Influence of annealing temperature on electrochemical properties of rapidly quenched LPC(NiAlMn)4.25Co0.75 hydrogen storage alloy electrodes
ZHENG Qun(郑 群), CHEN Yun-gui(陈云贵), WANG Jin-guo(王金国),
TAO Ming-da(陶明大), TANG Ding-xiang(唐定骧), TU Ming-jing(涂铭旌)
(Department of Metallic Materials, Sichuan University, Chengdu 610065, China)
Abstract: The influence of annealing temperature on the electrochemical properties and structure of the rapidly quenched LPC(NiAlMn)4.25Co0.75 hydrogen storage alloys was investigated, in which LPC represents the abbreviation of Nd-free La-Ce-Pr mischmetal after the extraction of most of Ce and Nd. After the annealing treatment between 700-900℃ for rapidly quenched alloys, their discharge capacity becomes larger and the P-C-T plateau tends to be flatter and lower. The alloy annealed at 700℃ has the highest discharge capacity and flattest plateau. The analyses by X-ray diffraction (XRD), different thermal analysis(DTA), scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and transmission electron microscopy (TEM) indicate that the microstructure reversion and recrystallization occur during the heating, and their feature temperatures are 477℃ and 696℃ respectively. The annealing treatments make cell volume increase, dislocations and strain decrease, and the distribution of alloy composition become homogeneous.
Key words: LPC mischmetal; hydrogen storage alloys; electrochemical properties; recrystallization CLC number: TG139.7
Document code: A
1 INTRODUCTION
As the negative material, the MH/Ni batteries using hydrogen storage alloys have been developed and have become the main competitor to Ni-Cd batteries due to the higher power densities, low memory effects and more environmentally friendly constituents. It has been found that the performance of the alloy depends on the alloy composition as well as the preparation conditions[1-16]. Sakai et al[1, 2, 7] researched the electrochemical properties of AB5-type cast alloys. Compared with the cast alloy, the durability of the rapidly quenched alloy can be greatly improved at the expense of a small decrease in capacity, and rapid quenching can also flatten the discharge voltage plateau, but the rapidly quenched alloy slowed down the initial activation rate[3, 9]. In addition, the influence of the annealing on the quenched alloy with the composition of ML(NiCoTi)5 has been studied[10, 11]. Annealing treatment improves the electrochemical properties to a large degree. In this work, distinctive composition—Sichuan LPC mischmetal is adopted, which is the remainder of Sichuan mischmetal after extracting the elements of Ce and Nd. The exploitation and application of LPC mischmetal make the LPC mischmetal a better application and balance the development of rare earth industry.
2 EXPERIMENTAL
LPC(NiAlMn)4.25Co0.75 hydrogen storage alloy was adopted in this work. The composition of A-side is LPC mischmetal. The compositions are listed in Table 1.
Table 1 Compositions of Sichuan LPC mischmetal(mass fraction, %)

A based ingot of the LPC(NiAlMn)4.25Co0.75 alloy was prepared by vacuum induction melting and cooling in a copper mould which was cooled by water. The as-cast alloy was re-melted and rapidly quenched to flakes by melt spinning with a molybdenum wheel. The rapidly quenched alloys were vacuum annealed separately for 10h at 400, 550, 700, 800 and 900℃.
All alloys were crushed and ground mechanically, then sieved. The size of the fine powder is less than 75μm.
Electrode pellets with 10mm in diameter were prepared by mixing alloy powder with fine copper powder in a mass ratio of 1∶2. As counter and reference electrode, a sintered nickel hydroxide (Ni(OH)2/NiOOH) plate and a Hg/HgO (6mol/L KOH+20g/L LiOH) electrode were employed, respectively.
The crystal structure of the alloy powders before charge-discharge cycling was identified by X-ray diffraction experiments with Co Kα1 radiation. The microstructure of the alloys, the distribution of elements and the surface morphology were studied by Hitachi X-650 scanning electron microscope (SEM) and energy dispersive X-ray detector.
The microstructure of the alloys was investigated by using a H-700 transmission electron microscope (TEM). The relation between the phase transformation of the annealed alloy and the temperature was determined by DUPONT 1090 DTA analysis.
