAN J C, LIU Y J. Heat resistance of hot roll bonded titanium alloy-stainless steel transition joint [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2013, 23(7): 1966-1970.
[12] BORTS B V. Formation of the joint dissimilar metals in the solid phase by the method of vacuum hot rolling [J]. Materials Science, 2012, 47(5): 689-695.
[13] WANG Q, LENG X S, YAN J C, GUO W, FU Y, LUAN T. Al 1060/pure iron clad materials by vacuum roll bonding and their solderability [J]. Journal of Materials Science and Technology, 2013, 29(10): 948-954.
[14] KUNDU S, CHATTERJEE S. Interface microstructure and strength properties of diffusion bonded joints of titanium-Al interlayer- 18Cr-8Ni stainless steel [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2010, 527: 2714-2719.
[15] LEE J G, HONG S J, LEE M K, RHEE C K. High strength bonding of titanium to stainless steel using an Ag interlayer [J]. Journal of Nuclear Materials, 2009, 395: 145-149.
[16] KUNDU S, CHATTERJEE S. Effects of temperature on interface microstructure and strength properties of titanium-niobium stainless steel diffusion bonded joints [J]. Materials Science and Technology, 2011, 27: 1177-1182.
[17] BARLOW C Y, NIELSEN P, HANSEN N. Multilayer roll bonded aluminium foil: Processing, microstructure and flow stress [J]. Acta Materialia, 2004, 52: 3967-3972.
采用铌中间层的钛合金与不锈钢的真空热轧连接界面的显微组织及性能
赵东升1,闫久春2,刘玉君1,纪卓尚1
1. 大连理工大学 船舶工程学院 工业装备结构分析国家重点实验室,大连 116024;
2. 哈尔滨工业大学 先进焊接与连接国家重点实验室,哈尔滨 150001
摘 要:进行了钛合金与不锈钢采用铌中间层的真空热轧连接实验,分析了连接界面的显微组织及性能。结果表明,采用铌中间层能够明显提高接头的塑性。当压缩率为25%,轧制速度为38 mm/s,热轧温度为800 °C和900 °C时,不锈钢与铌的连接界面没有明显的金属间化合物层;当热轧温度为1000 °C和1050 °C时,不锈钢与铌连接界面形成Fe-Nb金属间化合物层,并且当热轧温度为1050 °C时在金属间化合物层与不锈钢之间出现开裂。铌与钛合金连接界面的扩散层厚度随着热轧温度的升高而增大。热轧温度为900 °C的连接接头的拉伸强度可达~417.5 MPa,拉伸试样断裂于铌中间层,断口呈塑性断裂特征。热轧温度为800 °C的热轧过度接头分别与钛合金和不锈钢进行TIG焊接,TIG焊后热轧过度接头的拉伸强度可达~410.3 MPa,拉伸试样断裂于铌中间层,断口呈塑性断裂特征。
关键词:热轧焊;钛合金;不锈钢;铌
(Edited by Xiang-qun LI)
Foundation item: Project (AWPT-M07) supported by State Key Laboratory of Advanced Welding and Joining, China; Project (20120041120015) supported by Specialized Research Fund for the Doctoral Program of Higher Education, China
Corresponding author: Dong-sheng ZHAO; Tel: +86-411-84707334; E-mail: dszhao@dlut.edu.cn
DOI: 10.1016/S1003-6326(14)63416-6