Control of repair effect and hydrogen embrittlement risk by parameters optimization for BIEM
来源期刊:中南大学学报(英文版)2020年第8期
论文作者:毛江鸿 徐亦冬 张军 金伟良 樊玮洁 夏晋 李强
文章页码:2408 - 2423
Key words:electrochemical rehabilitation; concrete durability; chloride extraction; hydrogen embrittlement; electrochemical parameter
Abstract: Bidirectional electromigration rehabilitation (BIEM) is a novel electrochemical rehabilitation method involving the injection of inhibitors into steel bar surface. The BIEM effect and hydrogen embrittlement (HE) risk depend on the electrochemical parameters (current density and duration) and operating condition (stress level and concrete cover thickness) of reinforced concrete structures. Experiments were performed in this study to investigate the relationships between the aforementioned factors. For a small current density group, a linear relationship was established between electric flux and chloride extraction. For a large current density group, the reasonable current density, stress level, and treatment time were obtained. Finally, the querying method of electrochemical parameters combined with treatment time and current density was proposed.
Cite this article as: ZHANG Jun, MAO Jiang-hong, JIN Wei-liang, FAN Wei-jie, XIA Jin, XU Yi-dong, LI Qiang. Control of repair effect and hydrogen embrittlement risk by parameters optimization for BIEM [J]. Journal of Central South University, 2020, 27(8): 2408-2423. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-020-4458-z.

J. Cent. South Univ. (2020) 27: 2408-2423
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-020-4458-z

ZHANG Jun(张军)1, MAO Jiang-hong(毛江鸿)1, JIN Wei-liang(金伟良)1, 2,FAN Wei-jie(樊玮洁)1, XIA Jin(夏晋)2, XU Yi-dong(徐亦冬)1, LI Qiang(李强)1
1. Zhejiang University Ningbo Institute of Technology, Ningbo 315100, China;
2. Institute of Structural Engineering, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou 310058, China
 Central South University Press and Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer Nature 2020
Central South University Press and Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer Nature 2020
Abstract: Bidirectional electromigration rehabilitation (BIEM) is a novel electrochemical rehabilitation method involving the injection of inhibitors into steel bar surface. The BIEM effect and hydrogen embrittlement (HE) risk depend on the electrochemical parameters (current density and duration) and operating condition (stress level and concrete cover thickness) of reinforced concrete structures. Experiments were performed in this study to investigate the relationships between the aforementioned factors. For a small current density group, a linear relationship was established between electric flux and chloride extraction. For a large current density group, the reasonable current density, stress level, and treatment time were obtained. Finally, the querying method of electrochemical parameters combined with treatment time and current density was proposed.
Key words: electrochemical rehabilitation; concrete durability; chloride extraction; hydrogen embrittlement; electrochemical parameter
Cite this article as: ZHANG Jun, MAO Jiang-hong, JIN Wei-liang, FAN Wei-jie, XIA Jin, XU Yi-dong, LI Qiang. Control of repair effect and hydrogen embrittlement risk by parameters optimization for BIEM [J]. Journal of Central South University, 2020, 27(8): 2408-2423. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-020-4458-z.
1 Introduction
The service performance of a reinforced concrete (RC) structure depends on the interaction between concrete and reinforcing steel bars. However, steel bars inside concrete are vulnerable to chloride-ion erosion in seawater or marine environments, which is manifested as depassivation and corrosion [1, 2]. Subsequent durability issues with RC structures primarily include tensile strength loss and an increasing risk of brittle failure of steel bars, cracked concrete covers, and deteriorated bond performance [3]. Therefore, it is crucial to reduce the amount of chloride ions in concrete in advance. Electrochemical rehabilitation (ER) technologies are nondestructive methods for repairing and protecting RC structures [4]. The earliest on-site application of electrochemical chloride extraction (ECE) was conducted 30 years ago. Complete repassivation of the reinforcement occurred after ECE treatment. More importantly, it was reported in 2008 that the structure remained in a fully passive condition after the treatment [5]. To facilitate the implementation of ECE technology, UEDA et al [6] fastened an anode system onto the surface of concrete using ductile fiber-reinforced cementitious composites. Similarly, ZHU et al [7] adopted a carbon-fiber-reinforced polymer as an external anode. JIN et al [8] developed a conductive cement-based mortar with low shrinkage and high ductility as an external anode for ECE.
Although the aforementioned methods improved both the mechanical performance and durability of RC structures, contradictions between dechlorination efficiency and side effects induced by ER still remain. In addition, ECE is efficient in delaying the start of corrosion if used preventively; however, it cannot assure the repassivation effect if applied late [9]. Regarding the electrochemical rehabilitation effect, an increase in the current density can maximize chloride extraction within a relatively short ER duration [10]. However, the current density and duration must be restricted because side effects such as microstructure changes in concrete [11], bond degradation [12], long-term risk of alkali silica [13], and HE [14] may occur with inappropriate selections. By contrast, good modulated parameters (current density/voltage, time, etc.) for ER can minimize the aforementioned undesirable effects [15]. The risk of HE is an important factor affecting the role of steel bars in RC components [16]. It may result in the brittle failure of a structure without adequate warning [17]. In particular, for the pre-stress concrete structures, the risk should be strictly controlled [18, 19].
Although a hot-rolled bar used for RC structures is a type of mild steel with a long yield platform, and the susceptibility of HE is relatively low [20-23], HE risk should be considered when the current density is large. Recently, bidirectional electromigration technology [24-26] based on ECE technology has been proposed. Compared with traditional ECE, bidirectional electromigration rehabilitation (BIEM) not only extracts chloride ions, but also migrates the inhibitor toward the steel bar surface. SAWADA et al [27-29] successfully promoted the injection of corrosion inhibitors into carbonated-concrete specimens, thereby significantly reducing the corrosion rates of steel bars. XU et al [30] applied an electroinjected organic corrosion inhibitor, triethylenetetramine (TETA), to improve the durability of chloride- contaminated concrete. These corrosion inhibitors can prevent corrosion of steel bars effectively [31, 32]. Furthermore, the inhibitors can reduce the risk of HE in metallic materials. AGRAWAL et al [33] stated that two organic inhibitors (benzotriazole and benzonitrile) could mitigate hydrogen-induced ductility loss, although the fracture mode remained unaltered. SOUDANI et al [34] studied the effectiveness of Ruta Chalepensis (Fijil) in reducing the HE of API 5L X65 pipe steel. Results showed that the fracture toughness was improved by more than 40%. SIEGWART et al [14] reported the efficiency of inhibitors for the suppression of hydrogen uptake of steels in artificial concrete pore solution and evaluated the migration properties of inhibitors in concrete. Results confirmed that inhibitors can be used to mitigate hydrogen absorption. MAO et al [35] reported that inhibitors improved the critical current density and reduced the sensitivity of the HE risk of prestressed tendons. Owing to the contribution of corrosion inhibitors, BIEM technology offers better rehabilitation and good HE risk control ability. However, questions regarding the practical application of ECE technology on RC structures must be discussed comprehensively, to apply BIEM technology.