3 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
3.1 XRD analysis
The as-quenched and the annealed samples were analyzed by XRD. The comparison of the width of diffraction peaks of the alloys annealed at different temperatures is listed in Table 2. It can be seen that the width of diffraction peaks of (200), (111), (002) crystal surface becomes smaller after annealing treatments. The higher the temperature is, the smaller the peak is.
Table 2 Comparison of width of diffraction peaks at different temperatures
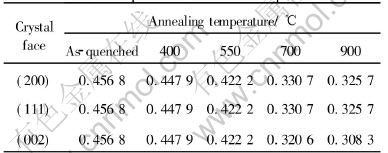
Compared with the width of diffraction peak of the as-quenched alloy, the width of diffraction peaks of the alloys annealed at 400℃ and 550℃ does not show obvious difference, but when the annealing temperature is 700℃, the width of diffraction peaks becomes smaller obviously. This phenomenon indicates that the annealing treatment reduces the lattice strain and defects, and the alloys annealed become more homogenous.
3.2 PCT isotherms
It can be seen from Fig.1 that the plateau region of the alloys become flat after the annealing treatments at 700, 800 and 900℃ compared with that of the as-quenched one. The alloys annealed at 400℃ and 550℃ show hardly any difference. This behavior can be attributed to the enhancement of compositional homogeneity and the decrease of lattice strain after annealing treatments. A similar annealing effect of AB5-type alloys was also observed by Sakai et al [1, 2, 4, 5].
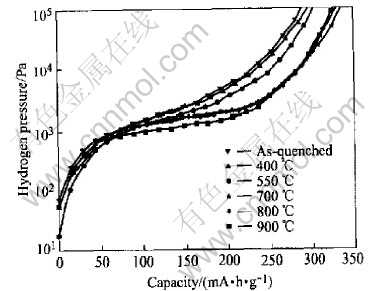
Fig.1 PCT curves of as-quenched and annealed LPC(NiAlMn)4.25Co0.75 alloy
3.3 Influence of annealing temperature on capacity and cycle life
The highest discharge capacities of LPC(NiAlMn)4.25Co0.75 alloy at 0.2C discharge rate treated at different annealing temperatures are shown in Fig.2. It can be seen that the discharge capacity is enhanced obviously when the annealing temperature is above 550℃.
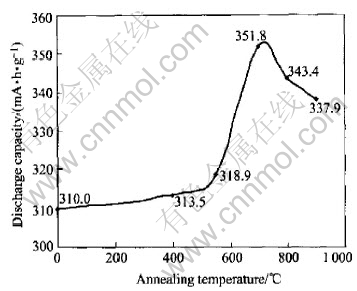
Fig.2 Highest discharge capacity of LPC(NiAlMn)4.25Co0.75 treated at different annealing temperatures
Fig.3 gives a comparison of electrochemical cycling stability between the as-quenched and the annealed samples under the same condition of charge-discharge 1.0C rate. As seen in Fig.3, the annealing treatment improves the cycling stability greatly. XRD analysis shows that the annealing treatment restrains pulverization by eliminating the lattice defects and decreasing the strain of lattice distortion. The highest discharge capacity of sample annealed at 900℃ under charge-discharge 1.0C rate is 285mA·h/g. The capacity retention after 500 cycles is 76%.
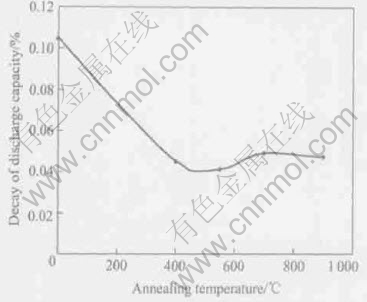
Fig.3 Relation between high discharge rate capability and annealing temperature
Fig.4 shows the influence of annealing treatments on the discharge capacity. The discharge capacity of the alloys with annealing treatments is higher than that of the as-quenched alloys. The increasing trend of the annealed sample is in good agreement with that of PCT data as show in Fig.1. The discharge curves of the annealed samples are also flatter than that of as-quenched sample.
Fig.5 shows the SEM images of the alloys annealed at different temperatures. The particle size of as-quenched alloy is small and columnar. When the annealing temperature is 400℃, the microstructure of the alloy keeps same and the growth of the particle is not obvious. When the annealing temperature is 900℃, the particle size of the annealed sample is obviously larger than that of the as-quenched sample. The organization of the alloy is better distributed. The characteristic of the as quenched alloy disappears. The grain boundaries are disordered. This is due to the recrystallization of the alloys. The phenomenon of the recrystallization of the alloys can be proved by DTA patterns.
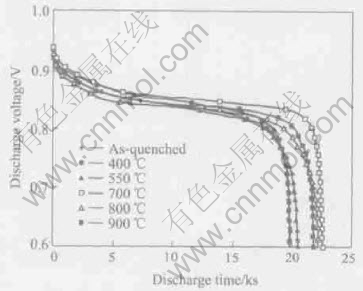
Fig.4 Discharge capacity of as-quenched and annealed LPC(NiAlMn)4.25Co0.75 alloy at different temperatures
The DTA patterns of the annealed alloys are shown in Fig.6. There are two exothermic peaks at 477℃ and 696℃. The as-quenched alloy has distortion and defects, so the alloy has high energy. When heating the alloy, the met-stable phase with high energy turns to stable phase with low energy. The first peak corresponds to the elimination of defects and the flabbiness of strains. The second peak corresponds to the recrystallization of the alloy, in which large energy is transformed. Annealed at low temperatures, the microstructures of the alloys dont change while the defects decrease and the macro-strains become flab. The annealing treatments under 700℃ make little change of appearance and electrochemical properties. The recrystallization of alloy is a process of re-organiza tion of microstructures. The process succeeds by nucleation and growth, i.e. the new non-distortion particles take the place of the distortion organizations. Thus the electrochemical properties change greatly.
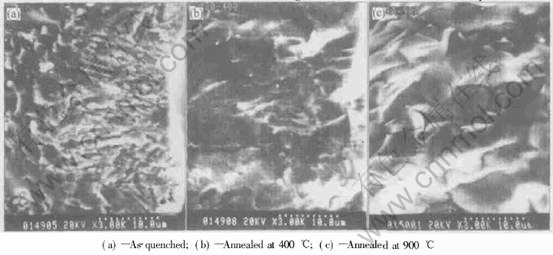
Fig.5 SEM photographs of LPC(NiAlMn)4.25Co0.75 alloy
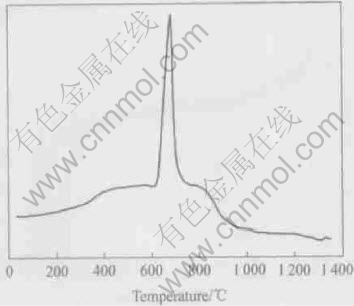
Fig.6 DTA curves for LPC(NiAlMn)4.25Co0.75 alloy
3.4 Influence of annealing temperature on rate capability
Fig.7 shows the dependence of the discharge capacity on the discharge current at different temperatures. The temperature sensitivity is not obvious at low discharge rate (0.2C), while the temperature sensitivity of high discharge rate (1.0C) is obvious. Under 1.0C discharge rate, the discharge capacity at 20℃ is lower than that at 40℃. This result shows that the high rate discharge ability tends to increase with the increasing of annealing temperature.
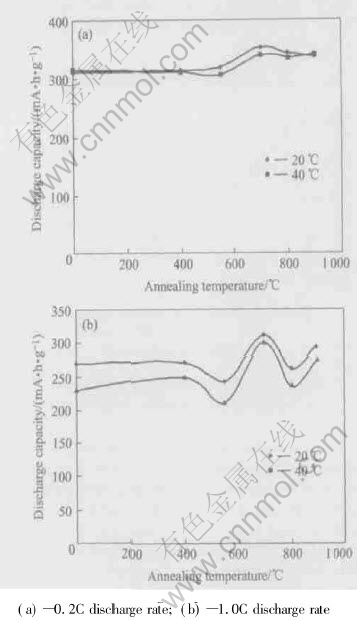
Fig.7 Dependence of discharge capacity of LPC(NiAlMn)4.25Co0.75 alloy on annealing temperature
4 CONCLUSIONS
The influence of annealing temperature on the electrochemical properties of rapidly quenched LPC(NiAlMn)4.25Co0.75 hydrogen storage alloys was investigated, and the mechanism of annealing on hydrogen storage alloy was discussed. Annealing treatments make cell volume increase, dislocations and strain decrease, and the alloy composition become homogeneous. After the annealing treatment for rapidly quenched alloys, the P-C-T plateau tends to be flatter and lower, the discharge capacity and the cycle stability are also improved. After annealing at 700℃, the alloy has the highest discharge capacity and flattest plateau compared with others. The analyses by XRD, SEM, DTA indicate that the microstructure recrystallization occurs during the heating, and its feature temperature is 696℃. The highest discharge capacity of the alloy after annealing treatment at 900℃ under 1.0C charge-discharge rate is 285mAh/g. The capacity retention after 500 cycles is 76%.