Hence, experimental studies regarding the laws between HE risk and actors of current density, treatment time, and concrete operating conditions were performed in this study. Finally, a parameter optimization method for BIEM technology based on the repair effect and HE risk is proposed and discussed.
2 Experiments
The technical roadmap of this study is shown in Figure 1. Two steps were involved in this study. The first step was to select the current density for BIEM through experiments involving hydrogen- evolution recognition and HE evaluation. In this step, BIEM strategies based on the critical current density were established, i.e., no HE risk and controllable HE risk. The second step was to investigate the durability-improving effect of different BIEM strategies. The durability index to evaluate the durability-improving effect and the mechanical index to evaluate negative HE were obtained; with these indexes, the parameter optimization method for BIEM technology was established.
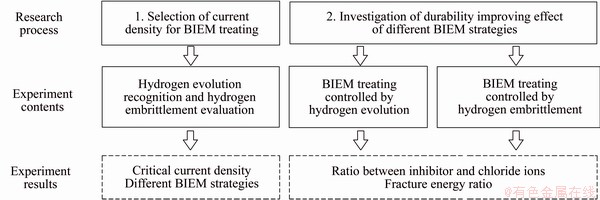
Figure 1 Technical roadmap for experiments
2.1 Specimen design
The principle of ER including ECE and BIEM is shown in Figure 2. An electric field is generated between the steel bar (cathode) and the external metal mesh (auxiliary anode). The electric field induces the movement of cations toward the steel bar surface and the harmful anions out of the concrete cover. Meanwhile, two main electrochemical reactions, i.e., oxygen consumption reaction and hydrogen evolution reaction occur at the cathode, which induces HE risk. Based on the basic principle of ER, the specimens are illustrated in Figure 3.

Figure 2 Schematic representation of electrochemical rehabilitation
The sizes of specimen measured were 150 mm×150 mm×100 mm with a 40-mm-thick concrete cover. Two steel bars were embedded inside the concrete specimen, steel bar I as the cathode and steel bar II the reference electrode for electrochemical parameter testing. The diameter of the steel bar was 12 mm. The length of the steel bar I was 300 mm. To apply a tensile stress, the end of steel bar I was manufactured as male threads and connected to a hydraulic jack. The compressive strength of concrete was designed to be 30.0 MPa. The concrete was mixed with sodium chloride, whose weight was 3% of the cement quality.
2.2 Design of experimental system
HE is related to the current density, treatment time, electrolyte solution type, and stress level. To consider these factors, an experiment system was designed, as shown in Figure 4. To maintain a stable stress during the experiment, a loading device was constructed, as shown in Figure 4(a). First, the steel bar connected to the screws was pulled using the hydraulic jack to the target stress. Subsequently, the anchor on the right side was tightened to maintain the stress. The force was recorded in real time using a fiber Bragg grating pressure sensor.
An electric field was applied to the concrete specimen, as shown in Figure 4(b). All of the surfaces except the concrete cover surface (defined as the operating surface) were coated with epoxy, affording control over the path of ion electromigration. The concrete specimens were immersed into water until saturation. A stainless steel mesh was spread evenly across the cushion block at the bottom of cell. The concrete bottom was completely immersed in the electrolyte solution. Steel bar I was connected to the negative pole of a direct current (DC) power supply, and the stainless-steel mesh was connected to the positive pole.
As shown in Figure 4(c), stress steel bar I and no-stress steel bar II served as the cathode and reference electrodes, respectively. During the entire experimental process, the pH of the electrolyte was maintained to obtain ideal concrete durability improving effects. Hence, the electrolyte solution was replaced once it decreased below 7.0. After the ER treatment, the load applied on the steel bar was removed.

Figure 3 Design plan of the specimens (Unit: mm):

Figure 4 Design plan and layout of the experiment:
2.3 Hydrogen evolution recognition experiments
HE research is a popular topic in the metal field [36]. HE occurs by several different mechanisms, including the bonding force reduction [37], local plastic deformation [38], surface energy reduction [39], and hydrogen pressure theories [40]. A commonality among all of the proposed mechanisms is the permeation of hydrogen atoms into high-stress regions in metal and the subsequent reduction in deformation capacity when the hydrogen concentration reaches a critical threshold. Reactions of the cathode include oxygen consumption and hydrogen evolution [41]:
2H2O+O2+4e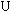 4OH- (1)
4OH- (1)
2H++2e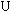 H2 (2)
H2 (2)
The variation in current density of the electrode reaction can be obtained through potentiodynamic polarization curves obtained via continuous potential scanning [42, 43]. This variation is associated with electrode reactions; therefore, the conversion between oxygen consumption reaction and hydrogen evolution reaction can be recognized according to an abrupt change in current density. A few researchers have indicated that changing the local microenvironment, such as by increasing the pH or applying an inhibitor can restrain hydrogen evolution [26-28]. However, the hydrogen evolution inside concrete differs from that in metal because the microenvironment of a steel bar depends on the mixture ratio of concrete [44, 45]. Hence, two types of hydrogen evolution recognition experiments were performed, as shown in Figure 5.
The pore solution experiment was performed to analyze the effect of inhibitors regarding the restraining of the hydrogen evolution reaction. A saturated calcium hydroxide solution and a TETA inhibitor were adopted as the electrolyte solution for comparative analysis. The electrolyte solution, steel bar, counter electrode, and reference electrode were placed in a container, as shown in Figure 5(a). The concrete-specimen experiment was performed to determine the critical hydrogen evolution current density Jc of the concrete adopted in this study, as shown in Figure 5(b). The mixture ratio of the concrete used in this study is shown in Table 1.

Figure 5 Design plan of hydrogen evolution recognition experiments:
Table 1 Concrete mixture ratio

2.4 BIEM treating controlled by hydrogen evolution
BIEM treatment can electromigrate the inhibitor toward the steel bar and hence prevent HE. This electromigration from the concrete surface to the steel bar surface consumes time owing to the thickness of the concrete cover. Therefore, the hydrogen evolution will be actively provided that the applied current density exceeds Jc and the inhibitor has not arrived at the steel bar surface. Inhibiting groups coating the steel bar below Jc is a prerequisite for the prevention of HE.
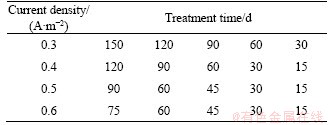
From the results of Section 3.1, the Jc for concrete specimens ranged from 0.398 to 0.559 A/m2, as shown in Table 2. The current density was extremely low; therefore, the HE can be restrained well, but the concrete durability- improving effect may be poor. To understand these issues, an experiment pertaining to BIEM-treatment controlled by hydrogen evolution was performed, the parameters of which are listed in Table 3. A 1 mol/L TETA solution was used as the electrolyte solution. The pH was adjusted to 10.0 through the addition of phosphoric acid. The repair effect of BIEM was assessed by measuring the contents of chloride ion and the rust inhibitor.
Table 2 Critical current density for concrete specimens
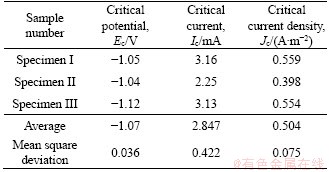
Table 3 Parameters of BIEM treatment controlled by hydrogen evolution
2.5 BIEM treatment controlled by HE
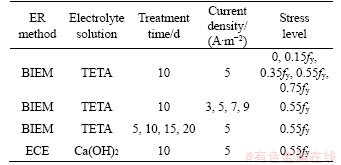
Atomic hydrogen produced at the steel bar surface during the hydrogen evolution reaction would permeate and then induce HE inevitably, resulting in the brittle damage or hysteresis damage of the steel bar [18]. Owing to the high susceptibility of brittle damage, HE should be strictly controlled for some metals, such as cold- drawn pearlitic steel wires [46], high-strength low-alloy structural steels [47], and prestressed strands [48]. For hot rolled bars with a long yield platform used in RC structures, CHALAFTRIS [20] indicated that they are generally safe for HE. Additionally, a study by HARDIE et al [21] suggested that steel is immune to HE when the yield strength is less than 350 MPa. However, DJUKIC et al [22] discovered through a hardness test that HE occurred in mild steel with yield strength of 400 MPa. Similarly, EGGUM [23] discovered degraded mechanical properties for samples with yield strength of 560 MPa. In addition, hydrogen atoms were produced rapidly, while steel bars were servicing with stress. Therefore, the mechanical properties of hot rolled bars after BIEM treatment must be investigated. The experimental parameters of each specimen are listed in Table 4. The concrete specimen dimensions, steel bar diameter, and concrete strength grade were set to those listed in Section 2.3. The device shown in Figure 4(a) was adopted for loading. Three parallel samples with the same electrochemical parameters were tested.
Table 4 Parameters of BIEM treatment controlled by HE
2.6 Testing method
1) Test of Jc
As mentioned in Section 2.3, the reaction of hydrogen evolution and oxygen consumption depends on the applied potential of steel and the pH of concrete. Hence, Jc can be identified using the potentiodynamic polarization curves of the specimens. The detailed recognition method of critical hydrogen evolution has been introduced previously [35, 44]. Before measurements were performed, the specimens were immersed in water for 24 h until saturation and their resistance was reduced. An electrochemical workstation (Reference 600, Gamry Company) was used to obtain the curves.
2) Test of chloride ions and inhibitor concentration
The overall effect of BIEM was evaluated via the chloride ion and inhibitor concentrations. A drill of diameter 10 mm was used to collect the powder at various depths of the concrete cover. The extraction depth was 5 mm for each layer. The content of chloride ions after BIEM treatment was obtained through a rapid chloride ion test. Nitrogen content represents the amount of electromigrated TETA. Hence, the migration degree of TETA after BIEM was obtained using an organic element analyzer EA1112.
3) Mechanical property test of steel bar
Typically, hydrogen-induced plasticity loss indexes, such as the fracture energy ratio and cross-section shrinkage, are used to mirror the HE susceptibility of steel bars after ER [49, 50]. A constant extension rate test can reflect the effect of these indexes of steel bars, and it was used to evaluate the HE risk of a steel bar with 72 h after ER in this study. The loading rate was 0.1 mm/min. The formula for the HE susceptibility coefficient is as follows[35, 39]:
 (3)
(3)
where δ0 represents the elongation of the steel bar without ER, and δ represents the elongation of the steel bar after ER. The fracture energy of metal materials is the total energy released during a tensile fracture and is equal to the area under the stress–strain curve. The fracture energy ratio Z was calculated as follows:
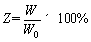 (4)
(4)
where W0 is the fracture energy of the steel bar without ER, and W is the fracture energy of the steel bar after ER.
3 Experimental results
3.1 Critical hydrogen evolution current density
This section details the potentiodynamic polarization curve of the concrete specimens. Three parallel specimens with the same mixture ratio were tested. The potentiodynamic polarization curve and its first derivative curve are shown in Figure 6.
Results obtained from the parallel concrete specimens were almost identical. The method 1) mentioned in Section 2.6 was adopted to obtain the critical values of potential, current, and current density for hydrogen evolution. Using specimen I for example, the analysis process is shown in Figure 7. The curve comprised three main areas, denoted AC, CE, and EF. Area AC represented the complete oxygen consumption reaction corresponding to Area I in Figure 7(a). Being the linear polarization region around the open-circuit potential, I increased rapidly with the applied potential. Area CE corresponded to Area II-stage ① based on the first derivative of the polarization curve. Oxygen consumption dominated this stage, and a current platform whose current density increased slowly with the applied potential was observed. At the end of this stage, hydrogen evolution appeared and became dominant in area EF. Area EF corresponded to Area II-stage ②. Hence, the current of point E corresponding to break point 1 was recognized as the critical hydrogen evolution current density Jc. Specifically, the polarization potential of point E was -1.05 V, and the current and current density were 3.16 mA and 0.559 A/m2, respectively. Hence, the Jc for specimen I was 0.559 A/m2. The critical hydrogen evolution current densities for the other specimens are listed in Table 2. The results summarized in Table 2 demonstrated good reproducibility. The mean square deviations for Ec, Ic and Jc were 0.036,0.042, and 0.075, respectively. The mean value of Jc for all concrete specimens was 0.504 A/m2.

Figure 6 Potentiodynamic polarization curve of concrete specimens:
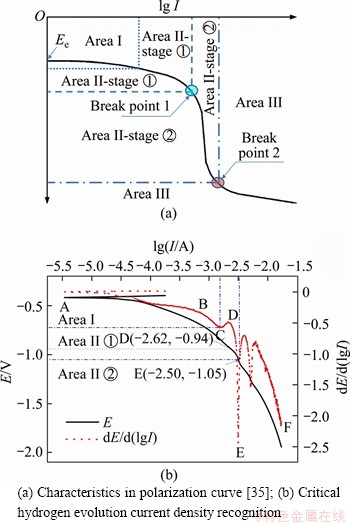
Figure 7 Potentiodynamic polarization curve:
3.2 Details of dechlorination and corrosion inhibition
The BIEM effect represented by dechlorination and corrosion inhibition with a current density of 3.0 A/m2 has been demonstrated [30]. This current density will lead to hydrogen evolution and increase the HE risk. As discussed in Section 2.4, using a small current density can prevent hydrogen evolution, but the electrochemical repairing time must be prolonged significantly to achieve the same chloride extraction effect. Meanwhile, the BIEM effect of a large current density was measured for a comparative analysis. The results presented in this section were obtained through ER experiments with small (Section 2.4) and large current densities (Section 2.5). The chloride ion content, chloride extraction efficiency, rust inhibitor content, and the ratio between the rust inhibitor and chloride ion are plotted in Figure 8.