REFERENCES
[1]Sakai T, Yoshinaga H, Miyamura H, et al. Rechargeable hydrogen batteries using rare-earth based hydrogen storage alloys[J]. J Alloys Comp, 1992, 180:37.
[2]Sakai T, Hazama T, Miyamura H, et al, Rare-earth-based alloy electrodes for a nickel-metal hydride battery[J]. J Less-common Met, 1991, 172-174: 1175-1184.
[3]Mishima R, Miyamura H, Sakai T, et al. Hydrogen storage alloys rapidly solidified by the melt-spinning method and their characteristics as metal hydride electrodes[J]. J Alloys Comp, 1993,192: 176-178.
[4]Hu W K, Lee H, Kim D M, et al. Electrochemical behaviors of low-Co Mm-based alloys as MH electrodes[J]. J Alloys Comp, 1998, 268: 261-265.
[5]Hu W K, Kim D M, Jeon S W, et al. Effect of annealing treatment on electrochemical properties of Mm-based hydrogen storage alloys for Ni/MH batteries[J]. J Alloys Comp, 1998, 270: 255-264.
[6]CHEN De-min, CHEN Lian, YANG Ke, et al. Electrochemical performance of Sn-substituted LaNi5-based rapidly solidified alloys[J]. J Alloys Comp, 1999, 293-295: 724-727.
[7]Zhang L Y, Klein M, Czajkowski B, et al. Effect of cooling rate during casting on performance metal hydride electrodes and nickel-metal hydride batteries[J]. J Alloys Comp, 1999, 293-295: 608-612.
[8]Jurczyk M, Majchrzycki W. Electrochemical behaviour of nanostructured Mm(Ni,Al,Co)5 alloy as MHx electrode[J]. J Alloys Comp, 2000, 311: 311.
[9]GE Fu-ding, LI Chuan-jian, WANG Xin-lin, et al. Microstructure of MmNi3.8Mn0.550Co0.6Ti0.05 hydrogen storage alloy[J]. Metallic Functional Materials, 1997(5): 216-219.(in Chinese)
[10]LI Chuan-jian, WANG Xin-lin. Research on rapidly solidified AB5 hydrogen storage alloy[J]. Metallic Functional Materials,1998, 5(5): 218-221.(in Chinese)
[11]LI Chuan-jian, WANG Xin-lin. The influence of the annealing temperature on the electrochemical properties and the structure of the melt-spun ML(NiMnTiCo)5 hydrogen storage alloy[J]. J Alloys Comp, 1998, 274: 278-283.
[12]LEI Yong-quan, LI Zhou-peng, CHEN Chang-pin, et al. Materials Science and Engineering, 1990, 8(1): 1-8.
[13]MA Zhi-hong, LEI Yong-quan, CHEN Li-xin, et al. Effect of heat treatment on electrochemical properties of the hydrogen storage alloy Ml(NiCoMnAl)4.76[J]. Rare Metal Materials and Engineering, 2000, 29(4): 255-257.(in Chinese)
[14]LI Feng, WU Chao-ling, CHEN Yun-gui, et al. Electrochemical properties of strip casting LPC(NiCoAlMn)5 hydrogen storage alloy[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2002, 12(Suppl.2): 103-107.(in Chinese)
[15]Nakamura H, Nakamura Y, Fujitani S. Influence of annealing on hydrogenation characteristics and microstructure of LaNi4.55Al0.45 alloy[J]. J Alloys Comp, 1995, 218: 216.
[16]WANG Jin-guo. Study of LPC Hydrogen Storage Alloy with Technique of Quenching and Annealing[D]. Chengdu: Sichuan University, 2001.(in Chinese)
(Edited by YUAN Sai-qian)
Foundation item: Project (1191(1997)) supported by Key Science and Technology Research and Development of Sichuan Planning Committee
Received date: 2004-02-26; Accepted date: 2004-07-21
Correspondence: ZHENG Qun, PhD candidate; E-mail: zq781205@163.net, ygchen60@yahoo.com.cn