The initial chloride ion contents in cement for the samples were 1.615×10-4 mol/g. As shown in Figure 8(a), the residual chloride ion content for each sample was smaller than the initial content, but the case for the extraction degree was different. Compared with the small current density group, the connection line slope of the large current density group that presented the rate of chloride ion extraction was much larger. This indicated that the small current density group required more time to achieve the same BIEM effect as that of the large current density group. The differences in the connection line slope among the samples in the small current density group were not obvious. In this case, the treatment time served as the main factor affecting the BIEM effect.

Figure 8 BIEM effects of different current densities:
The chloride extraction rate shown in Figure 8(b) was calculated by dividing the extracted chloride ions by the initial chloride ions. For a given conduction time, the chloride extraction efficiency was higher when higher current densities were applied. However, even at larger applied current densities, the chloride extraction rate did not increase indefinitely. A chloride extraction rate of 65% under current density 3 A/m2 in 15 d has been reported previously. To achieve a similar efficiency, 80 to 110 d is required for applied currents of 0.3 to 0.6 A/m2. Nonetheless, the results of these experiments demonstrated that BIEM with a small current density and prolonged conduction time yielded efficient chloride extraction.
The rust inhibitor that arrived at the steel bar surface after migrating from the electrolyte is shown in Figure 8(c). The rust inhibitor was detected around the steel bars only after a certain time period. The progression of rust inhibitor electromigration, depicted graphically in Figure 8(c), was consistent with the analysis above. Once the conduction time reached a critical threshold, the rust inhibitor was detected around the surface of the steel bar, after which the inhibitor content increased linearly with the current conduction time. The critical threshold for the rust inhibitor adsorption depended on the applied current density. The ratio of the rust inhibitor and chloride ions (TETA/Cl-) on the steel bar surface of each specimen is shown in Figure 8(d). When TETA/Cl- exceeded 1.0, the probability of steel corrosion was controlled at a low level [50]. The data indicated that the treatment time was short for a large current density group to achieve this goal; however, 50, 60, or 90 d was required by the small current density group.
The relationships between BIEM effect indexes and electric flux are plotted in Figure 9. The electric flux was calculated by multiplying the current density and treatment time. The linear relationship between electric flux and chloride extraction is shown in Figure 9(a). Additionally, a critical threshold of electric flux appeared for the inhibitor arriving at the steel bar surface, as shown in Figures 9(b) and (c). The critical threshold was 20 d·A/m2 in this study. Once the electric flux exceeded this critical threshold, the relationship between the electric flux and each of the rust inhibitor (TETA) content and TETA/Cl- became linear.
3.3 Analysis of HE sensitivity
The electrochemical parameters of the large current density group were set as follows: a stress level of 55%, a current conduction time of 10 d, and the use of a rust inhibitor, TETA. Samples with the maximum treatment time were selected for the small current density group, i.e., 150, 120, 90 and 75 d for 0.3, 0.4, 0.5 and 0.6 A/m2, respectively. The stress–strain curves of the steel bar treated with different current densities are shown in Figure 10. As observed, the samples’ yield stress ranged from 420.0 to 440 MPa, and no regular relationship between the current density and yield stress was observed. Meanwhile, the fluctuation range of the yield stress was acceptable. Hence, the effect of BIEM treatment on the yield strength was negligible. The tensile properties of the steel bars at the non-uniform stage differed significantly. Especially for the large current density group, the non-uniform deformation ability decreased as the current density increased. For a quantitative depiction, the changes in F(δ) and Z of the steel bars are shown in Figure 11.
As shown in Figure 11, no HE risk was involved for the small current density group because of the extremely small HE susceptibility coefficient and extremely large fracture energy ratio. However, for the large current density group, the increase in the current density afforded a gradual increase in the HE susceptibility coefficient and a gradual decrease in the fracture energy ratio. For 5 A/m2, the average HE susceptibility coefficient was 7.55%, which corresponded to a region of no-HE risk. When current density exceeded 5 A/m2,the HE risk increased rapidly. The fracture energy ratio changed slightly over the current density ranging from 3 to 5 A/m2, after which the fracture energy ratio increased with the current density. The trends of the HE susceptibility coefficient and fracture energy ratio indicated that when the stress level and current conduction time were constant, the current density of the BIEM exhibited a critical threshold. The HE risk was low for current densities between 3 and 5 A/m2 over a conduction period of 10 d in this study.
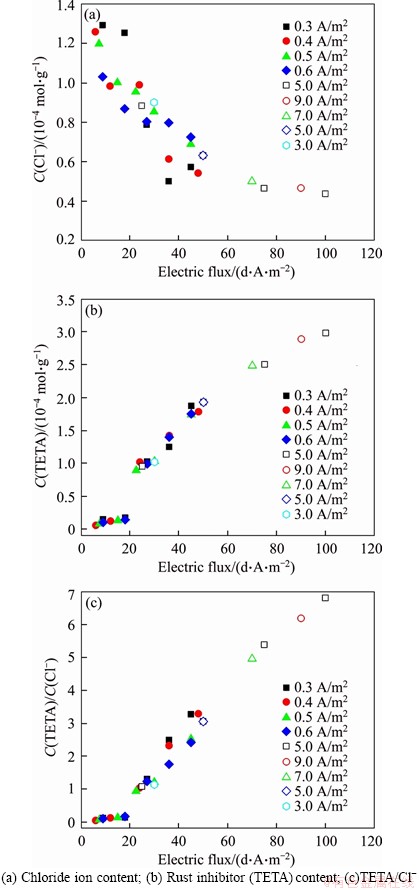
Figure 9 Relationship between BIEM effects and electric flux:
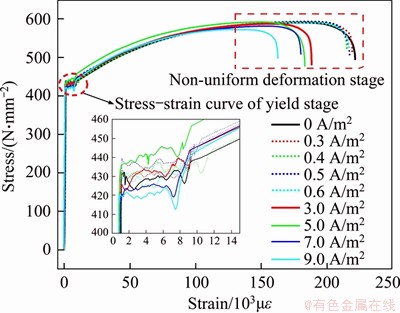
Figure 10 Stress–strain curves of different current densities

Figure 11 HE sensitivity analysis with different current densities:
3.4 Parameters selection based on BIEM effect and HE indexes
The HE susceptibility coefficient of another large current density group whose current density was 5 A/m2 but the treatment times were 5, 10, 15 and 20 d was measured as well. The relationship between the HE susceptibility coefficient and electric flux is plotted in Figure 12.
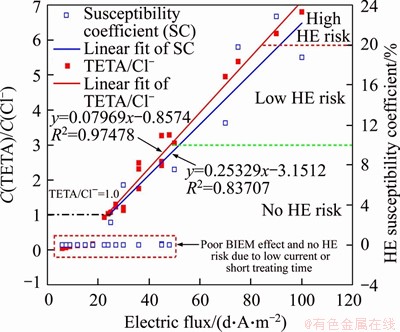
Figure 12 Fitting line of C(TETA)/C(Cl-) and HE susceptibility coefficient
Figure 12 facilitates in the selection of electrochemical parameters. Herein, the lower part of the graph marked by a dotted text box represents low current density and short treatment time. Although no HE risk was present, the electrochemical parameters could not be adopted because of the poor BIEM effect.
The red line represents the fitted relationship between TETA/Cl- and electric flux, and the blue line represents that between the HE susceptibility coefficient and electric flux. The linear relationship was reasonable owing to its high correlation coefficient during fitting. It was clear that a region whose BIEM effect was good (TETA/Cl- was larger than 1.0) while no HE risk occurred (HE susceptibility coefficient was smaller than 10%). The electric flux of this region ranged from 25.2 to 48.5 d·A/m2. Moreover, the electric flux for the region whose BIEM effect was good and HE risk was low ranged from 48.5 to 84.3 d·A/m2. Once the electric flux decreased to less than 25.2 d·A/m2, the HE risk was not presented but the BIEM effect was poor. Additionally, when the electric flux was larger than 84.3 d·A/m2, the BIEM effect was excellent but the HE risk was extremely high. Calculating using the fitting equation above, the possible combinations of treatment time and current density for each region are plotted in Figure 13.
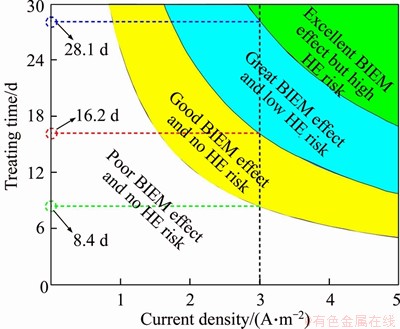
Figure 13 Combinations of electrochemical parameters based on BIEM effect and HE susceptibility coefficient
Four different regions are presented in Figure 13, namely, poor BIEM effect and no-HE risk, good BIEM effect and no-HE risk, great BIEM effect and low HE risk, and excellent BIEM effect but high HE risk. It was easy to obtain the combinations of electrochemical parameters for different requirements from the BIEM effect and HE risk. Owing to the requirement for rapid repair, the construction period was always limited to less than one month for on-site projects. Therefore, the maximum treatment time shown in the vertical ordinate was 30 d; additionally, owing to the power restriction of the DC device, the operating current density could not easily reach a high level for on-site projects. Hence, the maximum current density shown in the horizontal ordinate was 5.0 A/m2.
Once the current density was selected, we could determine the treatment time based on the BIEM effect and HE risk. Using current density 3.0 A/m2 for example, treatment time 8.4 d was the critical point for a poor and good BIEM effect with no-HE risk; treatment time 16.2 d was for a no- and low-HE risk with similar BIEM effects; treatment time 28.1 d was for a low- and high-HE risk with similar BIEM effects. In this case, the combination of 3.0 A/m2 current density and 8.4-16.2 d treatment time can yield both good BIEM effects and little deformation performance losses.
4 Discussions
4.1 Relevance between HE indexes and electrochemical rehabilitation method
ECE is a mature ER method; it has been adopted in the standards/codes of many countries or institutes, such as the British standard (BS EN 14038), Japanese standard (20011012-CP-ECR-ER- ED), Chinese standard (JTS152-2), and NACE standard (NACE SP0107). Considering the HE risk and other negative effects, the suggested current density of the standards above is less than 4 A/m2. The difference between ECE and BIEM is the type of electrolyte solution: saturated calcium hydroxide solution for ECE; TETA solution for BIEM. Several studies [14, 34, 35] have indicated that inhibitors are beneficial for controlling HE. The data in Section 3.3 show that the HE risk for 7.0 A/m2 was maintained at a low level. The main contribution of BIEM to HE risk control is that the inhibitors would prevent the hydrogen evolution reaction.
To demonstrate this, a hydrogen evolution recognition experiment using different electrolyte solutions was performed, as shown in Figure 5(a). Both the potential and current density of the hydrogen evolution reaction were derived from the cathodic polarization curves. The results of critical hydrogen evolution current density in each electrolyte solution are shown in Figure 14.
The first derivative curve revealed a fluctuation between -0.559 to -1.087 V in Figure 14(a). Subsequently, more fluctuations appeared, indicating the beginning of the hydrogen evolution reaction. The current between two intersection points shifted from 0.005 A (0.38 A/m2) to 0.040 A (3.03 A/m2). Owing to the damaged CCPA anode material owing to hydrogen evolution in the steel bar, SARASWATHY et al [51] selected 1.0 and 2.0 A/m2. When a saturated Ca(OH)2 solution was replaced with a TETA solution, an increase in the polarization current density was observed, as shown in Figure 14(b). Analogously,the potential ranged from -0.869 to -1.369 V, and the corresponding current density ranged from 3.11 to 5.76 A/m2. As reported in Ref. [34], the cationic protective film formed on the steel bar surface differentiated the polarization current density. Consequently, the TETA film inhibited the hydrogen evolution and improved Jc.

Figure 14 Potentiodynamic polarization curves:
Furthermore, CERTs were adapted to compare the steel bar deformation performance after BIEM and ECE, as listed in Table 4. Among them, the stress–strain curves of samples with a stress level of 55% and a current conduction time of 10 d were selected, as shown in Figure 15. As shown, the stress–strain curves of all steel bars were similar, and the elastic moduli (slope of elastic phase) were almost identical. The yield strength and ultimate strength were similar as well. These results suggested that the effect of the electrolyte solution on the elastic stage of the steel bars after ER was negligible. The main impact of the electrolyte solution on the tensile properties of the steel bars was reflected in the non-uniform plastic deformation (necking) stage.

Figure 15 Stress-strain curves of steel bar with different electrolyte solutions
The HE susceptibility coefficient and fracture energy ratio are presented in Figure 15. First, compared with the untreated sample, hydrogen-induced plasticity loss was observed in both the BIEM and ECE samples. The HE susceptibility coefficient of ECE samples treated with 5.0 A/m2 was higher than that of BIEM samples treated similarly and was similar to that of BIEM samples treated with 9.0 A/m2. It indicated that the plasticity reduction extent of the steel bar was smaller in the BIEM samples than that in the ECE samples. Considering the HE susceptibility coefficient and fracture energy ratio, the following conclusion was obtained: based on the same electrochemical parameters, the steel bar treated with BIEM exhibited a lower HE risk than that treated with ECE.
4.2 Relevance between HE indexes and concrete structure operating condition
The HE of metals is related to the hydrogen evolution degree and the number of hydrogen atoms migrated into a steel bar. The hydrogen atom content and migration behavior are related to the concrete structure’s operating condition. The stress level of metals is an important factor affecting the migration of hydrogen atoms into metals, which has been confirmed in other research fields. RC structures operate at different stress levels, which necessitates the discussion of the relationship between HE index and stress level. The concrete cover thickness is another factor, because a longer treatment time is required for thicker concrete covers when extracting chloride ions. Therefore, the relationship between HE index and treatment time is discussed herein.
The samples are listed in Table 4. The stress–strain curves of steel bars at different stress levels are shown in Figure 16, and the HE susceptibility coefficient and fracture energy ratio are presented. The characteristics of the stress–strain curves exhibited in Figure 16 agreed with those described in Sections 3.3 and 4.1. The data highlighted that increasing the stress level resulted in a gradual increase in the HE susceptibility coefficient and gradual decrease in the fracture energy ratio, implying a gradually increasing HE risk. When the stress level was lower than 55% of fy, the HE susceptibility coefficient was less than 10% and the fracture energy ratio was greater than 90%. However, for 75% of the fy stress level, the HE risk reached 19.79%. The results obtained from these experiments indicated that the stress level is a critical factor affecting the HE risk.
The stress–strain levels of steel bars treated with different times listed in Table 4 are shown in Figure 17, illustrating the effect of treatment time on the HE sensitivity coefficient and fracture energy ratio. The HE susceptibility coefficient of samples treated for 5 and 10 d was smaller than that treated for 15 and 20 d. Additionally, the data of samples treated for 15 and 20 d were similar. Results of these experiments indicate that the treatment time is another important factor affecting the HE risk.
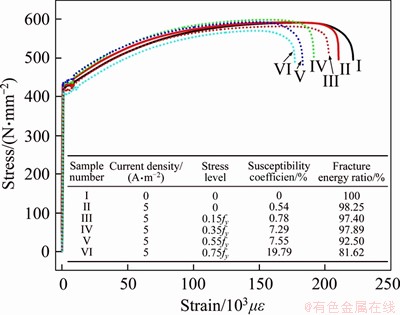
Figure 16 Stress-strain curves of steel bars with different stress levels
5 Conclusions
BIEM treatment not only extracted chloride ions, but also migrated the inhibitor inside. An experimental study was performed to investigate the relationships among the BIEM effect, HE risk, and electrochemical parameters. Combinations of electrochemical parameters based on the BIEM effect and HE susceptibility coefficient are proposed. The three main conclusions from this study are as follows:
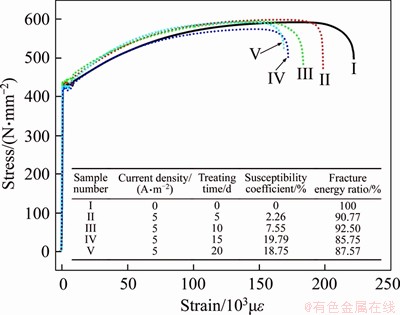
Figure 17 Stress-strain curves of steel bars with different treatment times
1) Owing to the small current density that was lower than the critical hydrogen evolution, no HE risk was encountered in the small current density group. The small current density group achieved an efficient BIEM effect by prolonging the treatment time. A linear relationship between electric flux and chloride extraction was established. A critical threshold of electric flux (20 d·A/m2) was discovered for the rust inhibitor arriving at the steel bar surface.
2) For the large current density group, a short treatment time was required to achieve an efficient BIEM effect. Compared with ECE, steel bars treated with BIEM exhibited a lower HE risk, although this risk existed in BIEM as well. The increase in current density resulted in a gradual increase in the HE risk. For a current density of 5 A/m2, the average HE susceptibility coefficient was 7.55%, which corresponded to a region of slight HE risk. When the current density exceeded 5 A/m2, the HE risk increased rapidly. Additionally, the increasing stress level and treatment time of the steel bar resulted in an increased HE risk.
3) A method combining treatment time and current density based on the BIEM effect and HE risk was proposed. Once the current density was selected, the critical treatment time for poor and good BIEM effects with no HE risk, that for no and low HE risks with similar BIEM effects, and that for low and high HE risks with similar BIEM effects could be determined. It should be emphasized that the fatigue behaviors of steel bars after ER differed significantly based on static experiments, thereby necessitating further studies.
References
[1] CHEEWAKET T, JATURAPITAKKU C L, CHALEE W. Initial corrosion presented by chloride threshold penetration of concrete up to 10 year-results under marine site [J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2012, 37: 693-698. DOI: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2012.07.061.
[2] LIU Qing-feng, HU Zhi, LU Xian-yang, YANG Jian. Prediction of chloride distribution for offshore concrete based on statistical analysis [J]. Materials, 2020, 13(1): 174. DOI: 10.3390/ma13010174.
[3] ALMUSALLAM A A. Effect of degree of corrosion on the properties of reinforcing steel bars [J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2001, 15: 361-368. DOI: 10.1016/ S0950-0618(01)00009-5.
[4] LIU Qing-feng, XIA Jin, EASTERBROOK D, YANG Jian, LI Long-yuan. Three-phase modelling of electrochemical chloride removal from corroded steel-reinforced concrete [J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2014, 70: 410-427. DOI: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2014.08.003.
[5] ELSENER B. Long-term durability of electrochemical chloride extraction [J]. Materials and Corrosion, 2008, 59(2): 91-97. DOI: 10.1002/maco.200804165.
[6] UEDA T, KAMEDA T, NANASAWA A. A new electrochemical rehabilitation method for reinforced concrete employing the DFRCC anode system [J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2011, 79(2): 204-207. DOI: 10.1016/j.seppur.2011.02.027.
[7] ZHU Ji-hua, WEI Liang-liang, WANG Zhao-hua, LIANG Cheng-ke, FANG Yuan, XING Feng. Application of carbon-fiber-reinforced polymer anode in electrochemical chloride extraction of steel-reinforced concrete [J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2016, 120: 275-283. DOI: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2016.05.103.
[8] JIN Zu-quan, HOU Dong-shuai, ZHAO Tie-jun. Electrochemical chloride extraction (ECE) based on the high performance conductive cement-based composite anode [J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2018, 173: 149-159. DOI: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2018.03.241.
[9] MIRANDA J M, GONZALEZ J A, COBO A, OTERO E. Several questions about electrochemical rehabilitation methods for reinforced concrete structures [J]. Corrosion Science, 2006, 48: 2172-2188. DOI: 10.1016/j.corsci.2005. 08.014.
[10] SHAN Hong-you, XU Jin-xia, WANG Zhu-yin, JIANG Lin-hua, XU Ning. Electrochemical chloride removal in reinforced concrete structures: Improvement of effectiveness by simultaneous migration of silicate ion [J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2016, 127: 344-352. DOI: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2016.09.137.
[11] LIU Qing-feng, FENG Gan-lin, XIA Jin, YANG Jian, LI Long-yuan. Ionic transport features in concrete composites containing various shaped aggregates: A numerical study [J]. Composite Structures, 2018. DOI: 10.1016/j.compstruct. 2017.03.088.
[12] CHANG J J. Bond degradation due to the desalination process [J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2003, 17: 281-287. DOI: 10.1016/S0950-0618(02)00113-7.
[13] MAO Li-xuan, HU Zhi, XIA Jin, FENG Gan-lin, AZIM I, YANG Jian, LIU Qing-feng. Multi-phase modelling of electrochemical rehabilitation for ASR and chloride affected concrete composites [J]. Composite Structures, 2019, 207: 176-189. DOI: 10.1016/S0950-0618(02)00113-7.
[14] SIEGWART M, MCFARLAND B J, LYNESS J F, ABU-TAIR A. Application of inhibitors to reduce the hydrogen uptake of steel during electrochemical chloride extraction [J]. Corrosion, 2002, 58(3): 257-266. DOI: 10.5006/1.3279877.
[15] YEIH W, CHANG J J, HUNG C C. Selecting an adequate procedure for the electrochemical chloride removal [J]. Cement and Concrete Research, 2006, 36(3): 562-570. DOI: 10.1016/j.cemconres.2005.12.008.
[16] SIEGWART M, LYNESS J F, MCFARLAND B J, DOYLE G. The effect of electrochemical chloride extraction on pre-stressed concrete [J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2005, 19: 585-594. DOI: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat. 2005.01.012.
[17] NAGUMO M. Fundamentals of hydrogen embrittlement [M]. Singapore, 2016. DOI: 10.1007/978-981-10-0161-1
[18] ISHII K, SEKI H, FUKUTE T, IKAWA K. Cathodic protection for prestressed concrete structures [J]. Construction and Building Materials, 1998, 12: 125-132. DOI: 10.1016/S0950-0618(97)00014-7.
[19] KLINOWSKI S, HARTT W H. Qualification of cathodic protection for corrosion control of prestressing tendons in concrete [J]. Special Publications of the Royal Society of Chemistry, 1996, 183: 354-368.
[20] CHALAFTRIS G. Evaluation of aluminium-based coatings for cadmium replacement [D]. Cranfield University, 2003.
[21] HARDIE D, CHARLES E A, LOPEZ A H. Hydrogen embrittlement of high strength pipeline steels [J]. Corrosion Science, 2006, 48(12): 4378-4385. DOI: 10.1016/j.corsci. 2006.02.011.
[22] DJUKIC M B, ZERAVCIC V S, BAKIC G, SEDMAK A, RAJICIC B. Hydrogen embrittlement of low carbon structural steel [J]. Procedia Material Science. 2014, 3: 1167-1172. DOI: 10.1016/j.mspro.2014.06.190.
[23] EGGUM T.J. Hydrogen in low carbon steel: Diffusion, effect on tensile properties, and an examination of hydrogen’s role in the initiation of stress corrosion cracking in a failed pipeline [D]. University of Calgary, 2013.
[24] ELSENER B, MOLINA M, BOHNI H. The electrochemical removal of chlorides from reinforced concrete [J]. Corrosion Science, 1993, 35(5-8): 1563-1570. DOI: 10.1016/0010- 938X(93)90385-T.
[25] FAJARDO G, ESCADEILLA G S, ARLIGUIE G. Electrochemical chloride extraction (ECE) from steel- reinforced concrete specimens contaminated by “artificial” sea-water [J]. Corrosion Science, 2006, 48(1): 110-125. DOI: 10.1016/j.corsci.2004.11.015.
[26] ELISA F, HUMBERTO V, MARIA E N, MARIA C B, JOSE M, LUCIANA R, EDUARDA P. Improvement of historic reinforced concrete/mortars by impregnation and electrochemical methods [J]. Cement and Concrete Composites, 2014, 49: 50-58. DOI: 10.1016/ j.cemconcomp.2013.12.013.
[27] SAWADA S, PAGE C L, PAGE M M. Electrochemical injection of organic corrosion inhibitors into concrete [J]. Corrosion Science, 2005, 47(8): 2063-2078. DOI: 10.1016/j.corsci.2004.10.001.
[28] SAWADA S, KUBO J, PAGE C L, PAGE M M. Electrochemical injection of organic corrosion inhibitors into carbonated cementitious materials: Part 1. Effects on pore solution chemistry [J]. Corrosion Science, 2007, 49(3): 1186-1204. DOI: 10.1016/j.corsci.2006.06.020.
[29] KUBO J, SAWADA S, PAGEC L, PAGE M M. Electrochemical inhibitor injection for control of reinforcement corrosion in carbonated concrete [J]. Materials and Corrosion, 2008, 59(2): 107-114. DOI: 10.1002/maco. 200804161.
[30] XU Chen, JIN Wei-liang, HUANG Nan, WU Hang-tong, LI Zhi-yuan, MAO Jiang-hong. Bidirectional electromigration of a corrosion inhibitor in chloride contaminated concrete [J]. Magazine of Concrete Research, 2016, 68(9): 1-12. DOI: 10.1680/jmacr.15.00121.
[31] NMAI C K. Multi-functional organic corrosion inhibitor [J]. Cement and Concrete Composites, 2004, 26(3): 199-207. DOI: 10.1016/S0958-9465(03)00039-8.
[32] ORMELLESE M, BOLZONI F, LAZZARI L, BRENNA A, PEDEFERRI M. Organic substances as inhibitors for chloride-induced corrosion in reinforced concrete [J]. Materials and Corrosion, 2011, 62(2): 170-177. DOI: 10.1016/S0958-9465(03)00039-8.
[33] AGRAWAL R, NAMBOODHIRI T K G. The inhibition of corrosion and hydrogen embrittlement of AISI 410 stainless steel [J]. Journal of Applied Electrochemistry, 1992, 22: 383-389. DOI: 10.1007/BF01092693.
[34] SOUDANI M, HADJ MELIANI M, EL-MILOUDI K, AZARI Z, SOROUR A A, MERAH N, PLUVINAGE G. Reduction of hydrogen embrittlement of API 5l X65 steel pipe using a green inhibitor [J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2018, 43(24): 11150-11159. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2018.04.236.
[35] MAO Jiang-hong, JIN Wei-liang, ZHANG Jun, XIA Jin, FAN Wei-jie, XU Yi-dong. Hydrogen embrittlement risk control of prestressed tendons during electrochemical rehabilitation based on bidirectional electro-migration [J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2019, 213: 582-591. DOI: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2019.04.008.
[36] LYNCH S. Hydrogen embrittlement phenomena and mechanisms [J]. Corrosion Reviews, 2012, 30(3, 4): 105-123. DOI: 10.1515/corrrev-2012-0502.
[37] TROIANO A R. The role of hydrogen and other interstitials in the mechanical behavior of metals [J]. Metallography, Microstructure, and Analysis, 2016, 5(6): 557-569. DOI: 10.1007/s13632-016-0319-4.
[38] LOUTHAN M R. Strain localization and hydrogen embrittlement [J]. Scripta Metallurgica, 1983, 17(4): 451-454. DOI: 10.1016/0036-9748(83)90329-0.
[39] PETCH N J, STABLES P. Delayed fracture of metals under static load [J]. Nature, 1952, 169(4307): 842-843. DOI: 10.1038/169842a0.
[40] ZAPFFE C, SIMS C. Hydrogen embrittlement, internal stress and defects in steel [M]. Technology Publication Contribution, 1941.
[41] GARCIA J, ALMERAYA F, BARRIOS C, GAONA C, NUNEZ R, LOPEZ I, RODRIGUEZ M, MARTINEZ- VILLAFANE A, BASTIDAS J M. Effect of cathodic protection on steel–concrete bond strength using ion migration measurements [J]. Cement and Concrete Composites, 2012, 34(2): 242-247. DOI: 10.1016/ j.cemconcomp.2011.09.014.
[42] BOIADJIEVA-SCHERZER T, KRONBERGER H, FAFILEK G, MONEV M. Hydrogen evolution reaction on electrodeposited Zn-Cr alloy coatings [J]. Journal of Electroanalytical Chemistry, 2016, 783: 68-75. DOI: 10.1016/j.jelechem.2016.10.059.
[43] NESIC S, POSTLETHWAITE J, OLSEN S. An electrochemical model for prediction of corrosion of mild steel in aqueous carbon dioxide solutions [J]. Corrosion, 1996, 52(4): 280-294. DOI: 10.5006/1.3293640.
[44] LI Teng, JIN Wei-liang, XU Chen, MAO Jiang-hong. Determination of steady critical current density of hydrogen evolution during electrochemical repair process of reinforced concrete [J]. Journal of the Chinese Society of Corrosion & Protection, 2017, 37(4): 382-388. DOI: 10.11902/1005. 4537.2016.067. (in Chinese)
[45] JIAO Ming-yuan, JIN Wei-liang, MAO Jiang-hong, LI Teng, XIA Jin. Effect of concrete inner environment on hydrogen evolution of rebar during electrochemical remediation [J]. Journal of Chinese Society for Corrosion and Protection, 2018, 38(5): 57-64. DOI: 10.11902/1005.4537.2017.168. (in Chinese)
[46] TORIBIO J, VERGARA D, LORENZO M. Hydrogen embrittlement and micro-damage in notched specimens of progressively cold-drawn pearlitic steel wires [J]. Theoretical and Applied Fracture Mechanics, 2017, 90: 276-286. DOI: 10.1016/j.tafmec.2017.06.014.
[47] SERGEEV N N, CHUKANOV A N, BARANOV V P, YAKOVENKO A A. Development of damage and decarburization of high-strength low-alloy steels under hydrogen embrittlement [J]. Metal Science and Heat Treatment, 2015, 57(1, 2): 63-68. DOI: 10.1007/s11041- 015-9836-z.
[48] PERRIN M, GAILLET L, TESSIER C, IDRISSI H. Hydrogen embrittlement of prestressing cables [J]. Corrosion Science, 2010, 52(6): 1915-1926. DOI: 10.1016/j.corsci. 2010.02.041.
[49] BILLINGHAM M, JOHN G. Determining the compatibility of high strength steels to cathodic protection [C]// NACE International Corrosion 2008 Conference & Expo. 08066: 1-14.
[50] BRIOTTET L, MORO I, LEMOINE P. Quantifying the hydrogen embrittlement of pipeline steels for safety considerations [J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2012, 37(22): 17616-17623. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijhydene. 2012.05.143.
[51] VELU S, LEE H S, KARTHICK S. Extraction of chloride from chloride contaminated concrete through electrochemical method using different anodes [J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2018, 158: 549-562. DOI: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2017.10.052.
(Edited by YANG Hua)
中文导读
基于修复效果和氢脆风险控制的双向电迁移参数优化方法
摘要:双向电迁移(BIEM)是一种新型的提升混凝土结构耐久性的电化学修复方法,可以实现除氯阻锈双重目的。但是,双向电迁移技术的修复效果和由此引起的钢筋氢脆风险取决于电化学参数的选择(电流密度和修复时间)和混凝土结构的服役条件(钢筋应力水平和混凝土保护层厚度)。本文通过系统的试验研究了上述因素间的关系:电流密度低于临界析氢电流密度时,无氢脆风险且电通量和除氯效果呈线性关系;当电流密度高于临界析氢电流密度时,电流密度、应力水平和修复时间的增加均会导致氢脆风险的增加。最后,本文建立了基于修复效果和氢脆风险控制的双向电迁移参数查询方法。
关键词:电化学修复;混凝土耐久性;除氯;氢脆;电化学参数
Foundation item: Projects(51908496, 51878610, 51820105012, 51778577, 51638013) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China; Projects (LY18E080003, LQ19E080011, LQ19E080012, LQ20E080001) supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Zhejiang Province, China; Project(2018A610359) supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Ningbo, China
Received date: 2020-02-28; Accepted date: 2020-05-15
Corresponding author: MAO Jiang-hong, PhD, Professor; Tel: +86-13757485317; E-mail: jhmao@nit.zju.edu.cn; ORCID: https://orcid. org/0000-0002-0686-418X; XU Yi-dong, PhD, Professor; Tel: +86-13857488759; E-mail: xyd@nit.zju.edu.cn; ORCID: https://orcid.org/0000-0003-3756-032X

